Defending Against the Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack on Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Using an Adjustable Optical Attenuator
Abstract
1. Introduction
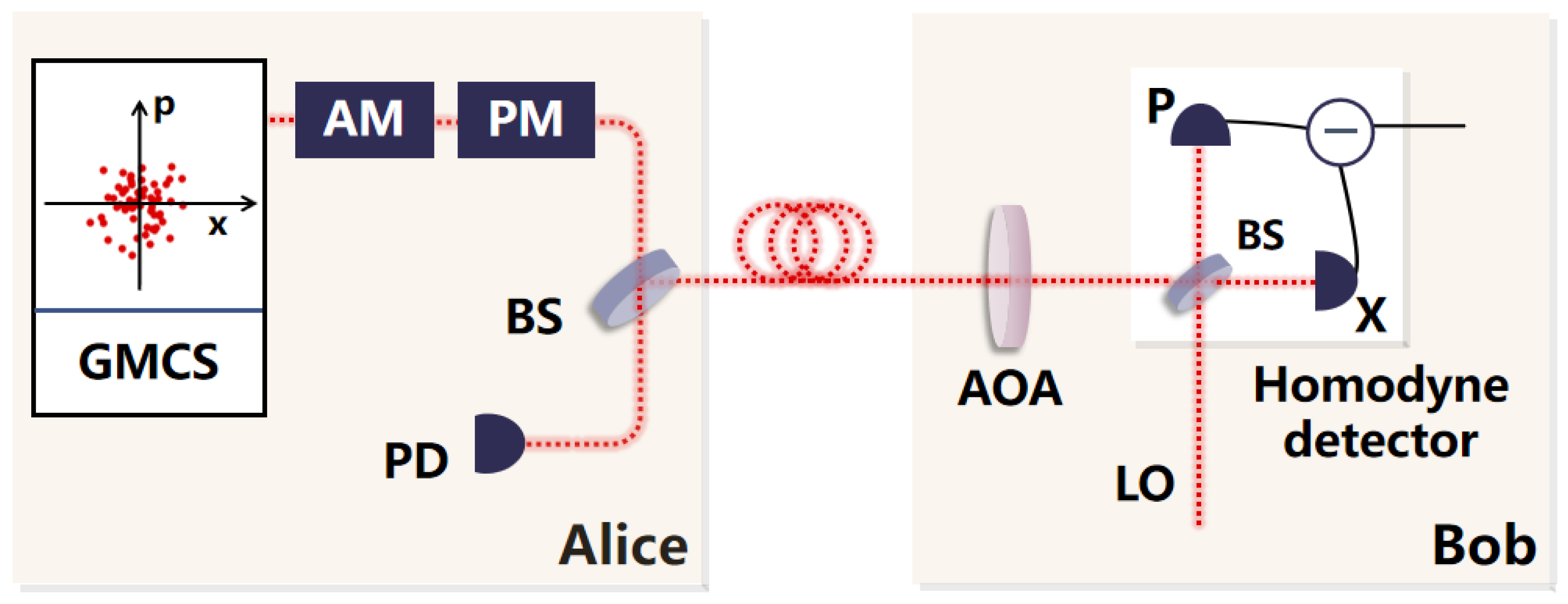
2. GMCS CV-QKD System
- •
- Alice uses a quantum random number generator to generate random numbers. The generated random numbers are encoded on the input laser so that Alice obtains the initial coherent state. The initial coherent state has its variance attenuated to the variance set by the system through the optical attenuator. The quadratures of the coherent state are the position X and the momentum P. Both X and P follow a Gaussian distribution, and their variance is , and their mean is 0. Subsequently, Alice sends the prepared coherent state and the LO together to Bob’s end through the optical fiber channel.
- •
- Bob randomly selects the measurement basis to measure the quadratures of the N coherent states sent by Alice. Bob creates a set of binary random sequences with N size, where 0 indicates the selection of X for measurement and 1 indicates the selection of P for measurement. Then, a homodyne detector is used to measure the selected quadratures to obtain the measurement results. Subsequently, Bob publicly discloses the measurement basis results, and Alice selects to retain either the quadratures X or P based on the publicly disclosed measurement basis.
- •
- Alice and Bob select a portion of the transmitted data for the estimation of transmittance and excess noise. Based on the results of parameter estimation, they calculate the mutual information and the upper bound of the information stolen by Eve and determine whether the communication is secure based on these results. This part of the data used for parameter estimation is discarded and does not participate in the calculation process of subsequent key generation.
- •
- When the parameter estimation indicates communication security, Alice and Bob conduct reverse reconciliation on the remaining data. Alice and Bob first discretize their respective data, and Bob publicly discloses a small portion of the bit data to Alice. Alice corrects her own data based on the error correction information sent by Bob. The error correction information is discarded and not used to generate the key. After the error correction, new data with smaller errors is obtained. Subsequently, Alice and Bob determine the hash values based on Bob’s data and the new data corrected by Alice. If the hash values overlap, the determination is successful and the protocol continues. If the hash values do not overlap, the determination fails and the protocol terminates. After successful determination, we perform confidentiality enhancement operations on the data and finally generate a security key that can be used for data encryption.
3. The Principle of the Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack
3.1. Imperfection of Detectors
3.2. The Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack
4. Countermeasure with Adjustable Optical Attenuator
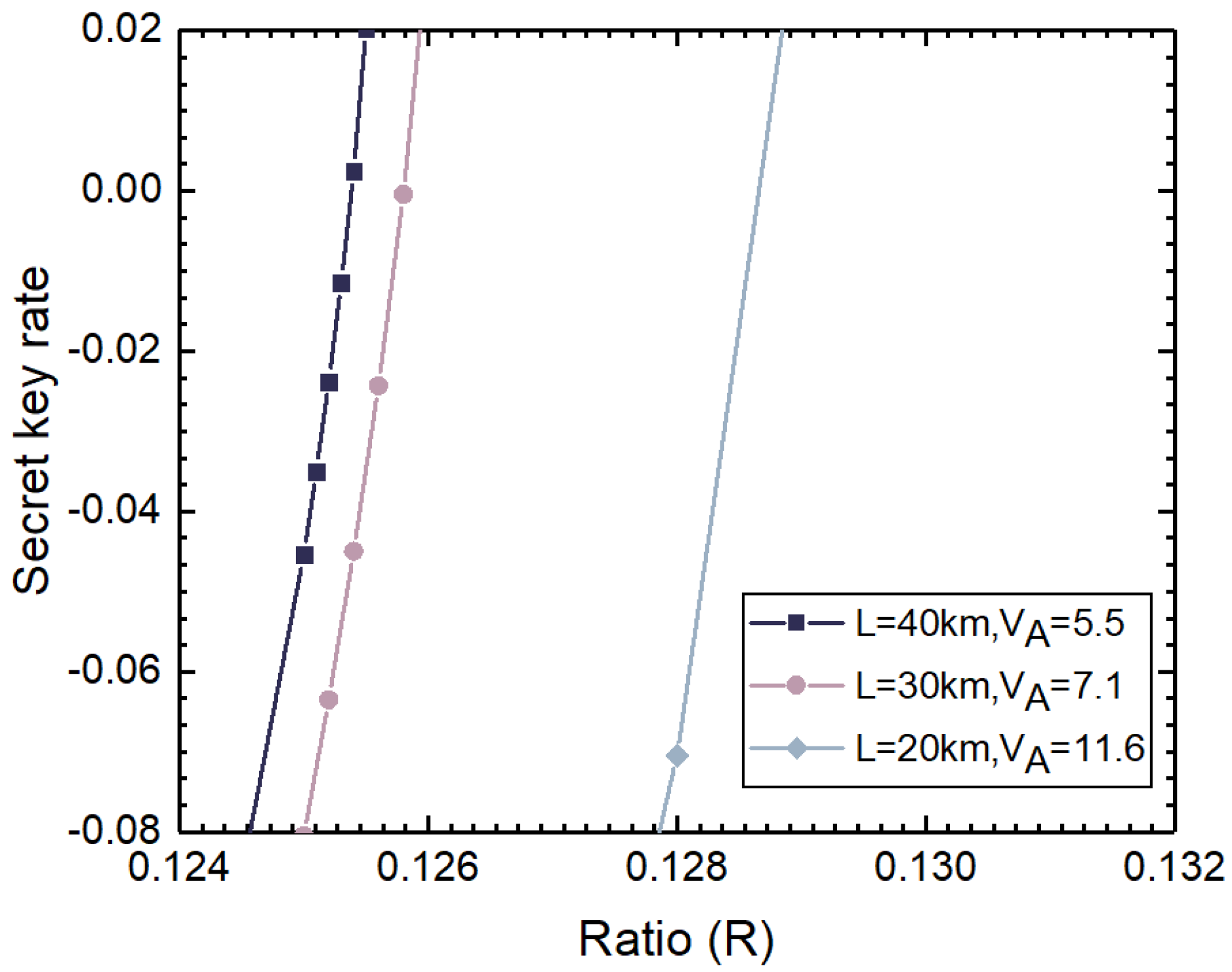
5. Performance Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lo, H.K.; Pan, J.W. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudenbach, F.; Pacher, C.; Fung, C.H.F.; Poppe, A.; Peev, M.; Schrenk, B.; Hentschel, M.; Walther, P.; Hübel, H. Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with Gaussian modulation—The theory of practical implementations. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2018, 1, 1800011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 057902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedbrook, C.; Pirandola, S.; García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Ralph, T.C.; Shapiro, J.H.; Lloyd, S. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 621–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Andersen, U.L.; Banchi, L.; Berta, M.; Bunandar, D.; Colbeck, R.; Englund, D.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 1012–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverrier, A.; Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Finite-size analysis of a continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2010, 81, 062343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navascués, M.; Grosshans, F.; Acín, A. Optimality of Gaussian attacks in continuous-variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 190502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J. Unconditional Optimality of Gaussian Attacks against Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 190503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, R.; Cirac, J.I. de Finetti representation theorem for infinite-dimensional quantum systems and applications to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Chin, H.M.; Mani, H.; Lupo, C.; Nikolic, D.S.; Kordts, A.; Pirandola, S.; Pedersen, T.B.; Kolb, M.; Ömer, B.; et al. Practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajomer, A.A.; Derkach, I.; Jain, N.; Chin, H.M.; Andersen, U.L.; Gehring, T. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution over 100-km fiber with local local oscillator. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadi9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zuo, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, G. Continuous-variable quantum key distribution without synchronized clocks. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2022, 18, 014064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountogiannakis, A.G.; Papanastasiou, P.; Braverman, B.; Pirandola, S. Composably secure data processing for Gaussian-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Res. 2022, 4, 013099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, P.; Mountogiannakis, A.G.; Pirandola, S. Composable security of CV-MDI-QKD with secret key rate and data processing. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountogiannakis, A.G.; Papanastasiou, P.; Pirandola, S. Data postprocessing for the one-way heterodyne protocol under composable finite-size security. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 106, 042606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S. Composable security for continuous variable quantum key distribution: Trust levels and practical key rates in wired and wireless networks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 043014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S. Architectures for QKD networks. In Proceedings of the Photonics for Quantum 2022, Strasbourg, France, 3–7 April 2022; SPIE: St. Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12243, pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, P.; Huang, A.; Peng, J.; Zeng, G. Security analysis of practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution systems under laser seeding attack. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 27369–27384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Gao, B.; Wang, D.; Liao, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Zhong, H.; Huang, A.; Guo, Y. Defending against a laser-seeding attack on continuous-variable quantum key distribution using an improved optical power limiter. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 108, 052616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Kumar, R.; Makarov, V.; Alléaume, R. Homodyne-detector-blinding attack in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 012312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Diamanti, E. Preventing calibration attacks on the local oscillator in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 87, 062313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Li, H.W.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Quantum hacking of a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system using a wavelength attack. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 87, 062329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Jouguet, P.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Quantum hacking on quantum key distribution using homodyne detection. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 032304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunstein, S.L.; Pirandola, S. Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirandola, S.; Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Weedbrook, C.; Braunstein, S.L.; Lloyd, S.; Gehring, T.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Andersen, U.L. High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photon. 2015, 9, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, C.; Lupo, C.; Laurenza, R.; Pirandola, S. Modular network for high-rate quantum conferencing. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalaii, M.; Pirandola, S. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution in free-space channels. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 108, 042621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.I.; Harney, C.; Ghalaii, M.; Papanastasiou, P.; Mountogiannakis, A.; Spedalieri, G.; Hajomer, A.A.; Gehring, T.; Pirandola, S. An Overview of CV-MDI-QKD. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.09818. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.C.; Sun, S.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Liang, L.M. Wavelength attack on practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system with a heterodyne protocol. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 87, 052309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Kumar, R.; Alléaume, R. Quantum hacking: Saturation attack on practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 012325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossier, S.; Diamanti, E.; Debuisschert, T.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Grangier, P. Improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution systems by using optical preamplifiers. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2009, 42, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Guo, Y. Defending Against the Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack on Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Using an Adjustable Optical Attenuator. Entropy 2025, 27, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060631
Wang Y, Li Y, Jiang W, Guo Y. Defending Against the Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack on Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Using an Adjustable Optical Attenuator. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060631
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yijun, Yanyan Li, Wenqi Jiang, and Ying Guo. 2025. "Defending Against the Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack on Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Using an Adjustable Optical Attenuator" Entropy 27, no. 6: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060631
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, Y., Jiang, W., & Guo, Y. (2025). Defending Against the Homodyne Detector-Blinding Attack on Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution Using an Adjustable Optical Attenuator. Entropy, 27(6), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060631





