Constructing Hetero-Microstructures in Additively Manufactured High-Performance High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Regulation of Performance by Minute Defects Within Crystals
2.1. Research on Data-Driven Microstructure Prediction of High Entropy Alloys
2.2. Research Progress on the Regulation of Mechanical Properties of HEAs by Heterogeneous Microstructures
2.3. Research Progress on Heterogeneous Microstructure AM-HEAs
3. Constructing Heterogeneous Microstructures in High-Entropy Alloys Through Additive Manufacturing Processes
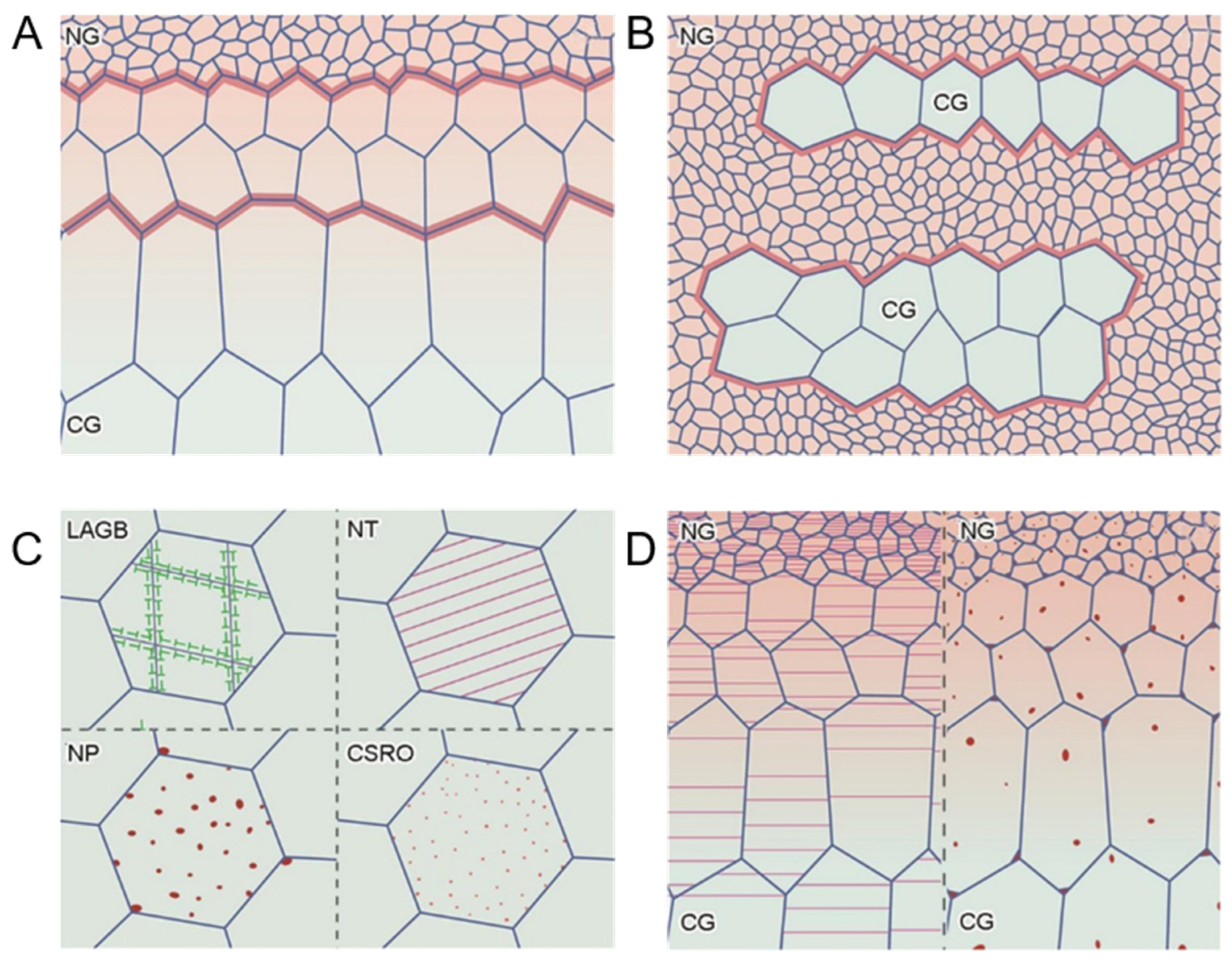
3.1. Different Types of Heterogeneous Microstructures
3.2. Additive Manufacturing of Gradient-Structured High-Entropy Alloys
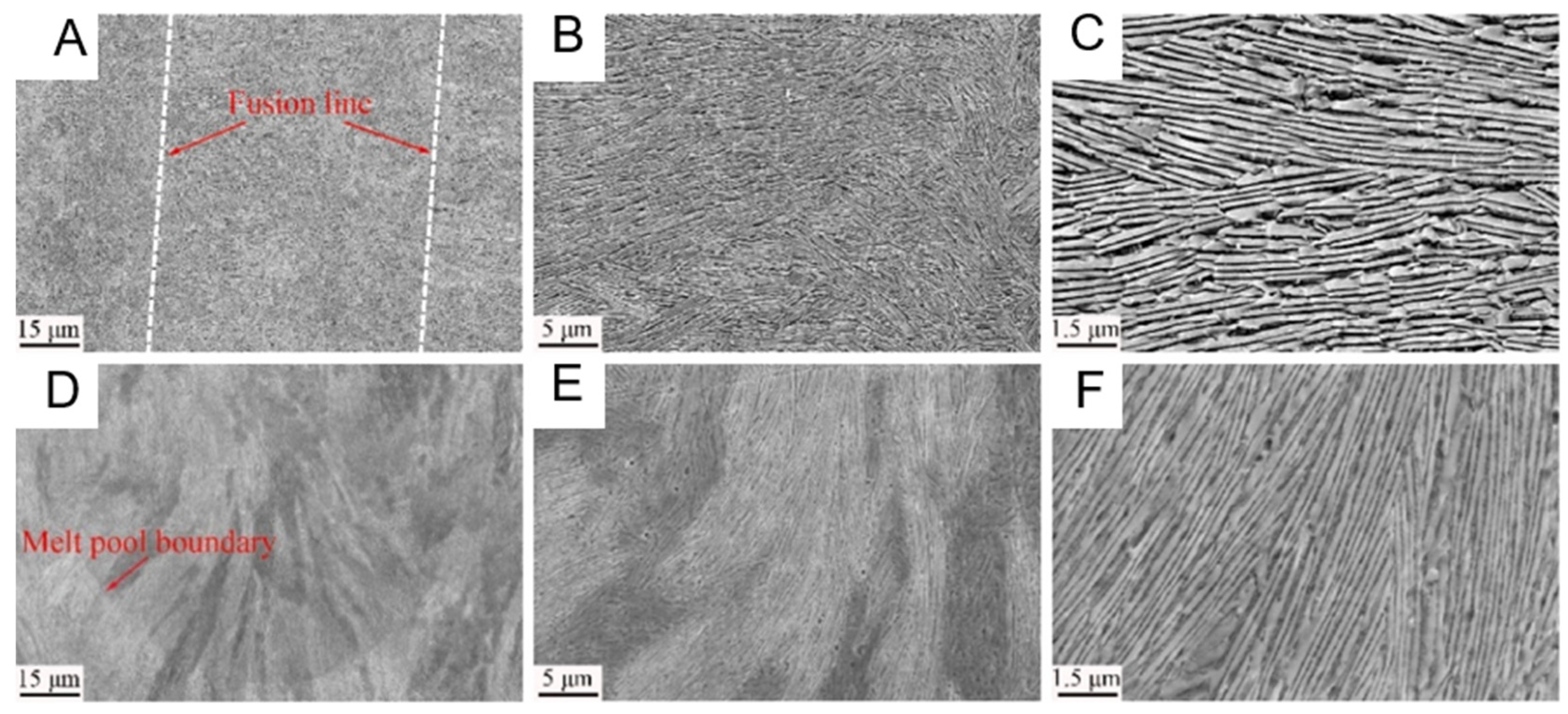
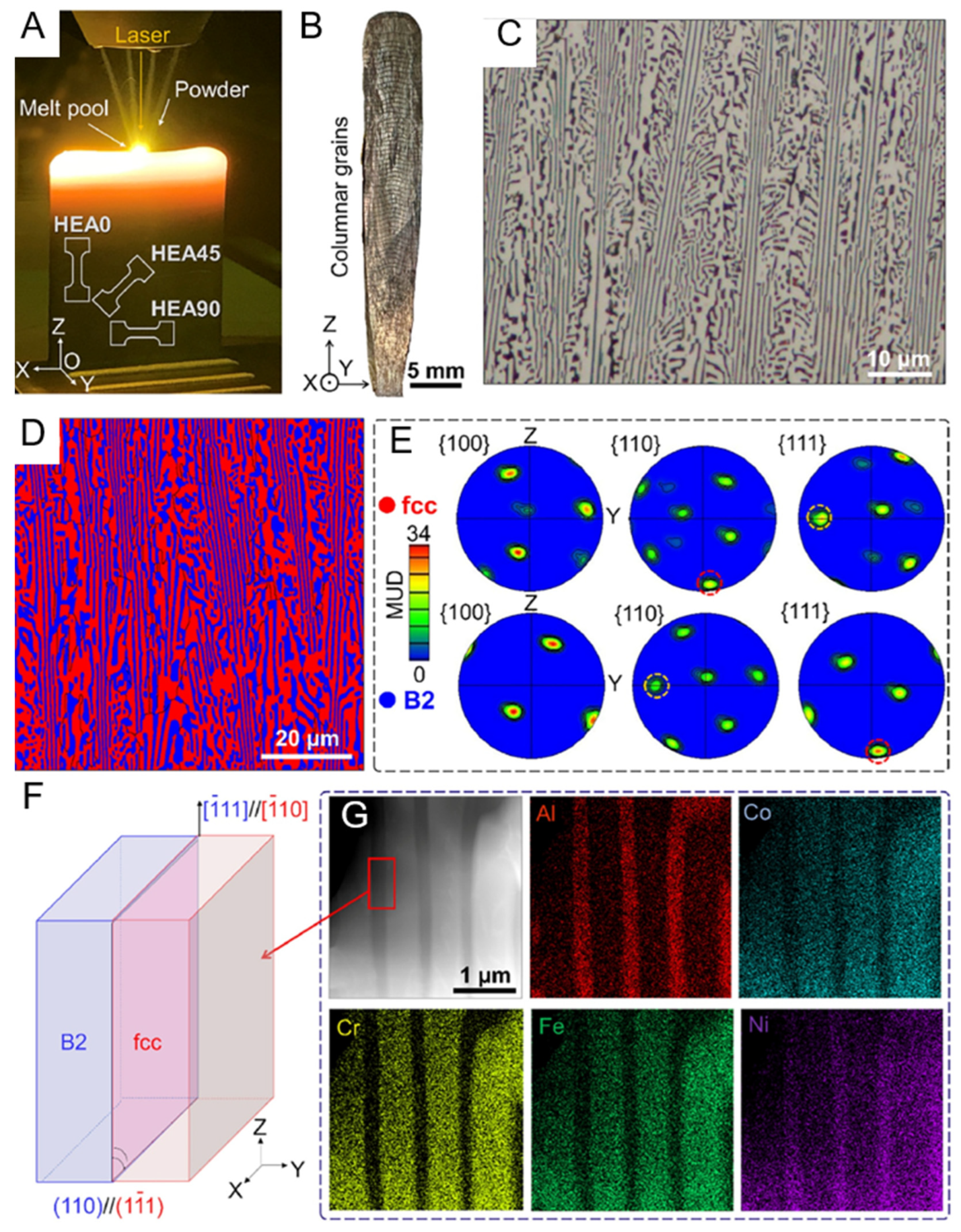
3.3. Additive Manufacturing of Heterogeneous Layered Structure High-Entropy Alloys
3.4. Additive Manufacturing of Multi-Level Heterogeneous Structure High-Entropy Alloy
4. Mechanical Performance Analysis
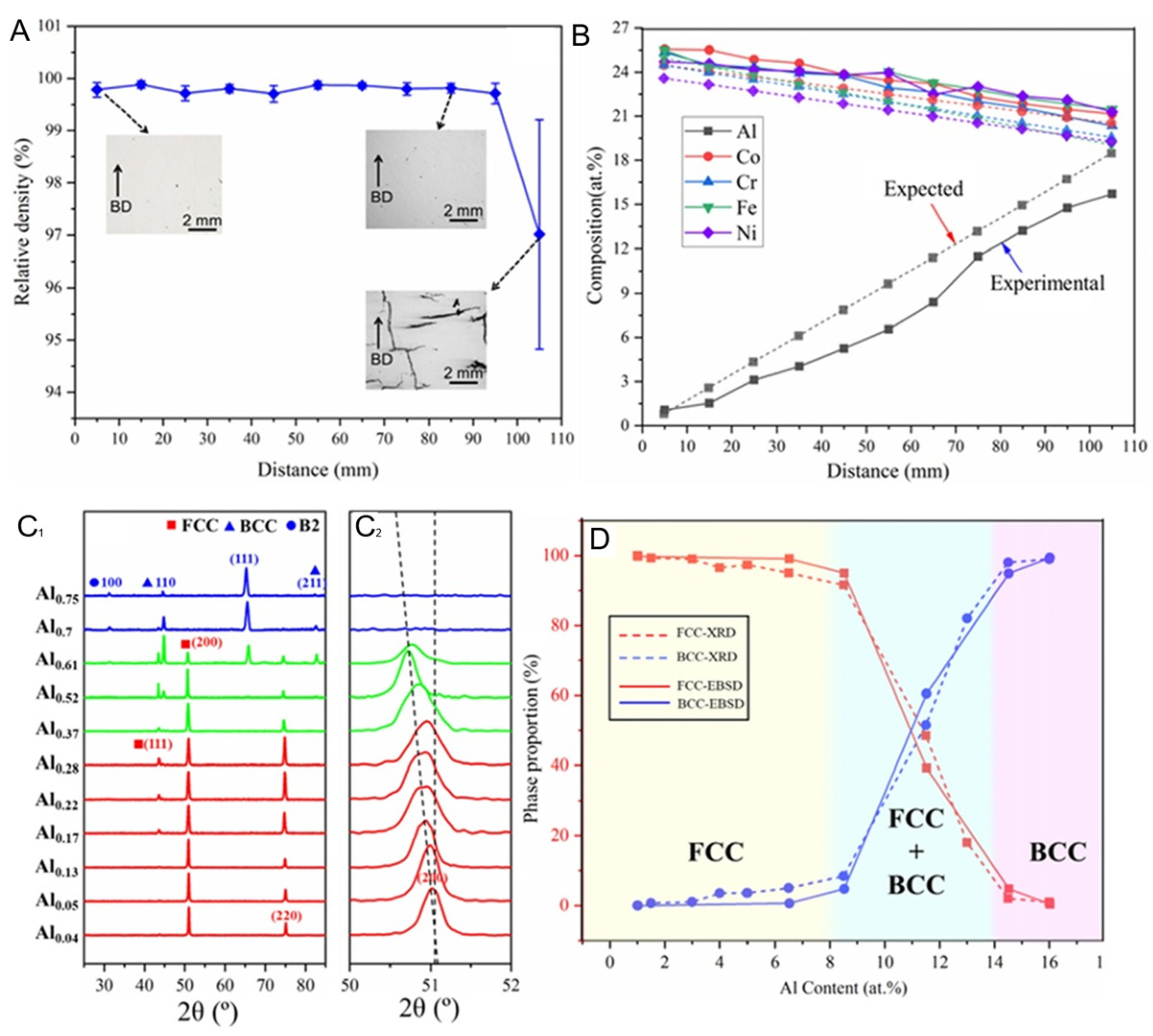
4.1. Additive Manufacturing of Gradient Structure Materials
4.2. Additive Manufacturing Layered Structural Materials
4.3. Additive Manufacturing of Multi-Level Heterogeneous Structures
5. Conclusions and Prospects
- (1)
- It is necessary to establish the connection between multi-dimensional microstructural defects and mechanical properties. Previous studies have demonstrated that the introduction of microstructural defects can to some extent enhance the mechanical properties of metal or alloy materials. However, the introduction of defects still dominates within the material, meaning that the influencing factors of the strengthening and toughening mechanism are relatively single. It is still difficult to achieve the simultaneous introduction of metastable structures dominated by multi-dimensional defects and the simultaneous attainment of high strength and plasticity, and the correlation of multi-dimensional defects with macroscopic mechanical properties remains unclear. Can we combine the inherent characteristics of high-entropy alloys and select additive manufacturing and other processes to achieve the superposition of multi-dimensional defects, and efficiently prepare high-entropy alloys with excellent comprehensive mechanical properties that combine multi-dimensional microstructural defects?
- (2)
- Interaction and metastable characteristics of microstructural defects. The formation of defect structures is mainly caused by the change in external conditions, resulting in the collapse of the intrinsic state of the material. That is, the atoms exhibit irregular local arrangements. As the external conditions continue to change, the defect intrinsic state eventually shows a superposition. Can the rational spatial distribution and configuration of multi-dimensional microstructural defects be precisely controlled, and can the intrinsic relationship between multi-dimensional microstructural defects and mechanical properties be established? However, how do we achieve the stable superposition of multi-dimensional defects under specific compositions and process conditions, and obtain complex spatial arrangements?
- (3)
- The influence laws of the cooperative deformation mechanism of microstructural defects. At present, there are no reports on the influence laws of the cooperative deformation mechanism of defect microstructures and the deformation interaction mechanism among various defects. In conclusion, related research should be a hot topic in the field of face-centered cubic structure high-entropy alloys in the coming years.
- (4)
- How can the parameters be adjusted to achieve more precise energy input during the manufacturing process, and can a controllable temperature gradient be utilized to achieve the directional design and stable regulation of heterogeneous microstructures, thereby fully exploiting the performance potential of HEAs?
- (5)
- For high-entropy alloys, adjusting their composition is an effective way to modify their properties. However, the composition of high-entropy alloys is highly flexible, and the combinations of various elements are diverse. Designing the composition to directly control the properties of the alloy is quite challenging and costly for the current preparation techniques and control methods. Therefore, the search for effective multi-microstructure co-regulation methods and the exploration of the co-deformation mechanisms of multiple types of microstructures are also urgent issues to be addressed at present.
- (6)
- Although there are reports on the research of additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys using artificial neural networks at present, how to establish a large-scale model that can predict the microstructure obtained from additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys with unknown components under multiple computational theories is still a rather difficult problem that needs to be solved at present.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Li, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, P.; Guo, R.; Wang, L. High-Entropy Alloys as a Platform for Catalysis: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 11280–11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Ritchie, R.O.; Meyers, M.A. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with emphasis on face-centered cubic alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 2019, 102, 296–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-J.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Cheng, B.; Wu, Q.; Cao, T.; Xiao, Q.; Xue, Y.; Sha, G.; Wang, Y.; et al. High-content ductile coherent nanoprecipitates achieve ultrastrong high-entropy alloys. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeweiss, O.; Friák, M.; Dudová, M.; Holec, D.; Šob, M.; Kriegner, D.; Holý, V.; Beran, P.; George, E.P.; Neugebauer, J.; et al. Magnetic properties of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 014437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Lu, Z.P. Thermoelectric high-entropy alloys with low lattice thermal conductivity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 52164–52170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, W.; Zheng, T.; Shen, Z.; Yang, B.; Peng, J.; Hu, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Multistage work hardening assisted by multi-type twinning in ultrafine-grained heterostructural eutectic high-entropy alloys. Mater. Today 2020, 41, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.L.; Xu, X.D.; Chen, M.W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; An, K.; Lu, Z.P. A precipitation-hardened high-entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2016, 102, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Wei, J.; Cai, J.; Han, X.; Chen, D.; Hu, A.; Kai, J. Multicomponent intermetallic nanoparticles and superb mechanical behaviors of complex alloys. Science 2018, 362, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, D.; Fieser, D.; Santiago, J.J.; Hu, A. Novel Frontiers in High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Katiyar, N.; Biswas, K.; Yeh, J.-W.; Sharma, S.; Sekhar Tiwary, C. A perspective on the catalysis using the high entropy alloys. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Züttel, A. Nanoscale engineering of solid-state materials for boosting hydrogen storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 972–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, L.; Moussa, M.; Yao, J.-Y.; Silva, G.; Bobet, J.-L.; Santos, S.F.; Cardoso, K.R. Development of Ti-V-Nb-Cr-Mn high entropy alloys for hydrogen storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 945, 169289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, R.R.; Gupta, A.K.; Kumari, P. Perspectives of high entropy alloys as hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 21412–21428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Wu, X. Tailoring heterogeneities in high-entropy alloys to promote strength–ductility synergy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, C.J.; Easton, M.A.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, D.; Bermingham, M.J.; Lui, E.W.; Brandt, M.; StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M. Grain structure control during metal 3D printing by high-intensity ultrasound. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Fang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Tor, S.B.; Chua, C.K.; Zhou, K. Recent Advances on High-Entropy Alloys for 3D Printing. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1903855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cui, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wei, N.; Gao, X.; Song, Q. Enhanced strength and ductility in a spark plasma sintered CoCrCu0·5NiAl0.5 high-entropy alloy via a double-step ball milling approach for processing powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762, 138071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Jones, N.G. High-entropy alloys: A critical assessment of their founding principles and future prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheriniya, S.; Davani, F.A.; Hilke, S.; Hepp, M.; Gadelmeier, C.; Chellali, M.R.; Boll, T.; Rösner, H.; Peterlechner, M.; Gammer, C.; et al. High entropy alloy nanocomposites produced by high pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2021, 208, 116714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, W.; Shen, Z.; Zheng, T.; Peng, J.; Liang, X. Hierarchical crack buffering triples ductility in eutectic herringbone high-entropy alloys. Science 2021, 373, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.; Liu, B.; Xu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y. Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of a novel (FeCoNi)86.93Al6.17Ti6.9 medium entropy alloy fabricated via powder metallurgy technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 860, 158460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xia, T.; Zhou, D.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D. A novel nanostructure to achieve ultrahigh strength and good tensile ductility of a CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 5347–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xia, T.; Zeng, W.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, D. Grain growth and strengthening mechanisms of ultrafine-grained CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy matrix nanocomposites fabricated by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Furuhara, T.; Park, E.S.; Tasan, C.C. Natural-mixing guided design of refractory high-entropy alloys with as-cast tensile ductility. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wardini, J.L.; MacDonald, B.E.; Wen, H.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Rupert, T.J.; Chen, W.; et al. A high-entropy alloy with hierarchical nanoprecipitates and ultrahigh strength. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Průša, F.; Šenková, A.; Kučera, V.; Čapek, J.; Vojtěch, D. Properties of a high-strength ultrafine-grained CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy prepared by short-term mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 734, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Cizek, J.; Zapletal, J.; Kovacova, Z.; Vesely, J.; Minarik, P.; Kitzmantel, M.; Neubauer, E.; Dlouhy, I. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni1,5Co1,5CrFeTi0,5 high entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedov, V. Spark plasma sintering as advanced PM sintering method. Powder Metall. 2002, 45, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutor, R.K.; Cao, Q.; Wei, R.; Su, Q.; Du, G.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.-Z. A dual-phase alloy with ultrahigh strength-ductility synergy over a wide temperature range. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Tabachnikova, E.; Shumilin, S.; Hryhorova, T.; Estrin, Y.; Brechtl, J.; Liaw, P.K.; Wang, W.; Dahmen, K.A.; Zargaran, A.; et al. Deformation behavior of a Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Mo medium-entropy alloy at extremely low temperatures. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Hao, J.; Gault, B.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, C.; Nieh, T.G. A Novel Soft-Magnetic B2-Based Multiprincipal-Element Alloy with a Uniform Distribution of Coherent Body-Centered-Cubic Nanoprecipitates. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Rao, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Ghazisaeidi, M.; Ungar, T.; Wang, H.; An, K.; et al. Enhancing fatigue life by ductile-transformable multicomponent B2 precipitates in a high-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Dai, S. High-entropy materials for catalysis: A new frontier. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuang, S.; Ding, Z.Y.; Chung, D.; Shi, S.Q.; Yang, Y. Corrosion resistant nanostructured eutectic high entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 164, 108315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Sohn, S.S.; Lu, W.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Soundararajan, C.K.; Krieger, W.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. A strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy resists hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Haghdadi, N.; Annasamy, M.; Kada, S.; Hodgson, P.D.; Barnett, M.R.; Fabijanic, D.M. On the enhanced wear resistance of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy at intermediate temperature. Scr. Mater. 2020, 186, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atwani, O.; Li, N.; Li, M.; Devaraj, A.; Baldwin, J.K.S.; Schneider, M.M.; Sobieraj, D.; Wróbel, J.S.; Nguyen-Manh, D.; Maloy, S.A.; et al. Outstanding radiation resistance of tungsten-based high-entropy alloys. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Mingers, A.M.; Raabe, D. Corrosion behavior of an equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy compared with 304 stainless steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2018, 134, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gan, K.; Yan, D.; Han, L.; Wu, P.; Li, Z. Multiple minor elements improve strength-ductility synergy of a high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 840, 142901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Ameyama, K. Enhanced synergy of strength-ductility and low-cycle fatigue resistance of high-entropy alloy through harmonic structure design. Scr. Mater. 2022, 213, 114591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Mao, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z. Effects of Ni and Al on precipitation behavior and mechanical properties of precipitation-hardened CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 839, 142879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jo, Y.H.; An, W.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.-J.; Lee, S.; Sung, H.; Sohn, S.S. Effects of deformation-induced martensitic transformation on cryogenic fracture toughness for metastable Si8V2Fe45Cr10Mn5Co30 high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2022, 225, 117568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Ultrastrong and ductile BCC high-entropy alloys with low-density via dislocation regulation and nanoprecipitates. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 110, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of C Hf0.25NbTaW0.5 refractory high-entropy alloys at room and high temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 97, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ji, S. High strength and ductility of an additively manufactured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy achieved by minor Mo doping. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 843, 143129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, H. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance characterization of a novel Co36Fe36Cr18Ni10 high-entropy alloy for bioimplants compared to 316L alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 906, 163947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, D.F.; Li, H.; Orhan, O.K.; Shao, C.; Hogan, J.D.; Ponga, M. Mechanical and microstructural properties of a CoCrFe0.75NiMo0.3Nb0.125 high-entropy alloy additively manufactured via cold-spray. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 893, 162309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehranpour, M.S.; Shahmir, H.; Asghari-Rad, P.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Rasooli, N.; Kim, H.S.; Nili-ahmadabadi, M. Upgrading of superior strength–ductility trade-off of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy by microstructural engineering. Materialia 2022, 22, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Tung, P.-Y.; Xie, R.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ferrari, A.; Klaver, T.P.C.; Körmann, F.; Sukumar, P.T.; Kwiatkowski da Silva, A.; et al. Machine learning–enabled high-entropy alloy discovery. Science 2022, 378, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Xie, Z.; Si, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. Exploration for the physical origin and impact of chemical short-range order in high-entropy alloys: Machine learning-assisted study. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Aitken, Z.H.; Pattamatta, S.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z.G.; Srolovitz, D.J.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y.-W. Simultaneously enhancing the ultimate strength and ductility of high-entropy alloys via short-range ordering. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oñate, A.; Sanhueza, J.P.; Dueña, G.; Wackerling, D.; Sauceda, S.; Salvo, C.; Valenzuela, M.; Medina, C.; Seidou, A.H.; Tchuindjang, J.T.; et al. Sigma Phase Stabilization by Nb Doping in a New High-Entropy Alloy in the FeCrMnNiCu System: A Study of Phase Prediction and Nanomechanical Response. Metals 2024, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, W.; Su, L.; Tang, D. Correlation mechanism of grain orientation/microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu–Ni–Si–Co alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 814, 141239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhao, H.; Liebscher, C.H.; He, J.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Ultrastrong lightweight compositionally complex steels via dual-nanoprecipitation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Luan, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, H.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, C.-T. Ultrahigh strength and ductility in newly developed materials with coherent nanolamellar architectures. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, S.; Hui, X.; Wu, Y.; Gault, B.; Kontis, P.; et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature 2018, 563, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, N.; Wu, G.; Sha, G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Microstructural origins of high strength and high ductility in an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 141, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, C.; Feng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, G.; Lewandowski, J.J.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High-entropy Al0.3CoCrFeNi alloy fibers with high tensile strength and ductility at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mater. 2017, 123, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; He, F.; Li, J.; Kim, H.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Phase-selective recrystallization makes eutectic high-entropy alloys ultra-ductile. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Maccari, F.; Souza Filho, I.R.; Peter, N.J.; Wei, Y.; Gault, B.; Gutfleisch, O.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. A mechanically strong and ductile soft magnet with extremely low coercivity. Nature 2022, 608, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Yao, M.; Gault, B.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Hirata, A.; et al. Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation. Nature 2017, 544, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.R.; Fan, L.; Han, B.; Jiao, Z.B.; Chen, D.; Liu, C.T.; Kai, J.J. Superior high-temperature properties and deformation-induced planar faults in a novel L12-strengthened high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Fan, L.; Wei, J.; Luan, J.H.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, C.; Jiao, Z.B.; Kai, J.J.; Liu, C.T. Control of nanoscale precipitation and elimination of intermediate-temperature embrittlement in multicomponent high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 189, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; An, K.; Wu, W.; Lu, Z. Phase-Transformation Ductilization of Brittle High-Entropy Alloys via Metastability Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Shi, X.; Poprawe, R.; Bourell, D.L.; Setchi, R.; Zhu, J. Material-structure-performance integrated laser-metal additive manufacturing. Science 2021, 372, eabg1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Surjadi, J.U.; Fan, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, S.; Lu, Y. Microalloyed medium-entropy alloy (MEA) composite nanolattices with ultrahigh toughness and cyclability. Mater. Today 2021, 42, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, S.L.; Yeong, W.Y. Laser powder bed fusion for metal additive manufacturing: Perspectives on recent developments. Virtual Phys. Prototyping 2020, 15, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Heer, B. Additive manufacturing of multi-material structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2018, 129, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourell, D.L. Perspectives on Additive Manufacturing. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, X.; Fu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, T.; Tian, Y.; Tan, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Ductile and ultrahigh-strength eutectic high-entropy alloys by large-volume 3D printing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, C.; Jiang, M.; Liu, C.; Jia, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Liu, Z. Strengthening and fracture mechanisms of a precipitation hardening high-entropy alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2022, 17, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Wan, D.; Solberg, K.; Berto, F.; Welo, T.; Yue, T.M.; Chan, K.C. Additive manufacturing of fine-grained and dislocation-populated CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy by laser engineered net shaping. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 761, 138056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Nai, M.L.S.; An, X. Enhanced thermal stability and mechanical properties of an additively manufactured CoCrNiFeMn high entropy alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 237, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagirici, M.; Wang, P.; Ng, F.L.; Nai, M.L.S.; Ding, J.; Wei, J. Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys by thermophysical calculations and in situ alloying. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 94, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Deepu, M.J.; Rahul, M.R.; Phanikumar, G. Microstructure prediction of eutectic high entropy alloy using physical and computer simulation for additive manufacturing condition. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Feng, H.; Peng, S. Microstructure and properties of selective laser melted Alx CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy via molecular dynamics simulation. Acta Mech. Sin. 2025, 42, 124311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, H.; Li, X.; Chen, X. Complex multiphase predicting of additive manufactured high entropy alloys based on data augmentation deep learning. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2388–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ding, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, J.; Wu, J.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Shen, Z. Dislocation network in additive manufactured steel breaks strength–ductility trade-off. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Dovgyy, B.; Xu, W.; Sha, A.; Li, X.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Pham, M.-S. Micro-cracking, microstructure and mechanical properties of Hastelloy-X alloy printed by laser powder bed fusion: As-built, annealed and hot-isostatic pressed. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 39, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; He, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Yuan, F. Medium/high entropy alloys with heterogeneous structures for superior properties: A review. Mater. Today Adv. 2025, 25, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Shen, Q.; Chen, X.; Wen, M.; Jayalakshmi, S. Dual wire arc additive manufacturing of compositionally graded Al -Co-Cr-Fe-Ni high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 4052–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Qiu, X.; Bian, X.; Wu, S.; Yu, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zheng, W.; Shi, J.; et al. Laser directed energy deposited eutectic high entropy alloy with tailored lamella structure via interlayer pause strategy. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 94, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, B.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, F.; Gong, L.; Liu, J. Additive manufacturing of CoCrFeNiMo eutectic high entropy alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 913, 165239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wei, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, B.; Ramamurty, U.; Qu, X. Effect of dual phase structure induced by chemical segregation on hot tearing reduction in additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2023, 228, 111847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kong, J.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Dong, K.; Yang, Y. High-strength AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy with ultrafine lamella structure via additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 854, 143816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Ng, F.L.; An, X.H.; Liao, X.Z.; Liaw, P.K.; Nai, S.M.L.; Wei, J. Hierarchical microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of a CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lang, L.; Shang, X.; Dash, S.S.; He, Y.; King, G.; Zou, Y. Anisotropic co-deformation behavior of nanolamellar structures in additively manufactured eutectic high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2024, 271, 119885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
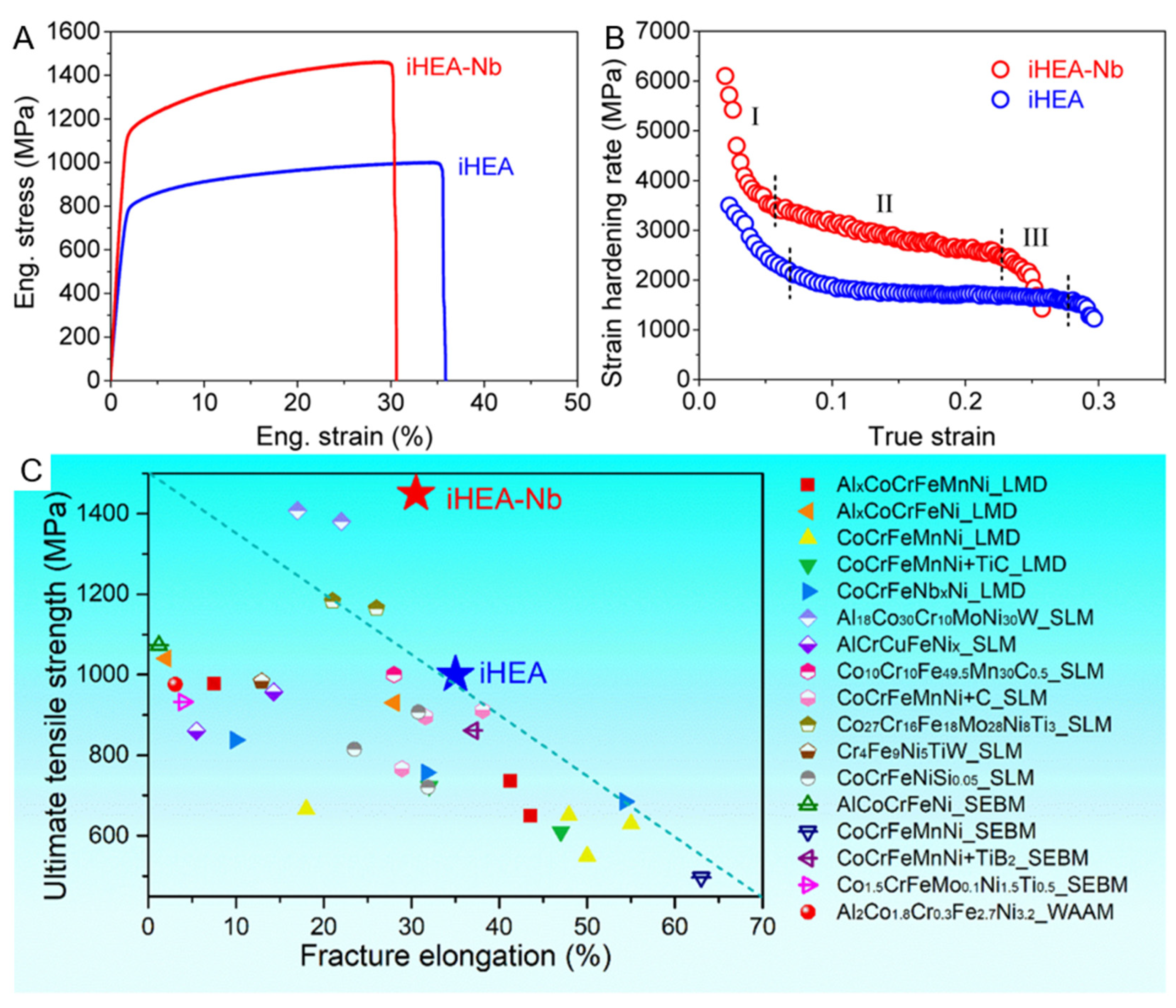
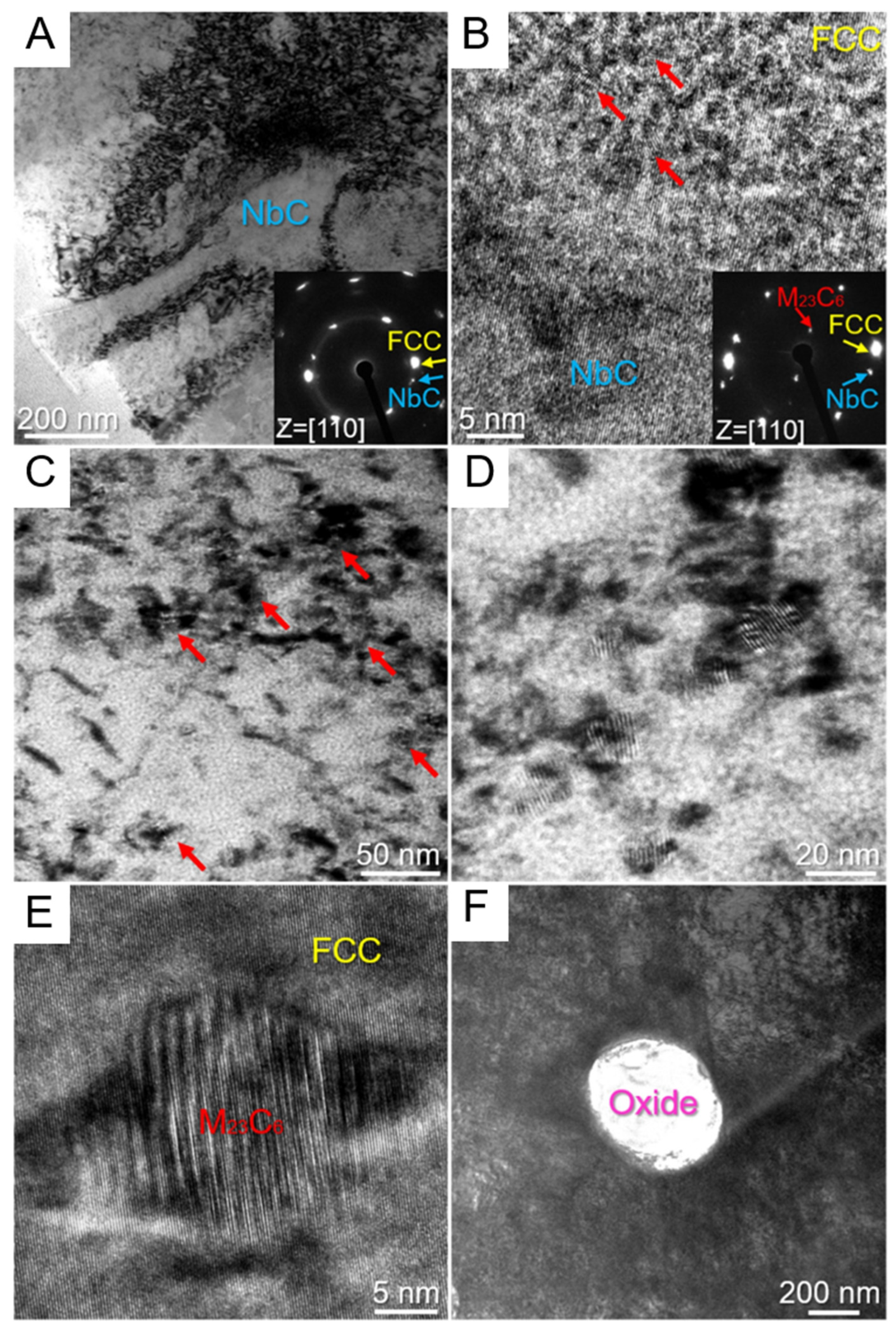
- Zhang, W.; Chabok, A.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Oliveira, J.P.; Feng, S.; Schell, N.; Kooi, B.J.; Pei, Y. Ultra-strong and ductile precipitation-strengthened high entropy alloy with 0.5% Nb addition produced by laser additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 187, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
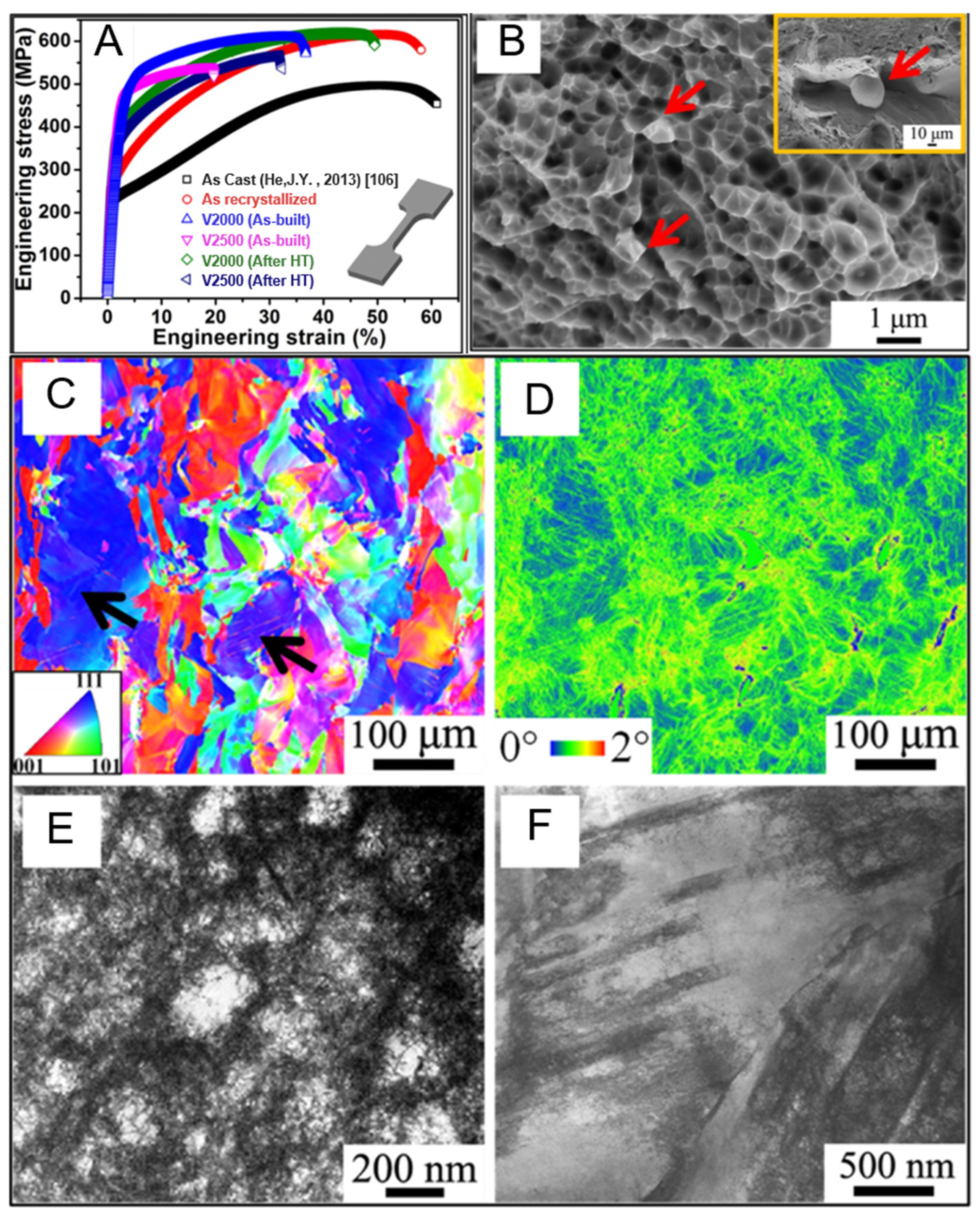
- Guo, L.; Wu, W.; Ni, S.; Yuan, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, M. Strengthening the FeCoCrNiMo0.15 high entropy alloy by a gradient structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 841, 155688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, G.M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, E.S.; Zargaran, A.; Sathiyamoorthi, P.; Park, J.M.; Jeong, S.G.; Gu, G.H.; Amanov, A.; Ungar, T.; et al. Gradient heterostructured laser-powder bed fusion processed CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 59, 103131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, C.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ge, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, G. Microstructures and room temperature tensile properties of as-cast and directionally solidified AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2020, 118, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, B.; Xiao, L.; Hu, J.; Xu, M.; Li, Z.; Meng, J.; Han, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Y. Heterostructured Metallic Structural Materials: Research Methods, Properties, and Future Perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, K.; Gao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, Z.J. Hardened austenite steel with columnar sub-grain structure formed by laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 625, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tan, X.; Tor, S.B.; Chua, C.K. Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility for 3D-printed stainless steel 316L by selective laser melting. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; Sanaullah, K.; Zhang, C.; Chu, J.; Nian, Y.; Cheng, J. Strengthening mechanisms in high entropy alloys: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Fan, J.; Yuan, F.; Wu, X. Superior dynamic shear properties and deformation mechanisms in a high entropy alloy with dual heterogeneous structures. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, C.; Vecchio, K. Non-equiatomic FeNiCoAl-based high entropy alloys with multiscale heterogeneous lamella structure for strength and ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Xu, S.M.; Wang, F.; Li, J.L.; Wen, G.D.; Xiong, J.T.; Guo, W. Simultaneously enhancing strength–ductility synergy in refractory high entropy alloys by a heterogeneous structure design. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 993, 174550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Fang, F. Dynamic tensile deformation of Al0.1Ti0.1CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy with heterogeneous grain structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haftlang, F.; Kim, E.S.; Kwon, J.; Heo, Y.-U.; Kim, H.S. Extraordinary combination of strength and ductility in an additively manufactured Fe-based medium entropy alloy through in situ formed η-nanoprecipitate and heterogeneous microstructure. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 63, 103421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 2014, 62, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

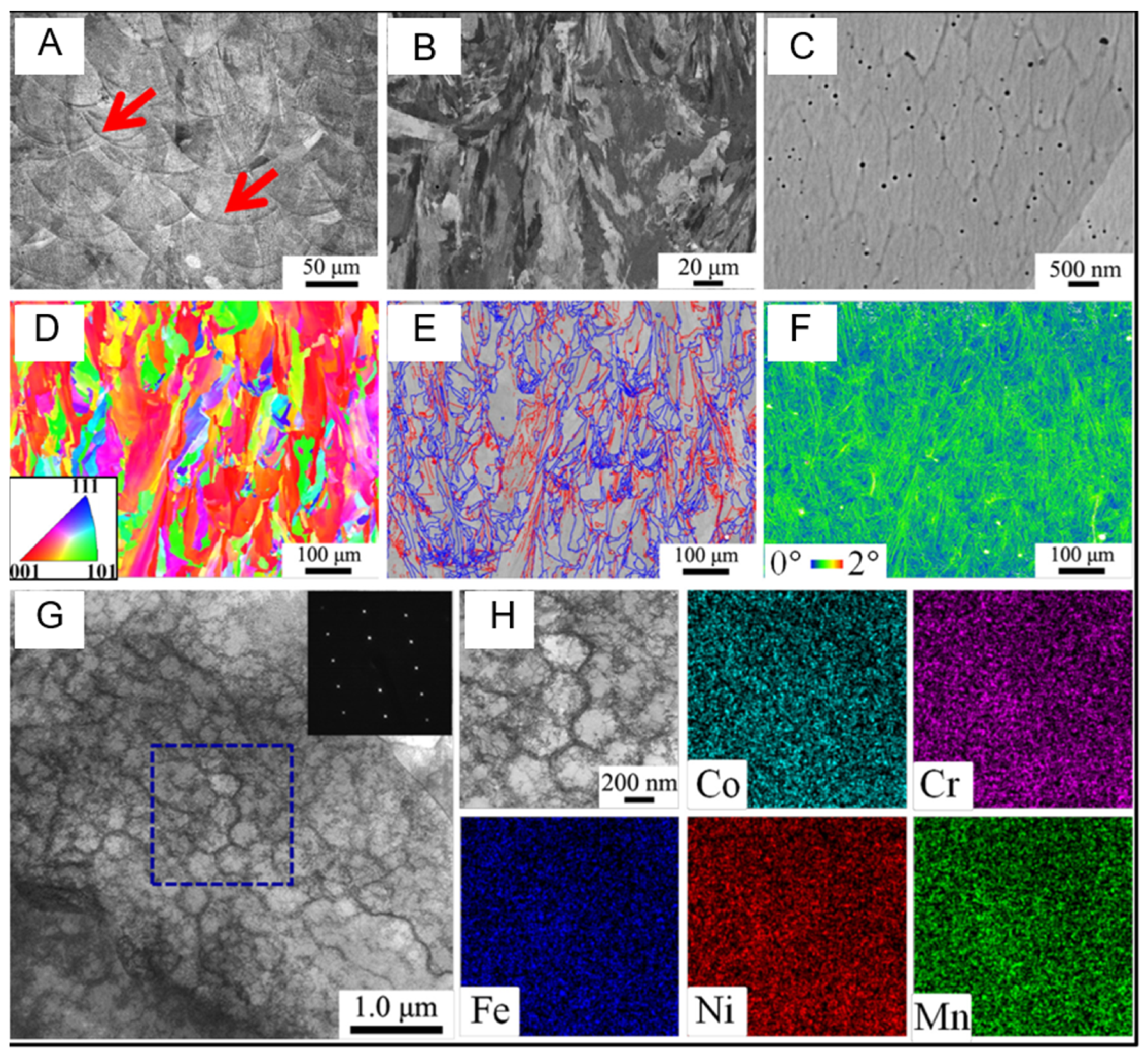
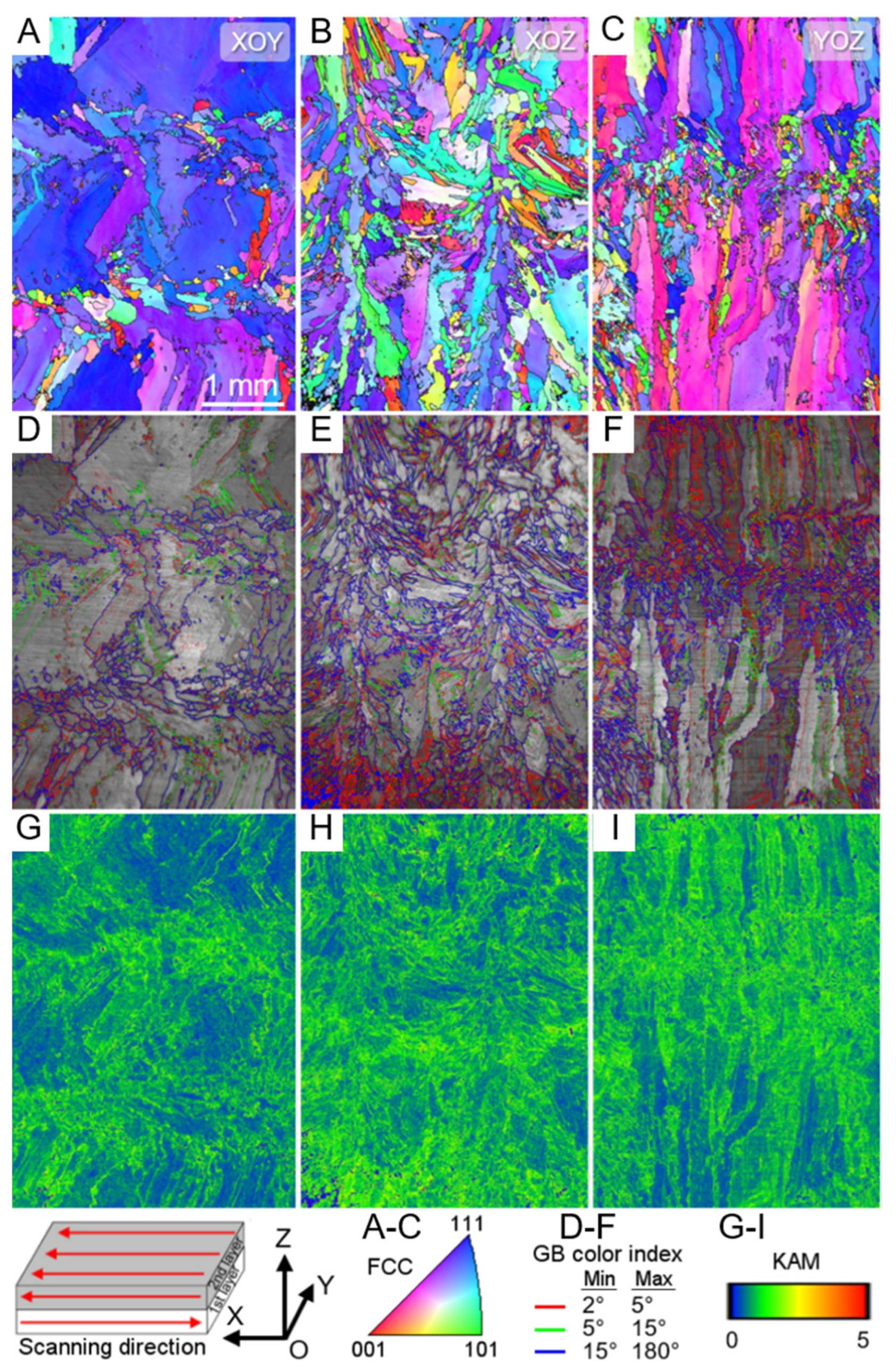
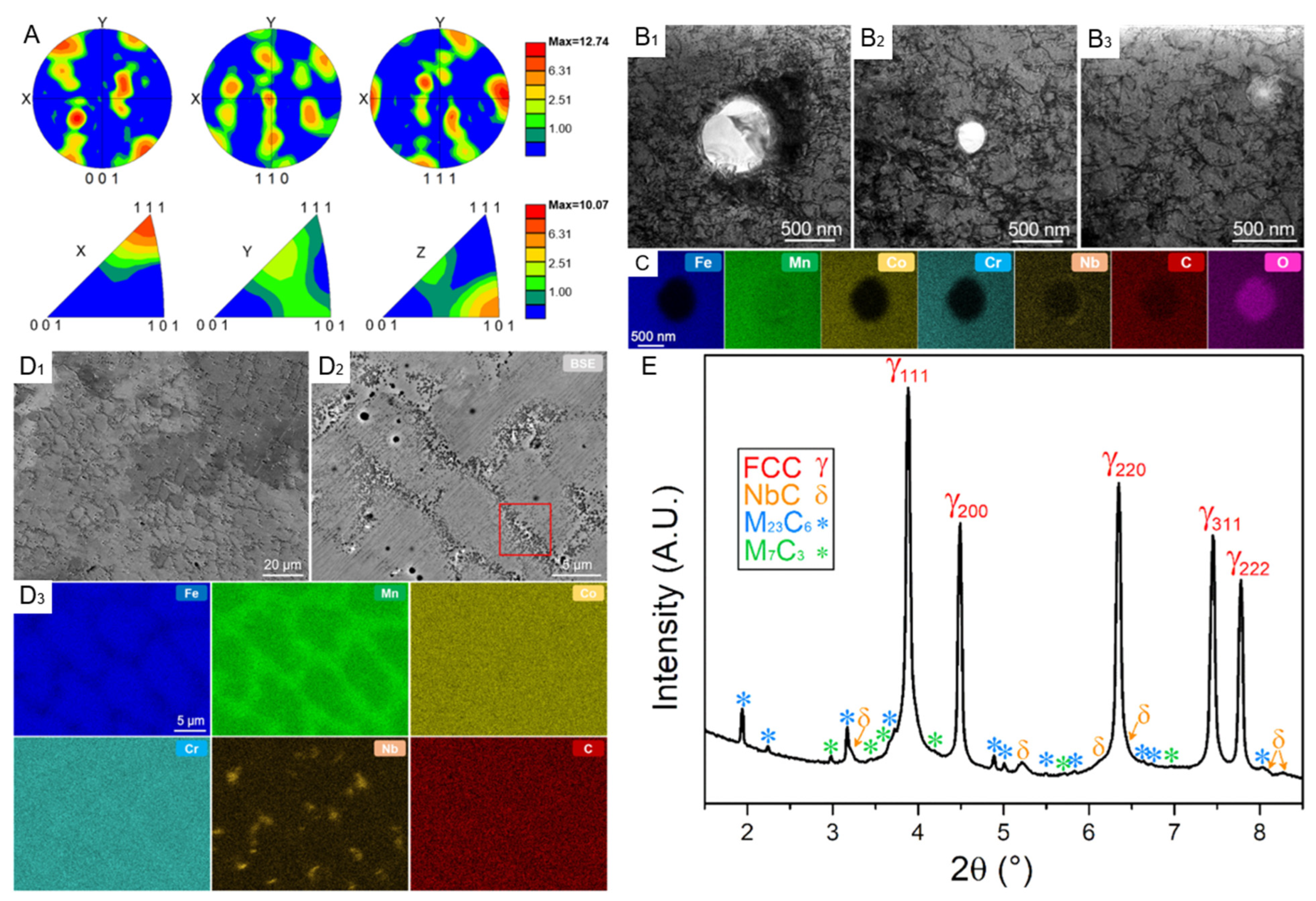
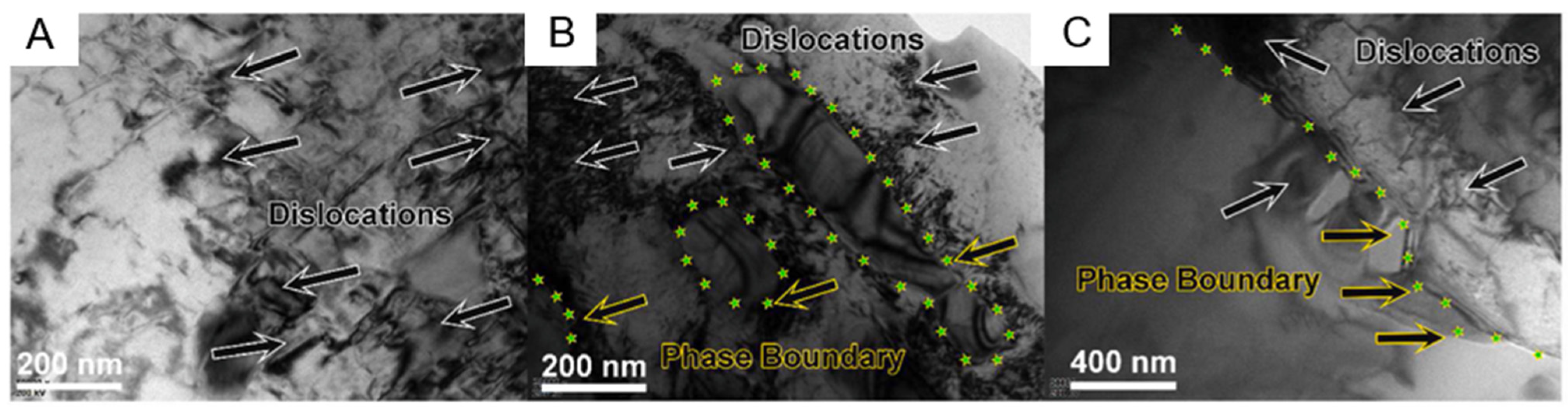




| Method | Composition | Microstructure | YS (Mpa) | UTS (Mpa) | HV | PS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WAAM [86] | AlCoCrFeNi (21%Al) | Bottom BCC + FCC | 827.4 ± 15.1 | 2720.8 ± 29.4 | 342.3 ± 9.4 | 42.3 ± 0.7 |
| AlCoCrFeNi (30%Al) | Middle BCC + FCC | 877.1 ± 21.3 | 2047.9 ± 18.5 | 370.6 ± 13.7 | 24.5 ± 1.8 | |
| AlCoCrFeNi (35%Al) | Top BCC | 955.5 ± 5.4 | 1712.0 ± 38.6 | 369.9 ± 7.3 | 17.1 ± 0.7 | |
| LPBF [89] | AlCoCrFeNi ( = 0.04–0.75) | BCC + FCC | 560–640 | 700–760 | 220–550 | 1.33–24 |
| SLM [90] | AlCoCrFeNi2.1 | B2 + FCC | 1329 ± 12 | - | ||
| SLM [91] | CoCrFeNiMn | Multi-level heterogeneous structure | 510 ± 10 | - | ||
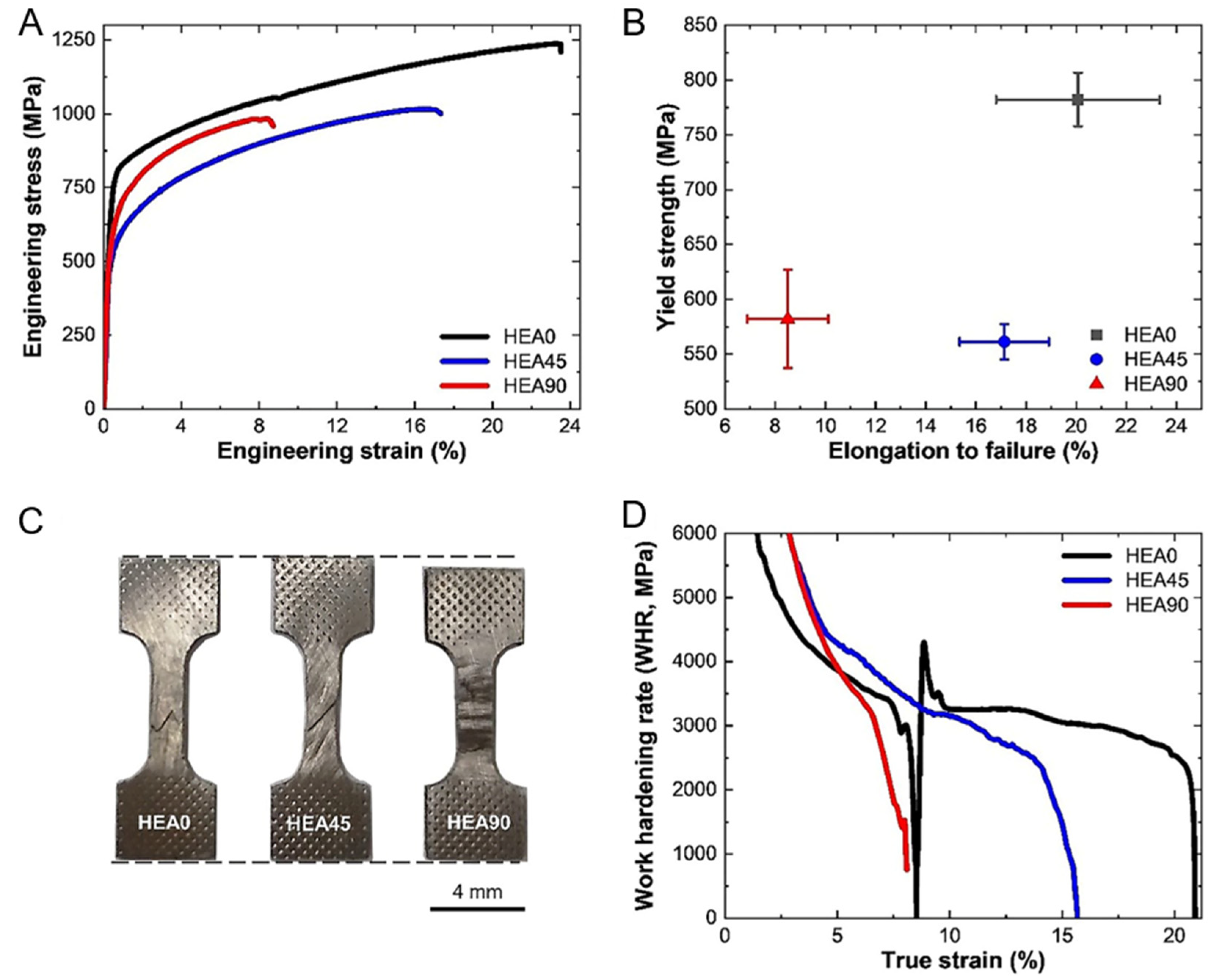
| LDED [92] | AlCoCrFeNi2.1-HEA0 | FCC + B2 | 800 | - | 23.5 | |
| AlCoCrFeNi2.1-HEA45 | 580 | - | 17.2 | |||
| AlCoCrFeNi2.1-HEA90 | 625 | - | 8.5 | |||
| LMD [93] | Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 | Multi-level heterogeneous structure | 1140 | 1450 | - | |
| LDED [87] | AlCoCrFeNi2.1 | B2 + FCC | 773 ± 18 | 1214 ± 20 | - | 16.3 ± 0.6 |
| LDED [88] | CoCrFeNiMo | FCC + | - | - | 658.44 | - |
| Region | Hardness (HV) | YS (MPa) | FS (MPa) | PS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | 369.9 ± 7.3 | 955.5 ± 5.4 | 1712.0 ± 38.6 | 17.1 ± 0.7 |
| Middle | 370.6 ± 13.7 | 877.1 ± 21.3 | 2047.9 ± 18.5 | 24.5 ± 1.8 |
| Bottom | 342.3 ± 9.4 | 827.4 ± 15.1 | 2720.8 ± 29.4 | 42.3 ± 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Mu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, G. Constructing Hetero-Microstructures in Additively Manufactured High-Performance High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2025, 27, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090917
Zhao Y, Wu Z, Mu Y, Jia Y, Jia Y, Wang G. Constructing Hetero-Microstructures in Additively Manufactured High-Performance High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090917
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yuanshu, Zhibin Wu, Yongkun Mu, Yuefei Jia, Yandong Jia, and Gang Wang. 2025. "Constructing Hetero-Microstructures in Additively Manufactured High-Performance High-Entropy Alloys" Entropy 27, no. 9: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090917
APA StyleZhao, Y., Wu, Z., Mu, Y., Jia, Y., Jia, Y., & Wang, G. (2025). Constructing Hetero-Microstructures in Additively Manufactured High-Performance High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy, 27(9), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090917







