Investigation of Signal Transmission Dynamics in Rulkov Neuronal Networks with Q-Learned Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Proposes a novel computational model for neuronal networks, comprising Rulkov neurons exhibiting nonlinear dynamics, where Q-learning autonomously configures signal transmission pathways based on learned Q-values.
- Quantitative analysis of how intrinsic neuronal dynamics (e.g., bursting and spiking) affect signal transmission.
2. Preliminaries
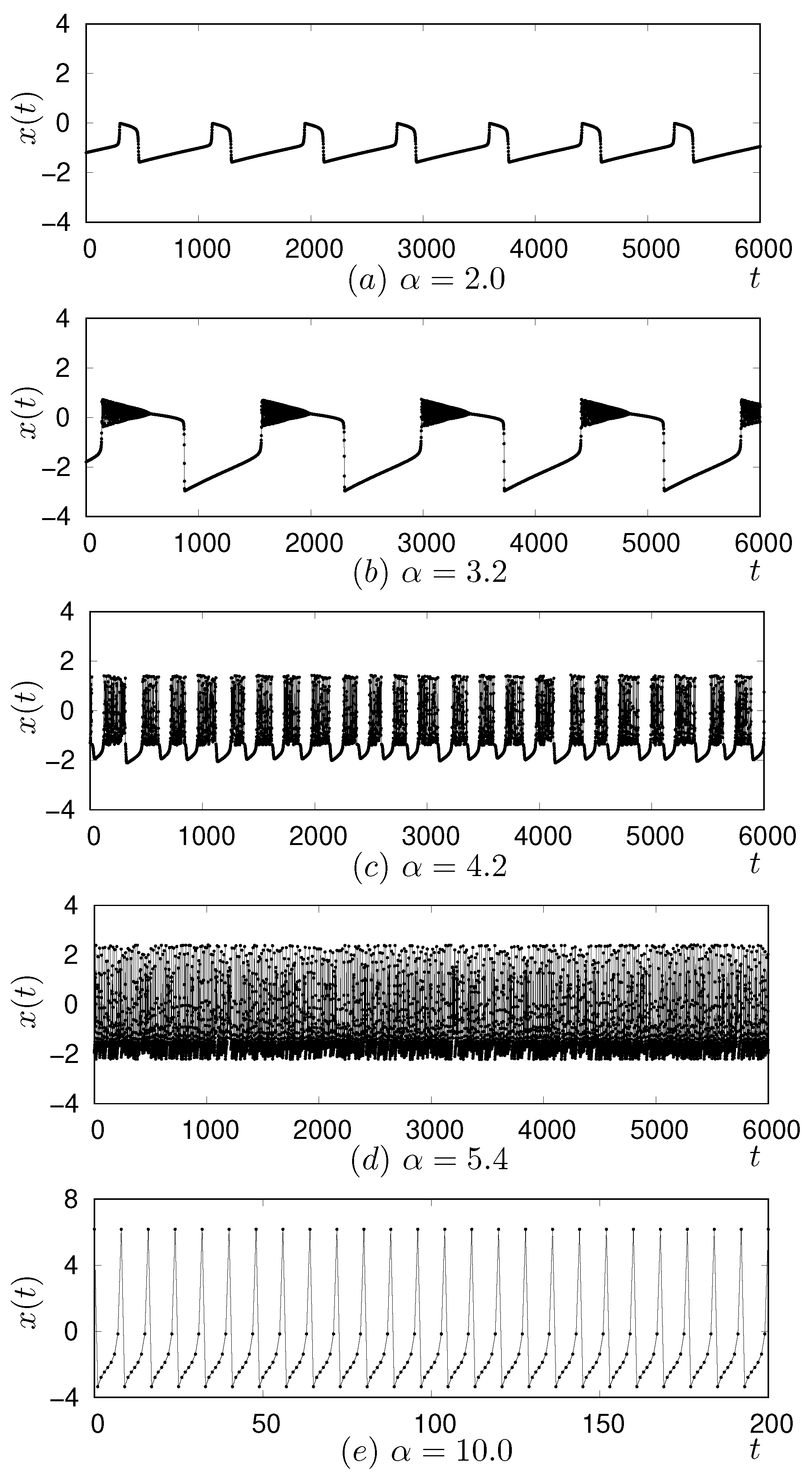
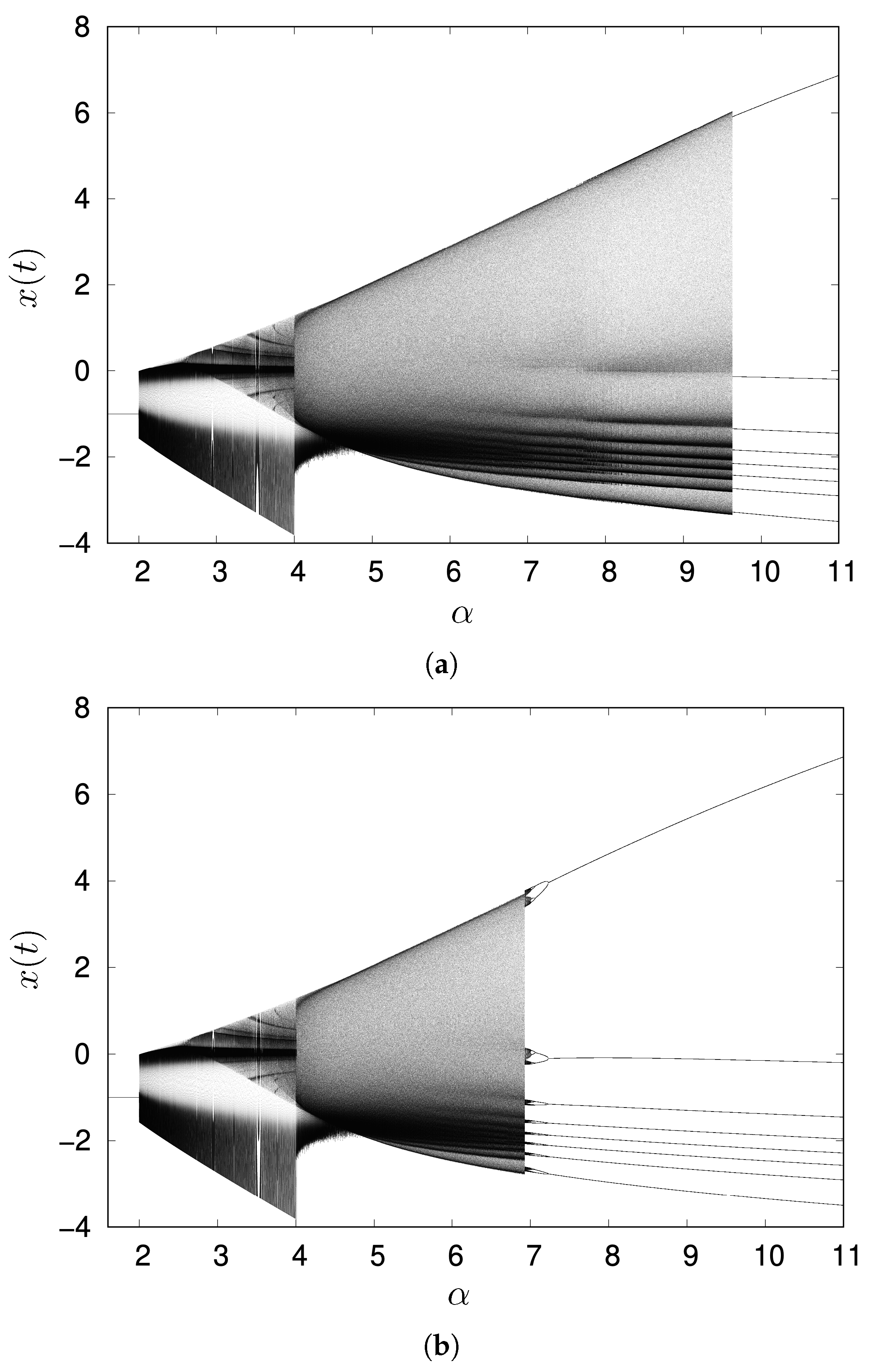
2.1. Rulkov Map
2.2. Q-Learning
- With a probability of , it exploits its current knowledge by choosing the action corresponding to the highest Q-value for the current state.
- With a probability of , it explores by choosing a random action from all possible actions in that state.
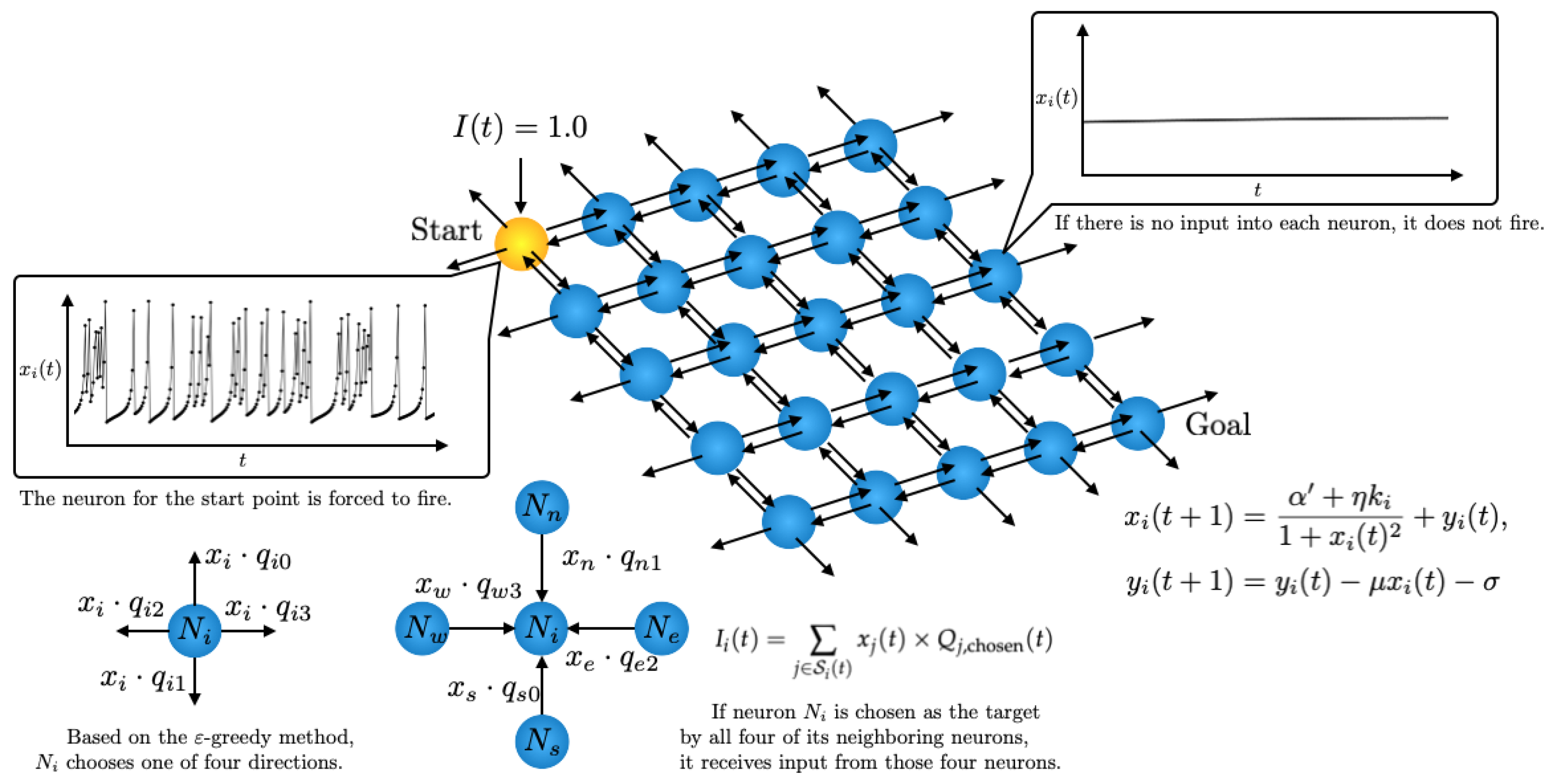
3. Method
3.1. Simulation Setup and Parameters
- : reward for reaching the goal state;
- : cost per action;
- : cost of moving out of bounds.
3.2. Signal Transmission Measurement and Analysis
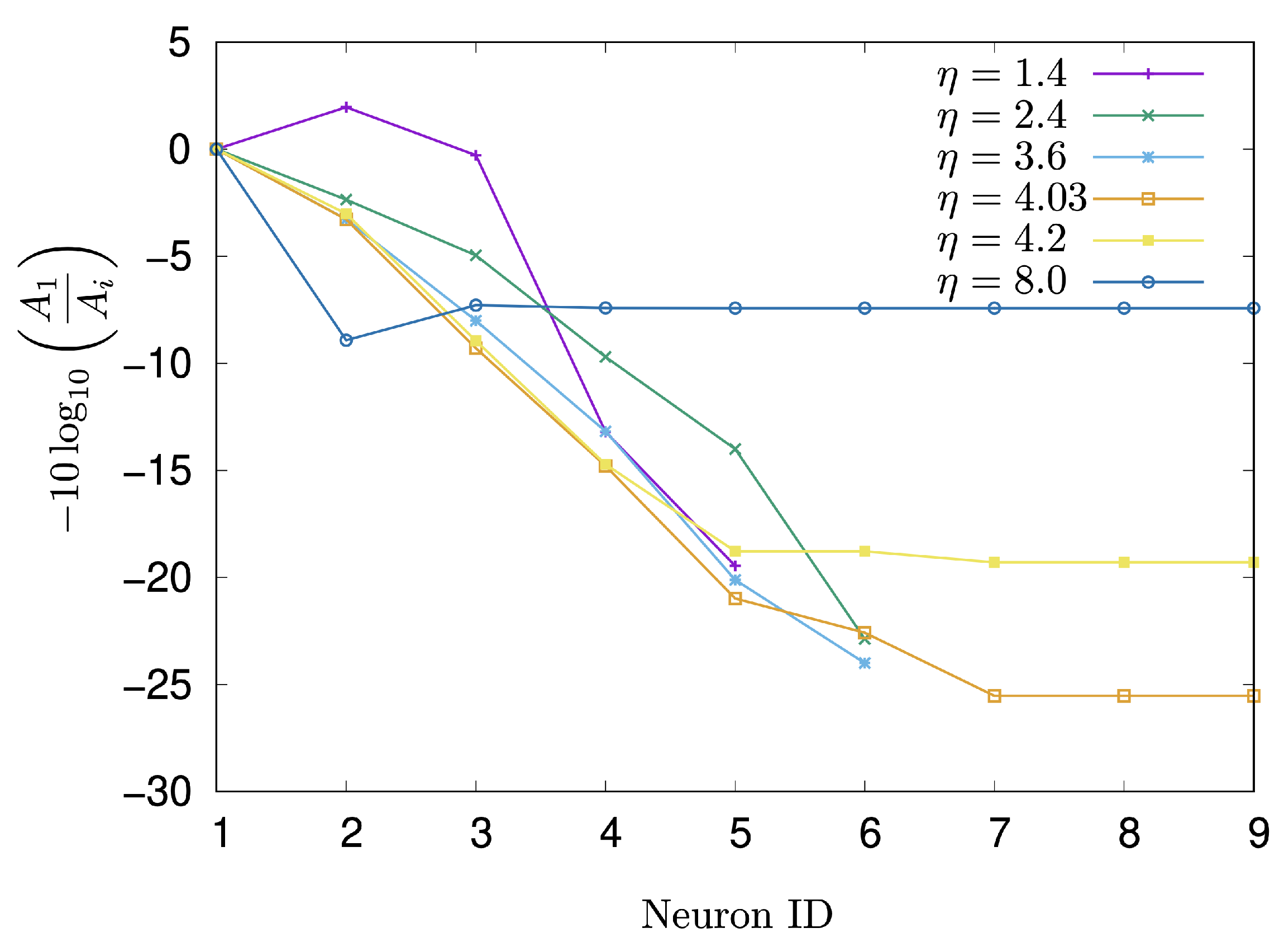
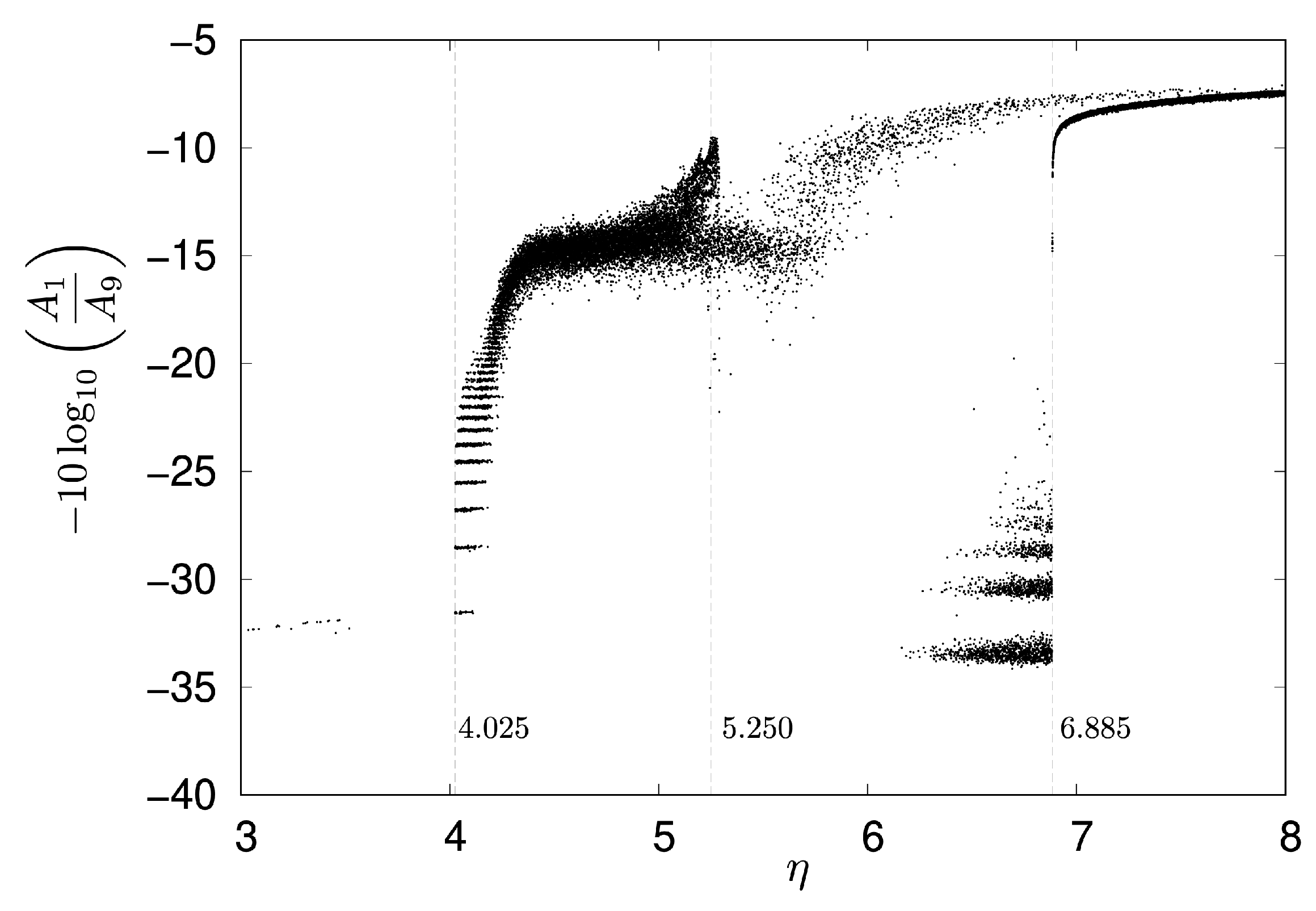
4. Results
- For in the range of to , the transmission rate was %.
- A dramatic increase in transmission rate was observed for between and , reaching %.
- In the range of to , the transmission rate decreased to %.
- Finally, for from to , the transmission rate achieved 100%.
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of Findings in Relation to Neuron Dynamics
5.2. Strengths, Limitations, and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodgkin, A.; Huxley, A. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. Bull. Math. Biol. 1990, 52, 25–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Ishizuka, S.; Ohta, M.; Hirakawa, K. Chaotic behavior in the Onchidium giant neuron under sinusoidal stimulation. Phys. Lett. A 1982, 88, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Ishizuka, S. Chaotic nature of bursting discharges in the Onchidium pacemaker neuron. J. Theor. Biol. 1992, 156, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J. Neurophysiological and Computational Principles of Cortical Rhythms in Cognition. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1195–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzHugh, R. Impulses and Physiological States in Theoretical Models of Nerve Membrane. Biophys. J. 1961, 1, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow. In The Theory of Chaotic Attractors; Hunt, B.R., Li, T.Y., Kennedy, J.A., Nusse, H.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, J. A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, K.; Takabe, T.; Toyoda, M. Chaotic neural networks. Phys. Lett. A 1990, 144, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.F. Modeling of spiking-bursting neural behavior using two-dimensional map. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 041922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.F. Regularization of Synchronized Chaotic Bursts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.; Timofeev, I.; Bazhenov, M. Oscillations in Large-Scale Cortical Networks: Map-Based Model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2004, 17, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagemakers, A.; Sanjuán, M.A. Electronic circuit implementation of the chaotic Rulkov neuron model. J. Frankl. Inst. 2013, 350, 2901–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Peng, X.; Li, C. Firing behaviors of memristor-based Rulkov neuron map using energy method. AEU - Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2024, 178, 155283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y.; Mou, J. A discrete Chialvo–Rulkov neuron network coupled with a novel memristor model: Design, Dynamical analysis, DSP implementation and its application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 179, 114466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Moroz, I.; Yang, Y. A joint image encryption based on a memristive Rulkov neuron with controllable multistability and compressive sensing. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2024, 182, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, G. Simulating heterogeneous corporate dynamics via the Rulkov map. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2022, 61, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cao, H. Stability and chaos of Rulkov map-based neuron network with electrical synapse. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 20, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Sun, K. Dynamics and synchronization of fractional-order Rulkov neuron coupled with discrete fracmemristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2025, 192, 116012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkirtseva, I.; Pisarchik, A.N.; Ryashko, L. Multistability and stochastic dynamics of Rulkov neurons coupled via a chemical synapse. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 125, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, C.J.C.H.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, L.; Barchi, F.; Manoni, S.; Tolu, S.; Bartolini, A.; Acquaviva, A. Exploring spiking neural networks for deep reinforcement learning in robotic tasks. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Sim, D.; Cho, Y.; Park, C. Designing Spiking Neural Network-Based Reinforcement Learning for 3D Robotic Arm Applications. Electronics 2025, 14, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, F. DEP-SNN-RL:Spiking Neural Networks Reinforcement Learning in Musculoskeletal Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), Hangzhou, China, 8–11 August 2024; pp. 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.S.; Casas-Roma, J.; Subirats, L.; Parada, R. Spiking neural networks for autonomous driving: A review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 138, 109415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J.E. Bursts as a unit of neural information: Making unreliable synapses reliable. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, S. Tonic and burst firing: Dual modes of thalamocortical relay. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu-Friedman, M.A. Stochastic Properties of Neurotransmitter Release Expand the Dynamic Range of Synapses. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14406–14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, S.; Benzing, F.; Steger, A. Presynaptic stochasticity improves energy efficiency and helps alleviate the stability-plasticity dilemma. eLife 2021, 10, e69884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, L. Lapicque’s introduction of the integrate-and-fire model neuron (1907). Brain Res. Bull. 1999, 50, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhikevich, E. Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, D.O. The Organization of Behavior: A Neuropsychological Theory. Available online: https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.226341/mode/2up (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Morris, R.G. D.O. Hebb: The Organization of Behavior, Wiley: New York; 1949. Brain Res. Bull. 1999, 50, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigworth, F.J. Voltage gating of ion channels. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1994, 27, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.M.; Hille, B. Voltage-gated ion channels and electrical excitability. Neuron 1998, 20, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Schuman, E.M. Dendritic Protein Synthesis, Synaptic Plasticity, and Memory. Cell 2006, 127, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic Plasticity: Multiple Forms, Functions, and Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 18–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, M. Investigation of Signal Transmission Dynamics in Rulkov Neuronal Networks with Q-Learned Pathways. Entropy 2025, 27, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080884
Kobayashi M. Investigation of Signal Transmission Dynamics in Rulkov Neuronal Networks with Q-Learned Pathways. Entropy. 2025; 27(8):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080884
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Mio. 2025. "Investigation of Signal Transmission Dynamics in Rulkov Neuronal Networks with Q-Learned Pathways" Entropy 27, no. 8: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080884
APA StyleKobayashi, M. (2025). Investigation of Signal Transmission Dynamics in Rulkov Neuronal Networks with Q-Learned Pathways. Entropy, 27(8), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080884





