Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Dynamic Rhombus Transformation and Digital Tube Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel 2D Sine-Cubic-May hyperchaotic map (2D-SCMH) is designed. By nonlinearly coupling the Sine map, Cubic map, and May map and incorporating the modulo operation to confine the chaotic range, the 2D-SCMH is able to maintain stable hyperchaotic characteristics throughout the entire parameter space while completely eliminating periodic windows.
- (2)
- To scramble pixel positions, a dynamic rhombus transformation is proposed by utilizing a chaotic sequence to dynamically select the transformation center and traversal order. This transformation ensures that the scrambling process exhibits stronger randomness and traverses the entire image.
- (3)
- To diffuse pixel values, a digital tube model is designed by utilizing chaotic sequences to control bit inversion and cyclic shift operation, integrated with XOR operation. This model enhances the randomness and unpredictability of the encryption process. In addition, it enables parallel processing of multiple pixels to significantly reduce the encryption time.
- (4)
- An image encryption algorithm is proposed based on the 2D-SCMH chaotic system, dynamic rhombus transformation and digital tube model. This algorithm provides strong protection for image information and effectively guarantees the security of image transmission and storage.
2. Chaotic System
2.1. Classic Chaotic Maps
2.1.1. Sine Map
2.1.2. Cubic Map
2.1.3. May Map
2.2. Definition of 2D-SCMH
2.3. Chaotic Performance Analysis
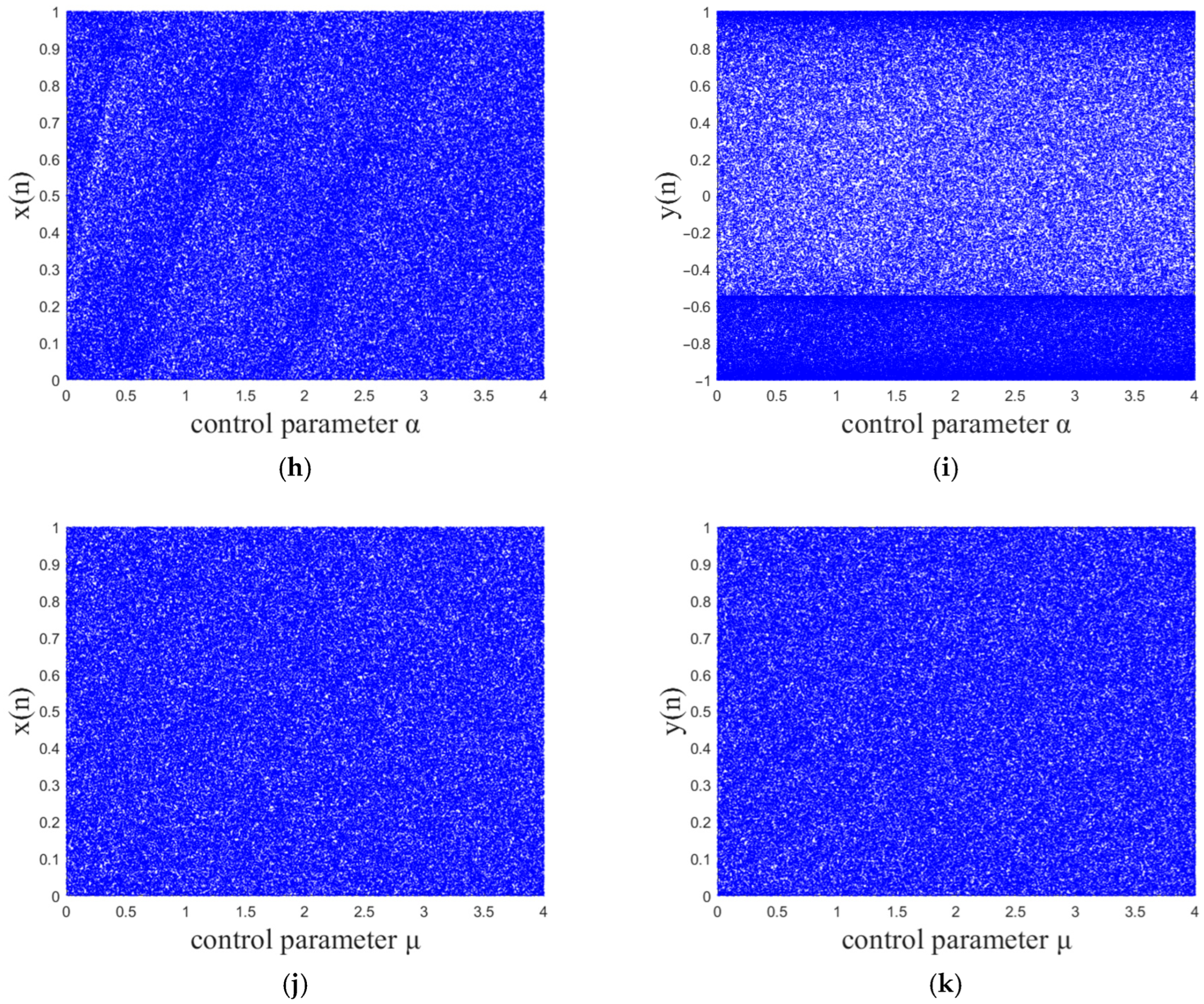
2.3.1. Bifurcation Diagram
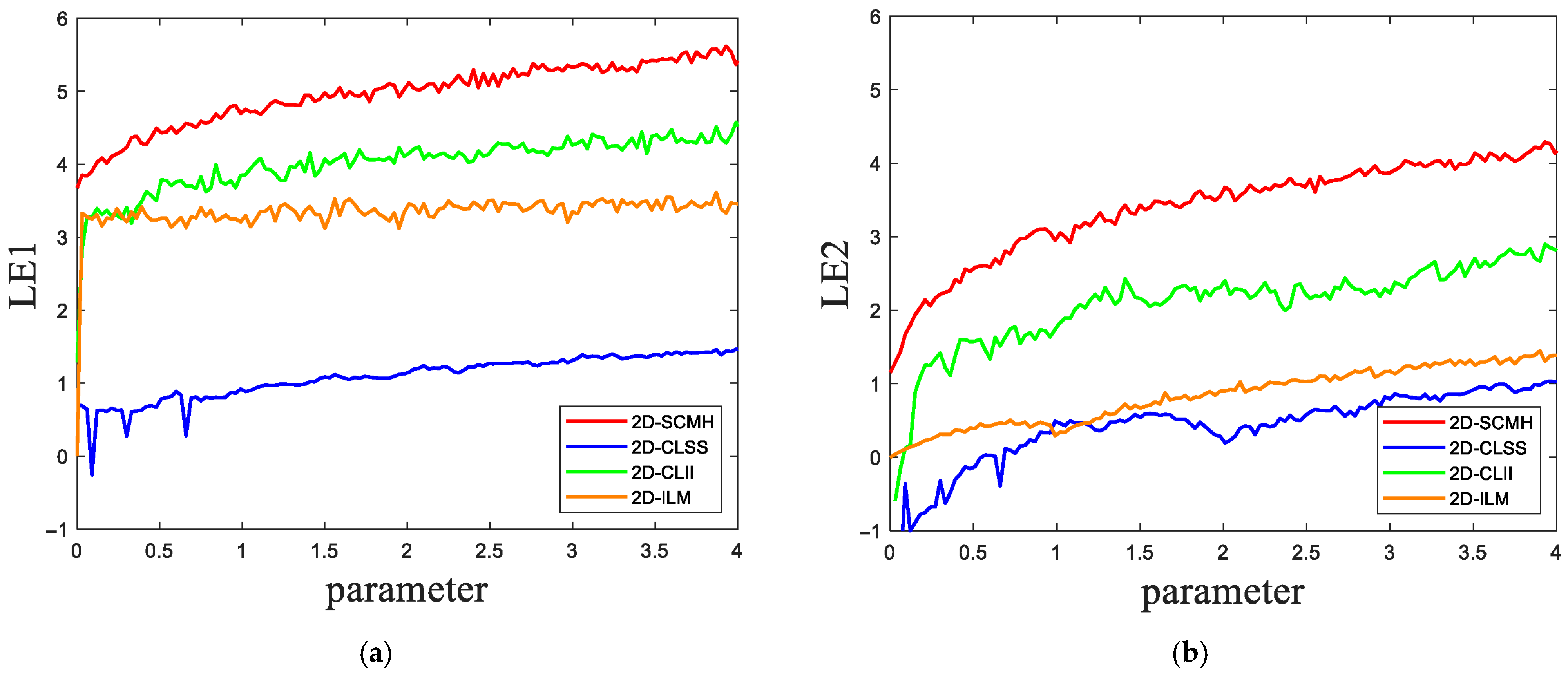
2.3.2. LE
2.3.3. Shannon Entropy
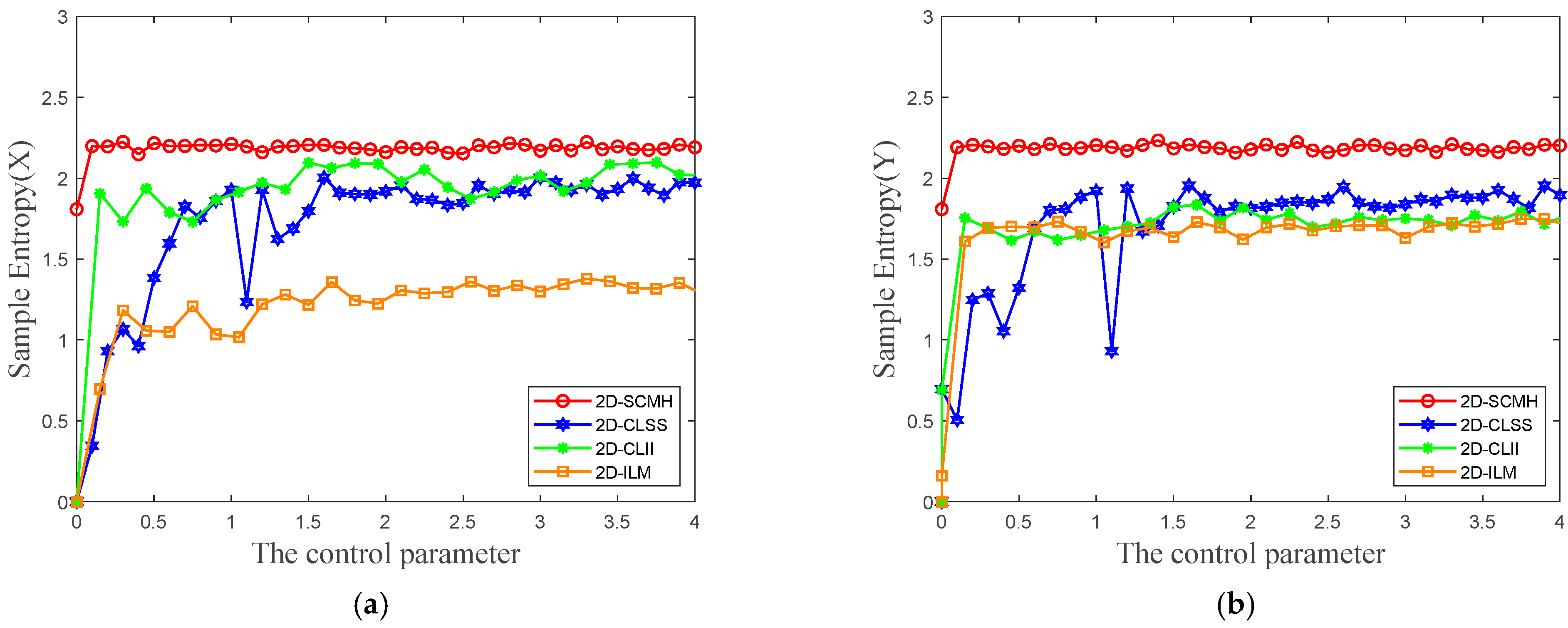
2.3.4. Sample Entropy
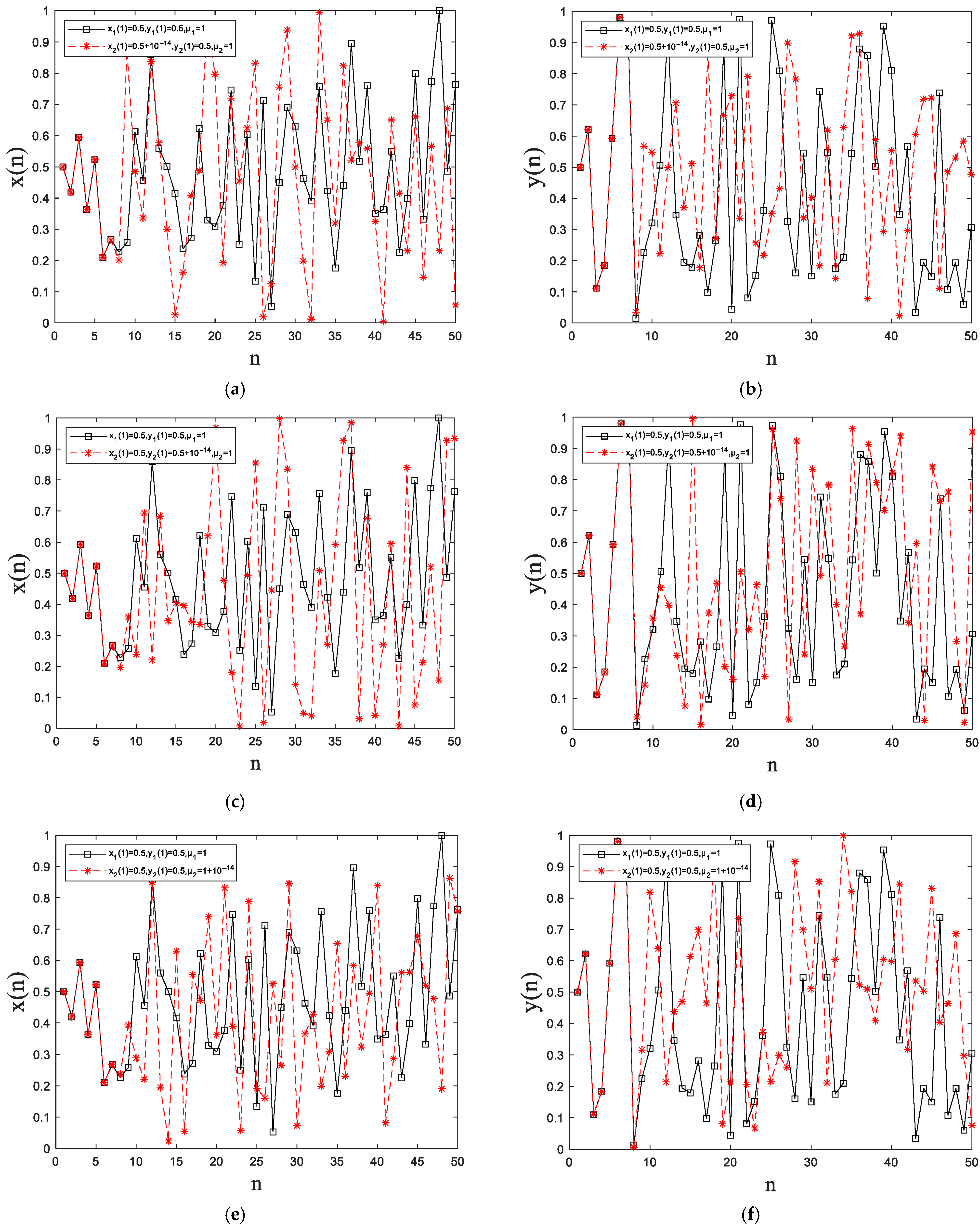
2.3.5. Sensitivity Analyses
2.3.6. 0-1 Test
2.3.7. NIST Test
3. Theoretical Principles
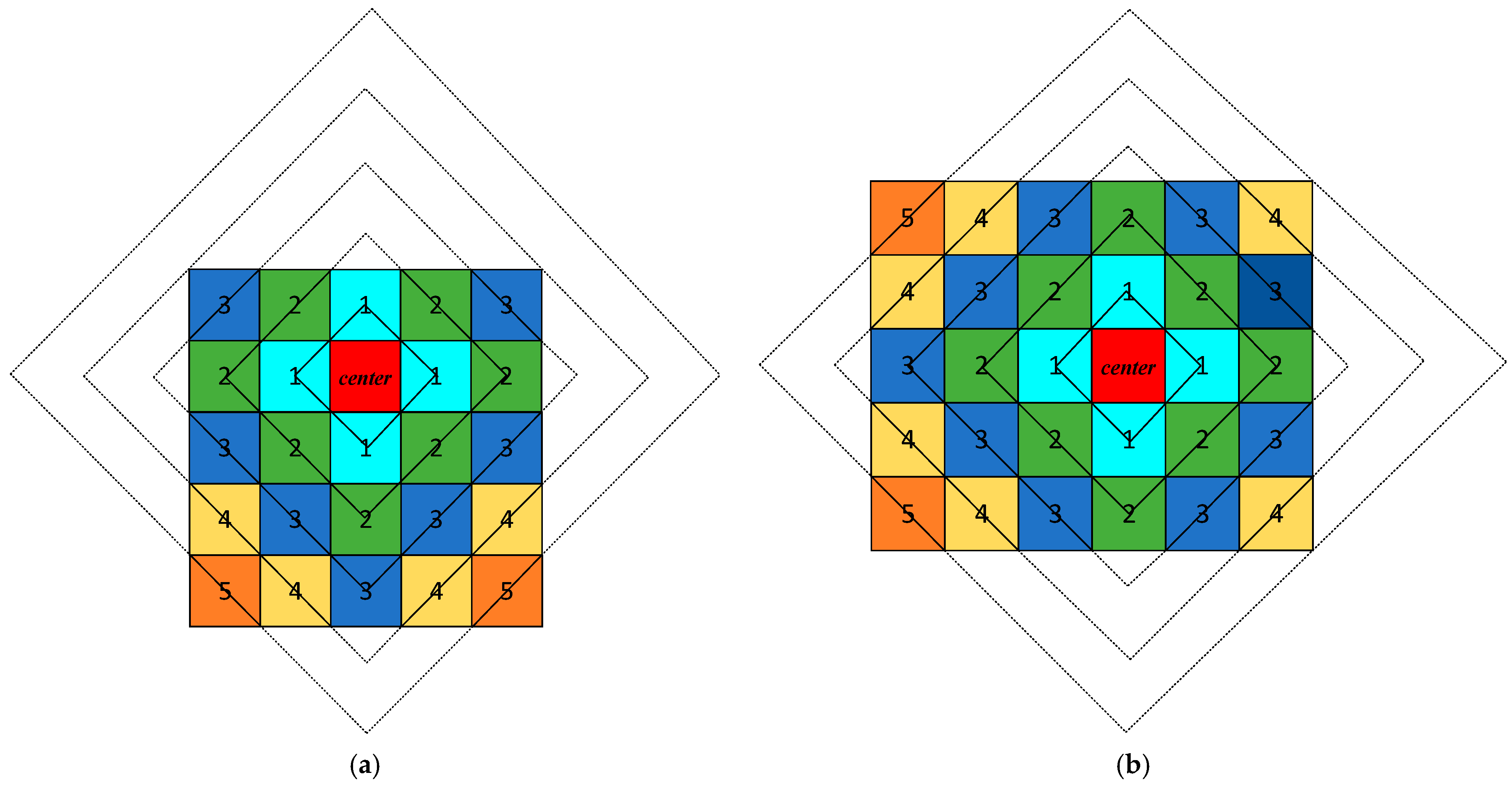
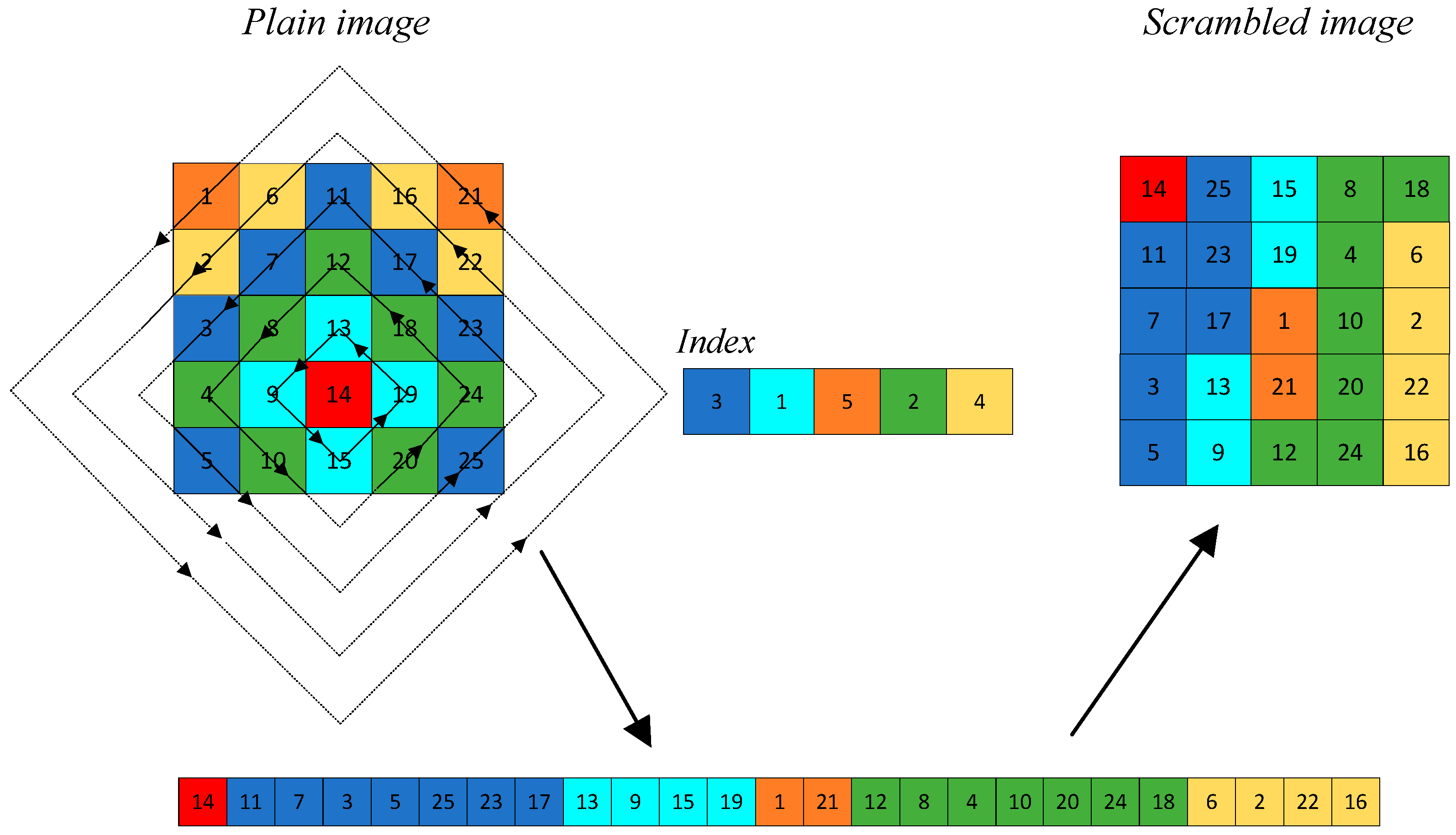
3.1. Dynamic Rhombus Transformation
3.2. Digital Tube Model
4. Proposed Image Encryption Algorithm
4.1. Key Generation
4.2. Encryption Process
| Algorithm 1: Encryption process |
| Input: the plain image I and the chaotic sequences W, X, Y and Z generated in the Section 4.1 Output: the cipher image C 1: [m, n] = size(I) 2: /* Calculating the transformation center point */ 3: C1 ← mod(floor(W(1) × 1016), m) + 1 4: C2 ← mod(floor(W(2) × 1016), n) + 1 5: /* Calculating the number and order of rhombuses */ 6: h1 ← abs(C1-1)+abs(C2-1) 7: h2 ← abs(C1-1)+abs(C2-n) 8: h3 ← abs(C1-m)+abs(C2-1) 9: h4 ← abs(C1-m)+abs(C2-n) 10: L ← max(h1, h2, h3, h4) 11: W′ ← W(3: L+2) 12: P ← sort(W′) 13: /* Dynamic rhombus transformation */ 14: for t ← 1 to L do 15: R(t) ← [ ] 16: for i ← 1 to m do 17: for j ← 1 to n do 18: MD←abs(i-C1)+ abs(j-C2) 19: if MD=P(t) then 20: R(t) ← (R(t), I(i, j)) 21: end 22: end 23: end 24: end 25: result ← [ ] 26: for i ← 1 to L do 27: result ← [result, R(i)] 28: end 29: result ← (I(C1, C2), result) 30: E ← reshape(result, m, n) 31: /* Normalizing chaotic sequences */ 32: S1 ← mod(floor(X × 1016), 256) 33: S2 ← mod(floor(Y × 1016), 10) 34: S3 ← mod(floor(Z × 1016), 7) 35:/* Digital tube inversion and diffusion operation */ 36: E ← reshape(E, 1, m × n) 37: parfor i ← 1 to m × n do 38: switch S2(i) do 39: case 0 40: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] 41: case 1 42: V ← [2, 3] 43: case 2 44: V ← [1, 2, 4, 5, 7] 45: case 3 46: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 7] 47: case 4 48: V ← [2, 3, 6, 7] 49: case 5 50: V ← [1, 3, 4, 6, 7] 51: case 6 52: V ← [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 53: case 7 54: V ← [1, 2, 6] 55: case 8 56: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 57: case 9 58: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7] 59: endsw 60: endsw 61: e ← dec2base(E(i), 2, 8) 62: for j ← 1 to length(V) do 63: temp ← e (V(j)) 64: if temp = ‘0’ then 65: modified_bit ← ‘1’ 66: else 67: modified_bit ← ‘0’ 68: end 69: e(V(j)) ← modified_bit 70: end 71: s1 ← dec2base(S1(i), 2, 8) 72: temp ← s1(1:7) 73: temp′ ← circshift(temp, S3(i)) 74: s1′ ← (temp′, s1(8)) 75: K(i) ← bin2dec(s1′⊕e) 76: end 77: C ← reshape(K, m, n) Remark: Notations are represented by ‘/* */’. |
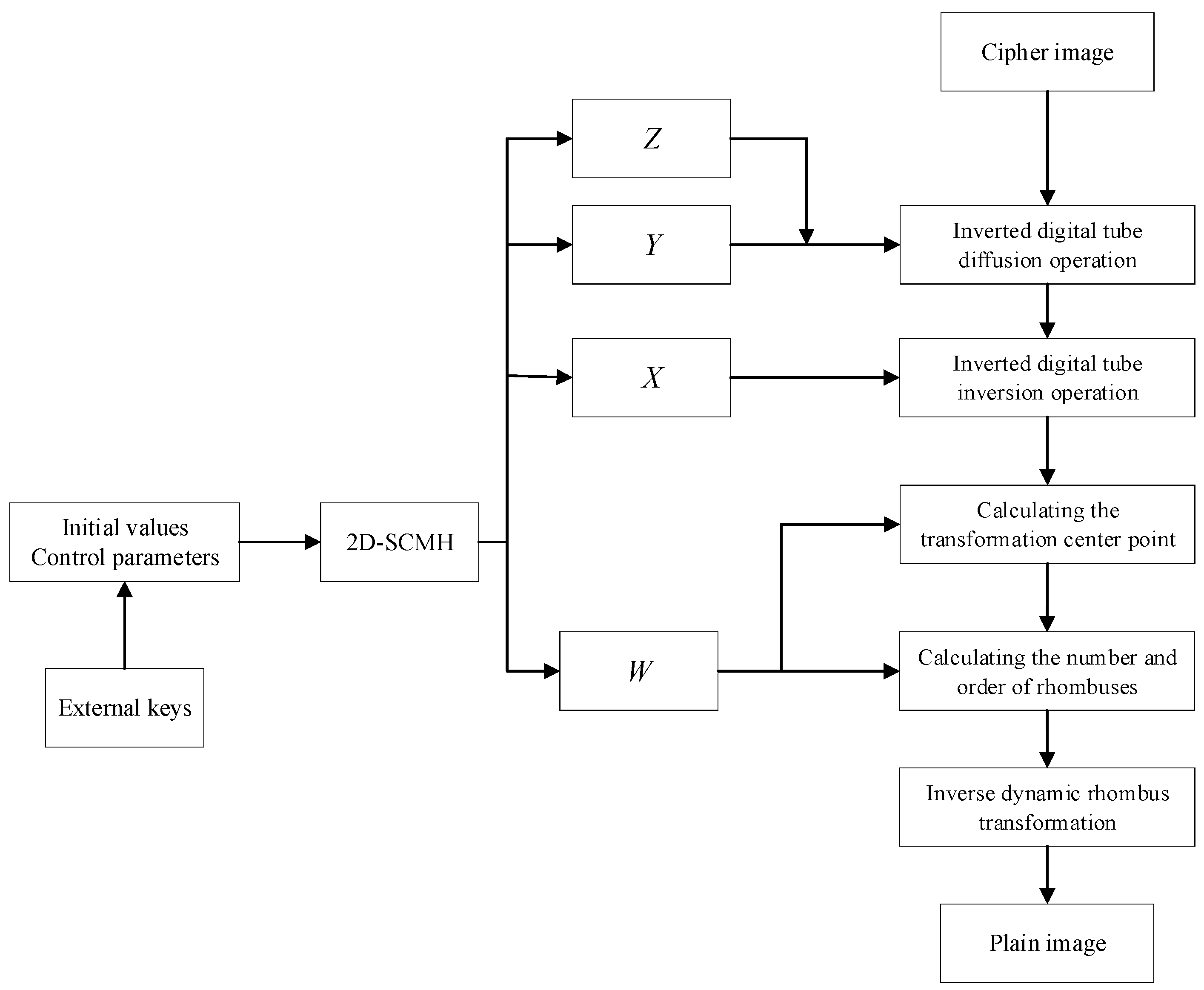
4.3. Decryption Process
| Algorithm 2: Decryption process |
| Input: the cipher image C and the chaotic sequences W, X, Y and Z generated in Section 4.1 Output: the plain image I 1: [m, n] = size(C) 2: /* Chaotic sequence generation */ 3: S1 ← mod(floor(X × 1016), 256) 4: S2 ← mod(floor(Y × 1016), 10) 5: S3 ← mod(floor(Z × 1016), 7) 6: /* Inversed digital tube inversion and diffusion operation */ 7: C ← reshape(C, 1, m × n) 8: parfor i←1 to m × n do 9: c ← dec2base(C(i), 2, 8) 10: s1 ← dec2base(S1(i), 2, 8) 11: temp ← s1(1:7) 12: temp′ ← circshift(temp, -S3(i)) 13: s1′ ← (temp′, s1(8)) 14: k ← c⊕s1′ 15: switch S2(i) do 16: case 0 17: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] 18: case 1 19: V ← [2, 3] 20: case 2 21: V ← [1, 2, 4, 5, 7] 22: case 3 23: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 7] 24: case 4 25: V ← [2, 3, 6, 7] 26: case 5 27: V ← [1, 3, 4, 6, 7] 28: case 6 29: V ← [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 30: case 7 31: V ← [1, 2, 6] 32: case 8 33: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 34: case 9 35: V ← [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7] 36: endsw 37: endsw 38: for j ←1 to length(V) do 39: temp ← k (V(j)) 40: if temp = ‘0’ then 41: modified_bit ← ‘1’ 42: else 43: modified_bit ← ‘0’ 44: end 45: k(V(j)) ← modified_bit 46: end 47: e(i) ← bin2dec(k) 48: end 49: E ← reshape(e, m, n) 50: /* Calculating the transformation center point */ 51: C1 ← mod(floor(W(1) × 1016), m) + 1 52: C2 ← mod(floor(W(2) × 1016), n) + 1 53: /* Calculating the number and order of rhombuses */ 54: h1 ← abs(C1-1) + abs(C2-1) 55: h2 ← abs(C1-1) + abs(C2-n) 56: h3 ← abs(C1-m) + abs(C2-1) 57: h4 ← abs(C1-m) + abs(C2-n) 58: L ← max(h1, h2, h3, h4) 59: W′ ← W(3: L + 2) 60: P ← sort(W′) 61:/* Inverse dynamic rhombus transformation */ 62: Q ← zeros(m, n) 63: R ← reshape(E, 1, m × n) 64: Q(C1, C2) ← R(1) 65: R(1) ← [ ] 66: for t ← 1 to L do 67: for i ← 1 to m do 68: for j ← 1 to n do 69: MD ← abs(i-C1) + abs(j-C2) 70: if MD = P(t) then 71: Q(i, j) ← R(1) 72: R(1) ← [ ] 73: end 74: end 75: end 76: end 77: I ← Q |
5. Experimental Results
6. Security Analyses
6.1. Histogram Analysis
6.2. Key Space Analysis
6.3. Key Sensitivity Analysis
6.4. Correlation Analysis
6.5. Information Entropy Analysis
6.6. Differential Attack Analysis
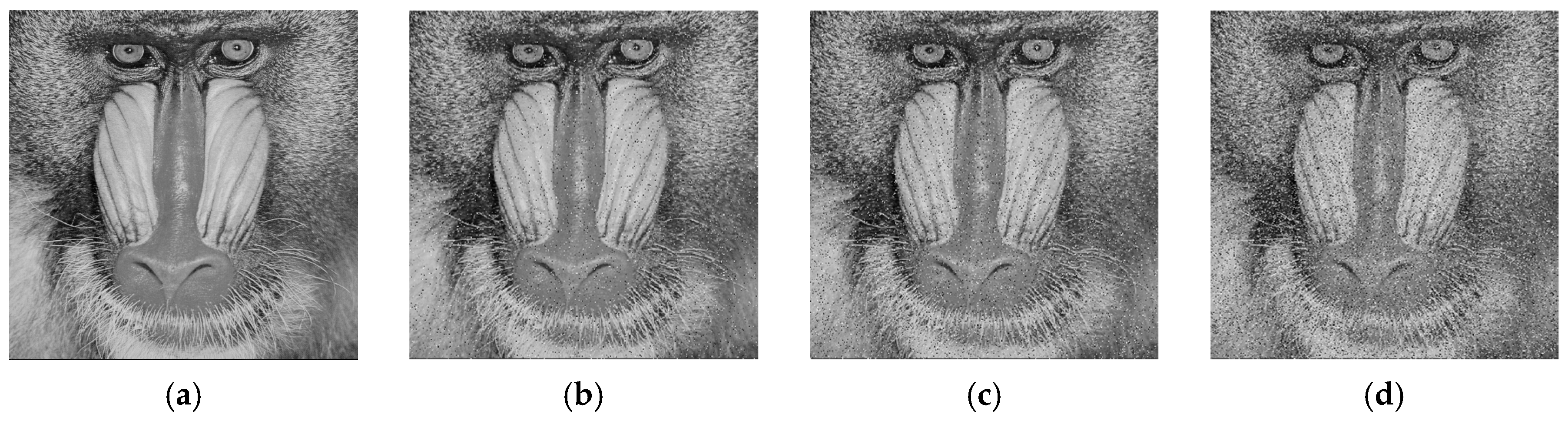
6.7. Cropping Attack
6.8. Noise Attack
6.9. Encryption Speed Analysis
6.10. Computational Complexity Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.M.; Wang, J. New 4D hyperchaotic system’s application in image encryption. J. Opt. 2024, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Xue, R. Color image encryption scheme for distributed architecture with SCFP chaotic map. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Tong, X.J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Image encryption algorithm based on DNA mutation and a novel four-dimensional hyperchaos. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Tang, J.E.; Zhang, Z.Z. Efficient and secure image encryption algorithm using 2D LIM map and Latin square matrix. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 22463–22483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Liu, Y. A meaningful image encryption method based on dynamic update pixel diffusion and 2D hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 14527–14546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Li, T.Y.; Wu, J.A.; Wu, J. Chaotic color image encryption based on eight-base DNA-level permutation and diffusion. Entropy 2023, 25, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Sun, B.; Bi, X.G.; Yan, H.Z.; Wang, L.N. A novel color image encryption algorithm based on cross-plane scrambling and diffusion. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2024, 29, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Sun, J.Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H. Fisher-Yates scrambling algorithm combined with S-box color image encryption technology based on 3D-SCCM chaotic system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 45233–45258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Chen, Z.; Long, B.F.; Liu, T.Z.; He, C.C.; Wang, L.J. Chaotic image encryption algorithm based on dynamic Hachimoji DNA coding and computing. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.P.; Hu, Q.; Teng, L. A novel color image encryption method based on new three-dimensional chaotic mapping and DNA coding. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 1799–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.R.; Lin, H.R.; Deng, X.H.; Yao, W.; Jin, J. A hidden multiwing memristive neural network and its application in remote sensing data security. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 277, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.M.; Yin, C.H.; Xu, C.; Yan, R. A quantum image encryption method for dual chaotic systems based on quantum logistic mapping. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.H.; Sun, B.; Mou, J. Multiple remote sensing image encryption scheme based on saliency extraction and magic cube circular motion. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Huang, Q.Y.; Cai, S.T.; Xiong, X.M.; Huang, L.Q. Image encryption based on novel Hill Cipher variant and 2D-IGSCM hyper-chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 2811–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Teng, L.; Zhou, W.J.; Yan, X.P.; Xia, Z.Q.; Zhou, S. A new 2D cross hyperchaotic Sine-modulation-Logistic map and its application in bit-level image encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 261, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Hu, H.P. An image encryption algorithm based on a compound-coupled chaotic system. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 146, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Xu, X.M.; Jiang, Z.H.; Sun, K.H. Multiple-image encryption scheme based on an n-dimensional chaotic modular model and overlapping block permutation-diffusion using newly defined operation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtas, M. Multiple-image encryption using sine quadratic polynomial mapping and U-shaped scanning techniques. Trait. Du Signal 2024, 41, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, C.X. Image encryption algorithm based on V-shaped scanning and matrix multiplication. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Si, R.Y. A new chaotic image encryption scheme based on dynamic L-shaped scrambling and combined map diffusion. Optik 2021, 245, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Hua, H.Q.; Zhao, X.W.; Erkan, U.; Toktas, A. Image encryption using fission diffusion process and a new hyperchaotic map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 175, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Teng, L. Double-image coupling encryption algorithm based on TLCS and misplacement diffusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhao, M.C. A new spatiotemporal chaos model and its application in bit-level image encryption. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 10481–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, Z.; Long, B.F.; Liu, T.Z.; Wu, X.M.; Zheng, Z.W.; Zou, S.L.; Cao, C. An image encryption algorithm based on a novel 4D hyperchaotic system and improved Knight’s Tour scrambling algorithm. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Teng, L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Si, R.Y.; Liu, P.B. Mutil-medical image encryption by a new spatiotemporal chaos model and DNA new computing for information security. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 235, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, S.X.; Feng, X.F.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhang, H. Remote sensing image compression and encryption based on block compressive sensing and 2D-LCCCM. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 2705–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkandeu, Y.P.K.; Tiedeu, A. An image encryption algorithm based on substitution technique and chaos mixing. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 10013–10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Xian, Y.J. Image encryption algorithm based on a 2D-CLSS hyperchaotic map using simultaneous permutation and diffusion. Inf. Sci. 2022, 605, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Tan, F. Multiple-image encryption scheme based on a new 2D hyperchaotic map with blurred pixels. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.F.; Teng, L. A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on sliding window and pseudo-random stack shuffling. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 13539–13569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.F.; Yang, H.F. Image encryption using a new hybrid chaotic map and spiral transformation. Entropy 2023, 25, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, X.M.; Teng, L.; Wang, X.Y. Selective region medical image encryption algorithm based on cascade chaos and two-dimensional Joseph traversal. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, H. A novel image encryption algorithm combined complex order chaotic system and modified AES. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 40361–40376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, S.H.; Zhang, Q.; Kasabov, N.K. Construction of new 5D Hamiltonian conservative hyperchaotic system and its application in image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 20425–20446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. A high-quality visual image encryption algorithm utilizing the conservative chaotic system and adaptive embedding. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 188, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Zhou, X.F.; Zheng, N.; Li, M.J.; Hu, M. Image encryption scheme based on optical chaos and DNA Rubik’s cube algorithm. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, A.; Biban, G.; Chugh, R.; Tassaddiq, A.; Alharbi, R. An efficient image encryption model based on 6D hyperchaotic system and symmetric matrix for color and gray images. Heliyon 2024, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.M.; Bao, T.Y. An image encryption algorithm based on cascade chaotic map and DNA coding. Iet Image Process. 2023, 17, 3510–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.Y.; He, C.C. Region of interest encryption algorithm for images based on lifting scheme and object detection. Clust. Comput. J. Netw. Softw. Tools Appl. 2025, 28, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shi, H.; Ji’e, M.; Duan, S.K.; Wang, L.D. A novel image compression and encryption scheme based on conservative chaotic system and DNA method. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 172, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Liu, M.R.; Niu, Y. Facial image encryption scheme based on improved 4-D hyperchaotic system. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Hong, L.; Jiang, J. Visual double image encryption scheme based on multilayer complex networks and wavelet transform. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 13599–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.H.; Mei, Q.X.; Jia, X.X.; Ye, G.D. Image encryption scheme based on pseudo-DWT and cubic S-box. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.L.; Gao, C.; Dai, Y.; Meng, X.F. Dynamic rotation medical image encryption scheme based on improved Lorenz chaos. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 13571–13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.D. Parallel multi-image encryption based on cross-plane DNA manipulation and a novel 2D chaotic system. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 8615–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.F.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.Q.; Yang, Y. Model construction and image encryption application of chaotic system under the influence of memristor and unknown parameters. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 13859–13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.M.; Sun, K.H.; Jiang, Z.H.; Li, M.J.; Wen, J. A color image encryption and hiding algorithm based on hyperchaotic system and discrete cosine transform. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 14513–14536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Liang, Z.H.; Wen, K.H.; Zhu, J.W.; Hu, Y.H. Holographic encryption algorithm based on DNA coding and bit-plane decomposition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 87385–87413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.H.; Liang, S.B.; Qi, L.G.; Zhong, Y. Image encryption based on four-dimensional multi-parameter robust chaotic system and dynamic spiral block transformation. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.S.; Liu, X.B. CLSM-IEA: A novel cosine-logistic-sine map and its application in a new image encryption scheme. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 3063–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Parah, S.A. HAIE: A hybrid adaptive image encryption algorithm using Chaos and DNA computing. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 28769–28796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







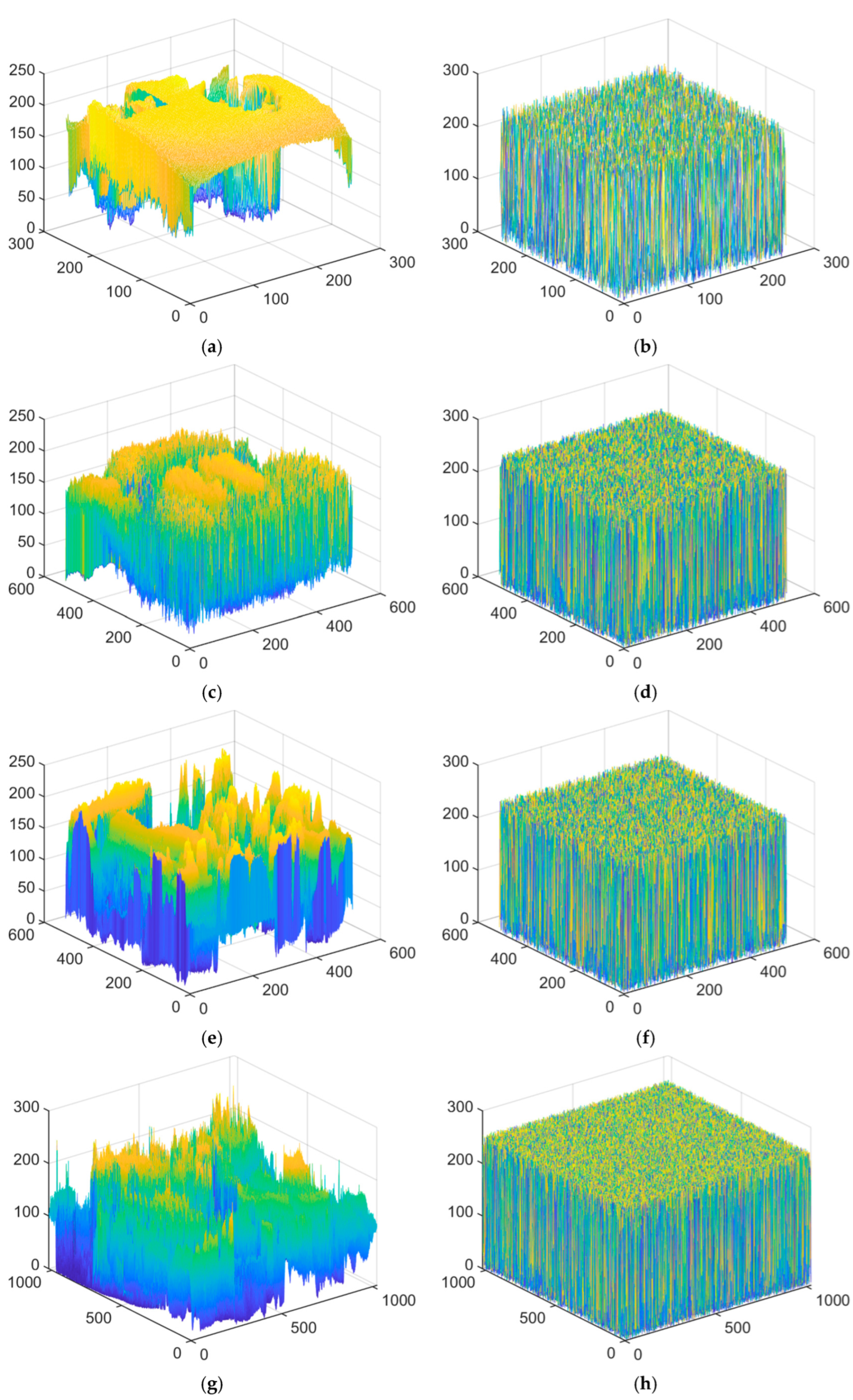



| Statistical Tests | p1 | p2 | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 0.8150 | 0.1862 | Passed |
| Block Frequency | 0.3655 | 0.2725 | Passed |
| Runs | 0.8807 | 0.9763 | Passed |
| Longest Run | 0.3434 | 0.1812 | Passed |
| Rank | 0.0371 | 0.0554 | Passed |
| FFT | 0.5617 | 0.0367 | Passed |
| Non-overlapping Template | 0.5193 | 0.8055 | Passed |
| Overlapping Template | 0.7245 | 0.9468 | Passed |
| Universal | 0.9620 | 0.1243 | Passed |
| Linear Complexity | 0.8492 | 0.7126 | Passed |
| Serial test p-value 1 | 0.3353 | 0.0466 | Passed |
| Serial test p-value 2 | 0.1103 | 0.0459 | Passed |
| Approximate Entropy | 0.6217 | 0.0654 | Passed |
| Cumulative Sums-forward | 0.9996 | 0.4444 | Passed |
| Cumulative Sums-reverse | 0.7784 | 0.9117 | Passed |
| Random Excursions Test (X = 1) | 0.4360 | 0.9500 | Passed |
| Random Excursions Variant Test (X = 1) | 0.7255 | 0.1028 | Passed |
| Image | Result | |
|---|---|---|
| Clock (256 × 256) | 273.7935 | Passed |
| Baboon (512 × 512) | 273.3711 | Passed |
| Peppers (512 × 512) | 245.2773 | Passed |
| Male (1024 × 1024) | 278.0063 | Passed |
| Plain Image | Test Image | Horizontal | Vertical | Diagonal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clock (256 × 256) | Plain image | 0.9383 | 0.9588 | 0.9736 |
| Cipher image | −0.0022 | 0.0011 | −0.0022 | |
| Baboon (512 × 512) | Plain image | 0.8667 | 0.7498 | 0.7158 |
| Cipher image | −0.0008 | −0.0017 | 0.0014 | |
| Peppers (512 × 512) | Plain image | 0.9767 | 0.9795 | 0.9625 |
| Cipher image | −0.0008 | −0.0001 | −0.0005 | |
| Male (1024 × 1024) | Plain image | 0.9637 | 0.9776 | 0.9805 |
| Cipher image | 0.0011 | −0.0019 | 0.0017 | |
| Peppers [37] | Cipher image | 0.0055 | 0.0026 | 0.0019 |
| Peppers [38] | Cipher image | −0.0033 | 0.0019 | −0.0088 |
| Peppers [39] | Cipher image | 0.0083 | −0.0077 | −0.0046 |
| Peppers [40] | Cipher image | 0.0026 | −0.0037 | 0.0017 |
| Peppers [41] | Cipher image | −0.0038 | 0.0014 | −0.0036 |
| Image | Plain Images | Cipher Images |
|---|---|---|
| Clock (256 × 256) | 6.7057 | 7.9974 |
| Baboon (512 × 512) | 7.3583 | 7.9992 |
| Peppers (512 × 512) | 7.5821 | 7.9993 |
| Male (1024 × 1024) | 7.5237 | 7.9998 |
| Peppers [37] | 7.5821 | 7.9973 |
| Peppers [38] | 7.5821 | 7.9969 |
| Peppers [39] | 7.5821 | 7.9976 |
| Peppers [40] | 7.5821 | 7.9948 |
| Peppers [41] | 7.5821 | 7.9974 |
| Image | NPCR (%) | UACI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Clock (256 × 256) | 99.6048 | 33.4681 |
| Baboon (512 × 512) | 99.6086 | 33.4644 |
| Peppers (512 × 512) | 99.6014 | 33.4621 |
| Male (1024 × 1024) | 99.6081 | 33.4640 |
| Average | 99.6057 | 33.4647 |
| Metric | Proposed Algorithm | Ref. [1] | Ref. [39] | Ref. [44] | Ref. [45] | Ref. [46] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPCR (%) | 99.6057 | 99.5893 | 99.5934 | 99.6182 | 99.6190 | 99.5899 |
| UACI (%) | 33.4647 | 33.3730 | 33.3054 | 33.3397 | 33.4931 | 33.6083 |
| Cropping Area | Clock (256 × 256) | Baboon (512 × 512) | Peppers (512 × 512) | Male (1024 × 1024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/16 | 19.4387 | 21.6272 | 20.0923 | 20.1356 |
| 1/8 | 16.3903 | 18.5846 | 17.9486 | 17.0742 |
| 1/4 | 13.3379 | 15.5898 | 14.9351 | 14.0755 |
| 1/2 | 10.3569 | 12.5724 | 11.9204 | 11.0361 |
| Noise Intensity | Clock (256 × 256) | Baboon (512 × 512) | Peppers (512 × 512) | Male (1024 × 1024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 20.2177 | 22.5324 | 21.9483 | 21.0056 |
| 0.1 | 17.3948 | 19.5341 | 18.8583 | 18.0037 |
| 0.2 | 14.2832 | 16.5614 | 15.8815 | 14.9865 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Huang, K. Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Dynamic Rhombus Transformation and Digital Tube Model. Entropy 2025, 27, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080874
Zhang X, Song Y, Huang K. Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Dynamic Rhombus Transformation and Digital Tube Model. Entropy. 2025; 27(8):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080874
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoqiang, Yupeng Song, and Ke Huang. 2025. "Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Dynamic Rhombus Transformation and Digital Tube Model" Entropy 27, no. 8: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080874
APA StyleZhang, X., Song, Y., & Huang, K. (2025). Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Dynamic Rhombus Transformation and Digital Tube Model. Entropy, 27(8), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080874







