Adsorption of Ternary Mixtures in the Presence of Multisite Occupancy: Theory and Monte Carlo Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
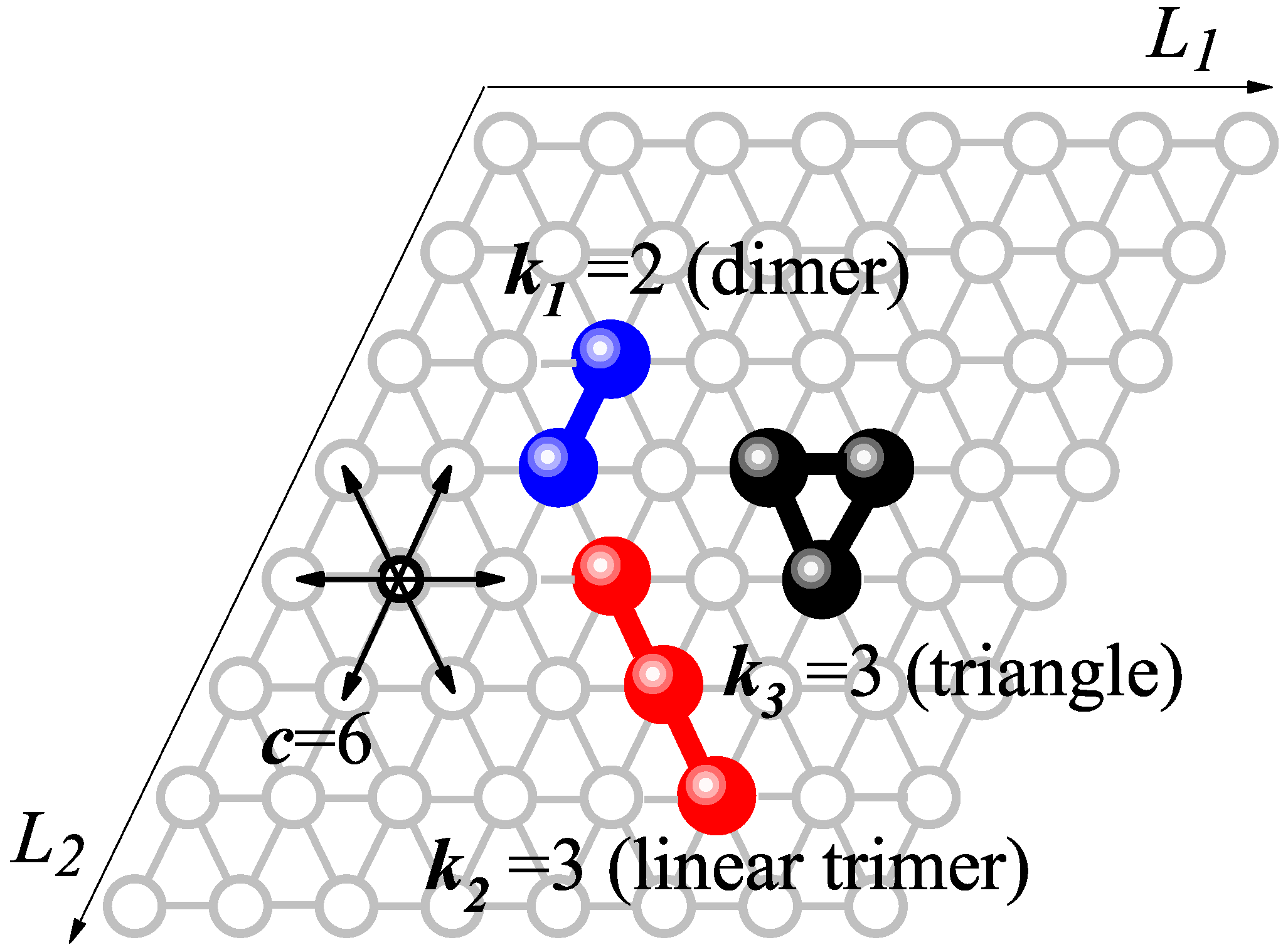
2. Model and Monte Carlo Simulation Scheme
- 1.
- Initialization:
- Set temperature T, pressure P, and molar compositions , , and . Accordingly,
- 2.
- Random species selection:
- Randomly select one of the three species.
- 3.
- Random -uple selection:
- Randomly select a set of sites on the lattice forming a -uple, according to the geometry of the species selected in step 2.
- -
- If the -uple is empty, attempt to adsorb a -mer of the type selected in step 2 with probability .
- -
- If the -uple is fully occupied by a -mer of the type selected in step 2, attempt to desorb it with probability .
- -
- If the -uple is partially occupied, or fully occupied, by elements belonging to different adsorbed particles, the attempt is rejected.
- 4.
- Repeat the simulation step:
- Repeat steps 2–3 a total of M times to complete one MCS.
3. Results
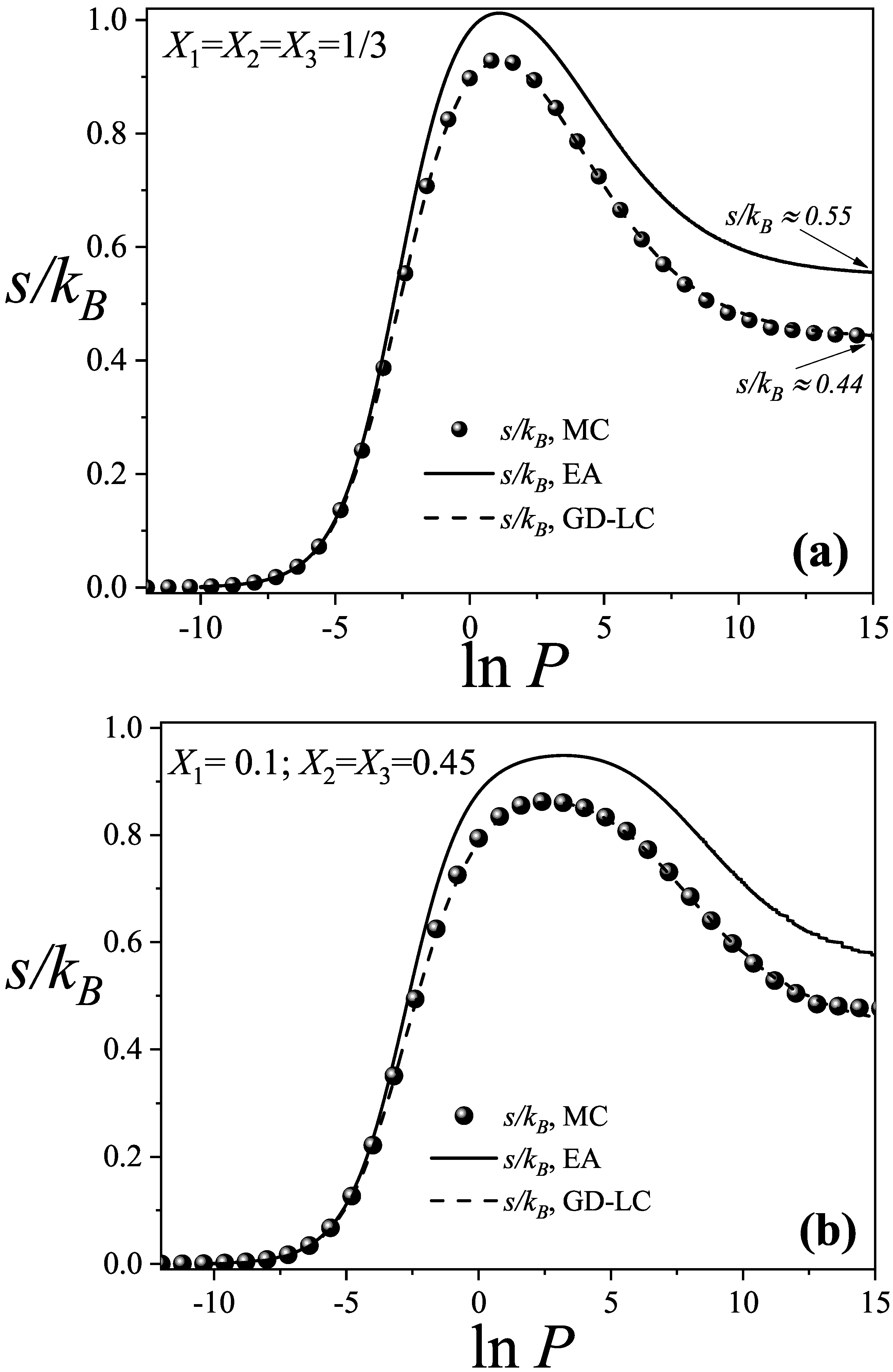
3.1. Adsorption Isotherms and Total Configurational Entropy per Site
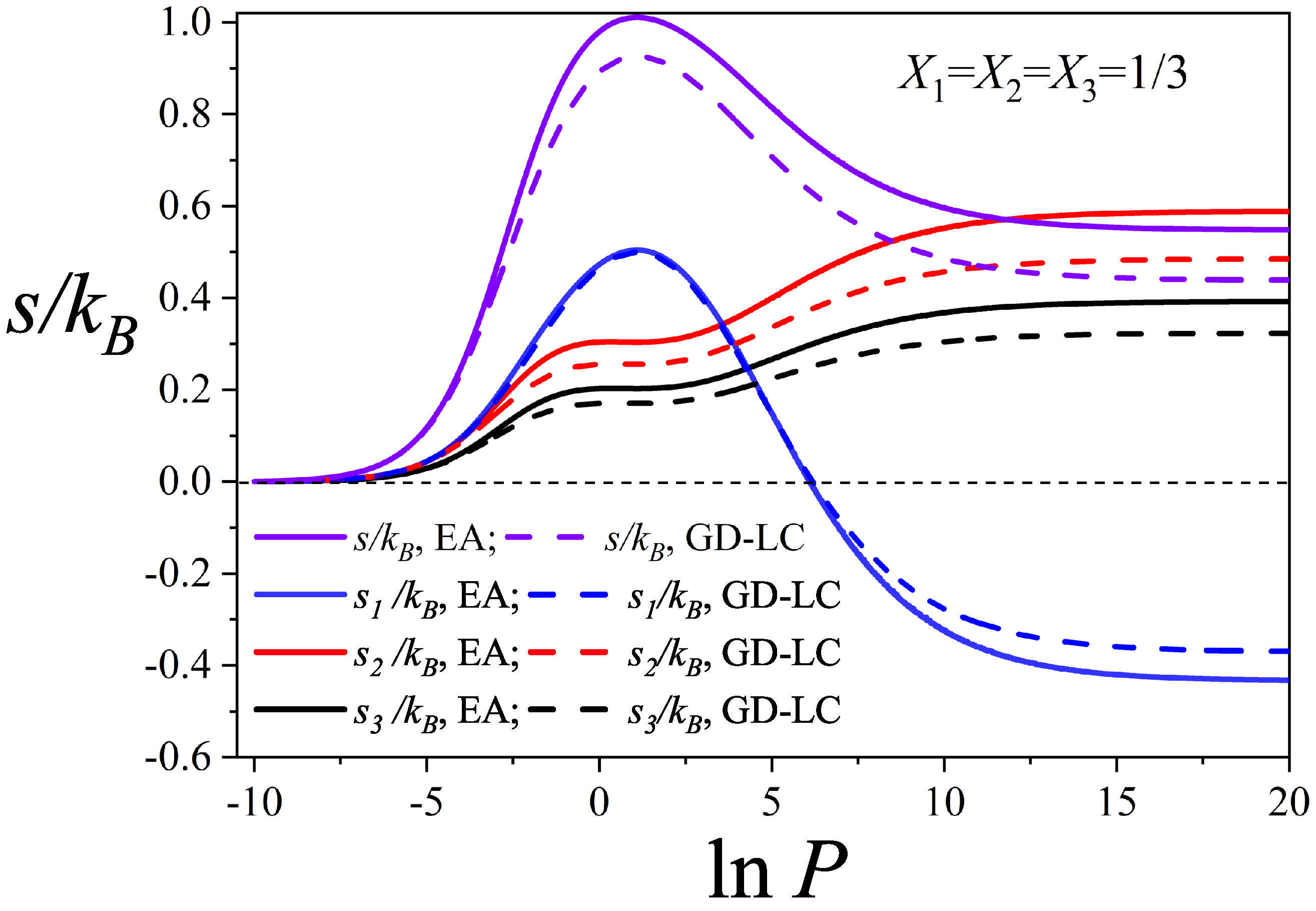
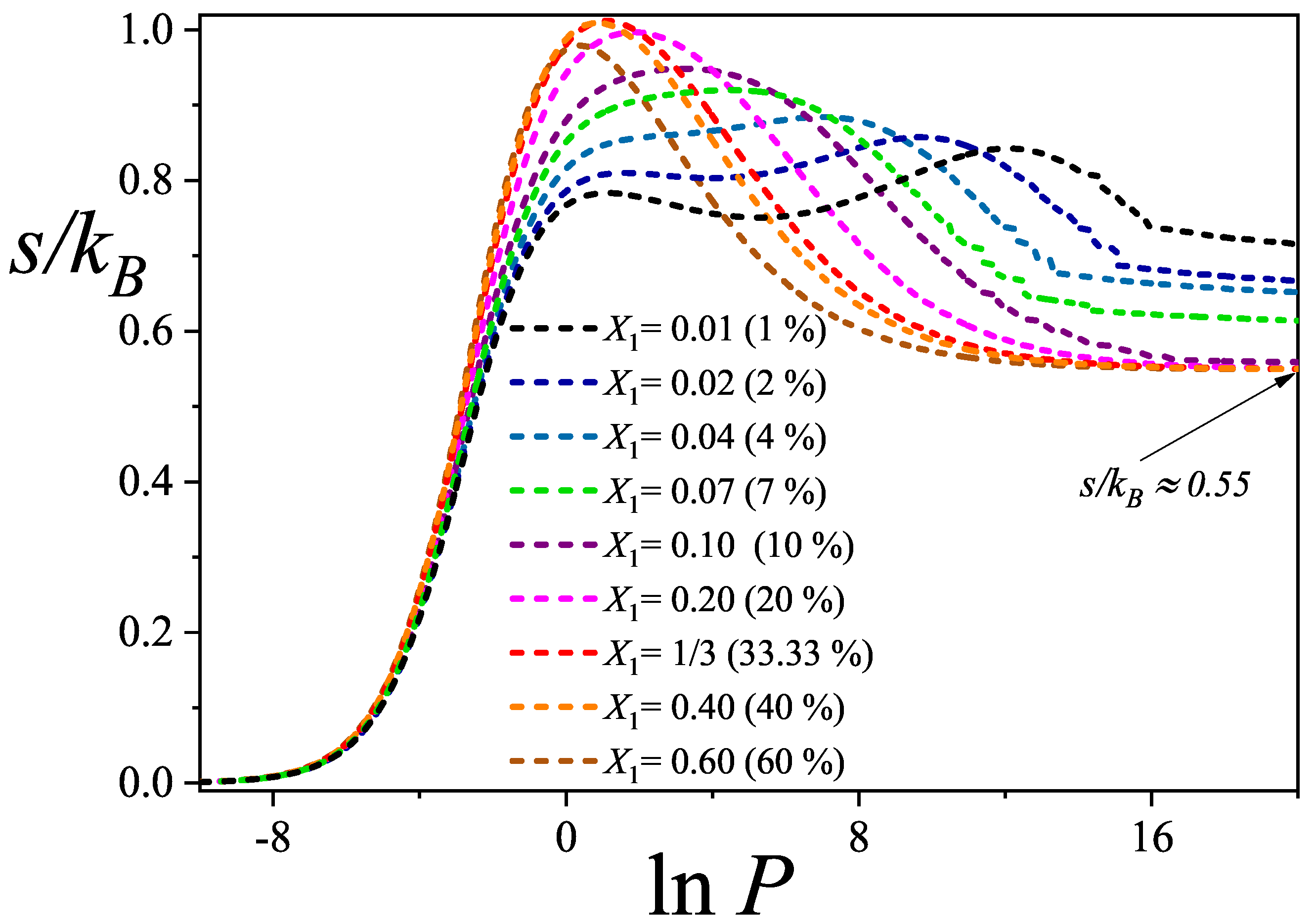
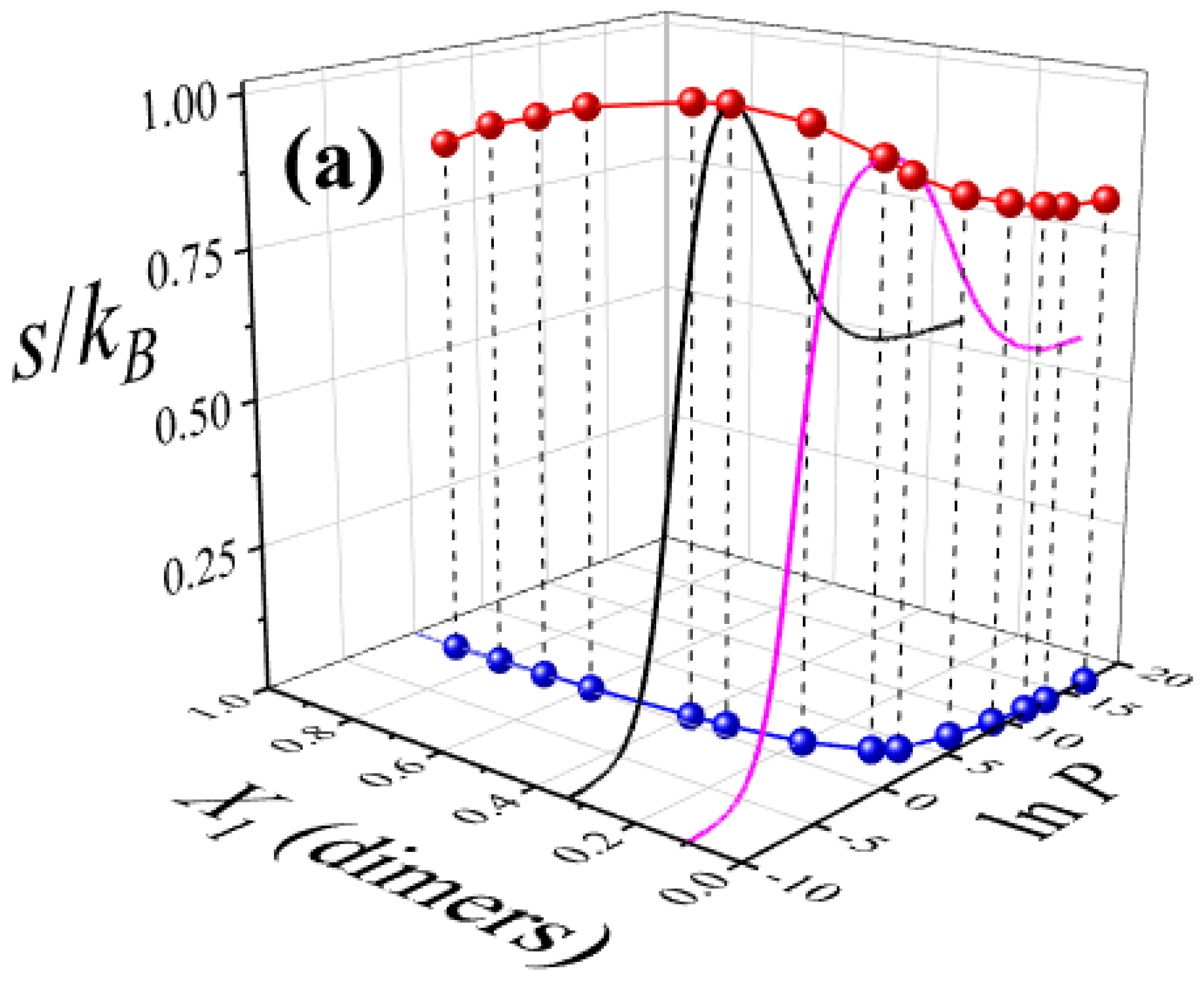
3.2. Configurational Entropy per Site for Different Molar Compositions
4. Conclusions
- The generalized lattice gas model effectively captures the competitive adsorption behavior driven by molecular size and shape, illustrating the essential role of multisite occupation in realistic surface processes.
- Analytical expressions for thermodynamic quantities, including the Helmholtz free energy, configurational entropy per site, and both total and partial coverages, were derived as functions of pressure within the EA and GD-LC approximations. These theoretical predictions show excellent qualitative agreement with MC simulations. Moreover, the GD-LC theory also shows remarkable quantitative agreement for both adsorption isotherms and configurational entropy, with the corresponding curves from MC simulations and GD-LC being nearly indistinguishable.
- A detailed entropy analysis reveals an entropy-driven displacement mechanism, where dimers progressively replace larger species at higher pressures, maximizing the system’s entropy prior to lattice saturation. In the high-coverage regime, entropy approaches a limiting value dominated by dimer adsorption, in line with previous studies on fully occupied lattices.
- Despite dimers playing a central role in the displacement process, larger molecules contribute cooperatively. Their ability to occupy residual voids left by smaller species supports the preservation of positive entropy and reinforces thermodynamic consistency, particularly in the behavior of mixing entropy.
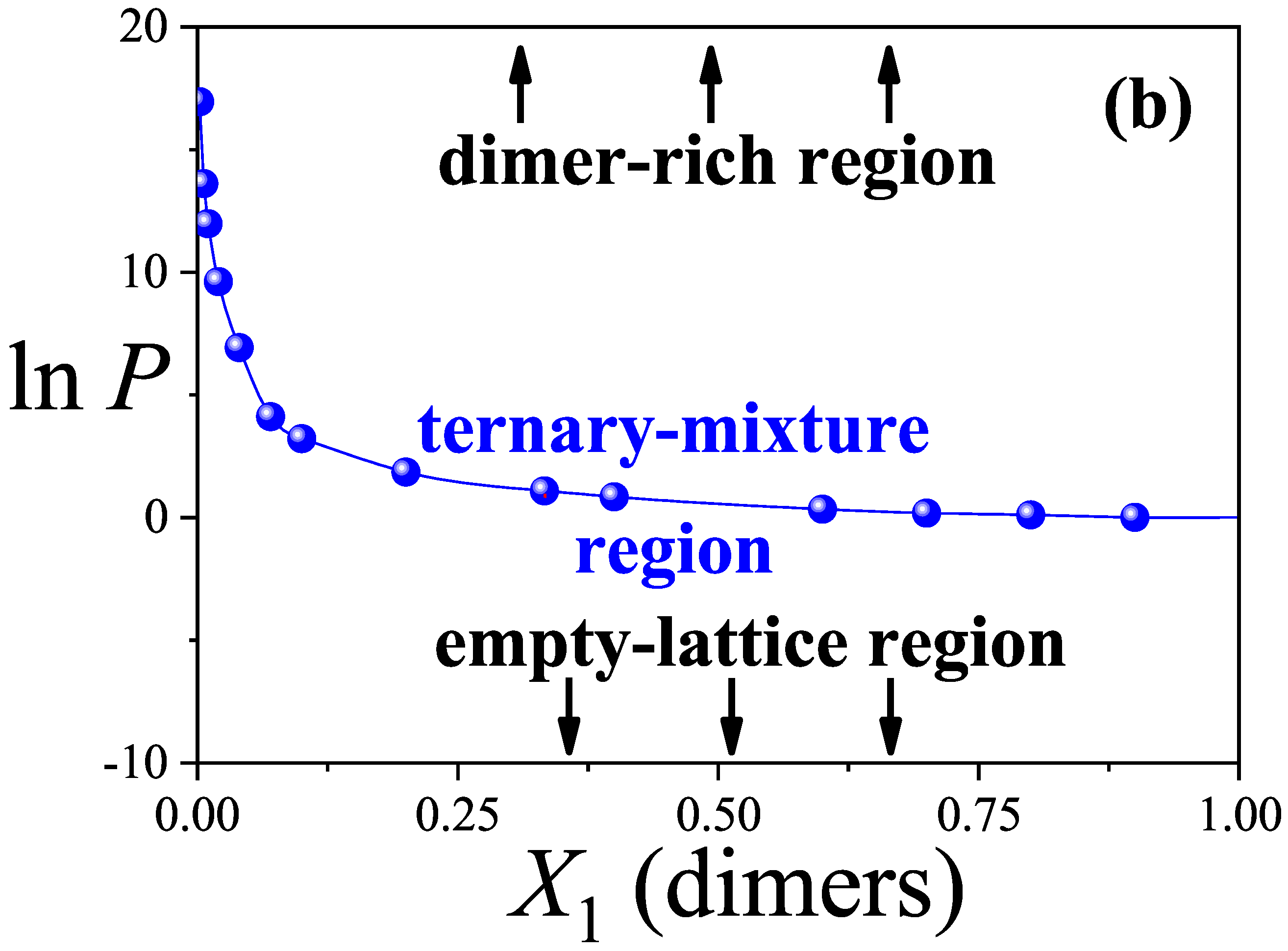
- The maximum entropy is attained for equimolar compositions, and the entropy landscape enables construction of an“entropic phase diagram” in the composition–pressure–maximum entropy space. This diagram delineates regions where competitive displacement is either enhanced or suppressed, offering a predictive tool for controlling surface composition and illustrating the richness of configurational possibilities in such systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Thermodynamic Functions of Multicomponent Lattice Gases with Hard-Core Interactions
Appendix B. Ideal Adsorbed Solution Theory (IAST)
| i | Species | Adsorption Isotherm Equation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | dimer | 2 | 3 | |
| 2 | linear trimer | 3 | 3 | |
| 3 | triangular trimer | 3 | 2 |
References
- Rudziński, W.; Steele, W.A.; Zgrablich, G. Equilibria and Dynamics of Gas Adsorption on Heterogeneous Solid Surfaces; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.T. Gas Separation by Adsorption Processes; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthven, D.M. Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Processes; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Talu, O. Needs, status, techniques and problems with binary gas adsorption experiments. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 77, 227–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.L.; Prausnitz, J.M. Thermodynamics of mixed-gas adsorption. AIChE J. 1965, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.S.; Sholl, D.S. Predicting multicomponent adsorption: 50 Years of the ideal adsorbed solution theory. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovbin, Y.K. The Theory of Physical Chemistry Processes at a Gas-Solid Interfaces; Mir Publishers & CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Votyakov, E.V.; Tovbin, Y.K. Phase States of Mixed Adspecies on Heterogeneous Surfaces. Langmuir 1997, 13, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefelov, V.F.; Stishenko, P.V.; Kutanov, V.M.; Myshlyavtsev, A.V.; Myshlyavtseva, M.D. Monte Carlo study of adsorption of additive gas mixture. Adsorption 2016, 22, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefelov, V.F.; Myshlyavtsev, A.V.; Myshlyavtseva, M.D. Phase diversity in the adsorption model of additive binary gas mixture for all sets of lateral interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 10359–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefelov, V.F.; Myshlyavtsev, A.V.; Myshlyavtseva, M.D. Complete analysis of phase diversity of the simplest adsorption model of a binary gas mixture for all sets of undirected interactions between nearest neighbors. Adsorption 2019, 25, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Virgiliis, A.; Meyra, A.; Ciach, A. Lattice Model Results for Pattern Formation in a Mixture with Competing Interactions. Molecules 2024, 29, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciach, A.; De Virgiliis, A.; Meyra, A.; Litniewski, M. Pattern Formation in Two-Component Monolayers of Particles with Competing Interactions. Molecules 2023, 28, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litniewski, M.; Ciach, A. Adsorption in Mixtures with Competing Interactions. Molecules 2021, 26, 4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borówko, M.; Rżysko, W.; Słyk, E. Self-assembly in two-dimensional mixtures of Janus disks and isotropic particles. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 044705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borówko, M.; Patrykiejew, A.; RżyskoS, W.; Sokołowski, S. A Monte Carlo Study of Adsorption from Mixtures of Dimers and Monomers on Heterogeneous Solid Surfaces. Langmuir 1997, 13, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrykiejew, A. The interplay between wetting and demixing in non-additive symmetric mixtures at selective walls. Eur. Phys. J. B 2018, 91, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrykiejew, A. Highly non-additive symmetric mixtures at a wall. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9228–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroniec, M.; Patrykiejew, A.; Borówko, M. Statistical Thermodynamics of Monolayer Adsorption from Gas and Liquid Mixtures on Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Solid Surfaces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Patrykiejew, A.; Sokołowski, S. Multilayer adsorption of binary mixtures: Mean-field theory and Monte Carlo simulation. Surf. Sci. 1995, 340, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, A. The general theory of diffusion in a mixture of molecules coadsorbed on a homogeneous two-dimensional lattice. Surf. Sci. 2019, 206, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, A. Diffusion in a binary mixture of molecules adsorbed on a multisite two-dimensional lattice. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 121984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, A. Analytical approach for the collective diffusion: Multicomponent mixture of particles coadsorbed on a multisite square lattice. Surf. Sci. 2023, 729, 122225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Dhar, D. On the orientational ordering of long rods on a lattice. Eur. Phys. Lett. 2007, 78, 20003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoz-Fernandez, D.A.; Linares, D.H.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Determination of the critical exponents for the isotropic-nematic phase transition in a system of long rods on two-dimensional lattices: Universality of the transition. Eur. Phys. Lett. 2008, 82, 50007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khettar, A.; Jalili, S.E.; Dunne, L.J.; Manos, G.; Du, Z. Monte-Carlo simulation and mean-field theory interpretation of adsorption preference reversal in isotherms of alkane binary mixtures in zeolites at elevated pressures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 362, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, L.J.; Manos, G.; Du, Z. Exact statistical mechanical one-dimensional lattice model of alkane binary mixture adsorption in zeolites and comparision with Monte-Carlo simulations. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 377, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, B.; Maesen, T.L.M. Molecular Simulations of Zeolites: Adsorption, Diffusion, and Shape Selectivity. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4125–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Reham, H.B.; Loughlin, K.F. Quaternary, Ternary, Binary, and Pure Component Sorption on Zeolites. 1. Light Alkanes on Linde S-115 Silicalite at Moderate to High Pressures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Manos, G.; Vlugt, T.J.H.; Smit, B. Molecular simulation of adsorption of short linear alkanes and their mixtures in silicalite. AIChE J. 1998, 44, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Smit, B.; Calero, S. Entropy effects during sorption of alkanes in zeolites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2002, 31, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Sandler, S.I.; Schenk, M.; Smit, B. Adsorption and separation of linear and branched alkanes on carbon nanotube bundles from configurational-bias Monte Carlo simulation. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 045447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Sandler, S.I. Monte Carlo Simulation for the Adsorption and Separation of Linear and Branched Alkanes in IRMOF-1. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5702–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. An Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics; Addison-Wesley: Reading, PA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J. Thermodynamics of High Polymer Solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1942, 10, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, M.L. Some properties of solutions of long-chain compounds. J. Chem. Phys. 1942, 46, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Cloizeaux, J.; Jannink, G. Polymers in Solution. Their Modelling and Structure; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, E.A. Statistical Thermodynamics of Mixtures with Zero Energies of Mixing. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1944, A183, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMarzio, E.A. Statistics of Orientation Effects in Linear Polymer Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1961, 35, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Pastor, A.J.; Eggarter, T.P.; Pereyra, V.; Riccardo, J.L. Statistical thermodynamics and transport of linear adsorbates. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 11027–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romá, F.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J.; Riccardo, J.L. Multisite Occupancy Adsorption: Comparative Study of New Different Analytical Approaches. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6770–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, J.L.; Romá, F.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Fractional Statistical Theory of Adsorption of Polyatomics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 186101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldane, F.D.M. “Fractional statistics” in arbitrary dimensions: A generalization of the Pauli principle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S. Statistical distribution for generalized ideal gas of fractional-statistics particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romá, F.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J.; Riccardo, J.L. Configurational entropy for adsorbed linear species (k-mers). J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 10932–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romá, F.; Riccardo, J.L.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Semiempirical Model for Adsorption of Polyatomics. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3192–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, J.L.; Romá, F.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Adsorption of polyatomics: Theoretical approaches in model systems and applications. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2006, 20, 4709–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, J.J.; Riccardo, J.L.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J.; Pasinetti, P.M. Multiple Exclusion Statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 020602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, J.J.; Pasinetti, P.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J.; Riccardo, J.L. Exclusion statistics for structured particles on topologically correlated states. I. Single species lattice gases. Phys. Rev. E 2025, 111, 014122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, J.J.; Pasinetti, P.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J.; Riccardo, J.L. Exclusion statistics for structured particles on topologically correlated states. II. Multicomponent lattice gases. Phys. Rev. E 2025, 111, 014123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, M.; Riccardo, J.L.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Exact statistical thermodynamics of alkane binary mixtures in zeolites: New interpretation of the adsorption preference reversal phenomenon from multisite-occupancy theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 477, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoz-Fernandez, D.A.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Adsorption preference reversal phenomenon frommultisite-occupancy theory for two-dimensional lattices. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 610–611, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, M.; Riccardo, J.L.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Fractional statistics description applied to adsorption of alkane binary mixtures in zeolites. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 174715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, L.; Cuesta, J.A. Elusiveness of Fluid-Fluid Demixing in Additive Hard-Core Mixtures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 145701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, L.; Cuesta, J.A. Fundamental measure theory for lattice fluids with hard-core interactions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 12079–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, L.; Cuesta, J.A. Phase behavior of hard-core lattice gases: A fundamental measure approach. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 10832–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, L.; Cuesta, J.A. Density functional theory for nearest-neighbor exclusion lattice gases in two and three dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 066120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, L.; Cuesta, J.A. Density functional theory for general hard-core lattice gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 130603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, L.; Cuesta, J.A. Cluster density functional theory for lattice models based on the theory of möbius functions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2005, 38, 7461–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Kuro-Oka, M.; Katayama, T. An adsorption isotherm of multi-site occupancy model for heterogeneous surface. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1984, 17, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Yamaguchi, A.J. A hybrid isotherm equation for mobile molecules adsorbed on heterogeneous surface of random topography. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1992, 25, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Oettel, M. Lattice Fundamental Measure Theory Beyond 0D Cavities: Dimers on Square Lattices. J. Stat. Phys. 2024, 191, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longone, P.; Martín, A.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Stability and cell distortion of sI clathrate hydrates of methane and carbon dioxide: A 2D lattice-gas model study. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2015, 402, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longone, P.; Martín, A.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Lattice-gas Monte Carlo study of sI clathrate hydrates of ethylene: Stability analysis and cell distortion. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2020, 521, 112739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longone, P.; Martín, A.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. CO2-CH4 Exchange Process in Structure I Clathrate Hydrates: Calculations of the Thermodynamic Functions Using a Flexible 2D Lattice-Gas Model and Monte Carlo Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, M. The classification of order-disorder transitions on surfaces. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1981, 11, 245–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, J.M. Statistical Mechanics of Phase Transitions; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kinzel, K.; Schick, M. Phenomenological scaling approach to the triangular Ising antiferromagnet. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 23, 3435–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.K.; Landau, D.P. Monte Carlo study of a triangular Ising lattice-gas model with two-body and three-body interactions. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 36, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phares, A.J.; Grumbine, D.W., Jr.; Wunderlich, F.J. Adsorption on an Equilateral Triangular Terrace Three Atomic Sites in Width: Application to Chemisorption of CO on Pt(112). Langmuir 2006, 22, 7646–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phares, A.J.; Grumbine, D.W., Jr.; Wunderlich, F.J. Monomer Adsorption on Equilateral Triangular Lattices with Attractive First-neighbor Interactions. Langmuir 2008, 24, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz Feliz, N.M.; Longone, P.J.; Sanchez-Varretti, F.O.; Bulnes, F.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Cluster approximation applied to multisite-occupancy adsorption: Configurational entropy of the adsorbed phase for dimers and trimers on triangular lattices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 14942–14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 627–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, D. Entropy-driven phase transitions. Physica A 1999, 263, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, R.; Vedmedenko, E.Y.; Wiesendanger, R. Entropy driven phase transition in itinerant antiferromagnetic monolayers. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 064410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson Spurling, R.; Lass, E.A.; Wang, X.; Page, K. Entropy-driven phase transitions in complex ceramic oxides. Phys. Rev. Materials 2022, 6, 090301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Ortiz, J.I.; Torres, P.; Quiroga, E.; Narambuena, C.F.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Adsorption of three-domain antifreeze proteins on ice: A study using LGMMAS theory and Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 31377–31388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, D.; Parsonage, N.G. Computer Simulation and the Statistical Mechanics of Adsorption; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, K. Applications of the Monte Carlo method in statistical physics. In Topics in Current Physics; Binder, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984; Volume 36, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, K. Static and dynamic critical phenomena of the two-dimensionalq-state Potts model. J. Stat. Phys. 1981, 24, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgreen, T.L. Monte Carlo simulation of the fcc antiferromagnetic Ising model. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 29, 1468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.P.; Verlet, L. Phase Transitions of the Lennard-Jones System. Phys. Rev. 1969, 184, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bulnes, F.M.; Pereyra, V.D.; Riccardo, J.L. Collective surface diffusion: n-fold way kinetic Monte Carlo simulation. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Varretti, F.O.; Garcia, G.D.; Pasinetti, P.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Adsorption of binary mixtures on two-dimensional surfaces: Theory and Monte Carlo simulations. Adsorption 2014, 20, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Varretti, F.O.; Bulnes, F.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. A cluster-exact approximation study of the adsorption of binary mixtures on heterogeneous surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Varretti, F.O.; Pasinetti, P.M.; Bulnes, F.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Adsorption of laterally interacting gas mixtures on homogeneous surfaces. Adsorption 2017, 23, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Varretti, F.O.; Bulnes, F.M.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Cluster-exact approximation applied to adsorption with non-additive lateral interactions. Physica A 2019, 518, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y. Dimers on two-dimensional lattices. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2006, 20, 5357–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberkmoes, A.; Nienhuis, B. Triangular Trimers on the Triangular Lattice: An Exact Solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 3986–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberkmoes, A.; Nienhuis, B. Bethe ansatz solution of triangular trimers on the triangular lattice. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 066122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatchard, G. The Gibbs Adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1962, 66, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longone, P.J.; Ramirez-Pastor, A.J. Adsorption of Ternary Mixtures in the Presence of Multisite Occupancy: Theory and Monte Carlo Simulations. Entropy 2025, 27, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080849
Longone PJ, Ramirez-Pastor AJ. Adsorption of Ternary Mixtures in the Presence of Multisite Occupancy: Theory and Monte Carlo Simulations. Entropy. 2025; 27(8):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080849
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongone, Pablo Jesús, and Antonio José Ramirez-Pastor. 2025. "Adsorption of Ternary Mixtures in the Presence of Multisite Occupancy: Theory and Monte Carlo Simulations" Entropy 27, no. 8: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080849
APA StyleLongone, P. J., & Ramirez-Pastor, A. J. (2025). Adsorption of Ternary Mixtures in the Presence of Multisite Occupancy: Theory and Monte Carlo Simulations. Entropy, 27(8), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080849







