Deep Learning-Based Min-Entropy-Accelerated Evaluation for High-Speed Quantum Random Number Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Dual-Quadrature Heterodyne Detection
2.2. High-Speed QRNG and Entropy Evaluation Setup
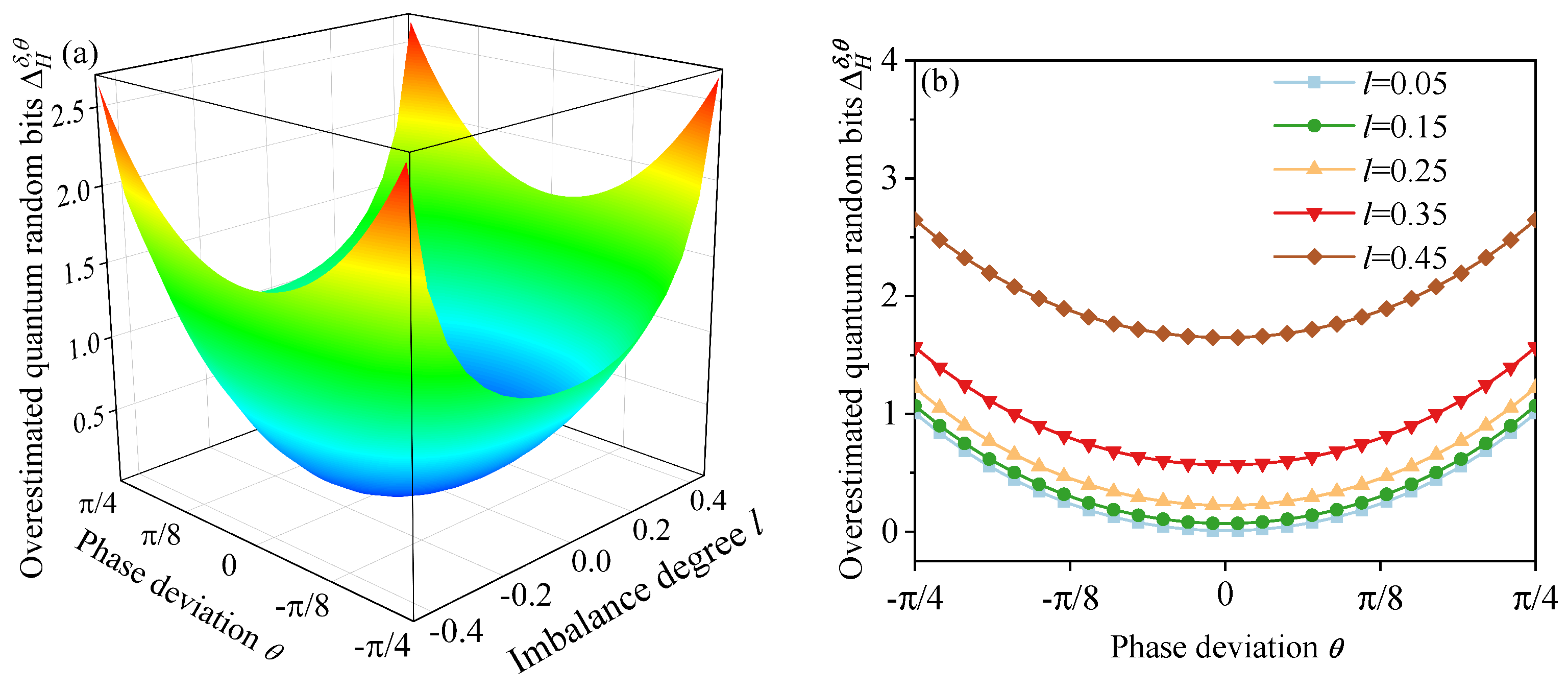
2.3. Security and Quantum Conditional Min-Entropy Evaluation
2.4. Deep Learning Method
3. Experimental Results
3.1. High-Speed and High-Security QRNG Using Dual-Quadrature Heterodyne Detection
3.2. Quantum Conditional Min-Entropy Evaluation with Deep Learning
3.3. Correlation and NIST Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QRNG | Quantum Random Number Generation |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| LO | Local Oscillator |
References
- Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.Q.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Certified randomness from untrusted sources and uncharacterized measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 050506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Andersen, U.L.; Banchi, L.; Berta, M.; Bunandar, D.; Colbeck, R.; Englund, D.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 1012–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambić, D. Security analysis and improvement of the pseudo-random number generator based on piecewise logistic map. J. Electron. Test. 2019, 35, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Piao, J.; Liu, J. ECDSA weak randomness in Bitcoin. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 102, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennewein, T.; Achleitner, U.; Weihs, G.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. A fast and compact quantum random number generator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, A.; Gisin, N.; Guinnard, O.; Guinnard, L.; Zbinden, H. Optical quantum random number generator. J. Mod. Opt. 2000, 47, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.; Leifgen, M.; Berlin, M.; Röhlicke, T.; Rahn, H.J.; Benson, O. An ultrafast quantum random number generator with provably bounded output bias based on photon arrival time measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 171105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.W. Practical and fast quantum random number generation based on photon arrival time relative to external reference. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 051110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Cheng, X.; Sarihan, M.C.; Wong, C.W. Recent advances in high-dimensional quantum frequency combs. Newton 2025, 1, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wu, E.; Liang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Wu, G.; Zeng, H. Quantum random-number generator based on a photon-number-resolving detector. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 023820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhao, B.; Liao, Q.; Zhou, N. Multi-bit quantum random number generation by measuring positions of arrival photons. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, M.; Thomas, O.; Dynes, J.; Yuan, Z.; Ritchie, D.; Shields, A. Efficient and robust quantum random number generation by photon number detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 071106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Sarihan, M.C.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, C.W. Large-alphabet time-bin quantum key distribution and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering via dispersive optics. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 015018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.; Wittmann, C.; Sych, D.; Dong, R.; Mauerer, W.; Andersen, U.L.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. A generator for unique quantum random numbers based on vacuum states. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tian, L.; Zou, H. Practical quantum random number generator based on measuring the shot noise of vacuum states. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 063814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symul, T.; Assad, S.M.; Lam, P.K. Real time demonstration of high bitrate quantum random number generation with coherent laser light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 231103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haw, J.Y.; Assad, S.; Lance, A.; Ng, N.; Sharma, V.; Lam, P.K.; Symul, T. Maximization of extractable randomness in a quantum random-number generator. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 3, 054004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán, C.; Amaya, W.; Jofre, M.; Curty, M.; Acín, A.; Capmany, J.; Pruneri, V.; Mitchell, M.W. Ultra-fast quantum randomness generation by accelerated phase diffusion in a pulsed laser diode. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Su, Q.; Li, Z.; Fan, F.; Xu, B.; Guo, H. 5.4 Gbps real time quantum random number generator with simple implementation. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 27475–27481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Nie, Y.Q.; Zhou, H.; Liang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.W. Note: Fully integrated 3.2 Gbps quantum random number generator with real-time extraction. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 076102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.; Salevan, J.C.; Li, X.; Roy, R.; Murphy, T.E. Fast physical random number generator using amplified spontaneous emission. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23584–23597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xie, G.; Dang, A.; Guo, H. High-speed and bias-free optical random number generator. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 24, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B. True randomness from an incoherent source. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, R.; Li, P.; Cheng, C.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y. Enhancing extractable quantum entropy in vacuum-based quantum random number generator. Entropy 2018, 20, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Kordts, A.; Solar Nikolic, D.; Jain, N.; Rydberg, T.; Pedersen, T.B.; Pirandola, S.; Andersen, U.L. Homodyne-based quantum random number generator at 2.9 Gbps secure against quantum side-information. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Guo, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Parallel CV-QRNG with Strict Entropy Evaluation. Photonics 2023, 10, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Yu, S. Practical security analysis of a continuous-variable quantum random-number generator with a noisy local oscillator. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 012422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B.; Yu, S. Finite-size analysis of continuous variable source-independent quantum random number generation. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Su, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H. High speed continuous variable source-independent quantum random number generation. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, D.G.; Vallone, G.; Villoresi, P. Source-device-independent ultrafast quantum random number generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 060503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.R.; Marangon, D.G.; Lucamarini, M.; Yuan, Z.; Shields, A. Simple source device-independent continuous-variable quantum random number generator. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 062326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Curty, M.; Qi, B.; Qian, L.; Lo, H.K. Discrete and continuous variables for measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapatero, V.; van Leent, T.; Arnon-Friedman, R.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Weinfurter, H.; Curty, M. Advances in device-independent quantum key distribution. Npj Quantum Inf. 2023, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avesani, M.; Marangon, D.G.; Vallone, G.; Villoresi, P. Source-device-independent heterodyne-based quantum random number generator at 17 Gbps. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avesani, M.; Tebyanian, H.; Villoresi, P.; Vallone, G. Semi-device-independent heterodyne-based quantum random-number generator. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 15, 034034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Qin, J.; Liang, S.; Li, J.; Yan, Z.; Jia, X.; Peng, K. Mutually testing source-device-independent quantum random number generator. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, T.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Jing, J. Entropy evaluation for oscillator-based true random number generators. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2014: 16th International Workshop, Busan, Republic of Korea, 23–26 September 2014; Proceedings 16; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 544–561. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey, J.; McKay, K.A.; Sönmez Turan, M. Predictive models for min-entropy estimation. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2015: 17th International Workshop, Saint-Malo, France, 13–16 September 2015; Proceedings 17; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 373–392. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, N.D.; Haw, J.Y.; Assad, S.M.; Lam, P.K.; Kavehei, O. Machine learning cryptanalysis of a quantum random number generator. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 14, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrer, F.; Berta, M.; Tomamichel, M.; Scholz, V.B.; Christandl, M. Position-momentum uncertainty relations in the presence of quantum memory. J. Math. Phys. 2014, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallone, G.; Marangon, D.G.; Tomasin, M.; Villoresi, P. Quantum randomness certified by the uncertainty principle. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 052327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, T.; Händchen, V.; Duhme, J.; Furrer, F.; Franz, T.; Pacher, C.; Werner, R.F.; Schnabel, R. Implementation of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable and one-sided-device-independent security against coherent attacks. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.M.; Jain, N.; Zibar, D.; Andersen, U.L.; Gehring, T. Machine learning aided carrier recovery in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Npj Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.M.; Hajomer, A.A.; Jain, N.; Andersen, U.L.; Gehring, T. Machine learning based joint polarization and phase compensation for CV-QKD. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–9 March 2023; Optica Publishing Group: Washtington, DC, USA, 2023; p. Th3J-2. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Guo, X. High-speed photon correlation monitoring of amplified quantum noise by chaos using deep-learning balanced homodyne detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 051101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Ge, W.; Song, Z.; Cui, X.; Guo, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, L. Seed Renewable Parallel and Real-Time Toeplitz Post-Processing for QRNG. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 42, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Huang, J.; Qiao, G.R.; Nie, Y.Q.; Tang, W.; Chu, T.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.W. 18.8 Gbps real-time quantum random number generator with a photonic integrated chip. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 264001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruynsteen, C.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Bauwelinck, J.; Yin, X. 100-Gbit/s integrated quantum random number generator based on vacuum fluctuations. PRX Quantum 2023, 4, 010330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Song, Z.; Li, Z.; Qu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, L. Real-time entropy source evaluated dual-parallel continuous variable quantum random number generator. Acta Phys. Sin. 2025, 74, 124202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, C.; Wu, M.; Gao, Q.; Li, P.; Guo, Y. Parallel real-time quantum random number generator. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 5566–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Test’s Name | p-Value | Proportion | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 0.16261 | 0.9876 | Passed |
| Block-frequency | 0.21792 | 0.9924 | Passed |
| Cumulative-sums | 0.01046 | 0.9843 | Passed |
| Runs | 0.90963 | 0.9821 | Passed |
| Longest-run | 0.42735 | 0.9894 | Passed |
| Rank | 0.04705 | 0.9885 | Passed |
| FFT | 0.1418 | 0.9830 | Passed |
| Non-Overlapping-Templates | 0.0115 | 0.9820 | Passed |
| Overlapping-templates | 0.22104 | 0.9923 | Passed |
| Universal | 0.8868 | 0.9998 | Passed |
| Approximate-Entropy | 0.63712 | 0.9856 | Passed |
| Random-excursions | 0.29161 | 0.9921 | Passed |
| Random-excursions-variant | 0.03263 | 0.9877 | Passed |
| Serial | 0.20285 | 0.9876 | Passed |
| Linear-complexity | 0.48334 | 0.9838 | Passed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Zhou, W.; Luo, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Bian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, L. Deep Learning-Based Min-Entropy-Accelerated Evaluation for High-Speed Quantum Random Number Generation. Entropy 2025, 27, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080786
Guo X, Zhou W, Luo Y, Meng X, Li J, Bian Y, Guo Y, Xiao L. Deep Learning-Based Min-Entropy-Accelerated Evaluation for High-Speed Quantum Random Number Generation. Entropy. 2025; 27(8):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080786
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaomin, Wenhe Zhou, Yue Luo, Xiangyu Meng, Jiamin Li, Yaoxing Bian, Yanqiang Guo, and Liantuan Xiao. 2025. "Deep Learning-Based Min-Entropy-Accelerated Evaluation for High-Speed Quantum Random Number Generation" Entropy 27, no. 8: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080786
APA StyleGuo, X., Zhou, W., Luo, Y., Meng, X., Li, J., Bian, Y., Guo, Y., & Xiao, L. (2025). Deep Learning-Based Min-Entropy-Accelerated Evaluation for High-Speed Quantum Random Number Generation. Entropy, 27(8), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080786









