Heterogeneity-Aware Personalized Federated Neural Architecture Search
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a resource-resilient federated supernet training strategy based on ensemble distillation in heterogeneous FL systems. Specifically, we use lightweight knowledge models to distill knowledge from FL clients to the server-side supernet, thereby alleviating the exacerbated gradient conflicts arising from the coupling of resource heterogeneity and statistical heterogeneity.
- We propose a predictor-guided personalized evolutionary search algorithm. Specifically, we establish a performance predictor using random forest to quickly predict the performance of candidate architectures on a target client, thus eliminating time-consuming inference evaluation and accelerating the search process.
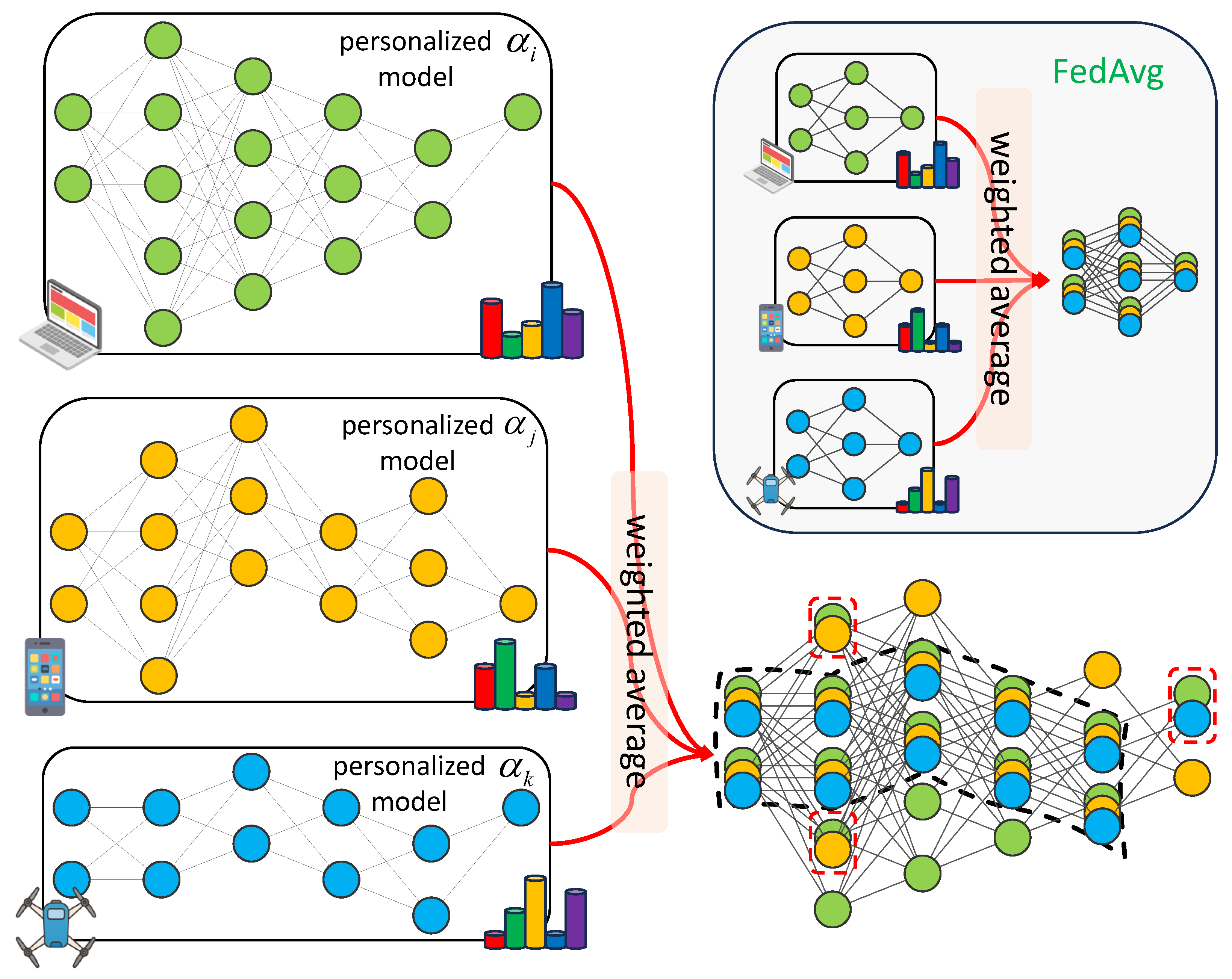
- Additionally, we develop a model-heterogeneous FL algorithm, termed heteroFedAvg, to facilitate collaborative learning among searched personalized models that originate in the same search space.
2. Related Works
2.1. Federated Neural Architecture Search
2.2. Model-Heterogeneous Federated Learning
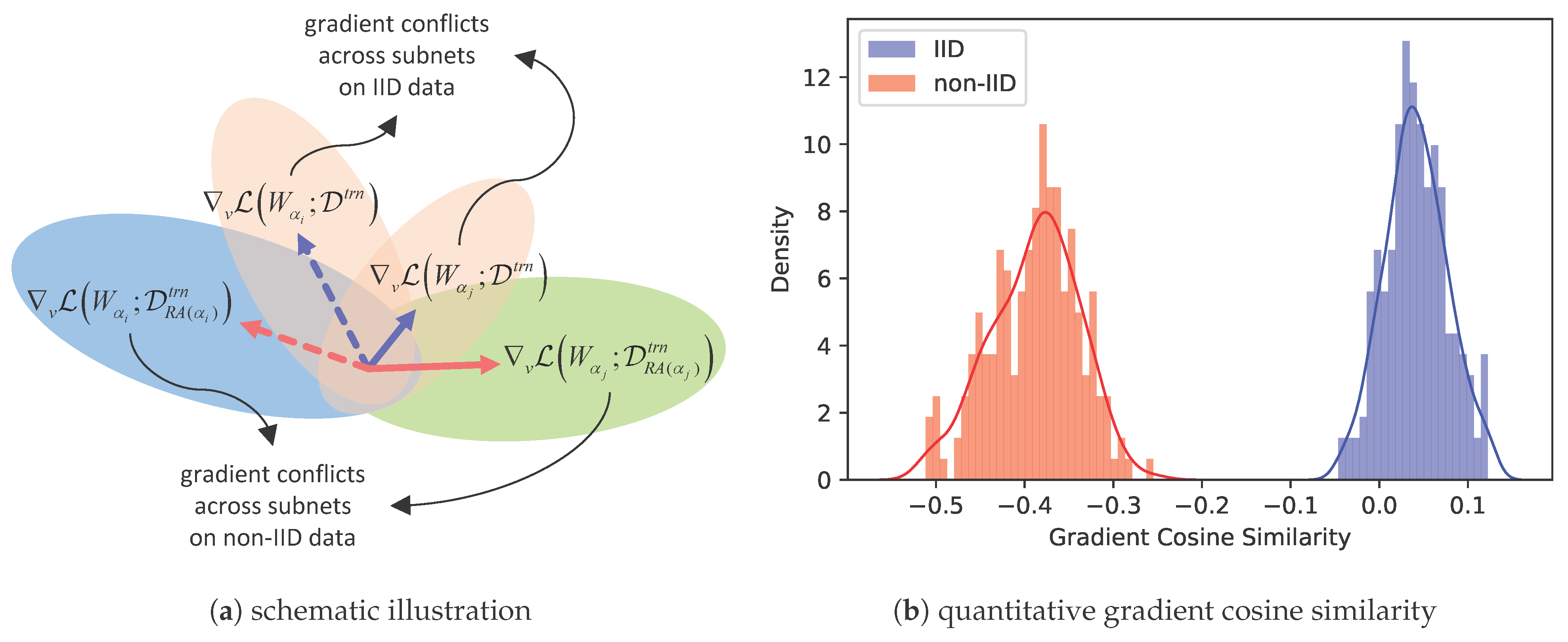
3. Preliminaries and Motivation
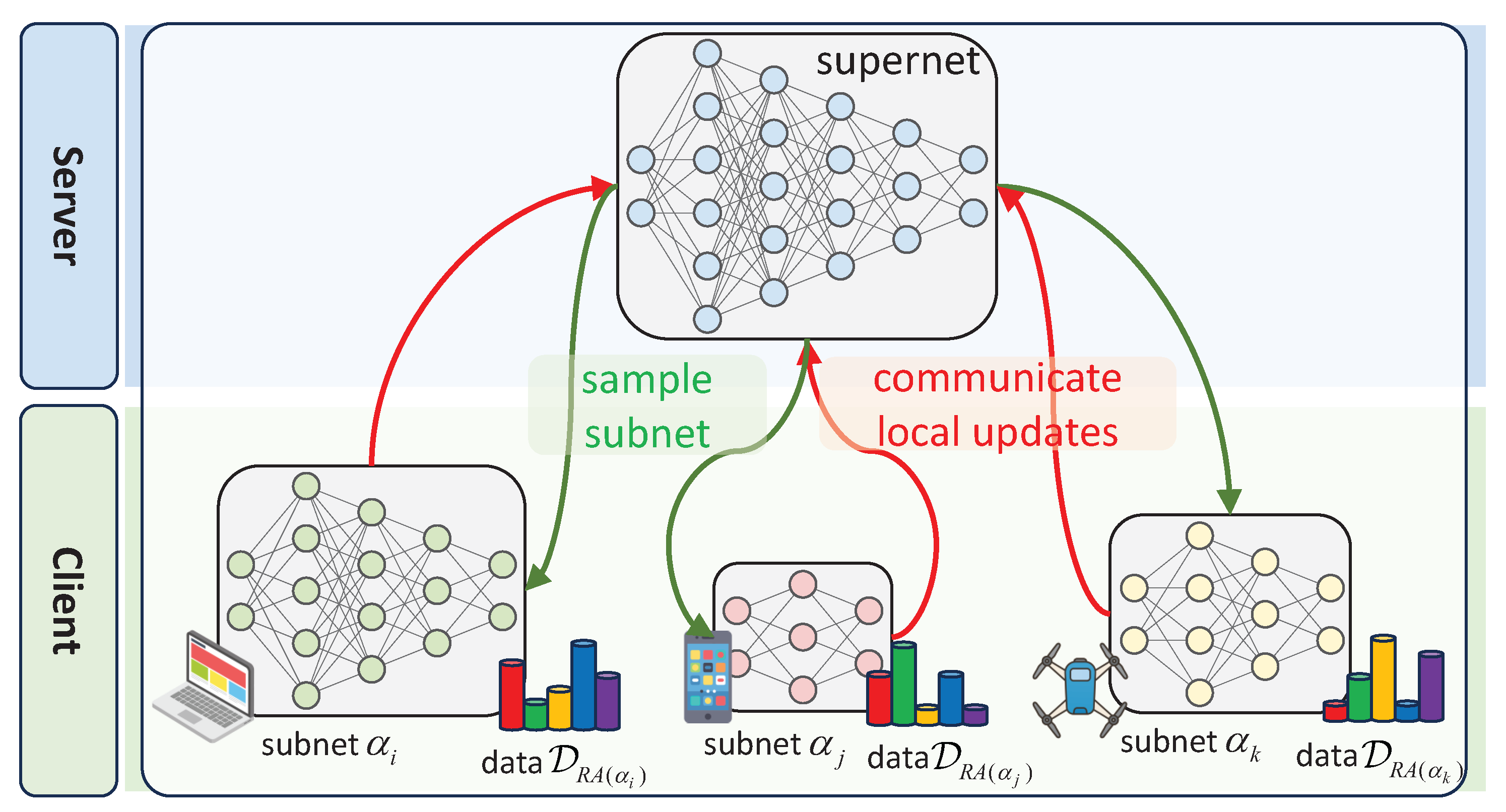
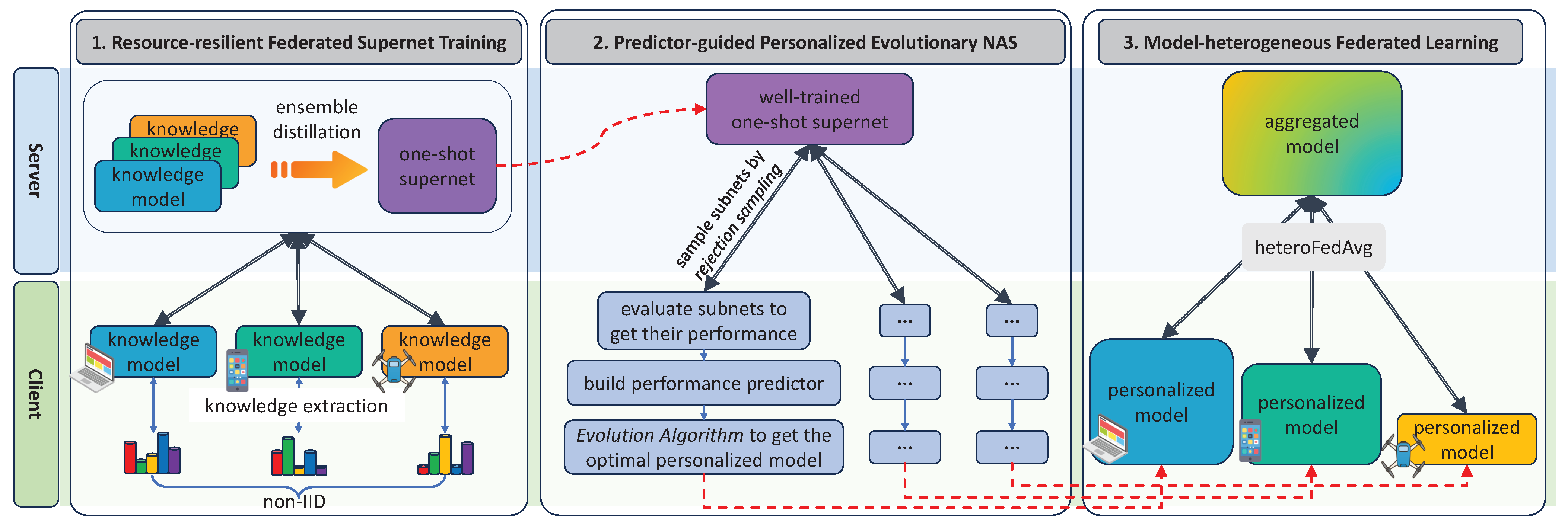
4. Methods
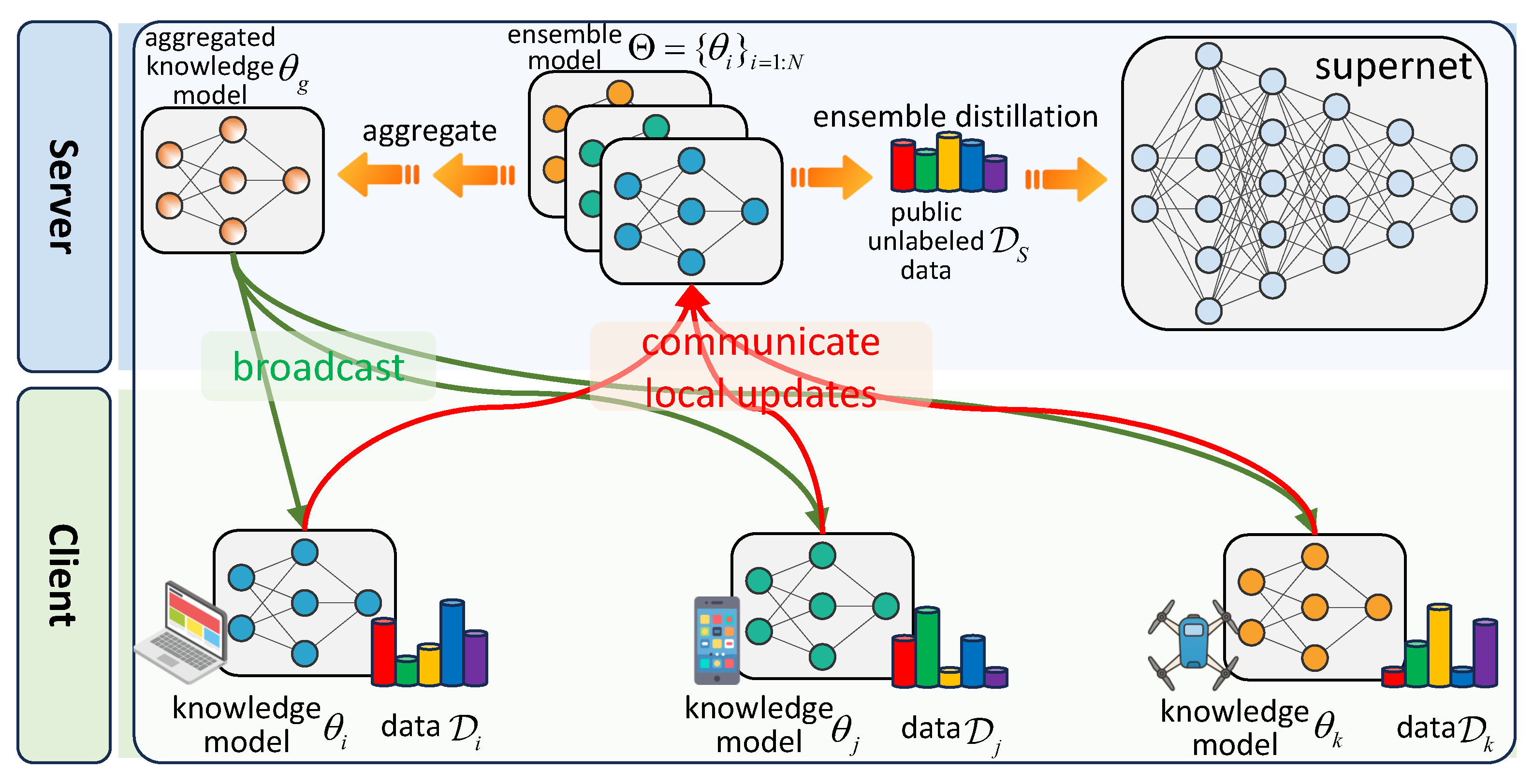
4.1. Resource-Resilient Federated Supernet Training
4.1.1. Knowledge Collection for Supernet Training
4.1.2. Supernet Training on the Server
| Algorithm 1 Resource-resilient Federated Supernet Training |
| Input: Initialize the knowledge model , supernet W, number of clients N, total round T ClientUpdate:
|
4.2. Predictor-Guided Personalized Evolutionary NAS
| Algorithm 2 Predictor-guided personalized evolutionary neural architecture search on client i |
Input: The well-trained trained supernet W, search space , total generations , population size , mutation size , crossover size
|
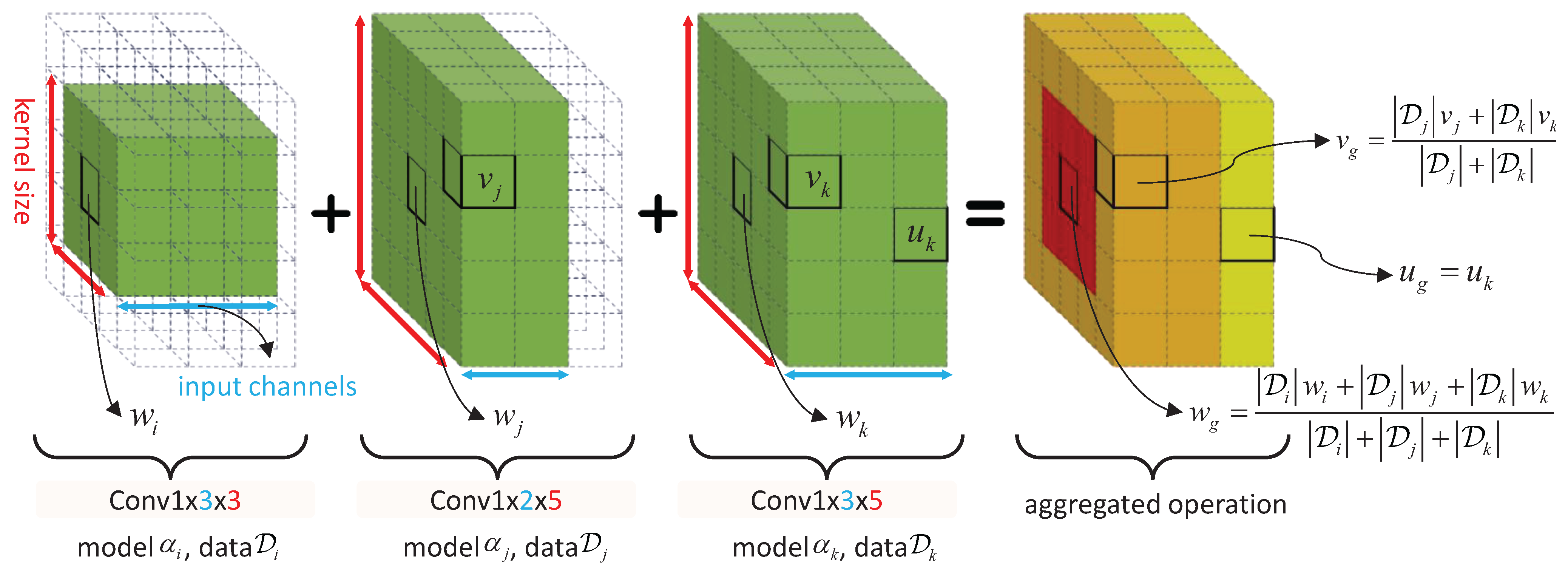
4.3. Model-Heterogeneous Federated Learning
5. Experiments
5.1. Experimental Setup
- Environment settings:
- Search space:
- Datasets:
- Federated settings:
- Supernet training settings:
- Search settings:
- Federated retraining settings:
5.2. Effectiveness of Resource-Resilient Supernet Training
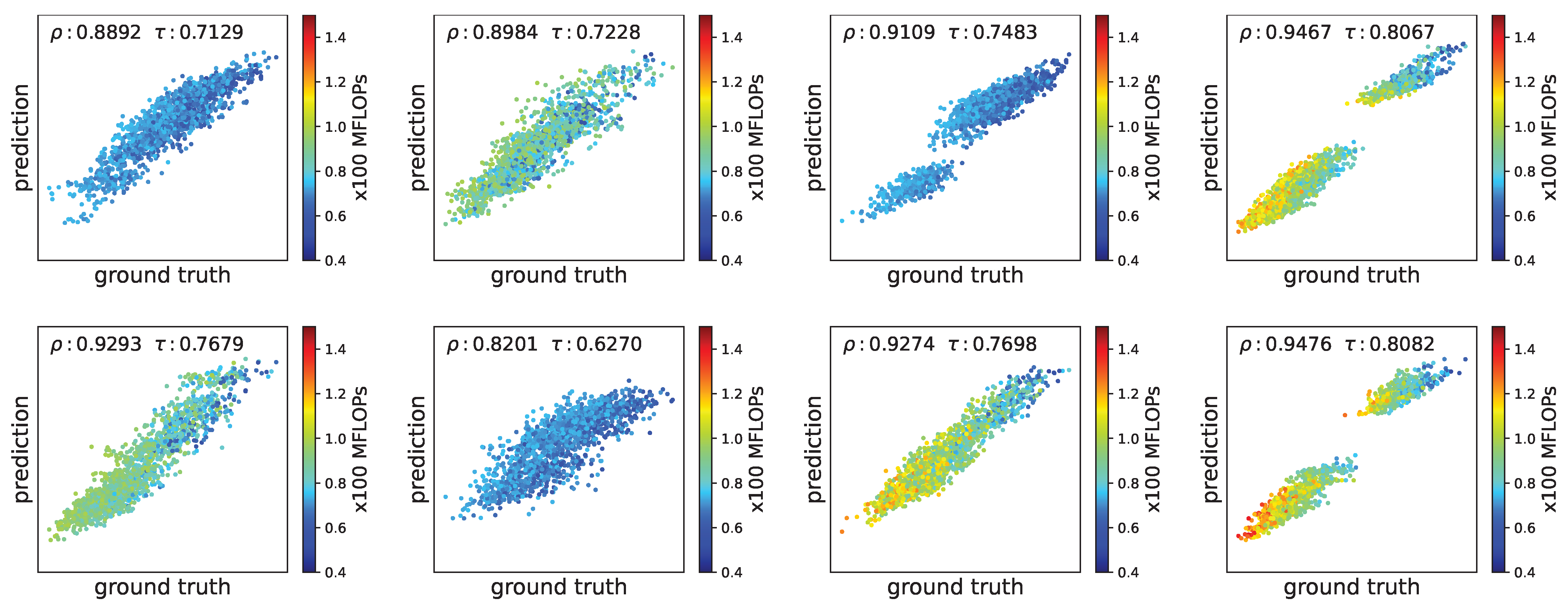
5.3. Effectiveness of Performance Predictor
5.4. Effectiveness of heteroFedAvg
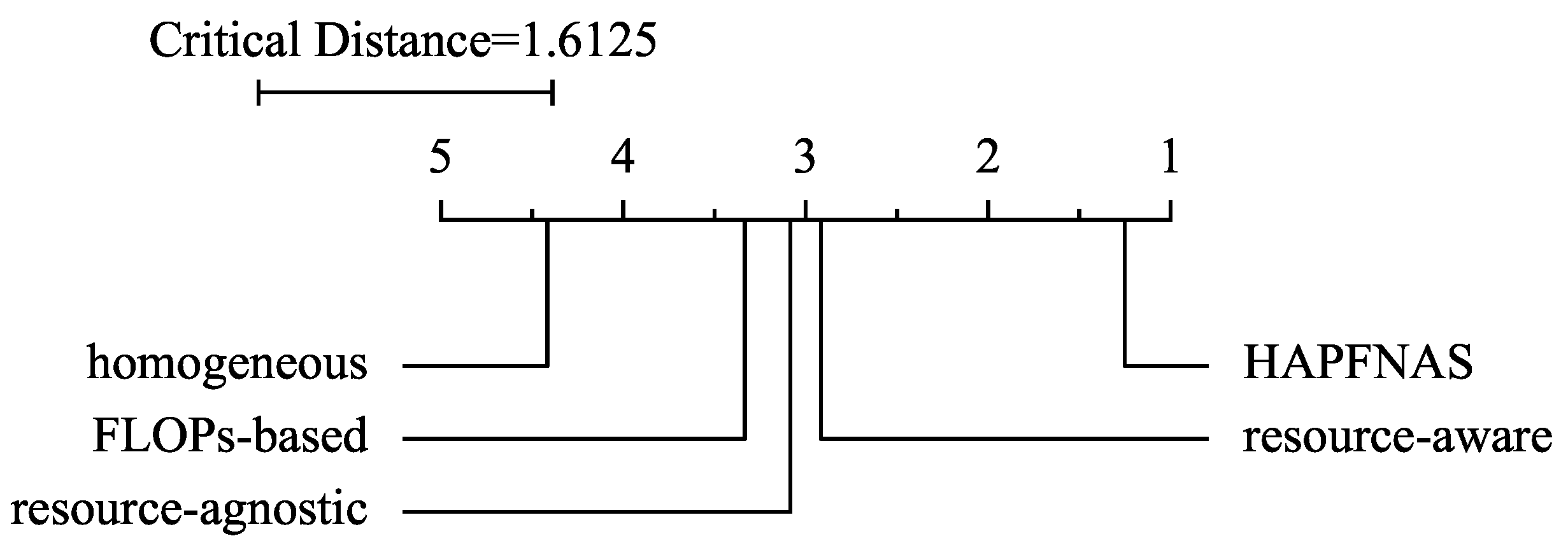
5.5. Effectiveness of HAPFNAS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; Arcas, B.A.y. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data. In Proceedings of the 20 th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; Volume 54, pp. 1273–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, A.Z.; Yu, H.; Cui, L.; Yang, Q. Towards Personalized Federated Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 9587–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhu, L.; Han, S. ProxylessNAS: Direct Neural Architecture Search on Target Task and Hardware. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1812.00332. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Xie, S.; Zheng, H.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Lin, D. DSNAS: Direct Neural Architecture Search Without Parameter Retraining. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 12081–12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ye, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, T. MiLeNAS: Efficient Neural Architecture Search via Mixed-Level Reformulation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11990–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, M.; Gong, C.; Chandra, V. AttentiveNAS: Improving Neural Architecture Search via Attentive Sampling. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6418–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Gan, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Han, S. Once-for-All: Train One Network and Specialize it for Efficient Deployment. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1908.09791. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Jin, P.; Liu, H.; Bender, G.; Kindermans, P.; Tan, M.; Huang, T.S.; Song, X.; Pang, R.; Le, Q. BigNAS: Scaling up Neural Architecture Search with Big Single-Stage Models. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Volume 12352, pp. 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R. FairNAS: Rethinking Evaluation Fairness of Weight Sharing Neural Architecture Search. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 12219–12228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, N. Privacy-Preserving Neural Architecture Search Across Federated IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 20th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), Shenyang, China, 20–22 October 2021; pp. 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Xiang, L.; Shao, S.; Chen, Y.; Tong, Y. Federated Model Search via Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 41st International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Washington, DC, USA, 7–10 July 2021; pp. 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskaridis, S.; Fernandez-Marques, J.; Dudziak, Ł. Cross-device Federated Architecture Search. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Federated Learning: Recent Advances and New Challenges (in Conjunction with NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesha, Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Panda, P. Divide-and-conquer the NAS puzzle in resource-constrained federated learning systems. Neural Netw. 2023, 168, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tan, X.; Song, K.; Luo, R.; Leng, Y.; Qin, T.; Liu, T.; Li, J. Analyzing and Mitigating Interference in Neural Architecture Search. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, ML, USA, 17–23 July 2022; Volume 162, pp. 24646–24662. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Pan, S.; Chang, X.; Zhou, C.; Ge, Z.; Su, S.W. One-Shot Neural Architecture Search: Maximising Diversity to Overcome Catastrophic Forgetting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2921–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Annavaram, M.; Avestimehr, S. Towards Non-I.I.D. and Invisible Data with FedNAS: Federated Deep Learning via Neural Architecture Search. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08546. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A.; Saha, A.K.; Dutta, D. Direct Federated Neural Architecture Search. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.06223. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Cheng, J. DPNAS: Neural Architecture Search for Deep Learning with Differential Privacy. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 6358–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Zhou, H.; Yang, K.; Ding, M.; Lin, B.; Xie, P. Differentially-private Federated Neural Architecture Search. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10559. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, M.; Kingsford, C. Personalized Neural Architecture Search for Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 1st NeurIPS Workshop on New Frontiers in Federated Learning (NFFL 2021), Virtual, 13 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, E.; He, C.; Ding, J.; Avestimehr, S. SPIDER: Searching Personalized Neural Architecture for Federated Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.13939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, N. Toward Tailored Models on Private AIoT Devices: Federated Direct Neural Architecture Search. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 17309–17322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, J.; Prasad, P.; Dhami, D.S.; Kersting, K. HANF: Hyperparameter Furthermore, Neural Architecture Search in Federated Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.12342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Li, C.; Zou, J.; Wang, S. FedAutoMRI: Federated Neural Architecture Search for MR Image Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2023 Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; Volume 14393, pp. 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jin, Y. Real-Time Federated Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2022, 26, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J. FedMD: Heterogenous Federated Learning via Model Distillation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.03581. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Aral, A. FedCD: Personalized Federated Learning via Collaborative Distillation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/ACM 15th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing (UCC), Vancouver, WA, USA, 6–9 December 2022; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Wu, F. Parameterized Knowledge Transfer for Personalized Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2021), Online, 6–14 December 2021; pp. 10092–10104. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Shejwalkar, V.; Shokri, R.; Houmansadr, A. Cronus: Robust and Heterogeneous Collaborative Learning with Black-Box Knowledge Transfer. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.11279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, G.; Varshney, P.K. Decentralized Federated Learning via Mutual Knowledge Transfer. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Oh, S.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; Bennis, M.; Kim, S. Communication-Efficient On-Device Machine Learning: Federated Distillation and Augmentation under Non-IID Private Data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.11479. [Google Scholar]
- Le, H.Q.; Shin, J.H.; Nguyen, M.N.H.; Hong, C.S. Distilling Knowledge in Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 22nd Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Tainan, Taiwan, 8–10 September 2021; pp. 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Kong, L.; Stich, S.U.; Jaggi, M. Ensemble Distillation for Robust Model Fusion in Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Yuan, X. FedZKT: Zero-Shot Knowledge Transfer towards Resource-Constrained Federated Learning with Heterogeneous On-Device Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 42nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Bologna, Italy, 10–13 July 2022; pp. 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Qian, W.; Jannesari, A. Resource-aware Federated Learning using Knowledge Extraction and Multi-model Fusion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.07978. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Nguyen, P.; Abebe, W.; Stanley, J.; Muñoz, J.P.; Jannesari, A. Resource-Aware Heterogeneous Federated Learning using Neural Architecture Search. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.05716. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Huang, T.S. Universally Slimmable Networks and Improved Training Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, G.; Kindermans, P.; Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Le, Q.V. Understanding and Simplifying One-Shot Architecture Search. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; Volume 80, pp. 549–558. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mu, H.; Heng, W.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Single Path One-Shot Neural Architecture Search with Uniform Sampling. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020, Online, 23–28 August 2020; Voume 12361, pp. 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images. 2009. Available online: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/learning-features-2009-TR.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Le, Y.; Yang, X. Tiny imagenet visual recognition challenge. CS 231N 2015, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, D.; Chen, D.; Yao, L.; Kuang, W.; Li, Y.; Ding, B.; Zhou, J. FederatedScope: A Flexible Federated Learning Platform for Heterogeneity. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2023, 16, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.C.; Tan, M.; Chu, G.; Vasudevan, V.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.H.; Qi, H.; Brown, M. Measuring the Effects of Non-Identical Data Distribution for Federated Visual Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.06335. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Jia, M.; Lin, T.; Song, Y.; Belongie, S.J. Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9268–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Bhardwaj, K.; Marculescu, R. ZiCo: Zero-shot NAS via inverse Coefficient of Variation on Gradients. In Proceedings of the ICLR, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Demsar, J. Statistical Comparisons of Classifiers over Multiple Data Sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]


| Methods | Average Top-1 Accuracy Across 8 Clients (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Heterogeneous Models | Homogeneous Models | |
| FedKEMF [35] | 68.94 | 66.07 |
| FedMD [26] | 68.86 | 66.18 |
| HeteroFedAvg (proposed) | 69.36 | 68.18 |
| Dataset | N Clients | Average Top-1 Accuracy Across N Clients (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAPFNAS | Resource-Aware | Resource-Agnostic | FLOPs-Based | Homogeneous † | ||
| CIFAR-10 [41] | 88.33 | 88.29 | 88.74 | 88.18 | 85.35 | |
| 85.38 | 86.01 | 84.76 | 84.87 | 83.39 | ||
| 84.41 | 84.49 | 83.00 | 83.39 | 83.27 | ||
| 79.28 | 78.52 | 77.76 | 78.14 | 79.11 | ||
| CIFAR-100 [41] | 69.36 | 68.49 | 68.92 | 68.34 | 65.46 | |
| 64.73 | 63.12 | 64.13 | 62.93 | 61.96 | ||
| 58.81 | 57.78 | 57.34 | 56.35 | 56.31 | ||
| 55.25 | 53.63 | 52.87 | 54.39 | 53.20 | ||
| Tiny-ImageNet [42] | 48.64 | 47.31 | 47.55 | 47.75 | 46.26 | |
| 46.47 | 45.96 | 46.24 | 45.68 | 44.37 | ||
| 45.45 | 43.56 | 43.90 | 44.55 | 43.45 | ||
| 42.10 | 40.78 | 41.34 | 40.88 | 41.19 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, A.; Liu, Y. Heterogeneity-Aware Personalized Federated Neural Architecture Search. Entropy 2025, 27, 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070759
Yang A, Liu Y. Heterogeneity-Aware Personalized Federated Neural Architecture Search. Entropy. 2025; 27(7):759. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070759
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, An, and Ying Liu. 2025. "Heterogeneity-Aware Personalized Federated Neural Architecture Search" Entropy 27, no. 7: 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070759
APA StyleYang, A., & Liu, Y. (2025). Heterogeneity-Aware Personalized Federated Neural Architecture Search. Entropy, 27(7), 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070759






