Graph-Theoretic Limits of Distributed Computation: Entropy, Eigenvalues, and Chromatic Numbers †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation and Literature Review
1.2. Overview and Contributions
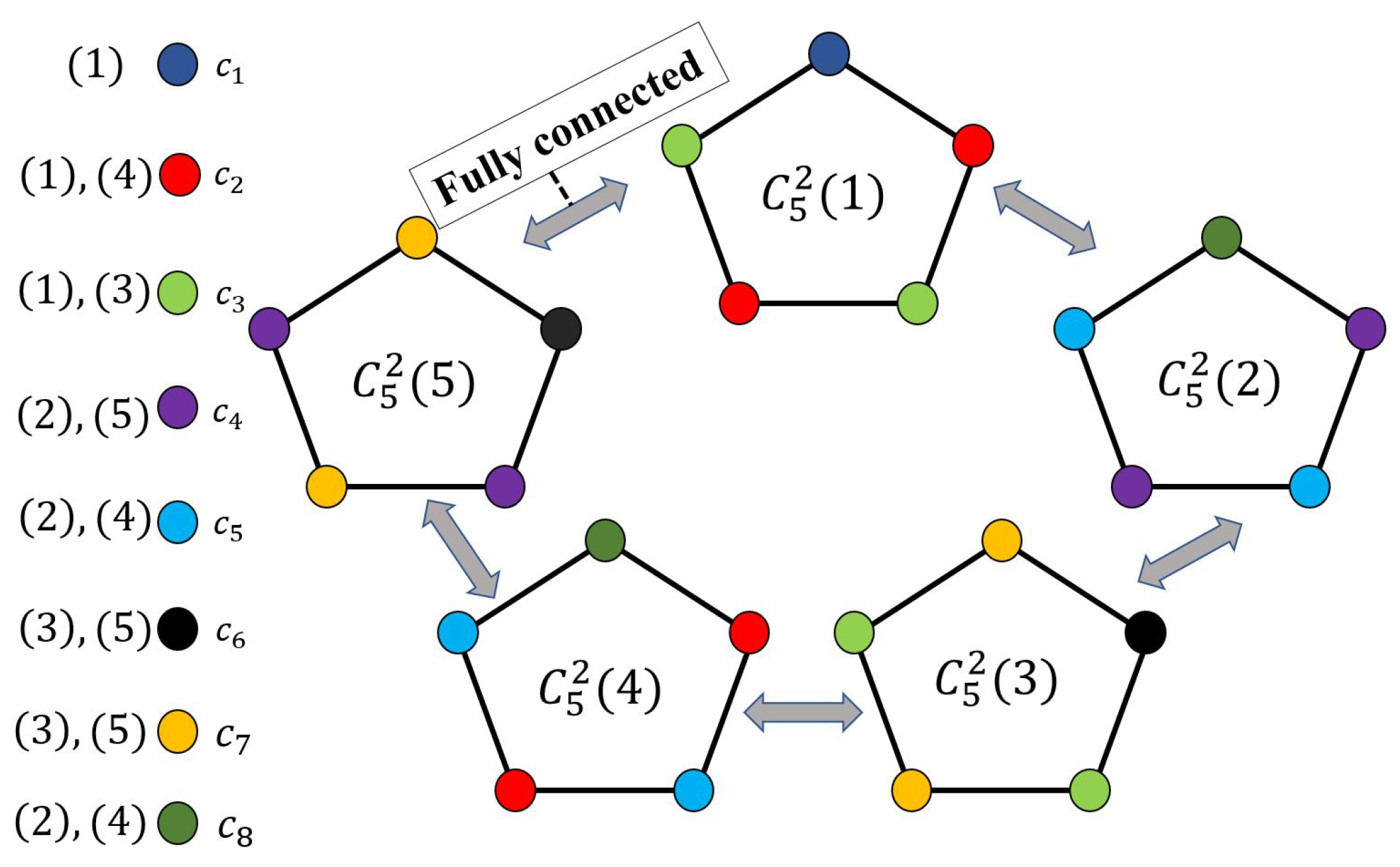
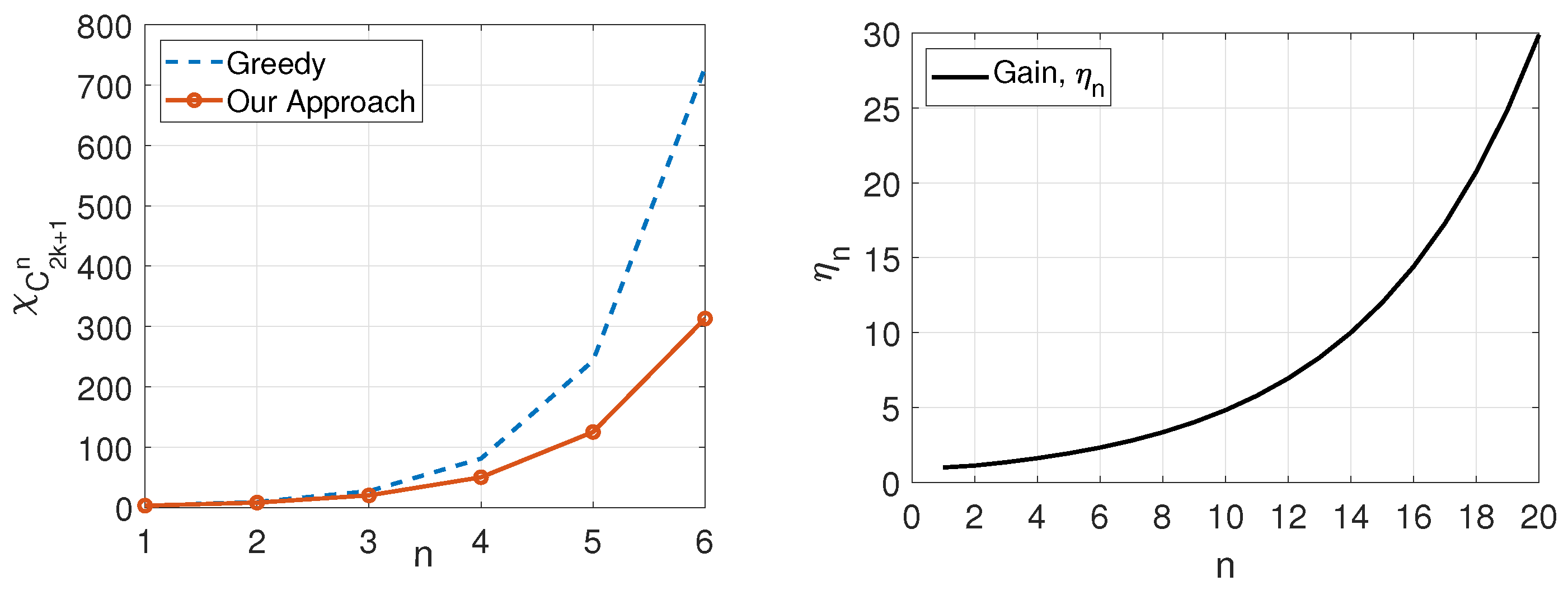
- Cyclic characteristic graphs: We derive exact expressions for the degree of a vertex in the n-fold OR product (as detailed by Alon and Orlitsky in [3]) of cycles (where , see Proposition 2), denoted by , and for the chromatic number of even cycles , denoted by where . Then, we devise a polynomial-time (finding a minimum entropy coloring in general graphs is an NP-hard problem [50]) achievable coloring scheme for odd cycles , leveraging the structure of and its OR products (see Proposition 3). Given , we investigate the largest eigenvalue of its adjacency matrix, and using that, we present bounds on the chromatic number (see Proposition 7). We also provide bounds on Körner’s graph entropy of (see Proposition 5).
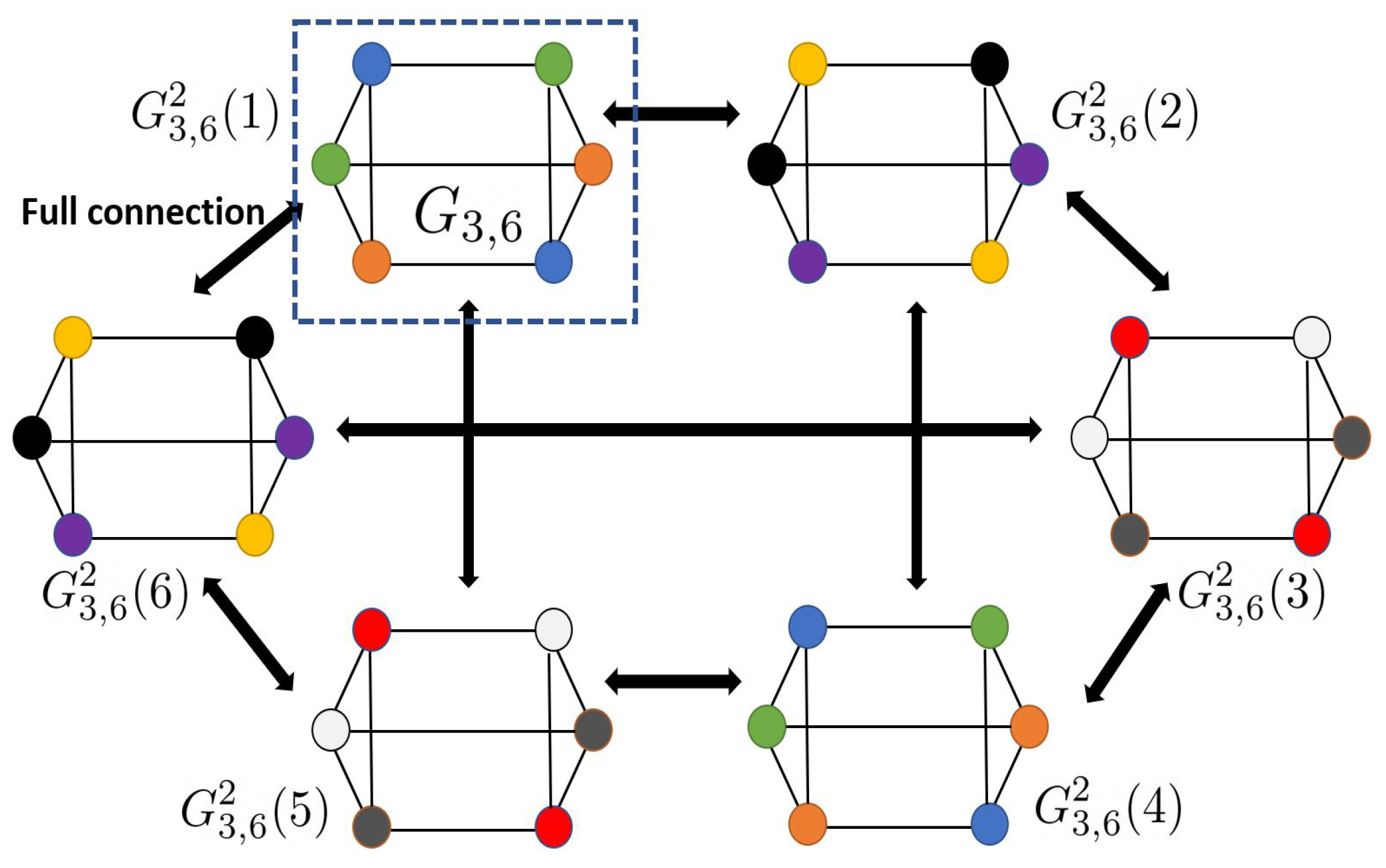
- d-regular characteristic graphs: We characterize the exact degree of a vertex and the chromatic number of d-regular graphs, denoted by and their n-fold OR products (see Propositions 8 and 9). Additionally, given a d-regular graph, the concept of graph expansion helps determine how the corresponding OR products are related. Capturing the structure of the OR products graphs, we then present a lower bound on the expansion rate of (see Proposition 10).
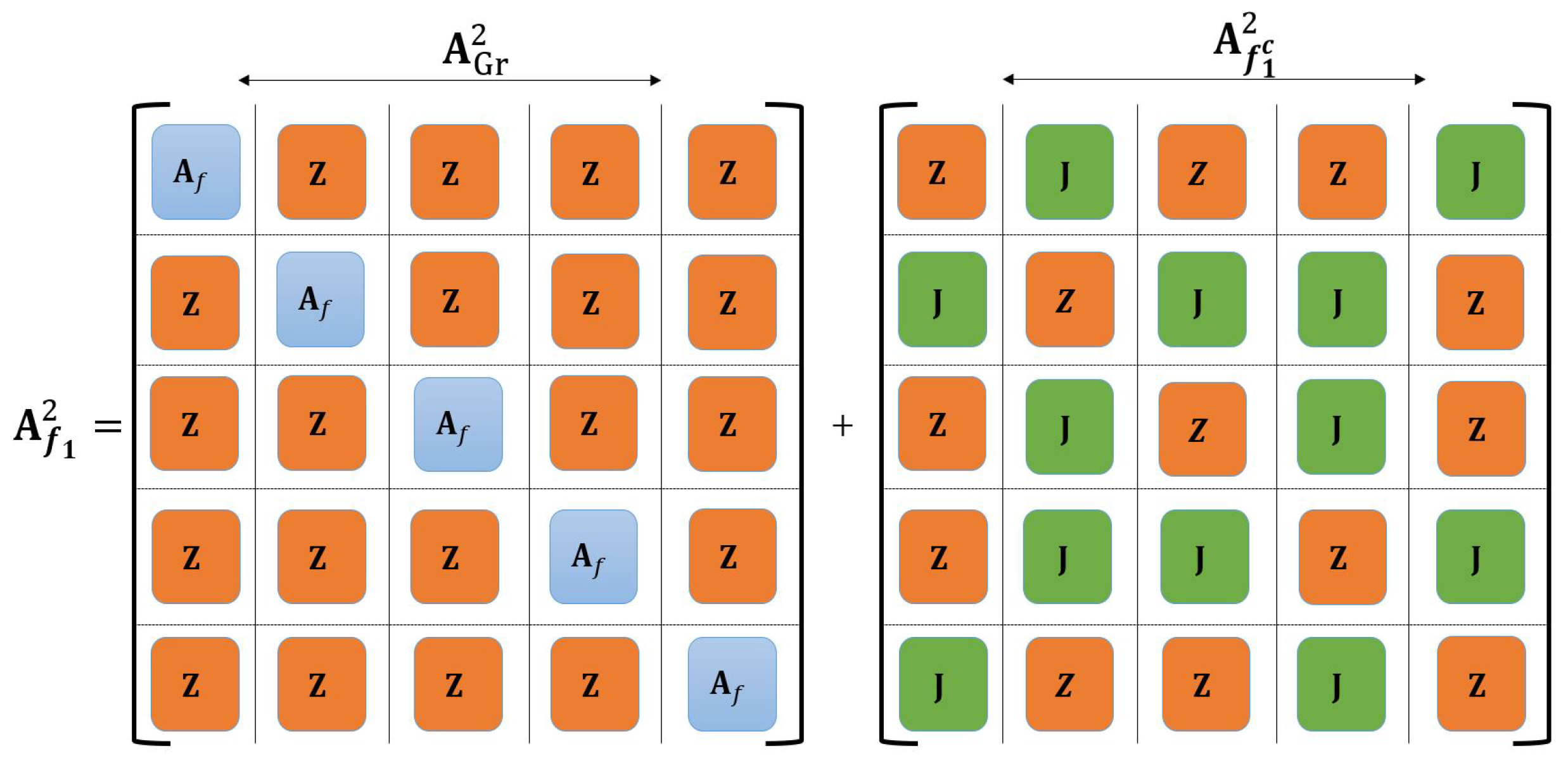
- General characteristic graphs: Given a general graph, , we calculate the degree of each vertex for its n-fold OR product (see Corollary 4). We present upper and lower bounds on the expansion rate (see Corollary 7). We then investigate the entropy of general characteristic graphs (see Proposition 11). We derive bounds on the largest eigenvalue (see Corollary 6) and the chromatic number (see Corollary 5) using the adjacency matrix of the n-fold OR product graph and the famous Gershgorin Circle Theorem (GCT), which is a theorem that identifies the range of the eigenvalues for a given square matrix [51]. We use GCT to bound eigenvalues of the adjacency matrix of a given graph n-fold OR product via exploiting the structure of OR products (see Theorem 2 and Corollary 9).
1.3. Organization
1.4. Notation
2. Technical Preliminary
2.1. Source Characteristic Graphs and Their OR Products
2.2. Coloring of Characteristic Graphs
2.3. Gershgorin Circle Theorem (GCT)
3. Bounds on Cyclic and Regular Graphs
3.1. Coloring Cyclic Graphs
3.1.1. Even Cycles
3.1.2. Odd Cycles
3.2. Bounding the Chromatic Entropy of Cycles
3.2.1. Entropy of an Even Cycle
3.2.2. Entropy of an Odd Cycle
3.3. Eigenvalues of the Adjacency Matrices of
3.4. Bounding the Chromatic Number of Using the Eigenvalues of
3.5. From Cycles to d-Regular Graphs
3.6. d-Regular Graphs and Graph Expansion
4. Bounds for General Characteristic Graphs
4.1. Degrees and Chromatic Numbers of General Graphs
4.2. Bounds on Expansion Rates of General Graphs
4.3. Bounds on Entropies of General Graphs
4.4. Spectra of General Graphs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Proposition 1
Appendix B. Proof of Proposition 3
Appendix C. Proof of Proposition 4
Appendix D. Proof of Proposition 5
Appendix E. Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix F. Proof of Proposition 8
Appendix G. Proof of Proposition 9
Appendix H. Proof of Corollary 7
Appendix I. Proof of Proposition 11
Appendix J. Proof of Corollary 8
Appendix K. Proof of Theorem 2
Appendix L. Proof of Corollary 9
References
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepian, D.; Wolf, J. Noiseless coding of correlated information sources. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1973, 19, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, N.; Orlitsky, A. Source coding and graph entropies. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1996, 42, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, M.; Rafajlowicz, E.; Krzyzak, A. Postfiltering versus prefiltering for signal recovery from noisy samples. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 3195–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.; Médard, M.; Koetter, R.; Karger, D.R.; Effros, M.; Shi, J.; Leong, B. A random linear network coding approach to multicast. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 4413–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlswede, R.; Cai, N.; Li, S.Y.; Yeung, R.W. Network information flow. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2000, 46, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C. The zero error capacity of a noisy channel. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 1956, 2, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, V.; Shah, D.; Medard, M.; Jaggi, S. Distributed functional compression through graph coloring. In Proceedings of the 2007 Data Compression Conference (DCC’07), Snowbird, UT, USA, 27–29 March 2007; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Doshi, V.; Shah, D.; Médard, M.; Effros, M. Functional compression through graph coloring. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 3901–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlitsky, A.; Roche, J.R. Coding for computing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2001, 47, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizi, S.; Médard, M. On network functional compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 5387–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, D. Fractional graph coloring for functional compression with side information. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Mumbai, India, 1–9 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Korner, J.; Marton, K. How to encode the modulo-two sum of binary sources (corresp.). IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1979, 25, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlswede, R.; Korner, J. Source coding with side information and a converse for degraded broadcast channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1975, 21, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, T.P.; Lee, A.H.; Médard, M.; Effros, M. Low-complexity approaches to slepian–wolf near-lossless distributed data compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 3546–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Kobayashi, K. A dichotomy of functions F(X, Y) of correlated sources (X, Y). IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1987, 33, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.S.; Ramchandran, K. Distributed source coding using syndromes (discus): Design and construction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, D.; Deylam Salehi, M.R.; Serbetci, B.; Elia, P. Multi-server multi-function distributed computation. Entropy 2024, 26, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malak, D.; Deylam Salehi, M.R.; Serbetci, B.; Elia, P. Multi-functional distributed computation. In Proceedings of the 2024 60th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Urbana, IL, USA, 24–27 September 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tanha, A.; Malak, D. The influence of placement on transmission in distributed computing of boolean functions. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Lucca, Italy, 10–13 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Khalesi, A.; Elia, P. Perfect multi-user distributed computing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 1349–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Witsenhausen, H. The zero-error side information problem and chromatic numbers (corresp.). IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deylam Salehi, M.R.; Purakkal, V.K.K.; Malak, D. Non-linear function computation broadcast. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 22–27 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wyner, A.; Ziv, J. The rate-distortion function for source coding with side information at the decoder. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Effros, M.; Savari, S. Functional source coding for networks with receiver side information. In Proceedings of the Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, IL, USA, 29 September–1 October 2004; pp. 1419–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, H. Wyner-Ziv theory for a general function of the correlated sources (corresp.). IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.; Yeung, R.W. Multiterminal source encoding with one distortion criterion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1989, 35, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Servetto, S.D. On the rate-distortion region for separate encoding of correlated sources. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Yokohama, Japan, 29 June–4 July 2003; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, A.B.; Tavildar, S.; Viswanath, P. Rate region of the quadratic gaussian two-encoder source-coding problem. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 1938–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Monedero, D.; Forne, J.; Domingo-Ferrer, J. From t-closeness-like privacy to postrandomization via information theory. IEEE Trans. Know. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, F.; Pradhan, S.S. A new achievable rate-distortion region for distributed source coding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2021, 67, 4485–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Guo, T.; Bai, B.; Han, W. Lossy computing with side information via multi-hypergraphs. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Mumbai, India, 1–9 November 2022; pp. 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Sefidgaran, M.; Tchamkerten, A. Computing a function of correlated sources: A rate region. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings, St. Petersburg, Russia, 31 July 2011–5 August 2011; pp. 1856–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Körner, J. Coding of an information source having ambiguous alphabet and the entropy of graphs. In Proceedings of the 6th Prague Conference on Information Theory, Prague, Hungary, 17–22 September 1973; pp. 411–425. [Google Scholar]
- Pettofrezzo, A.J.; Byrkit, D.R. Elements of Number Theory; Prentice-Hall: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Paar, C.; Pelzl, J. Understanding Cryptography: Textbook for Students; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Diffie, W.; Hellman, M.E. Multiuser cryptographic techniques. In Proceedings of the National Computer Conference and Exposition, New York, NY, USA, 7–10 June 1976; pp. 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Selent, D. Advanced encryption standard. Rivier Acad. J. 2010, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S. International data encryption algorithm (idea)—A typical illustration. J. Glob. Res. Comput. Sci. 2011, 2, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Knill, G. Applications: International standard book numbers. Math. Teach. 1981, 74, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Tillich, J.-P. Generalized alon—Boppana theorems and error-correcting codes. SIAM J. Discret. Math. 2005, 19, 700–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berestycki, N.; Lubetzky, E.; Peres, Y.; Sly, A. Random walks on the random graph. Ann. Probab. 2018, 46, 456–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahale, N. Better expansion for ramanujan graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium of Foundations of Computer Science, San Juan, PR, USA, 1–4 October 1991; pp. 398–404. [Google Scholar]
- Kahale, N. On the second eigenvalue and linear expansion of regular graphs. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 24–27 October 1992; pp. 296–303. [Google Scholar]
- Felber, P.; Kropf, P.; Schiller, E.; Serbu, S. Survey on load balancing in peer-to-peer distributed hash tables. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 16, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, A.; Massoulié, L.; Towsley, D. The effect of network topology on the spread of epidemics. In Proceedings of the IEEE 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, Miami, FL, USA, 13–17 March 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1455–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Tentes, A. Expander Graphs, Randomness Extractors and Error Correcting Codes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, G.; Fath, G. Evolutionary games on graphs. Phys. Rep. 2007, 446, 97–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Gomes-Selman, J.M.; Ying, R.; Leskovec, J. Identity-aware graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2–9 February; Volume 35, pp. 737–745.
- Cardinal, J.; Fiorini, S.; Joret, G. Tight results on minimum entropy set cover. Algorithmica 2008, 51, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretter, C. Spectral Theory of Block Operator Matrices and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Havel, V. A remark on the existence of finite graphs. Casopis Pest. Mat. 1955, 80, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, R. Finding maximum independent sets in sparse and general graphs. In SODA; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM): Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999; Volume 99, pp. 856–857. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-K. Graph Theory and Its Engineering Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 1997; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, J.F. On ordering and identifying undirected linear graphs. J. Math. Phys. 1966, 7, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilli, A. On the second eigenvalue of a graph. Discret. Math. 1991, 91, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, N. Graph powers. Contemp. Comb. 2002, 10, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bermond, J.-C. Hamiltonian graphs. In Selected Topics in Graph Theory; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979; pp. 127–167. [Google Scholar]
- Axenovich, M. Lecture Notes Graph Theory; Karlsruher Institut für Technologie: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bang-Jensen, J.; Gutin, G.Z. Digraphs: Theory, Algorithms and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Körner, J.; Orlitsky, A. Zero-error information theory. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1998, 44, 2207–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulgi, P.; Tuncel, E.; Regunathan, S.L.; Rose, K. On zero-error source coding with decoder side information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, E. Kraft inequality and zero-error source coding with decoder side information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4810–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinerman, E.R.; Ullman, D.H. Fractional Graph Theory: A Rational Approach to the Theory of Graphs; Courier Corporation: Mumbai, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, H.N. Gershgorin’s theorem for matrices of operators. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 1999, 291, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, D.A. A method for the construction of minimum-redundancy codes. Proc. IRE 1952, 40, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deylam Salehi, M.R.; Malak, D. An achievable low complexity encoding scheme for coloring cyclic graphs. In Proceedings of the 2023 59th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, IL, USA, 26–29 September 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Aspvall, B.; Gilbert, J.R. Graph coloring using eigenvalue decomposition. Siam J. Algebr. Discret. Methods 1984, 5, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoffman, A.J.; Howes, L. On eigenvalues and colorings of graphs, ii. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1970, 175, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilf, H.S. The eigenvalues of a graph and its chromatic number. J. Lond. Math. Soc. 1967, 1, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, R.C.; Dutton, R.D. Bounds on graph spectra. J. Comb. Theory Ser. 1984, 37, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y. Bounds of eigenvalues of a graph. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. 1988, 4, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.C.; Kumar, P. Some new bounds on the spectral radius of graphs. Disc. Math. 2004, 281, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajtai, M.; Komlós, J.; Szemerédi, E. Sorting in c log n parallel steps. Combinatorica 1983, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Leighton, T.; Maggs, B. On-line algorithms for path selection in a nonblocking network. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 13–17 May 1990; pp. 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bellare, M.; Goldreich, O.; Goldwasser, S. Randomness in interactive proofs. Comput. Comp. 1993, 3, 319–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajtai, M.; Komlós, J.; Szemerédi, E. Deterministic simulation in logspace. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, New York, NY, USA, 25–27 May 1987; pp. 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, R.M. Explicit concentrators from generalized N-gons. SIAM J. Algebr. Discret. Methods 1984, 5, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, D.S. Understanding the QR algorithm. SIAM Rev. 1982, 24, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverría, C.; Liesen, J.; Nabben, R. Block diagonal dominance of matrices revisited: Bounds for the norms of inverses and eigenvalue inclusion sets. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2018, 553, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn, K.; Sun, H. Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science; Max Planck Inst.: Munich, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, J.G. The QR transformation a unitary analogue to the LR transformation—Part 1. Comput. J. 1961, 4, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavžar, S.; Imrich, W. Product Graphs: Structure and Recognition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lovász, L. Three short proofs in graph theory. J. Comb. Theory Ser. B 1975, 19, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovász, L. On the ratio of optimal integral and fractional covers. Discret. Math. 1975, 13, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Miao, L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, L. Characterization of graphs with an eigenvalue of large multiplicity. Adv. Math. Phys. 2020, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deylam Salehi, M.R.; Malak, D. Graph-Theoretic Limits of Distributed Computation: Entropy, Eigenvalues, and Chromatic Numbers. Entropy 2025, 27, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070757
Deylam Salehi MR, Malak D. Graph-Theoretic Limits of Distributed Computation: Entropy, Eigenvalues, and Chromatic Numbers. Entropy. 2025; 27(7):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070757
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeylam Salehi, Mohammad Reza, and Derya Malak. 2025. "Graph-Theoretic Limits of Distributed Computation: Entropy, Eigenvalues, and Chromatic Numbers" Entropy 27, no. 7: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070757
APA StyleDeylam Salehi, M. R., & Malak, D. (2025). Graph-Theoretic Limits of Distributed Computation: Entropy, Eigenvalues, and Chromatic Numbers. Entropy, 27(7), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070757





