On the Change of Measure for Brownian Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Preliminaries
2.2. The Physical Model
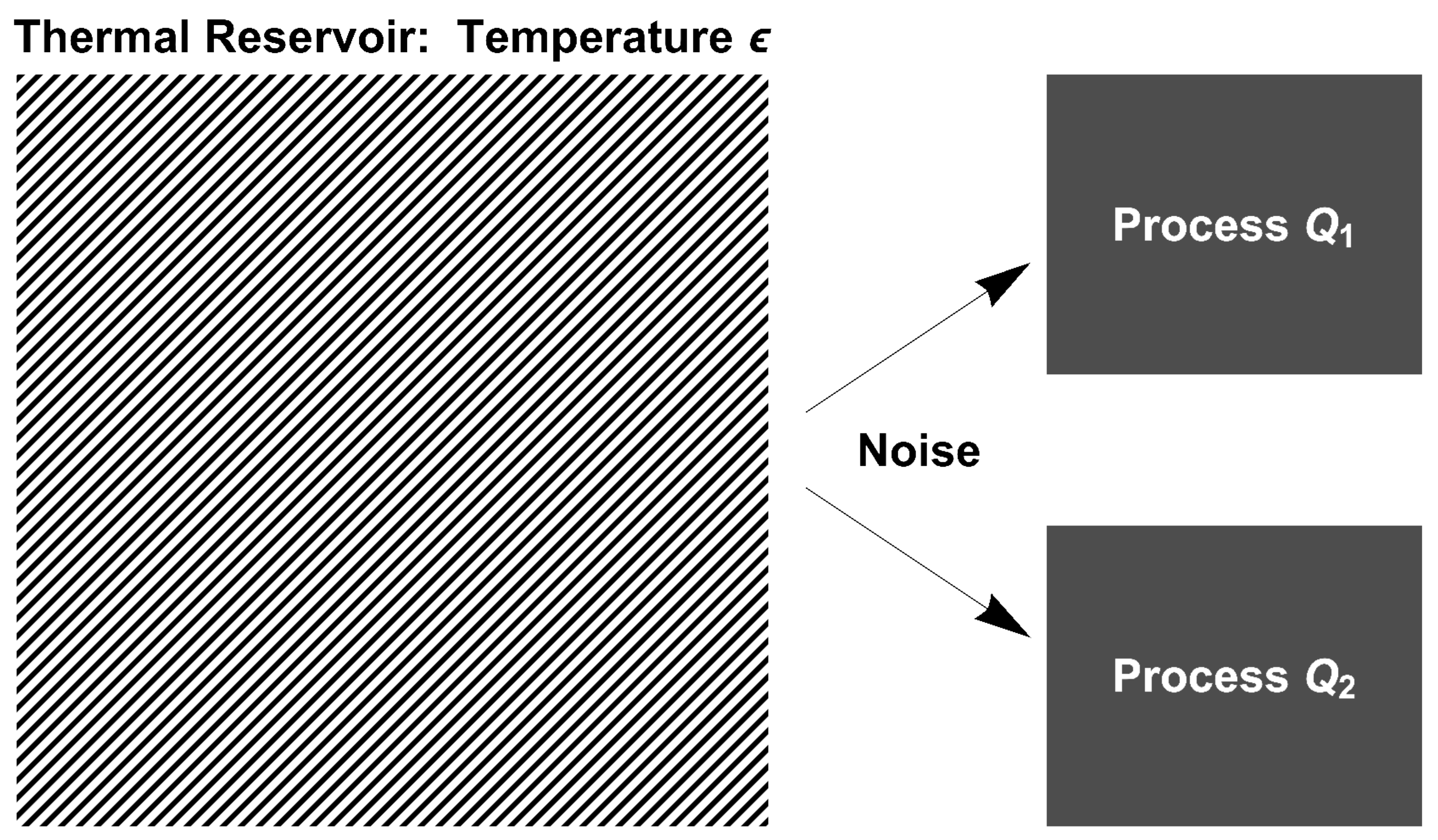
2.3. Common-Noise History
2.4. Common-Noise Construction Revisited
2.5. Common-Path Construction
3. Results
3.1. The Physical Limit
3.2. Bridge Paths
4. Discussion
4.1. Numerical Details
4.2. Thermodynamic Action
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Radon–Nikodym Derivative and the KL Divergence: A Scalar Example
Appendix B. Use of Itô Calculus
References
- Mazo, R.M. Historical Background. In Brownian Motion: Fluctuations, Dynamics, and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, N. The average of an analytic functional and the Brownian movement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1921, 7, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, N. Norbert Wiener: Collected Works; Masani, P., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- ksendal, B. Stochastic Differential Equations; Universitext; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Malsom, P. Rare Events and the Thermodynamic Action. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Malsom, P.J.; Pinski, F.J. Role of Ito’s lemma in sampling pinned diffusion paths in the continuous-time limit. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 042131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinski, F.J. A novel hybrid Monte Carlo algorithm for sampling path space. Entropy 2021, 23, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, D.; Bach, A. The Onsager-Machlup function as Lagrangian for the most probable path of a diffusion process. Commun. Math. Phys. 1978, 60, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, G. Continuous Markov processes and stochastic equations. Rend. Del Circ. Mat. Di Palermo 1955, 4, 48–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, V.; Lőrinczi, J.; Spohn, H. Gibbs measures on Brownian paths: Theory and applications. In Interacting Stochastic Systems; Deuschel, J.-D., Greven, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 75–102. [Google Scholar]
- Onsager, L.; Machlup, S. Fluctuations and irreversible processes. Phys. Rev. 1953, 91, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adib, A.B. Stochastic actions for diffusive dynamics: Reweighting, sampling, and minimization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 5910–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, L.; Weber, M.; Keller, B.G. A review of Girsanov reweighting and of square root approximation for building molecular markov state models. J. Math. Phys. 2022, 63, 123306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.; Hibbs, A. Quantum Mechanics and Path Integrals; International Series in Pure and Applied Physics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, A.; Dürr, D.; Stawicki, B. Functionals of paths of a diffusion process and the Onsager-Machlup function. Z. Für Phys. B Condens. Matter 1977, 26, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R. Path integral formulation of general diffusion processes. Z. Fur Phys. B Condens. Matter 1977, 26, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.; Riste, T. Fluctuations, Instabilities and Phase Transitions; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 215. [Google Scholar]
- Stratonovich, R. On the probability functional of diffusion processes. Sel. Trans. Math. Stat. Prob 1971, 10, 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke, W.; Bach, A. Onsager-Machlup function for one dimensional nonlinear diffusion processes. Z. Für Phys. B Condens. Matter 1975, 22, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.L.C.; Ross, J. Path integral solutions of stochastic equations for nonlinear irreversible processes: The uniqueness of the thermodynamic Lagrangian. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 75, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itô, H. Probabilistic construction of Lagrangian of diffusion process and its application. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1978, 59, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langouche, F.; Roekaerts, D.; Tirapegui, E. Short derivation of Feynman Lagrangian for general diffusion processes. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1980, 13, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavenda, B. Thermodynamic criteria governing the stability of fluctuating paths in the limit of small thermal fluctuations: Critical paths in the limit of small thermal fluctuations: Critical paths and temporal bifurcations. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1984, 17, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisza, L.; Manning, I. Fluctuations and irreversible thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 105, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, N.; Watanabe, S. The Onsager-Machlup functions for diffusion processes. In Stochastic Differential Equations and Diffusion Processes; Matthes, K., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1986; p. 510. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, U.; Häffner, W. The Uses of Instantons for Diffusion in Bistable Potentials; Plenum Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yasue, K. The role of the Onsager–Machlup Lagrangian in the theory of stationary diffusion process. J. Math. Phys. 1979, 20, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai Pra, P.; Pavon, M. Variational path-integral representations for the density of a diffusion process. Stoch. Int. J. Probab. Stoch. Process 1989, 26, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, M.; De Schepper, A.; Decamps, M. Closed-form approximations for diffusion densities: A path integral approach. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2004, 164, 337–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itô, H. Optimal Gaussian solutions of nonlinear stochastic partial differential equations. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 37, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yor, M. Exponential functionals of Brownian motion, ii: Some related diffusion processes. Probab. Surv. 2005, 2, 348–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, W.; Ren, W.; Vanden-Eijnden, E. Minimum action method for the study of rare events. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2004, 57, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, M.; Shibata, F. Path integral and Brownian motion. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 59, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyink, G.L. Action principle in statistical dynamics. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 1998, 130, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinski, F.J.; Stuart, A.M. Transition paths in molecules at finite temperature. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 184104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.; Koehl, P.; Doniach, S.; Delarue, M. Minactionpath: Maximum likelihood trajectory for large-scale structural transitions in a coarse-grained locally harmonic energy landscape. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35 (Suppl. S2), W477–W482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.W.; Chandrasekaran, S.N.; Weinreb, V.; Li, L.; Williams, T. Combining multi-mutant and modular thermodynamic cycles to measure energetic coupling networks in enzyme catalysis. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 4, 032101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Duan, J. The most probable transition paths of stochastic dynamical systems: A sufficient and necessary characterisation. Nonlinearity 2023, 37, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M. Singular Limits. Phys. Today 2002, 2002, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Ishimoto, K. Most probable path of an active brownian particle. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 106, 064120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beskos, A.; Pinski, F.; Sanz-Serna, J.; Stuart, A. Hybrid Monte Carlo on Hilbert spaces. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 2011, 121, 2201–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.W. More is different: Broken symmetry and the nature of the hierarchical structure of science. Science 1972, 177, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.L.W.V. Sur les fonctions convexes et les inégalitégs entre les valeurs Moyennes. Acta Math. 1906, 30, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decoster, A. Variational principles and thermodynamical perturbations. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2004, 37, 9051–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinski, F.J. On the Change of Measure for Brownian Processes. Entropy 2025, 27, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060594
Pinski FJ. On the Change of Measure for Brownian Processes. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060594
Chicago/Turabian StylePinski, Francis J. 2025. "On the Change of Measure for Brownian Processes" Entropy 27, no. 6: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060594
APA StylePinski, F. J. (2025). On the Change of Measure for Brownian Processes. Entropy, 27(6), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060594





