Transmitting Status Updates on Infinite Capacity Systems with Eavesdropper: Freshness Advantage of Legitimate Receiver
Abstract
1. Introduction
- For arbitrary packet arrival processes, we derive the explicit expression of freshness advantage F and prove that F is completely determined by average packet interarrival time and the ratio of and ;
- Assuming that packet arrivals form the Bernoulli process, we determine the specific distribution of instantaneous gap between two AoIs;
- By constructing the combined performance Q to be average AoI minus F, we derive the optimal packet generation rate such that Q is minimized, such that investigating the tradeoffs between the timeliness and security;
- In case of Bernoulli packet arrivals, and assuming that timeliness and security are both limited, we depict and analyze the feasible region composed of p and .
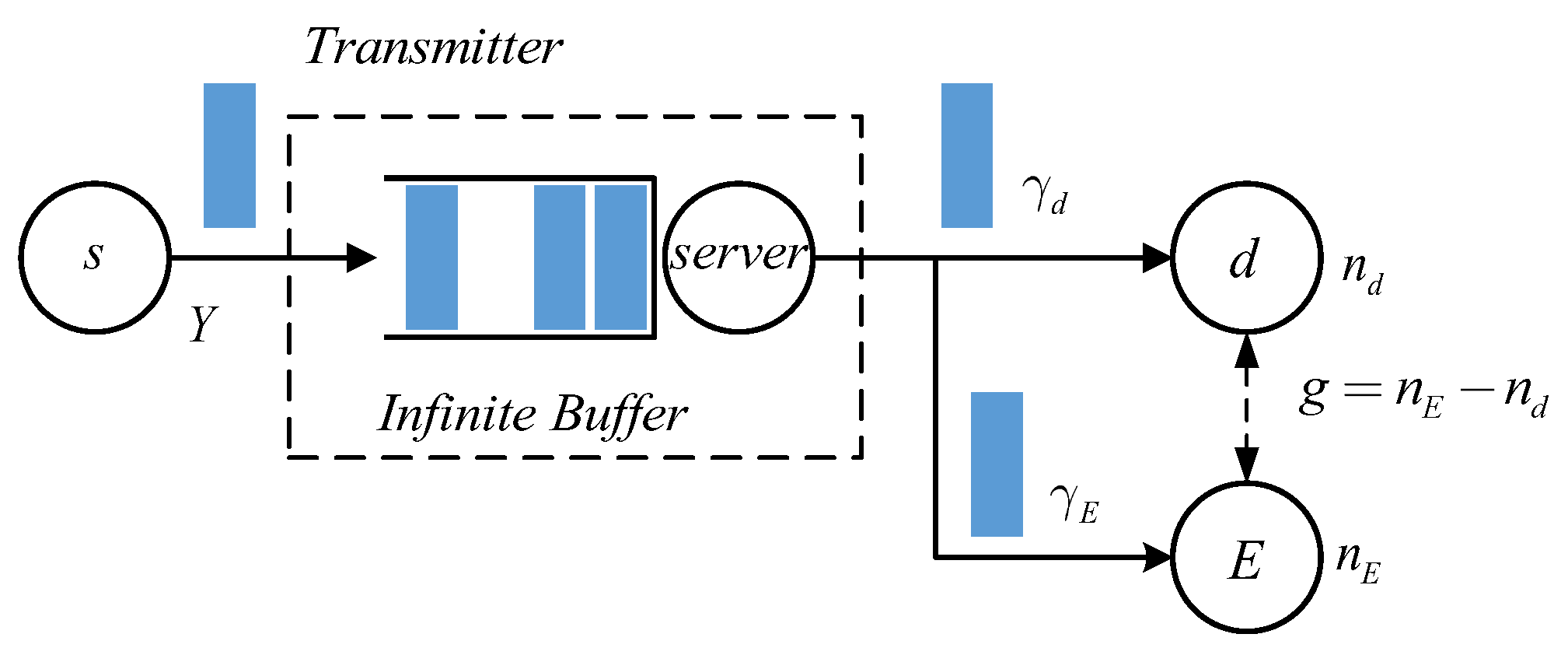
2. System Model and Problem Formulation
3. Freshness Advantage of Legitimate Receiver of Infinite Capacity Status Updating Systems
3.1. Freshness Advantage in General Packet Arrival Process
3.2. Age Gap g in Bernoulli Arrival Process Case
4. Joint Optimization of Transmission Timeliness and Security for Infinite Capacity Systems
4.1. Minimizing Combined Performance Metric Q
4.2. Feasible p and When Timeliness and Security Are Limited
5. Numerical Simulations
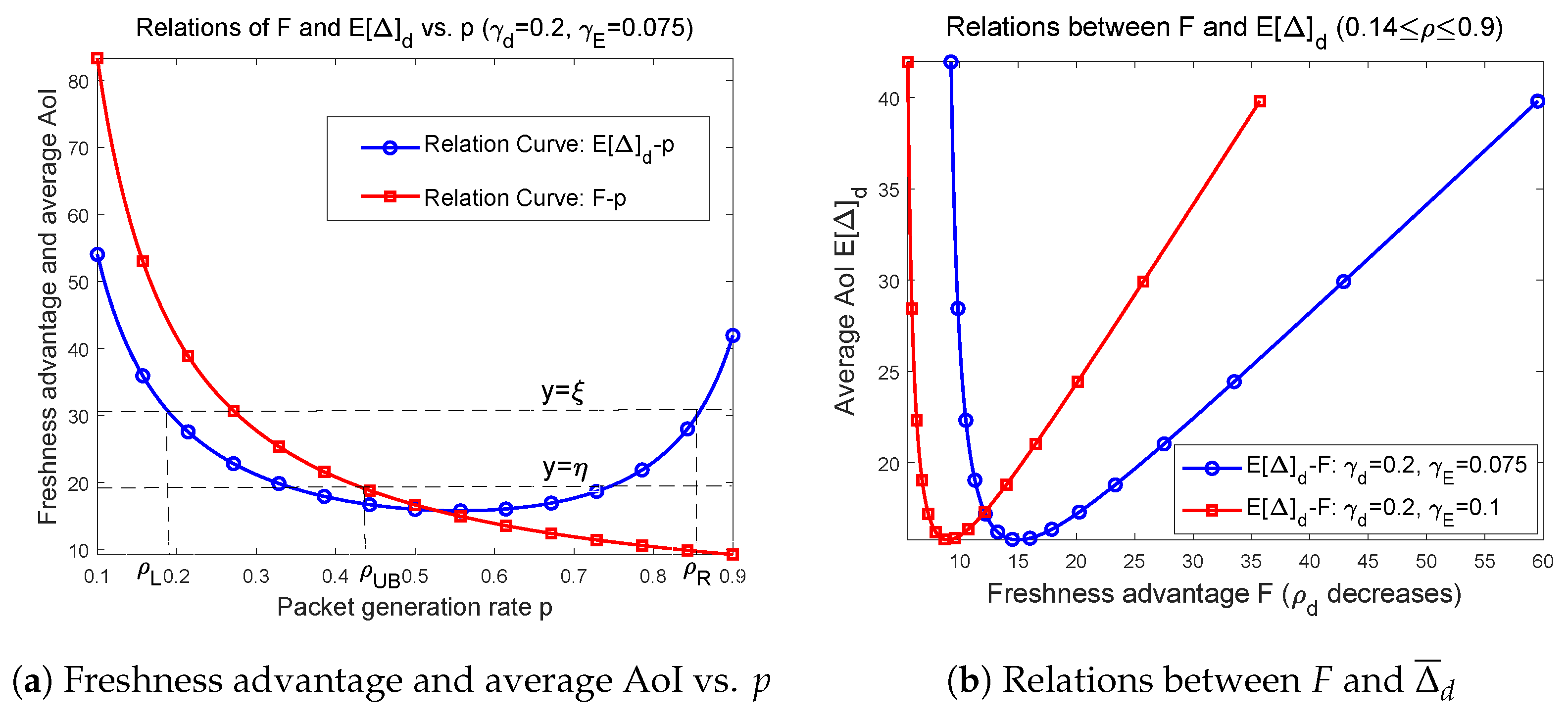
5.1. Relationship Between F, and as Well as Their Interrelations
5.2. Distribution of Instantaneous Gap g and the Correspondence Between and
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Lemma 1
References
- Kaul, S.; Gruteser, M.; Rai, V.; Kenney, J. Minimizing age of information in vehicular networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks (SECOM), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.; Yates, R.; Gruteser, M. Real-time status: How often should one update? In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (INFOCOM), Orlando, FL, USA, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 2731–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.K.; Yates, R.D.; Gruteser, M. Status updates through queues. In Proceedings of the 2012 46th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 21–23 March 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E.; Yates, R.; Koksal, C.E.; Shroff, N.B. Update or wait: How to keep your data fresh. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 April 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Masuyama, H.; Takine, T.; Tanaka, T. A General Formula for the Stationary Distribution of the Age of Information and Its Application to Single-Server Queues. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2019, 65, 8305–8324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, R.D.; Kaul, S.K. The Age of Information: Real-Time Status Updating by Multiple Sources. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2019, 65, 1807–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, N.; Gunnarsson, J.; Kratz, L.; Kountouris, M.; Angelakis, V. Age of information of multiple sources with queue management. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 5935–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosta, A.; Pappas, N.; Ephremides, A.; Angelakis, V. Age of information performance of multiaccess strategies with packet management. J. Commun. Netw. 2019, 21, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.K.; Yates, R.D. Age of Information: Updates with Priority. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Vail, CO, USA, 17–22 June 2018; pp. 2644–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gautam, N. Peak Age of Information in Priority Queuing Systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2021, 67, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.; Akar, N. The Multi-Source Probabilistically Preemptive M/PH/1/1 Queue with Packet Errors. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 7297–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, C.; Kompella, S.; Nguyen, G.D.; Wieselthier, J.E.; Ephremides, A. Age of information with a packet deadline. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Barcelona, Spain, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 2564–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, C.; Kompella, S.; Nguyen, G.D.; Wieselthier, J.E.; Ephremides, A. On the Age of Information with Packet Deadlines. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2018, 64, 6419–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. Analysis of the Age of Information with Packet Deadline and Infinite Buffer Capacity. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Vail, CO, USA, 17–22 June 2018; pp. 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, C.; Kompella, S.; Nguyen, G.D.; Ephremides, A. Effect of Message Transmission Path Diversity on Status Age. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2016, 62, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javani, A.; Zorgui, M.; Wang, Z. Age of Information for Multiple-Source Multiple-Server Networks. IEEE-ACM Trans. Netw. 2024, 33, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Pappas, N.; Yang, H.H.; Tian, Z.; Wang, M. Improving Information Freshness via Multi-Sensor Parallel Status Updating. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 73, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, R.D. The Age of Gossip in Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Melbourne, Australia, 12–20 July 2021; pp. 2984–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, R.D. Timely Gossip. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Lucca, Italy, 27–30 September 2021; pp. 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaswan, P.; Bastopcu, M.; Ulukus, S.; Etesami, S.R.; Basar, T. Optimizing Profitability in Timely Gossip Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Lucca, Italy, 10–13 September 2024; pp. 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukates, B.; Bastopcu, M.; Ulukus, S. Age of Gossip in Networks with Community Structure. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Lucca, Italy, 27–30 September 2021; pp. 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastopcu, M.; Buyukates, B.; Ulukus, S. Gossiping with Binary Freshness Metric. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Madrid, Spain, 7–11 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukates, B.; Bastopcu, M.; Ulukus, S. Version Age of Information in Clustered Gossip Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Inf. Theory 2022, 3, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakanth, R.V.; Tripathi, V.; Modiano, E. Monitoring Correlated Sources: AoI-Based Scheduling is Nearly Optimal. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradian, M.; Dadlani, A.; Khonsari, A.; Tabassum, H. Age-Aware Dynamic Frame Slotted ALOHA for Machine-Type Communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 72, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, N.; Sadeghi, P.; Zhou, X. Age of Information in Downlink Systems: Broadcast or Unicast Transmission? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, H. Age of Information in Reservation Multi-Access Networks With Stochastic Arrivals: Analysis and Optimization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 4707–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, E.; Charalambous, T.; Ephremides, A.; Pappas, N. Scheduling Policies for AoI Minimization with Timely Throughput Constraints. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 3905–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xiong, K.; Fan, P.; Zhong, Z.; Letaief, K.B. Age of Information-Based Wireless Powered Communication Networks with Selfish Charging Nodes. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 1393–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Yang, J. Precoding and Scheduling for AoI Minimization in MIMO Broadcast Channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2022, 68, 5185–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.; Talak, R.; Modiano, E. Age of Information for Discrete Time Queues. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.10463v1. [Google Scholar]
- Kosta, A.; Pappas, N.; Ephremides, A.; Angelakis, V. Non-linear Age of Information in a Discrete Time Queue: Stationary Distribution and Average Performance Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosta, A.; Pappas, N.; Ephremides, A.; Angelakis, V. The Age of Information in a Discrete Time Queue: Stationary Distribution and Non-Linear Age Mean Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, N.; Dogan, O. Discrete-Time Queueing Model of Age of Information with Multiple Information Sources. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 14531–14542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. On Age of Information for Discrete Time Status Updating System with Ber/G/1/1 Queues. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Kanazawa, Japan, 17–21 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. On Age of Information for Discrete Time Status Updating System with Infinite Size. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Mumbai, India, 1–9 November 2022; pp. 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Age Analysis of Status Updating System with Probabilistic Packet Preemption. Entropy 2022, 24, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Cao, D.; Xu, Y. Discrete Age of Information for Bufferless System with Multiple Prioritized Sources. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 20099–20119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hanzo, L. Permutation-Based Short-Packet Transmissions Improve Secure URLLCs in the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 11024–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Secure and Timely Status Updates in the IoT using Short-Packet Permutation-Based Transmissions. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 98th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2023-Fall), Hong Kong, China, 10–13 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Mohapatra, P.; Pappas, N. Secure Status Updates under Eavesdropping: Age of Information-based Secrecy Metrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Schmeink, A. Achieving Secure and Fresh Information Updates via Short-Packet Communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 3232–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Tang, S.; Liu, D. AoI-Based Transmission Scheduling for Cyber Physical Systems Over Fading Channel Against Eavesdropping. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 5455–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyner, A.D. The wiretap channel. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1975, 54, 1355–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L. Timeliness and Secrecy-Aware Uplink Data Aggregation for Large-Scale UAV-IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 17341–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Sagduyu, Y.E. Timely NextG Communications with Decoy Assistance against Deep Learning-based Jamming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Denver, CO, USA, 9–13 June 2024; pp. 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yun, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Quek, T.Q.S. Reinforcement Learning-Based Sensing Decision for Data Freshness in Blockchain-Empowered Wireless Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 3276–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Guo, D.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D.; Han, Z. Can We Realize Data Freshness Optimization for Privacy Preserving-Mobile Crowdsensing with Artificial Noise? IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 11357–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Pei, Q.; Dong, M.; Mumtaz, S.; Leung, V.C.M. Energy-Efficient Cooperative Secure Communications in mmWave Vehicular Networks Using Deep Recurrent Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 14460–14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Pei, Q.; Mumtaz, S.; Dong, M.; Guizani, M. NOMA-Assisted Secure Offloading for Vehicular Edge Computing Networks with Asynchronous Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 2627–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosara, L.; Laurenti, N.; Badia, L. Age of information is not just a number: Status updates against an eavesdropping node. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 155, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yates, R.D. Timeliness in Lossless Block Coding. In Proceedings of the Data Compression Conference (DCC), Snowbird, UT, USA, 30 March–1 April 2016; pp. 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yates, R.D.; Soljanin, E. Timely Lossless Source Coding for Randomly Arriving Symbols. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Guangzhou, China, 25–29 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Initial State | R.V.s | Next State and Transtion Probability |
|---|---|---|
| , | : g with | |
| : with | ||
| : with | ||
| : 0 with | ||
| , | : 0 with | |
| : with | ||
| : y with | ||
| : 0 with | ||
| , | : g with | |
| : 0 with |
| Mathematic Relation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 0.606 | 4.0 | 0.679 | 6.0 | 0.719 | 8.0 | 0.745 |
| 0.2 | 0.366 | 2.2 | 0.616 | 4.2 | 0.684 | 6.2 | 0.722 | 8.2 | 0.747 | |
| 0.4 | 0.434 | 2.4 | 0.626 | 4.4 | 0.688 | 6.4 | 0.725 | 8.4 | 0.750 | |
| 0.6 | 0.476 | 2.6 | 0.634 | 4.6 | 0.693 | 6.6 | 0.728 | 8.6 | 0.752 | |
| 0.8 | 0.507 | 2.8 | 0.642 | 4.8 | 0.697 | 6.8 | 0.730 | 8.8 | 0.754 | |
| 1.0 | 0.531 | 3.0 | 0.649 | 5.0 | 0.701 | 7.0 | 0.733 | 9.0 | 0.756 | |
| 1.2 | 0.551 | 3.2 | 0.656 | 5.2 | 0.705 | 7.2 | 0.736 | 9.2 | 0.758 | |
| 1.4 | 0.568 | 3.4 | 0.662 | 5.4 | 0.708 | 7.4 | 0.738 | 9.4 | 0.760 | |
| 1.6 | 0.582 | 3.6 | 0.668 | 5.6 | 0.712 | 7.6 | 0.741 | 9.6 | 0.761 | |
| 1.8 | 0.595 | 3.8 | 0.673 | 5.8 | 0.715 | 7.8 | 0.743 | 9.8 | 0.762 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, A.; Cao, D.; Xu, Y.; Lin, C. Transmitting Status Updates on Infinite Capacity Systems with Eavesdropper: Freshness Advantage of Legitimate Receiver. Entropy 2025, 27, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060571
Zhang J, Xu H, Zheng A, Cao D, Xu Y, Lin C. Transmitting Status Updates on Infinite Capacity Systems with Eavesdropper: Freshness Advantage of Legitimate Receiver. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060571
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jixiang, Han Xu, Anqi Zheng, Daming Cao, Yinfei Xu, and Chengyu Lin. 2025. "Transmitting Status Updates on Infinite Capacity Systems with Eavesdropper: Freshness Advantage of Legitimate Receiver" Entropy 27, no. 6: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060571
APA StyleZhang, J., Xu, H., Zheng, A., Cao, D., Xu, Y., & Lin, C. (2025). Transmitting Status Updates on Infinite Capacity Systems with Eavesdropper: Freshness Advantage of Legitimate Receiver. Entropy, 27(6), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060571






