Deep Hybrid Models: Infer and Plan in a Dynamic World
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present an active inference agent affording robust planning in dynamic environments. The basic unit of this agent maintains potential trajectories, enabling a high-level discrete model to infer the state of the world and plan composite movements. The units are hierarchically combined to represent potential body configurations, incorporating object affordances (e.g., grasping a cup by the handle or with the whole hand) and their hierarchical relationships (e.g., how a tool can extend the agent’s kinematic chain).
- We introduce a modular architecture designed for tasks that involve deep hierarchical modeling, such as tool use. Its multi-input and multi-output connectivity resembles traditional neural networks and represents an initial step toward designing deep structures in active inference capable of generalizing across and learning novel tasks.
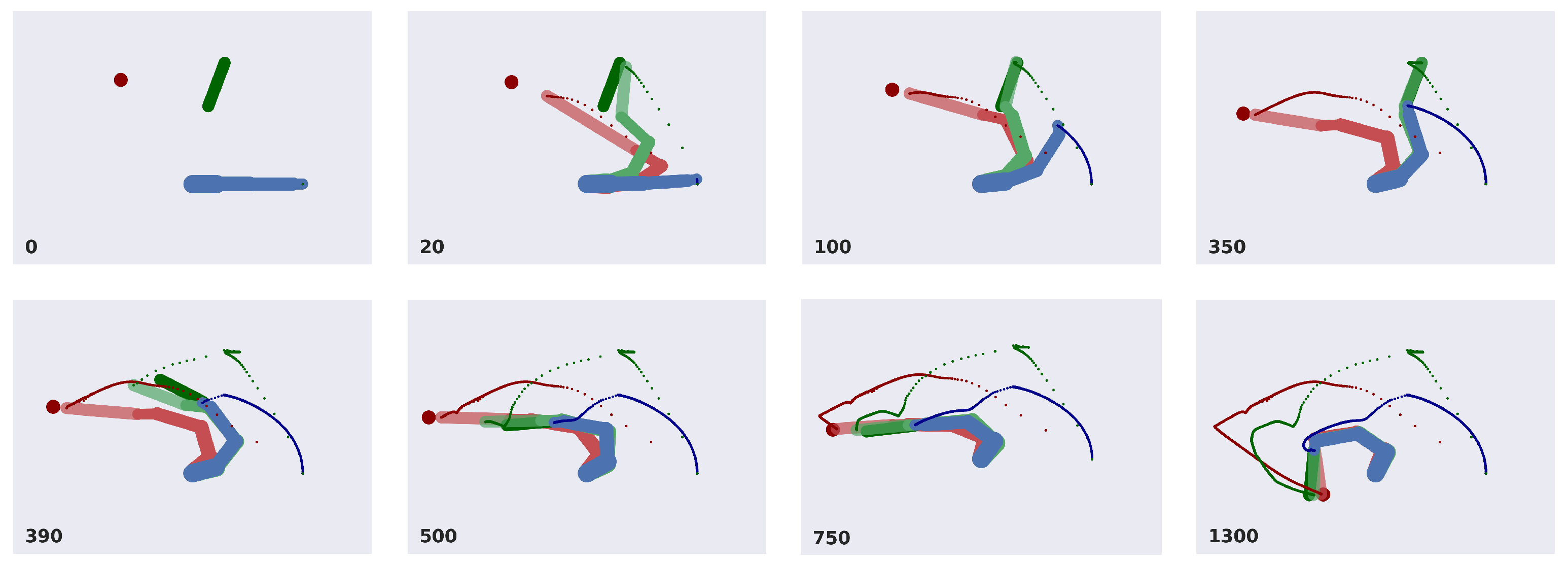
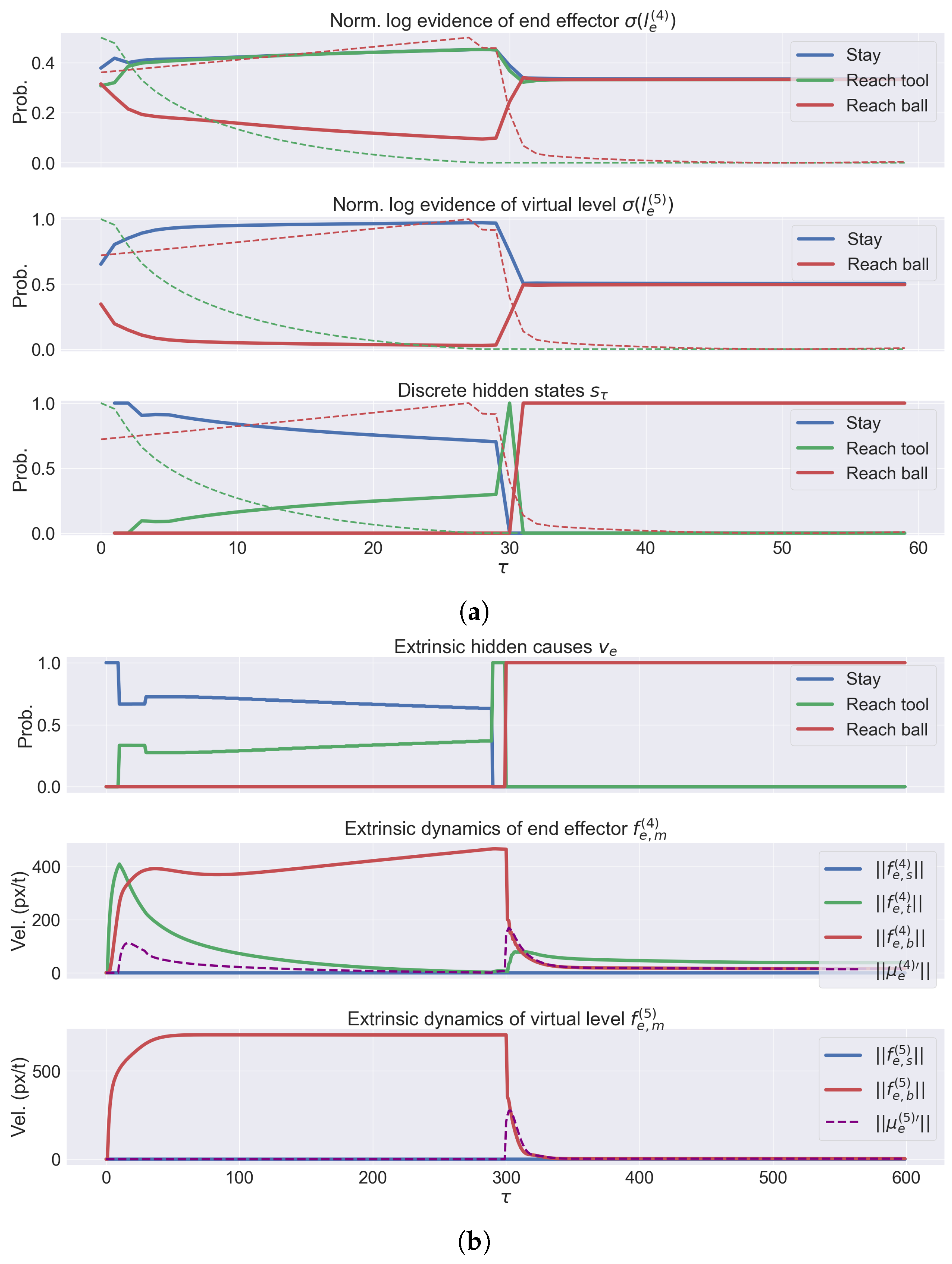
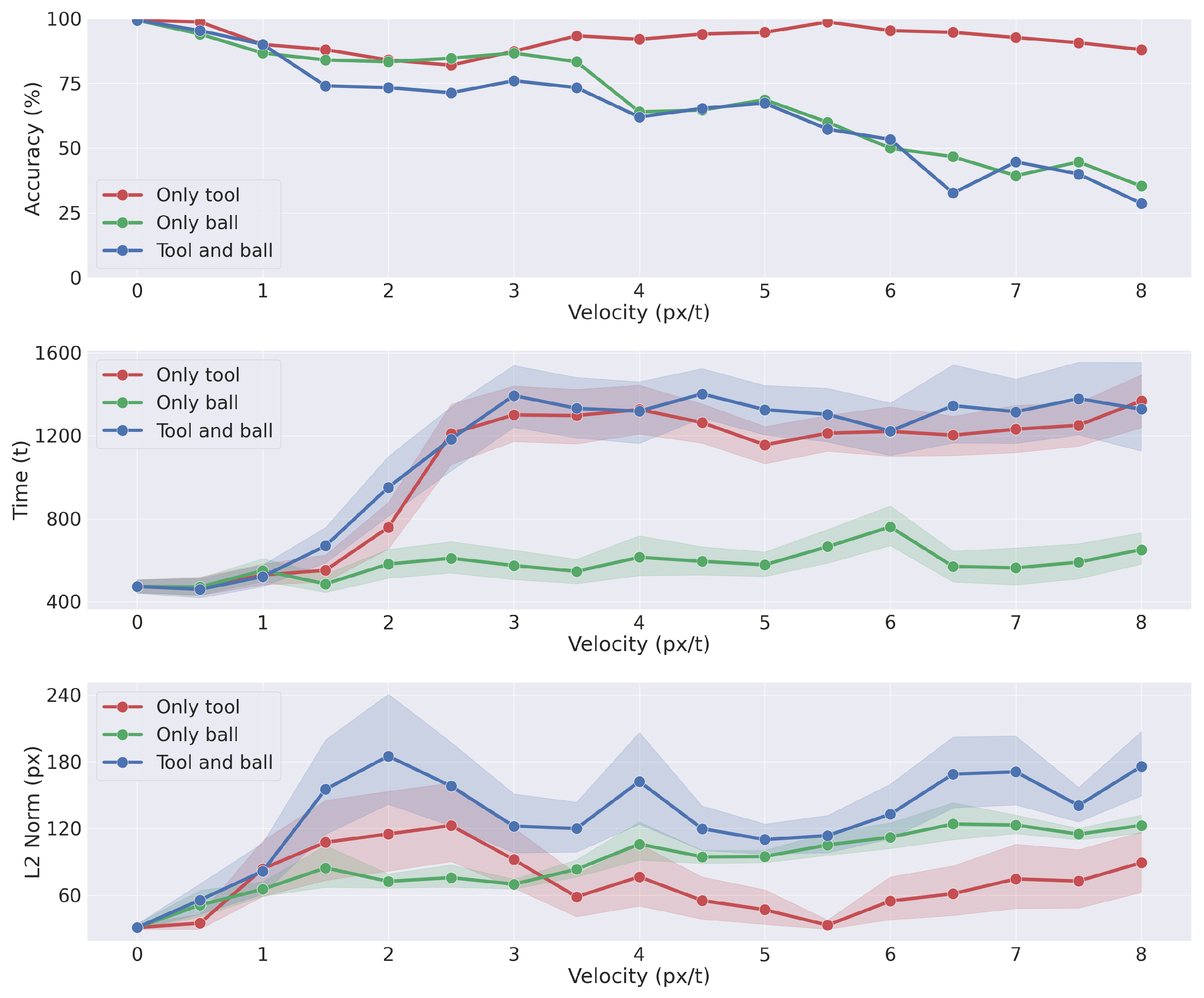
- We evaluate the agent’s performance in a common task: reaching a moving ball after reaching and picking a moving tool. The results highlight the interplay between the agent’s potential trajectories and the dynamic accumulation of sensory evidence. We demonstrate the agent’s ability to infer and plan under different conditions, such as random object positions and velocities.
2. Methods
2.1. Predictive Coding
2.2. Hierarchical Active Inference
2.3. Bayesian Model Comparison
3. Results
3.1. Deep Hybrid Models
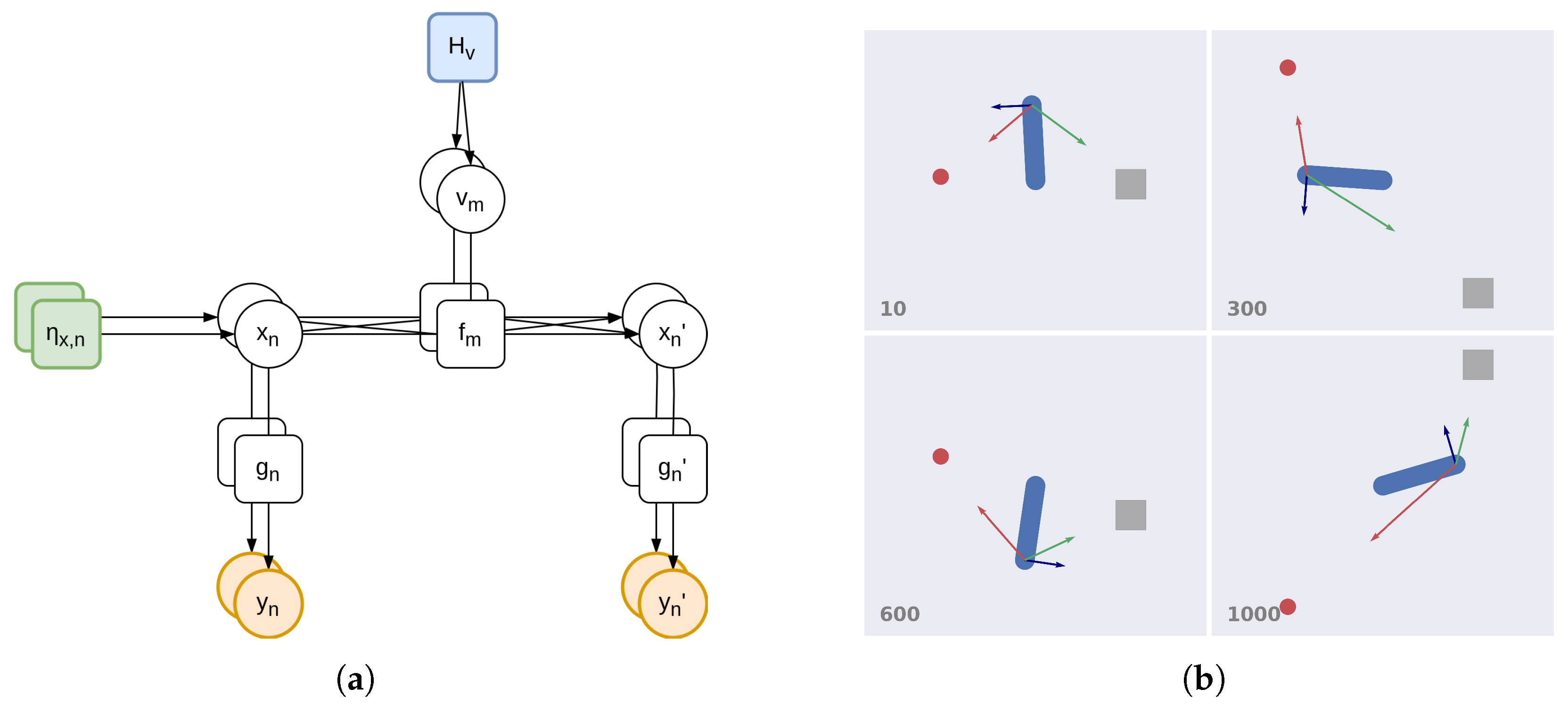
3.1.1. Factorial Depth and Flexible Behavior
3.1.2. Hierarchical Depth and Iterative Transformations
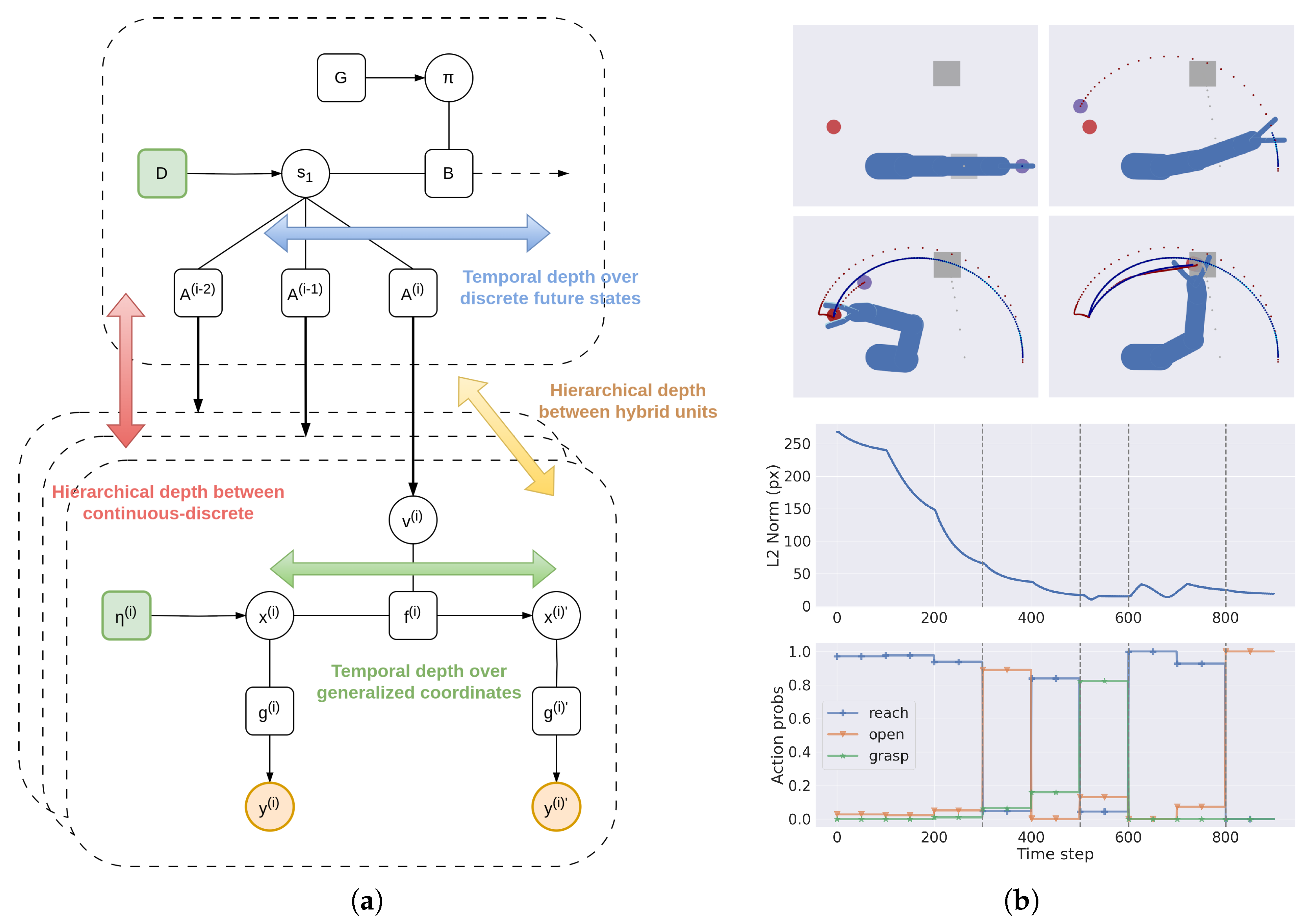
3.1.3. Temporal Depth and Dynamic Planning
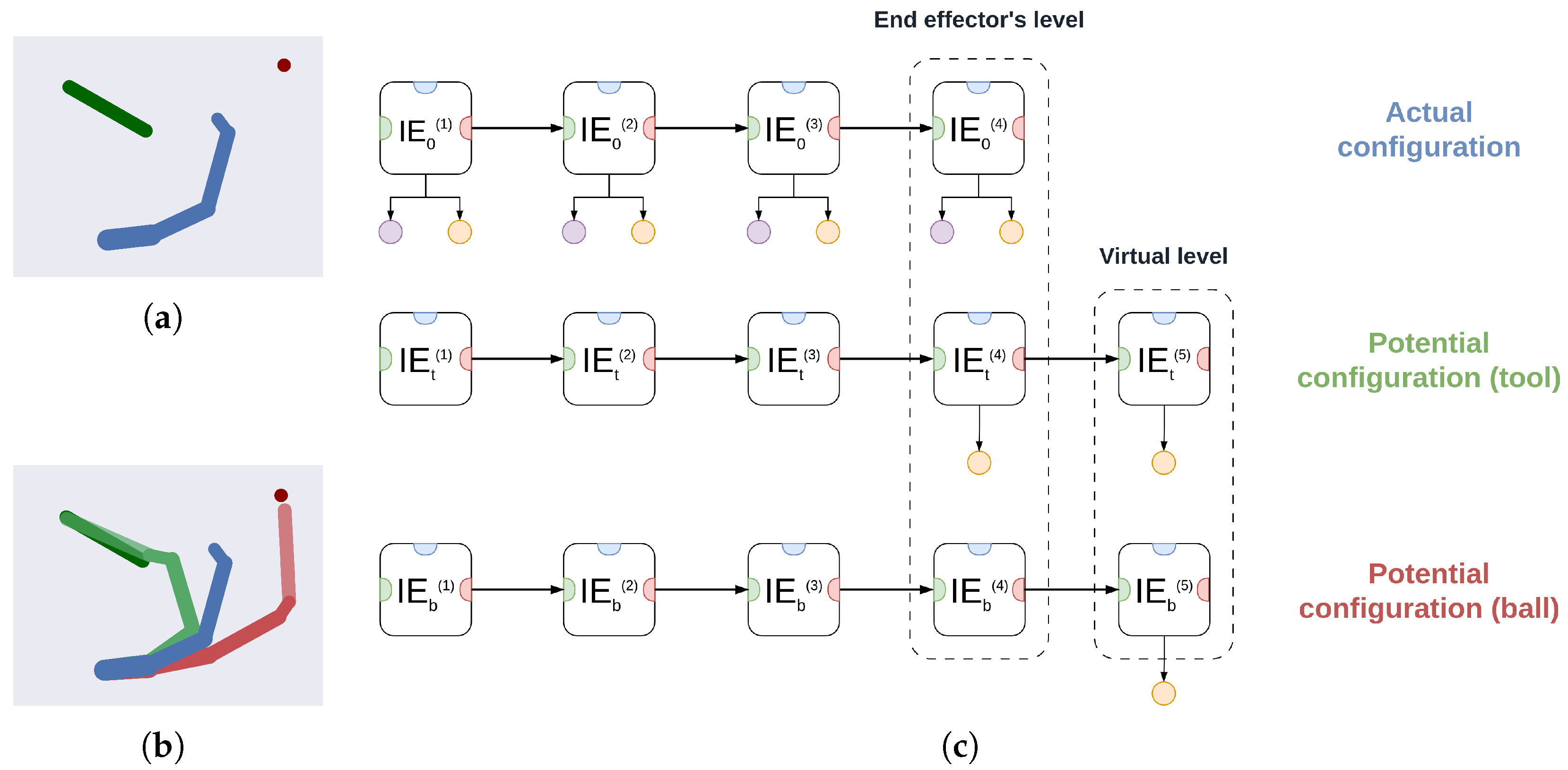
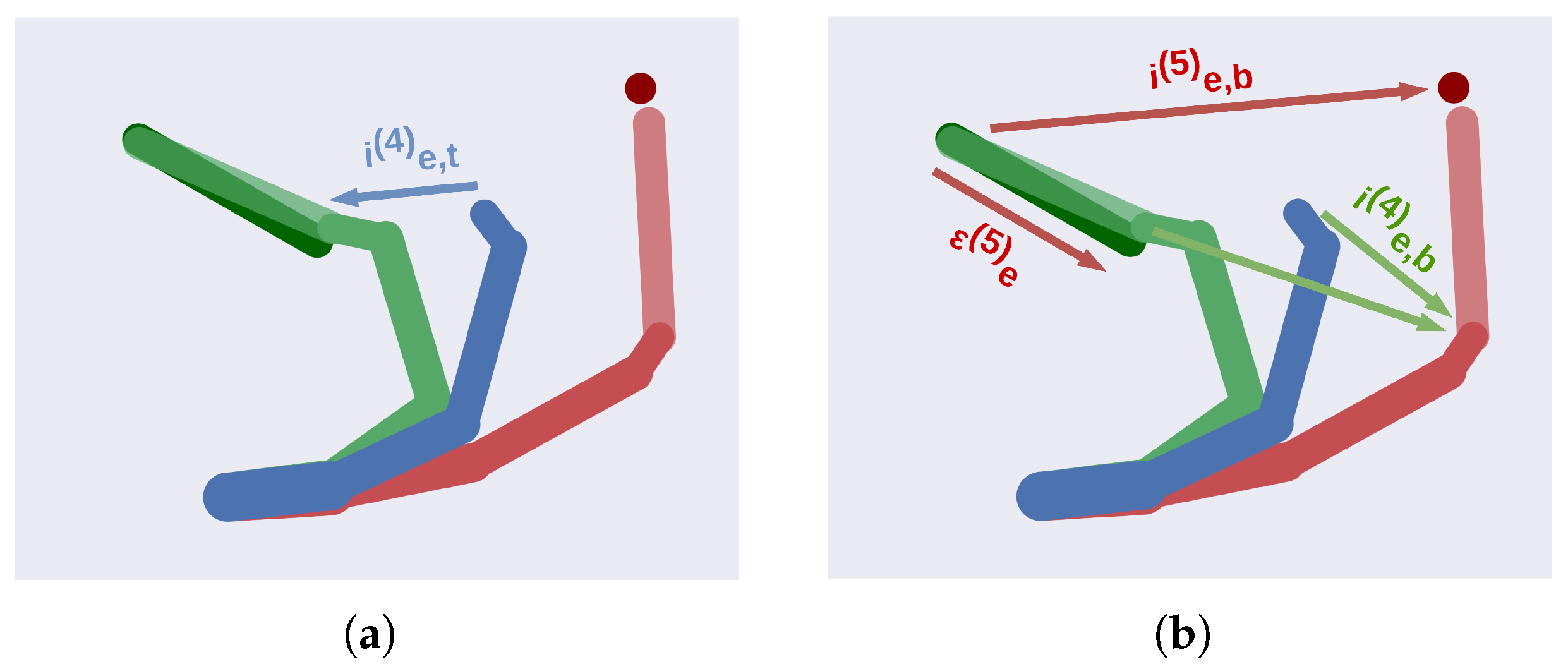
3.2. A Deep Hybrid Model for Tool Use
3.2.1. Implementation Details
3.3. Analysis of Model Performances
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1 Compute expected free energy |
| Input: length of policies discrete hidden states policies transition matrix preference Output: expected free energy for each policy do for to do end for end for |
| Algorithm A2 Accumulate log evidence |
| Input: mean of full prior mean of reduced priors mean of full posterior precision of full prior precision of reduced priors precision of full posterior log evidence Output: log evidence for each reduced model m do end for |
| Algorithm A3 Active inference with deep hybrid models |
| Input: continuous time T discrete time intrinsic units extrinsic units inverse dynamics proprioceptive precisions learning rate , action for to T do Get observations if then Update discrete model via Algorithm A4 end if for each unit and do Update intrinsic unit via Algorithm A5 Update extrinsic unit via Algorithm A6 end for Get proprioceptive prediction errors from intrinsic units Take action end for |
| Algorithm A4 Update discrete model at time |
| Input: discrete hidden states policies likelihood matrices transition matrix prior accumulated log evidence Output: accumulated log evidence discrete hidden causes for each unit do end for Compute expected free energy via Algorithm A1 for each unit do end for |
| Algorithm A5 Update intrinsic unit |
| Input: belief of extrinsic hidden states of previous level belief of intrinsic hidden states intrinsic (discrete) hidden causes proprioceptive observation belief of extrinsic hidden states intrinsic dynamics (reduced) functions proprioceptive likelihood extrinsic likelihood proprioceptive precision extrinsic precision intrinsic dynamics precision learning rate Output: proprioceptive prediction error extrinsic prediction error Accumulate log evidence via Algorithm A2 |
| Algorithm A6 Update extrinsic unit |
| Input: extrinsic prediction error belief of extrinsic hidden states extrinsic (discrete) hidden causes visual observation extrinsic prediction errors of next levels extrinsic dynamics (reduced) functions visual likelihood extrinsic precision extrinsic precisions of next levels visual precision extrinsic dynamics precision learning rate Output: belief of extrinsic hidden states Accumulate log evidence via Algorithm A2 |
References
- Todorov, E. Optimality principles in sensorimotor control. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedrichsen, J.; Shadmehr, R.; Ivry, R.B. The coordination of movement: Optimal feedback control and beyond. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Shiner, T.; FitzGerald, T.; Galea, J.M.; Adams, R.; Brown, H.; Dolan, R.J.; Moran, R.; Stephan, K.E.; Bestmann, S. Dopamine, Affordance and Active Inference. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Daunizeau, J.; Kiebel, S.J. Reinforcement learning or active inference? PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. What is optimal about motor control? Neuron 2011, 72, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Daunizeau, J.; Kilner, J.; Kiebel, S.J. Action and behavior: A free-energy formulation. Biol. Cybern. 2010, 102, 227–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. The free-energy principle: A unified brain theory? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, T.; Pezzulo, G.; Friston, K.J. Active Inference: The Free Energy Principle in Mind, Brain, and Behavior; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priorelli, M.; Maggiore, F.; Maselli, A.; Donnarumma, F.; Maisto, D.; Mannella, F.; Stoianov, I.P.; Pezzulo, G. Modeling motor control in continuous-time Active Inference: A survey. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2023, 16, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T.; Friston, K.J. Uncertainty, epistemics and active inference. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.P.; Ballard, D.H. Predictive coding in the visual cortex: A functional interpretation of some extra-classical receptive-field effects. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A. Whatever next? Predictive brains, situated agents, and the future of cognitive science. Behav. Brain Sci. 2013, 36, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohwy, J. The Predictive Mind; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Millidge, B.; Tschantz, A.; Seth, A.K.; Buckley, C.L. On the relationship between active inference and control as inference. In Active Inference; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1326, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Botvinick, M.; Toussaint, M. Planning as inference. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussaint, M.; Storkey, A. Probabilistic inference for solving discrete and continuous state Markov Decision Processes. ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser. 2006, 148, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, M. Probabilistic inference as a model of planned behavior. Künstliche Intell. 2009, 23, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Stoianov, I.; Pennartz, C.; Lansink, C.; Pezzulo, G. Model-based spatial navigation in the hippocampus-ventral striatum circuit: A computational analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. Hierarchical models in the brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Parr, T.; Yufik, Y.; Sajid, N.; Price, C.J.; Holmes, E. Generative models, linguistic communication and active inference. Neurosci. I Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M.; Siegelbaum, S.A.; Hudspeth, A.J. Principles of Neuroscience, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, L.; Frassinetti, F.; Brozzoli, C.; Urquizar, C.; Roy, A.C.; Farnè, A. Tool-use induces morphological updating of the body schema. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravita, A.; Iriki, A. Tools for the body (schema). Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, D.; Cui, H.; Andersen, R.A. The posterior parietal cortex encodes in parallel both goals for double-reach sequences. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10081–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisek, P.; Kalaska, J.F. Neural Correlates of Reaching Decisions in Dorsal Premotor Cortex: Specification of Multiple Direction Choices and Final Selection of Action. Neuron 2005, 45, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueltzhöffer, K. Deep Active Inference. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.02341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millidge, B. Deep active inference as variational policy gradients. J. Math. Psychol. 2020, 96, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountas, Z.; Sajid, N.; Mediano, P.A.; Friston, K. Deep active inference agents using Monte-Carlo methods. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, NeurIPS 2020, Online, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rood, T.; van Gerven, M.; Lanillos, P. A deep active inference model of the rubber-hand illusion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.07408. [Google Scholar]
- Sancaktar, C.; van Gerven, M.A.J.; Lanillos, P. End-to-End Pixel-Based Deep Active Inference for Body Perception and Action. In Proceedings of the 2020 Joint IEEE 10th International Conference on Development and Learning and Epigenetic Robotics (ICDL-EpiRob), Valparaiso, Chile, 26–30 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, T.; Grześ, M.; Bonheme, L.; Bowman, H. Deconstructing deep active inference. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.01618. [Google Scholar]
- Zelenov, A.; Krylov, V. Deep active inference in control tasks. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–13 June 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çatal, O.; Verbelen, T.; Van de Maele, T.; Dhoedt, B.; Safron, A. Robot navigation as hierarchical active inference. Neural Netw. 2021, 142, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Friston, K.; Li, Z.; Sajid, N. Hierarchical generative modelling for autonomous robots. Res. Sq. 2023, 5, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priorelli, M.; Stoianov, I.P. Flexible Intentions: An Active Inference Theory. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1128694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priorelli, M.; Pezzulo, G.; Stoianov, I.P. Deep kinematic inference affords efficient and scalable control of bodily movements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2309058120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Parr, T.; de Vries, B. The graphical brain: Belief propagation and active inference. Netw. Neurosci. 2017, 1, 381–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Rosch, R.; Parr, T.; Price, C.; Bowman, H. Deep temporal models and active inference. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 77, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, T.; Friston, K.J. Active inference and the anatomy of oculomotion. Neuropsychologia 2018, 111, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, T.; Friston, K.J. The computational pharmacology of oculomotion. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohwy, J. New directions in predictive processing. Mind Lang. 2020, 35, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Kiebel, S. Predictive coding under the free-energy principle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Ghahramani, Z.; Jaakkola, T.S.; Saul, L.K. An Introduction to Variational Methods for Graphical Models. Mach. Learn. 1999, 37, 183–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Bahl, L.R. Image Data Compression by Predictive Coding I: Prediction Algorithms. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1974, 18, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millidge, B.; Salvatori, T.; Song, Y.; Bogacz, R.; Lukasiewicz, T. Predictive Coding: Towards a Future of Deep Learning beyond Backpropagation? In Proceedings of the IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022; pp. 5538–5545. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatori, T.; Mali, A.; Buckley, C.L.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Rao, R.P.N.; Friston, K.; Ororbia, A. Brain-Inspired Computational Intelligence via Predictive Coding. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.07870. [Google Scholar]
- Millidge, B.; Tang, M.; Osanlouy, M.; Harper, N.S.; Bogacz, R. Predictive coding networks for temporal prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1011183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T.; Friston, K.J. The Discrete and Continuous Brain: From Decisions to Movement—And Back Again Thomas. Neural Comput. 2018, 30, 2319–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Stephan, K.; Li, B.; Daunizeau, J. Generalised Filtering. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 621670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Da Costa, L.; Sajid, N.; Heins, C.; Ueltzhöffer, K.; Pavliotis, G.A.; Parr, T. The free energy principle made simpler but not too simple. Phys. Rep. 2022, 1024, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.A.; Shipp, S.; Friston, K.J. Predictions not commands: Active inference in the motor system. Brain Struct. Funct. 2013, 218, 611–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzulo, G.; Rigoli, F.; Friston, K.J. Hierarchical Active Inference: A Theory of Motivated Control. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D. Active inference, communication and hermeneutics. Cortex 2015, 68, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T.; Friston, K.J. Generalised free energy and active inference. Biol. Cybern. 2019, 113, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Friston, K.J.; Whyte, C.J. A step-by-step tutorial on active inference and its application to empirical data. J. Math. Psychol. 2022, 107, 102632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, L.; Parr, T.; Sajid, N.; Veselic, S.; Neacsu, V.; Friston, K. Active inference on discrete state-spaces: A synthesis. J. Math. Psychol. 2020, 99, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Parr, T.; Zeidman, P. Bayesian model reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.07092. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.; Mattout, J.; Trujillo-Barreto, N.; Ashburner, J.; Penny, W. Variational free energy and the Laplace approximation. NeuroImage 2007, 34, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Penny, W. Post hoc Bayesian model selection. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Parr, T.; Heins, C.; Constant, A.; Friedman, D.; Isomura, T.; Fields, C.; Verbelen, T.; Ramstead, M.; Clippinger, J.; et al. Federated inference and belief sharing. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 156, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priorelli, M.; Stoianov, I. Dynamic Inference by Model Reduction. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio-Lopez, L.; Nizard, A.; Friston, K.; Pezzulo, G. Active inference and robot control: A case study. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20160616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priorelli, M.; Stoianov, I.P. Slow but flexible or fast but rigid? Discrete and continuous processes compared. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.A.; Aponte, E.; Marshall, L.; Friston, K.J. Active inference and oculomotor pursuit: The dynamic causal modelling of eye movements. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 242, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priorelli, M.; Pezzulo, G.; Stoianov, I. Active Vision in Binocular Depth Estimation: A Top-Down Perspective. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, C.; Buckley, C.; Verbelen, T. Why learn if you can infer? Robot arm control with Hierarchical Active Inference. In Proceedings of the The First Workshop on NeuroAI @ NeurIPS2024, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–15 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Priorelli, M.; Stoianov, I.P. Dynamic planning in hierarchical active inference. Neural Netw. 2025, 185, 107075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.; Da Costa, L.; Hafner, D.; Hesp, C.; Parr, T. Sophisticated inference. Neural Comput. 2021, 33, 713–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; de Maele, T.V.; Mazzaglia, P.; Verbelen, T.; Dhoedt, B. Disentangling Shape and Pose for Object-Centric Deep Active Inference Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.09097. [Google Scholar]
- van Bergen, R.S.; Lanillos, P.L. Object-based active inference. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.01258. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Maele, T.; Verbelen, T.; undefinedatal, O.; Dhoedt, B. Embodied Object Representation Learning and Recognition. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 840658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnarumma, F.; Costantini, M.; Ambrosini, E.; Friston, K.; Pezzulo, G. Action perception as hypothesis testing. Cortex 2017, 89, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Mattout, J.; Kilner, J. Action understanding and active inference. Biol. Cybern. 2011, 104, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, G.; Lanillos, P.; Cheng, G. An empirical study of active inference on a humanoid robot. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 14, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isomura, T.; Parr, T.; Friston, K. Bayesian filtering with multiple internal models: Toward a theory of social intelligence. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 2390–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, S.; Krayani, A.; Marin-Plaza, P.; Marcenaro, L.; Gomez, D.M.; Regazzoni, C. Active Inference Integrated with Imitation Learning for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49738–49756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, P.; Singh, R.; Kinghorn, P.F.; Buckley, C.L. Learning in Hybrid Active Inference Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.01066. [Google Scholar]
- Anil Meera, A.; Lanillos, P. Towards Metacognitive Robot Decision Making for Tool Selection. In Proceedings of the Active Inference, Ghent, Belgium, 13–15 September 2023; Buckley, C.L., Cialfi, D., Lanillos, P., Ramstead, M., Sajid, N., Shimazaki, H., Verbelen, T., Wisse, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2024; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Priorelli, M.; Stoianov, I.P. Efficient Motor Learning Through Action-Perception Cycles in Deep Kinematic Inference. In Proceedings of the Active Inference; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ororbia, A.; Kifer, D. The neural coding framework for learning generative models. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, J.C.R.; Bogacz, R. An Approximation of the Error Backpropagation Algorithm in a Predictive Coding Network with Local Hebbian Synaptic Plasticity. Neural Comput. 2017, 29, 1229–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, J.C.; Bogacz, R. Theories of Error Back-Propagation in the Brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millidge, B.; Tschantz, A.; Buckley, C.L. Predictive Coding Approximates Backprop Along Arbitrary Computation Graphs. Neural Comput. 2022, 34, 1329–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatori, T.; Song, Y.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Bogacz, R.; Xu, Z. Predictive Coding Can Do Exact Backpropagation on Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.03725. [Google Scholar]
- Stoianov, I.; Maisto, D.; Pezzulo, G. The hippocampal formation as a hierarchical generative model supporting generative replay and continual learning. Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 217, 102329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.P.; Rao, R.P.N. Dynamic predictive coding: A model of hierarchical sequence learning and prediction in the neocortex. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Shu, R.; Pham, T.; Bui, H.; Ermon, S. Temporal Predictive Coding For Model-Based Planning In Latent Space. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.07156. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Barron, H.; Bogacz, R. Sequential Memory with Temporal Predictive Coding. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.11982. [Google Scholar]
- Millidge, B. Combining Active Inference and Hierarchical Predictive Coding: A Tutorial Introduction and Case Study. PsyArXiv 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ororbia, A.; Mali, A. Active Predicting Coding: Brain-Inspired Reinforcement Learning for Sparse Reward Robotic Control Problems. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.09174. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.P.N.; Gklezakos, D.C.; Sathish, V. Active Predictive Coding: A Unified Neural Framework for Learning Hierarchical World Models for Perception and Planning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.13461. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, A.; Rao, R.P.N. Recursive neural programs: A differentiable framework for learning compositional part-whole hierarchies and image grammars. PNAS Nexus 2023, 2, pgad337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moerland, T.M.; Broekens, J.; Plaat, A.; Jonker, C.M. Model-based Reinforcement Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2006.16712. [Google Scholar]
- Albarracin, M.; Hipólito, I.; Tremblay, S.E.; Fox, J.G.; René, G.; Friston, K.; Ramstead, M.J.D. Designing explainable artificial intelligence with active inference: A framework for transparent introspection and decision-making. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.04025. [Google Scholar]
- de Maele, T.V.; Verbelen, T.; Mazzaglia, P.; Ferraro, S.; Dhoedt, B. Object-Centric Scene Representations using Active Inference. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.03288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Priorelli, M.; Stoianov, I.P. Deep Hybrid Models: Infer and Plan in a Dynamic World. Entropy 2025, 27, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060570
Priorelli M, Stoianov IP. Deep Hybrid Models: Infer and Plan in a Dynamic World. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060570
Chicago/Turabian StylePriorelli, Matteo, and Ivilin Peev Stoianov. 2025. "Deep Hybrid Models: Infer and Plan in a Dynamic World" Entropy 27, no. 6: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060570
APA StylePriorelli, M., & Stoianov, I. P. (2025). Deep Hybrid Models: Infer and Plan in a Dynamic World. Entropy, 27(6), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060570






