Complexity Analysis of Environmental Time Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
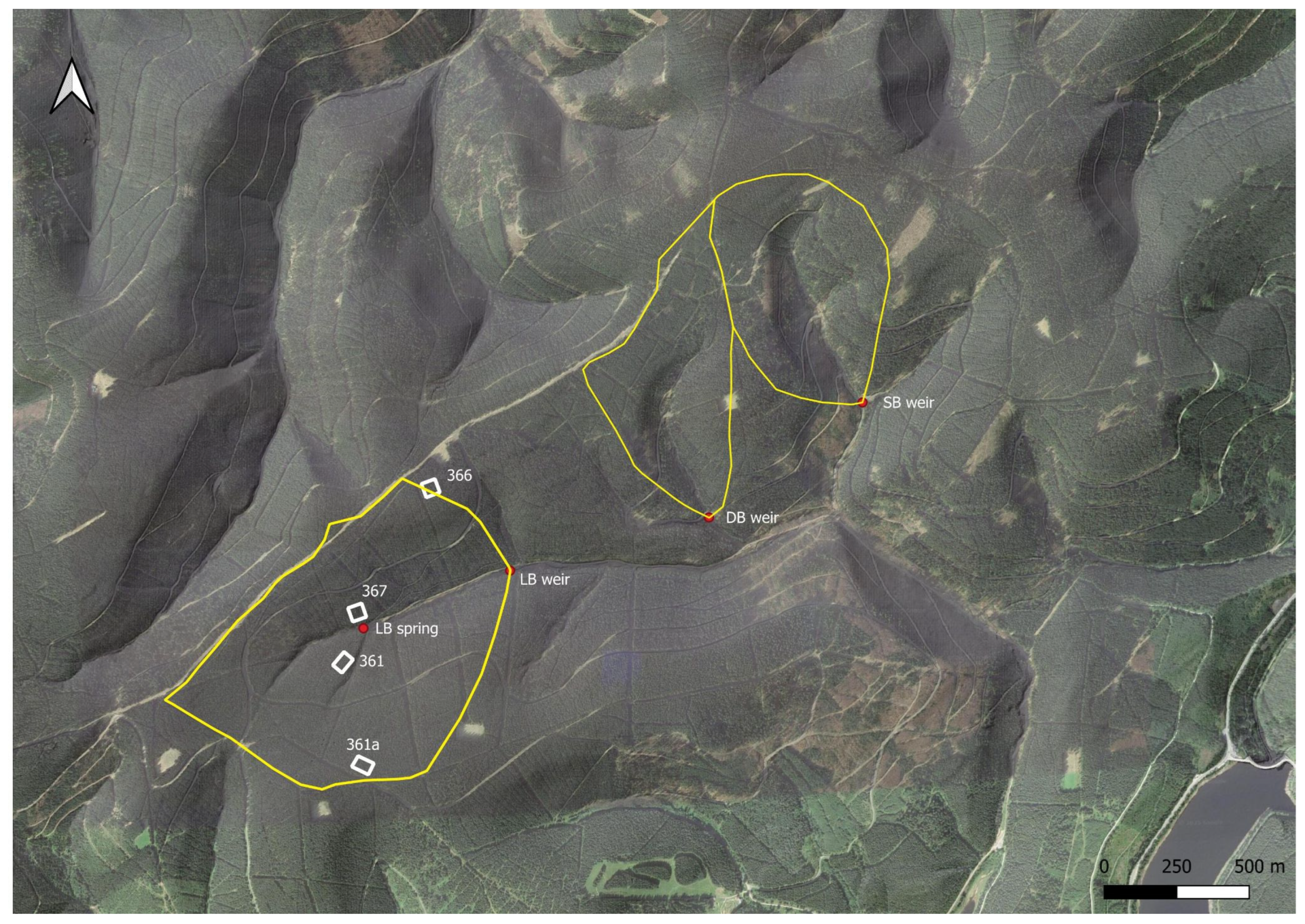
2.1. Site Description
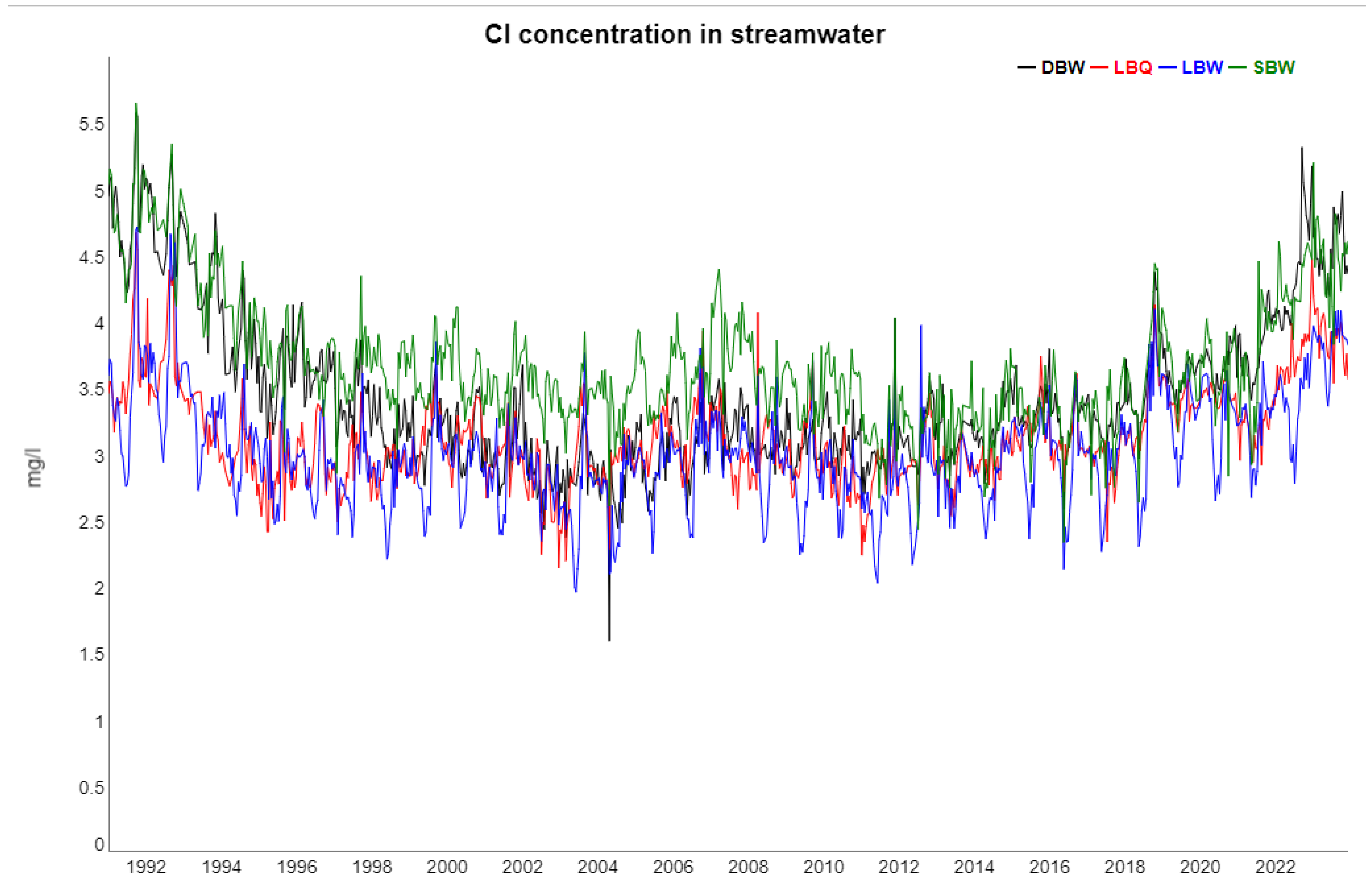
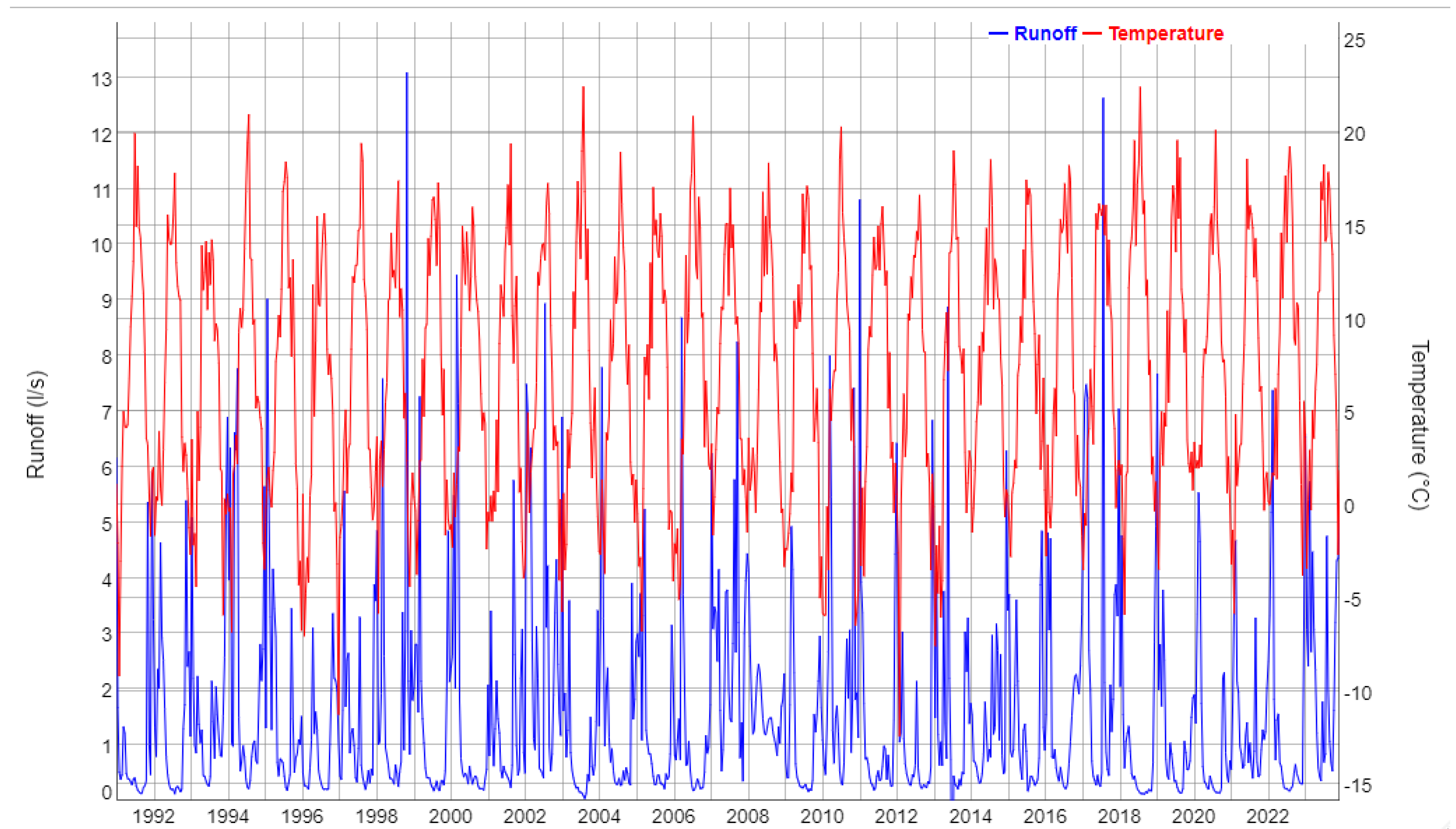
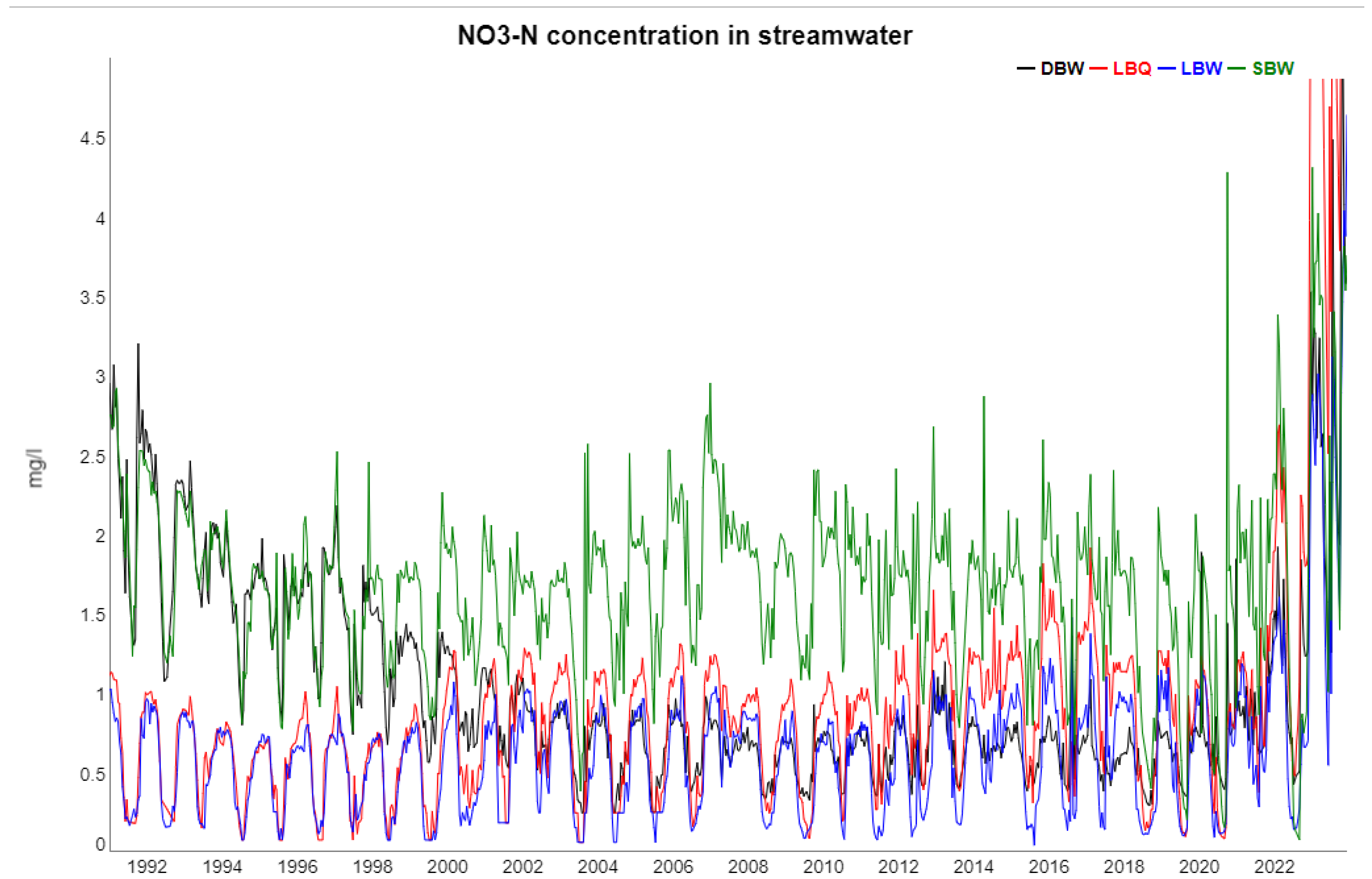
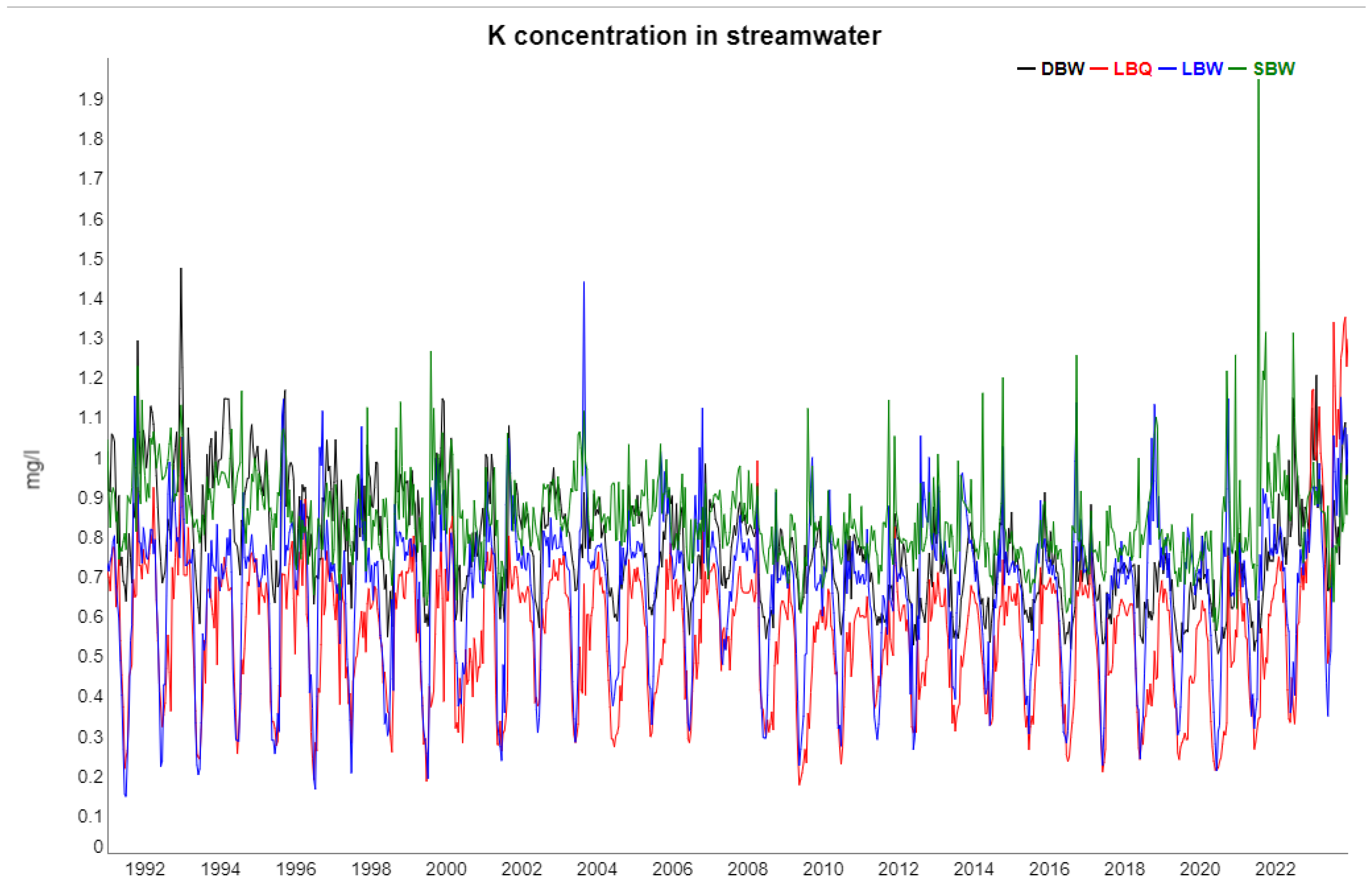
2.2. Time Series from the Sites
2.3. Data Preparation and Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Gap Filling, Detrending, and Deseasonalization: Singular System Analysis
2.3.2. Permutation Entropy and Complexity
2.3.3. Fisher Information
2.3.4. Rényi and Tsallis Entropy and Complexity
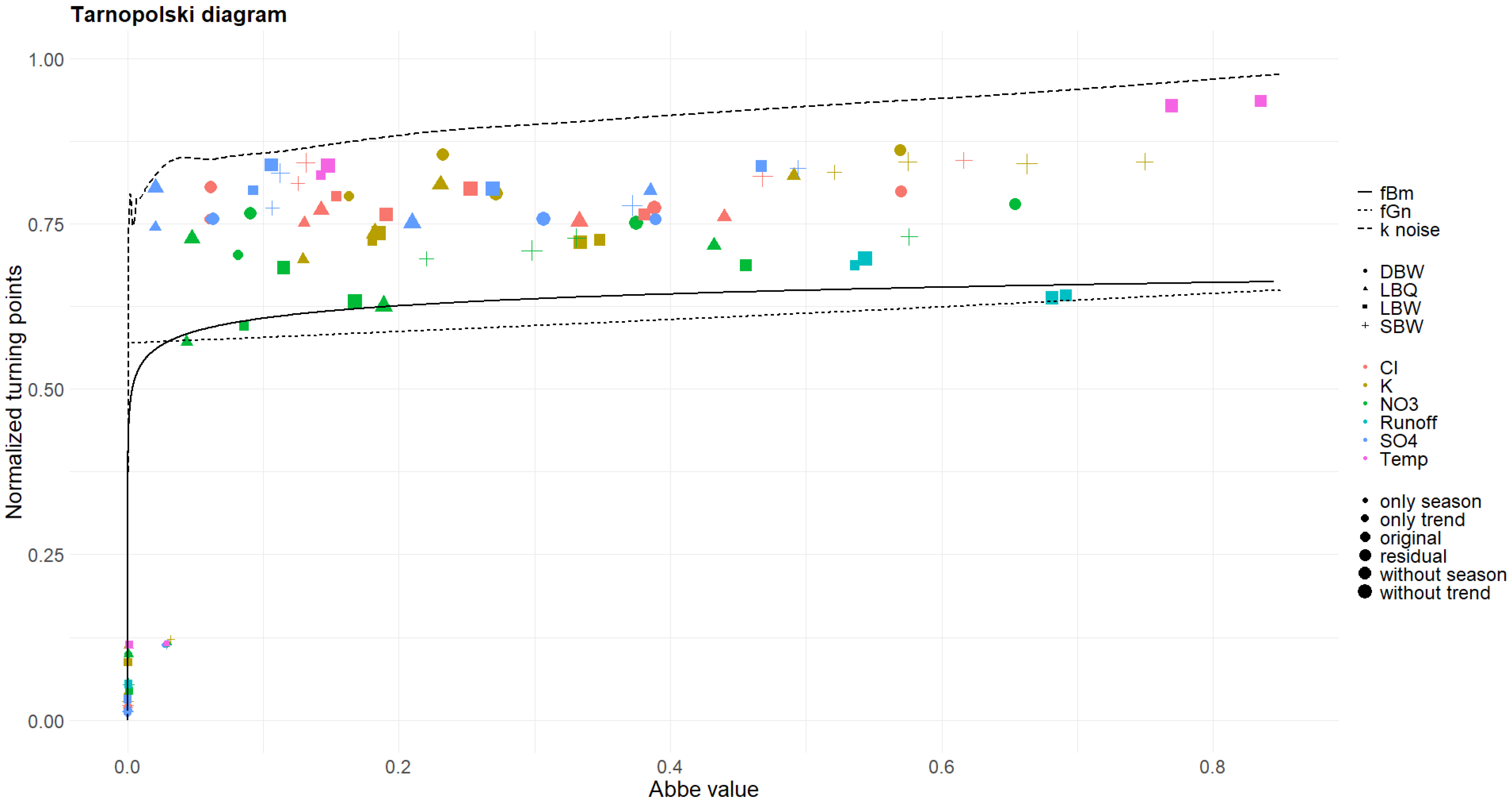
2.3.5. Tarnopolski Diagrams
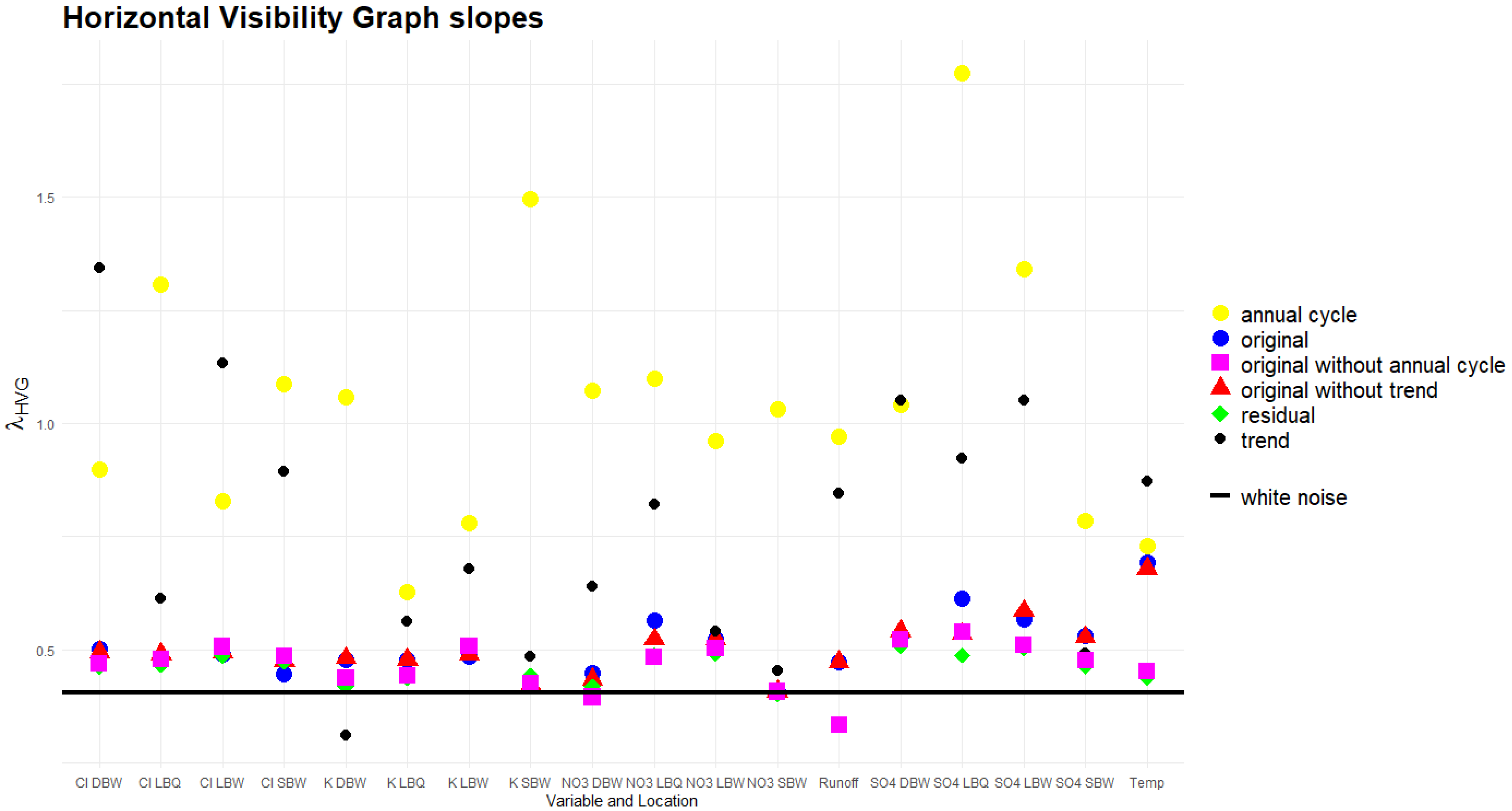
2.3.6. Horizontal Visibility Graphs
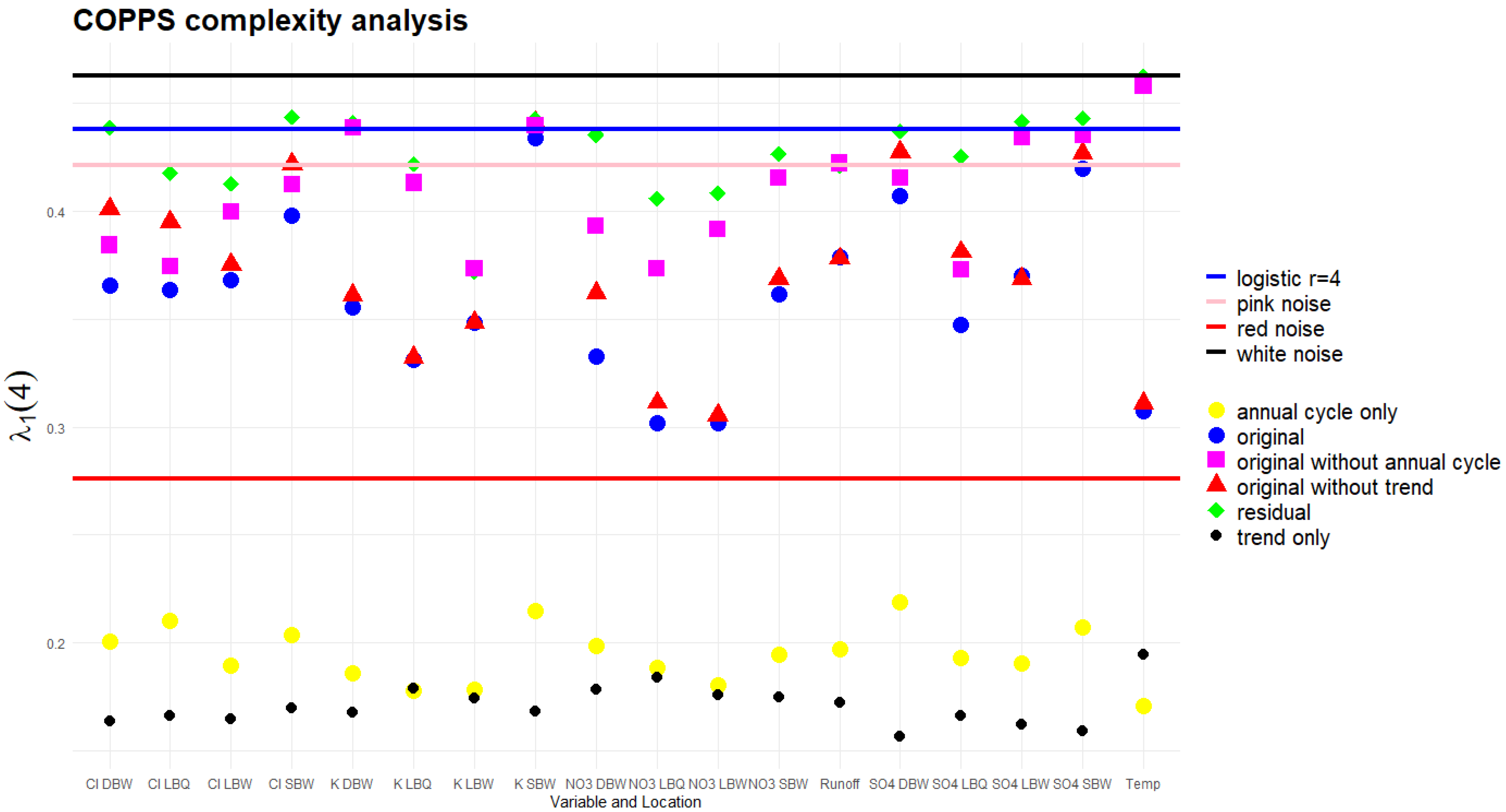
2.3.7. Complexity of Ordinal Pattern Positioned Slopes (COPPS)
3. Results
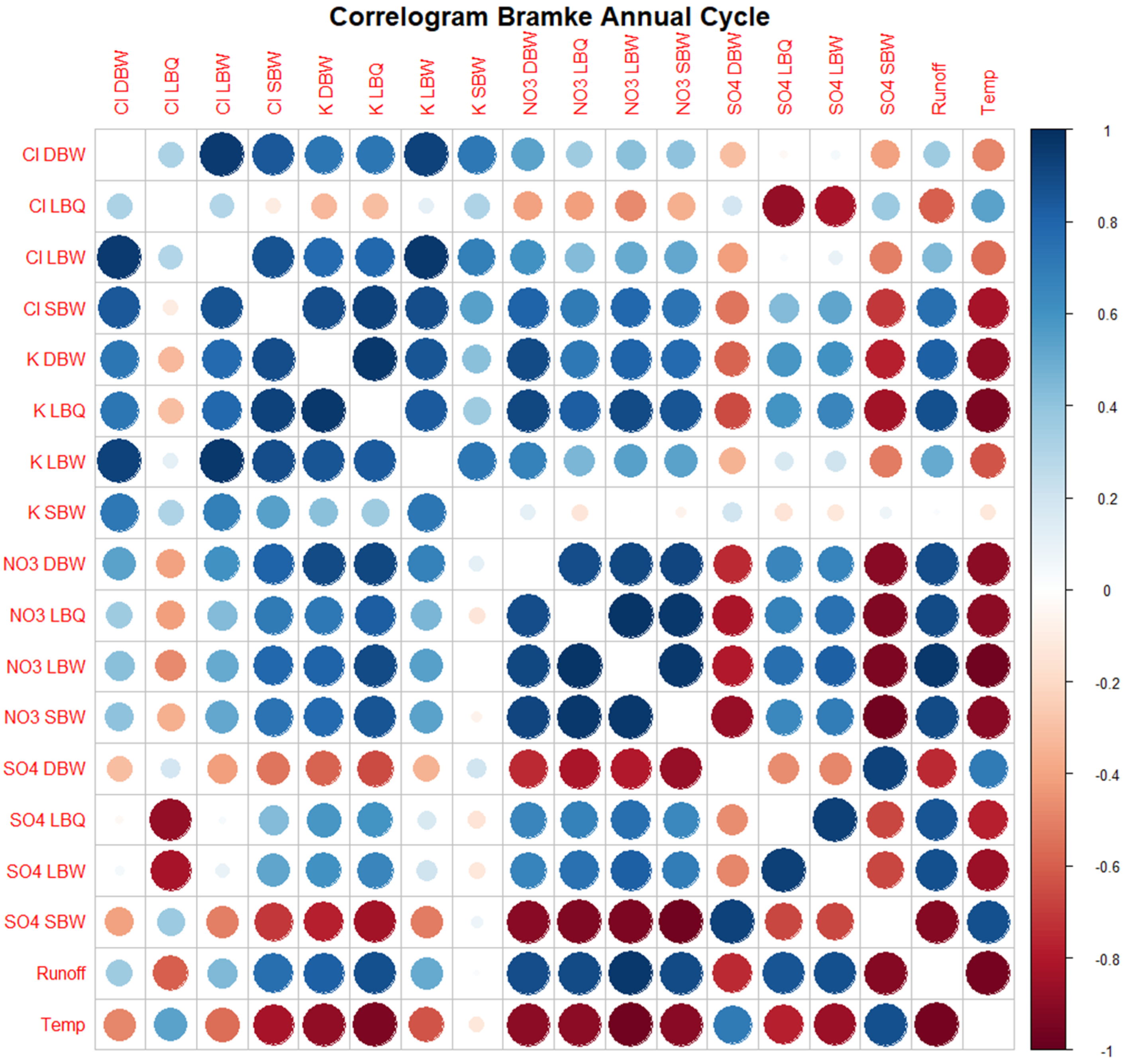
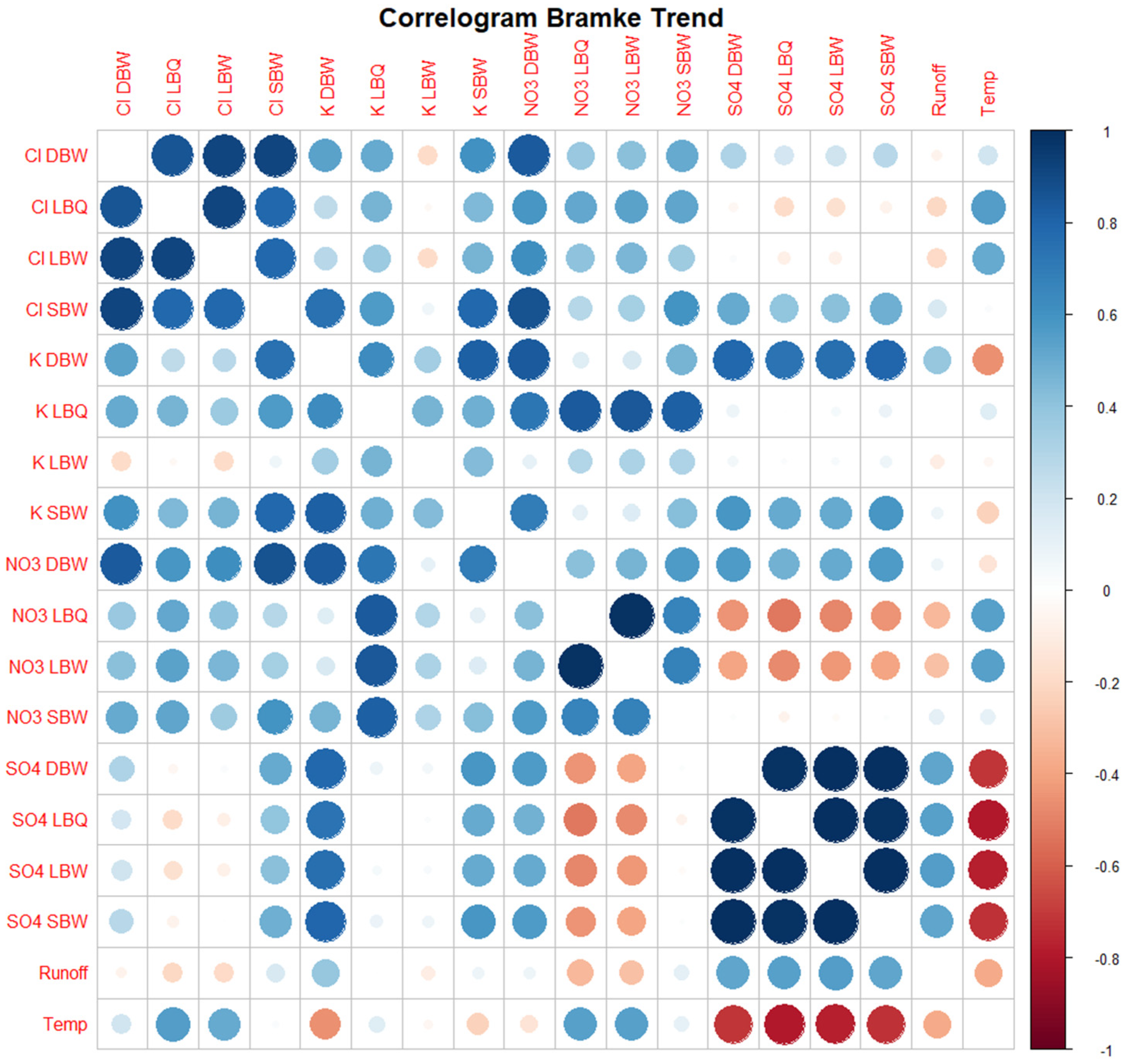
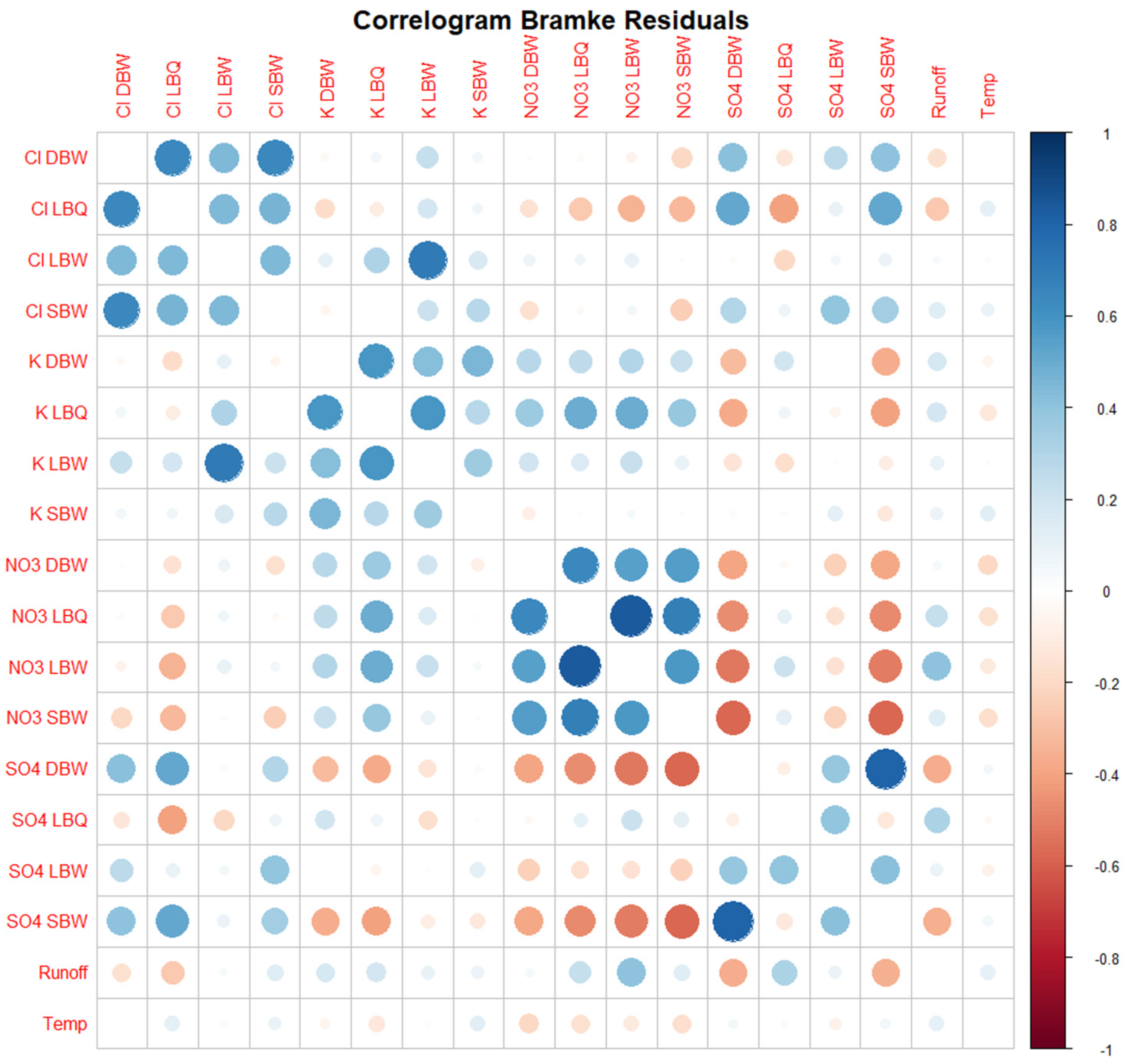
3.1. Correlograms, Phase Shifts, and Jensen–Shannon Divergence of the Time Series Set
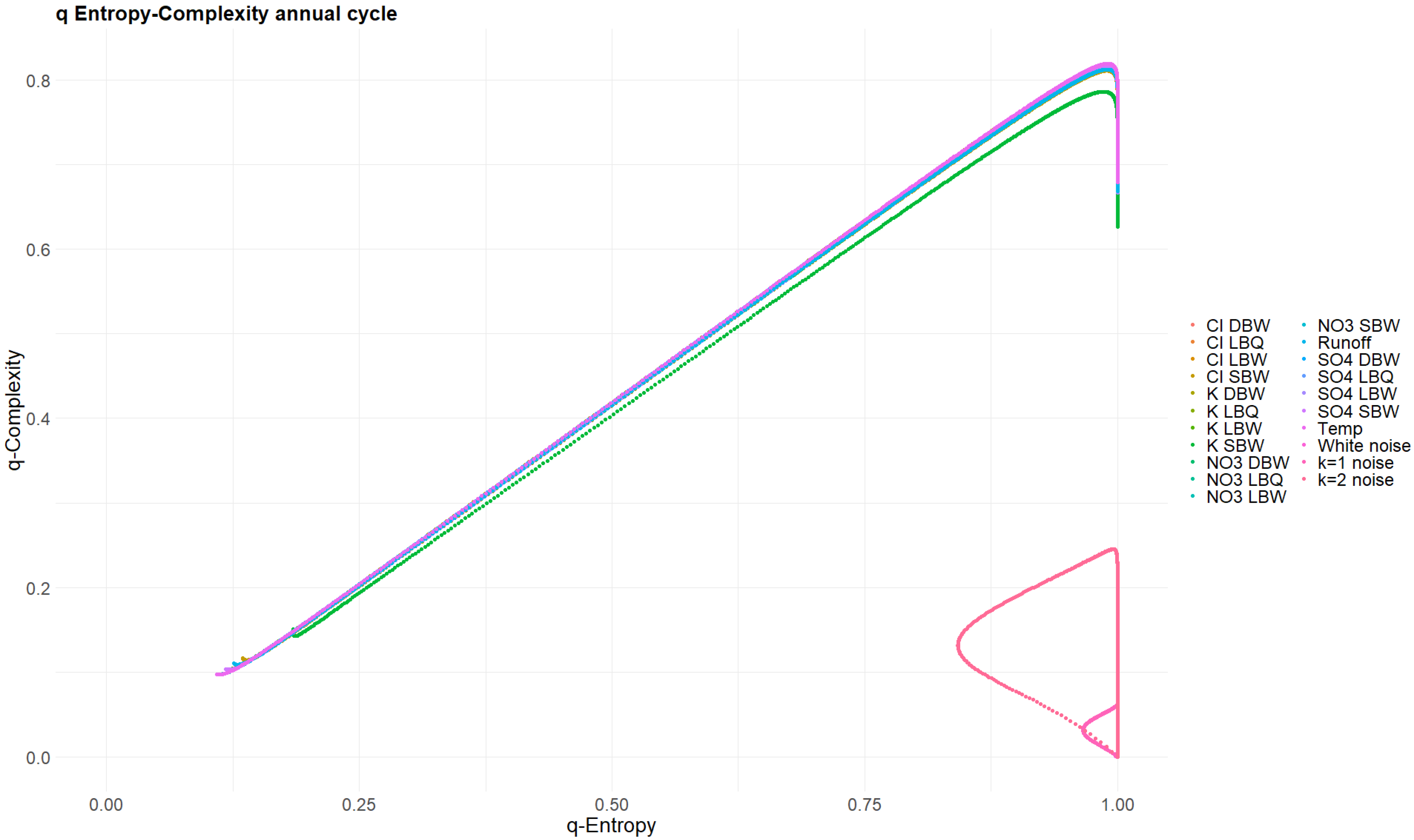
3.2. Entropy–Complexity Plane
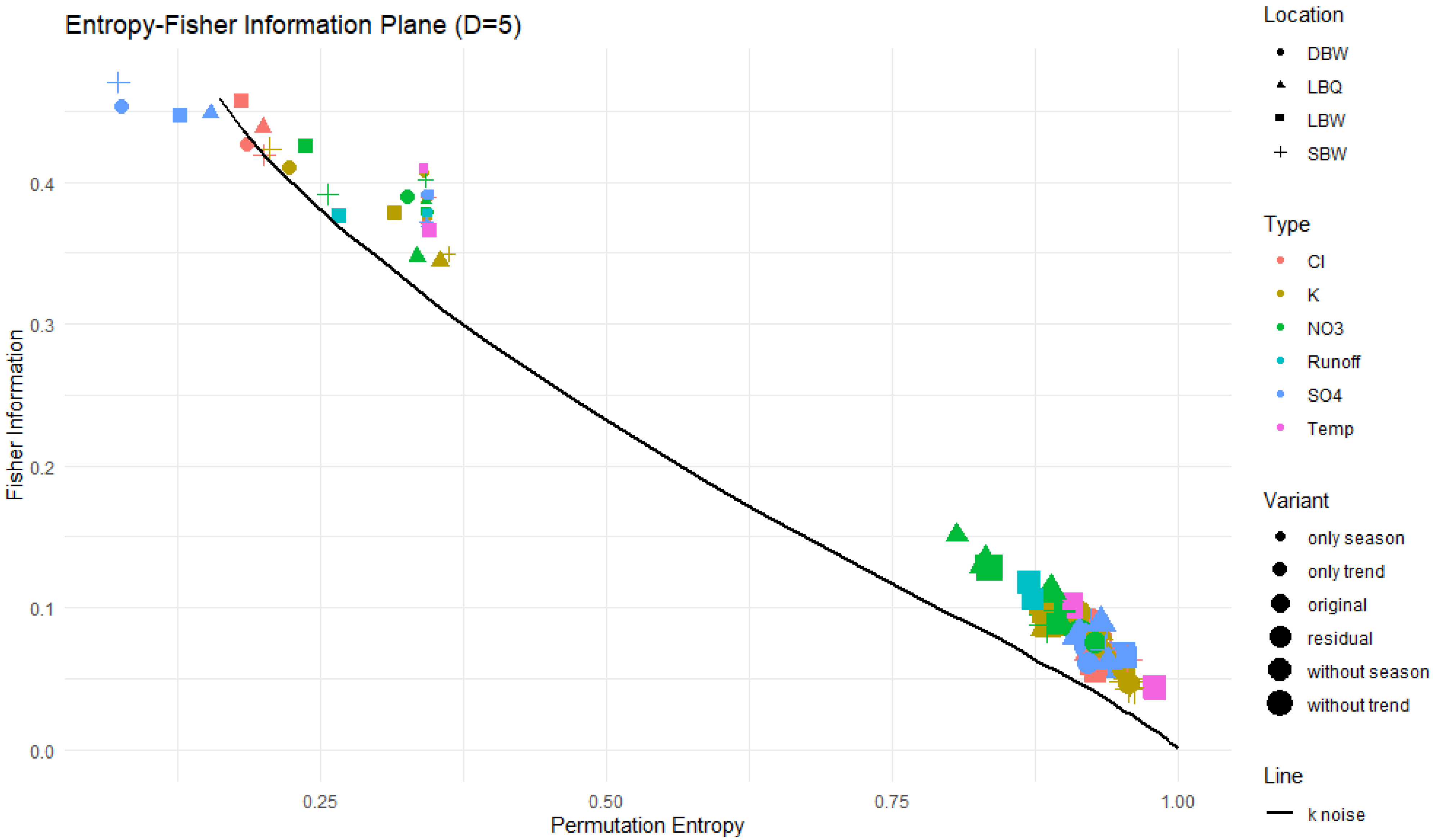
3.3. Entropy–Fisher Information Plane
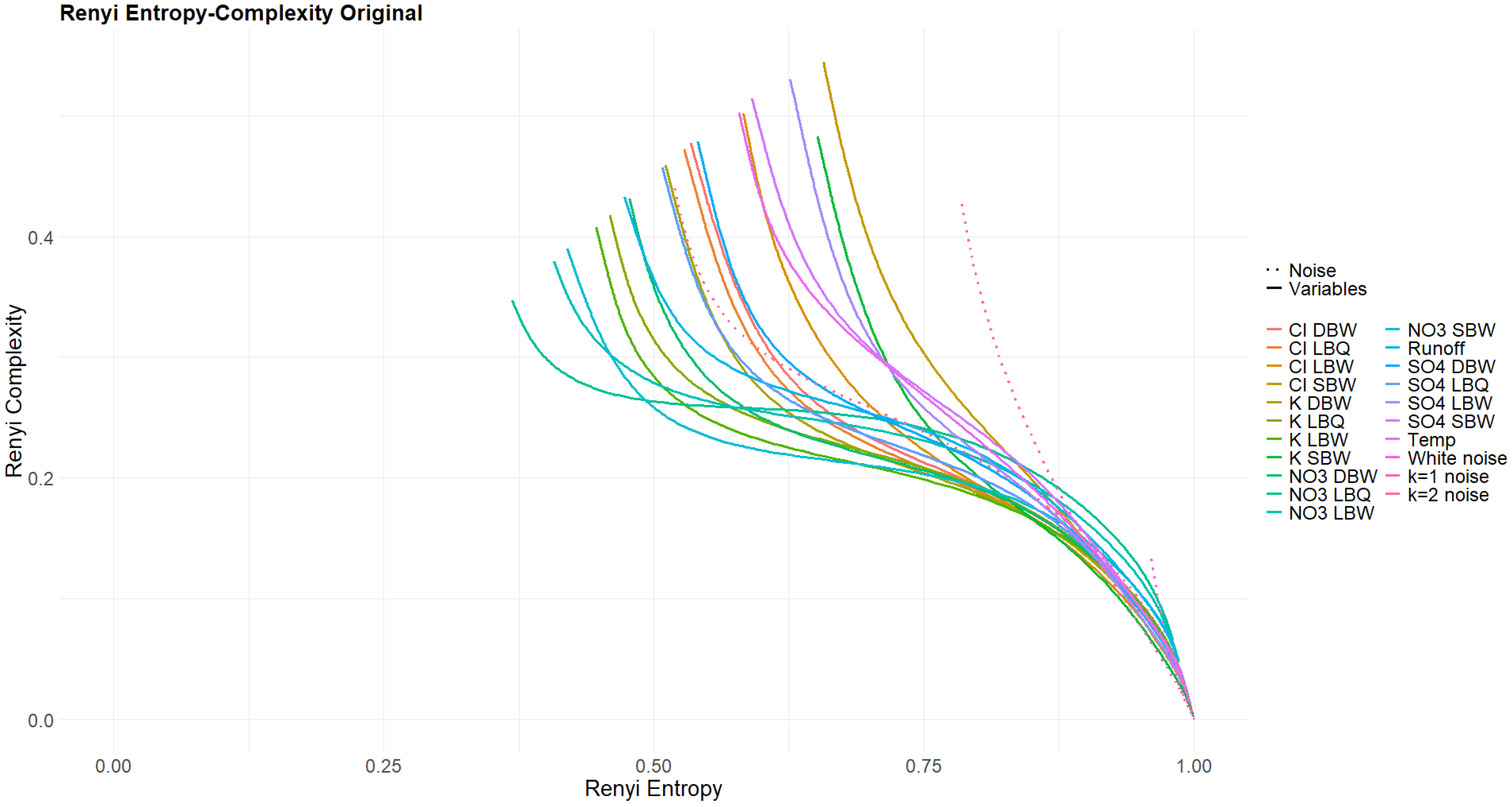
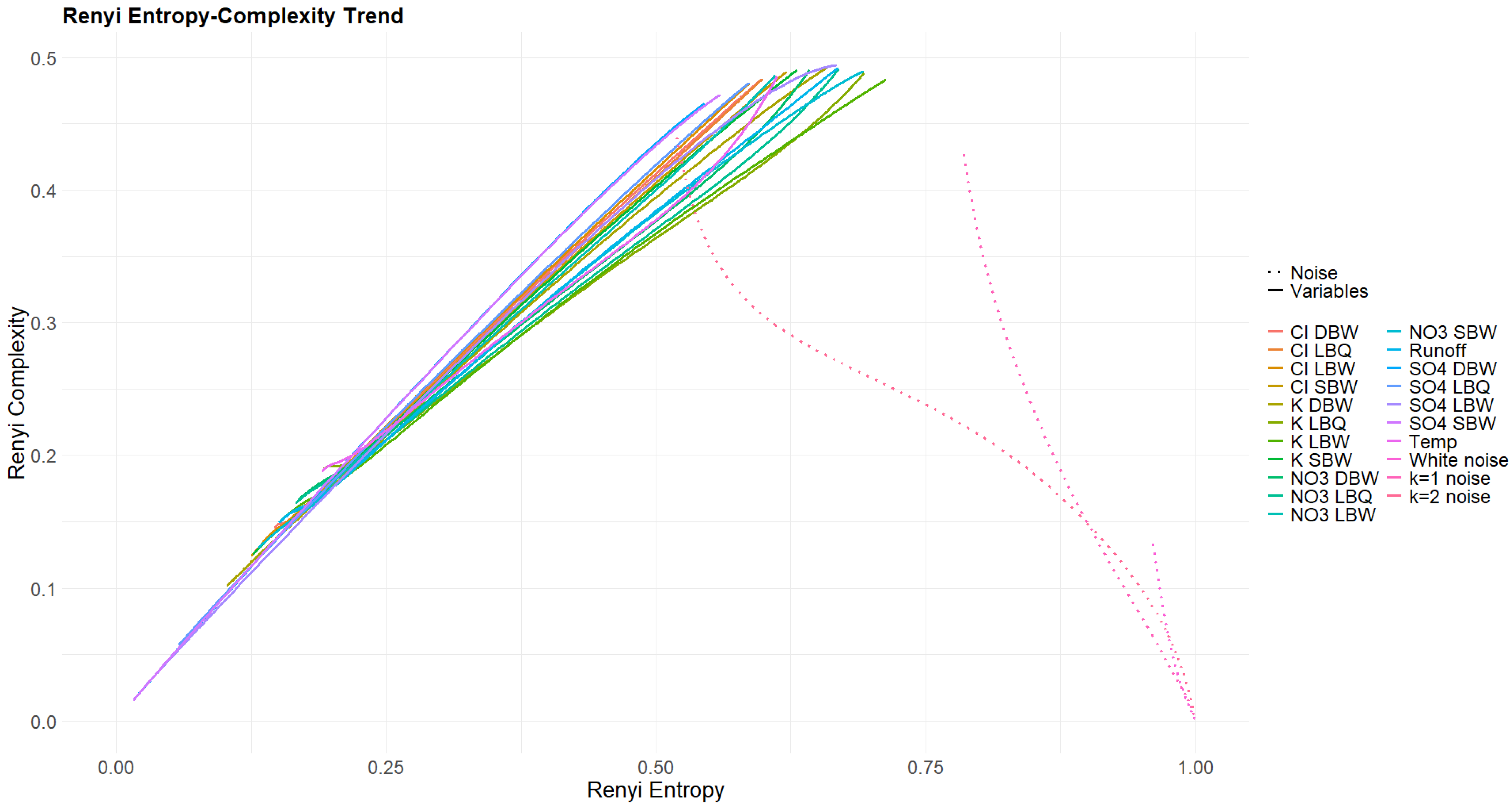
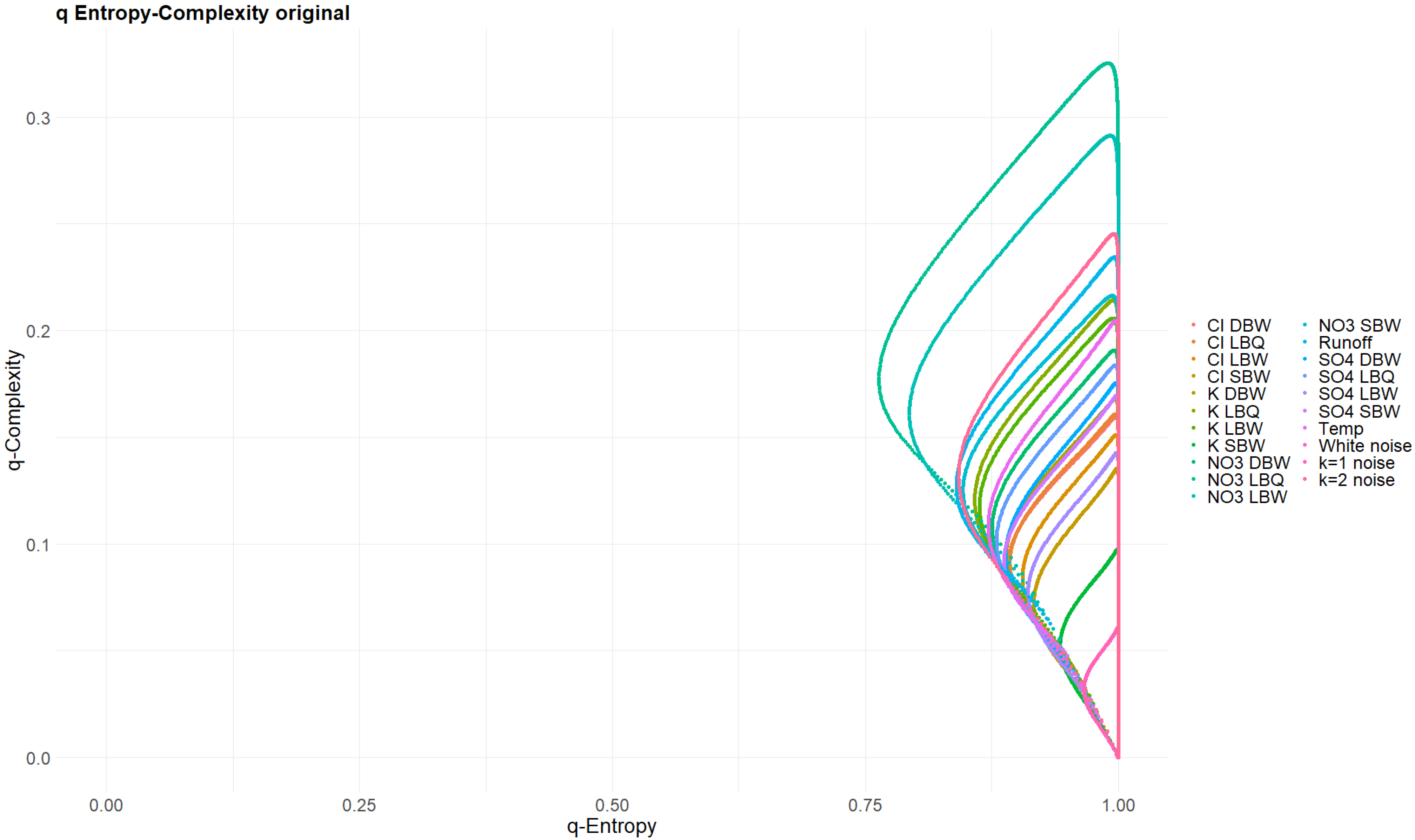
3.4. Rényi and Tsallis Entropy–Complexity Planes
3.5. Tarnopolski Diagram
3.6. Horizontal Visibility Graph Analysis
3.7. COPPS Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Trend and Seasonality
4.2. Complexity
4.3. Abbe Values
4.4. HVG Slopes
4.5. COPPS
4.6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Additional Figures
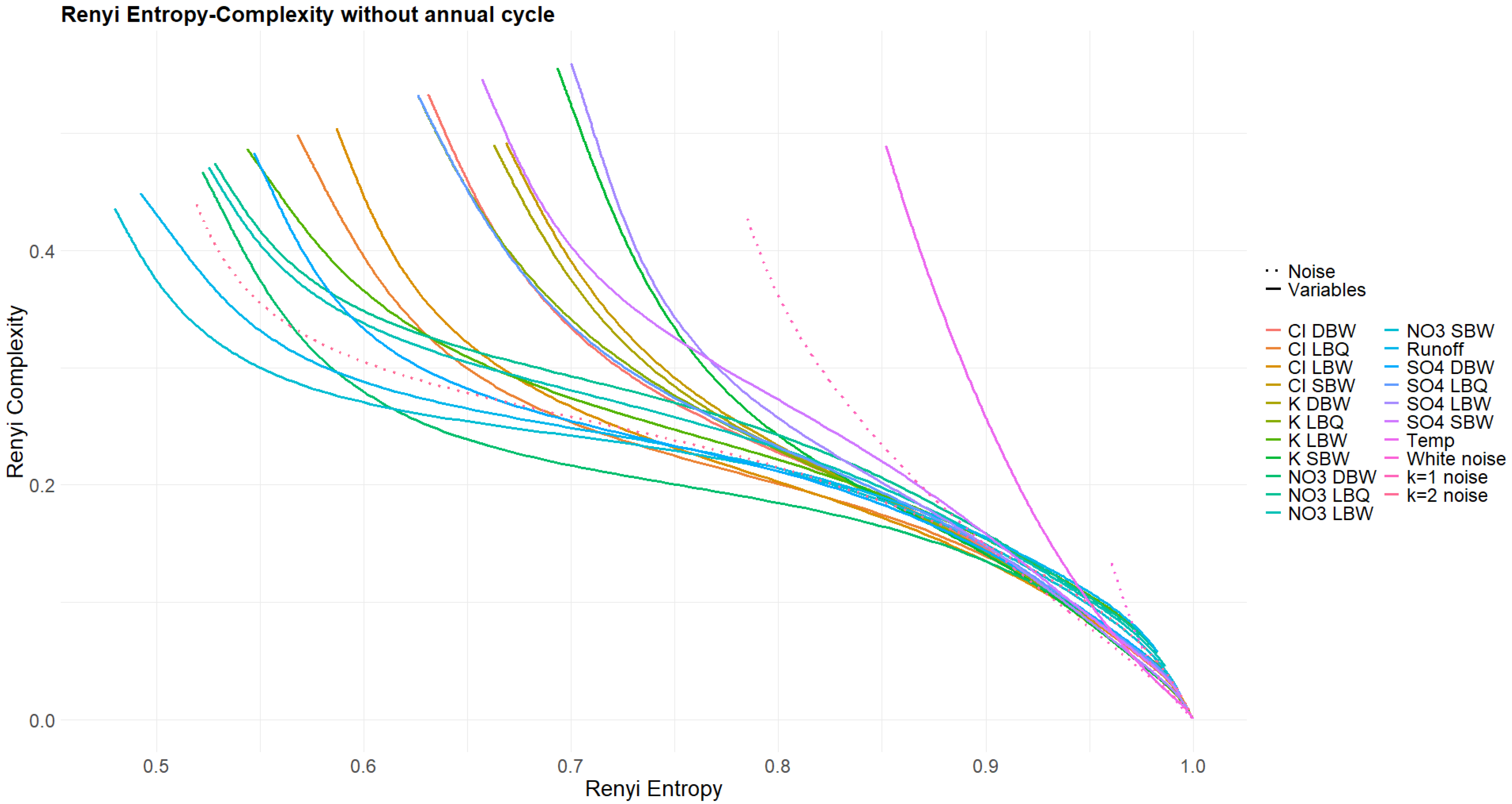

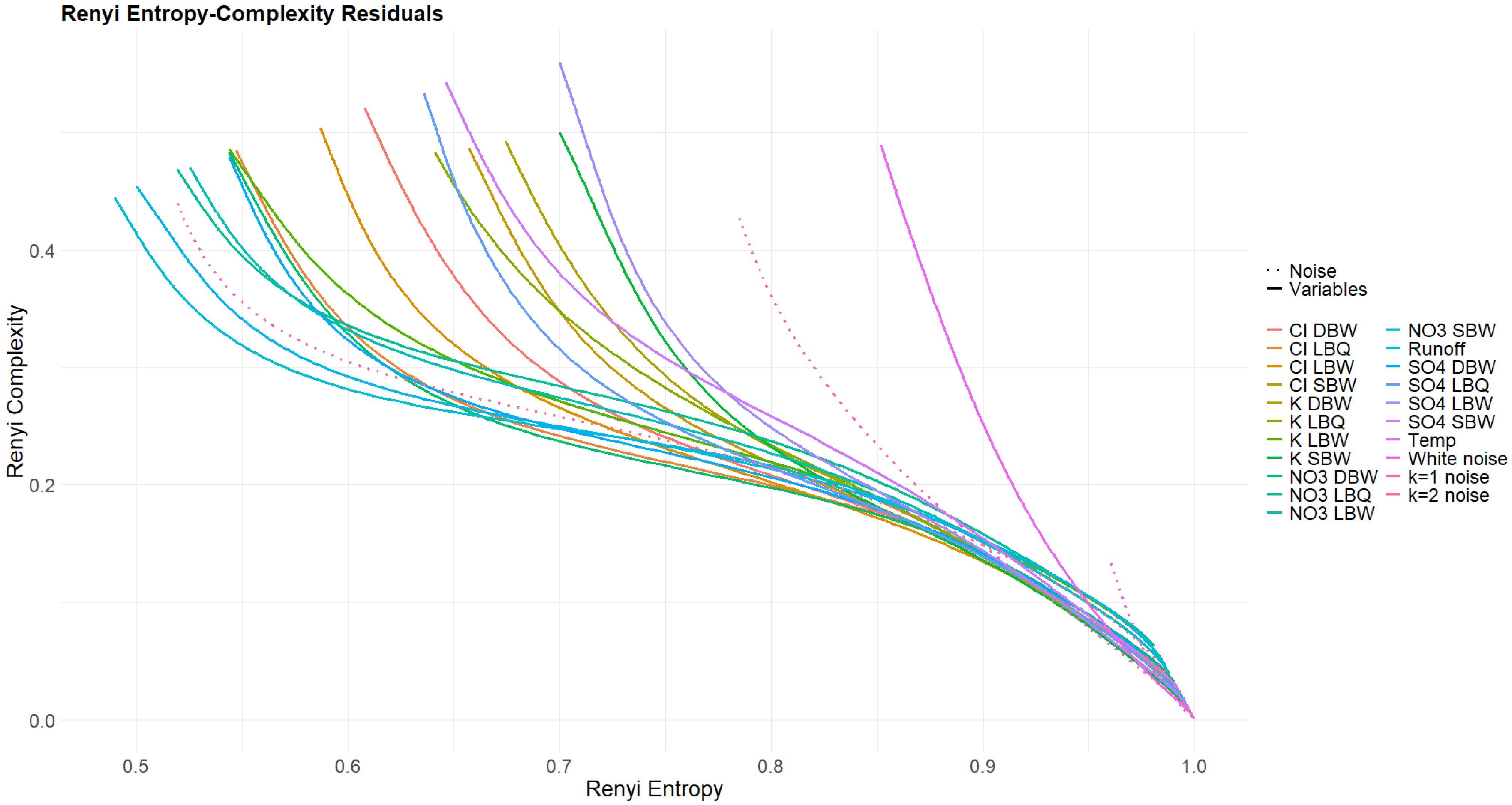


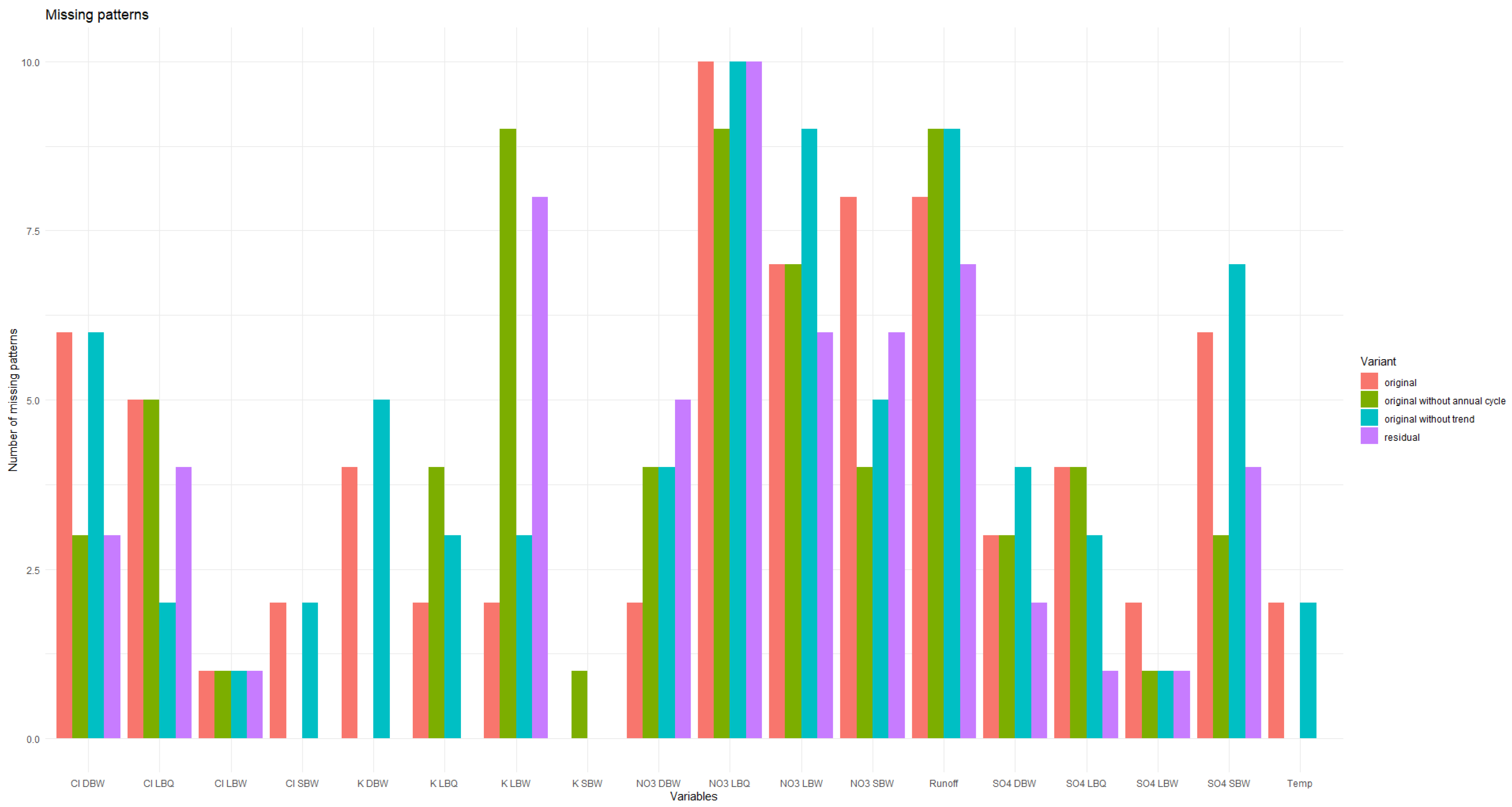
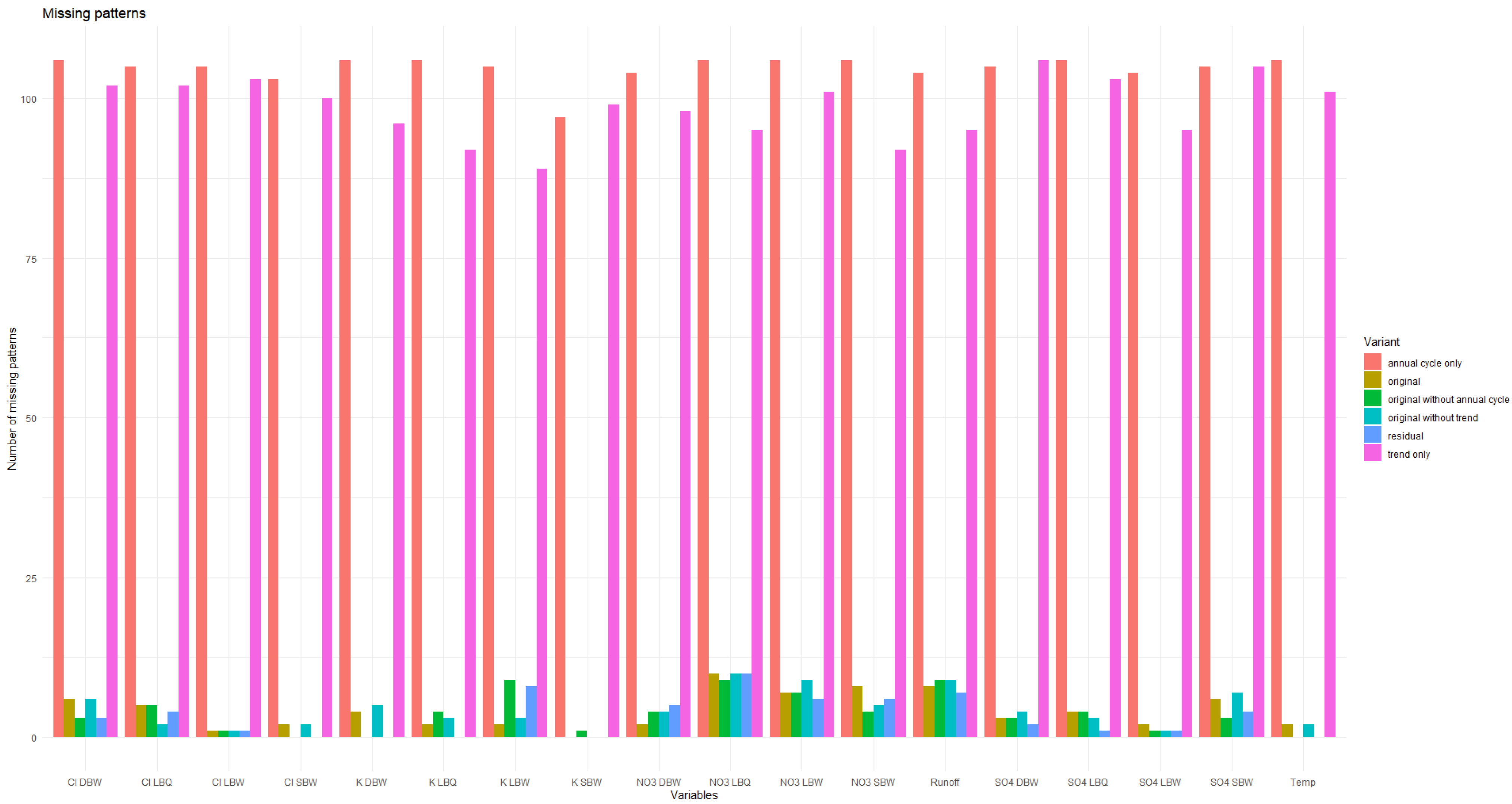
References
- Tang, L.; Lv, H.; Yang, F.; Yu, L. Complexity testing techniques for time series data: A comprehensive literature review. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 81, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Bariviera, A.; Belen Guercio, M.; Martinez, L.B.; Rosso, O.A. A permutation information theory tour through different interest rate maturities: The Libor case. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Mathematical Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 373, 20150119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Olivares, F.; Bariviera, A.F.; Rosso, O.A. A simple and fast representation space for classifying complex time series. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 381, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, F.; Rosso, O.A.; Matias, F.S.; Bressler, S.L.; Mirasso, C.R. A symbolic information approach to determine anticipated and delayed synchronization in neuronal circuit models. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 373, 20150110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, L.C.; Rosso, O.A.; Saco, P.M.; Ravetti, M.G. Analyzing complex networks evolution through Information Theory quantifiers. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 375, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Carpi, L.C.; Saco, P.M.; Gómez Ravetti, M.; Plastino, A.; Larrondo, H.A. Causality and the entropy-complexity plane: Robustness and missing ordinal patterns. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2012, 391, 42–55. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; Olivares, F.; Zunino, L.; De Micco, L.; Aquino, A.L.L.; Plastino, A.; Larrondo, H.A. Characterization of chaotic maps using the permutation Bandt-Pompe probability distribution. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martin, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Fuentes, M.A. Distinguishing noise from chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 154102. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; De Micco, L.; Plastino, A.; Larrondo, H.A. Info-quantifiers’ map-characterization revisited. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2010, 389, 4604–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Olivares, F.; Plastino, A. Noise versus chaos in a causal Fisher-Shannon plane. Pap. Phys. 2015, 7, 070006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farthing, M.W.; Ogden, F.L. Numerical Solution of Richards’ Equation: A Review of Advances and Challenges. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, H. Forest Dynamics, Growth, and Yield. In Forest Dynamics, Growth and Yield: From Measurement to Model; Pretzsch, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, N.; Astrup, R.; Antón-Fernández, C. PixSim: Enhancing high-resolution large-scale forest simulations. Softw. Impacts 2024, 21, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauhs, M. A model of ion-transport through a forested catchment at Lange Bramke, West-Germany. Geoderma 1986, 38, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forests, I. International Co-Operative Programme on Assessment and Monitoring of Air Pollution Effects on Forests. Available online: http://icp-forests.net/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Keller, R. Wald und Wasserhaushalt: Die Bedeutung neuer Versuche im Harz. Erdkunde 1953, 7, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Broomhead, D.S.; King, G.P. On the qualitative analysis of experimental dynamical systems. In Nonlinear Phenomena and Chaos; Sarkar, S., Ed.; Adam Hilger: Bristol, UK, 1986; pp. 113–144. [Google Scholar]
- Golyandina, N.; Korobeynikov, A. Basic Singular Spectrum Analysis and forecasting with R. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 71, 934–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobeynikov, A. Rssa: A Collection of Methods for Singular Spectrum Analysis; CRAN project 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Golyandina, N.; Osipov, E. The “Caterpillar”-SSA method for analysis of time series with missing values. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2007, 137, 2642–2653. [Google Scholar]
- Palus, M.; Novotna, D. Common oscillatory modes in geomagnetic activity, NAO index and surface air temperature records. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation Entropy: A Natural Complexity Measure for Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Generalized statistical complexity measures: Geometrical and analytical properties. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 369, 439–462. [Google Scholar]
- Zunino, L.; Olivares, F.; Ribeiro, H.V.; Rosso, O.A. Permutation Jensen-Shannon distance: A versatile and fast symbolic tool for complex time-series analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 045310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Porte, X.; Soriano, M.C. Identifying Ordinal Similarities at Different Temporal Scales. Entropy 2025, 26, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rényi, A. On Measures of Entropy and Information. In Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1961; Volume 1961, pp. 547–561. [Google Scholar]
- Tsallis, C. Possible generalization of Boltzmann-Gibbs statistics. J. Stat. Phys. 1988, 52, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, M.; Zunino, L.; Lenzi, E.K.; Mendes, R.S.; Ribeiro, H.V. Characterization of time series via Rényi complexity–entropy curves. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 498, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.V.; Jauregui, M.; Zunino, L.; Lenzi, E.K. Characterizing time series via complexity-entropy curves. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 062106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnopolski, M. On the relationship between the Hurst exponent, the ratio of the mean square successive difference to the variance, and the number of turning points. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 461, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnopolski, M. Analytical representation of Gaussian processes in the A-T plane. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 062144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, B.; Lacasa, L.; Ballesteros, F.; Luque, J. Horizontal visibility graphs: Exact results for random time series. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 046103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Sippel, S.; Rosso, O.A. Nonlinear dynamics of river runoff elucidated by horizontal visibility graphs. Chaos 2018, 28, 075520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyebe Fouda, J.S.A.; Koepf, W.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J.; Penzel, T. Complexity from ordinal pattern positioned slopes (COPPS). Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 181, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, J.M.; Zambrano, S.; Sanjuán, M.A.F. True and false forbidden patterns in deterministic and random dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 2007, 79, 50001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


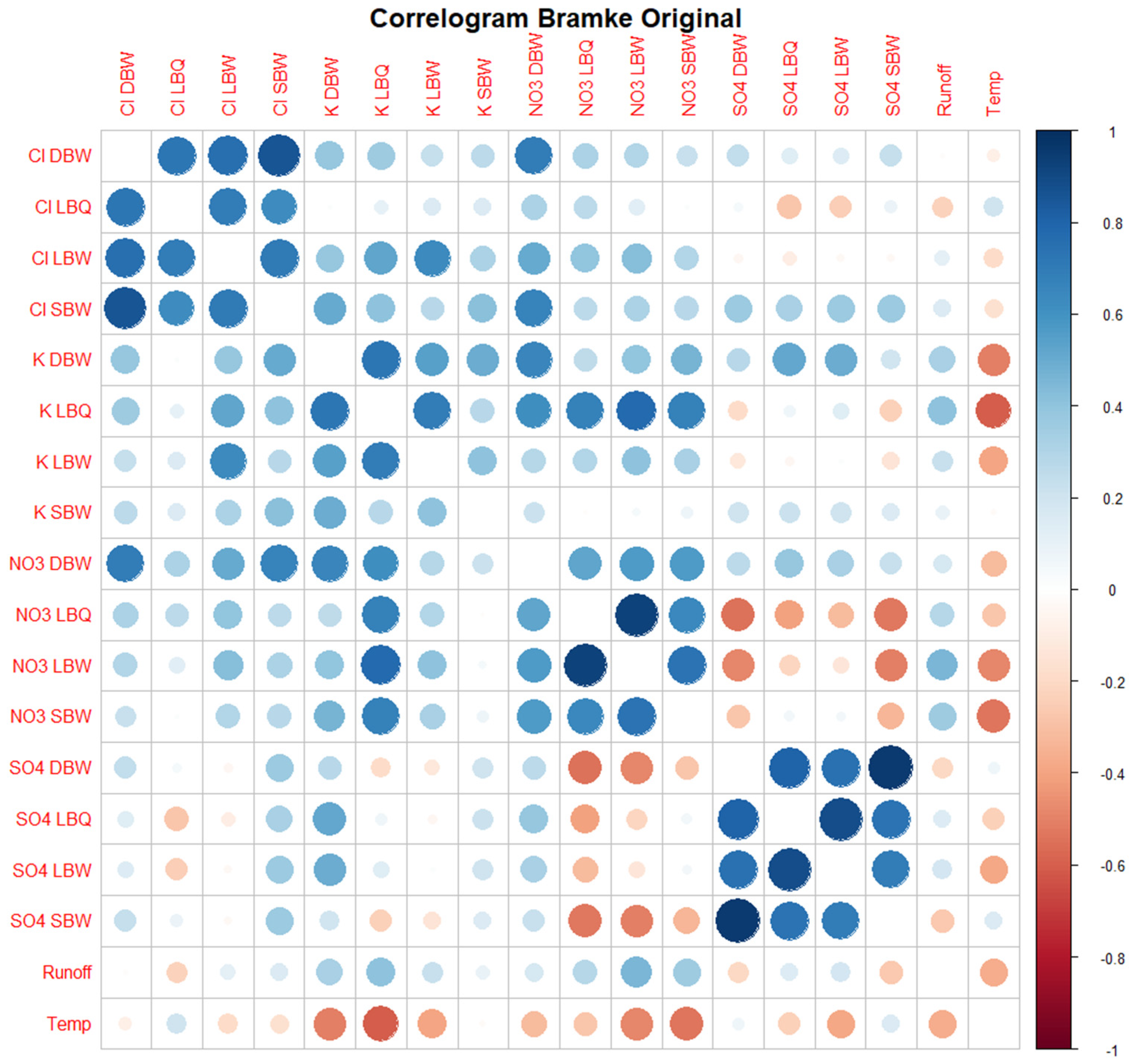
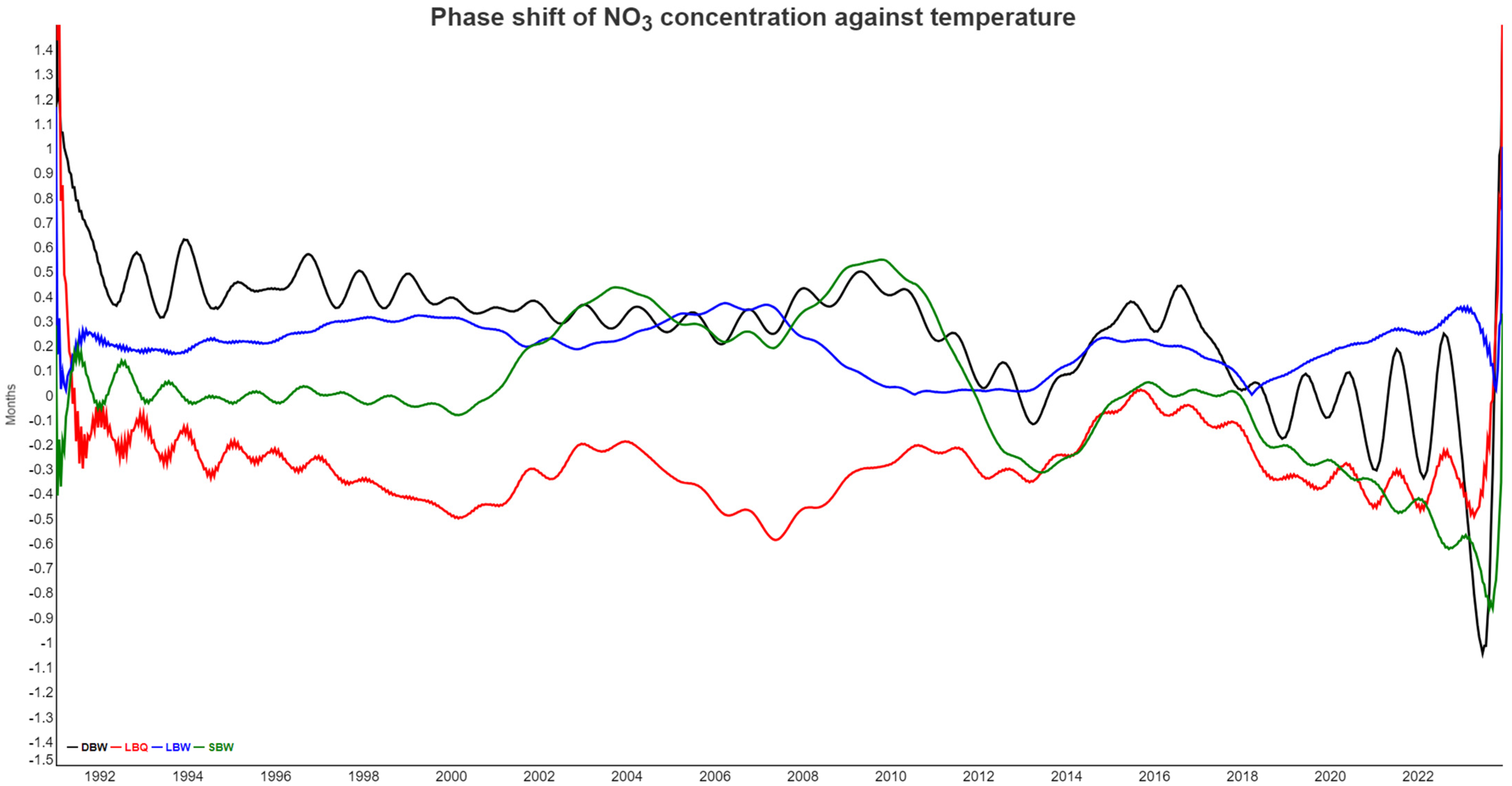
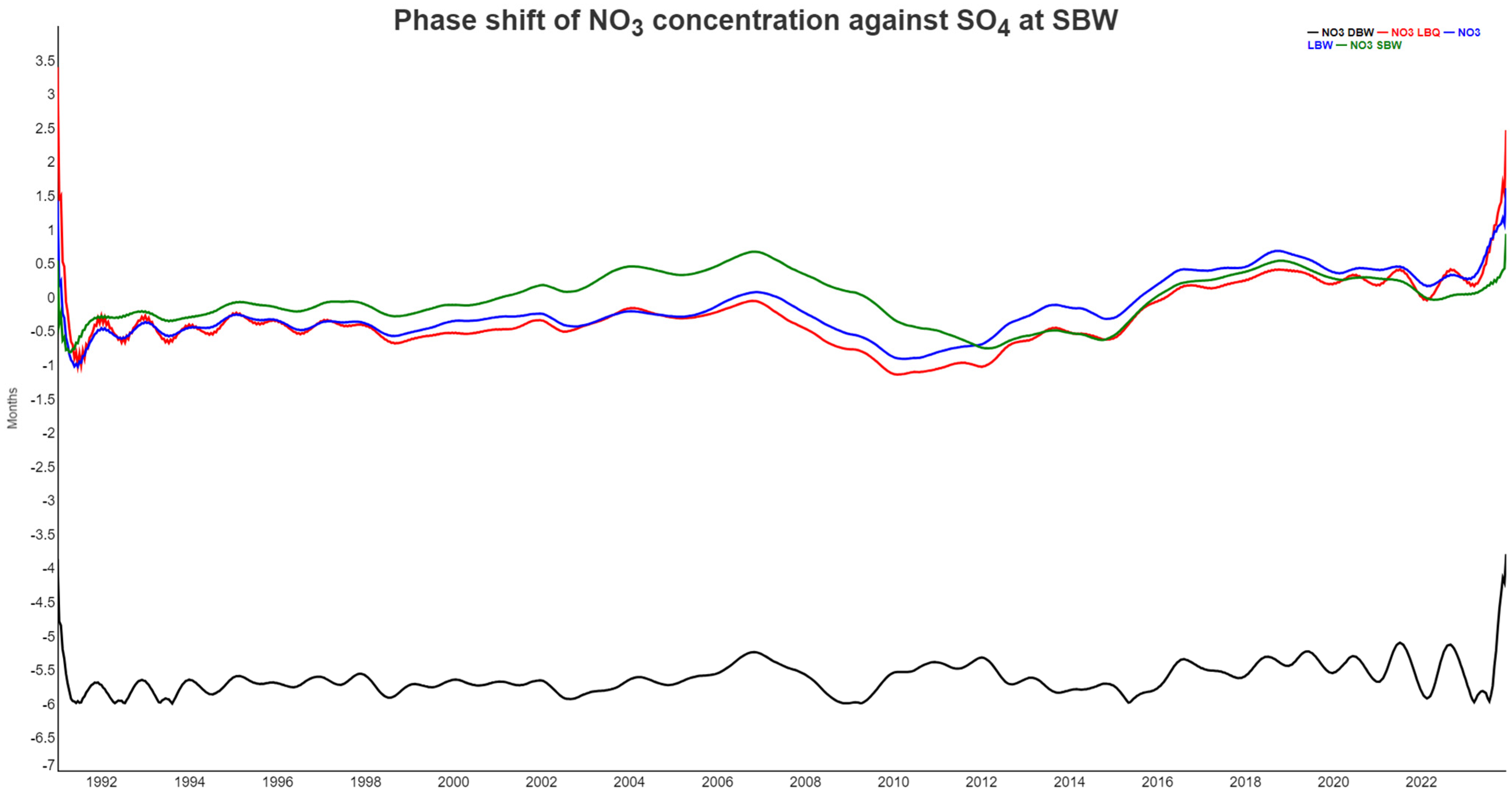
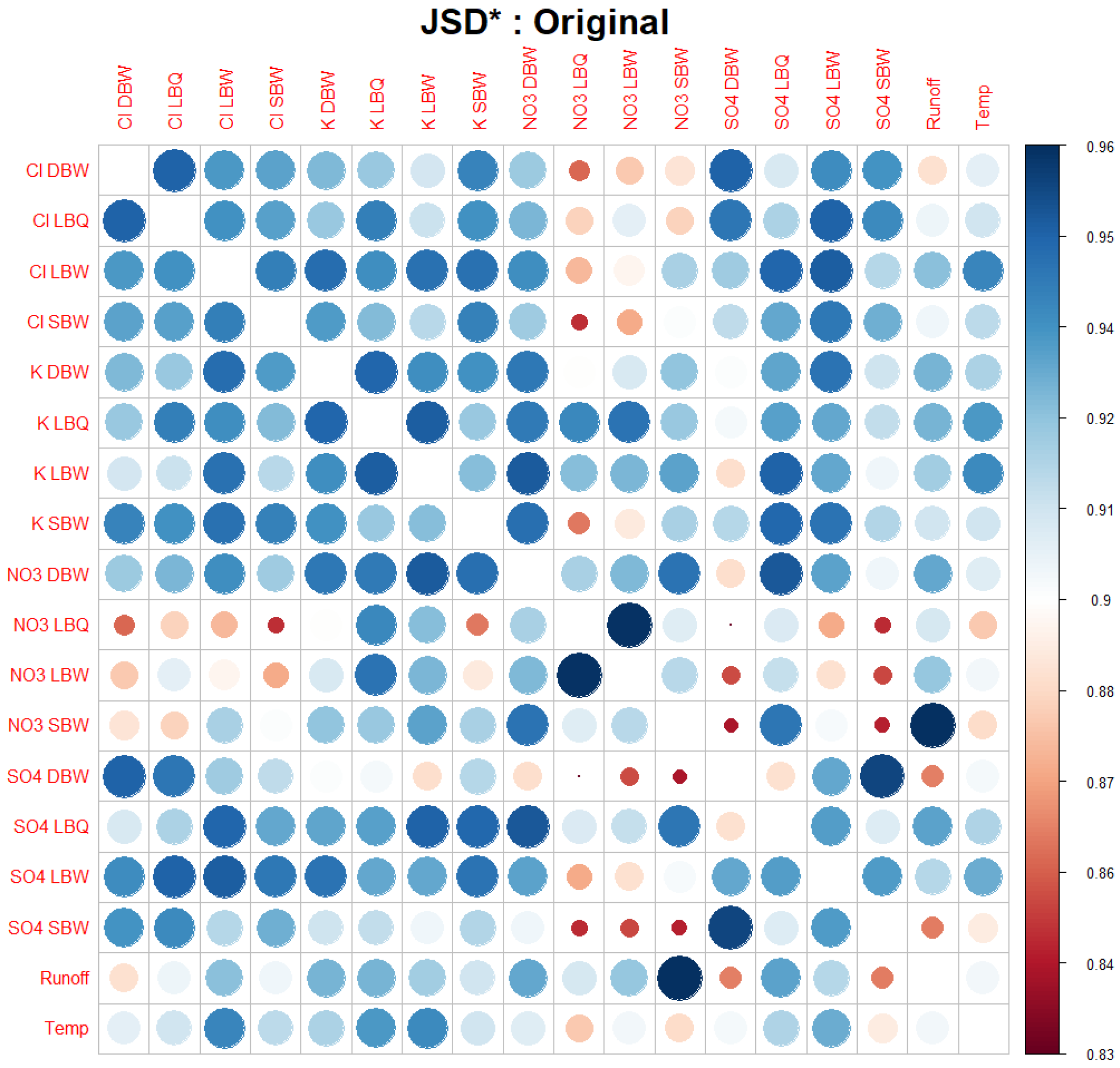

| Variable | Process | %Variance per Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Trend | 0.97 | |||
| Season | 80.99 | ||||
| DBW | LBQ | LBW | SBW | ||
| Runoff | Trend | - | - | 0.48 | - |
| Season | - | - | 20.69 | - | |
| Cl | Trend | 86.05 | 57.43 | 24.00 | 73.93 |
| Season | 4.42 | 5.57 | 19.15 | 4.90 | |
| K | Trend | 39.74 | 24.51 | 0.76 | 19.41 |
| Season | 31.84 | 46.11 | 45.89 | 4.48 | |
| NO3 | Trend | 72.06 | 74.16 | 45.41 | 20.59 |
| Season | 7.39 | 11.45 | 30.27 | 32.56 | |
| SO4 | Trend | 75.91 | 88.02 | 64.65 | 70.12 |
| Season | 3.17 | 4.46 | 15.33 | 6.68 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lange, H.; Hauhs, M. Complexity Analysis of Environmental Time Series. Entropy 2025, 27, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040381
Lange H, Hauhs M. Complexity Analysis of Environmental Time Series. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040381
Chicago/Turabian StyleLange, Holger, and Michael Hauhs. 2025. "Complexity Analysis of Environmental Time Series" Entropy 27, no. 4: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040381
APA StyleLange, H., & Hauhs, M. (2025). Complexity Analysis of Environmental Time Series. Entropy, 27(4), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040381