Distributed Data Classification with Coalition-Based Decision Trees and Decision Template Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel framework for distributed data classification that integrates coalition formation based on conflict analysis with decision tree induction and decision template fusion.
- An interpretable modeling approach, where decision trees are used instead of rule-based classifiers, enabling the representation of complex attribute dependencies while maintaining transparency.
- A robust fusion mechanism, which leverages decision templates to integrate predictions from multiple coalition-based models, improving classification accuracy and consistency across diverse data sources.
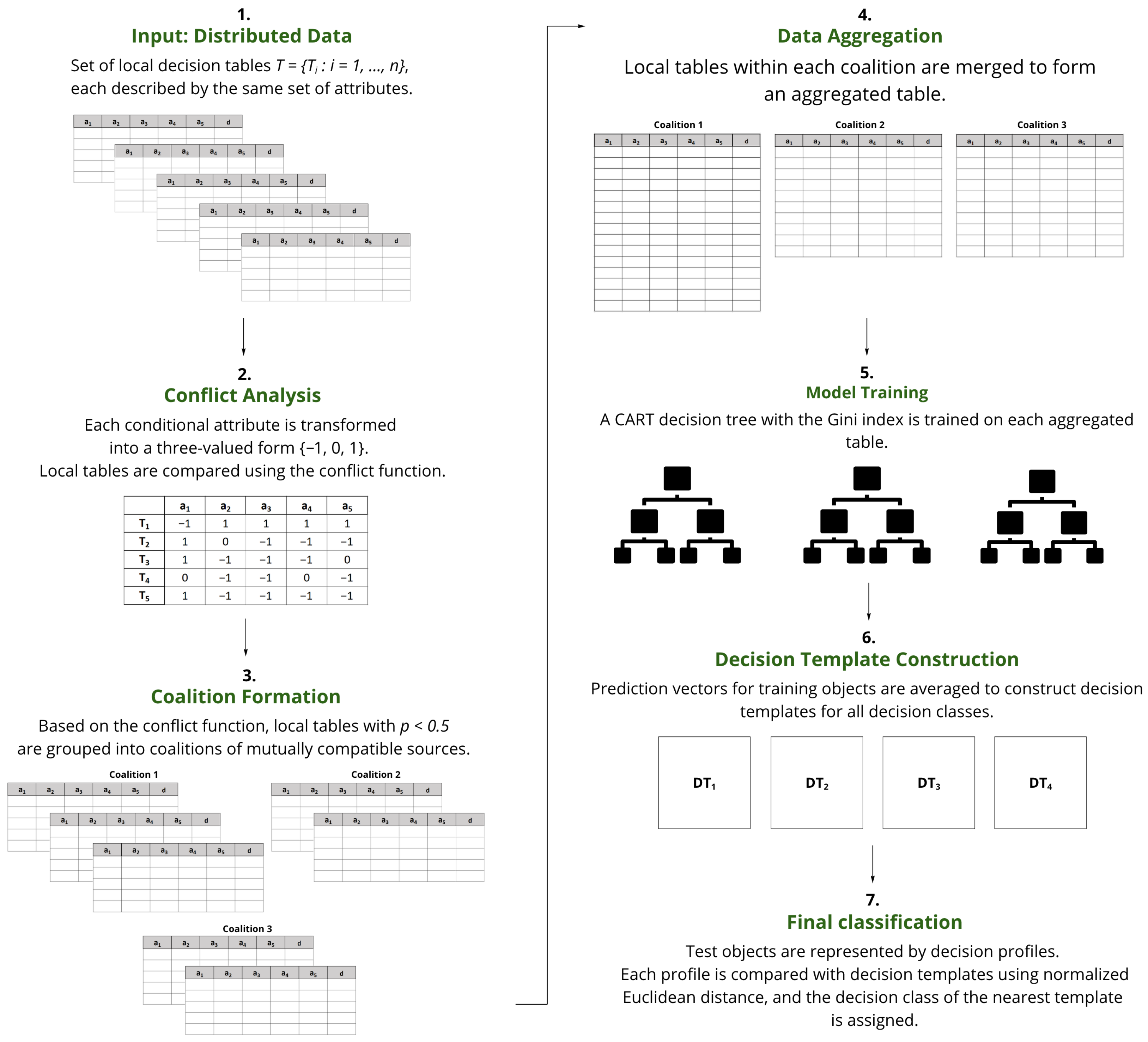
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Representation and Notation
2.2. Proposed Classification Framework
- Forming coalitions of sources using conflict analysis;
- Combining data within each coalition and training a decision tree model on the aggregated set;
- Deriving prediction vectors for training instances and generating a decision template corresponding to each decision class;
- Conducting the final classification, where prediction vectors of test samples are matched against the decision templates using normalized Euclidean distance.
| Algorithm 1 Pseudo-code of the proposed classification framework for distributed data |
Input: A set of local decision tables . Output: Final classification result for a test object . Creation of information system for each conditional attribute , define the function :
Form the information system . Coalition formation for each pair :
Data aggregation for each coalition :
Model training for each aggregated table :
Construction of decision templates for each training object x:
for each decision class i:
Final classification for a (new) test object : |
2.3. Illustrative Example
2.4. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Procedure
- Creation of coalitions among local decision tables;
- Training decision tree models using the data combined within each coalition;
- Construction of prediction vectors for training and test instances with reference to the built decision trees;
- Generation of class-specific decision templates;
- Final classification of test samples based on normalized Euclidean distance to the decision templates.
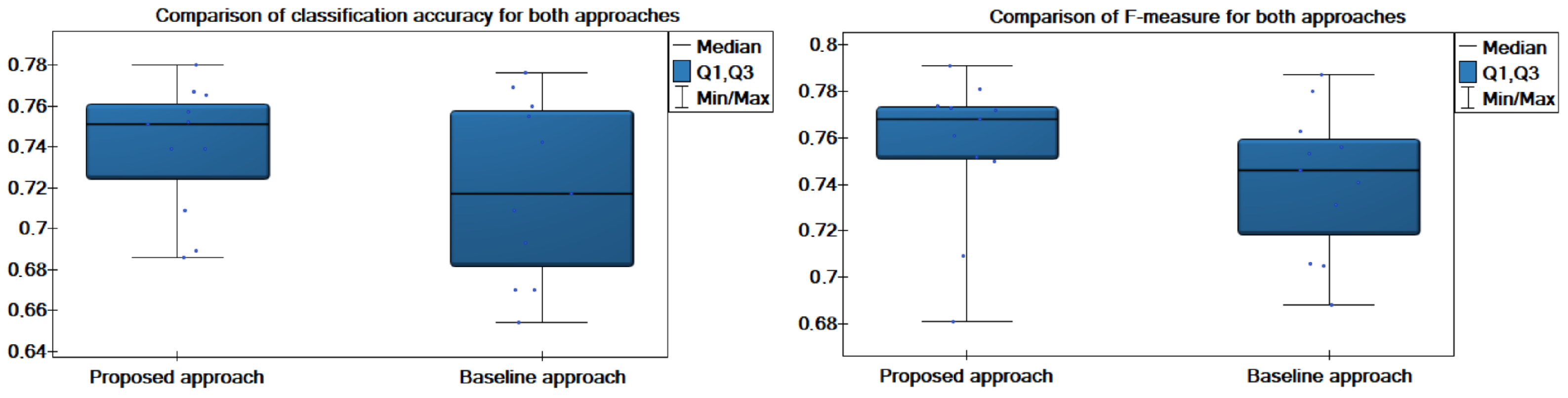
3. Results
3.1. Comparison with the Baseline Approach
3.2. Interpretability Analysis
- Balance Scale (7 local tables, 4 coalitions): {}, {}, {}, {};
- Vehicle Silhouettes (5 local tables, 4 coalitions): {}, {}, {}, {};
- Car Evaluation (7 local tables, 6 coalitions): {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}.
3.3. Comparison with Rule-Based Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pękala, B.; Kosior, D.; Rząsa, W.; Garwol, K.; Czuma, J. Unique Method for Prognosis of Risk of Depressive Episodes Using Novel Measures to Model Uncertainty Under Data Privacy. Entropy 2025, 27, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentkowska, U.; Gałka, W.; Mrukowicz, M.; Wojtowicz, A. Ensemble Classifier Based on Interval Modeling for Microarray Datasets. Entropy 2024, 26, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollaert, H.; Palangetić, M.; Cornelis, C.; Greco, S.; Słowiński, R. FRRI: A novel algorithm for fuzzy-rough rule induction. Inf. Sci. 2025, 686, 121362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdymyradov, K.; Moshkov, M. Deterministic and Nondeterministic Decision Trees for Recognition of Properties of Decision Rule Systems. In International Joint Conference on Rough Sets; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Faliszewski, P.; Gawron, G.; Kusek, B. Robustness of approval-based multiwinner voting rules. Rev. Econ. Des. 2025, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouyanfar, S.; Sadiq, S.; Yan, Y.; Tian, H.; Tao, Y.; Reyes, M.P.; Shyu, M.L.; Chen, S.C.; Iyengar, S.S. A survey on deep learning: Algorithms, techniques, and applications. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2018, 51, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Minku, L.L.; Gama, J.; Stefanowski, J.; Woźniak, M. Ensemble learning for data stream analysis: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2017, 37, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lv, H.; Chen, N. A survey on ensemble learning under the era of deep learning. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 5545–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyczkowski, K.; Pękala, B.; Szkoła, J.; Wilbik, A. Federated learning with uncertainty on the example of a medical data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Padua, Italy, 18–23 July 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, N.; Ashour, M.; Mashaly, M. Comprehensive review of federated learning challenges: A data preparation viewpoint. J. Big Data 2025, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valmadre, J. Hierarchical classification at multiple operating points. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 18034–18045. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, A.P. Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann. Math. Stat. 1967, 38, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, G. A Mathematical Theory of Evidence; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Z.; Martínez-García, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, L. A multisensor information fusion method for high-reliability fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Ding, L. Improved fuzzy Bayesian network-based risk analysis with interval-valued fuzzy sets and D-S evidence theory. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, R.; Guan, H.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y. Probabilistic transformation of basic probability assignment based on weighted visibility graph networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 184, 113821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, P.; Kennes, R. The transferable belief model. Artif. Intell. 1994, 66, 191–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Dezert, J.; Han, C.; Yang, Y. Is entropy enough to evaluate the probability transformation approach of belief function? In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Information Fusion, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 July 2010; IEEE: Edinburgh, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y. A new probability transformation based on the ordered visibility graph. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 44–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, Y.; Cheong, K.H. Probability transformation of mass function: A weighted network method based on the ordered visibility graph. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 105, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiroušek, R.; Shenoy, P.P. A new definition of entropy of belief functions in the Dempster–Shafer theory. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2018, 92, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. An inquiry into anatomy of conflicts. Inf. Sci. 1998, 109, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deja, R.; Ślęzak, D. Rough set theory in conflict analysis. In Annual Conference of the Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y. Three-way decision and granular computing. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2018, 103, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Ma, W.; Zhao, H. Rough set-based conflict analysis model and method over two universes. Inf. Sci. 2016, 372, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Deja, R.; Wakulicz-Deja, A. Hierarchical system in conflict scenarios constructed based on cluster analysis-inspired method for attribute significance determination. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 167, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncheva, L.I.; Bezdek, J.C.; Duin, R.P. Decision templates for multiple classifier fusion: An experimental comparison. Pattern Recognit. 2001, 34, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Kusztal, K. Integrating Conflict Analysis and Rule-Based Systems for Dispersed Data Classification. In Proceedings of the ICCS 2025 Conference, Singapore, 24–26 June 2025; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kusztal, K.; Przybyła-Kasperek, M. Coalition-Based Rule Induction and Decision Template Matching for Distributed Tabular Data. In Proceedings of the ISD 2025 Conference, Belgrade, Serbia, 3–5 September 2025; AIS eLibrary: Belgrade, Serbia, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyła-Kasperek, M.; Kusztal, K.; Addo, B.A. Dispersed Data Classification Model with Conflict Analysis and Parameterized Allied Relations. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 246, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mienye, I.D.; Jere, N. A survey of decision trees: Concepts, algorithms, and applications. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 86716–86727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aning, S.; Przybyła-Kasperek, M. Comparative study of twoing and entropy Criterion for decision tree classification of dispersed data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 207, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, J.P. Vehicle Recognition Using Rule Based Methods; Turing Institute: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bohanec, M.; Rajkovič, V. Knowledge acquisition and explanation for multi-attribute decision making. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Expert Systems and their Applications, Avignon, France, 30 May–3 June 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dua, D.; Graff, C. UCI Machine Learning Repository; University of California, School of Information and Computer Science: Irvine, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
| d | ||||
| 8 | 10 | online | 1 | |
| 9 | 10 | online | 1 | |
| 8 | 11 | retail | 2 | |
| d | ||||
| 9 | 11 | retail | 1 | |
| 8 | 12 | business | 2 | |
| 9 | 10 | retail | 2 | |
| d | ||||
| 13 | 7 | business | 1 | |
| 13 | 7 | retail | 1 | |
| 14 | 8 | business | 2 | |
| 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 |
| Dataset | # Local | Proposed Approach | Baseline Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tables | Acc/BAcc/Prec./Recall/F-m./G-Mean | Acc/BAcc/Prec./Recall/F-m./G-Mean | |
| Balance Scale | 7 | 0.739/0.627/0.819/0.739/0.772/0.816 | 0.670/0.633/0.866/0.670/0.741/0.791 |
| 9 | 0.686/0.644/0.867/0.686/0.752/0.801 | 0.654/0.676/0.893/0.654/0.731/0.788 | |
| 11 | 0.739/0.738/0.889/0.739/0.791/0.838 | 0.670/0.688/0.902/0.670/0.746/0.800 | |
| Vehicle Silhouettes | 5 | 0.752/0.745/0.751/0.752/0.750/0.832 | 0.693/0.675/0.688/0.693/0.688/0.791 |
| 7 | 0.709/0.691/0.714/0.709/0.709/0.804 | 0.709/0.696/0.710/0.709/0.705/0.804 | |
| 9 | 0.780/0.766/0.786/0.780/0.781/0.853 | 0.760/0.750/0.770/0.760/0.756/0.840 | |
| 11 | 0.689/0.673/0.682/0.689/0.681/0.787 | 0.717/0.698/0.707/0.717/0.706/0.807 | |
| Car Evaluation | 5 | 0.767/0.670/0.786/0.767/0.774/0.779 | 0.755/0.697/0.777/0.755/0.763/0.765 |
| 7 | 0.765/0.750/0.792/0.765/0.773/0.782 | 0.742/0.741/0.782/0.742/0.753/0.775 | |
| 9 | 0.751/0.702/0.783/0.751/0.761/0.775 | 0.769/0.769/0.810/0.769/0.780/0.811 | |
| 11 | 0.757/0.760/0.795/0.757/0.768/0.791 | 0.776/0.797/0.823/0.776/0.787/0.822 |
| Dataset | # Local Tables | Proposed Approach | Baseline Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balance Scale | 7 | 1.975 | 3.555 |
| 9 | 2.980 | 4.077 | |
| 11 | 2.678 | 5.003 | |
| Vehicle Silhouettes | 5 | 3.181 | 3.889 |
| 7 | 3.262 | 5.211 | |
| 9 | 3.327 | 6.400 | |
| 11 | 2.848 | 7.747 | |
| Car Evaluation | 5 | 5.756 | 6.951 |
| 7 | 8.209 | 9.213 | |
| 9 | 9.367 | 11.977 | |
| 11 | 10.904 | 14.278 |
| Proposed Approach | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Template | Local Model | p(B) | p(L) | p(R) |
| 0.588 | 0.235 | 0.176 | ||
| 0.206 | 0.529 | 0.265 | ||
| 0.294 | 0.235 | 0.471 | ||
| 0.235 | 0.382 | 0.382 | ||
| 0.030 | 0.950 | 0.020 | ||
| 0.055 | 0.806 | 0.139 | ||
| 0.134 | 0.776 | 0.090 | ||
| 0.050 | 0.866 | 0.085 | ||
| 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.955 | ||
| 0.054 | 0.153 | 0.792 | ||
| 0.134 | 0.079 | 0.787 | ||
| 0.084 | 0.104 | 0.812 | ||
| Baseline Approach | ||||
| Decision Template | Local Model | p(B) | p(L) | p(R) |
| 0.206 | 0.529 | 0.265 | ||
| 0.324 | 0.324 | 0.353 | ||
| 0.235 | 0.382 | 0.382 | ||
| 0.324 | 0.382 | 0.294 | ||
| 0.235 | 0.265 | 0.500 | ||
| 0.265 | 0.529 | 0.206 | ||
| 0.294 | 0.235 | 0.471 | ||
| 0.055 | 0.806 | 0.139 | ||
| 0.104 | 0.761 | 0.134 | ||
| 0.050 | 0.866 | 0.085 | ||
| 0.060 | 0.871 | 0.070 | ||
| 0.040 | 0.701 | 0.259 | ||
| 0.060 | 0.886 | 0.055 | ||
| 0.134 | 0.776 | 0.090 | ||
| 0.054 | 0.153 | 0.792 | ||
| 0.069 | 0.114 | 0.817 | ||
| 0.084 | 0.104 | 0.812 | ||
| 0.074 | 0.084 | 0.842 | ||
| 0.099 | 0.030 | 0.871 | ||
| 0.059 | 0.158 | 0.782 | ||
| 0.134 | 0.079 | 0.787 | ||
| Proposed Approach | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Template | Local Model | p(Bus) | p(opel) | p(saab) | p(van) |
| 0.918 | 0.014 | 0.041 | 0.027 | ||
| 0.856 | 0.027 | 0.110 | 0.007 | ||
| 0.836 | 0.075 | 0.041 | 0.048 | ||
| 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.062 | 0.041 | ||
| 0.043 | 0.713 | 0.189 | 0.055 | ||
| 0.085 | 0.591 | 0.268 | 0.055 | ||
| 0.018 | 0.530 | 0.372 | 0.079 | ||
| 0.043 | 0.585 | 0.341 | 0.030 | ||
| 0.053 | 0.267 | 0.600 | 0.080 | ||
| 0.053 | 0.287 | 0.580 | 0.080 | ||
| 0.053 | 0.340 | 0.507 | 0.100 | ||
| 0.080 | 0.307 | 0.567 | 0.047 | ||
| 0.023 | 0.045 | 0.023 | 0.909 | ||
| 0.068 | 0.076 | 0.045 | 0.811 | ||
| 0.030 | 0.008 | 0.076 | 0.886 | ||
| 0.008 | 0.121 | 0.038 | 0.833 | ||
| Baseline Approach | |||||
| Decision Template | Local Model | p(Bus) | p(opel) | p(saab) | p(van) |
| 0.863 | 0.000 | 0.096 | 0.041 | ||
| 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.062 | 0.041 | ||
| 0.836 | 0.075 | 0.041 | 0.048 | ||
| 0.856 | 0.027 | 0.110 | 0.007 | ||
| 0.911 | 0.021 | 0.027 | 0.041 | ||
| 0.024 | 0.689 | 0.232 | 0.055 | ||
| 0.043 | 0.585 | 0.341 | 0.030 | ||
| 0.018 | 0.530 | 0.372 | 0.079 | ||
| 0.085 | 0.591 | 0.268 | 0.055 | ||
| 0.079 | 0.549 | 0.329 | 0.043 | ||
| 0.027 | 0.460 | 0.447 | 0.067 | ||
| 0.080 | 0.307 | 0.567 | 0.047 | ||
| 0.053 | 0.340 | 0.507 | 0.100 | ||
| 0.053 | 0.287 | 0.580 | 0.080 | ||
| 0.087 | 0.247 | 0.593 | 0.073 | ||
| 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.083 | 0.841 | ||
| 0.008 | 0.121 | 0.038 | 0.833 | ||
| 0.030 | 0.008 | 0.076 | 0.886 | ||
| 0.068 | 0.076 | 0.045 | 0.811 | ||
| 0.068 | 0.114 | 0.061 | 0.758 | ||
| Proposed Approach | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Template | Local Model | p(acc) | p(Good) | p(unacc) | p(vgood) |
| 0.704 | 0.019 | 0.277 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.692 | 0.017 | 0.280 | 0.011 | ||
| 0.652 | 0.017 | 0.314 | 0.017 | ||
| 0.599 | 0.041 | 0.346 | 0.015 | ||
| 0.599 | 0.043 | 0.325 | 0.033 | ||
| 0.665 | 0.032 | 0.281 | 0.022 | ||
| 0.229 | 0.510 | 0.219 | 0.042 | ||
| 0.219 | 0.552 | 0.208 | 0.021 | ||
| 0.104 | 0.549 | 0.285 | 0.062 | ||
| 0.292 | 0.458 | 0.229 | 0.021 | ||
| 0.188 | 0.469 | 0.240 | 0.104 | ||
| 0.104 | 0.490 | 0.240 | 0.167 | ||
| 0.093 | 0.010 | 0.890 | 0.007 | ||
| 0.097 | 0.009 | 0.882 | 0.011 | ||
| 0.077 | 0.009 | 0.896 | 0.018 | ||
| 0.119 | 0.019 | 0.845 | 0.017 | ||
| 0.103 | 0.014 | 0.870 | 0.014 | ||
| 0.135 | 0.005 | 0.836 | 0.024 | ||
| 0.122 | 0.000 | 0.278 | 0.600 | ||
| 0.022 | 0.044 | 0.278 | 0.656 | ||
| 0.022 | 0.067 | 0.144 | 0.767 | ||
| 0.311 | 0.044 | 0.267 | 0.378 | ||
| 0.000 | 0.222 | 0.156 | 0.622 | ||
| 0.111 | 0.233 | 0.167 | 0.489 | ||
| Baseline Approach | |||||
| Decision Template | Local Model | p(acc) | p(Good) | p(unacc) | p(vgood) |
| 0.599 | 0.041 | 0.346 | 0.015 | ||
| 0.558 | 0.024 | 0.392 | 0.026 | ||
| 0.665 | 0.032 | 0.281 | 0.022 | ||
| 0.550 | 0.056 | 0.394 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.654 | 0.071 | 0.268 | 0.007 | ||
| 0.617 | 0.098 | 0.285 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.599 | 0.043 | 0.325 | 0.033 | ||
| 0.292 | 0.458 | 0.229 | 0.021 | ||
| 0.271 | 0.458 | 0.271 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.104 | 0.490 | 0.240 | 0.167 | ||
| 0.208 | 0.479 | 0.271 | 0.042 | ||
| 0.271 | 0.521 | 0.125 | 0.083 | ||
| 0.229 | 0.444 | 0.243 | 0.083 | ||
| 0.188 | 0.469 | 0.240 | 0.104 | ||
| 0.119 | 0.019 | 0.845 | 0.017 | ||
| 0.083 | 0.006 | 0.901 | 0.009 | ||
| 0.135 | 0.005 | 0.836 | 0.024 | ||
| 0.164 | 0.015 | 0.812 | 0.008 | ||
| 0.112 | 0.030 | 0.849 | 0.009 | ||
| 0.133 | 0.015 | 0.837 | 0.014 | ||
| 0.103 | 0.014 | 0.870 | 0.014 | ||
| 0.311 | 0.044 | 0.267 | 0.378 | ||
| 0.178 | 0.222 | 0.289 | 0.311 | ||
| 0.111 | 0.233 | 0.167 | 0.489 | ||
| 0.178 | 0.000 | 0.289 | 0.533 | ||
| 0.311 | 0.044 | 0.133 | 0.511 | ||
| 0.200 | 0.111 | 0.156 | 0.533 | ||
| 0.000 | 0.222 | 0.156 | 0.622 | ||
| Dataset | # Local Tables | Best Rule Induction Method | Acc/BAcc/Prec./Recall/F-m./G-Mean | Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balance Scale | 7 | Exh/Gen | 0.745/0.742/0.890/0.745/0.795/0.841 | −0.006 |
| 9 | Exh/Gen | 0.686/0.681/0.856/0.686/0.745/0.798 | 0.000 | |
| 11 | Exh/Gen | 0.697/0.670/0.863/0.697/0.756/0.806 | +0.042 | |
| Vehicle Silhouettes | 5 | Exh | 0.713/0.700/0.711/0.713/0.706/0.803 | +0.039 |
| 7 | Exh | 0.701/0.686/0.697/0.701/0.693/0.796 | +0.008 | |
| 9 | Exh | 0.701/0.695/0.707/0.701/0.693/0.797 | +0.079 | |
| 11 | Gen | 0.701/0.690/0.706/0.701/0.696/0.796 | −0.012 | |
| Car Evaluation | 5 | Gen | 0.744/0.674/0.761/0.744/0.750/0.745 | +0.023 |
| 7 | Exh/Gen | 0.748/0.641/0.760/0.748/0.752/0.743 | +0.017 | |
| 9 | Exh/Gen | 0.765/0.726/0.786/0.765/0.772/0.774 | −0.014 | |
| 11 | Exh/Gen | 0.765/0.758/0.790/0.765/0.773/0.783 | −0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kusztal, K.; Przybyła-Kasperek, M. Distributed Data Classification with Coalition-Based Decision Trees and Decision Template Fusion. Entropy 2025, 27, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121205
Kusztal K, Przybyła-Kasperek M. Distributed Data Classification with Coalition-Based Decision Trees and Decision Template Fusion. Entropy. 2025; 27(12):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121205
Chicago/Turabian StyleKusztal, Katarzyna, and Małgorzata Przybyła-Kasperek. 2025. "Distributed Data Classification with Coalition-Based Decision Trees and Decision Template Fusion" Entropy 27, no. 12: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121205
APA StyleKusztal, K., & Przybyła-Kasperek, M. (2025). Distributed Data Classification with Coalition-Based Decision Trees and Decision Template Fusion. Entropy, 27(12), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121205







