Morphology, Polarization Patterns, Compression, and Entropy Production in Phase-Separating Active Dumbbell Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model and Methods
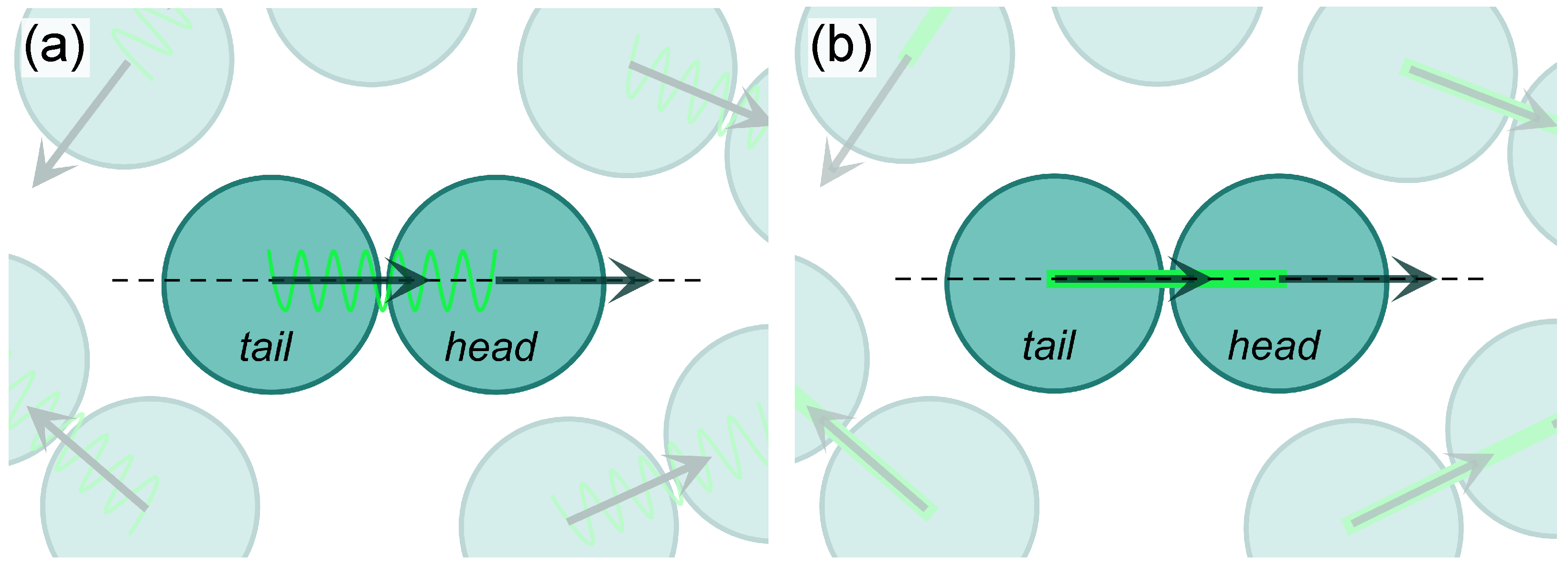
2.1. Model
- In the LJ case, we promote bead overlapping; thus, is set as a finite extensible non-linear elastic (FENE) force [76], which at the same time avoids unlimited bead separation (see Figure 1a). In symbols, FENE force is defined aswhere k is an elastic constant, is the maximum distance between beads, and , , with () when the i-the bead is tail (head).
2.2. Numerical Methods
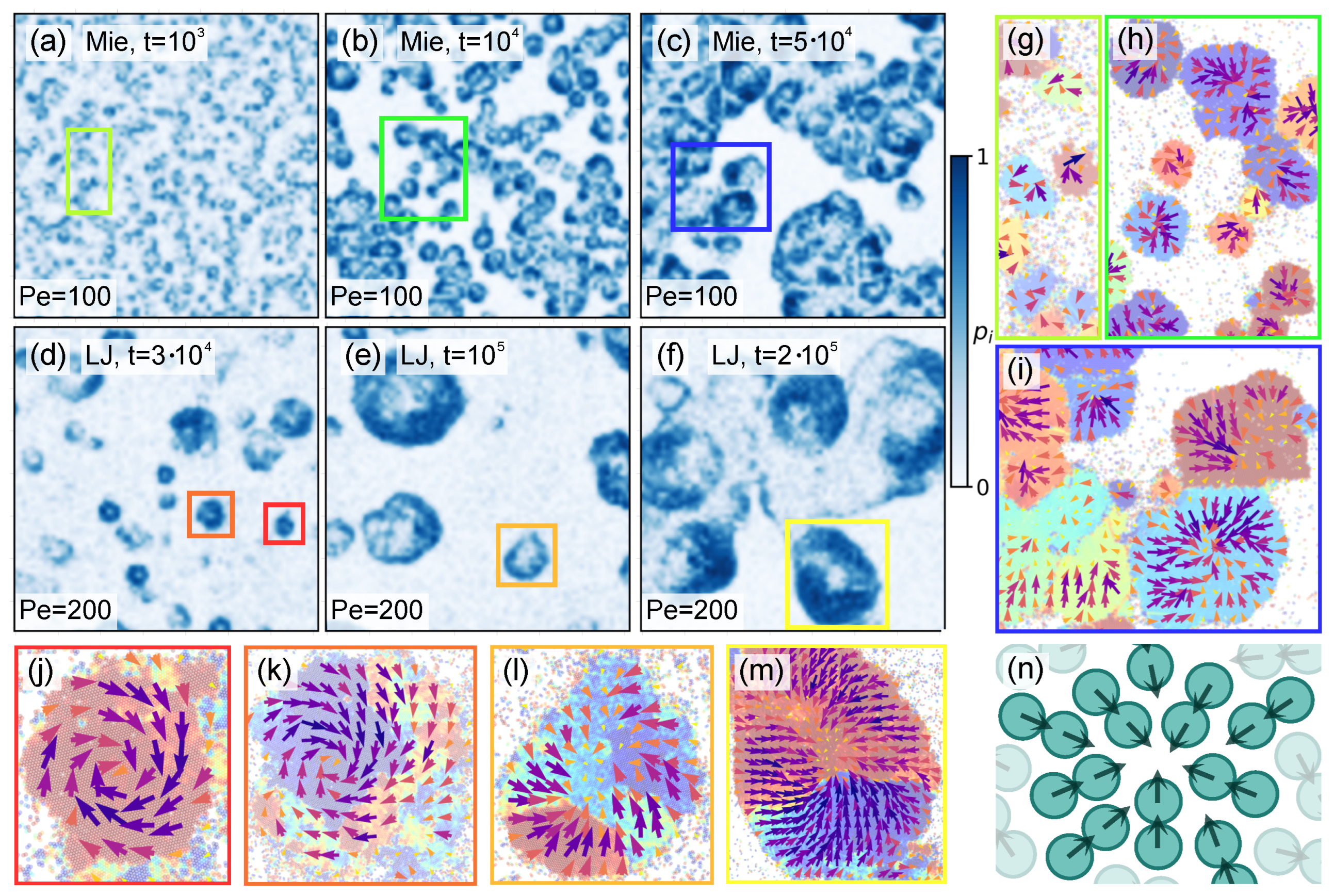
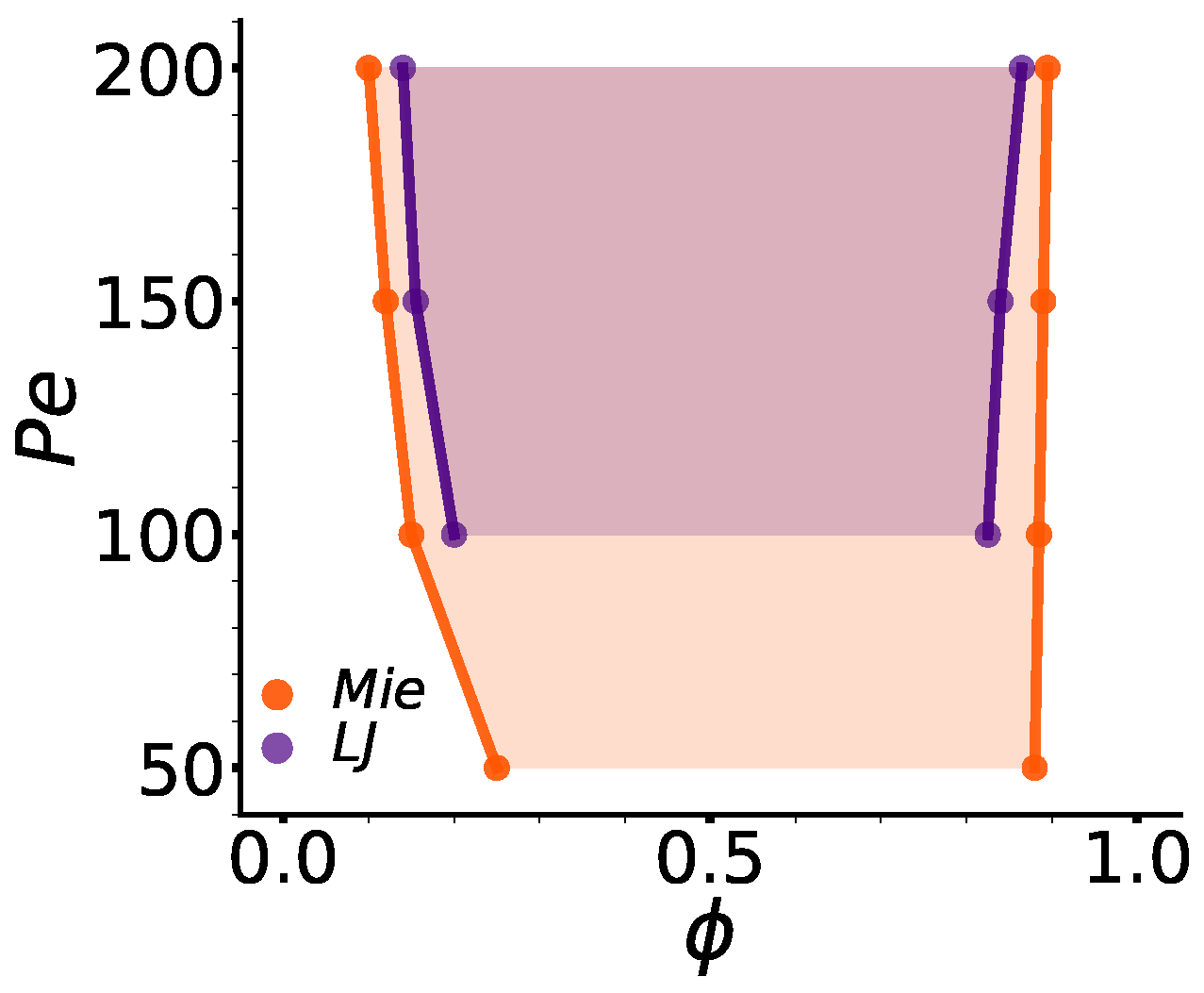
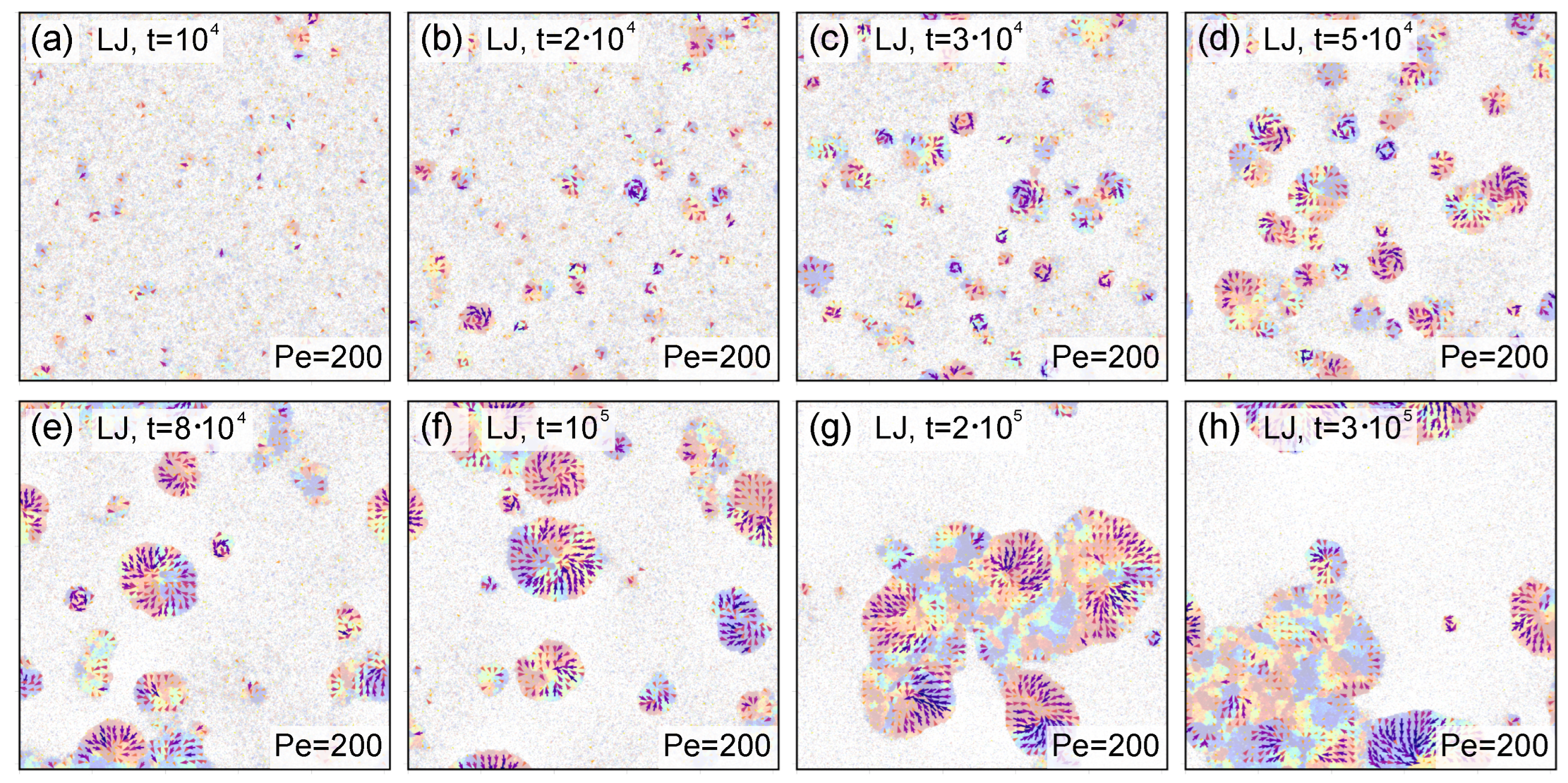
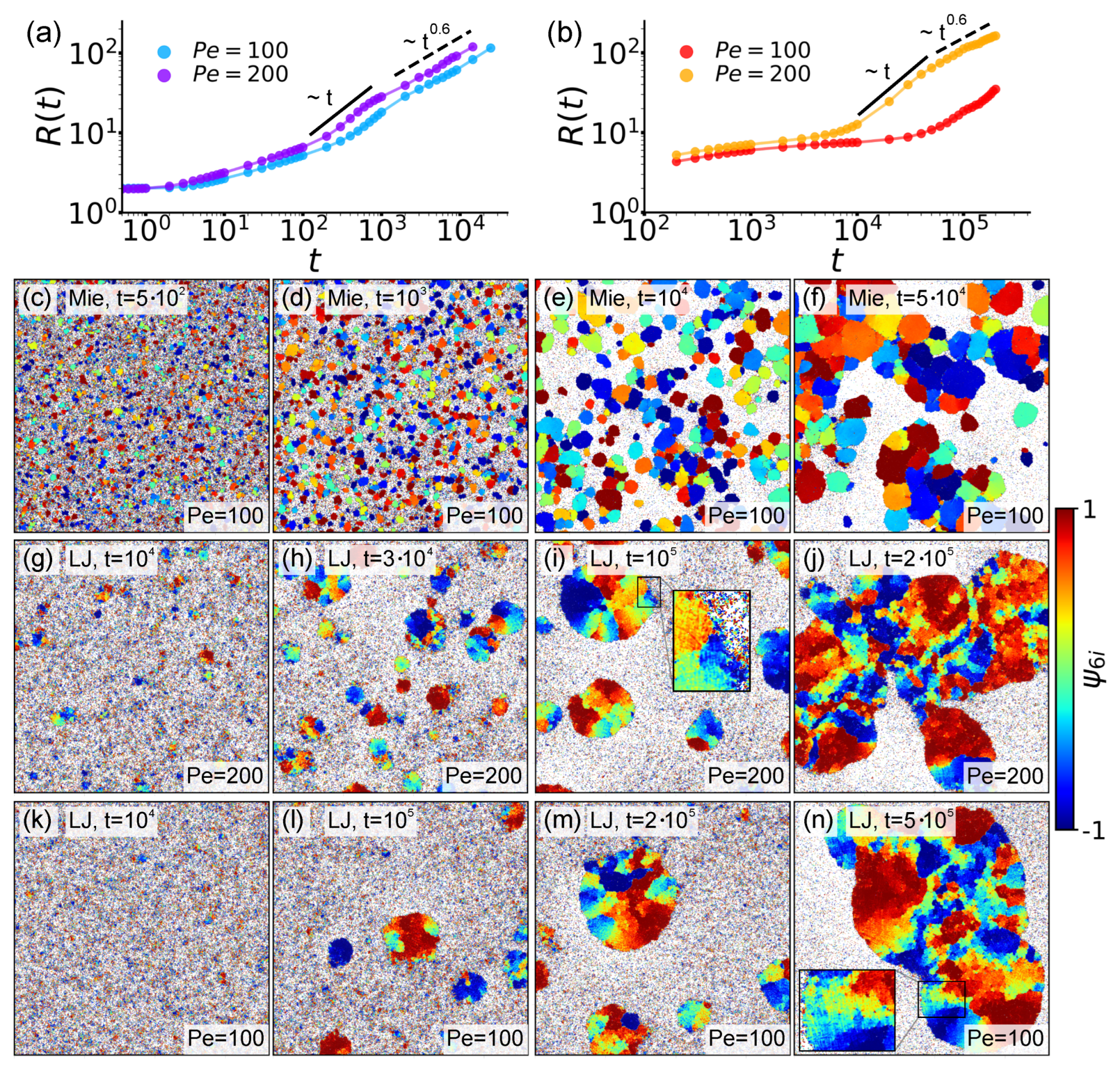
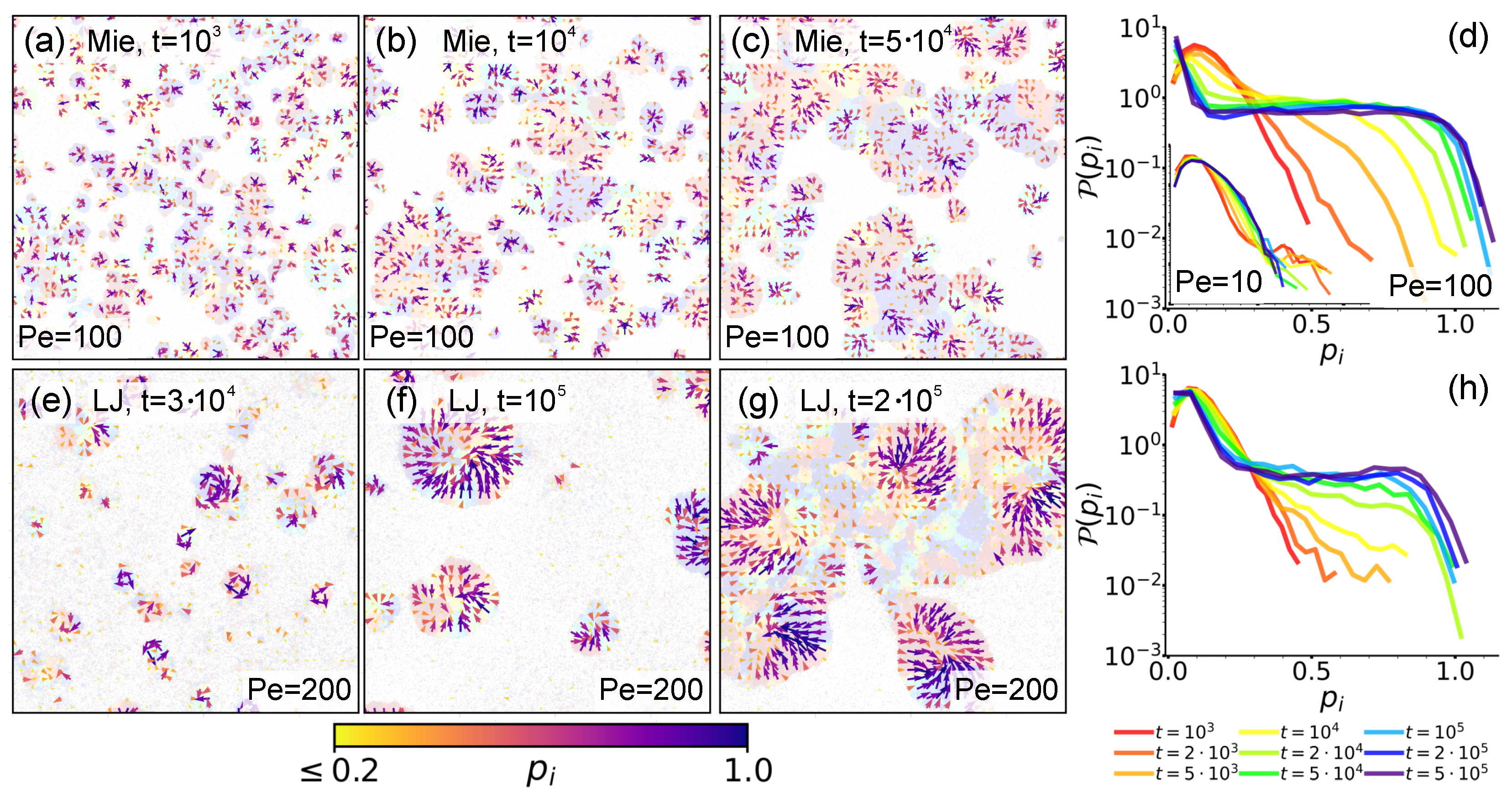
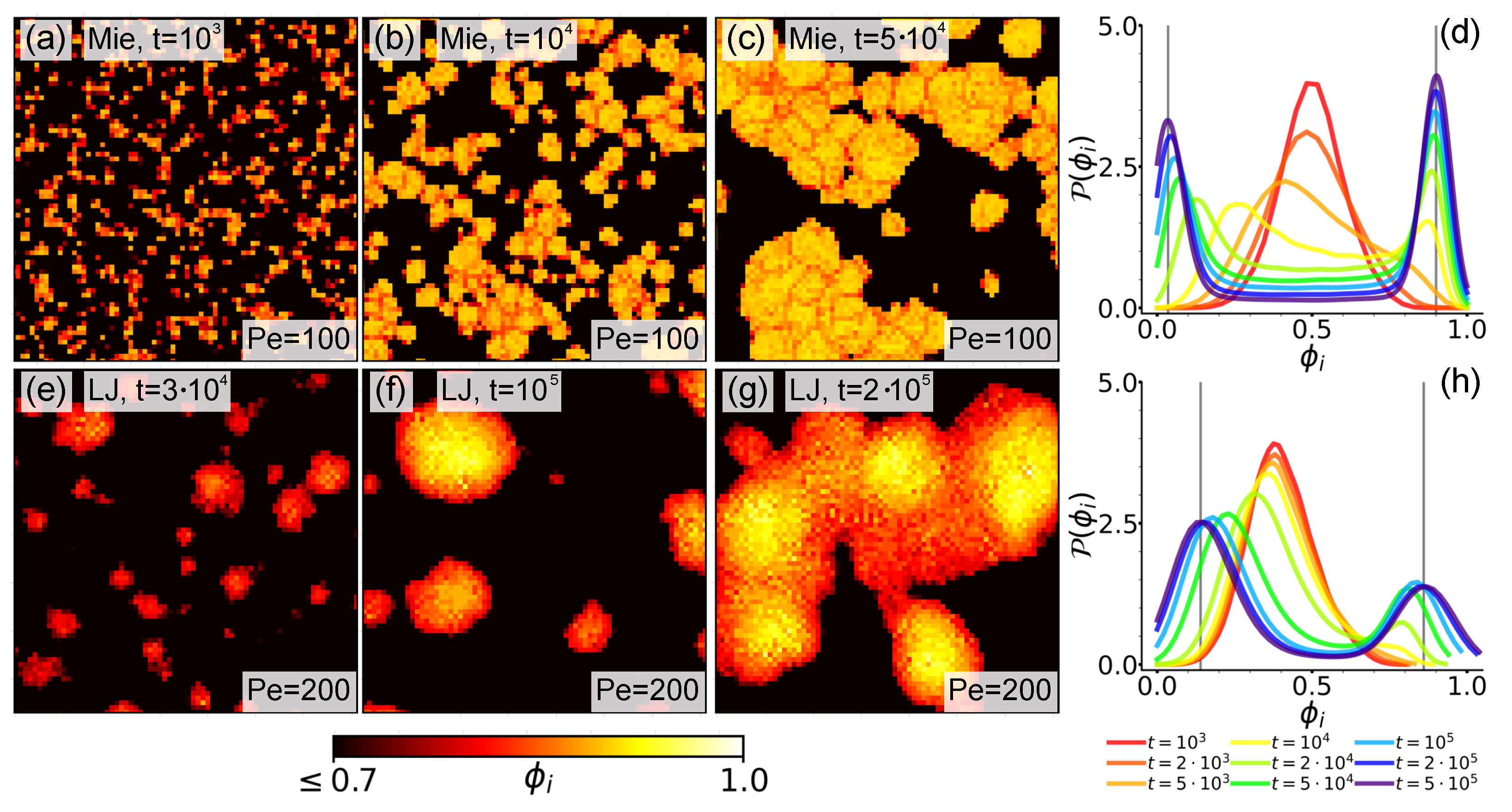
3. Overview of System Phenomenology: Domain Growth, Hexatic Order, Polarization Patterns, and Compression
3.1. Domain Growth, Hexatic Order, and Cluster Shape
3.2. Local Polarization Density Field and Polarization Patterns
3.3. Local Density Field and Compression
4. Local Density and Polarization Density Fields in Isolated Clusters
4.1. Topological Defects
4.2. Density Profiles

5. Entropy Production of Clusters and Aggregates
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Supplementary Figures

References
- Marchetti, M.C.; Joanny, J.F.; Ramaswamy, S.; Liverpool, T.B.; Prost, J.; Rao, M.; Simha, R.A. Hydrodynamics of soft active matter. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013, 85, 1143–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S. The Mechanics and Statistics of Active Matter. Annu. Rev. Condens. Mat. Phys. 2010, 1, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechinger, C.; Di Leonardo, R.; Löwen, H.; Reichhardt, C.; Volpe, G.; Volpe, G. Active particles in complex and crowded environments. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2016, 88, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needleman, D.; Dogic, Z. Active matter at the interface between materials science and cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mat. 2017, 2, 17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, É.; Marchetti, C.M. The statistical physics of active matter: From self-catalytic colloids to living cells. Physica A 2018, 504, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, J.K.; Hamner, W.; Hamner, W.M. Animal Groups in Three Dimensions: How Species Aggregate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.W. Flocks, herds, and schools: A distributed behavioral model. In Seminal Graphics: Pioneering Efforts That Shaped the Field, Volume 1; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicsek, T.; Zafeiris, A. Collective motion. Phys. Rep. 2012, 517, 71–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.C. E. coli in Motion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Yang, X.; Marchetti, M.C.; Manning, M.L. Motility-Driven Glass and Jamming Transitions in Biological Tissues. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.; Saglimbeni, F.; Sosa, V.C.; Di Leonardo, R.; Nath, B.; Puglisi, A. Thermodynamic Limits of Sperm Swimming Precision. PRX Life 2023, 1, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, W.F.; Kistler, K.C.; Olmeda, C.C.; Sen, A.; St. Angelo, S.K.; Cao, Y.; Mallouk, T.E.; Lammert, P.E.; Crespi, V.H. Catalytic nanomotors: Autonomous movement of striped nanorods. J. Americ. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13424–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestanian, R.; Liverpool, T.B.; Ajdari, A. Designing phoretic micro- and nano-swimmers. N. J. Phys. 2007, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Müller, A.H.E. Janus particles. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacci, J.; Sacanna, S.; Steinberg, A.S.; Pine, D.; Chaikin, P.M. Living Crystals of Light-Activated Colloidal Surfers. Science 2013, 339, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.P.; Be’er, A.; Florin, E.L.; Swinney, H.L. Collective motion and density fluctuations in bacterial colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13626–13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, T.; Chen, D.T.N.; DeCamp, S.J.; Heymann, M.; Dogic, Z. Spontaneous motion in hierarchically assembled active matter. Nature 2012, 491, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgeti, J.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G. Physics of microswimmers—Single particle motion and collective behavior: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 056601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, V.; Silberzan, P. Collective cell migration: A physics perspective. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 80, 076601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttinoni, I.; Bialké, J.; Kümmel, F.; Löwen, H.; Bechinger, C.; Speck, T. Dynamical Clustering and Phase Separation in Suspensions of Self-Propelled Colloidal Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 238301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J. Motility-Induced Phase Separation. Annu. Rev. Cond. Matt. Phys. 2015, 6, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialké, J.; Speck, T.; Löwen, H. Active colloidal suspensions: Clustering and phase behavior. J. Non-Crystall. Sol. 2015, 407, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradenigo, G.; Majumdar, S.N. A first-order dynamical transition in the displacement distribution of a driven run-and-tumble particle. J. Stat. Mech. 2019, 2019, 053206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, M.; Gonnella, G.; Suma, A.; Zamparo, M. Work Fluctuations for a Harmonically Confined Active Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Particle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 158302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gompper, G.; Stone, H.A.; Kurzthaler, C.; Saintillan, D.; Peruani, F.; Fedosov, D.A.; Auth, T.; Cottin-Bizonne, C.; Ybert, C.; Clément, E.; et al. The 2025 motile active matter roadmap. J. Phys. Cond. Matt. 2025, 37, 143501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toner, J.; Tu, Y.; Ramaswamy, S. Hydrodynamics and phases of flocks. Ann. Phys. 2005, 318, 170–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaté, H. Dry Aligning Dilute Active Matter. Annu. Rev. Cond. Matt. Phys. 2020, 11, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoluzzi, M.; Levis, D.; Pagonabarraga, I. From flocking to glassiness in dense disordered polar active matter. Comm. Phys. 2024, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, H.M.; Gachelin, J.; Douarche, C.; Auradou, H.; Clément, E. Turning Bacteria Suspensions into Superfluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 028301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lång, E.; Lång, A.; Blicher, P.; Rognes, T.; Dommersnes, P.G.; Bøe, S.O. Topology-guided polar ordering of collective cell migration. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, V.; Weber, C.; Semmrich, C.; Frey, E.; Bausch, A.R. Polar patterns of driven filaments. Nature 2010, 467, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, M.; Großmann, R.; Heidenreich, S.; Peruani, F. Self-Propelled Rods: Insights and Perspectives for Active Matter. Annu. Rev. Cond. Matt. Phys. 2020, 11, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagna, A.; Giardina, I. Bird Flocks as Condensed Matter. Annu. Rev. Cond. Matt. Phys. 2014, 5, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solon, A.P.; Chaté, H.; Tailleur, J. From Phase to Microphase Separation in Flocking Models: The Essential Role of Nonequilibrium Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 068101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginelli, F.; Peruani, F.; Bär, M.; Chaté, H. Large-Scale Collective Properties of Self-Propelled Rods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 184502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suma, A.; Gonnella, G.; Laghezza, G.; Lamura, A.; Mossa, A.; Cugliandolo, L.F. Dynamics of a homogeneous active dumbbell system. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 052130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyeux, M.; Bertin, E. Pressure of a gas of underdamped active dumbbells. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 032605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Bhuyan, P.J.; Chaudhuri, P.; Rao, M.; Dasgupta, C. Glassy swirls of active dumbbells. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 042605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopès, J.; Gompper, G.; Winkler, R.G. Alignment and propulsion of squirmer pusher-puller dumbbells. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 156, 194901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnella, G.; Lamura, A.; Suma, A. Phase segregation in a system of active dumbbells. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2014, 25, 1441004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.; Harder, J.; Valeriani, C.; Cacciuto, A. Micro-phase separation in two dimensional suspensions of self-propelled spheres and dumbbells. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugliandolo, L.F.; Digregorio, P.; Gonnella, G.; Suma, A. Phase Coexistence in Two-Dimensional Passive and Active Dumbbell Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 268002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatareddy, N.; Lin, S.T.; Maiti, P.K. Phase behavior of active and passive dumbbells. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, 034607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporusso, C.B.; Cugliandolo, L.F.; Digregorio, P.; Gonnella, G.; Suma, A. Phase separation kinetics and cluster dynamics in two-dimensional active dumbbell systems. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 4208–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digregorio, P.; Caporusso, C.B.; Carenza, L.M.; Gonnella, G.; Moretti, D.; Negro, G.; Semeraro, M.; Suma, A. Transverse Self-Propulsion Enhances the Aggregation of Active Dumbbells. Entropy 2025, 27, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, I.; Digregorio, P.; Cugliandolo, L.F.; Gonnella, G.; Suma, A. Active dumbbells: Dynamics and morphology in the coexisting region. Eur. Phys. J. E 2018, 41, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporusso, C.B.; Negro, G.; Suma, A.; Digregorio, P.; Carenza, L.N.; Gonnella, G.; Cugliandolo, L.F. Phase behaviour and dynamics of three-dimensional active dumbbell systems. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 923–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angheluta, L.; Lång, A.; Lång, E.; Bøe, S.O. Topological defects in polar active matter. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.03284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, K.; Joanny, J.F.; Jülicher, F.; Prost, J.; Sekimoto, K. Asters, Vortices, and Rotating Spirals in Active Gels of Polar Filaments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 078101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgeti, J.; Cates, M.E.; Marenduzzo, D. Defect hydrodynamics in 2D polar active fluids. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Popli, P.; Sarkar, S. Coarsening dynamics of aster defects in model polar active matter. Soft Matter 2024, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, P.C.; Kroy, K.; Holubec, V.; Cichos, F. Spontaneous vortex formation by microswimmers with retarded attractions. Nat. Comm. 2023, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, V.; Bausch, A.R. Topological defects and density fluctuations in collectively moving systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4488–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricard, A.; Caussin, J.B.; Das, D.; Savoie, C.; Chikkadi, V.; Shitara, K.; Chepizhko, O.; Peruani, F.; Saintillan, D.; Bartolo, D. Emergent vortices in populations of colloidal rollers. Nat. Commu. 2015, 6, 7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segerer, F.J.; Thüroff, F.; Alicia, P.A.; Frey, E.; Rädler, J.O. Emergence and Persistence of Collective Cell Migration on Small Circular Micropatterns. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 228102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamat, P.; Blanch-Mercader, C.; Pernollet, G.; Kruse, K.; Roux, A. Integer topological defects organize stresses driving tissue morphogenesis. Nat. Mat. 2022, 21, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogvoll, V.; Rønning, J.; Salvalaglio, M.; Angheluta, L. A unified field theory of topological defects and non-linear local excitations. Comput. Mat. 2023, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.D.J.G.; Bøe, S.O.; Dysthe, D.K.; Angheluta, L. Role of tissue fluidization and topological defects in epithelial tubulogenesis. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 023315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carenza, L.M.; Negro, G.; Digregorio, P.; Suma, A.; Gonnella, G. Arrested phase separation and chiral symmetry breaking in active dumbbells under shear. Phys. Rev. Res. 2025, 7, 043089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, M.; Cugliandolo, L.F.; Gonnella, G.; Tiribocchi, A. Phase Separation Kinetics in a Polar Active Field Model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabelow, L.; Bo, S.; Eichhorn, R. Irreversibility in Active Matter Systems: Fluctuation Theorem and Mutual Information. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 021009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, É.; Jack, R.L.; Cates, M.E. Irreversibility and Biased Ensembles in Active Matter: Insights from Stochastic Thermodynamics. Annu. Rev. Cond. Matt. Phys. 2022, 13, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, É.; Nardini, C.; Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J.; Visco, P.; van Wijland, F. How Far from Equilibrium Is Active Matter? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 038103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Klymko, K.; DeWeese, M.R. Entropy Production and Fluctuation Theorems for Active Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 258001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzonka, P.; Seifert, U. Entropy production of active particles and for particles in active baths. J. Phys. A 2017, 51, 01LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GrandPre, T.; Klymko, K.; Mandadapu, K.K.; Limmer, D.T. Entropy production fluctuations encode collective behavior in active matter. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 103, 012613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebon, R.; Robinson, J.F.; Speck, T. Thermodynamics of Active Matter: Tracking Dissipation across Scales. Phys. Rev. X 2025, 15, 021050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosato, E.; Prokopenko, M.; Spinney, R.E. Irreversibility and emergent structure in active matter. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 042613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borthne, Ø.L.; Fodor, É.; Cates, M.E. Time-reversal symmetry violations and entropy production in field theories of polar active matter. N. J. Phys. 2020, 22, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprini, L.; Löwen, H.; Marini, U.B.M. Inhomogeneous entropy production in active crystals with point imperfections. J. Phys. A 2023, 56, 465001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, A.; Neimand, E.D.; Corbett, D.; Pearce, D.J.G.; Ariel, G.; Yashunsky, V. Irreversibility and symmetry breaking in the creation and annihilation of defects in active living matter. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.15622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, M.; Negro, G.; Suma, A.; Corberi, F.; Gonnella, G. Entropy production of active Brownian particles going from liquid to hexatic and solid phases. Europhys. Lett. 2024, 148, 37001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütter, M. Configurational entropy of a finite number of dumbbells close to a wall. Eur. Phys. J. E 2022, 45, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard-Jones, J.E. Cohesion. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1931, 43, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, G. Zur kinetischen Theorie der einatomigen Körper. Ann. Phys. 1903, 316, 657–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner Jr, H.R. Kinetic theory and rheology of dilute suspensions of finitely extendible dumbbells. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1972, 11, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.C. Rattle: A “velocity” version of the shake algorithm for molecular dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Phys. 1983, 52, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandia National Laboratories. LAMMPS. Available online: https://www.lammps.org/#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Allen, M.P.; Tildesley, D.J. Computer Simulation of Liquids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, V.M.; Cates, M.E.; Pagonabarraga, I.; Desplat, J.C.; Blandon, P. Inertial effects in three-dimensional spinodal decomposition of a symmetric binary fluid mixture: A lattice Boltzmann study. J. Fluid Mech. 2001, 440, 147–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.P.; Krauth, W. Two-Step Melting in Two Dimensions: First-Order Liquid-Hexatic Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 155704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporusso, C.B.; Digregorio, P.; Levis, D.; Cugliandolo, L.F.; Gonnella, G. Motility-induced microphase and macrophase separation in a two-dimensional active Brownian particle system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 178004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjhung, E.; Nardini, C.; Cates, M.E. Cluster Phases and Bubbly Phase Separation in Active Fluids: Reversal of the Ostwald Process. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digregorio, P.; Levis, D.; Cugliandolo, L.F.; Gonnella, G.; Pagonabarraga, I. Unified analysis of topological defects in 2D systems of active and passive disks. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 566–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Statist. 1962, 33, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digregorio, P.; Levis, D.; Suma, A.; Cugliandolo, L.F.; Gonnella, G.; Pagonabarraga, I. 2D melting and motility induced phase separation in Active Brownian Hard Disks and Dumbbells. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1163, 012073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikin, P.M.; Lubensky, T.C. Principles of Condensed Matter Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scikit-Learn Developers. DBSCAN—Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise. 2025. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.DBSCAN.html (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- De Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals; Number 83 in Oxford Scholarship Online; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Marchetti, M.C. Hidden entropy production and work fluctuations in an ideal active gas. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 020604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, J.; Kafri, Y.; Tailleur, J.; van Wijland, F. Time irreversibility in active matter, from micro to macro. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2022, 4, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Baek, Y. Effects of the self-propulsion parity on the efficiency of a fuel-consuming active heat engine. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 024602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzonka, P.; Fodor, É.; Lohrmann, C.; Cates, M.E.; Seifert, U. Autonomous Engines Driven by Active Matter: Energetics and Design Principles. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 041032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keta, Y.E.; Fodor, É.; van Wijland, F.; Cates, M.E.; Jack, R.L. Collective motion in large deviations of active particles. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 103, 022603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, E.; Cates, M.E. Active engines: Thermodynamics moves forward. EPL 2021, 134, 10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarantoni, P.; Cagnetta, F.; Corberi, F.; Gonnella, G.; Suma, A. Work fluctuations of self-propelled particles in the phase separated state. J. Phys. A 2020, 53, 36LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; O’Byrne, J.; Cates, M.E.; Fodor, É.; Nardini, C.; Tailleur, J.; van Wijland, F. Statistical mechanics of active Ornstein-Uhlenbeck particles. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 103, 032607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.J.; Reichhardt, C.; McCloskey, M.; Zieve, R.J. Effect of grain anisotropy on ordering, stability and dynamics in granular systems. Europhys. Lett. 2002, 57, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbode, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Liddell, C.M.; Cohen, I. Restricted Dislocation Motion in Crystals of Colloidal Dimer Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 058302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbode, S.J.; Agarwal, U.; Ong, D.C.; Liddell, C.M.; Escobedo, F.; Cohen, I. Glassy Dislocation Dynamics in 2D Colloidal Dimer Crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 078301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbode, S.J.; Ong, D.C.; Liddell, C.M.; Cohen, I. Dislocations and vacancies in two-dimensional mixed crystals of spheres and dimers. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 041404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichhardt, C.; Olson Reichhardt, C.J. Aspects of jamming in two-dimensional athermal frictionless systems. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2932–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carenza, L.M.; Caporusso, C.B.; Digregorio, P.; Suma, A.; Gonnella, G.; Semeraro, M. Morphology, Polarization Patterns, Compression, and Entropy Production in Phase-Separating Active Dumbbell Systems. Entropy 2025, 27, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111105
Carenza LM, Caporusso CB, Digregorio P, Suma A, Gonnella G, Semeraro M. Morphology, Polarization Patterns, Compression, and Entropy Production in Phase-Separating Active Dumbbell Systems. Entropy. 2025; 27(11):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111105
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarenza, Lucio Mauro, Claudio Basilio Caporusso, Pasquale Digregorio, Antonio Suma, Giuseppe Gonnella, and Massimiliano Semeraro. 2025. "Morphology, Polarization Patterns, Compression, and Entropy Production in Phase-Separating Active Dumbbell Systems" Entropy 27, no. 11: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111105
APA StyleCarenza, L. M., Caporusso, C. B., Digregorio, P., Suma, A., Gonnella, G., & Semeraro, M. (2025). Morphology, Polarization Patterns, Compression, and Entropy Production in Phase-Separating Active Dumbbell Systems. Entropy, 27(11), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111105





