Violations of Hyperscaling in Finite-Size Scaling above the Upper Critical Dimension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Finite-Size Scaling
- At a fixed T in the limit we have so
- At L fixed and , is not singular because there can be no sharp transition in a finite system. This means that the behavior of for should compensate for the divergence of , i.e.,where we used Equation (1).
- Replace the second term in Equation (11) by , i.e.,
- My preferred solution is to replace Equation (10) bywhere indicates the spin which is in every direction away from i, i.e., as far as possible from i. The second term is exponentially small in above , while below it tends to cancel the first term. Unfortunately, this definition of in a finite system has not been adopted.
- Ignore the second term in Equations (10) and (11) completely. Typically, one also neglects the factor of since this varies only slightly in the vicinity of the transition. We will, therefore, define the correlation functionWell above this is the susceptibility, apart from the factor of , but below the dominant part varies as N times the magnetization squared, i.e., where is the order parameter exponent defined by for . For this part is canceled by the second term in Equation (11). From Equation (7) we writewhere we used the scaling relationin which the exponent characterizes the power-law decay of correlations with distance at the critical point. The scaling function must have the following limiting behaviors:where, in the last line, we used the following “hyperscaling” scaling relationHyperscaling relations, which are the main focus of this volume, give connections between exponents which involve the space dimension d.
3. Renormalization Group Justification for Finite-Size Scaling
4. Finite-Size Scaling above the Upper Critical Dimension
4.1. Dangerous Irrelevant Variables
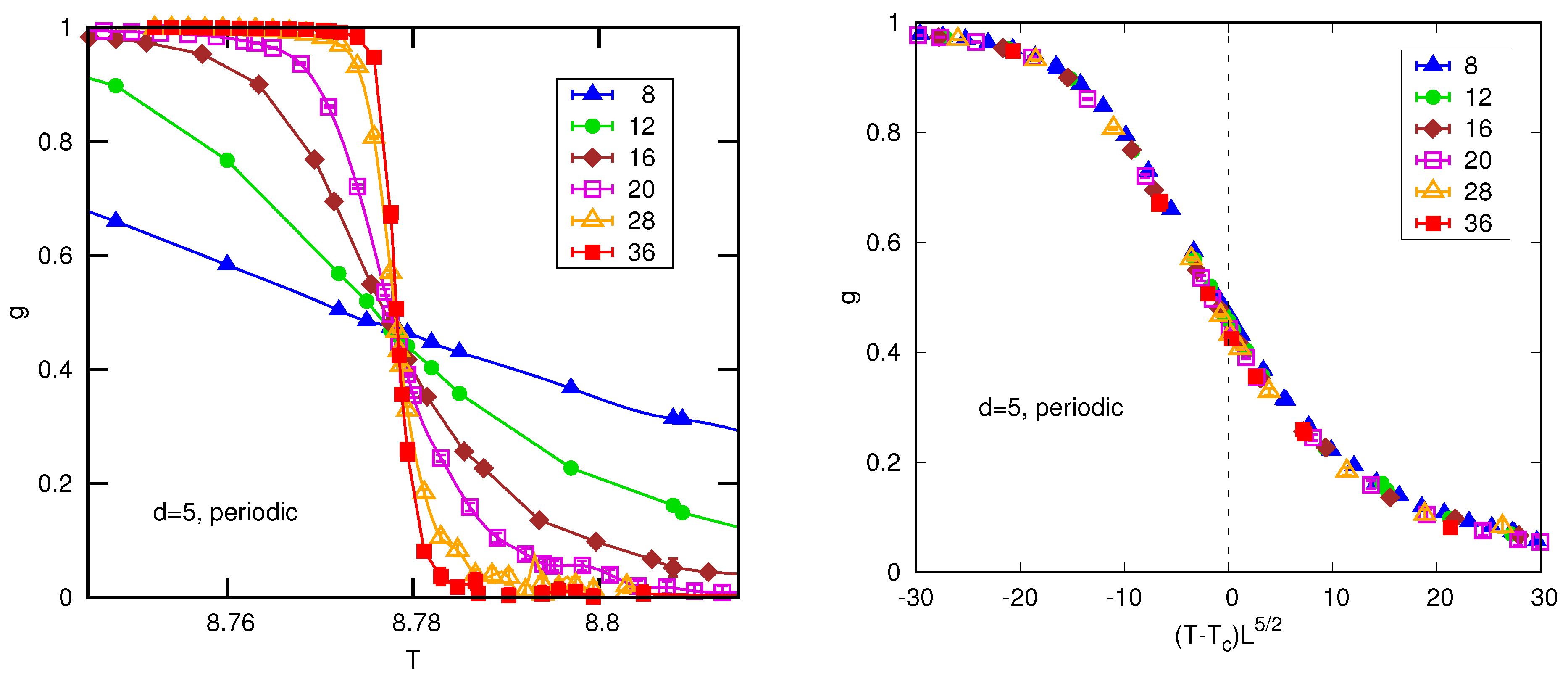
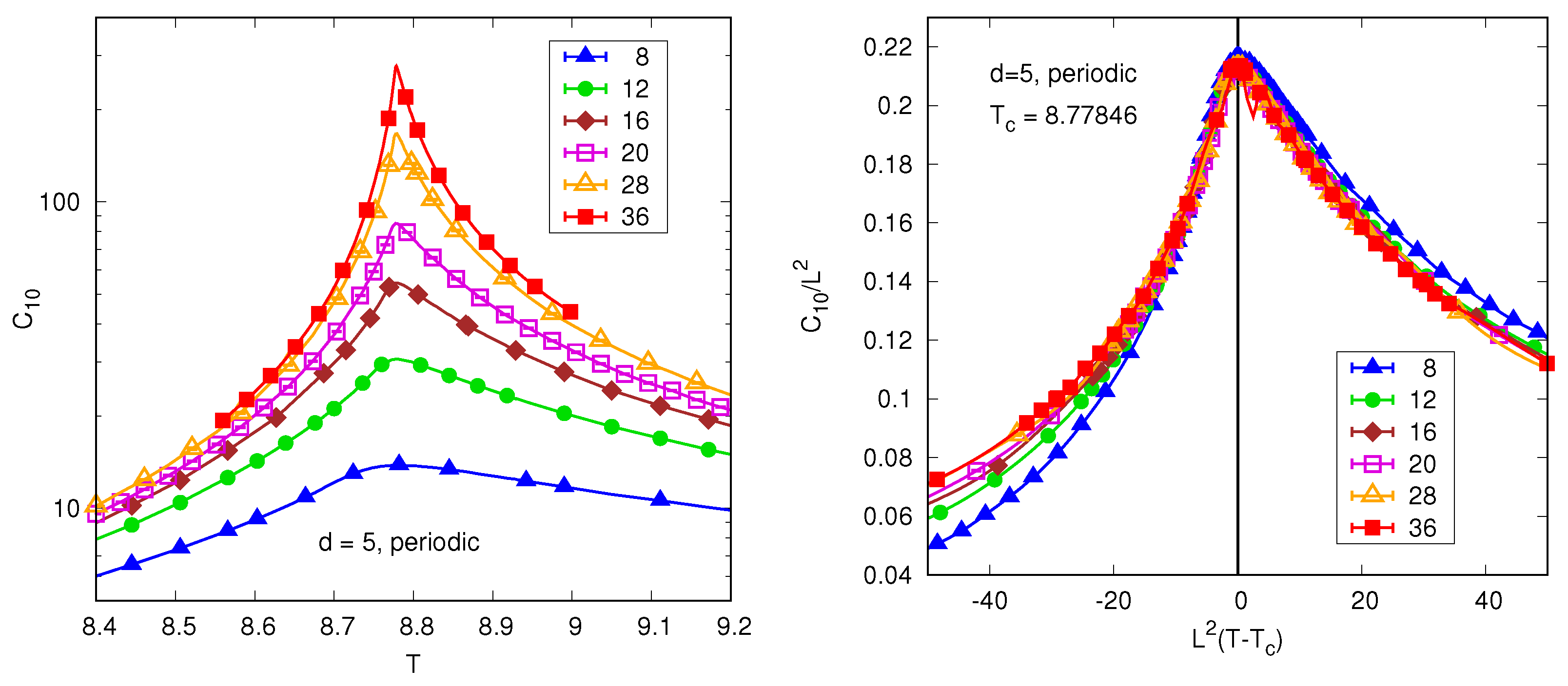
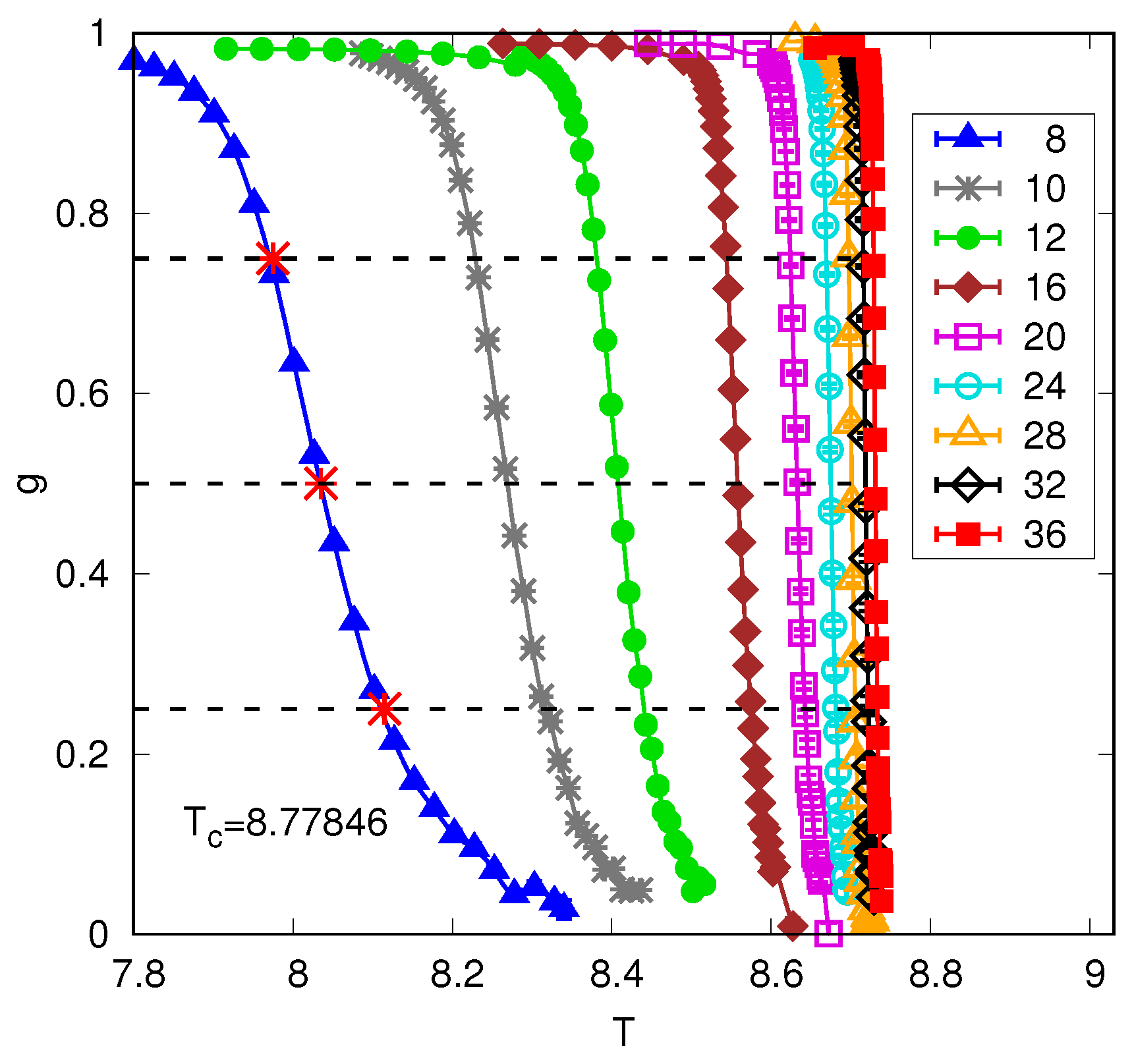
4.2. Numerical Results for Periodic Boundary Conditions
4.3. The Finite-Size Correlation Length
4.4. Free Boundary Conditions above the Upper Critical Dimension
5. Conclusions
- Below the upper critical dimension.Here, standard FSS applies:
- Above the upper critical dimension with periodic boundary conditions.For quantities that involve uniform magnetization, FSS scaling is modified toFor quantities that are orthogonal to the uniform magnetization, such as for (but ), we have standard FSS with mean-field exponents, soThese results imply that the correlation function at the critical point varies according to Gaussian behavior, i.e., for but this is superimposed on a uniform background contribution (which only affects the mode) of order . This was stated explicitly in Ref. [19], who demonstrated it numerically for the self-avoiding walk-in , which is expected to be in the same universality class as the Ising model above the upper critical dimension.
- Above the upper critical dimension with free boundary conditions.For most quantities, we need to define a shift and a rounding. The shift exponent is , and the rounding exponent is (the same as for periodic boundary conditions). Please note that the temperature range due to the shift is bigger than the temperature range due to rounding. Defining a pseudocritical temperature for each size, most quantities behave as in Equation (54) but with replaced by , i.e.,where is related to by Equation (46) with . However, as discussed in Section 4.4, some of the normal modes are orthogonal to the uniform magnetization, and for these, only the exponent appears and their correlations behave as in Equation (55).
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berche, B.; Ellis, T.; Holovatch, Y.; Kenna, R. Phase transitions above the upper critical dimension. SciPost Phys. Lect. Notes 2022, 60, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, M.E. The theory of critical point singularities. In Critical Phenomena, Proceedings of the 51st Enrico Fermi Summer School, Varenna; Green, M.S., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, M.E.; Barber, M.N. Scaling theory for finite-size effects in the critical region. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1972, 28, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, K. Finite size scaling analysis of Ising model block distribution functions. Z. Phys. B 1981, 43, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privman, V.; Fisher, M.E. Universal critical amplitudes in finite-size scaling. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berche, B.; Kenna, R.; Walter, J.C. Hyperscaling above the upper critical dimension. Nucl. Phys. B 2012, 865, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenna, R.; Berche, B. Fisher’s scaling relation above the upper critical dimension. Europhys. Lett. 2014, 105, 26005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brézin, E.; Zinn-Justin, J. Finite size effects in phase transitions. Nucl. Phys. B 1985, 257, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, K.; Nauenberg, M.; Privman, V.; Young, A.P. Finite-size tests of hyperscaling. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swendsen, R.H.; Wang, J. Nonuniversal critical dynamics in Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, U. Collective Monte Carlo updating for spin systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 62, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, M.; Young, A.P. Finite-size scaling above the upper critical dimension. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 062137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K. Application of finite size scaling to Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Young, A.P. Finite size scaling of the correlation length above the upper critical dimension. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 174438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, J.; Gaspari, G.; Privman, V. Effect of boundary conditions on the critical behavior of a finite high-dimensional Ising model. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunton, J.D. Finite-size effects at the critical point. Phys. Lett. A 1968, 26, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.G. Surface and size effects in lattice models. In Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena; Domb, C., Green, M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1973; Volume 2, p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Lundow, P.H.; Markström, K. Finite size scaling of the 5D Ising model with free boundary conditions. Nucl. Phys. B 2014, 889, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, J.; Elci, E.M.; Zhou, Z.; Garoni, T.M.; Deng, Y. Geometric explanation of anomalous finite-size scaling in high dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett 2017, 118, 115701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Grimm, J.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, Y. Complete graph and Gaussian fixed point asymptotics in the five-dimensional Fortuin-Kasteleyn Ising model with periodic boundaries. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 022125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, Y. Geometric scaling behaviors of the Fortuin-Kasteleyn Ising model in high dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fytas, N.G.; Martin-Mayor, V.; Parisi, G.; Picco, M.; Sourlas, N. Finite-size scaling of the random-field Ising model above the upper critical dimension. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 044146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Young, A.P. Violations of Hyperscaling in Finite-Size Scaling above the Upper Critical Dimension. Entropy 2024, 26, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060509
Young AP. Violations of Hyperscaling in Finite-Size Scaling above the Upper Critical Dimension. Entropy. 2024; 26(6):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060509
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoung, A. Peter. 2024. "Violations of Hyperscaling in Finite-Size Scaling above the Upper Critical Dimension" Entropy 26, no. 6: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060509
APA StyleYoung, A. P. (2024). Violations of Hyperscaling in Finite-Size Scaling above the Upper Critical Dimension. Entropy, 26(6), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060509




