Agreeing to Stop: Reliable Latency-Adaptive Decision Making via Ensembles of Spiking Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel ensemble-based SNN model that can reliably decide when to stop in order to produce set predictions with coverage guarantees and with an average latency that is significantly lower than that of the state of the art.
- As shown in Table 1, we compare two ensembling strategies—deep ensembles (DE) [18,19] and Bayesian learning via variational inference (VI) [14,15]—and introduce two methods to efficiently combine the decisions from multiple models: namely, confidence merging (CM) and p-variable merging (PM). In both cases, the resulting set predictors satisfy theoretical reliability guarantees.
- Experiments show that VI-based ensembles with PM significantly reduce the average latency of state-of-the-art methods while maintaining reliability guarantees.
2. Problem Definition
2.1. Multi-Class Classification with SNNs
2.2. Ensemble Inference and Learning for SNNs
2.3. Set Prediction and Latency Adaptivity
3. Ensemble-Based Adaptive Point Classification via SNNs
3.1. DC-SNN
3.2. Ensemble-Based DC-SNN
4. Ensemble-Based Adaptive Set Classification via SNNs
4.1. SpikeCP
4.2. Ensemble-Based SpikeCP with Confidence Merging
4.3. Ensemble-Based SpikeCP with P-Variable Merging
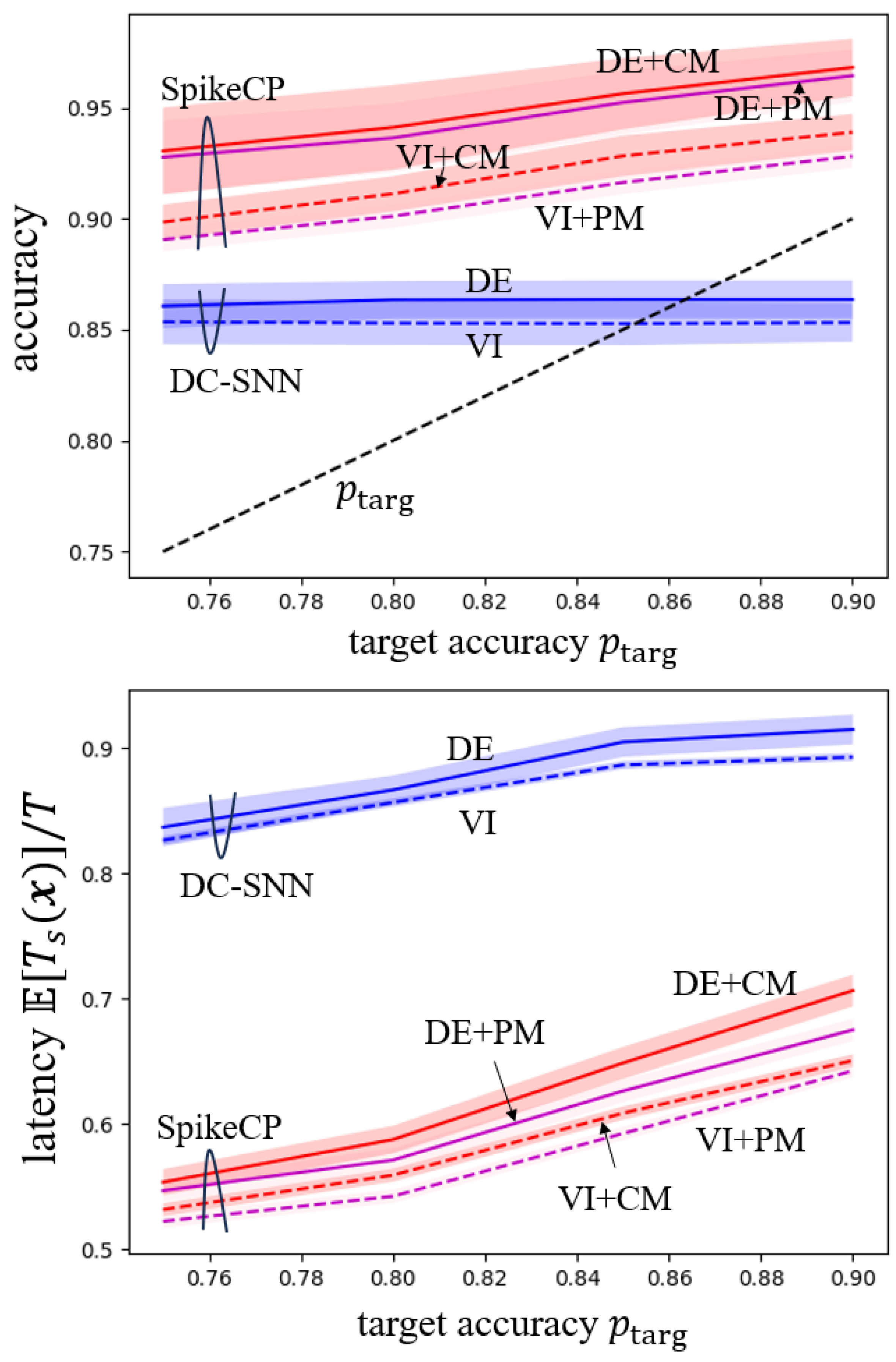
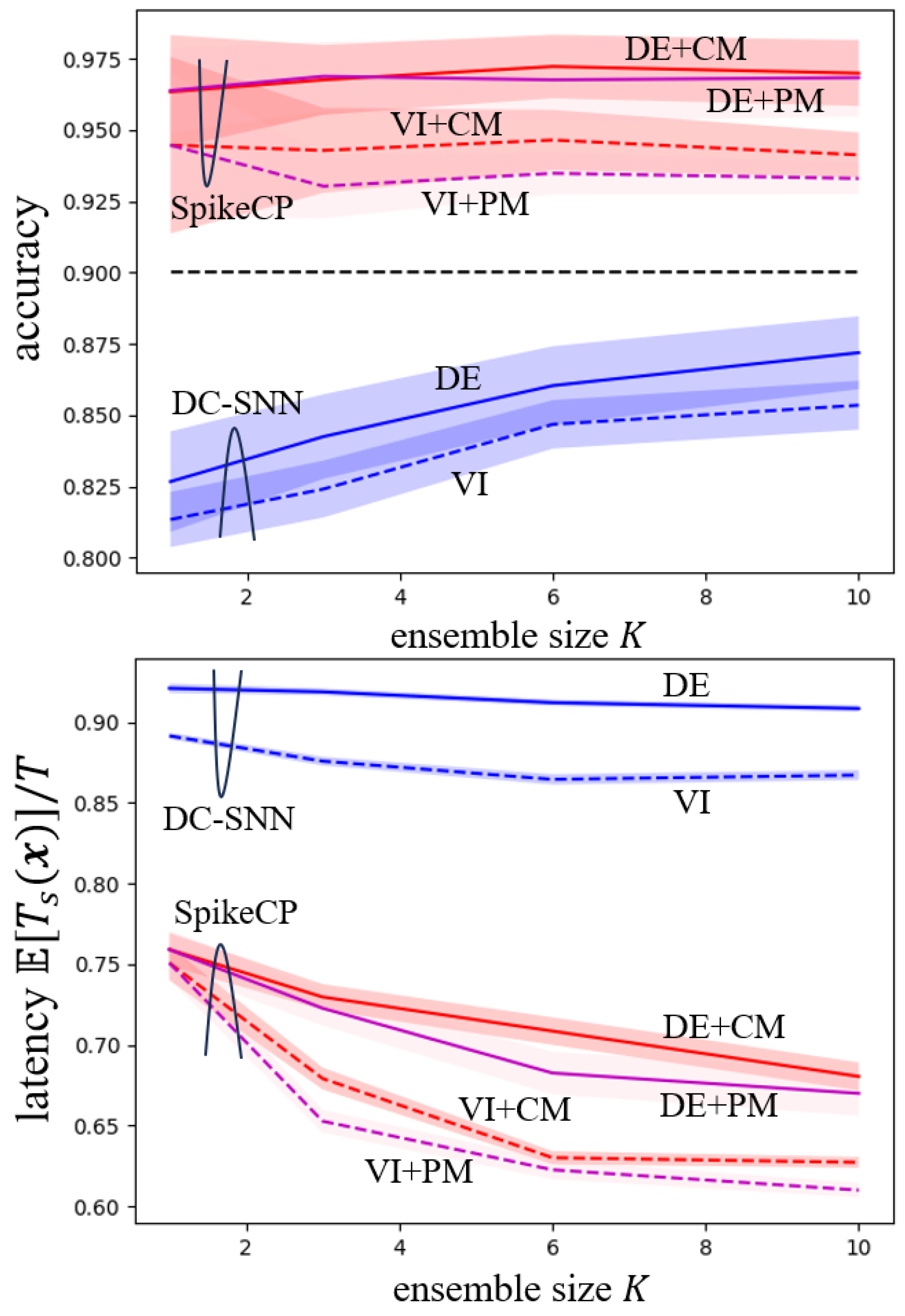
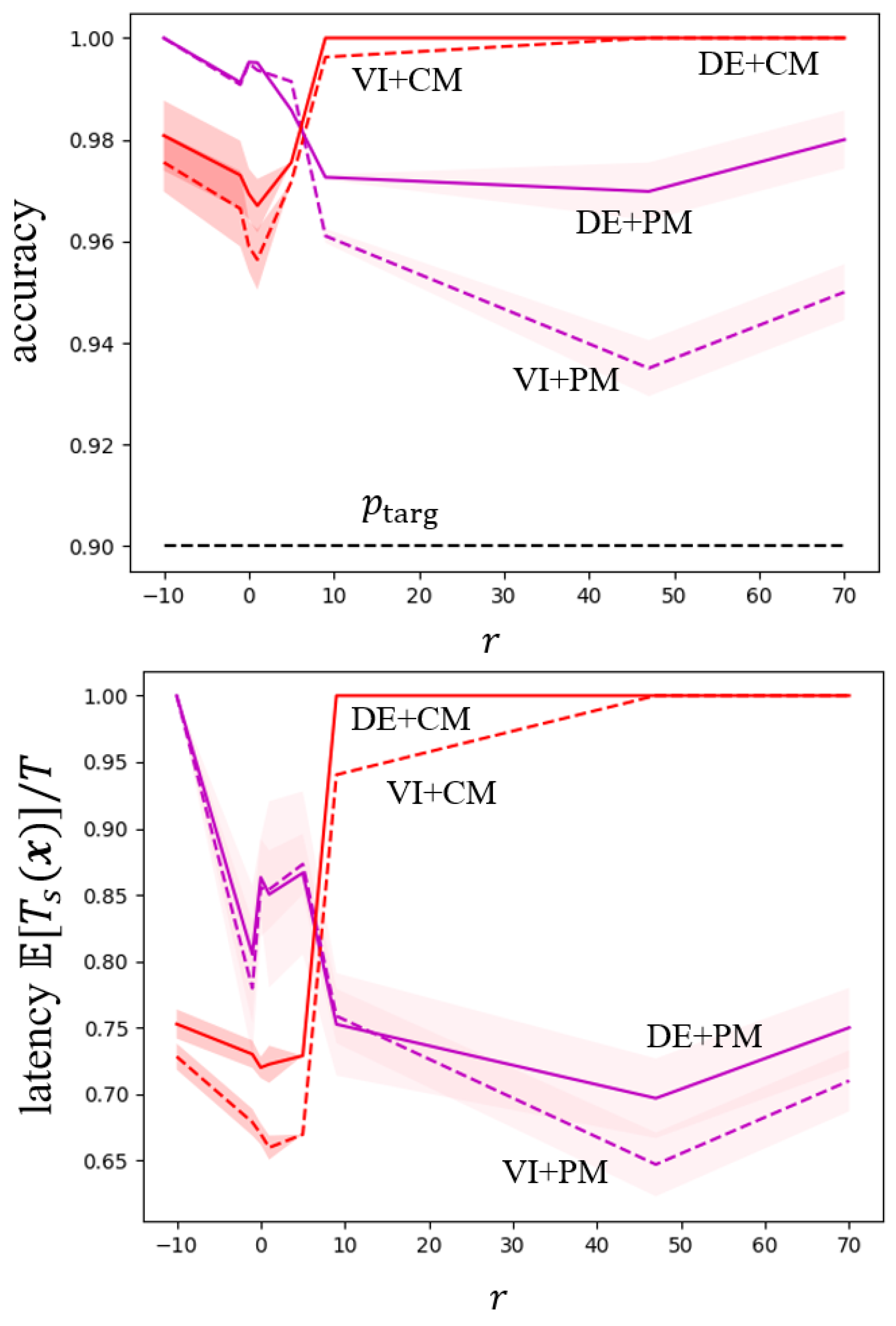
5. Experiments
5.1. MNIST-DVS Dataset
5.2. DVS128 Gesture Dataset
5.3. CIFAR-10 Dataset
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jang, H.; Simeone, O.; Gardner, B.; Gruning, A. An Introduction to Probabilistic Spiking Neural Networks: Probabilistic Models, Learning Rules, and Applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh-Dastidar, S.; Adeli, H. Spiking neural networks. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2009, 19, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavanaei, A.; Ghodrati, M.; Kheradpisheh, S.R.; Masquelier, T.; Maida, A. Deep learning in spiking neural networks. Neural Netw. 2019, 111, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehonic, A.; Sebastian, A.; Rajendran, B.; Simeone, O.; Vasilaki, E.; Kenyon, A.J. Memristors—From in-memory computing, deep learning acceleration, and spiking neural networks to the future of neuromorphic and bio-inspired computing. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jones, E.; Furber, S. Unleashing the Potential of Spiking Neural Networks by Dynamic Confidence. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Geller, T.; Kim, Y.; Panda, P. SEENN: Towards Temporal Spiking Early-Exit Neural Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.01230. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Pleiss, G.; Sun, Y.; Weinberger, K.Q. On calibration of modern neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1321–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Park, S.; Simeone, O. SpikeCP: Delay-Adaptive Reliable Spiking Neural Networks via Conformal Prediction. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.11322. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos, A.N.; Bates, S. A gentle introduction to conformal prediction and distribution-free uncertainty quantification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.07511. [Google Scholar]
- Shafer, G.; Vovk, V. A Tutorial on Conformal Prediction. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 371–421. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, V.; Ho, S.S.; Vovk, V. Conformal Prediction for Reliable Machine Learning: Theory, Adaptations and Applications; Morgan Kaufmann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vovk, V.; Gammerman, A.; Shafer, G. Algorithmic Learning in a Random World; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hüllermeier, E.; Waegeman, W. Aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty in machine learning: An introduction to concepts and methods. Mach. Learn. 2021, 110, 457–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, O. Machine Learning for Engineers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Skatchkovsky, N.; Jang, H.; Simeone, O. Bayesian continual learning via spiking neural networks. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1037976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, P.; Skatchkovsky, N.; Simeone, O.; Rajendran, B.; Al-Hashimi, B.M. Bayesian Inference on Binary Spiking Networks Leveraging Nanoscale Device Stochasticity. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.01302. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, R.; Ren, A.; Liu, N.; Ding, C.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Pedram, M.; Wang, Y. VIBNN: Hardware acceleration of Bayesian neural networks. ACM SIGPLAN Not. 2018, 53, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, B.; Pritzel, A.; Blundell, C. Simple and scalable predictive uncertainty estimation using deep ensembles. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6405–6416. [Google Scholar]
- Ganaie, M.A.; Hu, M.; Malik, A.; Tanveer, M.; Suganthan, P. Ensemble deep learning: A review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.B.; Timcheck, J.; Frady, P.; Campos-Macias, L.; Davies, M. Efficient Video and Audio processing with Loihi 2. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.03251. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstner, W. Spike-response model. Scholarpedia 2008, 3, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Skatchkovsky, N.; Simeone, O. Neuromorphic Wireless Cognition: Event-Driven Semantic Communications for Remote Inference. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2023, 9, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doya, K. Bayesian Brain: Probabilistic Approaches to Neural Coding; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Neftci, E.O.; Mostafa, H.; Zenke, F. Surrogate gradient learning in spiking neural networks: Bringing the power of gradient-based optimization to spiking neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, H. Inductive conformal prediction: Theory and application to neural networks. In Tools in Artificial Intelligence; InTech: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vovk, V. Conditional validity of inductive conformal predictors. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Singapore, 4–6 November 2012; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg, Y.; Tamhane, A.C. Multiple Comparison Procedures; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Koliander, G.; El-Laham, Y.; Djurić, P.M.; Hlawatsch, F. Fusion of probability density functions. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 404–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kwak, N. Generalized mean for robust principal component analysis. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 54, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Ma, H.; Ou, W.; Zeng, S.; Rao, Y.; Yang, H. A generalized mean distance-based k-nearest neighbor classifier. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 115, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.L. Posterior predictive p-values. Ann. Stat. 1994, 22, 1142–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovk, V.; Wang, B.; Wang, R. Admissible ways of merging p-values under arbitrary dependence. Ann. Stat. 2022, 50, 351–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovk, V.; Wang, R. Combining p-values via averaging. Biometrika 2020, 107, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Taba, B.; Berg, D.; Melano, T.; McKinstry, J.; Di Nolfo, C.; Nayak, T.; Andreopoulos, A.; Garreau, G.; Mendoza, M.; et al. A low power, fully event-based gesture recognition system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7243–7252. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Gotarredona, T.; Linares-Barranco, B. Poker-DVS and MNIST-DVS. Their history, how they were made, and other details. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Masquelier, T.; Huang, T.; Tian, Y. Incorporating learnable membrane time constant to enhance learning of spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2661–2671. [Google Scholar]
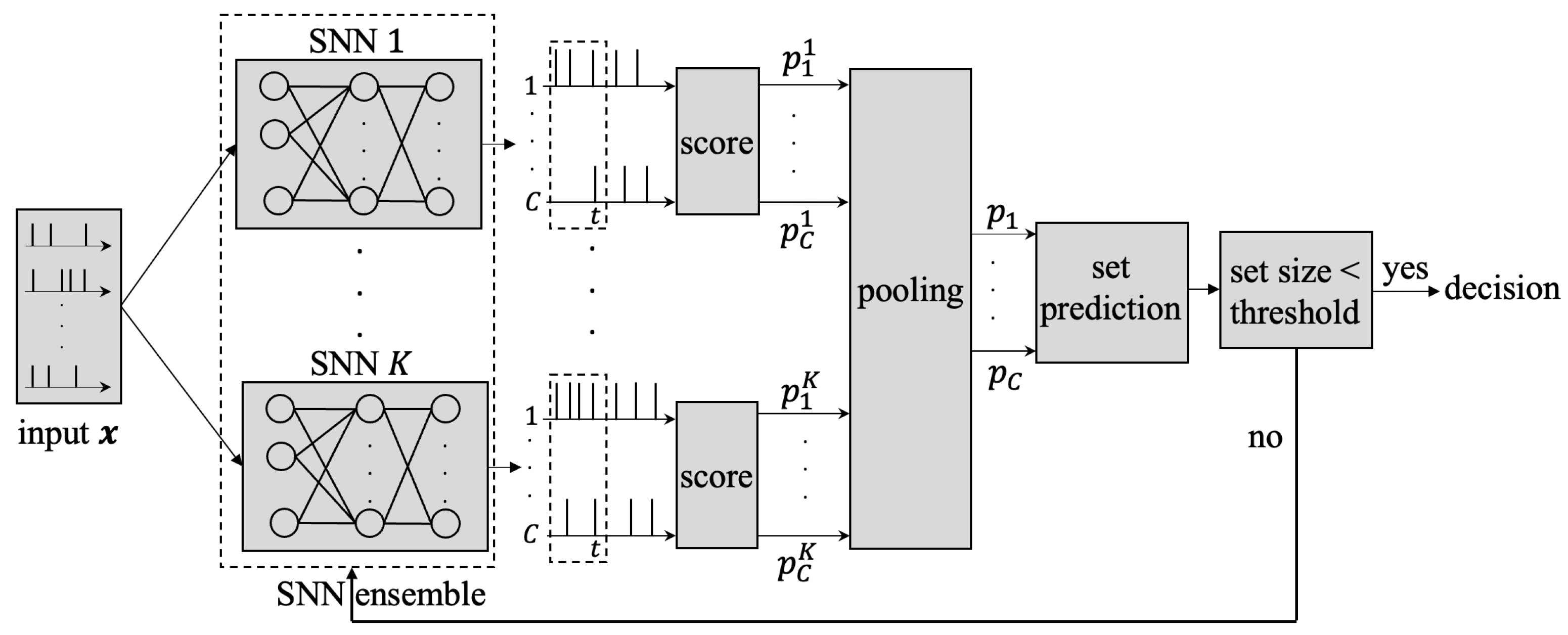
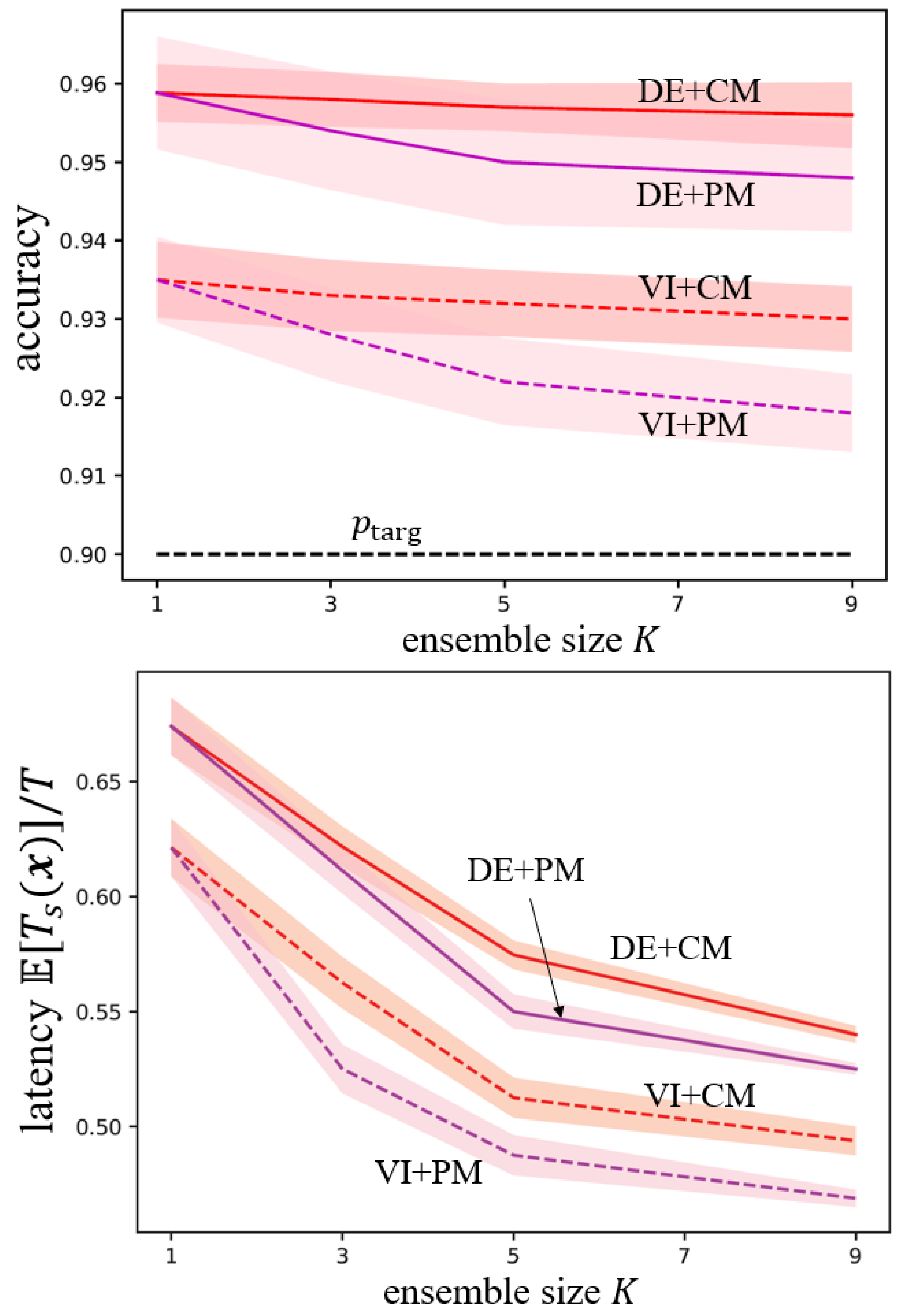
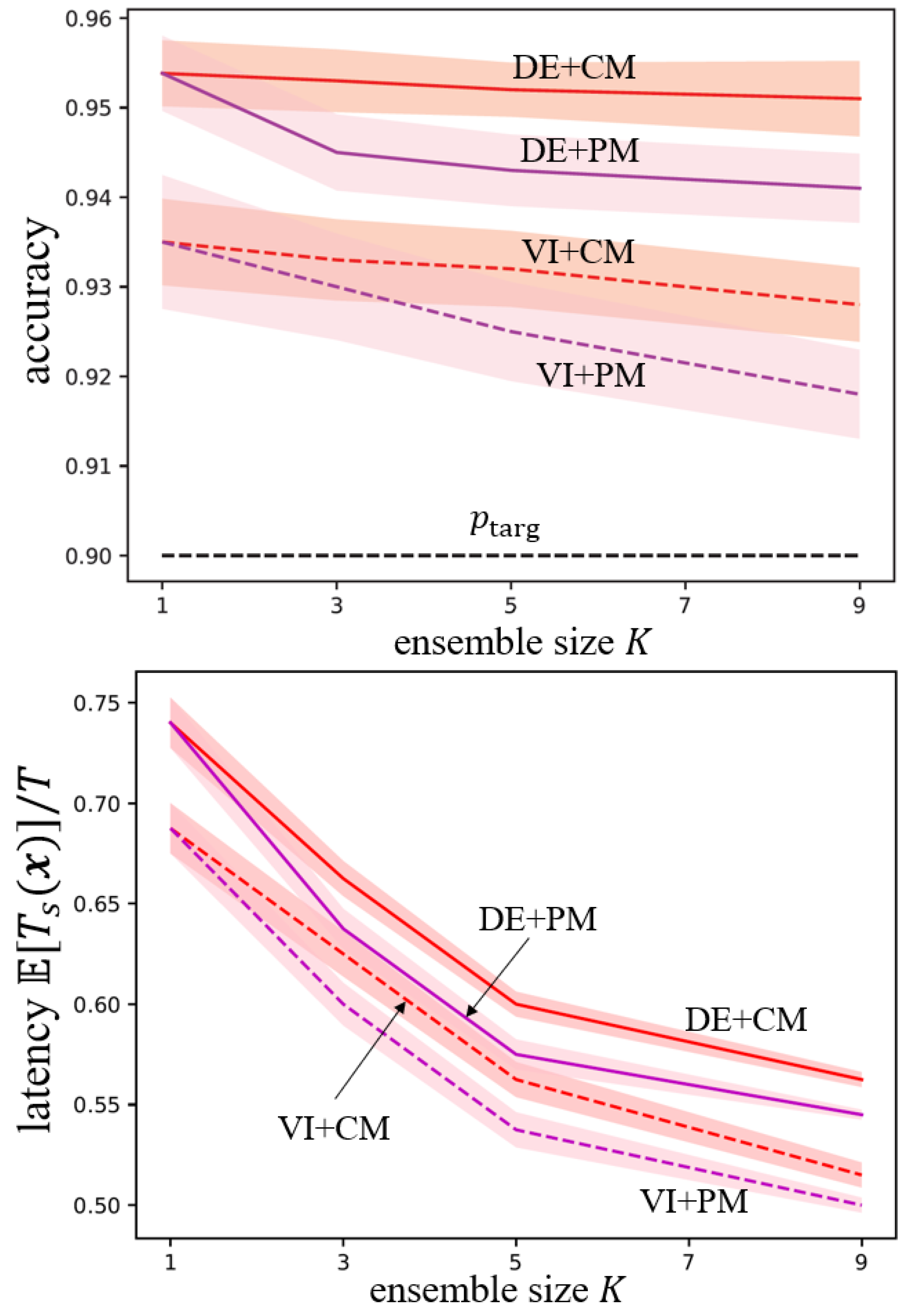
| ensembling stategies | variational inference (VI) | deep ensembles (DE) |
| information pooling | confidence merging (CM) | p-variable merging (PM) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Park, S.; Simeone, O. Agreeing to Stop: Reliable Latency-Adaptive Decision Making via Ensembles of Spiking Neural Networks. Entropy 2024, 26, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26020126
Chen J, Park S, Simeone O. Agreeing to Stop: Reliable Latency-Adaptive Decision Making via Ensembles of Spiking Neural Networks. Entropy. 2024; 26(2):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26020126
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiechen, Sangwoo Park, and Osvaldo Simeone. 2024. "Agreeing to Stop: Reliable Latency-Adaptive Decision Making via Ensembles of Spiking Neural Networks" Entropy 26, no. 2: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26020126
APA StyleChen, J., Park, S., & Simeone, O. (2024). Agreeing to Stop: Reliable Latency-Adaptive Decision Making via Ensembles of Spiking Neural Networks. Entropy, 26(2), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26020126






