Identifying Important Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Node Propagation Entropy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Centrality Indicators
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Node Propagation Entropy
| Algorithm 1: Propagation entropy (PE) computation procedure |
| Input: G = (V,E) |
| 1: Initialize network G |
| 2: for each vertex i in V do |
| 3: if i degree ≤ 1: |
| 4: ci = 0 |
| 5: else: |
| 6: compute ci via Equation (10) |
| 7: end for |
| 8: sumcn = 0.0 |
| 9: for each vertex i in V do |
| 10: sumneigh = N(i) + N2(i) |
| 11: cni = sumneigh/(1 + ci) |
| 12: sumcn += cni |
| 13: end for |
| 14: for each vertex i in V do |
| 15: Ii = cni/sumcn |
| 16: end for |
| 17: for each vertex i in V do |
| 18: sum_Ii = 0.0 |
| 19: for each vertex j in N(i) do |
| 20: sum_Ii += −Ijln(Ij) |
| 21: PEi = sum_Ii |
| 22: end for |
| 23: Rank the PE value of all nodes |
| Output: An ordered list of nodes |
3.2. Effectiveness of the Proposed Node Propagation Entropy Metric
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Date
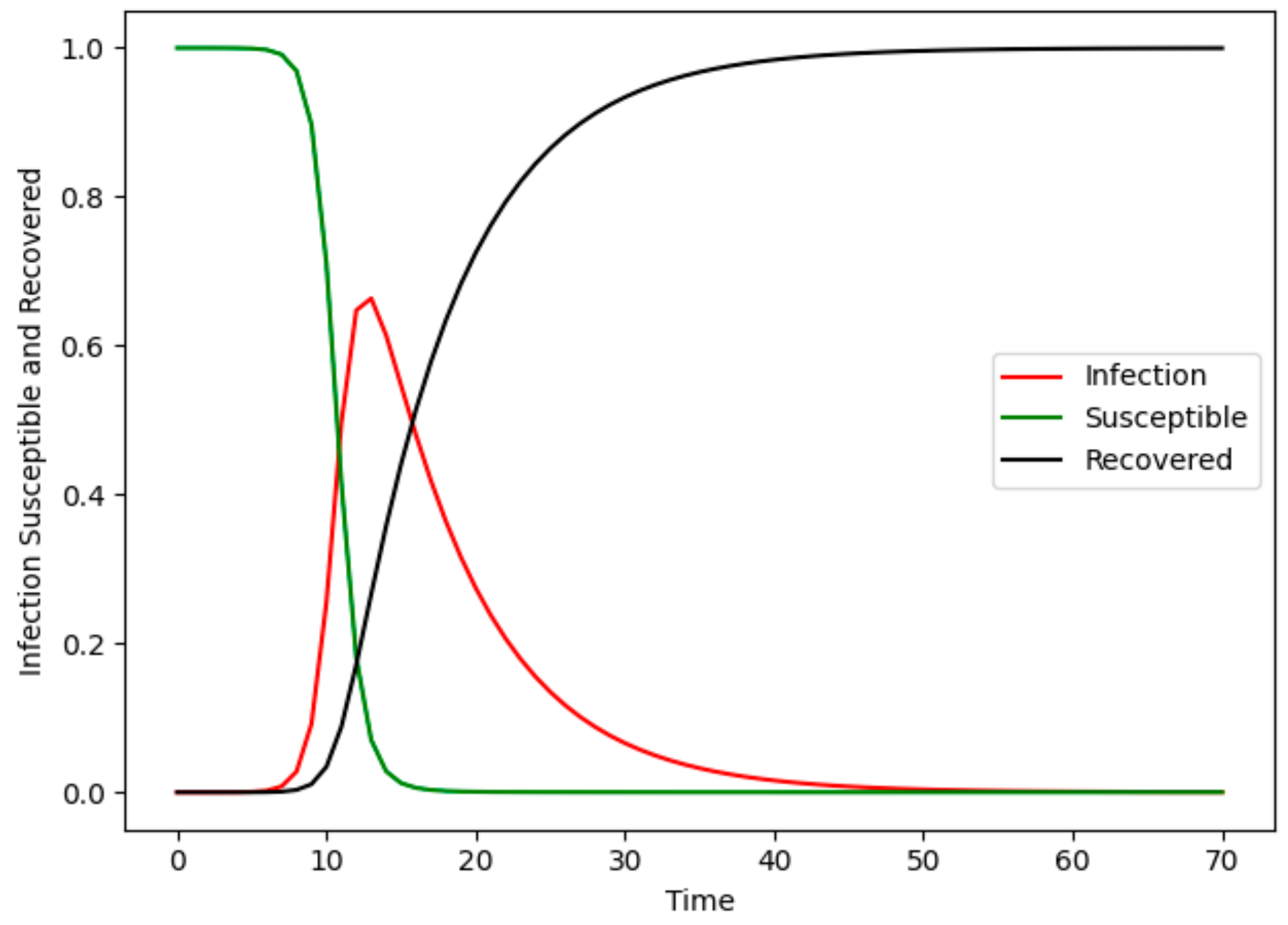
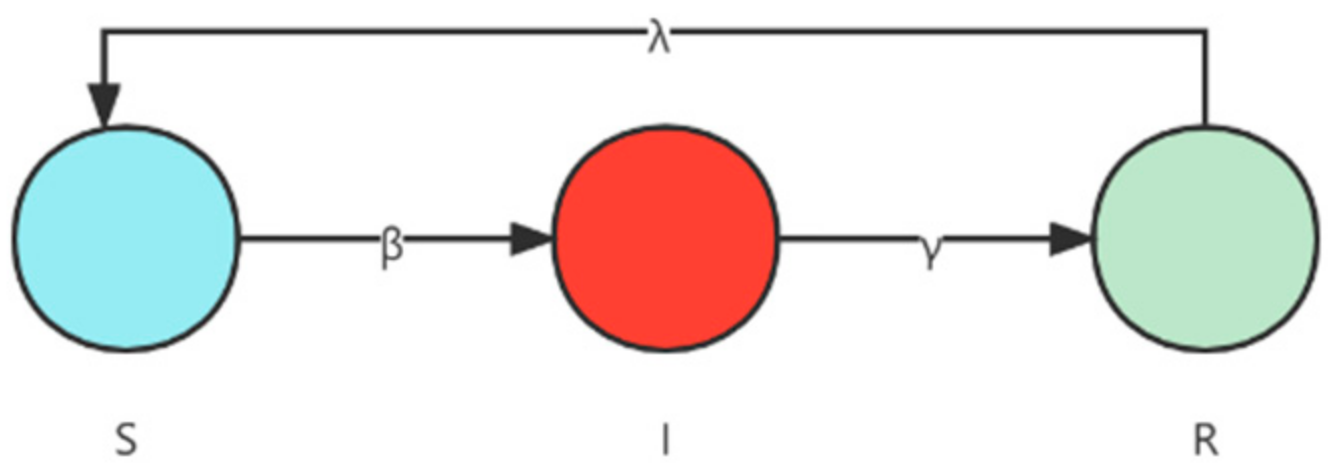
4.2. Evaluation of the Susceptible–Infected–Removed Model
4.3. Evaluation of the Susceptible–Infected–Removed–Susceptible Model
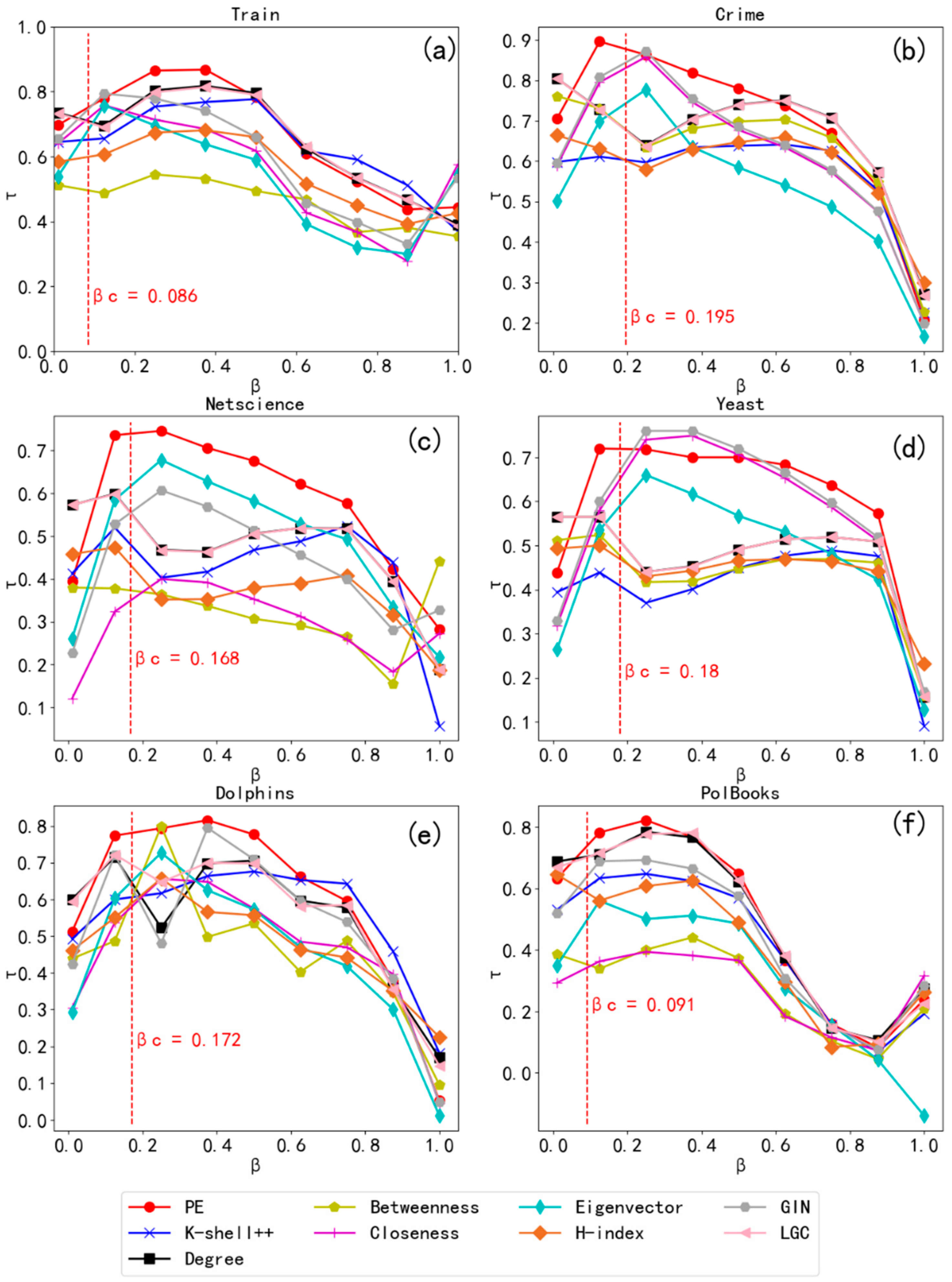
4.4. Kendall Coefficient (τ)
4.5. Epidemic Models Experiment
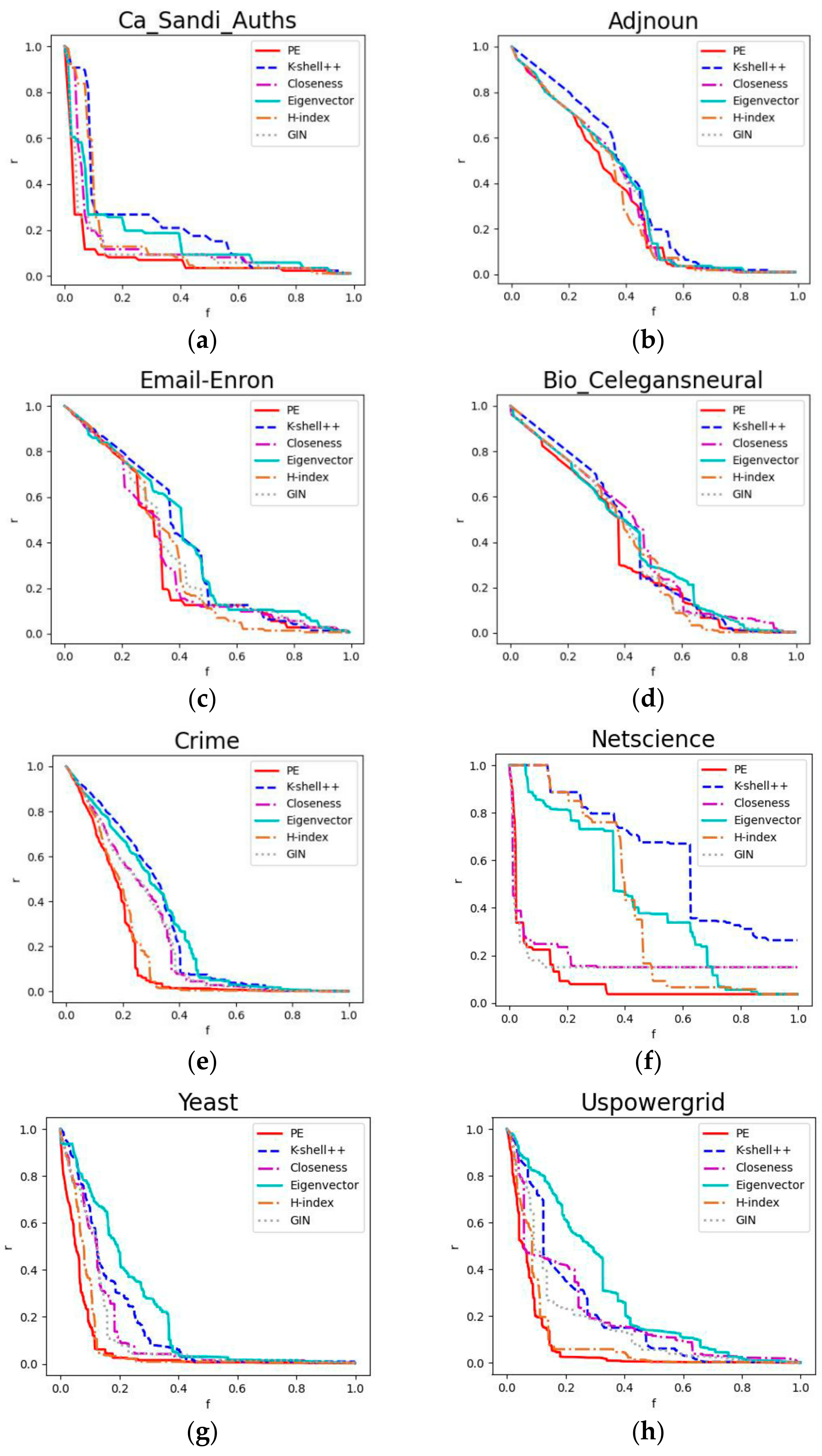
4.6. Robustness Experiment
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pagani, G.A.; Aiello, M.J. The power grid as a complex network: A survey. Phys. A Stat. Mech. 2013, 392, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrat, O. Social network analysis. In Knowledge Solutions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.J. Social network analysis: Developments, advances, and prospects. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2011, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyapriya, R.; Vijayabaskar, M.; Vishveshwara, S.J. Insights into protein–DNA interactions through structure network analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saberi, M.; Hamedmoghadam, H.; Ashfaq, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Gu, Z.; Shafiei, S.; Nair, D.J.; Dixit, V.; Gardner, L.; Waller, S.T. A simple contagion process describes spreading of traffic jams in urban networks. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bracken, C.P.; Scott, H.S.; Goodall, G.J. A network-biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, M.C.; Woolhouse, M.E. Controlling infectious disease through the targeted manipulation of contact network structure. Epidemics 2015, 12, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaters, G.; Johnson, P.; Cleaveland, S.; Crispell, J.; De Glanville, W.; Doherty, T.; Matthews, L.; Mohr, S.; Nyasebwa, O.; Rossi, G.J. Analysing livestock network data for infectious disease control: An argument for routine data collection in emerging economies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X.; Hao, F.J. Incentive mechanisms for crowdblocking rumors in mobile social networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 9220–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Giua, A.J. Containment of rumor spread in complex social networks. J. Inf. Sci. 2020, 506, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi, S.; Wang, L.; Pryke, S.J. Relationship marketing in Guanxi networks: A social network analysis study of Chinese construction small and medium-sized enterprises. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 60, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Duan, J.; Yang, N.; Xie, L.; Yuan, Y.; Li, S.; Bi, C.; Yang, B.J. Techniques and strategies for potential protein target discovery and active pharmaceutical molecule screening in a pandemic. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4242–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, L.C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsak, M.; Gallos, L.K.; Havlin, S.; Liljeros, F.; Muchnik, L.; Stanley, H.E.; Makse, H.A. Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonacich, P.; Lloyd, P.J. Eigenvector-like measures of centrality for asymmetric relations. Soc. Netw. 2001, 23, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.J. Identifying influential nodes in complex networks from global perspective. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2020, 133, 109637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Wang, B.; Sheng, J.; Long, J.; Khan, N.; Sun, Z.J. Identifying vital nodes from local and global perspectives in complex networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 186, 115778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, S.; Page, L. The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual web search engine. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 1998, 30, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yeung, C.H.; Zhou, T.J. Leaders in social networks, the delicious case. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.X.; Chen, D.B.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, Z.D. Identifying a set of influential spreaders in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, J.M. Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment. J. ACM 1999, 46, 604–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Gao, H.; Ma, J.J. Influential nodes identification in complex networks via information entropy. Entropy 2020, 22, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zareie, A.; Sheikhahmadi, A.; Fatemi, A.J. Influential nodes ranking in complex networks: An entropy-based approach. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2017, 104, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Deng, Y.J. A new method to identify influential nodes based on relative entropy. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2017, 104, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Mei, T.J. Ranking influential nodes in complex networks with structural holes. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 490, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Fan, T.; Li, M. Identifying vital nodes by Achlioptas process. N. J. Phys. 2021, 23, 033036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Q.M.; Stanley, H.E. The H-index of a network node and its relation to degree and coreness. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, K.; Lu, Z.M. Using mapping entropy to identify node centrality in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 453, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y. A new essential protein discovery method based on the integration of protein-protein interaction and gene expression data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turpin, A.; Scholer, F. User performance versus precision measures for simple search tasks. In Proceedings of the International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–11 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kunegis, J. KONECT: The Koblenz network collection. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 13–17 May 2013; Association for Computing Machinery: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013; pp. 1343–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Zachary, W.W. An Information Flow Model for Conflict and Fission in Small Groups. Anthropol. Res. 1977, 33, 452–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, R.; Ahmed, N. The network data repository with interactive graph analytics and visualization. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pellis, L.; Ball, F.; Bansal, S.; Eames, K.; House, T.; Isham, V.; Trapman, P.J. Eight challenges for network epidemic models. Epidemics 2015, 10, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salavati, C.; Abdollahpouri, A.; Manbari, Z. Ranking nodes in complex networks based on local structure and improving closeness centrality. Neurocomputing 2019, 336, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, C.; Pastor-Satorras, R.J. Thresholds for epidemic spreading in networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 218701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruhi, N.A.; Hassibi, B. SIRS epidemics on complex networks: Concurrence of exact Markov chain and approximated models. In Proceedings of the Conference on Decision and Control, Osaka, Japan, 15–18 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Biometrika, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.; Moreira, A.; Andrade, J.; Havlin, S.; America, H.J. Mitigation of malicious attacks on networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3838–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dereich, S.; Probability, P.M. Random networks with sublinear preferential attachment: The giant component. Ann. Probab. 2013, 41, 329–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, R.; Jeong, H.; Barabási, A.L. Error and attack tolerance of complex networks. Nature 2000, 406, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Network | PE | K − Shell + + | DC | BC | CC | EC | VoteRank | H-Index | GIN | LGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saccharomyces | 0.375 | 0.404 | 0.402 | 0.35 | 0.354 | 0.367 | 0.351 | 0.405 | 0.364 | 0.404 |
| Network | n | m | <c> | <k> | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdjNoun | 112 | 425 | 0.173 | 7.589 | 0.068 |
| Train | 64 | 243 | 0.561 | 7.593 | 0.120 |
| Karate | 34 | 78 | 0.255 | 4.588 | 0.139 |
| Ca_Sandi_Auth | 86 | 124 | 0.414 | 2.883 | 0.034 |
| Email-Enron | 143 | 623 | 0.434 | 8.713 | 0.061 |
| Dolphins | 62 | 159 | 0.308 | 5.129 | 0.084 |
| Polbooks | 105 | 441 | 0.348 | 7.589 | 0.068 |
| Bio_celegansneural | 297 | 2300 | 0.311 | 15 | 0.053 |
| Crime | 1380 | 1476 | 0.009 | 2.14 | 0.002 |
| Yeast | 1870 | 2277 | 0.094 | 2.435 | 0.001 |
| Netscience | 1461 | 2742 | 0.694 | 3.753 | 0.001 |
| Uspowergrid | 4941 | 6594 | 0.08 | 2.669 | 0.001 |
| Network | PE | K − Shell + + | DC | BC | C | EC | PE(N2) | H-Index | GIN | LGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdjNoun | 0.894 | 0.780 | 0.828 | 0.641 | 0.866 | 0.925 | 0.844 | 0.716 | 0.905 | 0.827 |
| Train | 0.892 | 0.740 | 0.830 | 0.558 | 0.763 | 0.761 | 0.849 | 0.661 | 0.857 | 0.809 |
| Ca_Sandi_Auth | 0.858 | 0.555 | 0.572 | 0.428 | 0.658 | 0.772 | 0.808 | 0.433 | 0.776 | 0.578 |
| Email − Enron | 0.854 | 0.768 | 0.822 | 0.488 | 0.676 | 0.853 | 0.844 | 0.703 | 0.852 | 0.827 |
| Dolphins | 0.909 | 0.713 | 0.747 | 0.541 | 0.652 | 0.707 | 0.898 | 0.577 | 0.856 | 0.75 |
| Polbooks | 0.864 | 0.715 | 0.762 | 0.362 | 0.378 | 0.601 | 0.802 | 0.611 | 0.737 | 0.775 |
| Crime | 0.869 | 0.596 | 0.648 | 0.654 | 0.854 | 0.786 | 0.857 | 0.582 | 0.861 | 0.647 |
| Netscience | 0.751 | 0.471 | 0.540 | 0.378 | 0.337 | 0.656 | 0.730 | 0.424 | 0.551 | 0.539 |
| Yeast | 0.748 | 0.407 | 0.503 | 0.474 | 0.672 | 0.606 | 0.689 | 0.460 | 0.694 | 0.503 |
| Network | PE | K − Shell + + | DC | BC | CC | EC | H-Index | GIN | LGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 0.770 | 0.676 | 0.722 | 0.477 | 0.718 | 0.696 | 0.635 | 0.762 | 0.716 |
| Dolphins | 0.802 | 0.646 | 0.691 | 0.497 | 0.596 | 0.672 | 0.525 | 0.768 | 0.688 |
| Polbooks | 0.745 | 0.641 | 0.676 | 0.341 | 0.352 | 0.550 | 0.522 | 0.670 | 0.671 |
| Crime | 0.875 | 0.592 | 0.649 | 0.651 | 0.853 | 0.775 | 0.582 | 0.868 | 0.649 |
| Netscience | 0.744 | 0.473 | 0.552 | 0.378 | 0.341 | 0.644 | 0.431 | 0.549 | 0.551 |
| Yeast | 0.747 | 0.400 | 0.495 | 0.468 | 0.668 | 0.610 | 0.473 | 0.692 | 0.495 |
| Network. | PE | K − Shell + + | CC | EC | H − Index | GIN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca_Sandi_Auth | 0.082 | 0.210 | 0.131 | 0.164 | 0.143 | 0.112 |
| AdjNoun | 0.315 | 0.373 | 0.329 | 0.338 | 0.316 | 0.333 |
| Email − Enron | 0.319 | 0.386 | 0.325 | 0.391 | 0.324 | 0.347 |
| Bio_celegansneural | 0.351 | 0.387 | 0.398 | 0.389 | 0.364 | 0.374 |
| Crime | 0.168 | 0.291 | 0.246 | 0.290 | 0.180 | 0.247 |
| Netscience | 0.093 | 0.625 | 0.186 | 0.434 | 0.408 | 0.172 |
| Yeast | 0.065 | 0.163 | 0.132 | 0.213 | 0.084 | 0.123 |
| Uspowergrid | 0.073 | 0.200 | 0.197 | 0.294 | 0.097 | 0.165 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Chen, L.; Gao, T.; Liu, J. Identifying Important Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Node Propagation Entropy. Entropy 2022, 24, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020275
Yu Y, Zhou B, Chen L, Gao T, Liu J. Identifying Important Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Node Propagation Entropy. Entropy. 2022; 24(2):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020275
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yong, Biao Zhou, Linjie Chen, Tao Gao, and Jinzhuo Liu. 2022. "Identifying Important Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Node Propagation Entropy" Entropy 24, no. 2: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020275
APA StyleYu, Y., Zhou, B., Chen, L., Gao, T., & Liu, J. (2022). Identifying Important Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Node Propagation Entropy. Entropy, 24(2), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020275






