Modelling Spirals of Silence and Echo Chambers by Learning from the Feedback of Others
Abstract
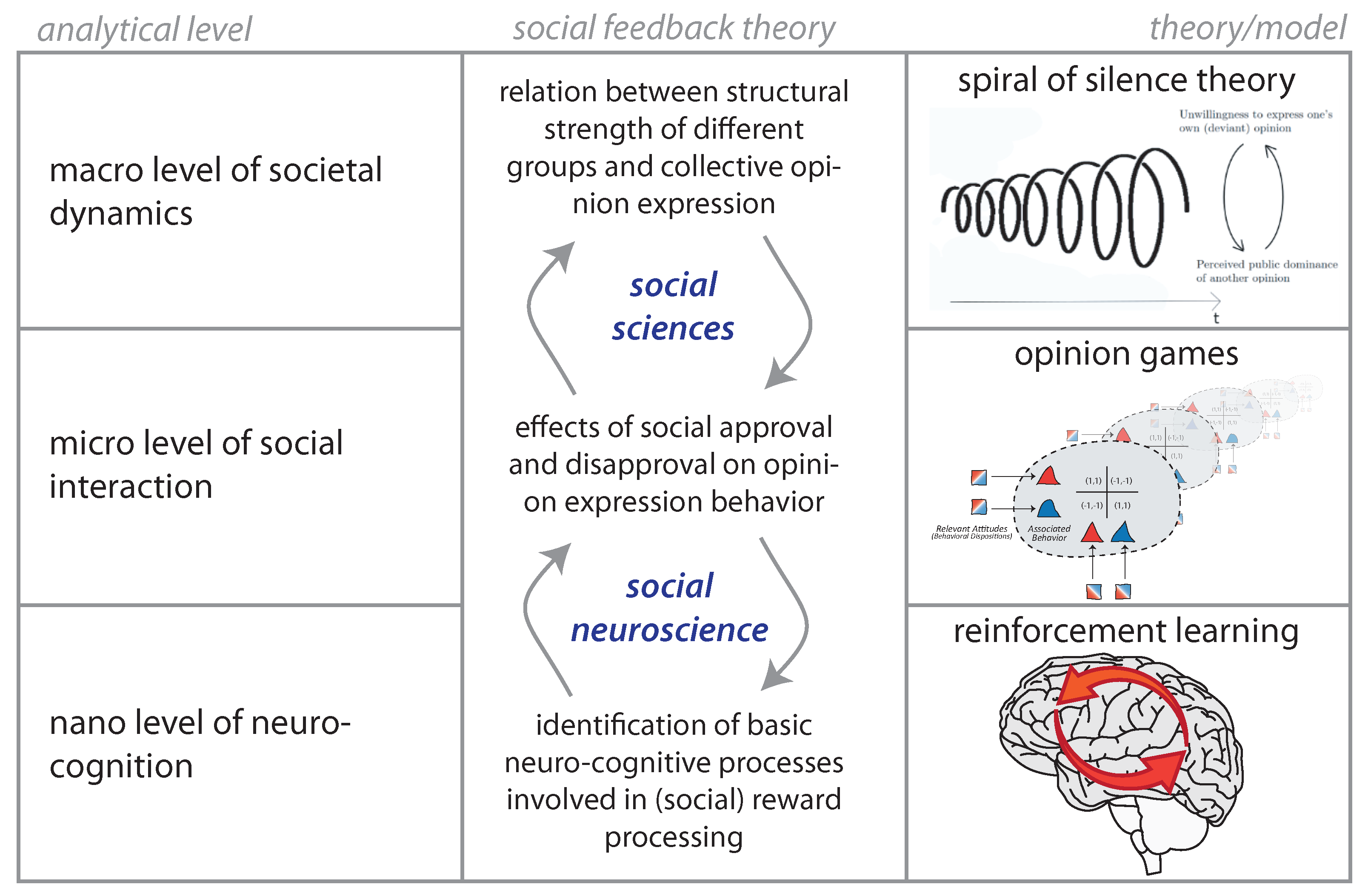
1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Social Feedback Processing in the Brain
2.2. Opinion Expression Games
2.3. Group Setting
3. Applications
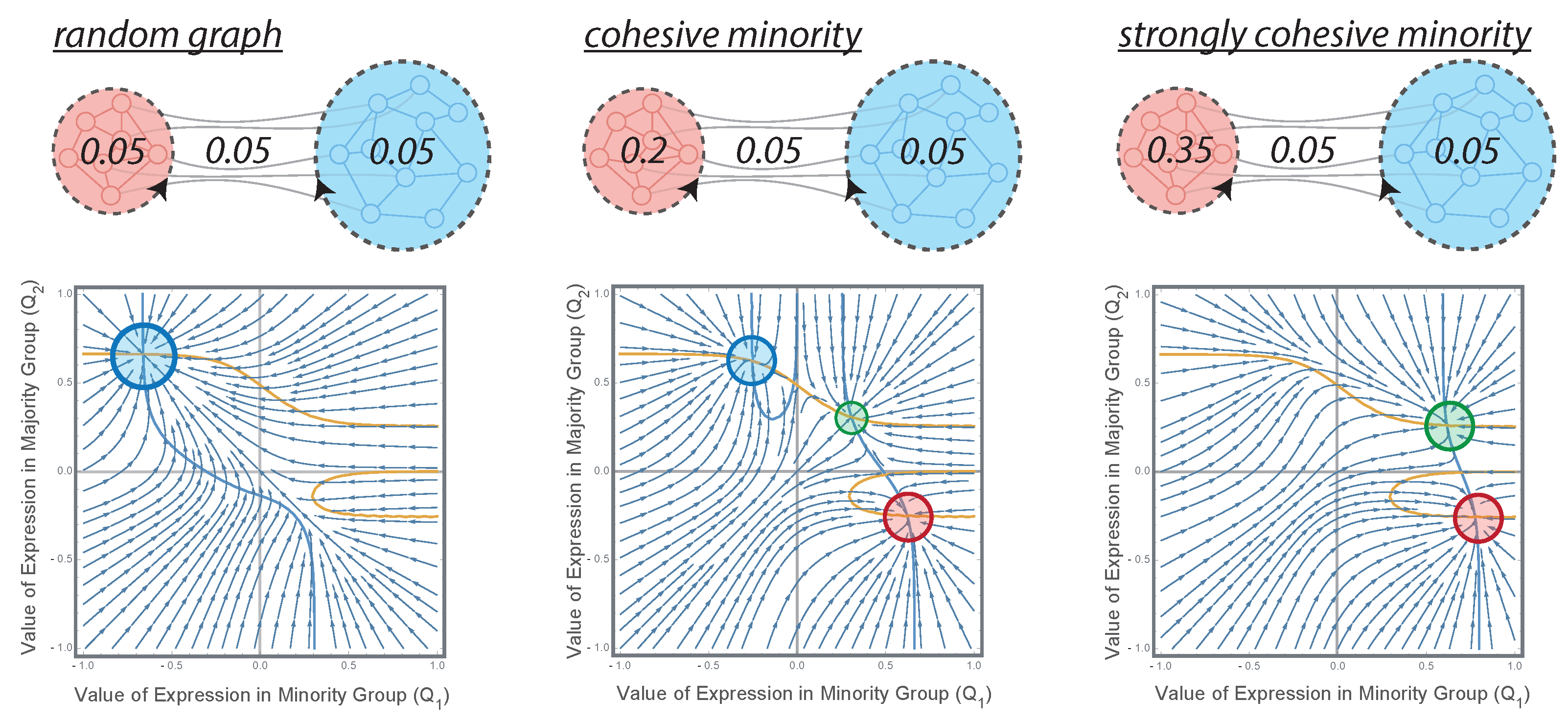
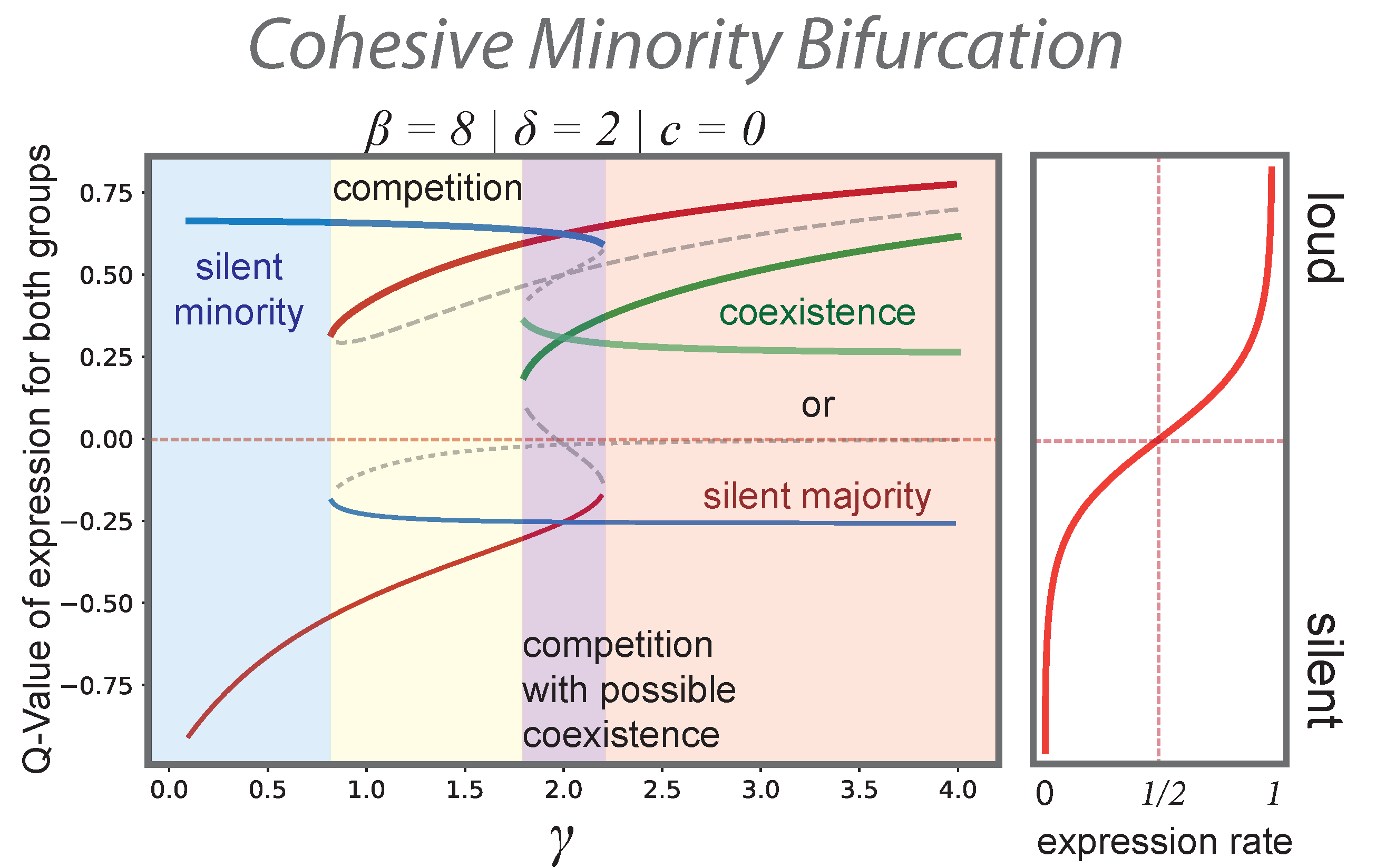
3.1. Organized Minorities and Silent Majorities
3.2. “Spirals of Silence” as a Particular Regime of a More General Process
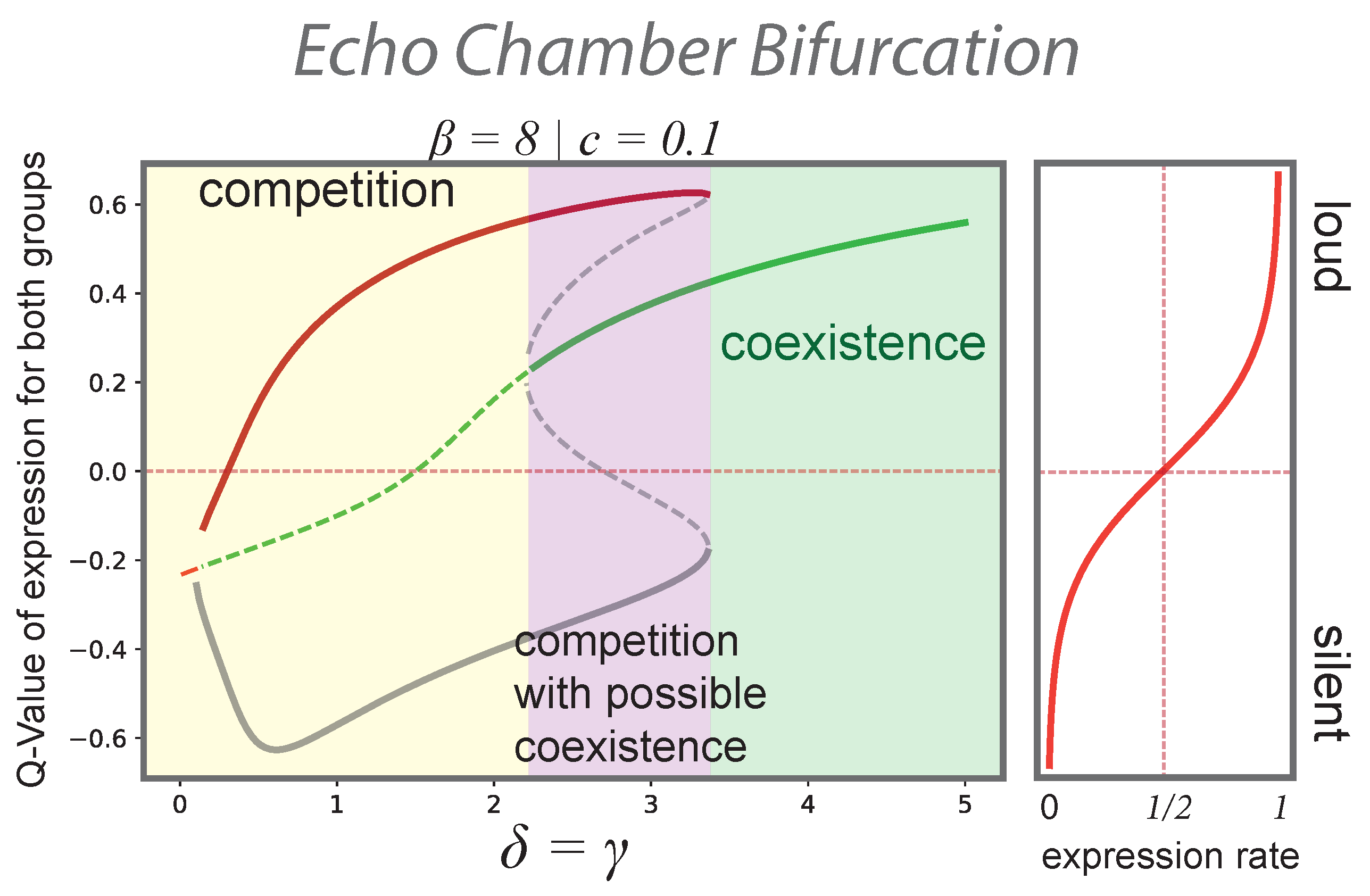
3.3. Social Feedback and Echo Chambers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, M.E.; Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Random graph models of social networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.; Barabási, A.L.E.; Watts, D.J. The Structure and Dynamics of Networks; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Borgatti, S.P.; Mehra, A.; Brass, D.J.; Labianca, G. Network analysis in the social sciences. Science 2009, 323, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtel, W.; Abrahamsen, A. Explanation: A mechanist alternative. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. Part C Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2005, 36, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedström, P.; Ylikoski, P. Causal mechanisms in the social sciences. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2010, 36, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovetter, M.; Soong, R. Threshold models of diversity: Chinese restaurants, residential segregation, and the spiral of silence. Sociol. Methodol. 1988, 18, 69–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuran, T. Sparks and prairie fires: A theory of unanticipated political revolution. Public Choice 1989, 61, 41–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, S. Collective Action Cascades: An Informational Rationale for the Power in Numbers. J. Econ. Surv. 2000, 14, 655–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centola, D. An experimental study of homophily in the adoption of health behavior. Science 2011, 334, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, R.M.; Fariss, C.J.; Jones, J.J.; Kramer, A.D.; Marlow, C.; Settle, J.E.; Fowler, J.H. A 61-million-person experiment in social influence and political mobilization. Nature 2012, 489, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakis, N.A.; Fowler, J.H. Social contagion theory: Examining dynamic social networks and human behavior. Stat. Med. 2013, 32, 556–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedkin, N.E.; Proskurnikov, A.V.; Tempo, R.; Parsegov, S.E. Network science on belief system dynamics under logic constraints. Science 2016, 354, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centola, D.; Becker, J.; Brackbill, D.; Baronchelli, A. Experimental evidence for tipping points in social convention. Science 2018, 360, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, J. An Essay Concerning Human Understanding: And a Treatise on the Conduct of the Understanding. Complete in One Volume with the Author’s Last Additions and Corrections; Hayes & Zell: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1860. [Google Scholar]
- Noelle-Neumann, E. The spiral of silence a theory of public opinion. J. Commun. 1974, 24, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noelle-Neumann, E. Öffentliche Meinung: Die Entdeckung der Schweigespirale; Ullstein: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Banisch, S.; Olbrich, E. Opinion polarization by learning from social feedback. J. Math. Sociol. 2019, 43, 76–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noelle-Neumann, E.; Petersen, T. The spiral of silence and the social nature of man. In Handbook of Political Communication Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2004; pp. 357–374. [Google Scholar]
- Fareri, D.S.; Delgado, M.R. Social rewards and social networks in the human brain. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, C.C.; Fehr, E. The neurobiology of rewards and values in social decision making. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, M.G.; Lebiere, C.; Stocco, A.; Pirolli, P.; Pires, B.; Kennedy, W.G. Multi-scale resolution of neural, cognitive and social systems. Comput. Math. Organ. Theory 2019, 25, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, W.; Dayan, P.; Montague, P.R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 1997, 275, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.N.; Knutson, B. The reward circuit: Linking primate anatomy and human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.E.; Hunt, L.T.; Rushworth, M.F. The computation of social behavior. Science 2009, 324, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, T.V. Reinforcement learning, conditioning, and the brain: Successes and challenges. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 9, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Doherty, J.P.; Dayan, P.; Friston, K.; Critchley, H.; Dolan, R.J. Temporal difference models and reward-related learning in the human brain. Neuron 2003, 38, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbeck, B.B.; Costa, V.D. Motivational neural circuits underlying reinforcement learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, H.A. Rationality as process and as product of thought. Am. Econ. Rev. 1978, 68, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, L.E.; Payton, A.A.; Hernandez, L.M.; Greenfield, P.M.; Dapretto, M. The power of the like in adolescence: Effects of peer influence on neural and behavioral responses to social media. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 27, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, L.E.; Hernandez, L.M.; Greenfield, P.M.; Dapretto, M. What the brain ‘Likes’: Neural correlates of providing feedback on social media. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.I.; Shultz, S. Evolution in the social brain. Science 2007, 317, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.I. The social brain hypothesis. Evol. Anthropol. Issues News Rev. Issues News Rev. 1998, 6, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.; Törnberg, P. Toward a Macroevolutionary Theory of Human Evolution: The Social Protocell. Biol. Theory 2019, 14, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldrack, R.A. Can cognitive processes be inferred from neuroimaging data? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2006, 10, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareri, D.S.; Chang, L.J.; Delgado, M.R. Effects of direct social experience on trust decisions and neural reward circuitry. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuma, K.; Saito, D.N.; Sadato, N. Processing of social and monetary rewards in the human striatum. Neuron 2008, 58, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klucharev, V.; Hytönen, K.; Rijpkema, M.; Smidts, A.; Fernández, G. Reinforcement learning signal predicts social conformity. Neuron 2009, 61, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell-Meiklejohn, D.K.; Bach, D.R.; Roepstorff, A.; Dolan, R.J.; Frith, C.D. How the opinion of others affects our valuation of objects. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuma, K.; Saito, D.N.; Sadato, N. Processing of the incentive for social approval in the ventral striatum during charitable donation. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rilling, J.K.; Sanfey, A.G. The neuroscience of social decision-making. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2011, 62, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, F. Action, outcome, and value: A dual-system framework for morality. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 17, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, D.M.; Frith, C.D. Meeting of minds: The medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuma, K. The social neuroscience of reputation. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 72, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G.; Williams, R.J. Reinforcement learning is direct adaptive optimal control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1992, 12, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hollerman, J.R.; Schultz, W. Dopamine neurons report an error in the temporal prediction of reward during learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Doherty, J.P. Reward representations and reward-related learning in the human brain: Insights from neuroimaging. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaisbauer, F.; Olbrich, E.; Banisch, S. The dynamics of opinion expression. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, S.; Faust, K. Social Network Analysis: Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, S. Contagion. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2000, 67, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyls, K.; Verbeeck, K.; Lenaerts, T. A selection-mutation model for q-learning in multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the Second International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Melbourne, Australia, 14–18 July 2003; pp. 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Crutchfield, J.P. Coupled replicator equations for the dynamics of learning in multiagent systems. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 015206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianercy, A.; Galstyan, A. Dynamics of Boltzmann Q learning in two-player two-action games. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 041145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdos, P.; Rényi, A. On the evolution of random graphs. Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci. 1960, 5, 17–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.N. Random graphs. Ann. Math. Stat. 1959, 30, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarsfeld, P.F.; Berelson, B.; Gaudet, H. The People’s Choice. How the Voter Makes Up Their Mind in a Presidential Campaign; Columbia University Press: New York City, NY, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Walther, S.; McCoy, A. US extremism on Telegram. Perspect. Terror. 2021, 15, 100–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tuters, M.; Hagen, S. (((They))) rule: Memetic antagonism and nebulous othering on 4chan. New Media Soc. 2020, 22, 2218–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Karimi, F.; Wagner, C.; Jo, H.H.; Strohmaier, M.; Galesic, M. Homophily and minority-group size explain perception biases in social networks. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2019, 3, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, J.T. Ideological asymmetries and the essence of political psychology. Political Psychol. 2017, 38, 167–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaisbauer, F.; Pournaki, A.; Banisch, S.; Olbrich, E. How Twitter affects the perception of public opinion: Two case studies. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.01666. [Google Scholar]
- Hume, D. Essays: Moral, Political and Literary; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1963; pp. 1741–1742. [Google Scholar]
- The Gettysburg Address Delivered by Abraham Lincoln Nov. 19 1863 at the Dedication Services on the Battle Field. Available online: https://www.loc.gov/item/2004671506/ (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Dayan, P.; Daw, N.D. Decision theory, reinforcement learning, and the brain. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2008, 8, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glimcher, P.W.; Fehr, E. Neuroeconomics: Decision Making and the Brain; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J. Social network analysis. Sociology 1988, 22, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazer, D.; Pentland, A.; Adamic, L.; Aral, S.; Barabási, A.L.; Brewer, D.; Christakis, N.; Contractor, N.; Fowler, J.; Gutmann, M.; et al. Computational social science. Science 2009, 323, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, M.D.; Ratkiewicz, J.; Francisco, M.; Gonçalves, B.; Menczer, F.; Flammini, A. Political polarization on twitter. In Proceedings of the Fifth International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Garimella, K.; Morales, G.D.F.; Gionis, A.; Mathioudakis, M. Quantifying controversy on social media. ACM Trans. Soc. Comput. 2018, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumont, N.; Panahi, M.; Chavalarias, D. Reconstruction of the socio-semantic dynamics of political activist Twitter networks—Method and application to the 2017 French presidential election. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuran, T. Now out of never: The element of surprise in the East European revolution of 1989. World Politics 1991, 44, 7–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festinger, L. A Theory of Cognitive Dissonance; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1957; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, B.L.; Leong, J.K.; Shiv, B.; Zaki, J. Wanting to like: Motivation influences behavioral and neural responses to social feedback. bioRxiv 2018, 300657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerubavel, N.; Hoffman, M.A.; Reich, A.; Ochsner, K.N.; Bearman, P. Neural precursors of future liking and affective reciprocity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4375–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banisch, S.; Gaisbauer, F.; Olbrich, E. Modelling Spirals of Silence and Echo Chambers by Learning from the Feedback of Others. Entropy 2022, 24, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101484
Banisch S, Gaisbauer F, Olbrich E. Modelling Spirals of Silence and Echo Chambers by Learning from the Feedback of Others. Entropy. 2022; 24(10):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101484
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanisch, Sven, Felix Gaisbauer, and Eckehard Olbrich. 2022. "Modelling Spirals of Silence and Echo Chambers by Learning from the Feedback of Others" Entropy 24, no. 10: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101484
APA StyleBanisch, S., Gaisbauer, F., & Olbrich, E. (2022). Modelling Spirals of Silence and Echo Chambers by Learning from the Feedback of Others. Entropy, 24(10), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101484






