An Overview of Geometrical Optics Restricted Quantum Key Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
2.1. BB84
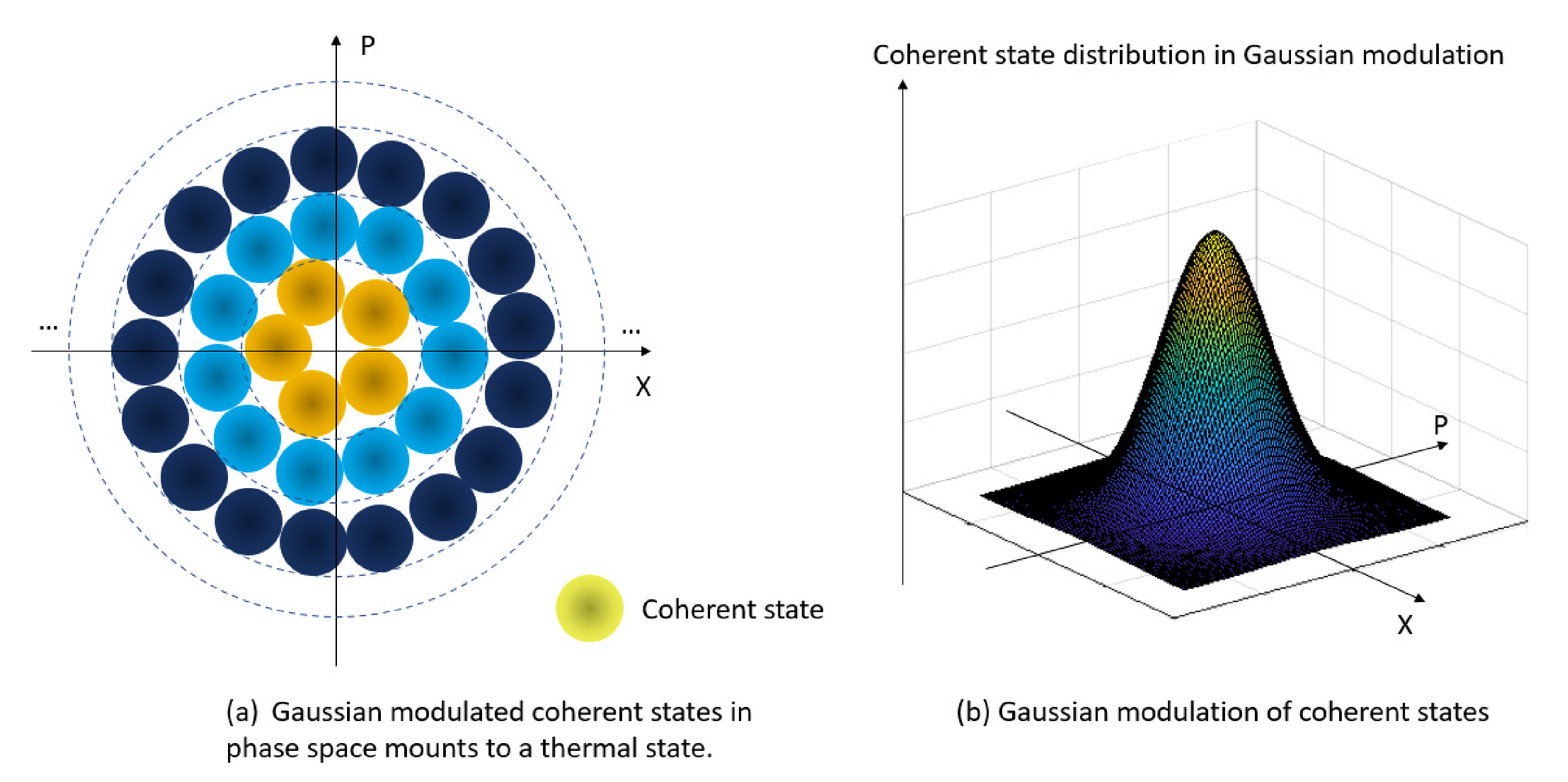
2.2. GG02
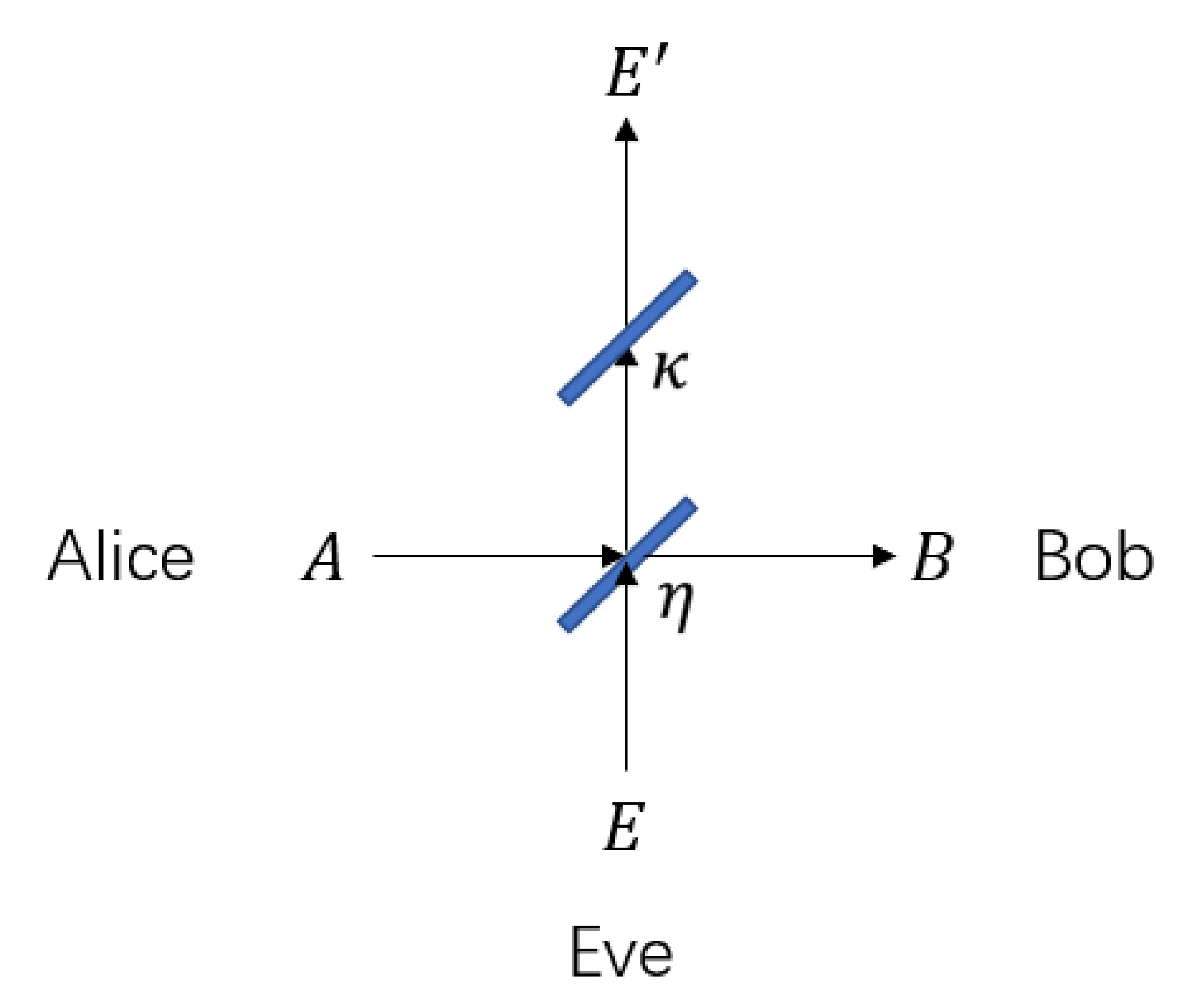
3. Geometrical Optics Restricted Model
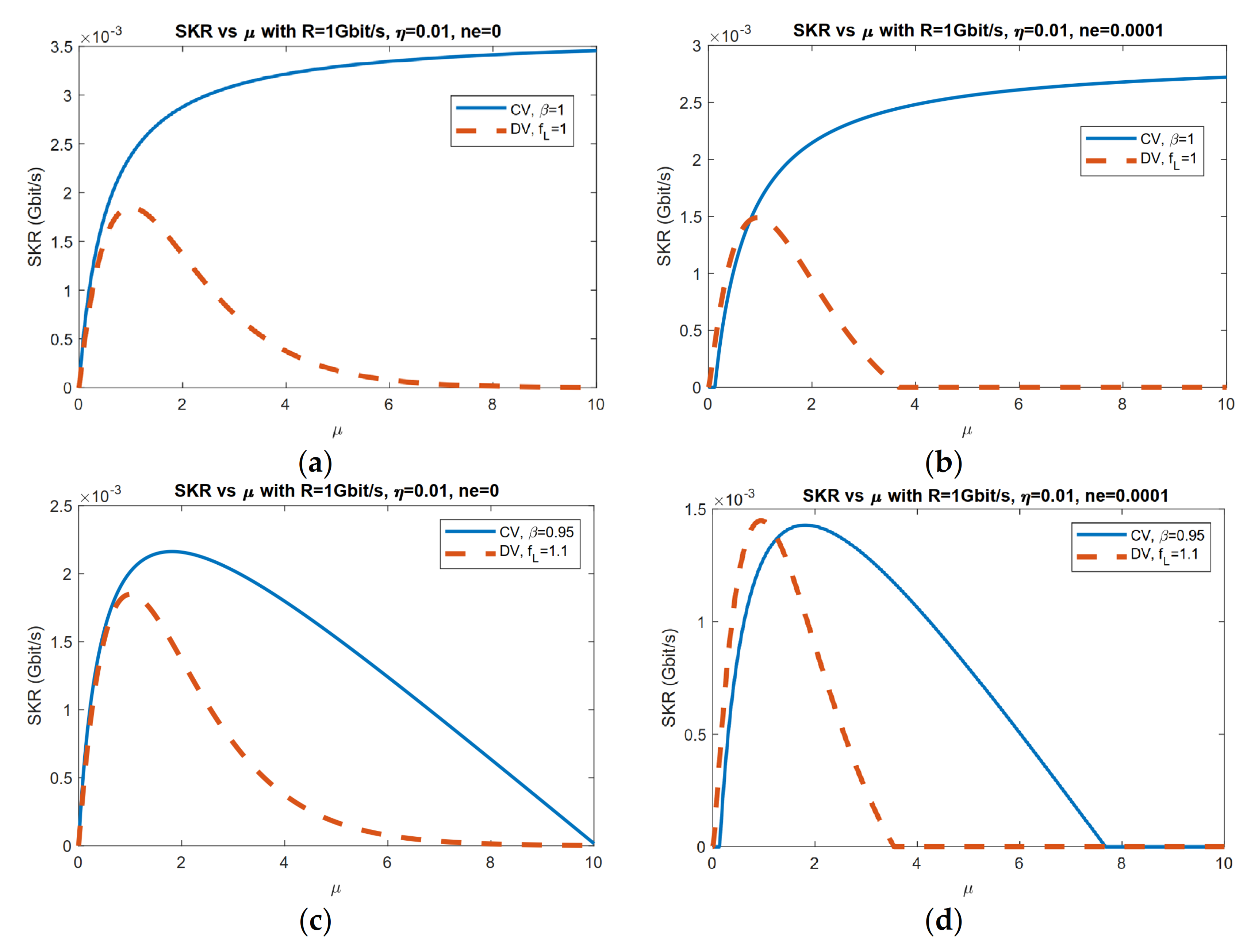
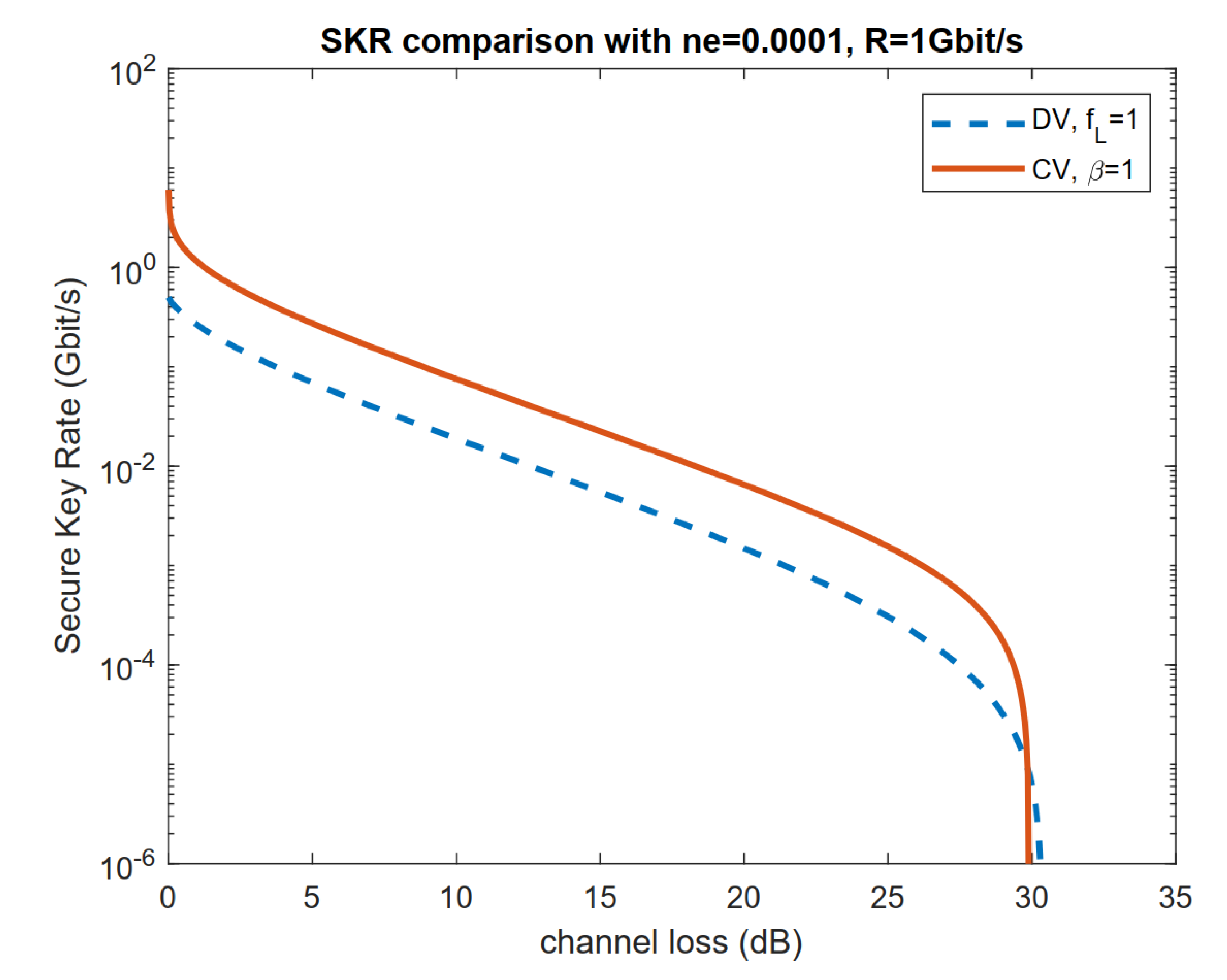
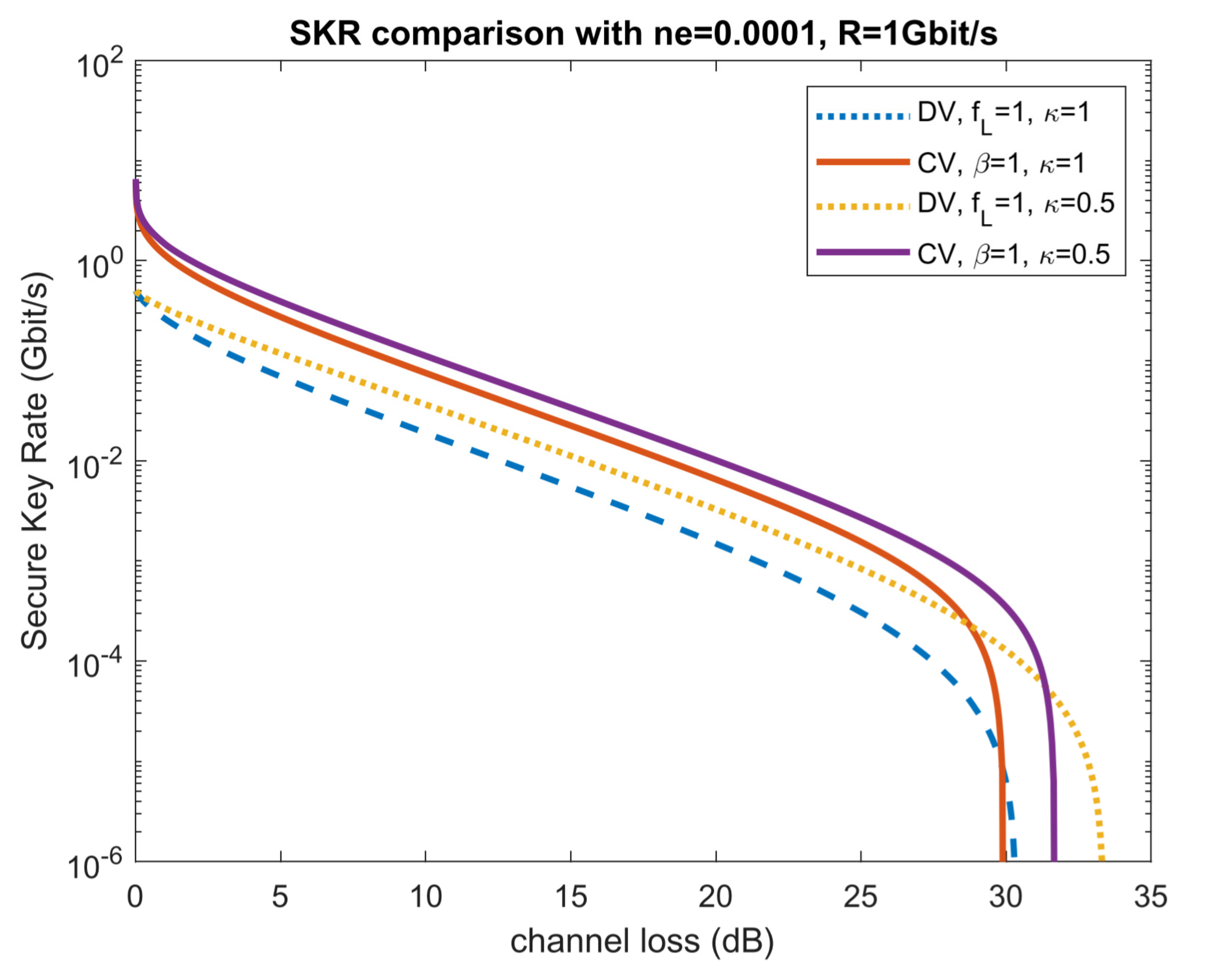
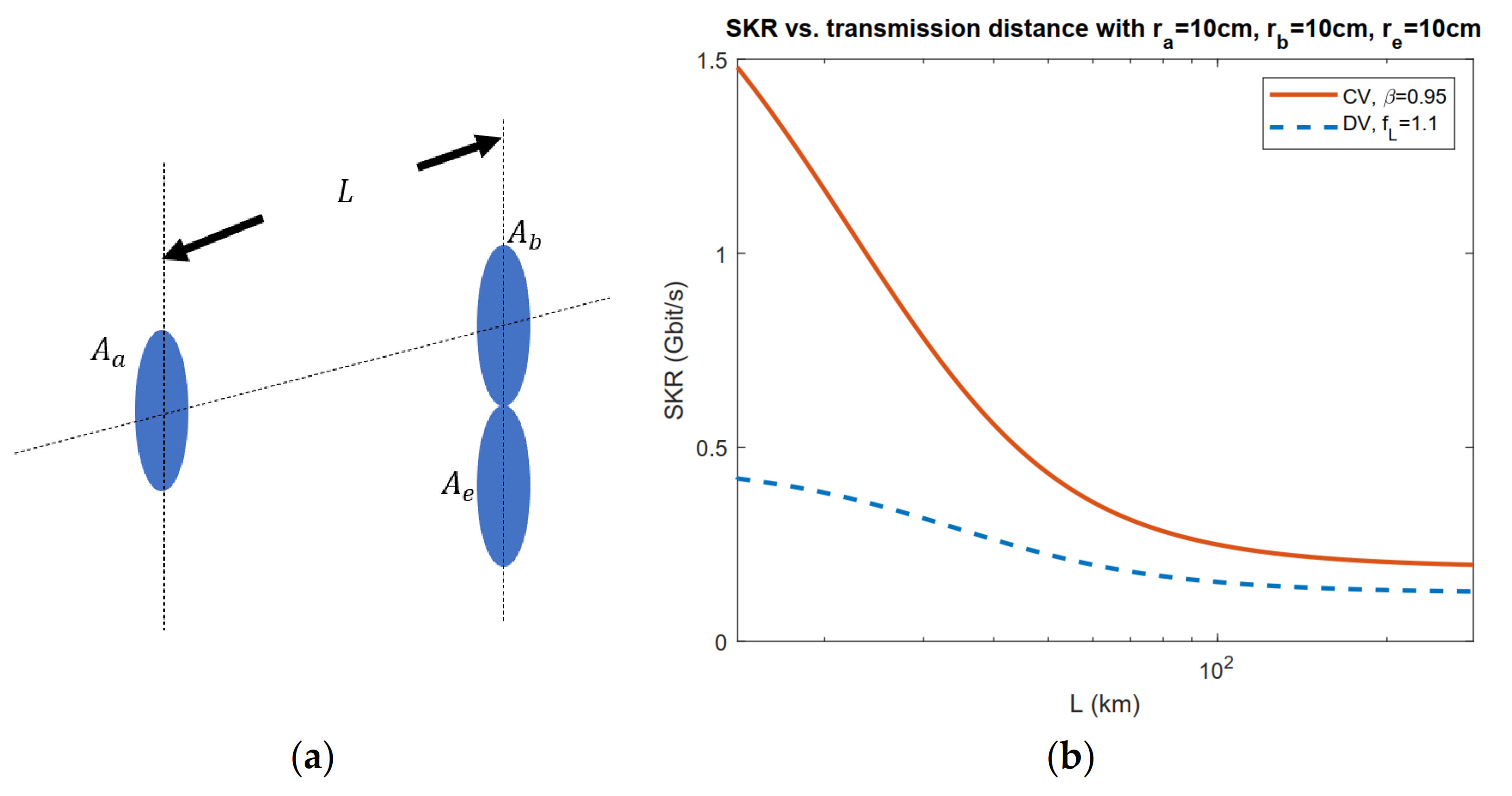
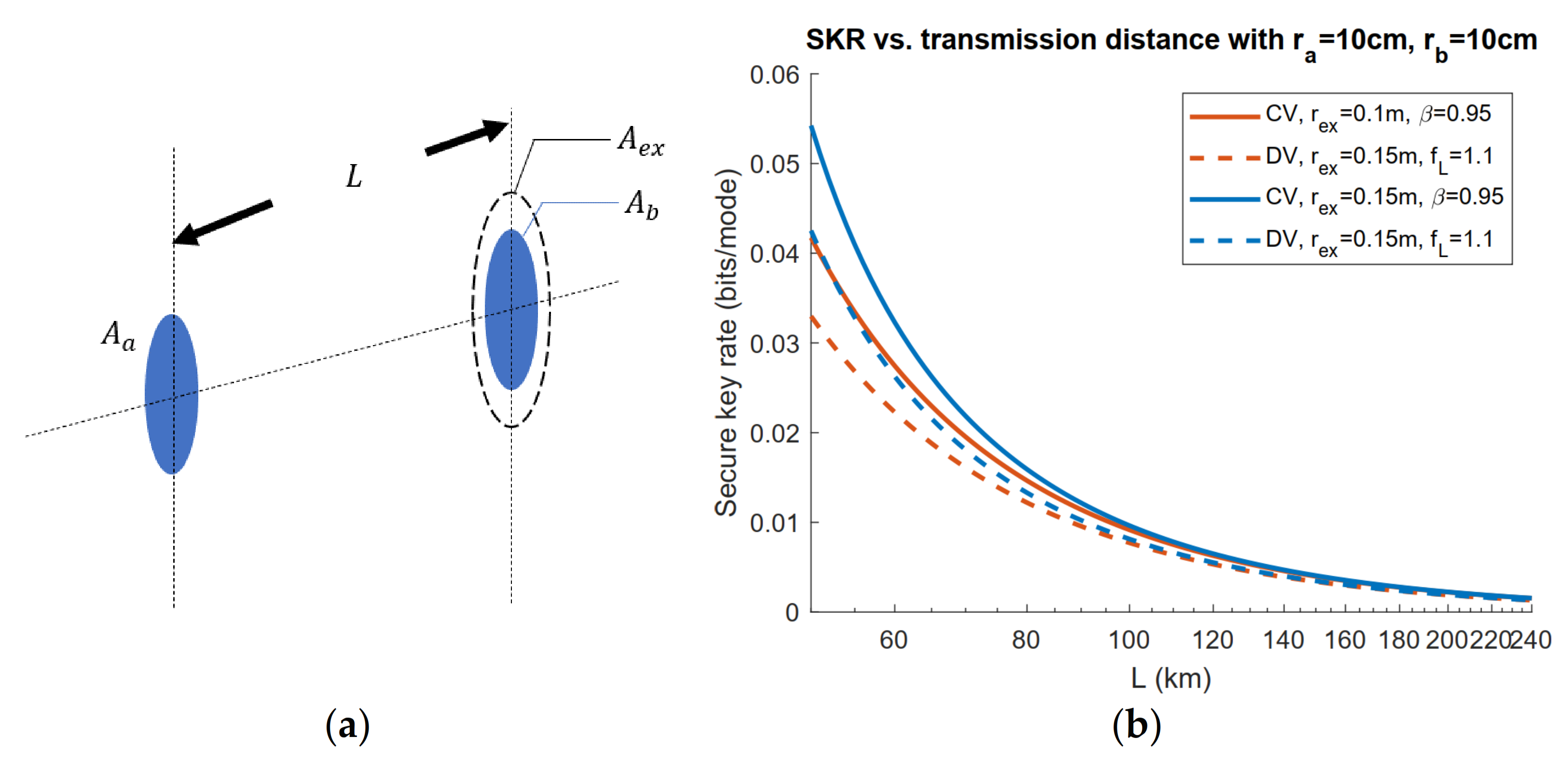
3.1. Application of Geometrical Optics Restricted Model: Limited Aperture Size Analysis
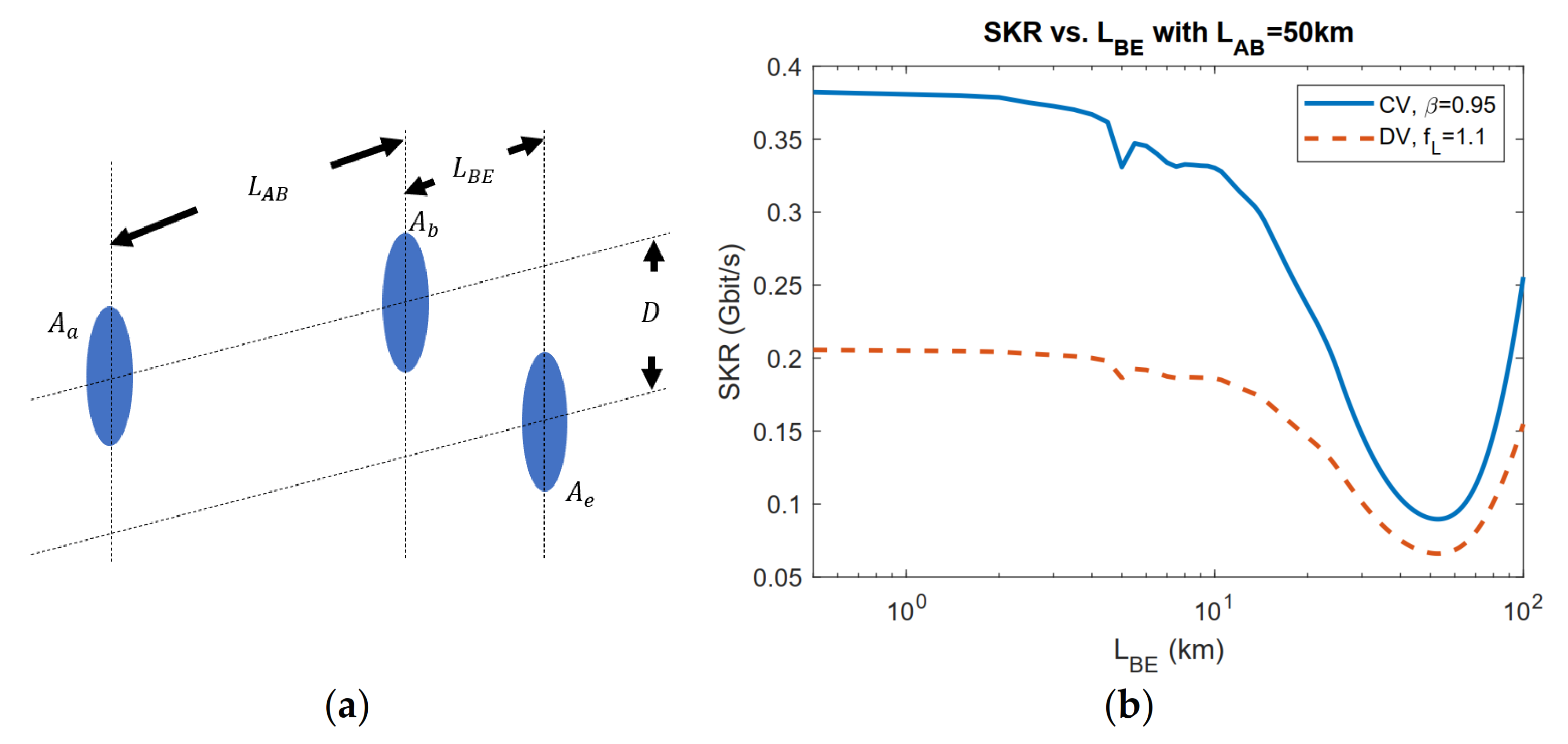
3.2. Application of Geometrical Optics Restricted Model: Exclusion Zone Analysis
4. Discussion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, C.E. Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1949, 28, 656–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Gilles, B. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H. Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 21, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.H.; Gilles, B.; Mermin, N.D. Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekert, A.K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayers, D.; Yao, A. Quantum Cryptography with Imperfect Apparatus. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (Cat. No. 98CB36280), Palo Alto, CA, USA, 8–11 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, J.; Yehuda, L. Introduction to Modern Cryptography; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nyquist, H. Regeneration theory. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1932, 11, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, H. Certain factors affecting telegraph speed. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1924, 3, 324–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, H. Certain topics in telegraph transmission theory. Trans. AIEE 1928, 47, 617–644, Reprint as classic paper in Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 280–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.V.L. Relations of Carrier and Side-Bands in Radio Transmission. Proc. IRE 1923, 11, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.V.L. Transmission of Information. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1928, 7, 535–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data Encryption Standard. Available online: https://telluur.com/utwente/master/SyS%20-%20System%20Security/2018/Aanvullende%20docs/Data_Encryption_Standard.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Advanced Encryption Standard. Available online: https://telluur.com/utwente/master/SyS%20-%20System%20Security/2018/Aanvullende%20docs/AES.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Rivest, R.L.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems. Commun. ACM. 1978, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffie, W.; Hellman, M. New Directions in Cryptography (PDF). IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 6, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskill, J. Quantum Computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroeidis, V.; Kamer, V.; Mateusz, D.Z.; Audun, J. The impact of quantum computing on present cryptography. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, P.W. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Washington, DC, USA, 20–22 November 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, L.K. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 May 1996; pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, J.; Hardy, L.L.; Kent, A.A. No Signaling and Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 010503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironio, S.; Acín, A.; Brunner, N.; Gisin, N.; Massar, S.; Scarani, V. Device-independent quantum key distribution secure against collective attacks. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 045021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKague, M. Device independent quantum key distribution secure against coherent attacks with memoryless meas-urement devices. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerf, N.J.; Lévy, M.; Van Assche, G. Quantum distribution of Gaussian keys using squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 63, 052311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Continuous Variable Quantum Cryptography Using Coherent States. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 057902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B. Decoy-state protocol for quantum cryptography with four different intensities of coherent light. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 012322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Ma, X.; Chen, K. Decoy State Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 230504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Qi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Lo, H.-K. Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 012326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafu, M.; Dudley, A.; Goyal, S.; Giovannini, D.; McLaren, M.; Padgett, M.; Konrad, T.; Petruccione, F.; Lutkenhaus, N.; Forbes, A. Higher-dimensional orbital-angular-momentum-based quantum key distribution with mutually unbiased bases. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 032305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, C. Quantum Key Distribution with High Order Fibonacci-like Orbital Angular Momentum States. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2017, 56, 2622–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Djordjevic, I.B. Deep-space and near-Earth optical communications by coded orbital angular momentum (OAM) modulation. Opt. Express 2015, 19, 14277–14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Seshadreesan, K.P.; Clark, W.; Adcock, M.R.; Djordjevic, I.B.; Shapiro, J.H.; Guha, S. Secret-Key Distillation across a Quantum Wiretap Channel under Restricted Eavesdropping. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 14, 024044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Seshadreesan, K.P.; Clark, W.; Adcock, M.R.; Djordjevic, I.B.; Shapiro, J.H.; Guha, S. Secret key distillation over a pure loss quantum wiretap channel under restricted eavesdropping. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Paris, France, 7–12 July 2019; pp. 3032–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Djordjevic, I.B. Security of Satellite-Based CV-QKD under Realistic Assumptions. In Proceedings of the 2020 22nd International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 19–23 July 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Gariano, J.; Djordjevic, I.B. Secret Key Distillation over Satellite-to-satellite Free-space Channel with Eavesdropper Dynamic Positioning. In OSA Advanced Photonics Congress (AP) 2020 (IPR, NP, NOMA, Networks, PVLED, PSC, SPPCom, SOF); The Optical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; p. SpTu3I.4. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Djordjevic, I.B. Secret key distillation over satellite-to-satellite free-space optics channel with a lim-ited-sized aperture eavesdropper in the same plane of the legitimate receiver. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 37129–37148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Gariano, J.; Clark, W.; Djordjevic, I.B. Secret key distillation over realistic satellite-to-satellite free-space channel. In Proceedings of the OSA Quantum 2.0 Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 14–17 September 2020; p. QTh7B.15. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Djordjevic, I.B. Secret key distillation over realistic satellite-to-satellite free-space channel: Exclusion zone analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.05929. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Djordjevic, I.B. Secret Key Distillation over Satellite-to-satellite Free-space Optics Channel with Eaves-dropper Dynamic Positioning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich, B.; Dynes, J.F.; Lucamarini, M.; Sharpe, A.W.; Yuan, Z.; Shields, A.J. A quantum access network. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 501, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimble, H.J. The quantum internet. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 453, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallone, G.; Bacco, D.; Dequal, D.; Gaiarin, S.; Luceri, V.; Bianco, G.; Villoresi, P. Experimental Satellite Quantum Communications. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-Yu, S.; Yang, B.; Sheng-Kai, L.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.; Xiao-Fang, H.; Jin-Cai, W. Direct and full-scale experimental verifications towards ground–satellite quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.-K.; Cai, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.-G.; Yin, J.; Shen, Q.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z.-P.; et al. Satellite-to-ground quantum key distribution. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 549, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedington, R.; Arrazola, J.M.; Ling, A. Progress in satellite quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, S.; Liu, B.; Handsteiner, J.; Fink, M.; Rauch, D.; Steinlechner, F.; Scheidl, T.; Zeilinger, A.; Ursin, R. Strategies for achieving high key rates in satellite-based QKD. Npj Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironio, S.; Acín, A.; Massar, S.; Boyer de La Giroday, A.; Matsukevich, N.D.; Maunz, P.; Olmschenk, S. Random numbers certified by Bell’s theorem. Nature 2010, 464, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanes, L.; Pironio, S.; Acín, A. Secure device-independent quantum key distribution with causally in-dependent measurement devices. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironio, S.; Masanes, L.; Leverrier, A.; Acín, A. Security of Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution in the Bounded-Quantum-Storage Model. Phys. Rev. X 2013, 3, 031007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirani, U.; Vidick, T. Fully Device Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 62, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusey, M.F. Verifying the quantumness of a channel with an untrusted device. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2015, 32, A56–A63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunstein, S.L.; Van Loock, P. Quantum information with continuous variables. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 77, 513–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Manderbach, T.; Weier, H.; Fürst, M.; Ursin, R.; Tiefenbacher, F.; Scheidl, T.; Perdigues, J. Experimental demonstration of free-space decoy-state quantum key distribution over 144 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutkenhaus, N. Security against individual attacks for realistic quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 61, 052304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarani, V.; Renato, R. Quantum cryptography with finite resources: Unconditional security bound for discrete-variable protocols with one-way postprocessing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 200501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittel, W.; Brendel, J.; Zbinden, H.; Gisin, N. Quantum Cryptography Using Entangled Photons in Energy-Time Bell States. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 4737–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B. Single-photon continuous-variable quantum key distribution based on the energy-time uncertainty relation. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2795–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Laurenza, R.; Ottaviani, C.; Banchi, L. Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, M.; Seshadreesan, K.P.; Wilde, M.M. Unconstrained distillation capacities of a pure-loss bosonic broadcast channel. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Barcelona, Spain, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, M.; Seshadreesan, K.P.; Wilde, M.M. Unconstrained Capacities of Quantum Key Distribution and Entanglement Distillation for Pure-Loss Bosonic Broadcast Channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 150501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devetak, I.; Winter, A. Distillation of secret key and entanglement from quantum states. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 461, 207–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
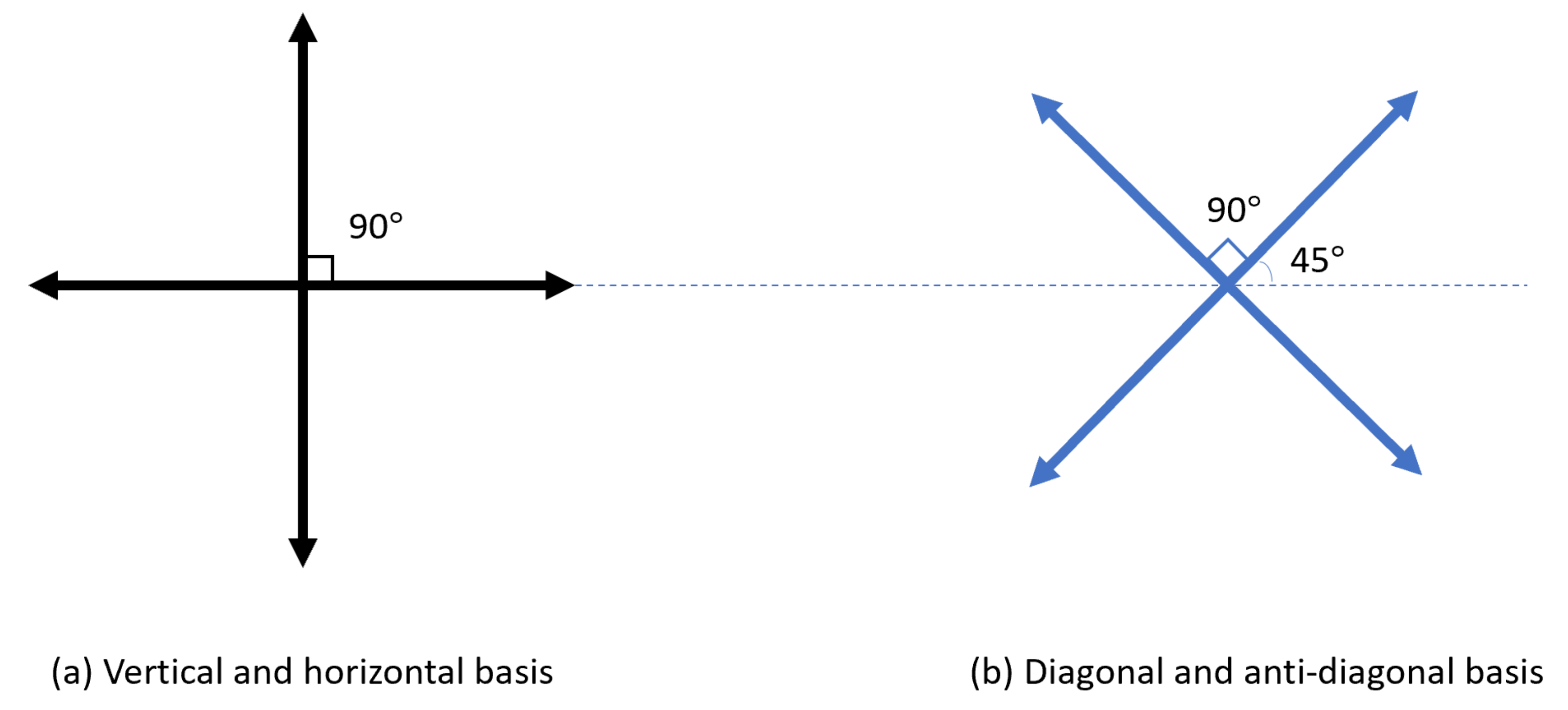
| Random Bits | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alice basis | a | a | b | a | b | a | b | b | a |
| Polarization state sent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Bob basis | b | a | a | b | b | a | b | a | b |
| Bob measurement results | random | 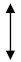 | random | random |  | 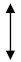 |  | random | random |
| Sifted keys | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Z.; Djordjevic, I.B. An Overview of Geometrical Optics Restricted Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy 2021, 23, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23081003
Pan Z, Djordjevic IB. An Overview of Geometrical Optics Restricted Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy. 2021; 23(8):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23081003
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Ziwen, and Ivan B. Djordjevic. 2021. "An Overview of Geometrical Optics Restricted Quantum Key Distribution" Entropy 23, no. 8: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23081003
APA StylePan, Z., & Djordjevic, I. B. (2021). An Overview of Geometrical Optics Restricted Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy, 23(8), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23081003







