Clinical Value of Information Entropy Compared with Deep Learning for Ultrasound Grading of Hepatic Steatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ultrasound Protocol
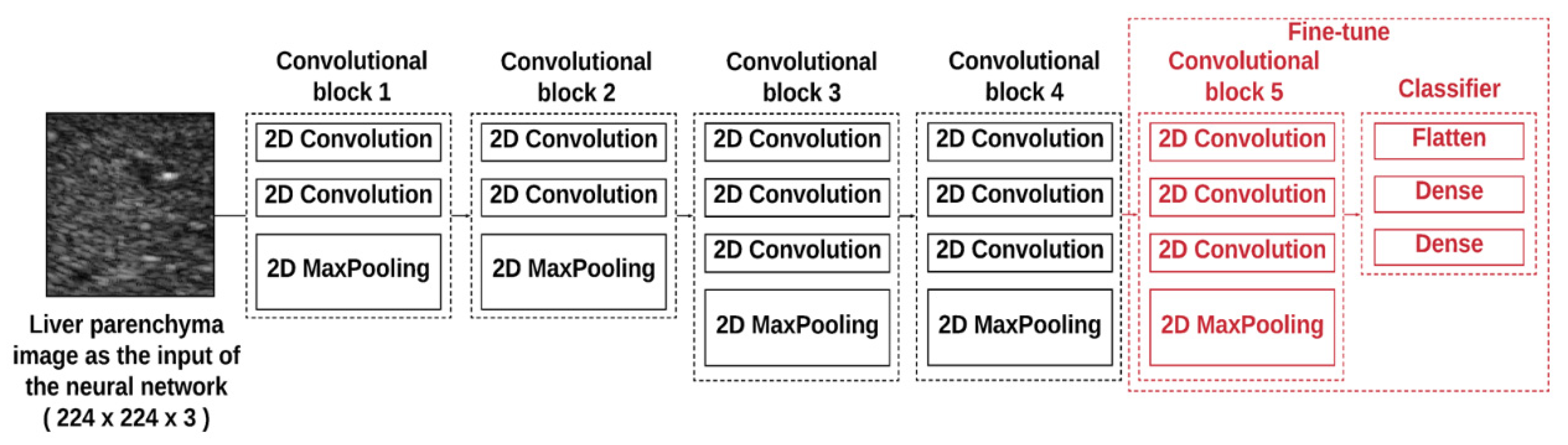
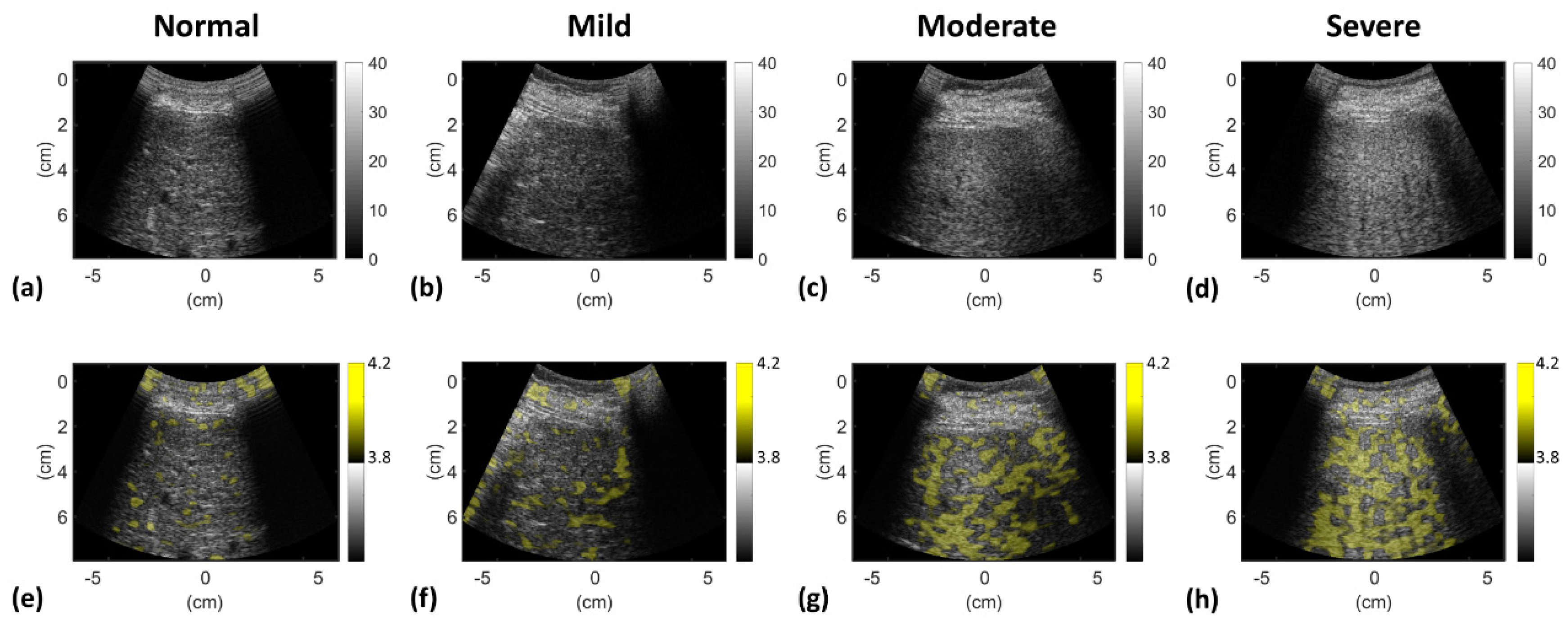
2.3. Ultrasound Data Preprocessing
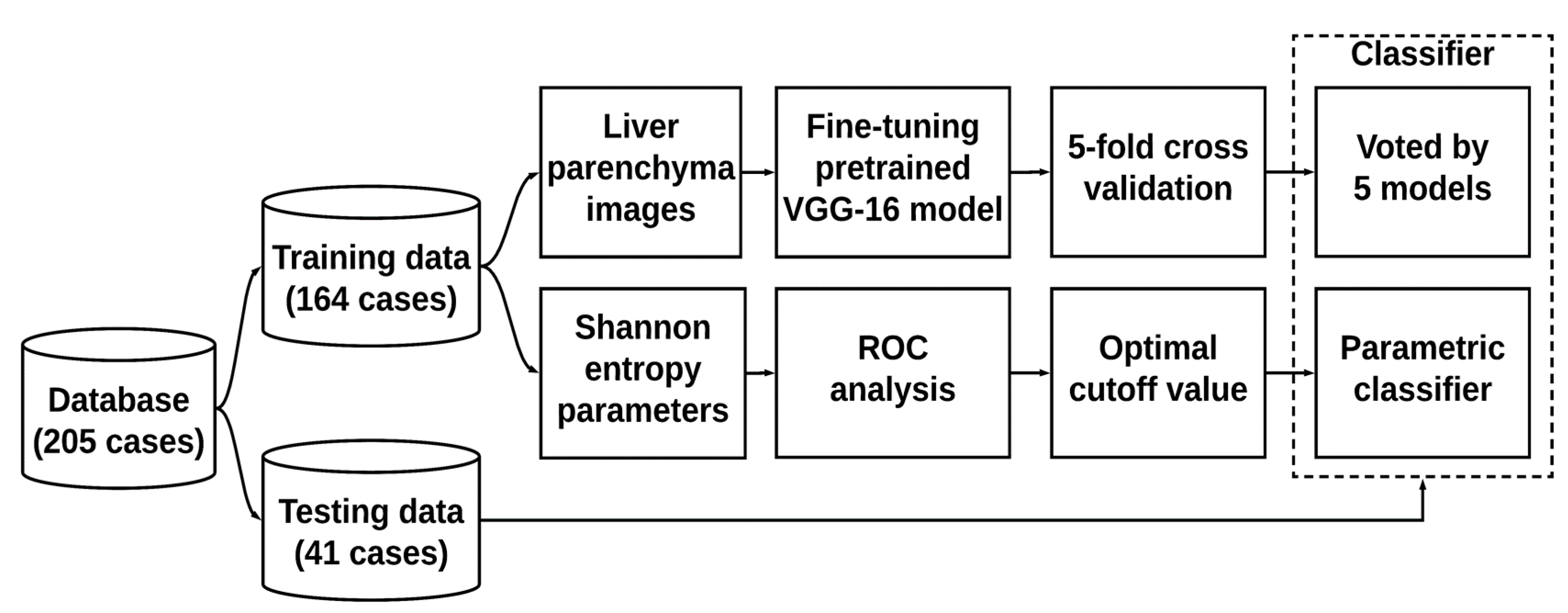
2.4. Training and Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Significance of this Study
4.2. Comparisons of Information Entropy with Deep Learning
4.3. Considerations of Using Deep Learning in Grading Hepatic Steatosis
4.4. Physical Interpretations of Information Entropy
4.5. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.F.Y.; Li, A.M.; Chu, W.C.W.; Chan, M.H.M.; Wong, E.M.C.; Liu, E.K.H.; Chan, I.H.S.; Yin, J.; Lam, C.W.K.; Fok, T.F.; et al. Hepatic steatosis in obese Chinese children. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, S.; Gavish, E.; Gottlieb, P.; Katsnelson, L. Interobserver and Intraobserver Variability in the Sonographic Assessment of Fatty Liver. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, W320–W323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirmoazen, A.M.; Khurana, A.; El Kaffas, A.; Kamaya, A. Quantitative ultrasound approaches for diagnosis and monitoring hepatic steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4277–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, P.-H.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Y.-H.; Hung, C.-M.; Chung, S.-J.; Wan, Y.-L. Effect of ultrasound frequency on the Nakagami statistics of human liver tissues. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamou, J.; Oelze, M.L. Quantitative Ultrasound in Soft Tissues; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Fang, J.; Cristea, A.; Lin, Y.-H.; Tsai, Y.-W.; Wan, Y.-L.; Yeow, K.-M.; Ho, M.-C.; Tsui, P.-H. Value of homodyned K distribution in ultrasound parametric imaging of hepatic steatosis: An animal study. Ultrasonics 2020, 101, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Lin, Y.-H.; Tai, D.-I.; Tseng, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-R.; Wu, S.; Tsui, P.-H. Hepatic steatosis assessment using ultrasound homodyned-K parametric imaging: The effects of estimators. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1932–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, S.; Lin, M.-Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, H.-L.; Tsui, P.-H. Three-dimensional Visualization of Ultrasound Backscatter Statistics by Window-modulated Compounding Nakagami Imaging. Ultrason. Imaging 2018, 40, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.-L.; Tai, D.-I.; Ma, H.-Y.; Chiang, B.-H.; Chen, C.-K.; Tsui, P.-H. Effects of fatty infiltration in human livers on the backscattered statistics of ultrasound imaging. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2015, 229, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, P.-H. Ultrasound Detection of Scatterer Concentration by Weighted Entropy. Entropy 2015, 17, 6598–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.S. Analysis of digitized waveforms using Shannon entropy. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, P.-H.; Wan, Y.-L. Effects of Fatty Infiltration of the Liver on the Shannon Entropy of Ultrasound Backscattered Signals. Entropy 2016, 18, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chang, N.-F.; Tsui, P.-H. Performance Evaluations on Using Entropy of Ultrasound Log-Compressed Envelope Images for Hepatic Steatosis Assessment: An In Vivo Animal Study. Entropy 2018, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tai, D.-I.; Wan, Y.-L.; Tseng, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-R.; Wu, S.; Yang, K.-C.; Liao, Y.-Y.; Yeh, C.-K.; Tsui, P.-H. Hepatic Steatosis Assessment with Ultrasound Small-Window Entropy Imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Liao, Y.-Y.; Yeh, C.-K.; Yang, K.-C.; Tsui, P.-H. Ultrasound Entropy Imaging of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Association with Metabolic Syndrome. Entropy 2018, 20, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xue, K.; Zhang, K. Current status and future trends of clinical diagnoses via image-based deep learning. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7556–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byra, M.; Styczyński, G.; Szmigielski, C.; Kalinowski, P.; Michałowski, Ł.; Paluszkiewicz, R.; Ziarkiewicz-Wróblewska, B.; Zieniewicz, K.; Sobieraj, P.; Nowicki, A. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for liver steatosis assessment in ultrasound images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.-C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M.; Hoo-Chang, S. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, F.; Zhu, J.; Xu, N.; Kong, D. A pre-trained convolutional neural network based method for thyroid nodule diagnosis. Ultrasonics 2017, 73, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.M.; Malhi, H.S. Transfer Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks for Classification of Abdominal Ultrasound Images. J. Digit. Imaging 2016, 30, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ping, B.; Li, D.; Du, J.; Qin, Y.; Lu, H.; Wan, X.; Xiang, J. Deep convolutional neural network VGG-16 model for differential diagnosing of papillary thyroid carcinomas in cytological images: A pilot study. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.S.; Jadhav, S.M. Deep convolutional neural network based medical image classification for disease diagnosis. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S.; Bharath, R.; Rajalakshmi, P. A Novel Computer-Aided Diagnosis Framework Using Deep Learning for Classification of Fatty Liver Disease in Ultrasound Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Ostrava, Czech Republic, 17–20 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Wan, Y.-L.; Tai, D.-I.; Tseng, J.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-W.; Lin, Y.-R.; Chang, T.-Y.; Tsui, P.-H. Considerations of Ultrasound Scanning Approaches in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Assessment through Acoustic Structure Quantification. Ultrasound Med. Boil. 2019, 45, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, W.; Wu, S.; Jia, K.; Tsui, P.-H. Empirical Mode Decomposition of Ultrasound Imagingfor Gain-Independent Measurement on Tissue Echogenicity: A Feasibility Study. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, P.-H.; Chen, C.-K.; Kuo, W.-H.; Chang, K.-J.; Fang, J.; Ma, H.-Y.; Chou, D. Small-window parametric imaging based on information entropy for ultrasound tissue characterization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, I. Defining an Optimal Cut-Point Value in ROC Analysis: An Alternative Approach. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2017, 2017, 3762651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ling, C. Using AUC and accuracy in evaluating learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; An, X.; Cong, L.; Lyu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, R. Application of Deep Learning in Quantitative Analysis of 2-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 39, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-F.; Chang, I.-C.; Hong, C.-C.; Yen, T.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Wu, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-C.; Ho, M.-C.; Lee, W.-C.; Yu, H.-C.; et al. Metabolic risk factors are associated with non-hepatitis B non-hepatitis C hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan, an endemic area of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelvecchi, D. Can we open the black box of AI? Nat. News 2016, 538, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Fukusato, T. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15539–15548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Chan, A.W.H. Pathology of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Dig. Dis. 2016, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Parton, R. Lipid droplets: A unified view of a dynamic organelle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Male/Female | 130/75 |
| Age, years | |
| Mean standard deviation (range) | 55 11.6 (24–79) |
| Median | 57 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | |
| Mean standard deviation (range) | 25.3 3.8 (16.8–37.8) |
| Median | 24.9 |
| AST, U/L | |
| Mean standard deviation (range) | 67.2 68.6 (15–507) |
| Median | 46 |
| ALT, U/L | |
| Mean standard deviation (range) | 86.8 99.0 (8–595) |
| Median | 52 |
| PLT, 103/mm3 | |
| Mean standard deviation (range) | 193 68.2 (73–542) |
| Median | 186 |
| Steatosis grade, no. of patients | |
| Normal | 79 |
| Mild | 74 |
| Moderate | 35 |
| Severe | 17 |
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatic steatosis grade | ≥mild | ≥moderate | ≥severe |
| (Number of subjects, Amount of data) for Label 1 | (79, 395) | (153, 765) | (188, 940) |
| (Number of subjects, Amount of data) for Label 2 | (126, 630) | (52, 260) | (17, 85) |
| (Number of subjects, Amount of data) for training set | (164, 820) | (164, 820) | (164, 820) |
| (Number of subjects, Amount of data) for test set | (41, 205) | (41, 205) | (41, 205) |
| Parameter | Shannon Entropy | VGG-16 Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥Mild | ≥Moderate | ≥Severe | ≥Mild | ≥Moderate | ≥Severe | |
| Cutoff value | 3.75 | 3.79 | 3.82 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Accuracy | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.97 |
| Sensitivity, % | 64.10 | 70.00 | 78.82 | 73.18 | 63.25 | 85.23 |
| Specificity, % | 70.16 | 86.54 | 93.30 | 60.00 | 74.82 | 84.12 |
| Precision, % | 58.62 | 93.86 | 99.33 | 54.12 | 88.39 | 97.93 |
| Recall, % | 63.75 | 69.03 | 78.42 | 73.75 | 63.87 | 74.73 |
| F1-score | 0.61 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.85 |
| AUROC (95% CI) | 0.68 (0.60–0.76) | 0.85 (0.80–0.90) | 0.90 (0.85–0.95) | 0.71 (0.64–0.78) | 0.75 (0.67–0.82) | 0.88 (0.80–0.94) |
| DeLong test (P-value) | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.54 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.54 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-R.; Chao, Y.-P.; Tsai, Y.-W.; Chan, H.-J.; Wan, Y.-L.; Tai, D.-I.; Tsui, P.-H. Clinical Value of Information Entropy Compared with Deep Learning for Ultrasound Grading of Hepatic Steatosis. Entropy 2020, 22, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091006
Chen J-R, Chao Y-P, Tsai Y-W, Chan H-J, Wan Y-L, Tai D-I, Tsui P-H. Clinical Value of Information Entropy Compared with Deep Learning for Ultrasound Grading of Hepatic Steatosis. Entropy. 2020; 22(9):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091006
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jheng-Ru, Yi-Ping Chao, Yu-Wei Tsai, Hsien-Jung Chan, Yung-Liang Wan, Dar-In Tai, and Po-Hsiang Tsui. 2020. "Clinical Value of Information Entropy Compared with Deep Learning for Ultrasound Grading of Hepatic Steatosis" Entropy 22, no. 9: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091006
APA StyleChen, J.-R., Chao, Y.-P., Tsai, Y.-W., Chan, H.-J., Wan, Y.-L., Tai, D.-I., & Tsui, P.-H. (2020). Clinical Value of Information Entropy Compared with Deep Learning for Ultrasound Grading of Hepatic Steatosis. Entropy, 22(9), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091006







