A Novel Method to Rank Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Tsallis Entropy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
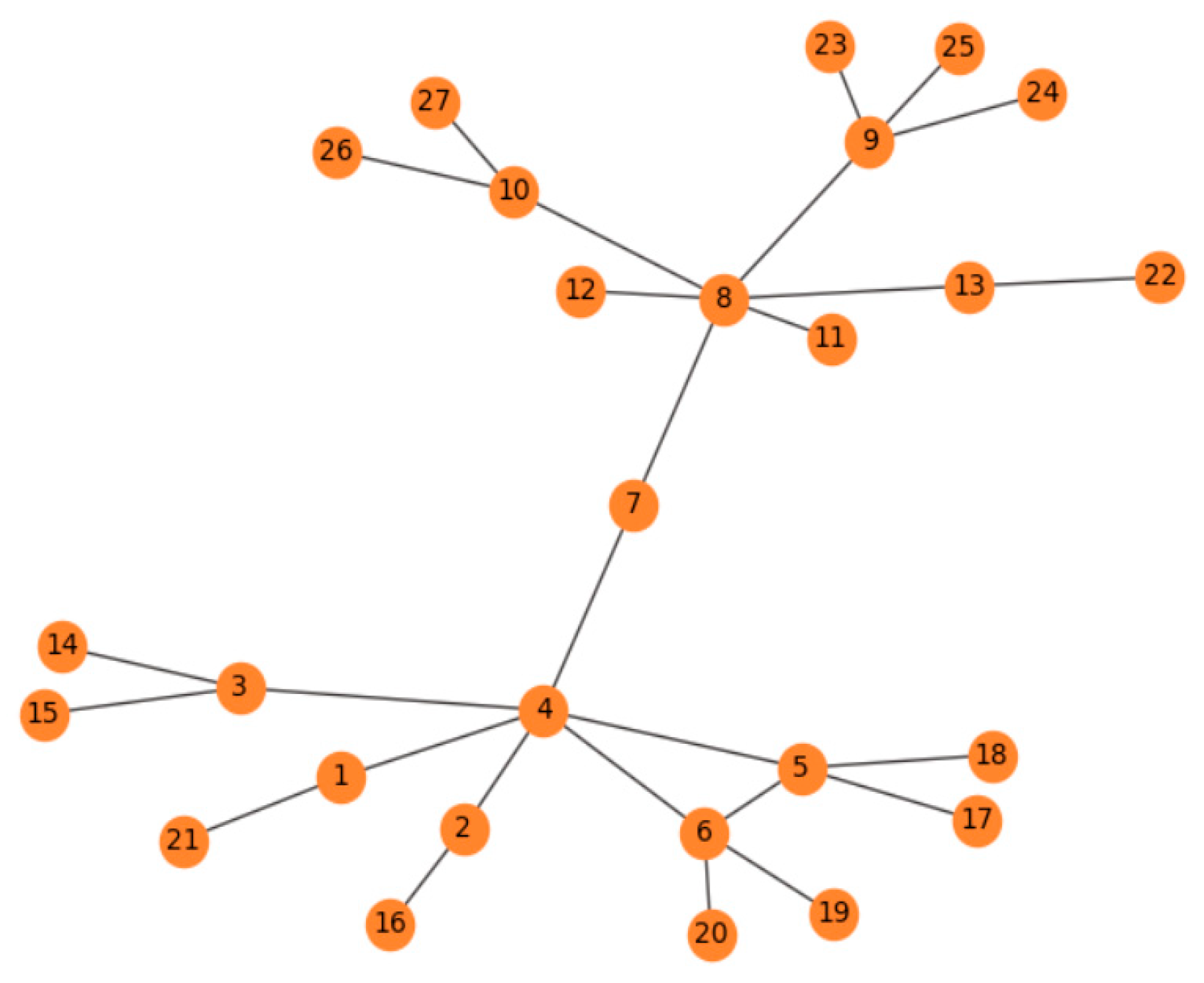
3. Motivation and Proposed Approach
3.1. Tsallis Entropy
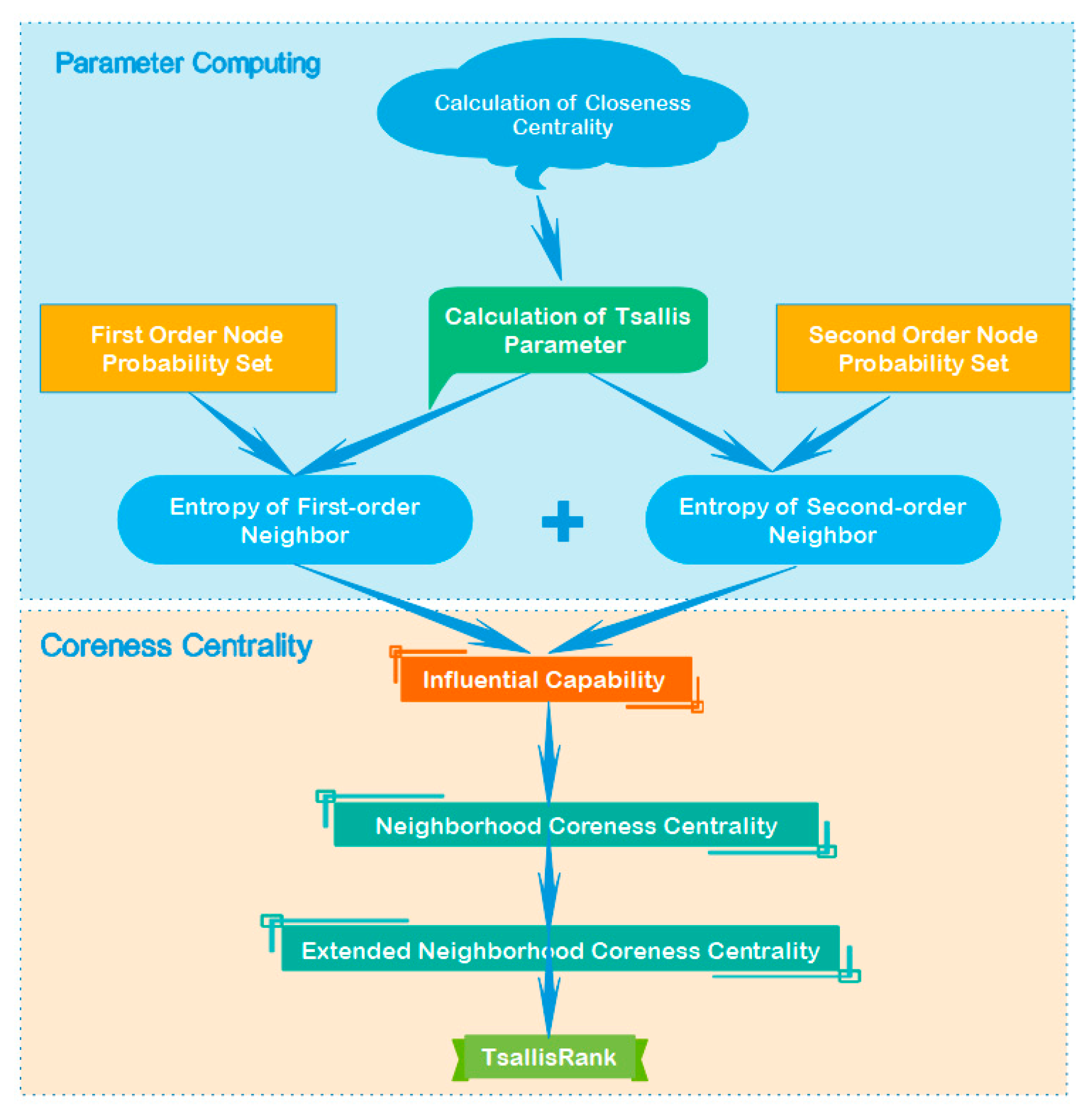
3.2. TsallisRank
3.2.1. Parameter Computing
- Calculate compactness centrality
- Calculate the Tsallis parameters
- Calculating the probability set
- Neighbor entropy
3.2.2. Coreness Centrality
- Ability to calculate the impact
- Computing the neighborhood core
- TsallisRank
3.3. Algorithm Description
| Algorithm 1: TRank algorithm. |
| Input: Network G(V,E) Output: TRank Value for each node 1. Find neighboring nodes of node 2. Compute for node 3. For node in do 4. compute ratio1 = degree ()/sum(degree(all neighbors of )) 5. = (pow(ratio1,) − ratio1)/(1-) 6. End For 7. For node in do 8. compute second_neighbor_degree= the degree of the second neighbor for node 9. compute ratio2 = sum(degree(all neighbors of ))/sum(second_neighbor_degree()) 10. = (pow(ratio2,) − ratio2)/(1-) 11. End For 12. compute 13. For node in do 14. = sum() 15. End For 16. For node in do 17. = sum(SI) 18. End For |
4. Experiment
4.1. Network Datasets
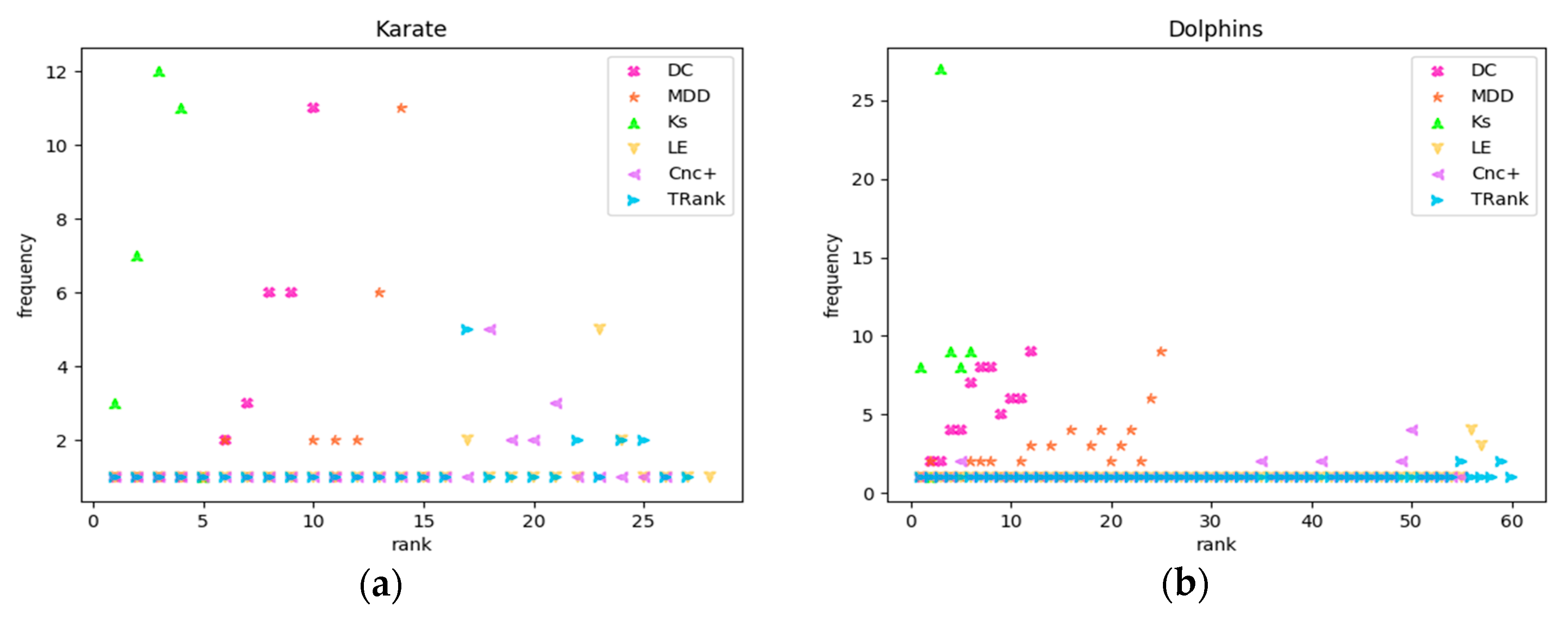
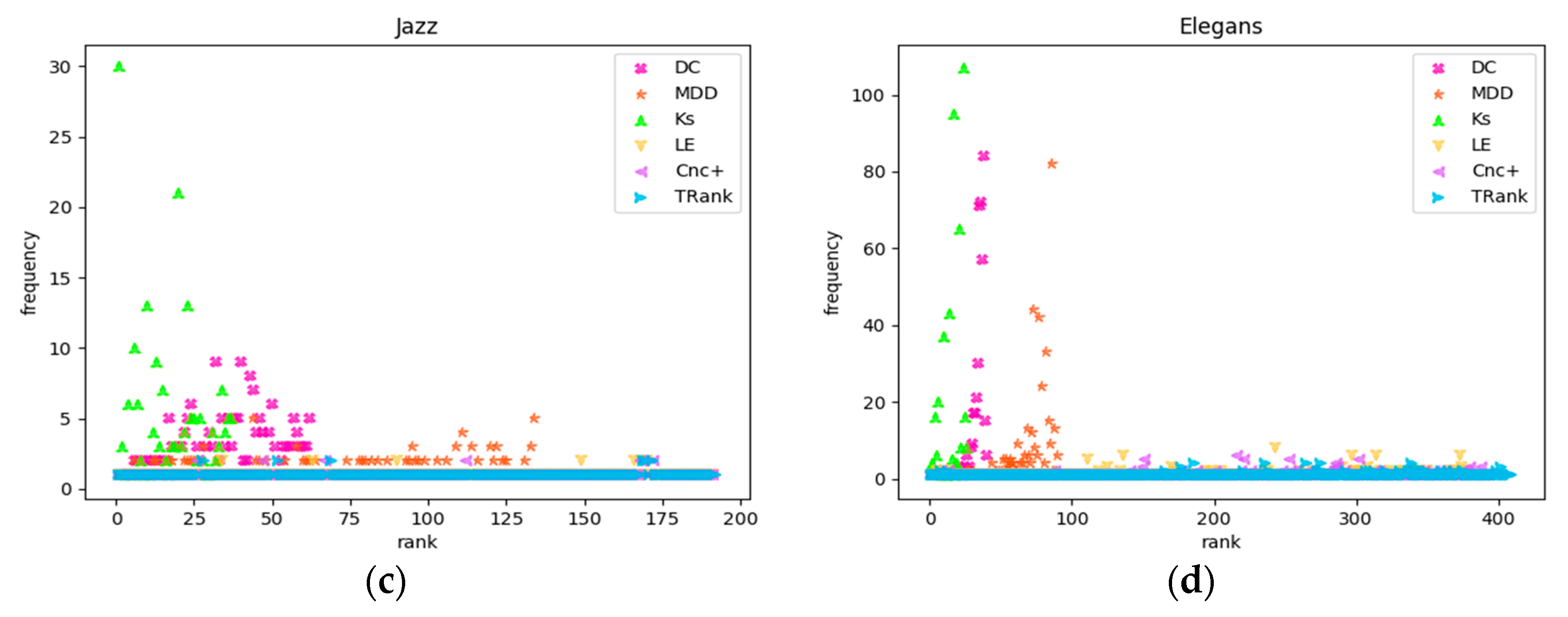
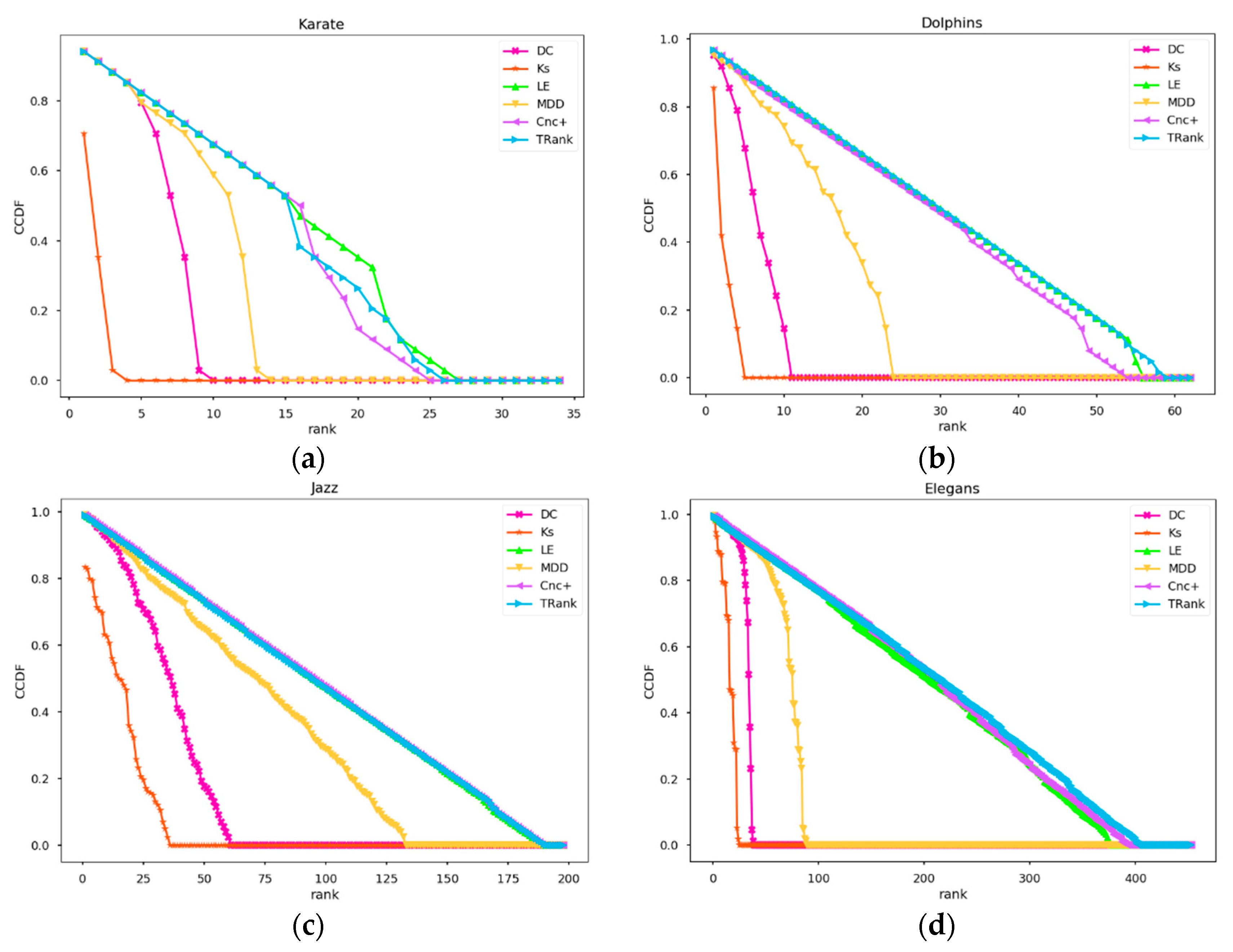
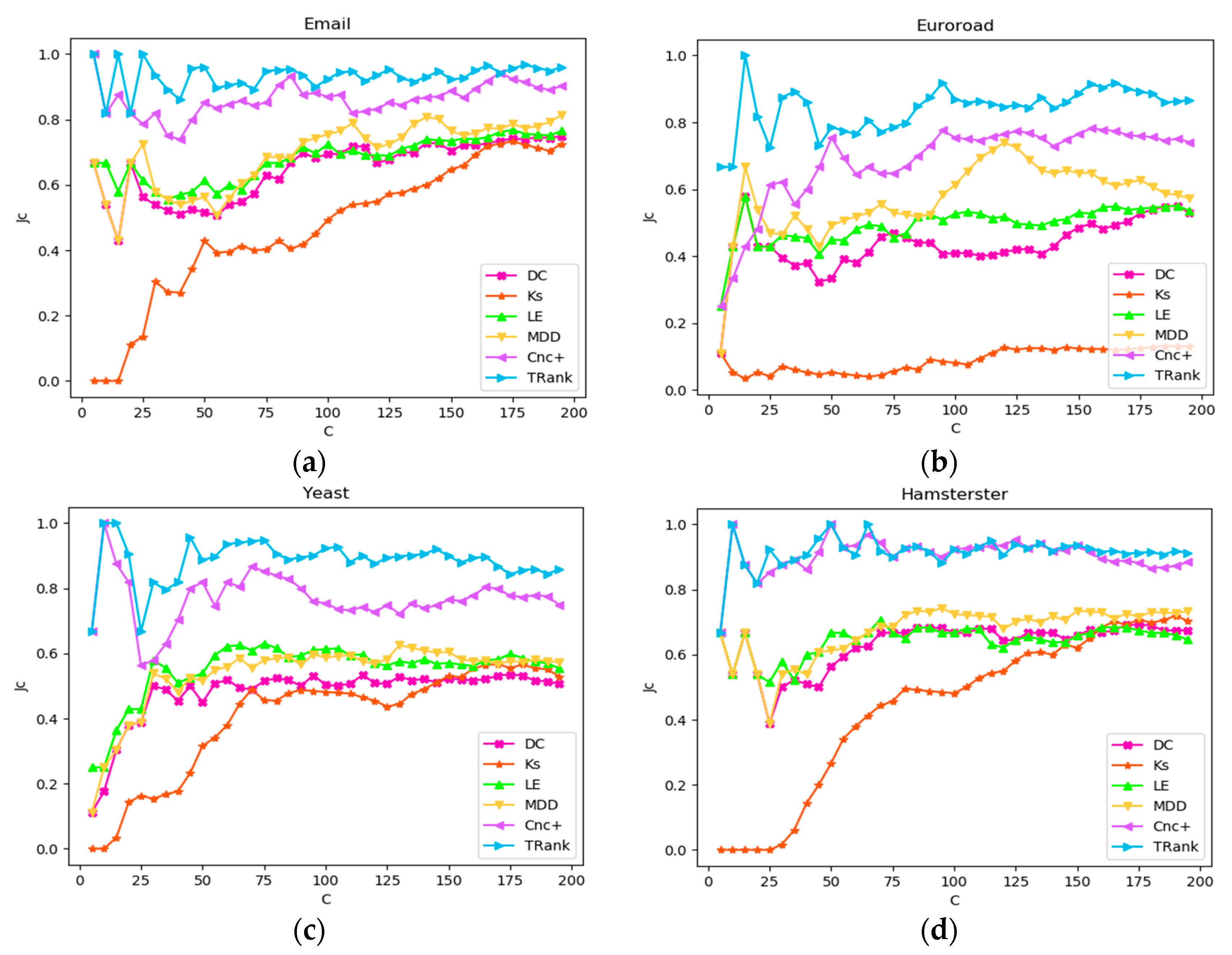
4.2. TsallisRank Algorithm Recognition Analysis
- D method
- CCDF method
- M method
- Jaccard similarity coefficient
4.3. Algorithm Correctness
4.4. Algorithm Efficiency
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, N.; Gillet, D. Identifying Influential Scholars in Academic Social Media Platforms. IEEE Comput. Soc. 2013, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shuai, X.; Sun, G.; Tang, J.; Ding, Y.; Luo, Z. Mining topic-level opinion influence in microblog. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Tang, J. A Survey of Models and Algorithms for Social Influence Analysis. In Social Network Data Analytics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in Social Networks’ Conceptual Clarification. Soc. Netw. 1979, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabidussi, G. The Centrality Index of a Graph. Psychometrika 1966, 31, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.C. A Set of Measures of Centrality Based on Betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P.; Lloyd, P. Eigenvector-Like Measures of Centrality for Asymmetric Relations. Soc. Netw. 2001, 23, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L. A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika 1953, 18, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lü, L.; Shang, M.S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhou, T. Identifying influential nodes in complex networks. Physica A 2012, 391, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Pu, C.; Yang, J. Link prediction based on path entropy. Physica A 2016, 456, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Shan, W.; Zhou, C. How to identify the most powerful node in complex networks? A novel entropy centrality approach. Entropy 2017, 19, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; He, D.; Chen, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Exploring the characteristics of issue-related behaviors in github using visualization techniques. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 24003–24015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhao, B.; Liu, S.; Jin, H.; He, D.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J. A prediction model of the project life-span in open source software ecosystem. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2019, 24, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P. Factoring and weighting approaches to status scores and clique identification. J. Math. Sociol. 1972, 2, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsak, M.; Gallos, L.K.; Havlin, S.; Liljeros, F.; Muchnik, L.; Stanley, H.E.; Makse, H.A. Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Kim, S. Identifying and ranking influential spreaders in complex networks by neighborhood coreness. Physica A 2014, 395, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Zhang, C.J. Ranking spreaders by decomposing complex networks. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, J.; Du, C. Fast ranking influential nodes in complex networks using a k-shell iteration factor. Physica A 2016, 461, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Lim, E.P.; Jiang, J.; He, Q. Twitterrank: Finding topic-sensitive influential twitterers. In Proceedings of the Third ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, S.; He, X.; Jiang, F. Influencerank: An efficient social influence measurement for millions of users in microblog. In 2012 Second International Conference on Cloud and Green Computing; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 563–570. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, S.; Yang, T. ConformRank: A conformity-based rank for finding top-k influential users. Physica A 2017, 474, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, J.; Yang, A. Entropy-based social influence evaluation in mobile social networks. In International Conference on Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberger, Germany, 2015; pp. 637–647. [Google Scholar]
- Sathanur, A.V.; Jandhyala, V. An activity-based information-theoretic annotation of social graphs. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM Conference on Web Science; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Deng, Y. Toward uncertainty of weighted networks: An entropy-based model. Physica A 2018, 508, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.H.; Wu, W.T.; Wang, H.; Xiong, M.; Wang, W. Symmetry-based structure entropy of complex networks. Physica A 2008, 387, 2611–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, K.; Lu, Z.M. Using mapping entropy to identify node centrality in complex networks. Physica A 2016, 453, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsallis, C. Possible generalization of Boltzmann–Gibbs statistics. J. Stat. Phys. 1988, 52, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rak, R.; Rak, E. The Fractional Preferential Attachment scale-free network model. Entropy 2020, 22, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Du, Y.; Deng, Y. Local structure entropy of complex networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3910. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3910 (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic dynamics and endemic states in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 066117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Kui, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W. Visual analytics for electromagnetic situation awareness in radio monitoring and management. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 26, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, W.R. A computer method for calculating Kendall’s tau with ungrouped data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1966, 61, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
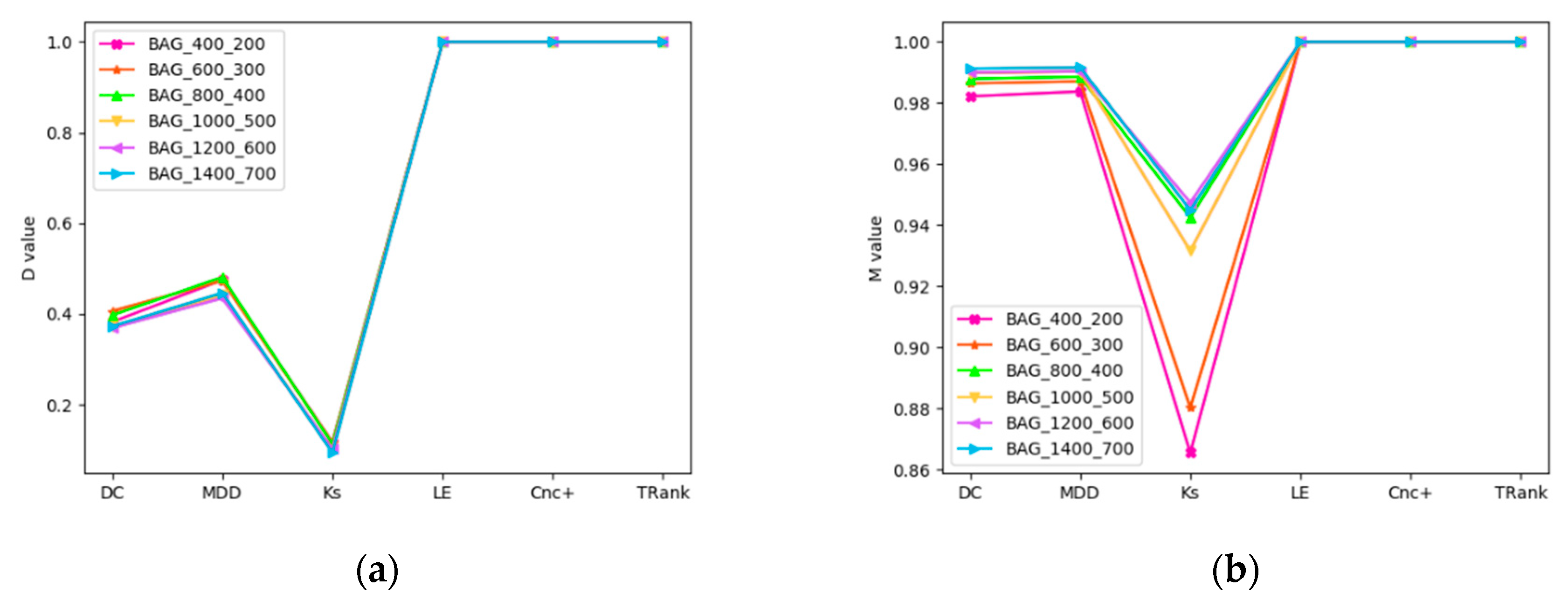
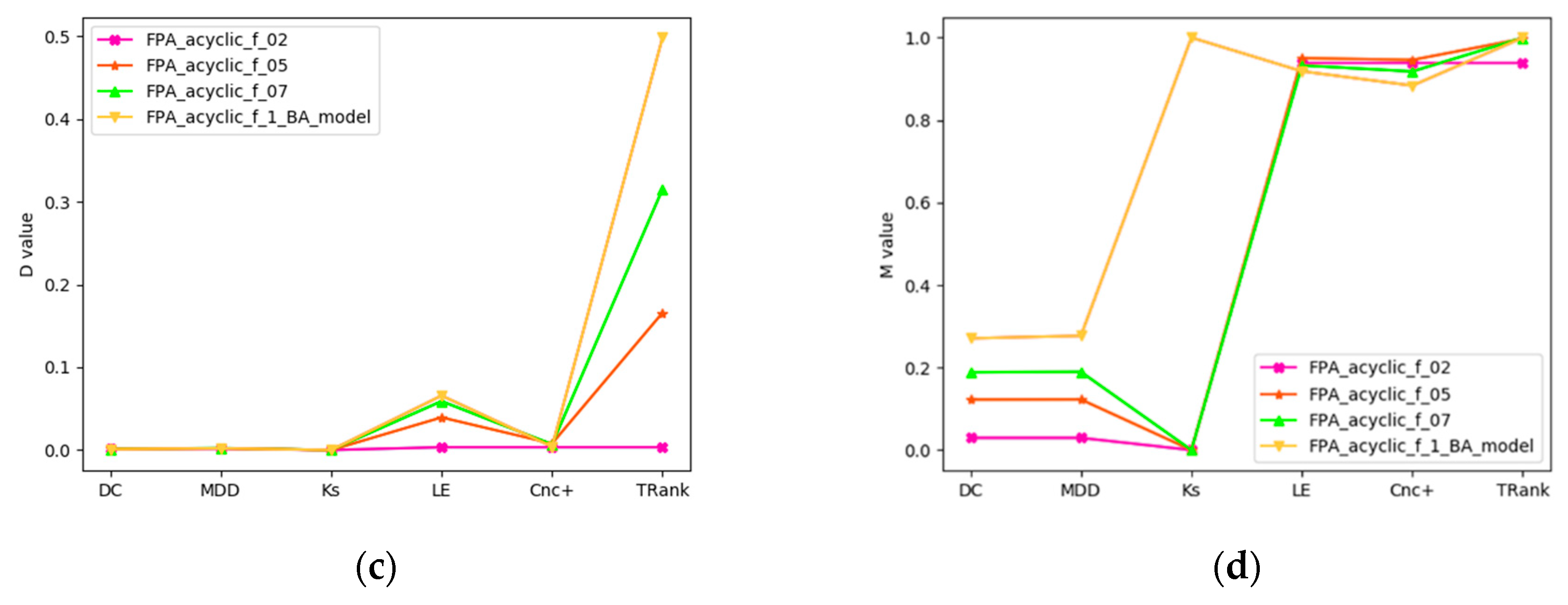
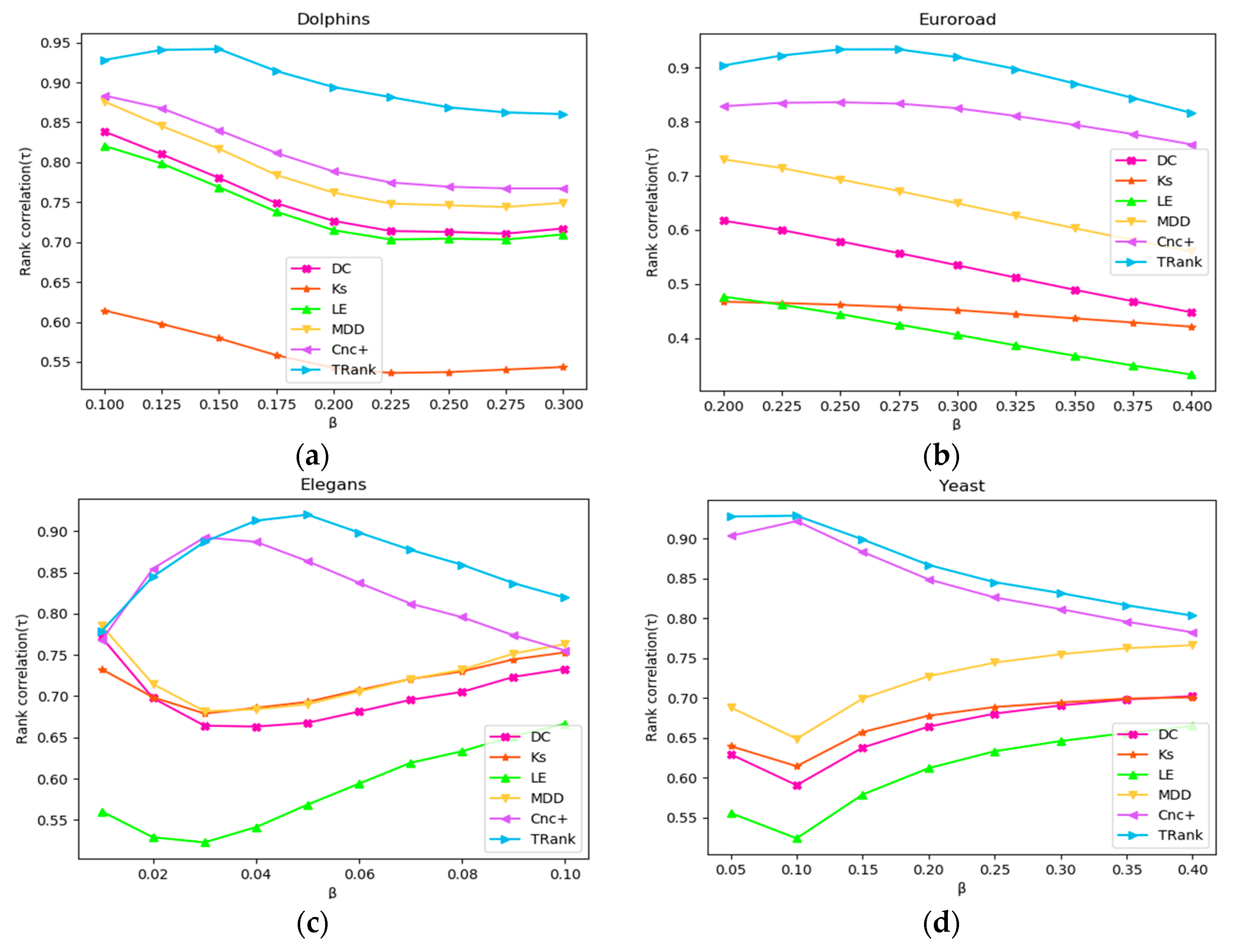
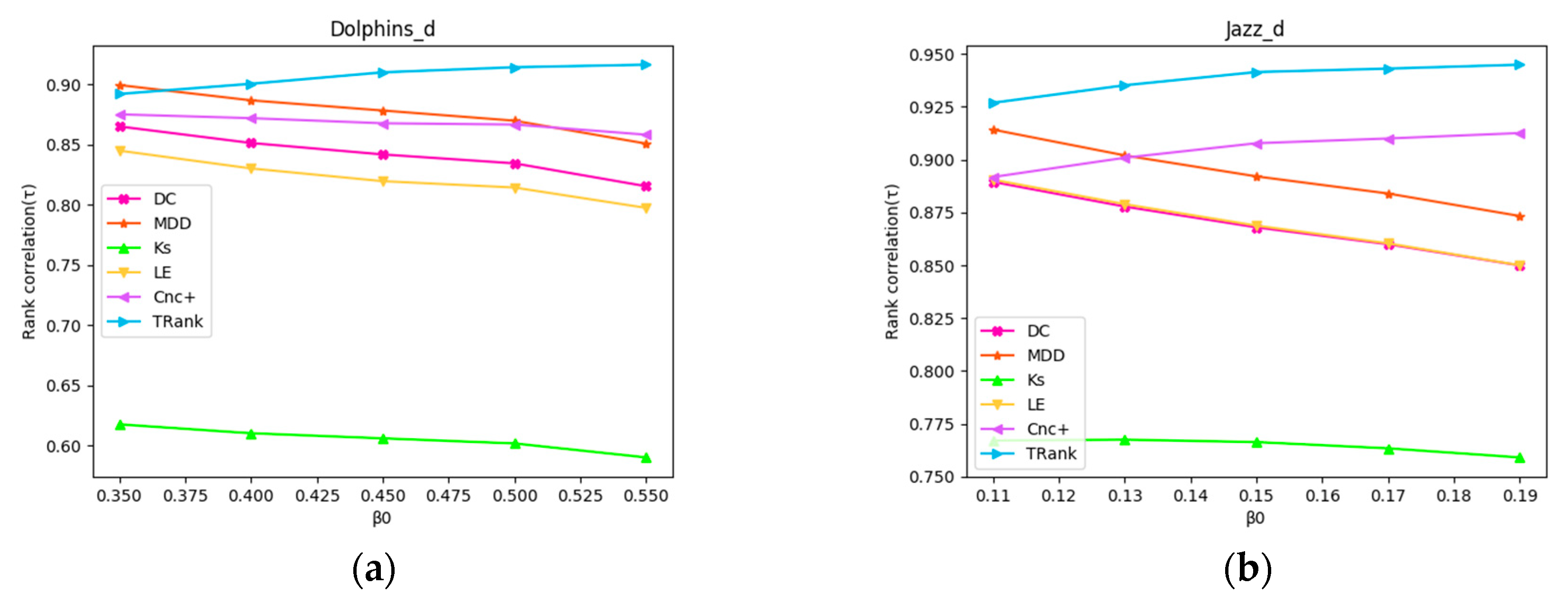
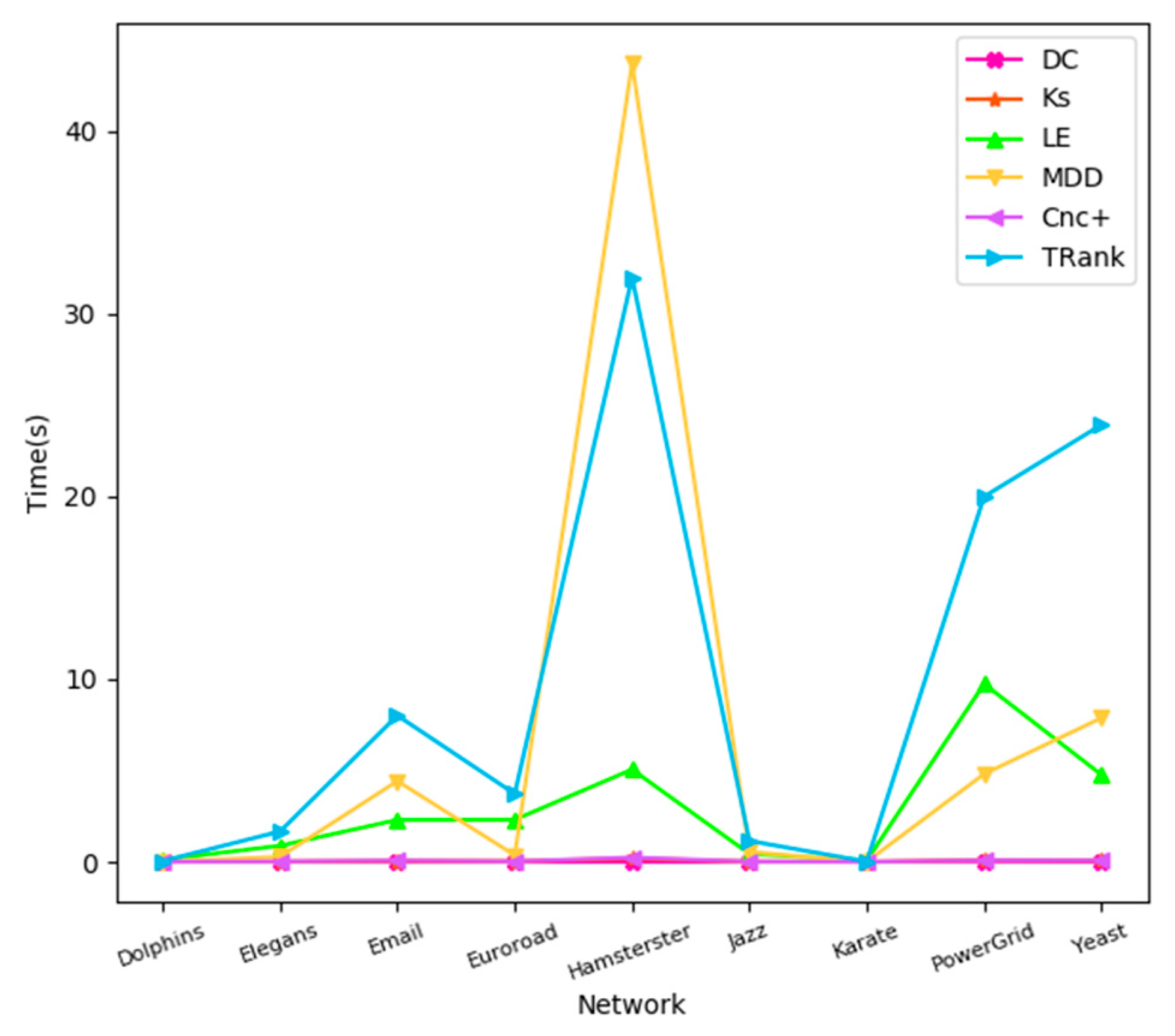
| Network | |V| | |E| | Average Degree | Maximum Degree | Assortativity | Clustering Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAG_400_200 | 400 | 40,000 | 200.0 | 384 | −0.398111 | 0.722654 |
| BAG_600_300 | 600 | 90,000 | 300.0 | 577 | −0.397054 | 0.721492 |
| BAG_800_400 | 800 | 160,000 | 400.0 | 776 | −0.397650 | 0.724718 |
| BAG_1000_500 | 1000 | 250,000 | 500.0 | 967 | −0.397126 | 0.722987 |
| BAG_1200_600 | 1200 | 360,000 | 600.0 | 1159 | −0.397411 | 0.723613 |
| BAG_1400_700 | 1400 | 490,000 | 700.0 | 1347 | −0.397143 | 0.723255 |
| FPA_acyclic_f_1_BA_model | 100,006 | 100,005 | 1.99998 | 1340 | −0.014383 | 0.0 |
| FPA_acyclic_f_07 | 100,006 | 100,005 | 1.99998 | 1621 | −0.028993 | 0.0 |
| FPA_acyclic_f_05 | 100,006 | 100,005 | 1.99998 | 4981 | −0.047784 | 0.0 |
| FPA_acyclic_f_02 | 100,006 | 100,005 | 1.99998 | 21,951 | −0.157886 | 0.0 |
| Network | |V| | |E| | Average Degree | Maximum Degree | Assortativity | Clustering Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karate | 34 | 78 | 4.588 | 17 | −0.4756 | 0.5706 |
| Dolphins | 62 | 159 | 5.129 | 12 | −0.043594 | 0.2590 |
| Jazz | 198 | 2742 | 27.697 | 100 | 0.0202 | 0.6175 |
| Elegans | 453 | 2025 | 8.940 | 237 | −0.2258 | 0.6465 |
| 1133 | 5451 | 9.622 | 71 | 0.0782 | 0.2203 | |
| Euroroad | 1174 | 1417 | 2.414 | 10 | 0.1267 | 0.0167 |
| Yeast | 2361 | 7182 | 6.0839 | 66 | −0.0846 | 0.1301 |
| Hamsterster | 2426 | 16,631 | 13.711 | 273 | 0.0474 | 0.5376 |
| PowerGrid | 4941 | 6594 | 2.669 | 273 | 0.0035 | 0.0801 |
| PGP | 10,680 | 24,316 | 4.554 | 205 | 0.2382 | 0.2659 |
| Network | D(DC) | D(Ks) | D(LE) | D(MDD) | D(Cnc+) | D(TRank) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karate | 0.3235 | 0.1471 | 0.8235 | 0.4412 | 0.7647 | 0.7941 |
| Dolphins | 0.1935 | 0.0968 | 0.9194 | 0.4032 | 0.8871 | 0.9677 |
| Jazz | 0.3131 | 0.1869 | 0.9646 | 0.6768 | 0.9646 | 0.9697 |
| Elegans | 0.0883 | 0.0574 | 0.8366 | 0.1987 | 0.8676 | 0.9029 |
| 0.0424 | 0.0477 | 0.8914 | 0.1703 | 0.9170 | 0.9762 | |
| Euroroad | 0.0077 | 0.0068 | 0.1806 | 0.0187 | 0.0707 | 0.9446 |
| Yeast | 0.0237 | 0.0216 | 0.6357 | 0.0923 | 0.6192 | 0.7954 |
| Hamsterster | 0.0458 | 0.0528 | 0.6587 | 0.1620 | 0.6686 | 0.7003 |
| PowerGrid | 0.0032 | 0.0040 | 0.2117 | 0.0105 | 0.0565 | 0.9041 |
| PGP | 0.0078 | 0.0124 | 0.3727 | 0.0329 | 0.2902 | 0.7456 |
| Network | M(DC) | M(Ks) | M(LE) | M(MDD) | M(Cnc+) | M(TRank) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karate | 0.7079 | 0.5499 | 0.9577 | 0.7536 | 0.9472 | 0.9542 |
| Dolphins | 0.8312 | 0.5576 | 0.9905 | 0.9091 | 0.9895 | 0.9979 |
| Jazz | 0.9659 | 0.8951 | 0.9993 | 0.9911 | 0.9993 | 0.9994 |
| Elegans | 0.7922 | 0.7399 | 0.9972 | 0.8768 | 0.9980 | 0.9988 |
| 0.8874 | 0.8521 | 0.9990 | 0.9233 | 0.9997 | 0.9999 | |
| Euroroad | 0.4442 | 0.3312 | 0.9181 | 0.6510 | 0.9463 | 0.9990 |
| Yeast | 0.7472 | 0.7052 | 0.9921 | 0.7477 | 0.9962 | 0.9972 |
| Hamsterster | 0.8980 | 0.8907 | 0.9853 | 0.9274 | 0.9856 | 0.9858 |
| PowerGrid | 0.5927 | 0.3713 | 0.9635 | 0.6940 | 0.9568 | 0.9999 |
| PGP | 0.6193 | 0.5000 | 0.9781 | 0.6679 | 0.9939 | 0.9997 |
| Network | τ(σ,DC) | τ(σ,Ks) | τ(σ,LE) | τ(σ,MDD) | τ(σ,Cnc+) | τ(σ, TRank) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karate | 0.250 | 0.129 | 0.6310 | 0.5490 | 0.6542 | 0.6542 | 0.9269 | 0.8128 |
| Dolphins | 0.150 | 0.147 | 0.7805 | 0.5796 | 0.7689 | 0.8170 | 0.8403 | 0.9418 |
| Jazz | 0.040 | 0.026 | 0.8371 | 0.7847 | 0.8415 | 0.8663 | 0.9455 | 0.9726 |
| Elegans | 0.050 | 0.025 | 0.6677 | 0.6931 | 0.5685 | 0.6902 | 0.8636 | 0.9199 |
| 0.050 | 0.054 | 0.7892 | 0.7962 | 0.7654 | 0.8073 | 0.9413 | 0.9578 | |
| Euroroad | 0.275 | 0.333 | 0.5572 | 0.4571 | 0.4249 | 0.6721 | 0.8337 | 0.9341 |
| Yeast | 0.100 | 0.061 | 0.5908 | 0.6147 | 0.5241 | 0.6490 | 0.9222 | 0.9289 |
| Hamsterster | 0.020 | 0.024 | 0.7447 | 0.7333 | 0.6416 | 0.7510 | 0.9234 | 0.9349 |
| PowerGrid | 0.200 | 0.258 | 0.6244 | 0.4503 | 0.5055 | 0.6667 | 0.7887 | 0.9107 |
| PGP | 0.100 | 0.053 | 0.3644 | 0.3651 | 0.2026 | 0.3745 | 0.7840 | 0.6913 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Liao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Method to Rank Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Tsallis Entropy. Entropy 2020, 22, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080848
Chen X, Zhou J, Liao Z, Liu S, Zhang Y. A Novel Method to Rank Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Tsallis Entropy. Entropy. 2020; 22(8):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080848
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xuegong, Jie Zhou, Zhifang Liao, Shengzong Liu, and Yan Zhang. 2020. "A Novel Method to Rank Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Tsallis Entropy" Entropy 22, no. 8: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080848
APA StyleChen, X., Zhou, J., Liao, Z., Liu, S., & Zhang, Y. (2020). A Novel Method to Rank Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Tsallis Entropy. Entropy, 22(8), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080848





