A Bayesian Entropy Approach to Sectoral Systemic Risk Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Systemic Risk Measures
3.2. Bayesian Entropy Estimation
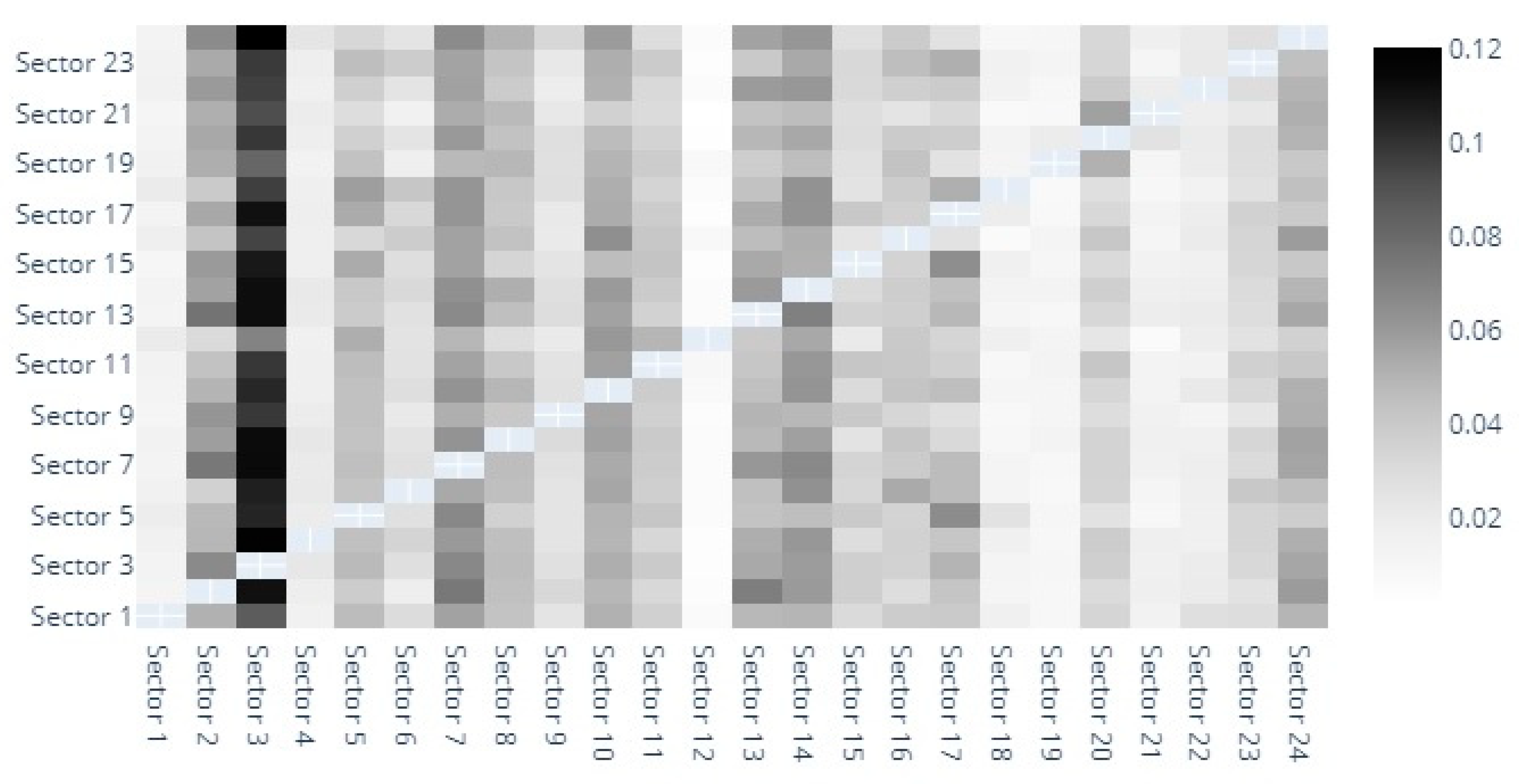
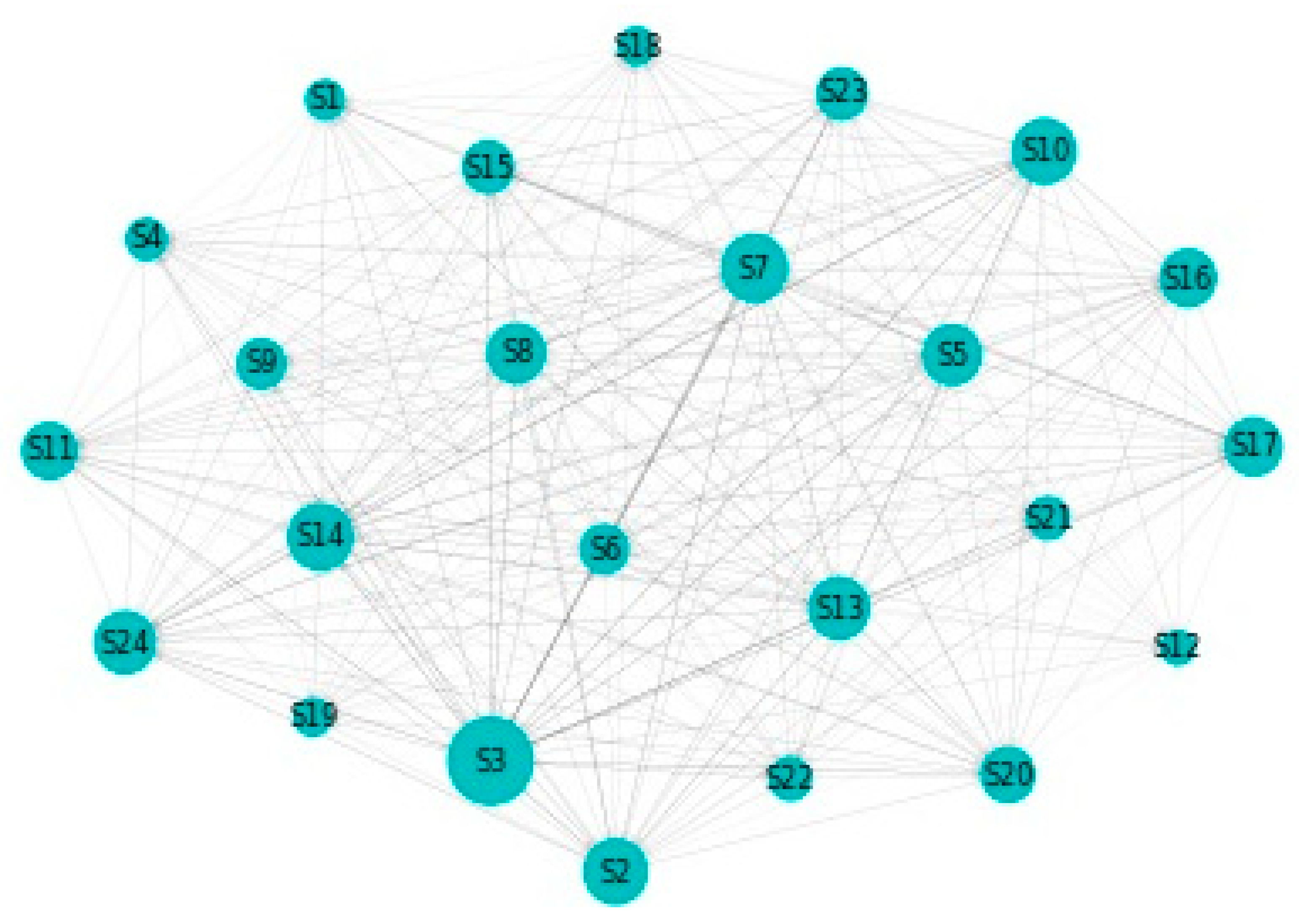
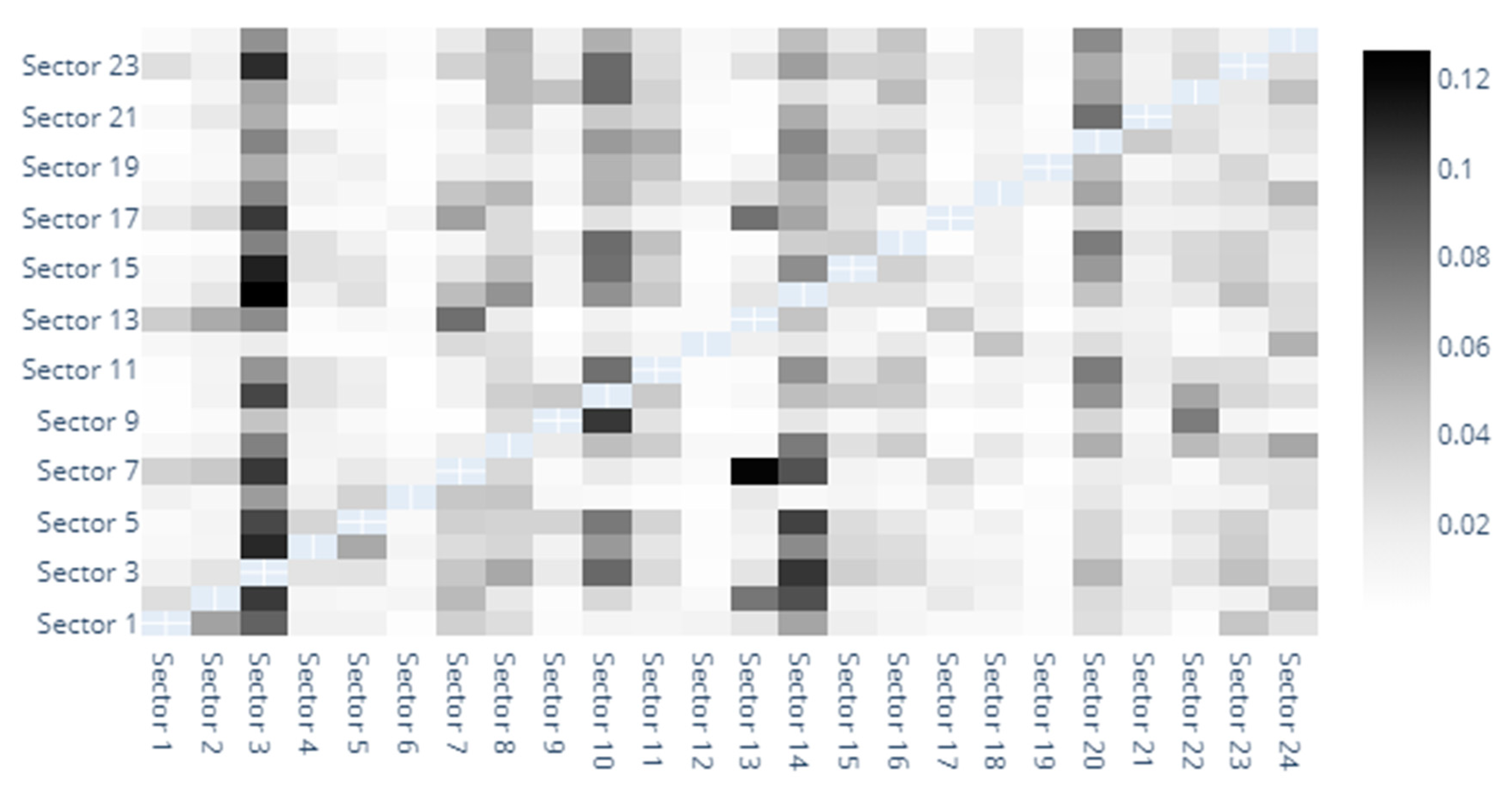
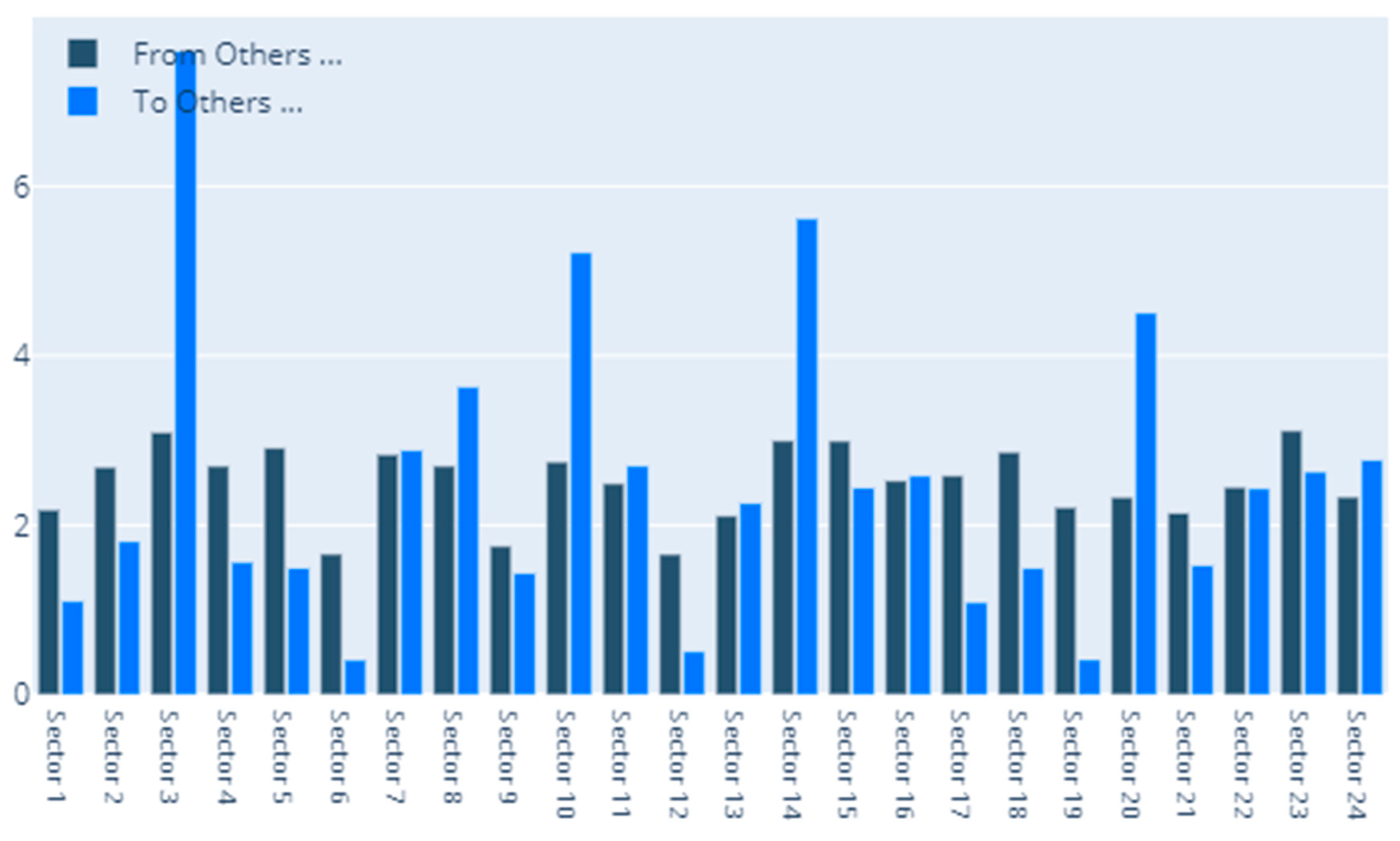
3.3. Diebold-Yilmaz Spillover Index Computation
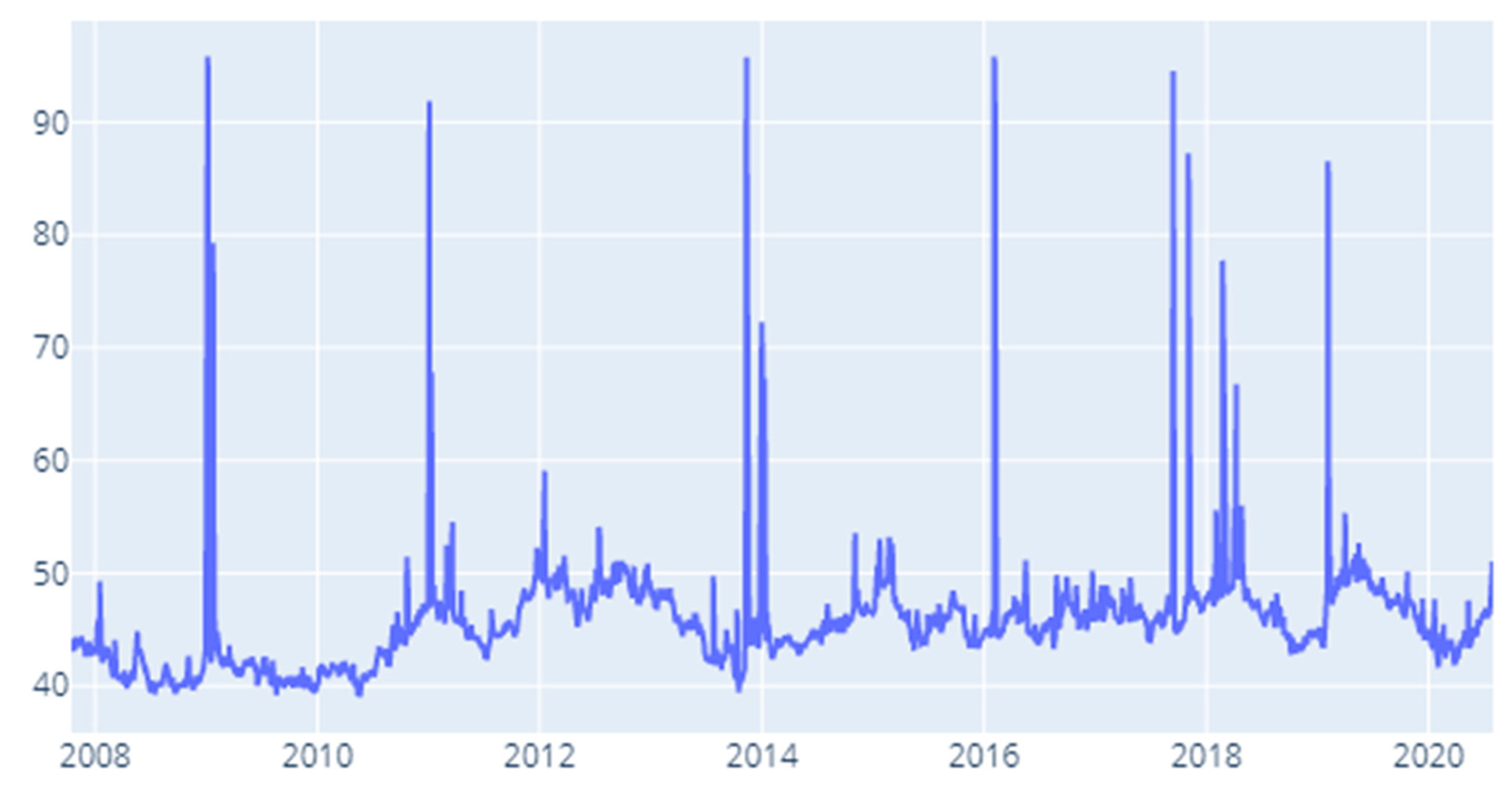
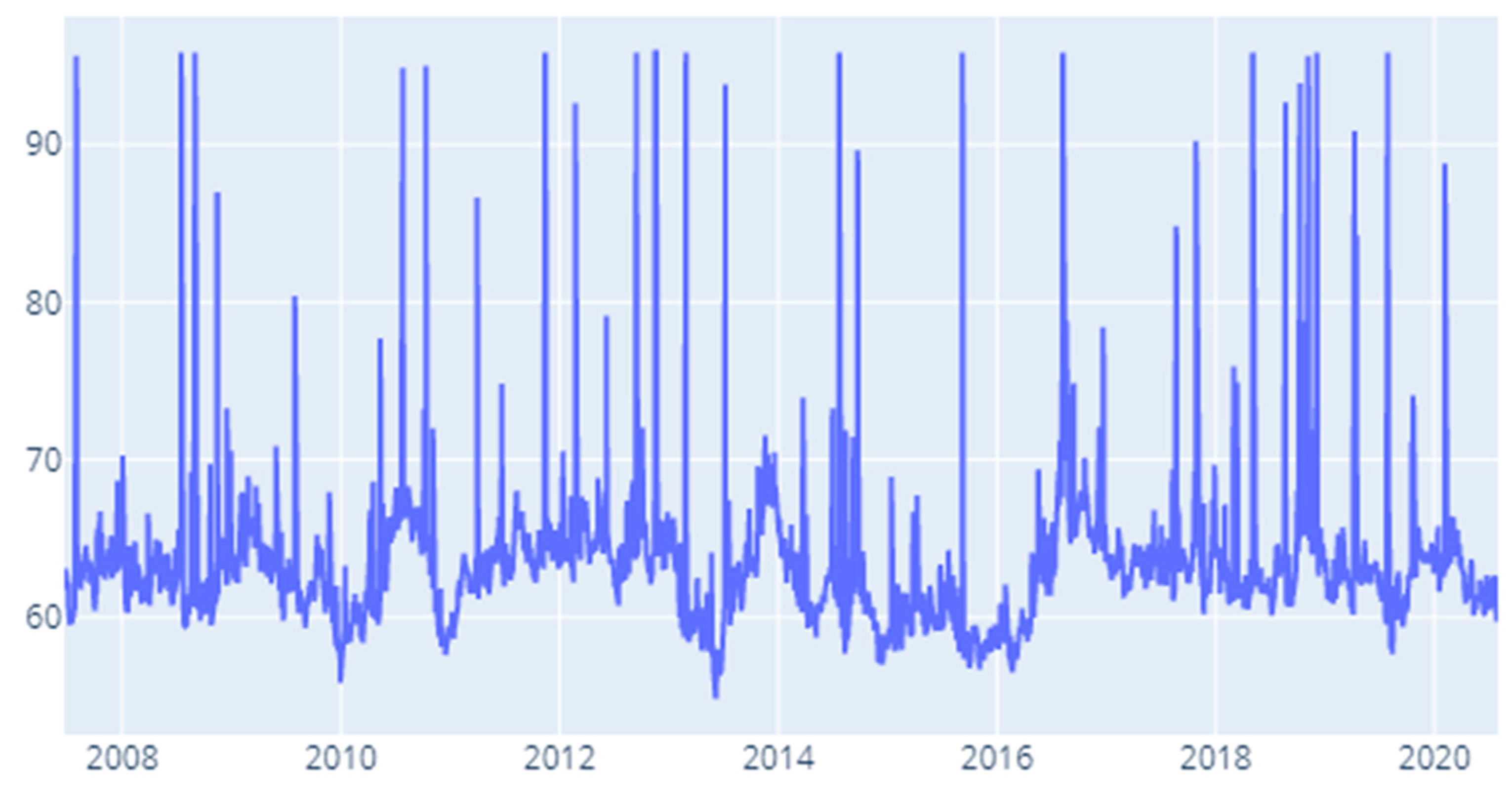
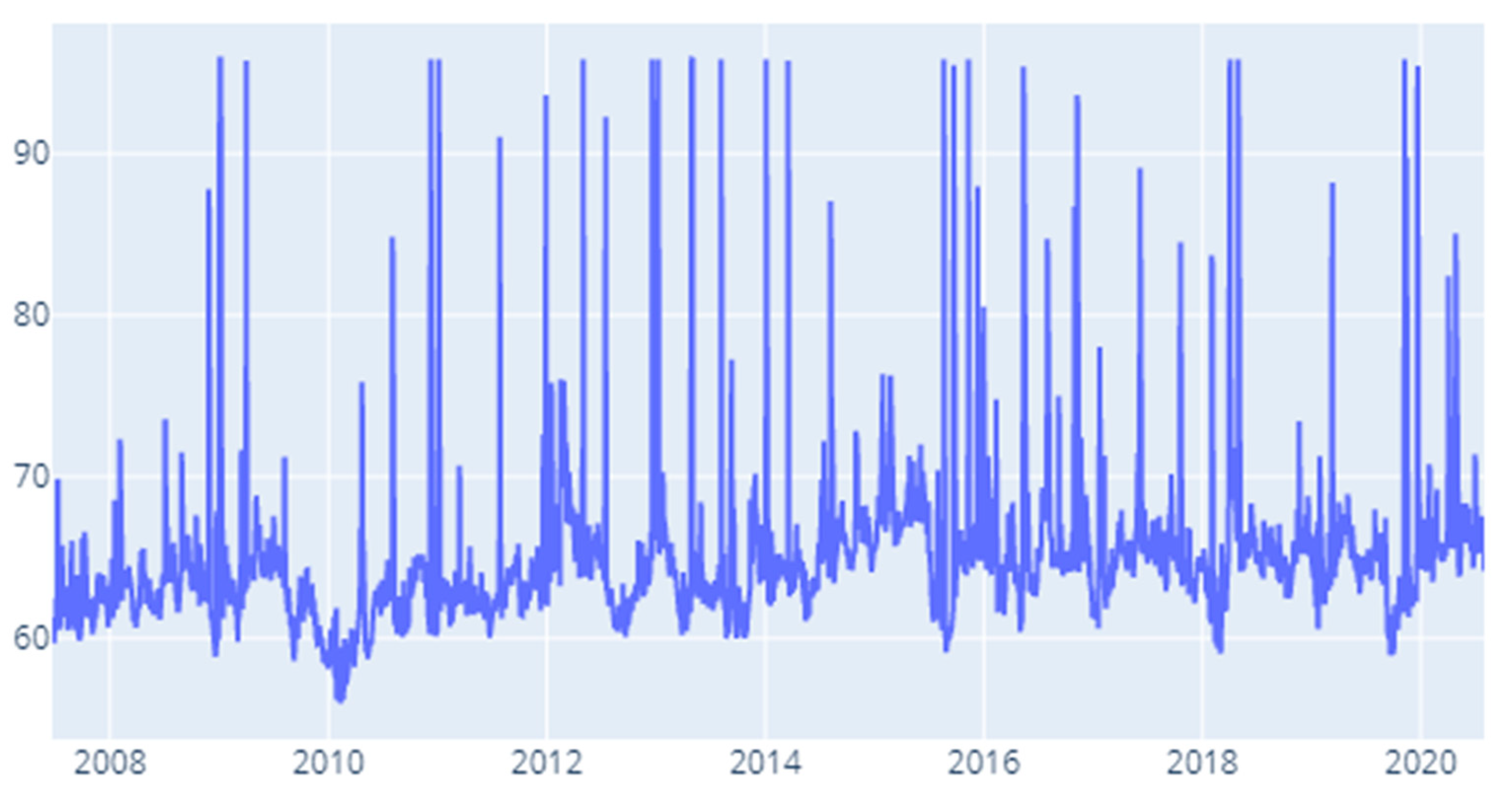
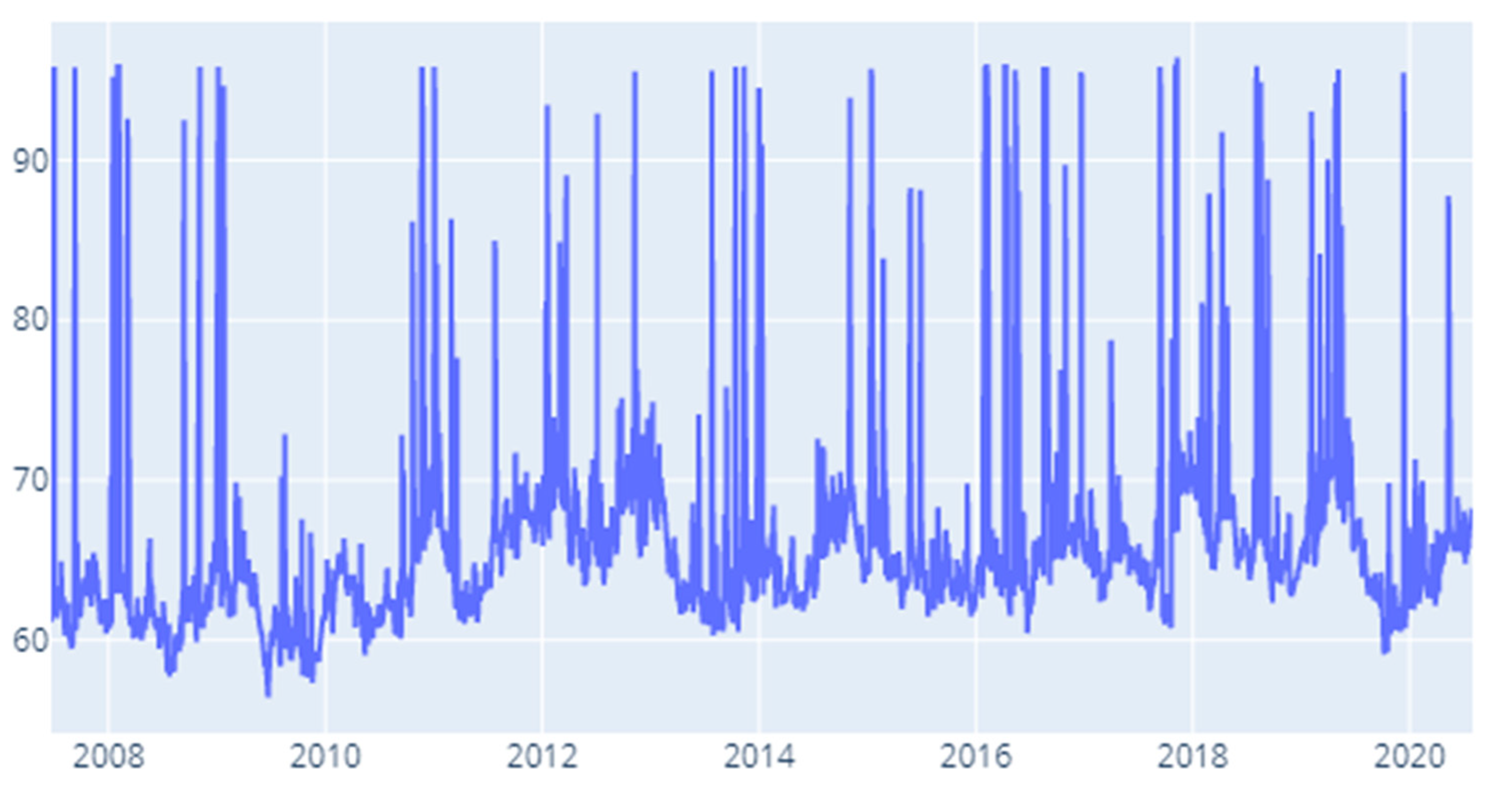
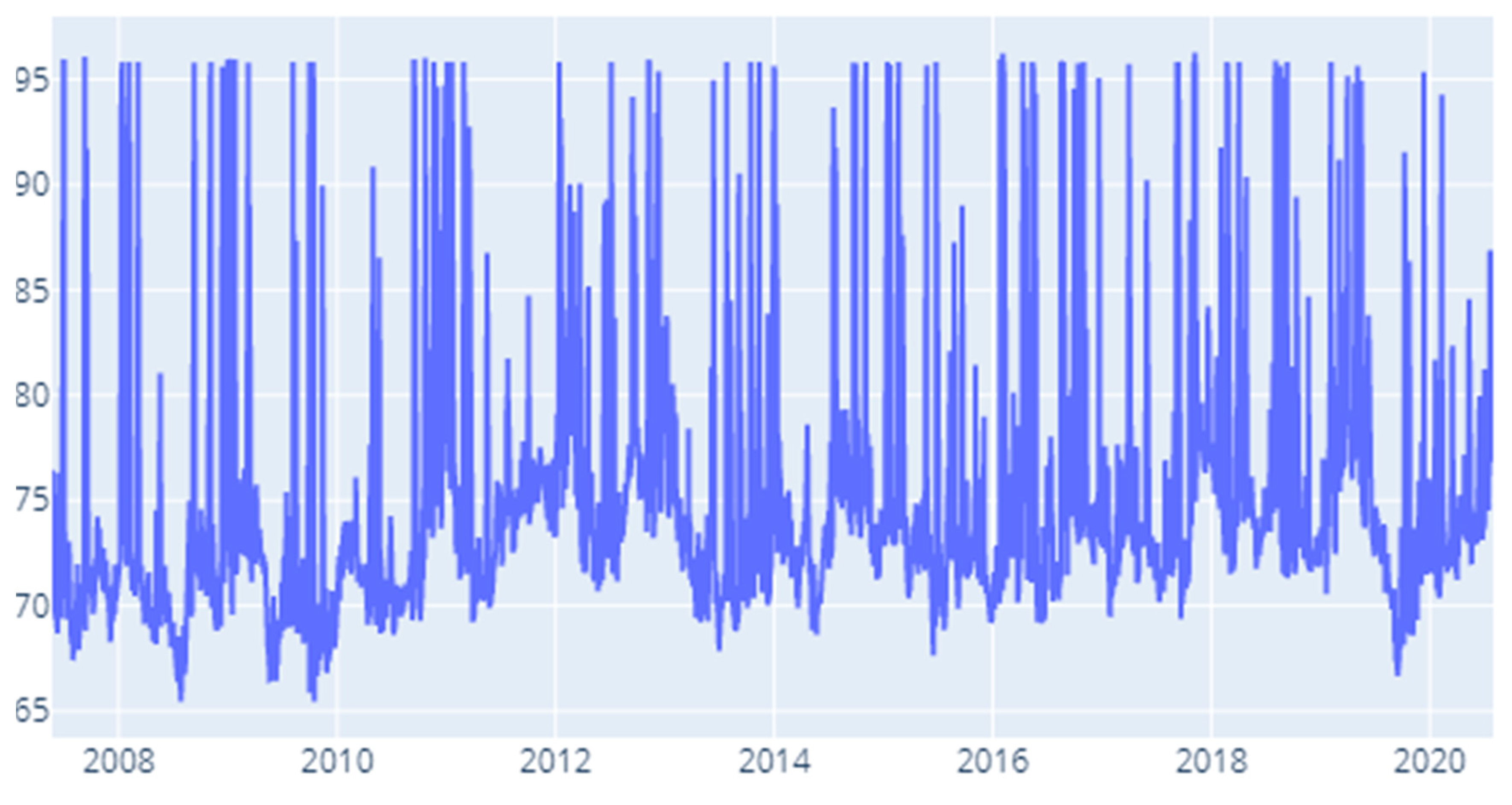
4. Results and Discussion
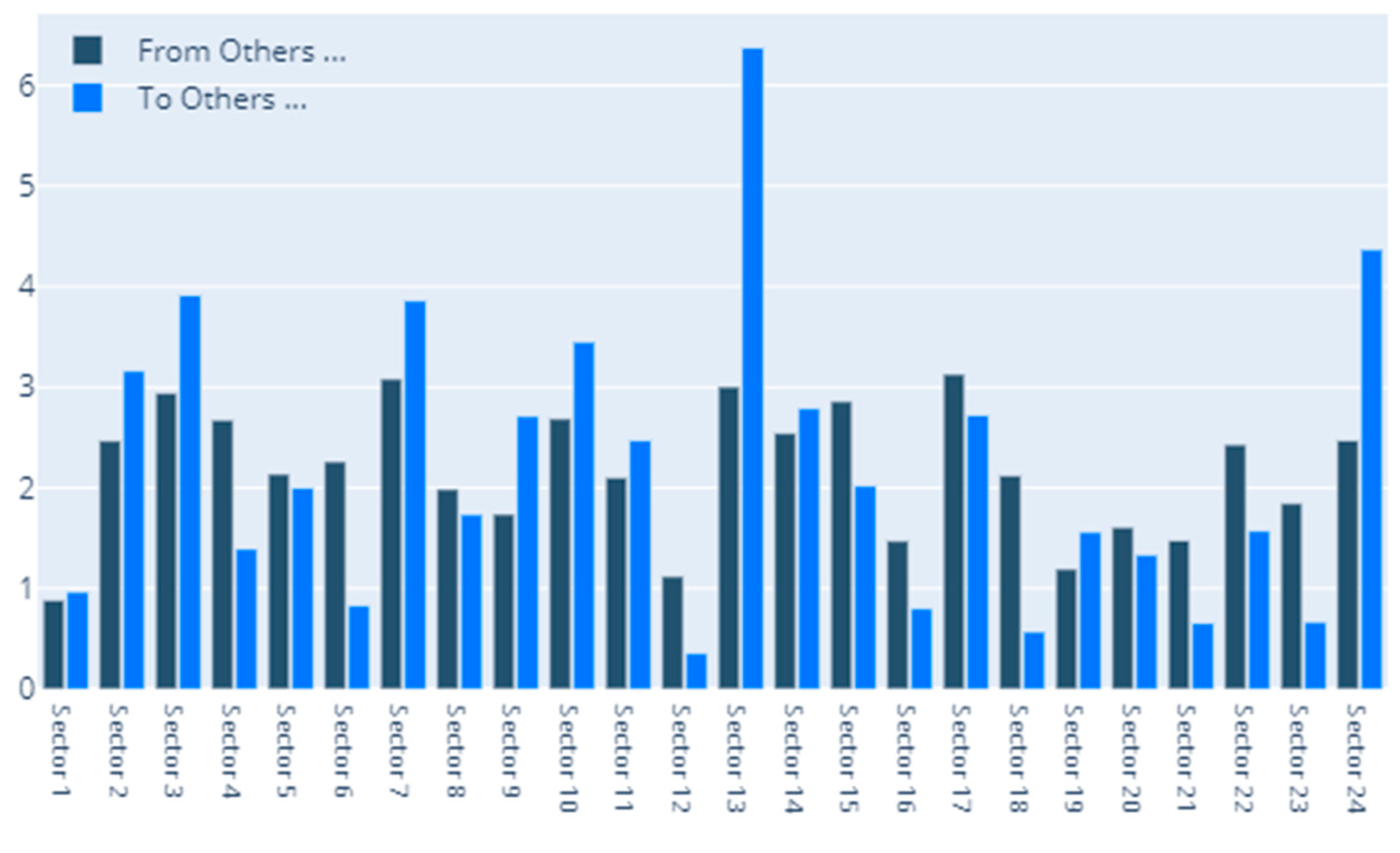
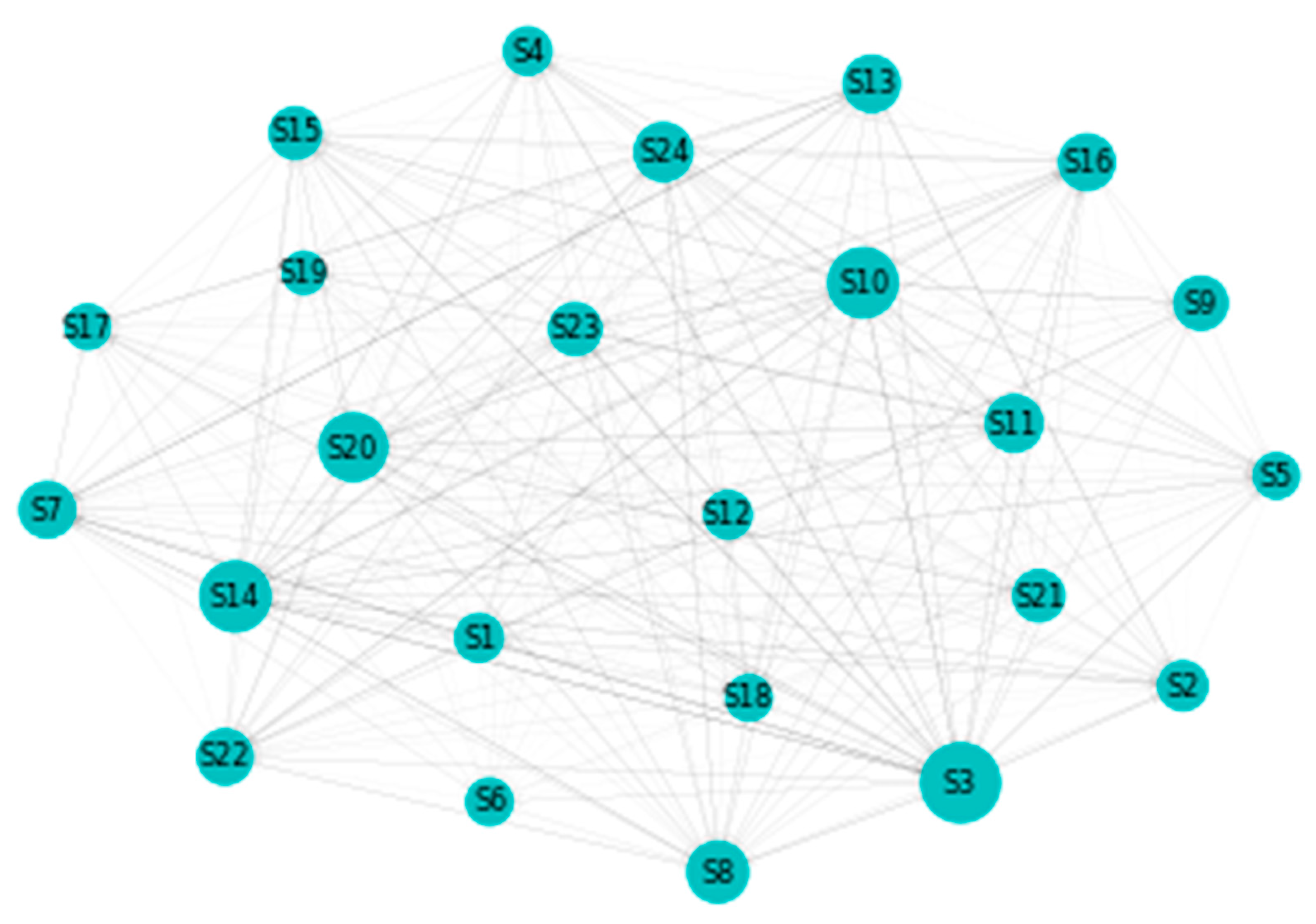
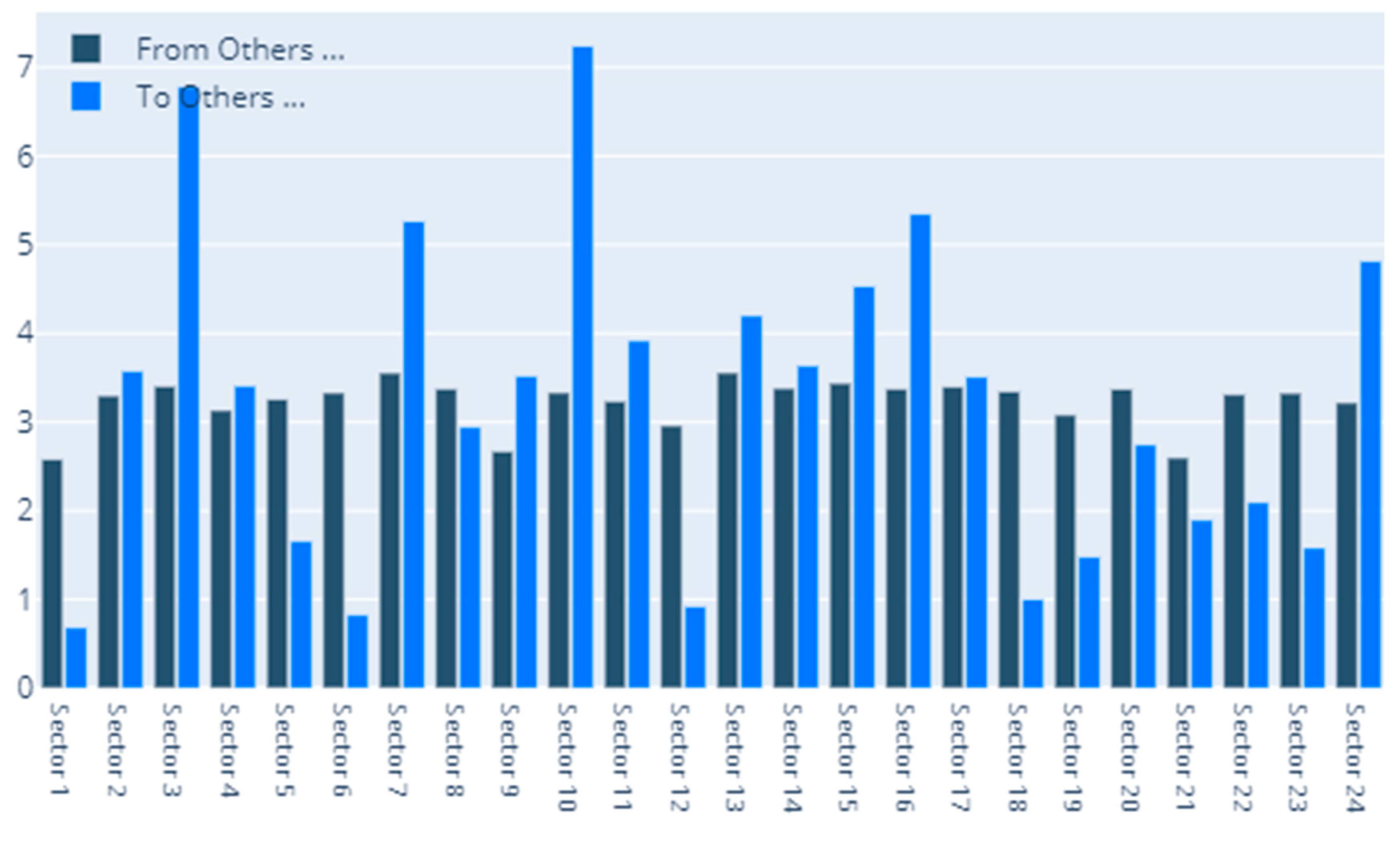
4.1. Static DY Approach
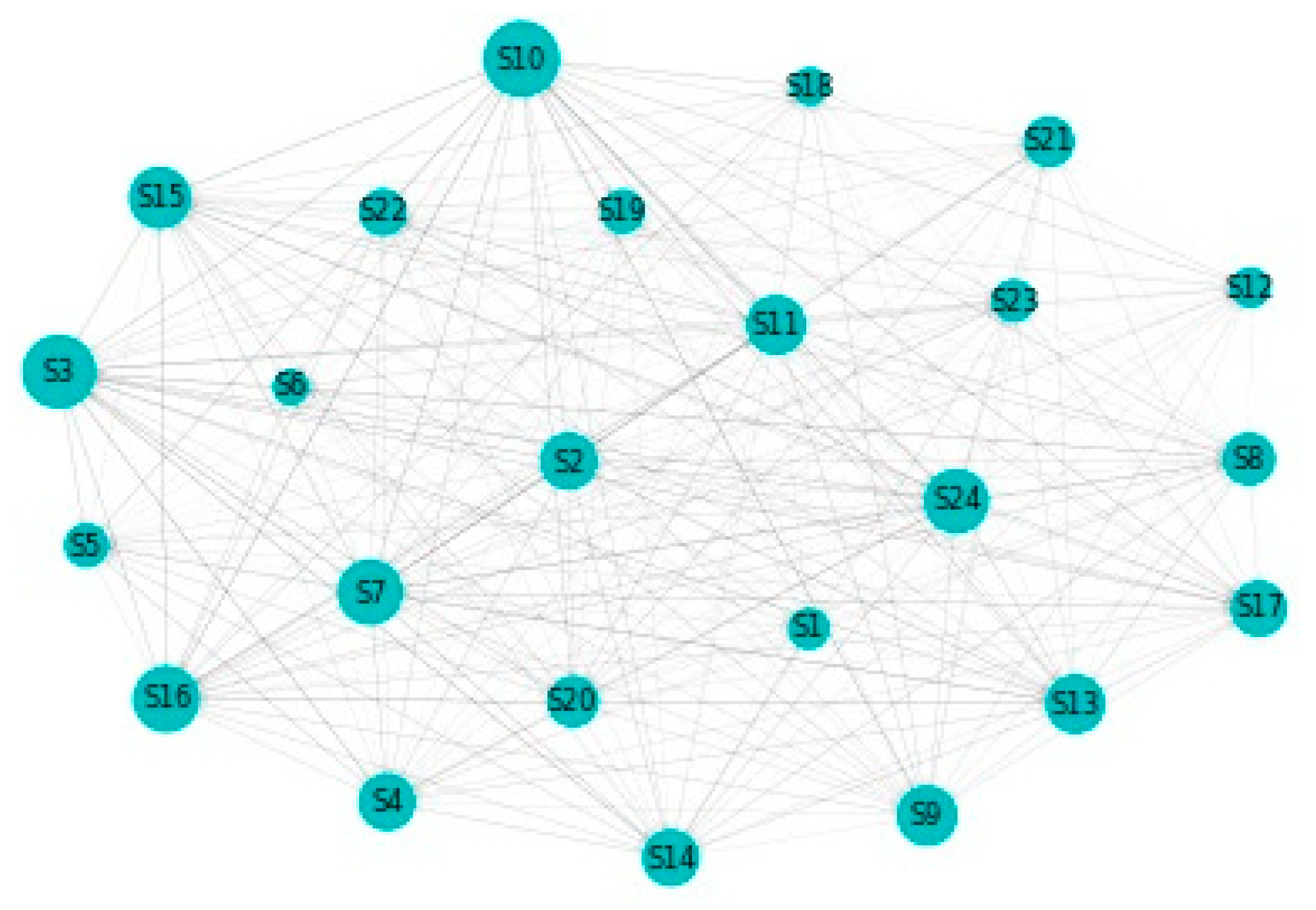
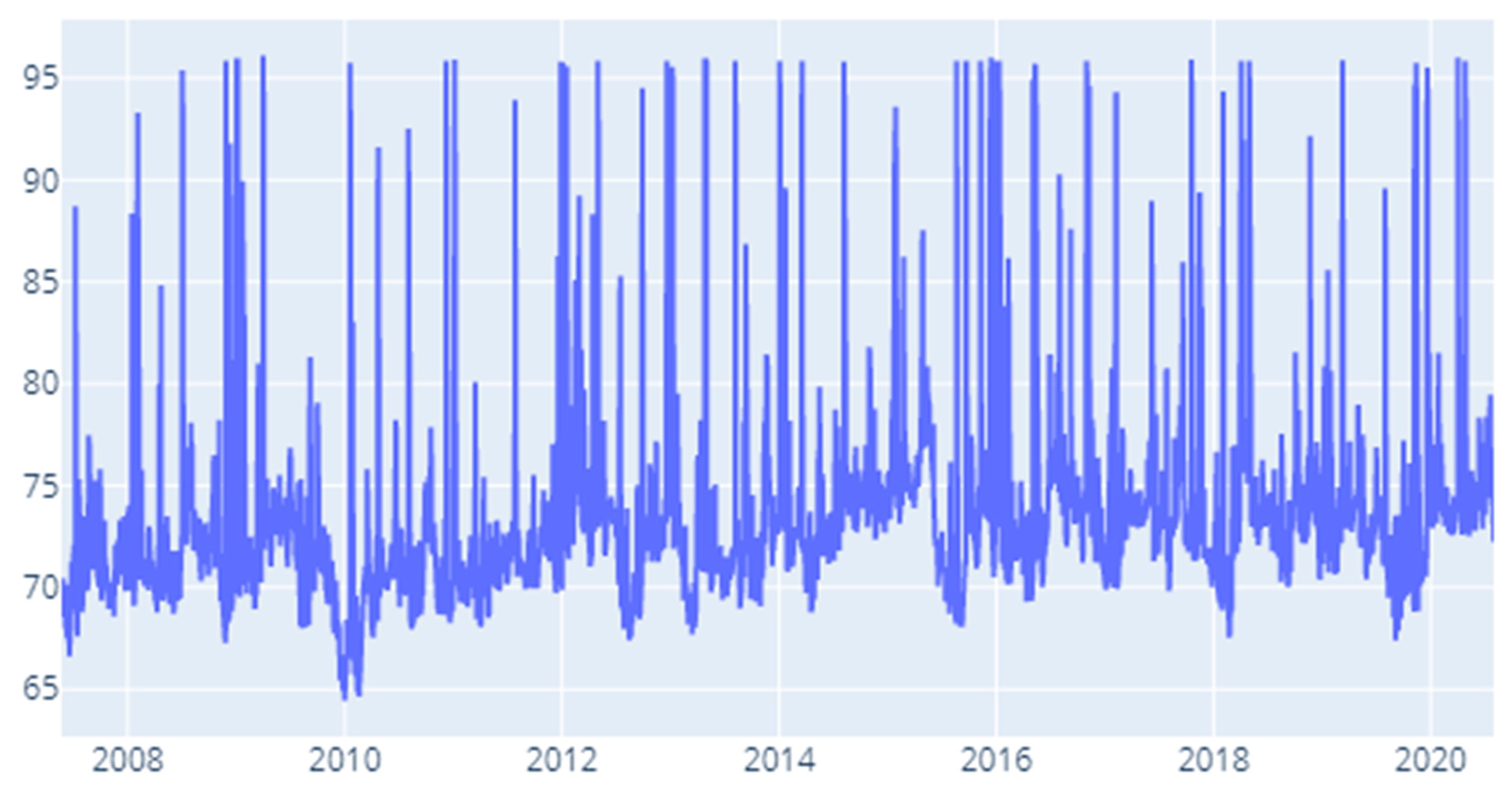
4.2. Rolling Window DY Approach
4.3. Robustness Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
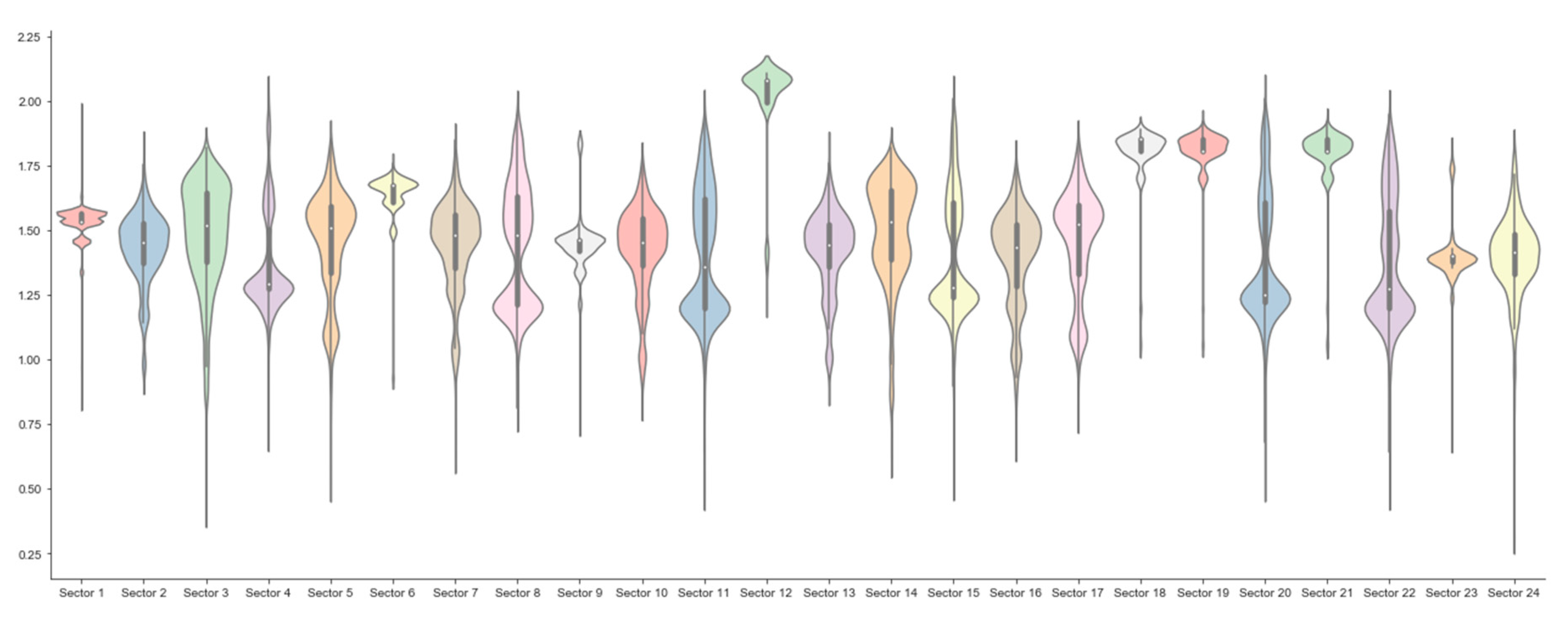
Appendix A. Economic Sectors
| Sectors | |
| 1. | Automobiles & Components |
| 2. | Banks |
| 3. | Capital Goods |
| 4. | Commercial & Professional Services |
| 5. | Consumer Durables & Apparel |
| 6. | Consumer Services |
| 7. | Diversified Financials |
| 8. | Energy |
| 9. | Food & Staples Retailing |
| 10. | Food, Beverage & Tobacco |
| 11. | Health Care Equipment & Services |
| 12. | Household & Personal Products |
| 13. | Insurance |
| 14. | Materials |
| 15. | Media & Entertainment |
| 16. | Pharmaceuticals, Biotechnology &Life Sciences |
| 17. | Real Estate |
| 18. | Retailing |
| 19. | Semiconductors & Semiconductor Equipment |
| 20. | Software & Services |
| 21. | Technology Hardware & Equipment |
| 22. | Telecommunication Services |
| 23. | Transportation |
| 24. | Utilities |
Appendix B. Risk Measures Computation
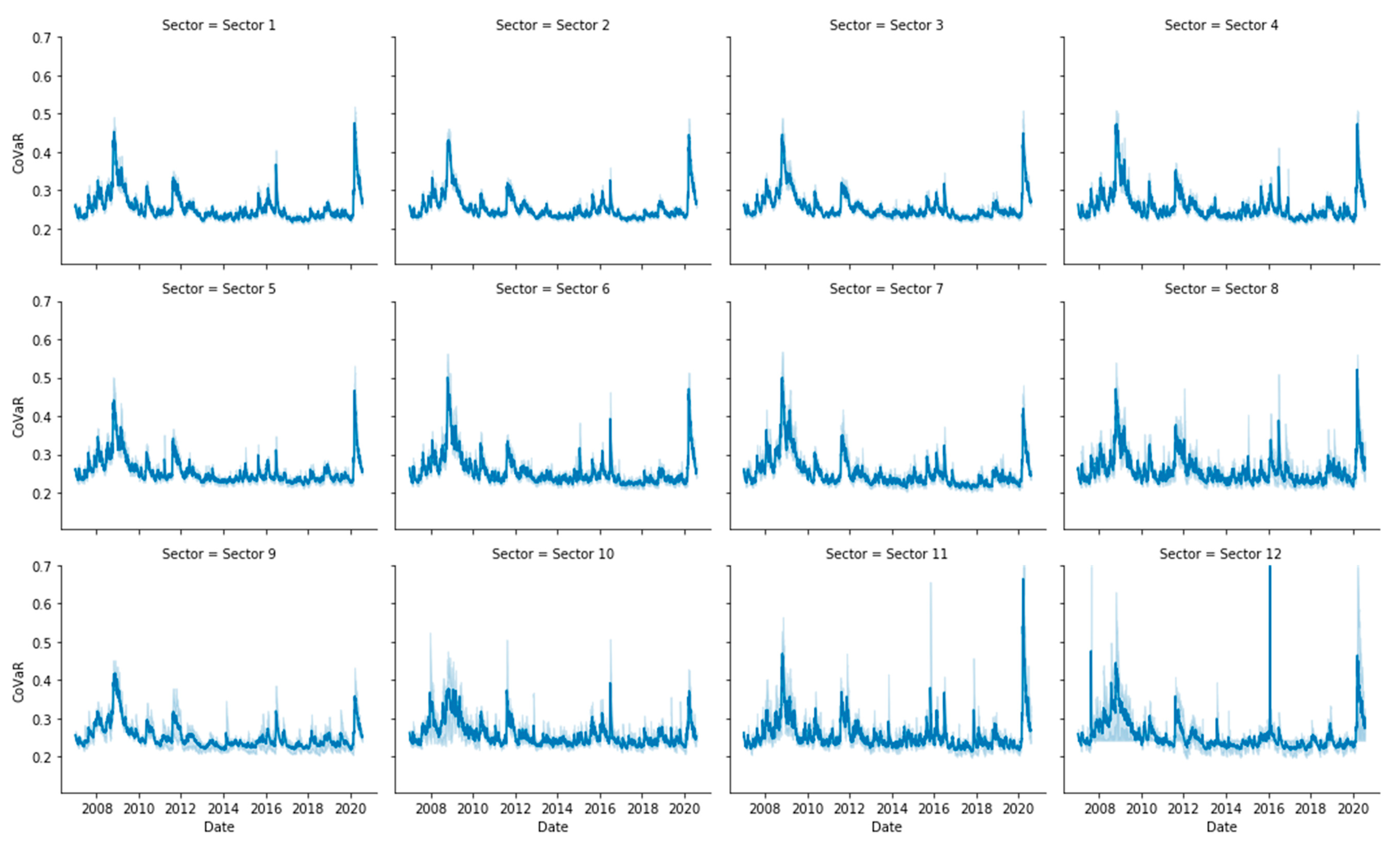
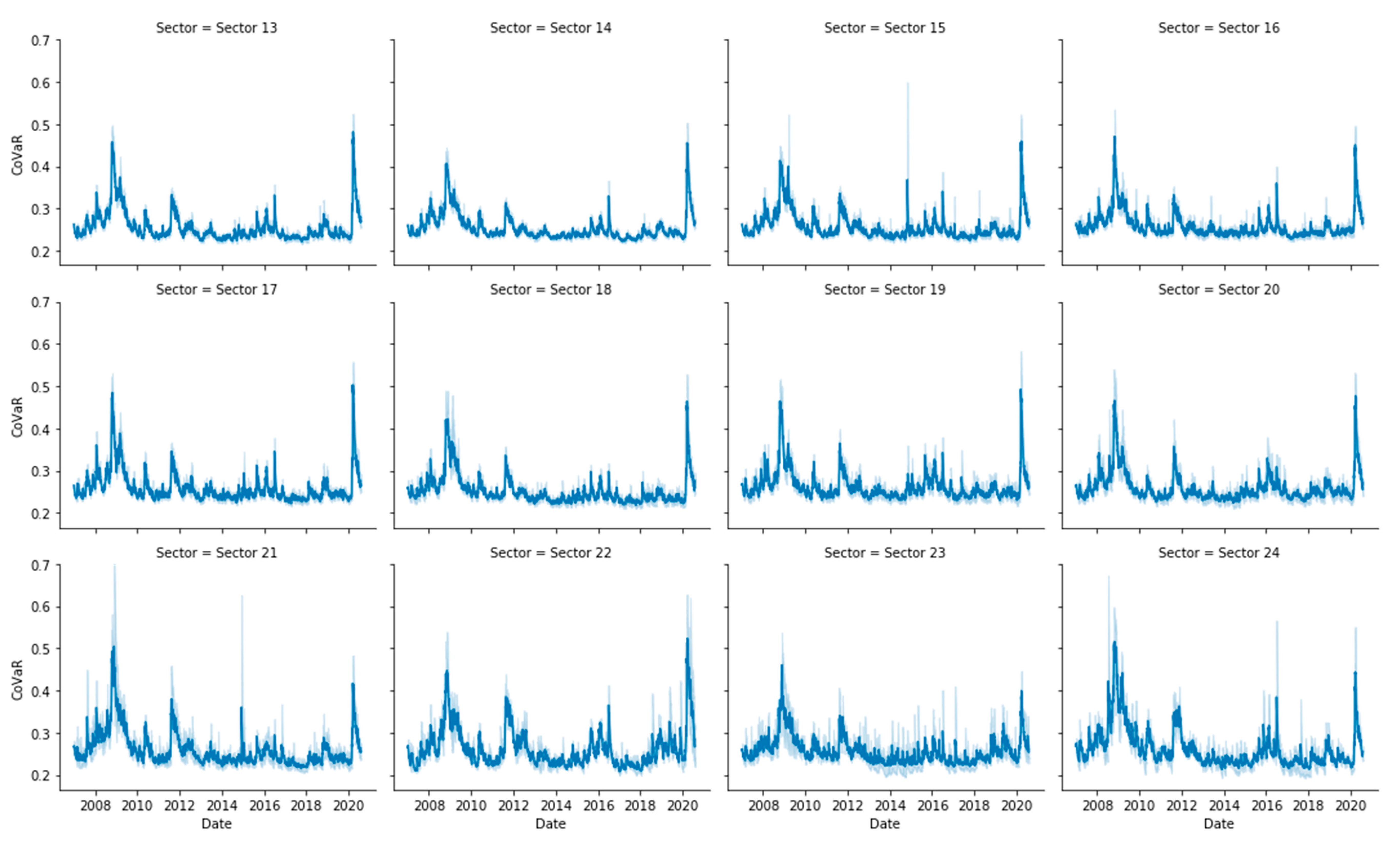
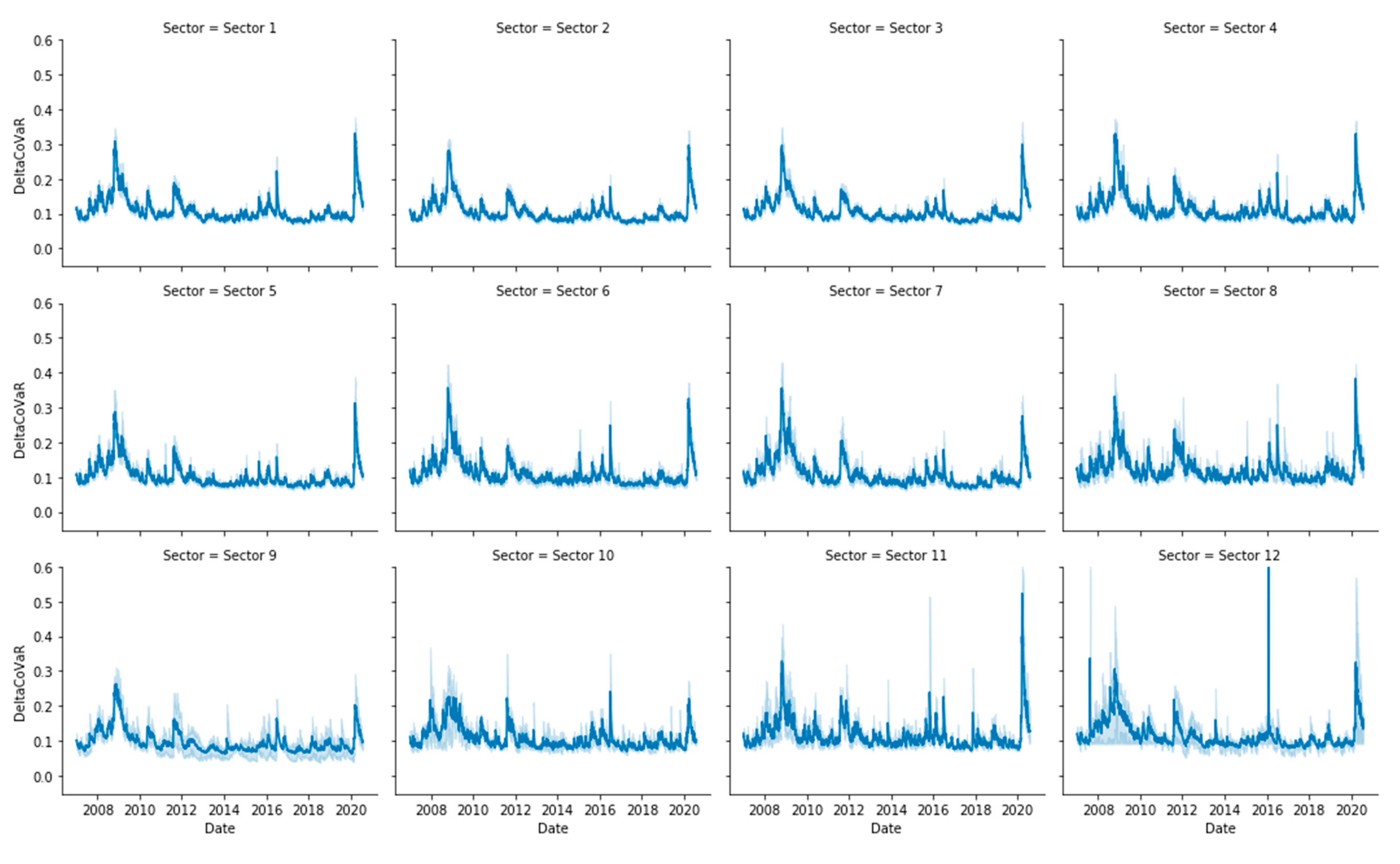
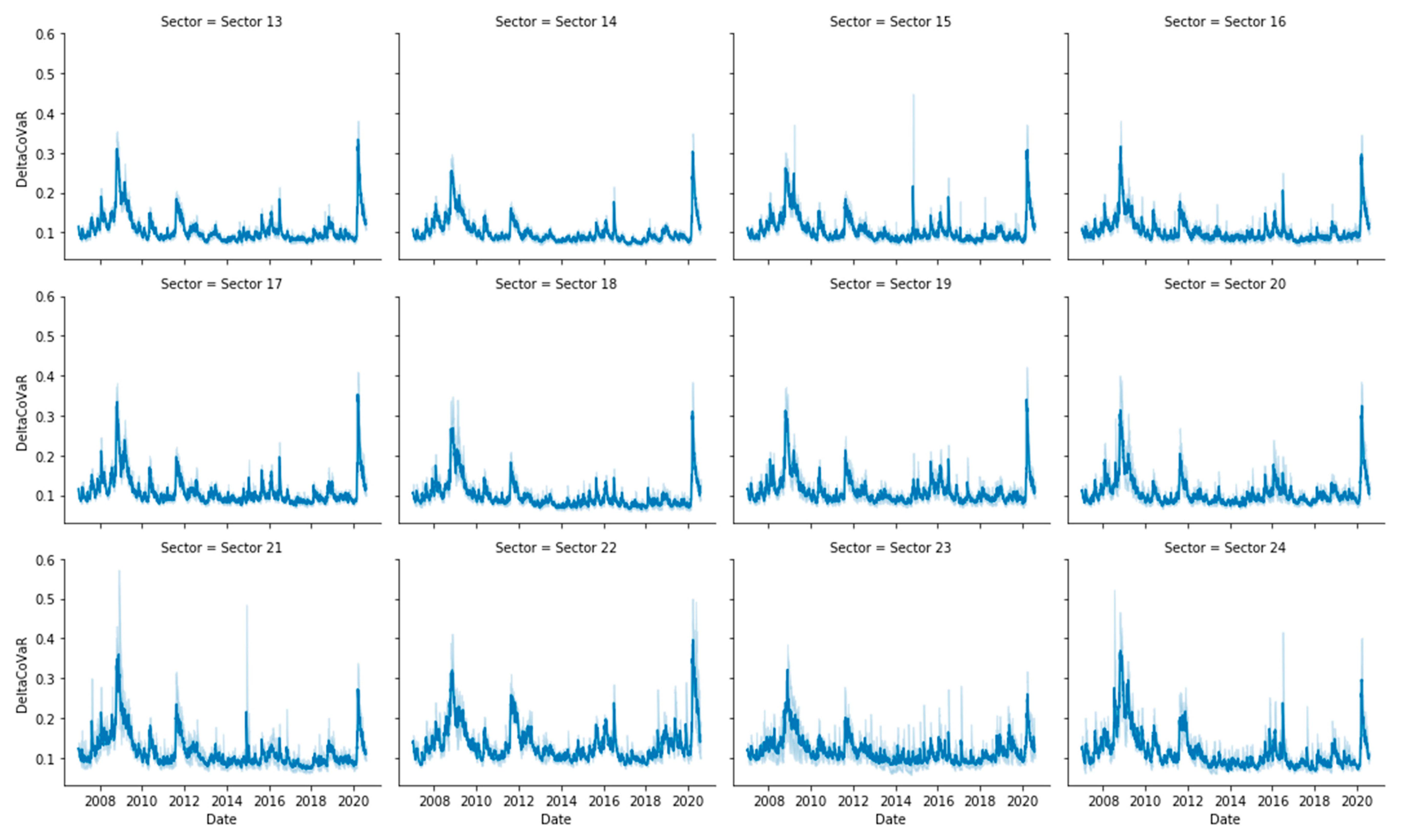
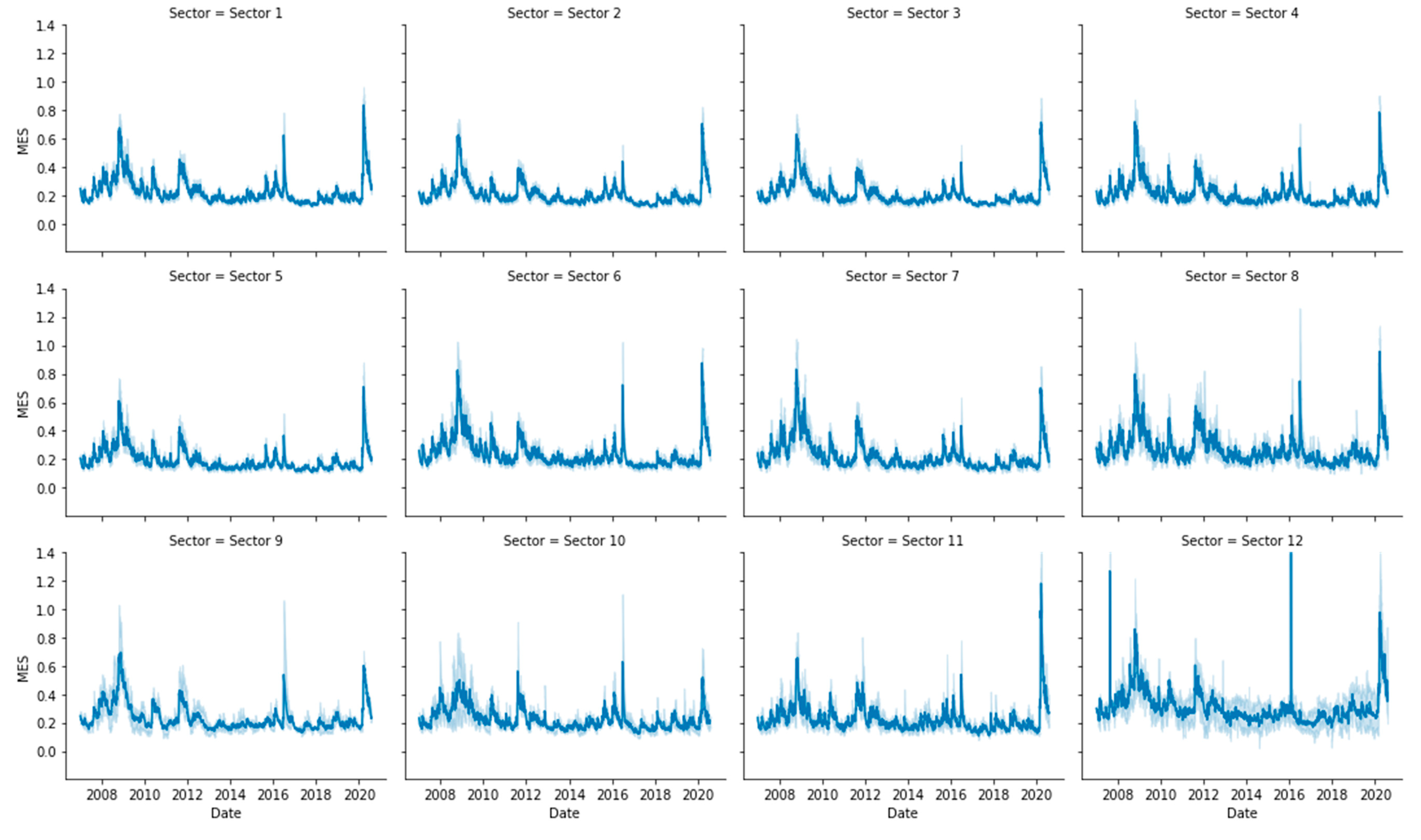
Appendix C. Entropy Computation

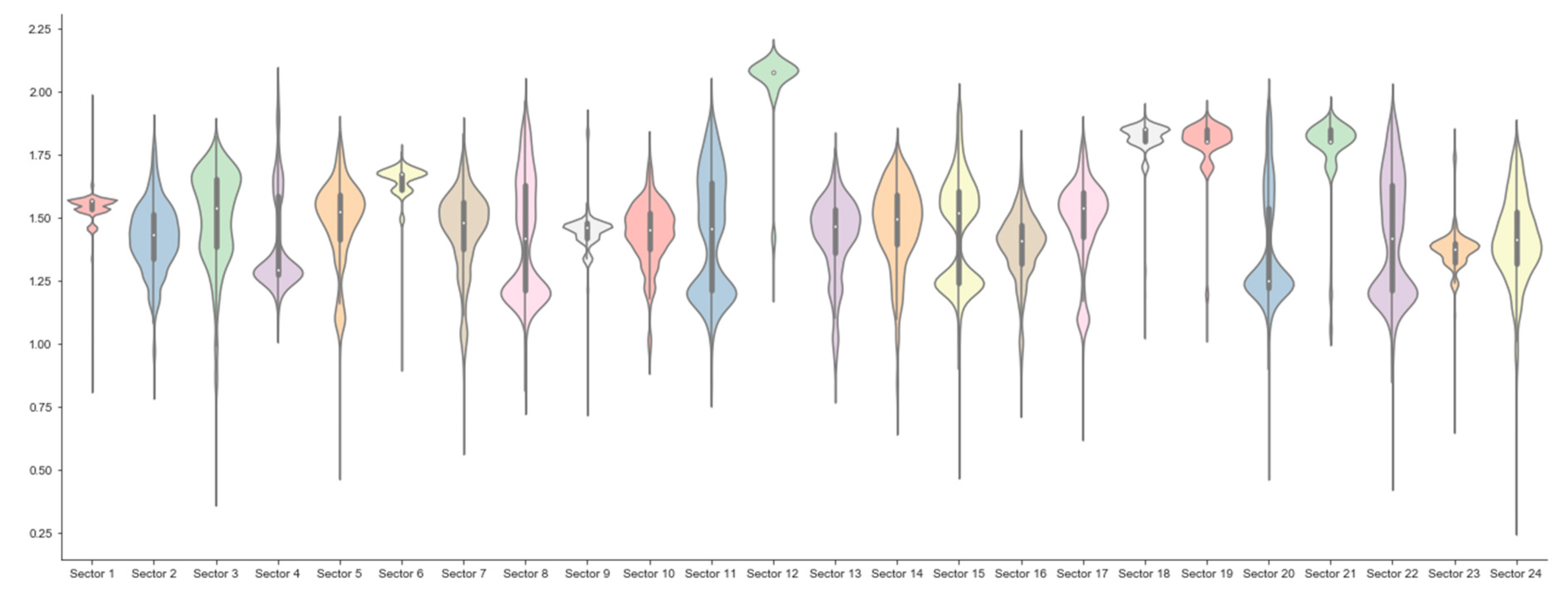

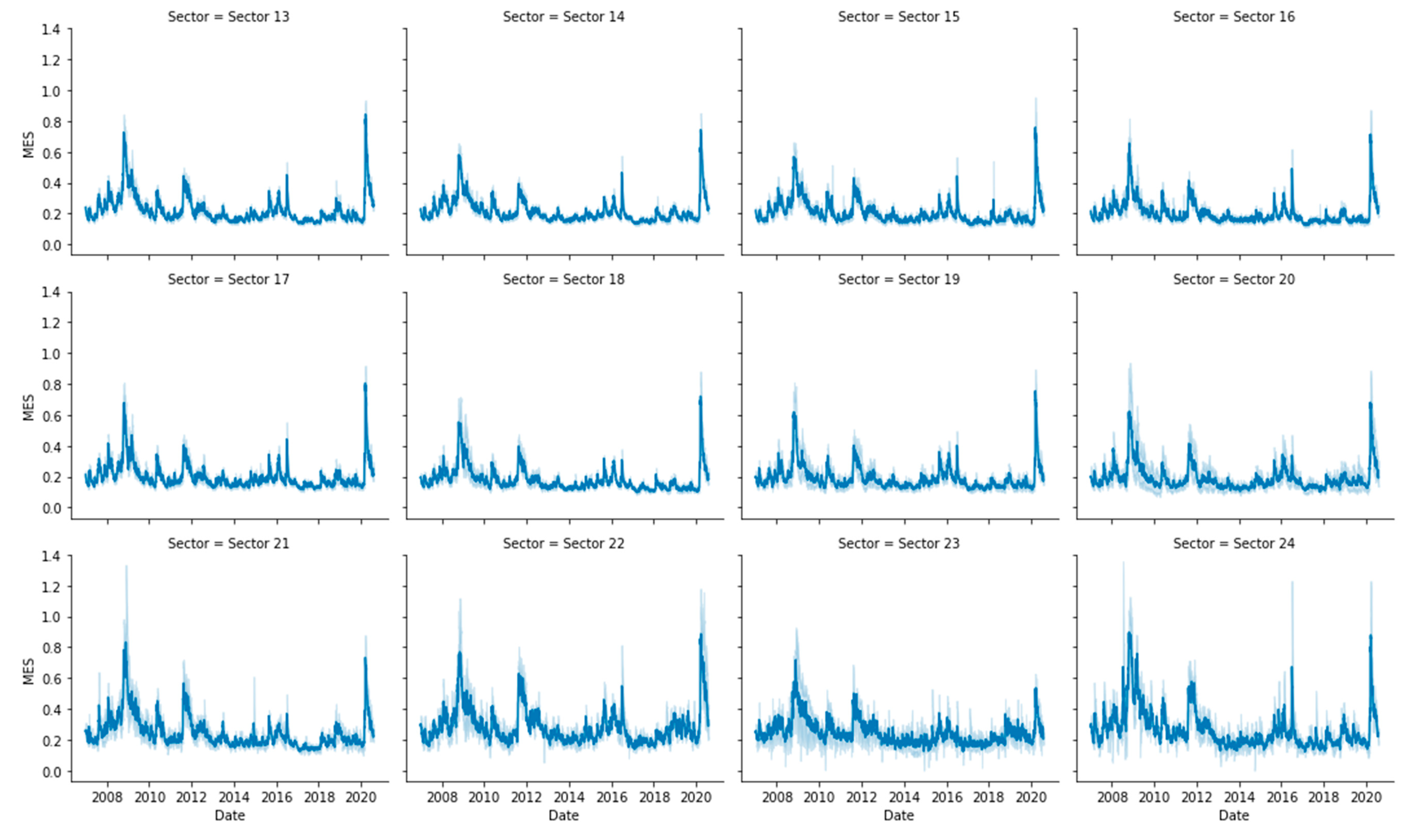
Appendix D. Results for Beta Robustness
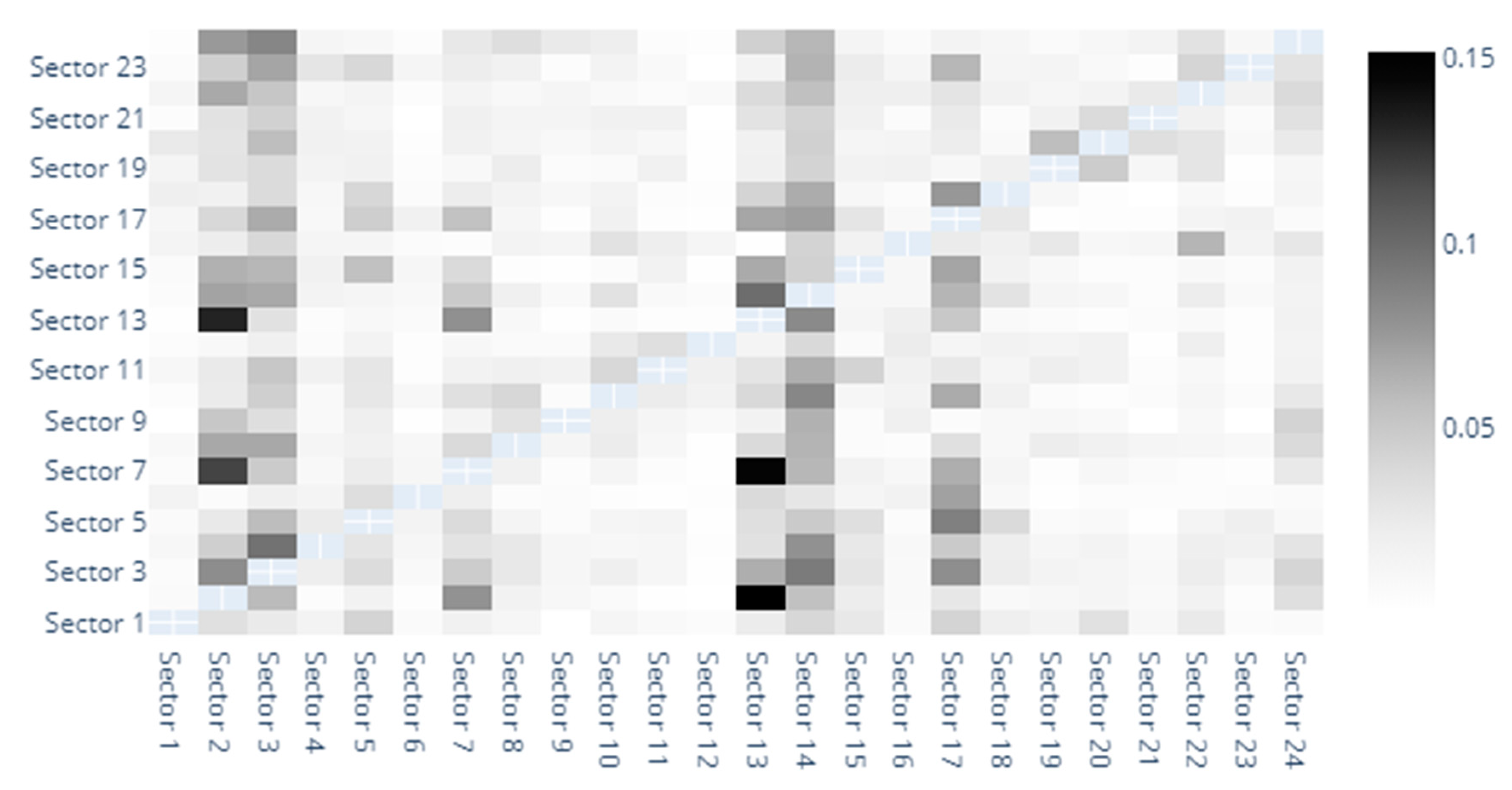
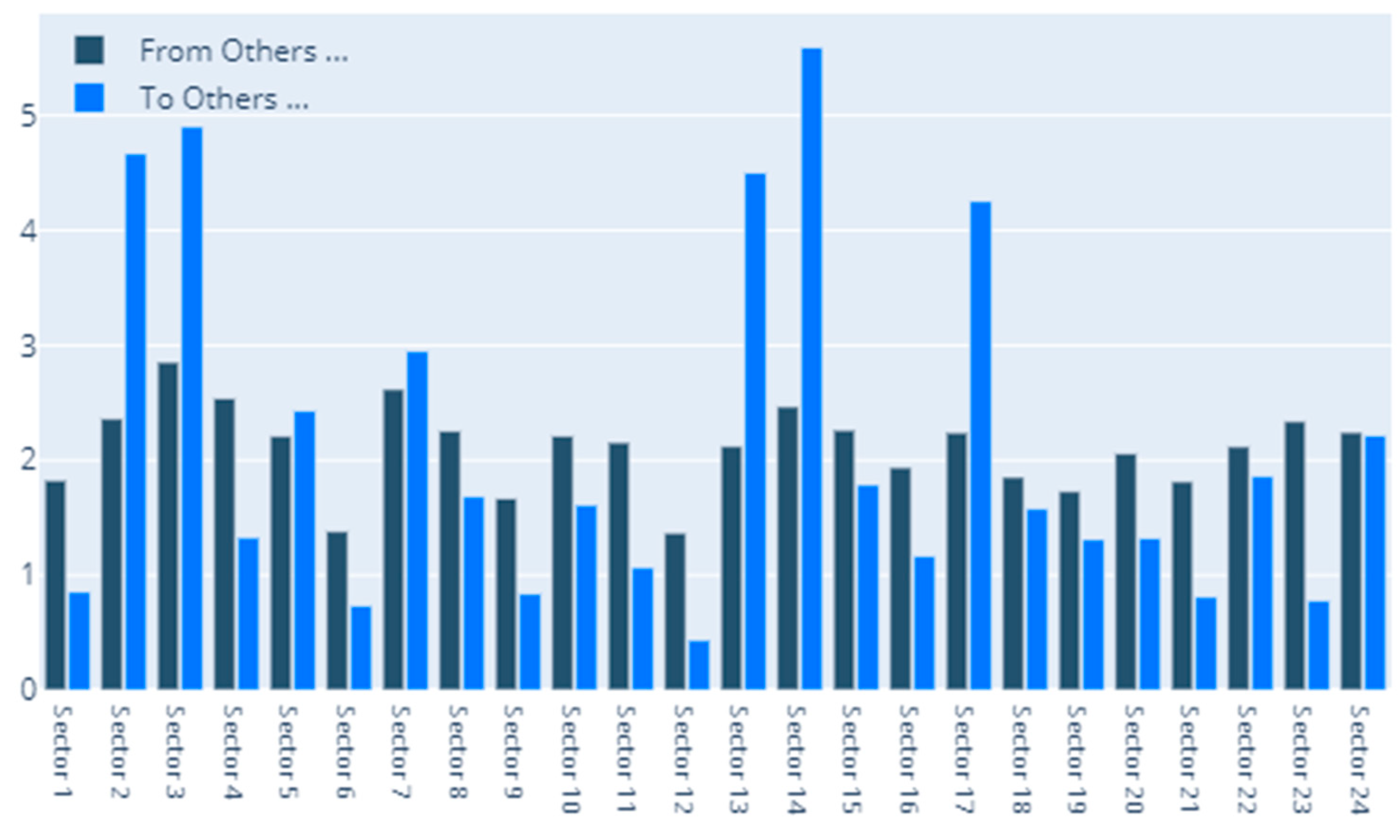
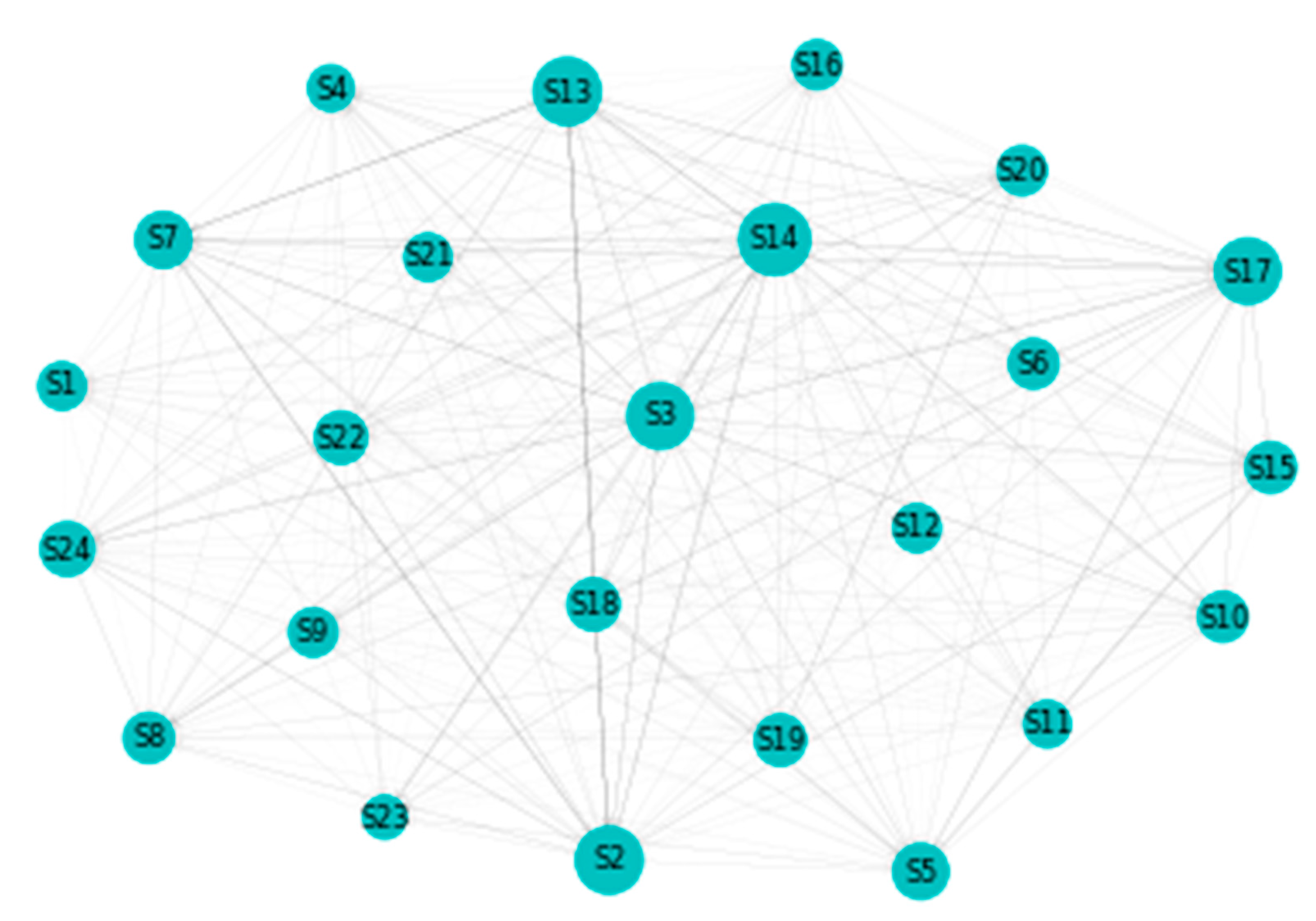
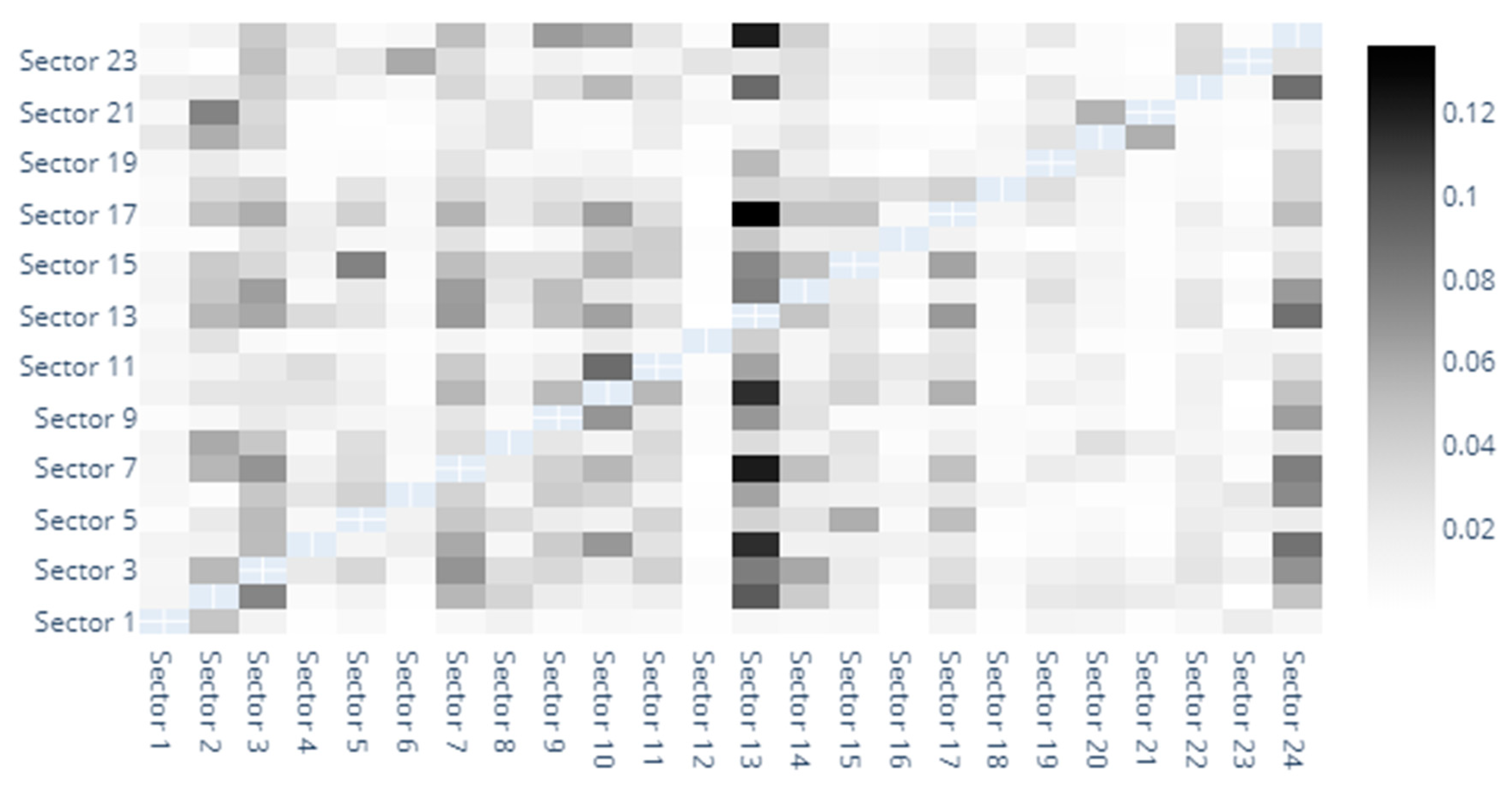
Appendix E. Results for VaR Robustness

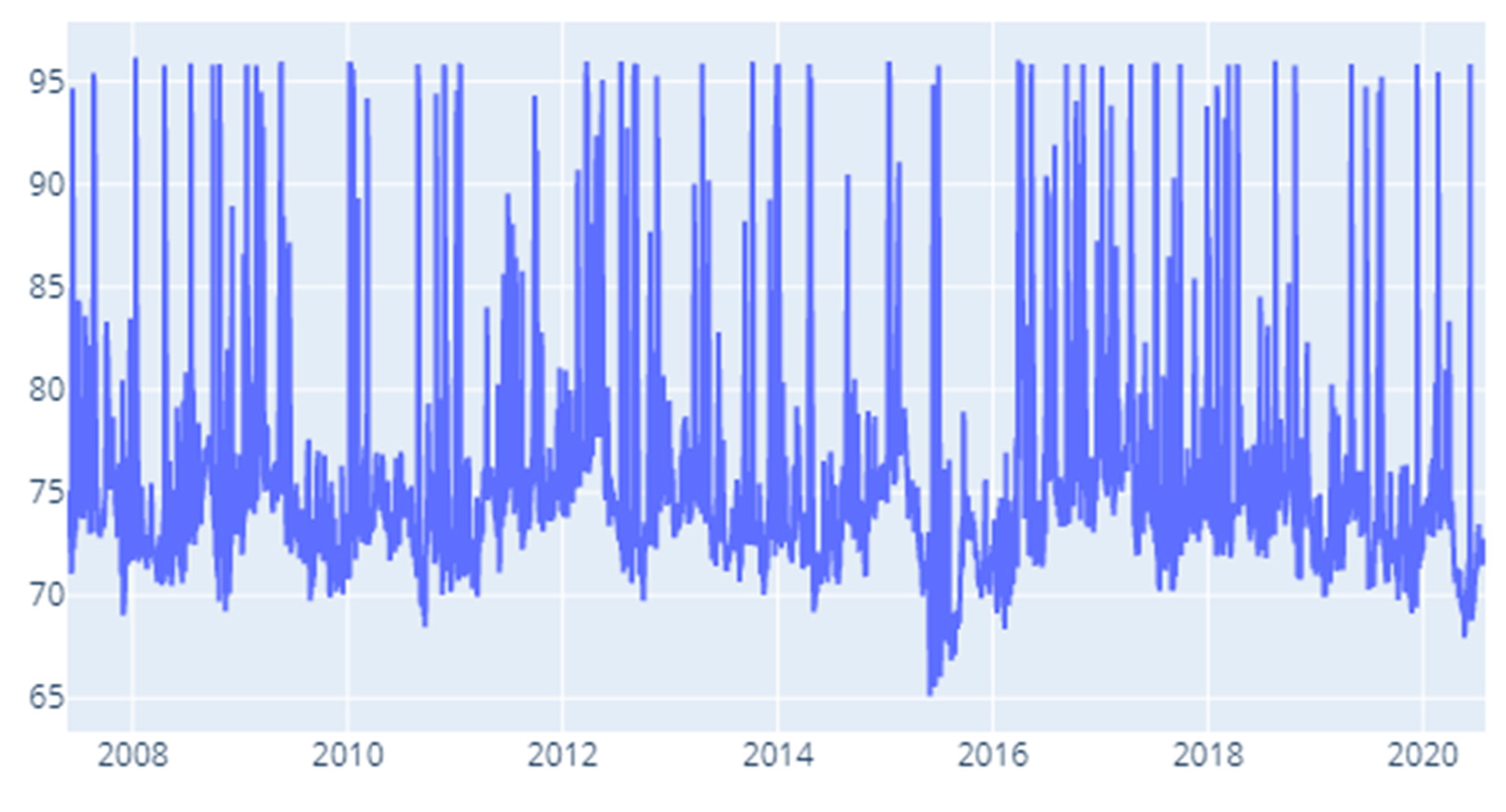
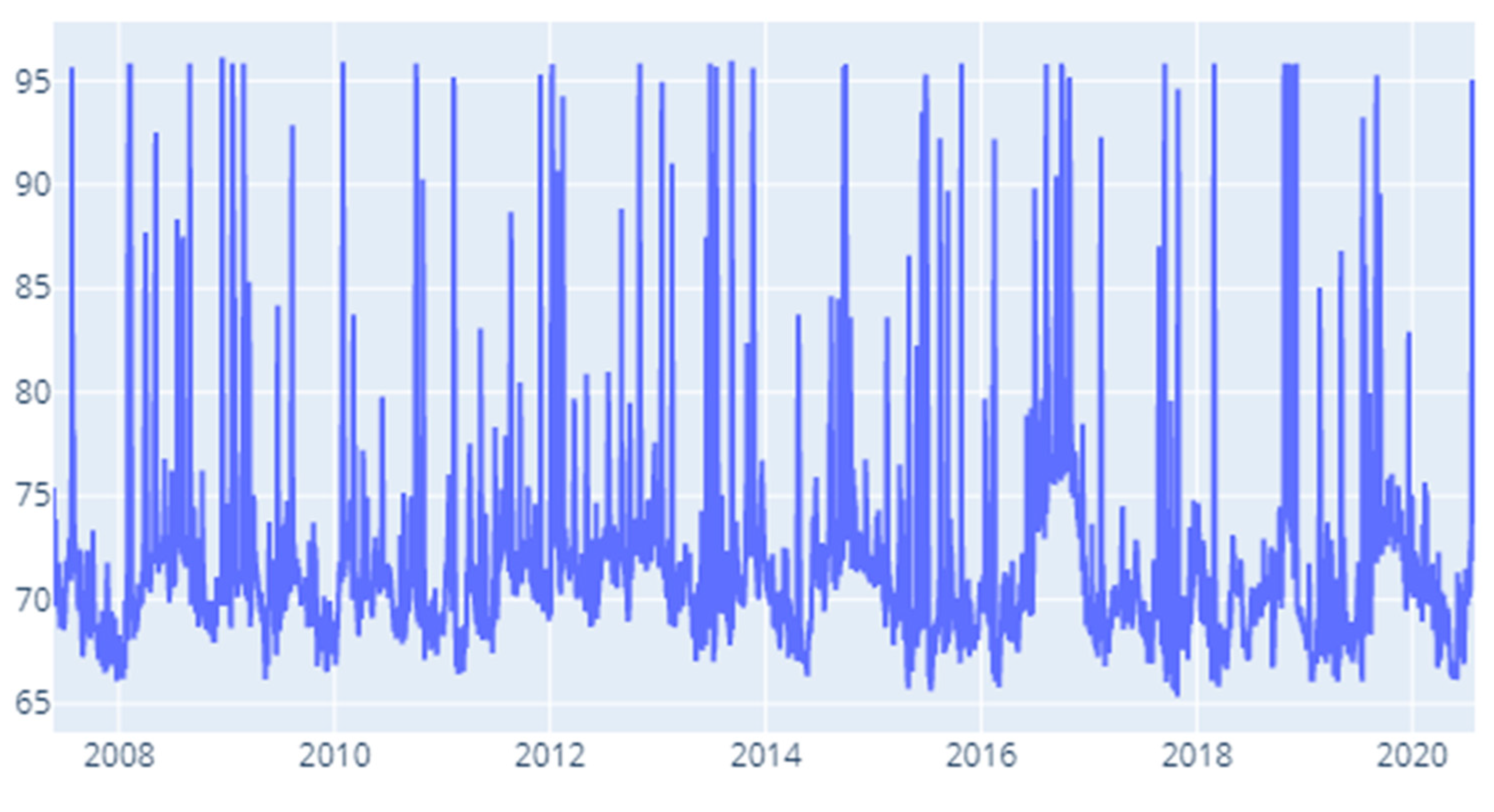
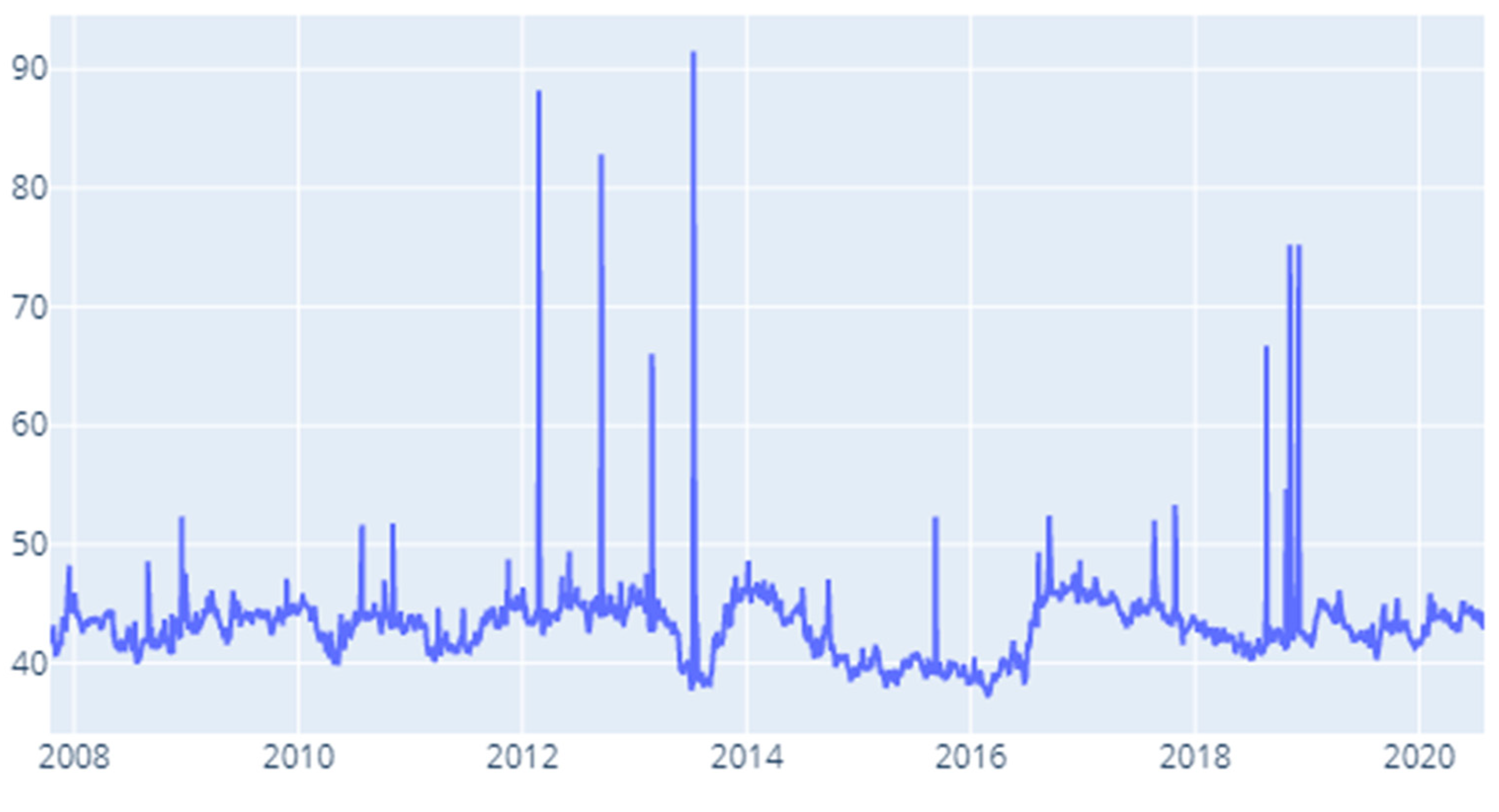
Appendix F. Results for Robustness Testing for Different Rolling Window Specifications
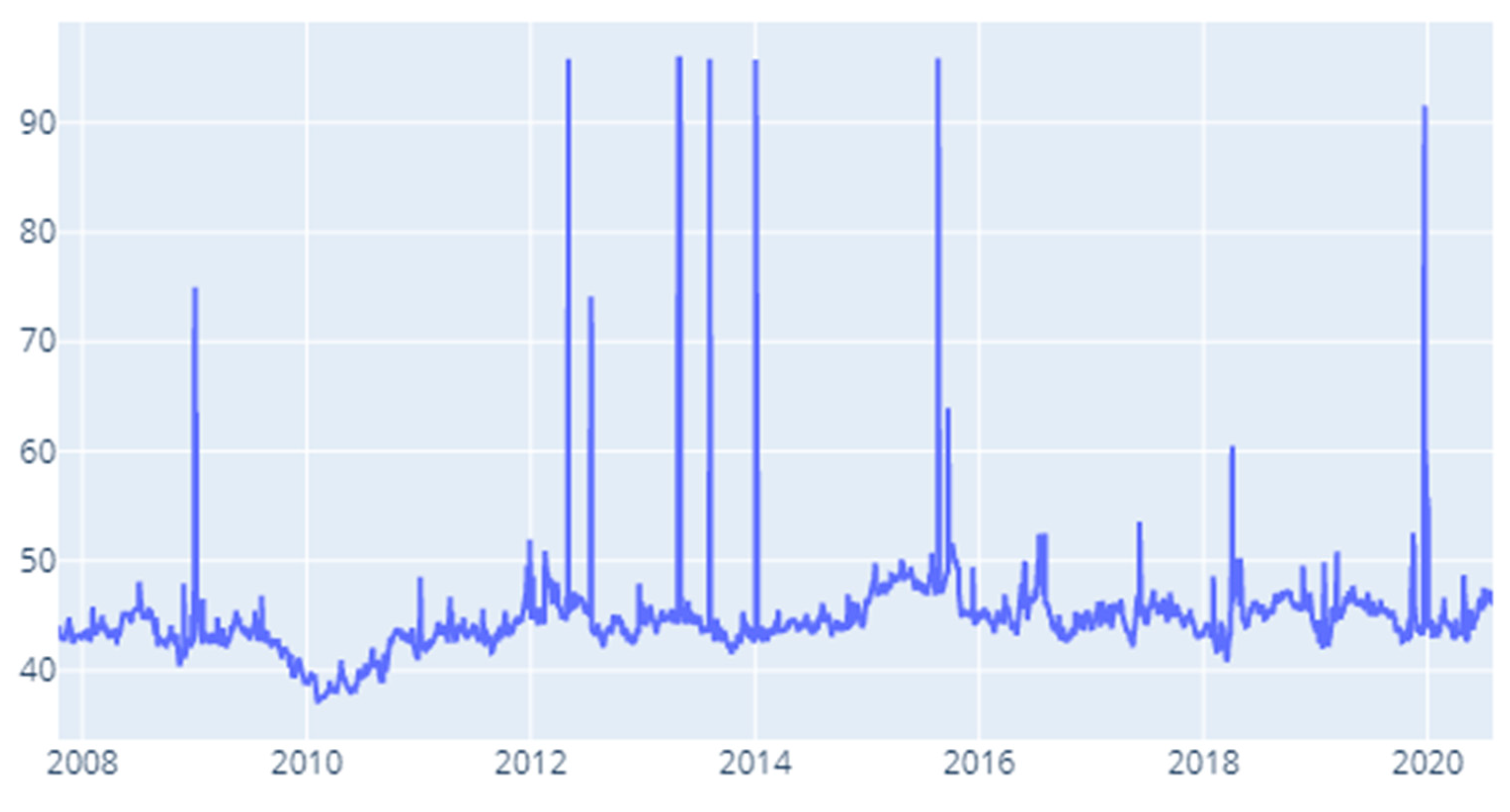
References
- Wang, G.J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Lin, M.; Xie, C.; Stanley, H.E. Interconnectedness and systemic risk of China’s financial institutions. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2018, 35, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofman, M. Efficiency and stability of a financial architecture with too-interconnected-to-fail institutions. J. Financ. Econ. 2017, 124, 113–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.L.; Liu, X.H.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, W. Financial systemic risk measurement based on causal network connectedness analysis. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2019, 64, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Le, W.; Sun, X.; Li, J. Financial stress dynamics in China: An interconnectedness perspective. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2020, 68, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, S.; Kelly, B.; Pruitt, S. Systemic risk and the macroeconomy: An empirical evaluation. J. Financ. Econ. 2016, 119, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billio, M.; Casarin, R.; Costola, M.; Pasqualini, A. An entropy-based early warning indicator for systemic risk. J. Int. Financ. Mark. Inst. Money 2016, 45, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfl, T.; Peter, F.J. Analyzing volatility transmission using group transfer entropy. Energy Econ. 2018, 75, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shang, P.; Zhao, X. Multifractal diffusion entropy analysis on stock volatility in financial markets. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2012, 391, 5739–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, J. Quantifying complexity of financial short-term time series by composite multiscale entropy measure. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 22, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, A.; Schlotter, R. Entropy based risk measures. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 285, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, F.X.; Yilmaz, K. Better to give than to receive: Predictive directional measurement of volatility spillovers. Int. J. Forecast. 2012, 28, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Ramirez, J.; Rodriguez, E.; Alvarez, J. A multiscale entropy approach for market efficiency. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2012, 21, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Cruz, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Ibarra Valdez, C.; Alvarez Ramirez, J. Efficiency of crude oil markets: Evidences from informational entropy analysis. Energy Policy 2012, 41, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarin, R.; Costola, M. Structural changes in large economic datasets: A nonparametric homogeneity test. Econ. Lett. 2019, 176, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, W.A. The informational efficiency: The emerging markets versus the developed markets. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2009, 16, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfl, T.; Peter, F.J. Using transfer entropy to measure information flows between financial markets. Stud. Nonlinear Dyn. Econom. 2013, 17, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfl, T.; Peter, F.J. The impact of the financial crisis on transatlantic information flows: An intraday analysis. J. Int. Financ. Mark. Inst. Money 2014, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, L.S.; Mullokandov, A.; Kenett, D.Y. Dependency relations among international stock market indices. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2015, 8, 227–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasoumi, E.; Racine, J. Entropy and predictability of stock market returns. J. Econom. 2002, 107, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Marfatia, H.; Gupta, R. Information spillover across international real estate investment trusts: Evidence from an entropy-based network analysis. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2018, 46, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrada-Félix, J.; Fernandez-Perez, A.; Sosvilla-Rivero, S. Fear connectedness among asset classes. Appl. Econ. 2018, 50, 4234–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, A.; Beyer, A. The dynamics of spillover effects during the European sovereign debt turmoil. J. Bank. Financ. 2014, 42, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, F.; Deesomsak, R. Does linkage fuel the fire? The transmission of financial stress across the markets. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2014, 36, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistrulli, P.E. Assessing financial contagion in the interbank market: Maximum entropy versus observed interbank lending patterns. J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Craig, B.; Von Peter, G. Filling in the blanks: Network structure and interbank contagion. Quant. Financ. 2015, 15, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Lee, D.; Sohn, S.; Yang, B. Stock market uncertainty and economic fundamentals: An entropy-based approach. Quant. Financ. 2019, 19, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gangi, D.; Lillo, F.; Pirino, D. Assessing systemic risk due to fire sales spillover through maximum entropy network reconstruction. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2018, 94, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradojevic, N.; Caric, M. Predicting systemic risk with entropic indicators. J. Forecast. 2017, 36, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltalidis, N.; Gounopoulos, D.; Kizys, R.; Koutelidakis, Y. Transmission channels of systemic risk and contagion in the European financial network. J. Bank. Financ. 2015, 61, S36–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billio, M.; Getmansky, M.; Lo, A.W.; Pelizzon, L. Econometric measures of connectedness and systemic risk in the finance and insurance sectors. J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 104, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, J.; Nguyen, D.K.; Siverskog, J.; Uddin, G.S. Market integration and financial linkages among stock markets in Pacific Basin countries. J. Empir. Financ. 2018, 46, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziantoniou, I.; Gabauer, D.; Marfatia, H.A. Dynamic Connectedness and Spillovers Across Sectors: Evidence from The Indian Stock Market (No. 2020-04); University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth Business School, Economics and Finance Subject Group: Portsmouth, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Hamori, S. Spillovers to Renewable Energy Stocks in the US and Europe: Are They Different? Energies 2020, 13, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, E.; Park, I.M.; Pillow, J.W. Bayesian entropy estimation for countable discrete distributions. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 2833–2868. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, T.; Brunnermeier, M.K. CoVaR. Am. Econ. Rev. 2016, 106, 1705–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, V.V.; Pedersen, L.H.; Philippon, T.; Richardson, M. Measuring systemic risk. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2017, 30, 2–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemenman, I.; Shafee, F.; Bialek, W. Entropy and inference, revisited. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 14, pp. 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Collet, J.; Ielpo, F. Sector spillovers in credit markets. J. Bank. Financ. 2018, 94, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.J.; Xie, C.; He, K.; Stanley, H.E. Extreme risk spillover network: Application to financial institutions. Quant. Financ. 2017, 17, 1417–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyasiani, E.; Kalotychou, E.; Staikouras, S.K.; Zhao, G. Return and volatility spillover among banks and insurers: Evidence from pre-crisis and crisis periods. J. Financ. Serv. Res. 2015, 48, 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, Z.; Füss, R.; Gropp, R. Spillover effects among financial institutions: A state-dependent sensitivity value-at-risk approach. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 2014, 49, 575–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.C.; Peña, J.I.; Wang, C.W. Industry characteristics and financial risk contagion. J. Bank. Financ. 2015, 50, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, N.A.; Savvides, A. Real effects of banking crises: Imports of capital goods by developing countries. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2018, 22, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.F.; Treepongkaruna, S.; Brooks, R.; Gray, S. Asset market linkages: Evidence from financial, commodity and real estate assets. J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, Y. Tail dependence in international real estate securities markets. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2012, 45, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouri, E.; Gupta, R.; Wang, S. Nonlinear contagion between stock and real estate markets: International evidence from a local Gaussian correlation approach. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Industries return and volatility spillover in Chinese stock market: An early warning signal of systemic risk. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 9046–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Abdel-Qader, W.; Hammami, H.; Shams, S. Is China a source of financial contagion? Financ. Res. Lett. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.L.; Liu, X.H.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, W. Research on China’s financial systemic risk contagion under jump and heavy-tailed risk. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2020, 72. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, S.; Goodell, J.W.; Günay, S. Co-movements and spillovers of oil and renewable firms under extreme conditions: New evidence from negative WTI prices during COVID-19. Energy Econ. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruník, J.; Kočenda, E.; Vácha, L. Asymmetric connectedness on the US stock market: Bad and good volatility spillovers. J. Financ. Mark. 2016, 27, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirer, M.; Diebold, F.X.; Liu, L.; Yilmaz, K. Estimating global bank network connectedness. J. Appl. Econom. 2018, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfatia, H.; Zhao, W.L.; Ji, Q. Uncovering the global network of economic policy uncertainty. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2020, 53, 101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupu, R.; Călin, A.C.; Zeldea, C.G.; Lupu, I. A Bayesian Entropy Approach to Sectoral Systemic Risk Modeling. Entropy 2020, 22, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121371
Lupu R, Călin AC, Zeldea CG, Lupu I. A Bayesian Entropy Approach to Sectoral Systemic Risk Modeling. Entropy. 2020; 22(12):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupu, Radu, Adrian Cantemir Călin, Cristina Georgiana Zeldea, and Iulia Lupu. 2020. "A Bayesian Entropy Approach to Sectoral Systemic Risk Modeling" Entropy 22, no. 12: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121371
APA StyleLupu, R., Călin, A. C., Zeldea, C. G., & Lupu, I. (2020). A Bayesian Entropy Approach to Sectoral Systemic Risk Modeling. Entropy, 22(12), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121371






