Generalization of the Landauer Principle for Computing Devices Based on Many-Valued Logic
Abstract
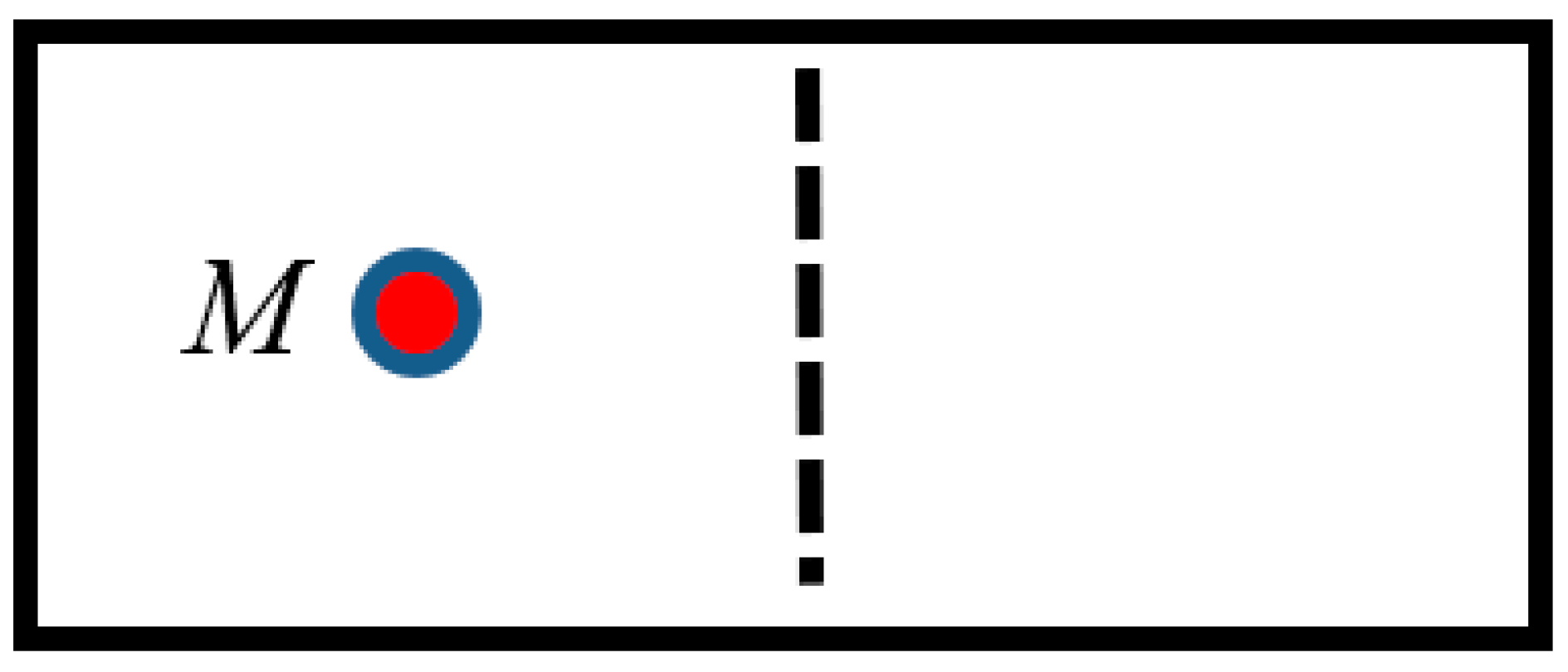
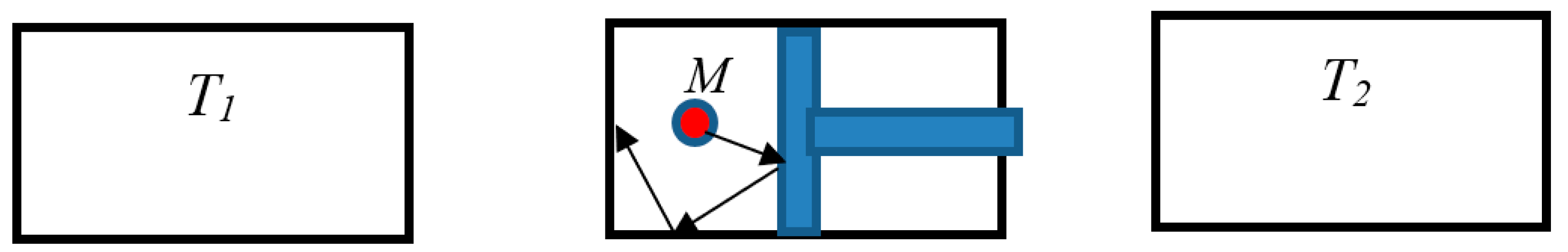
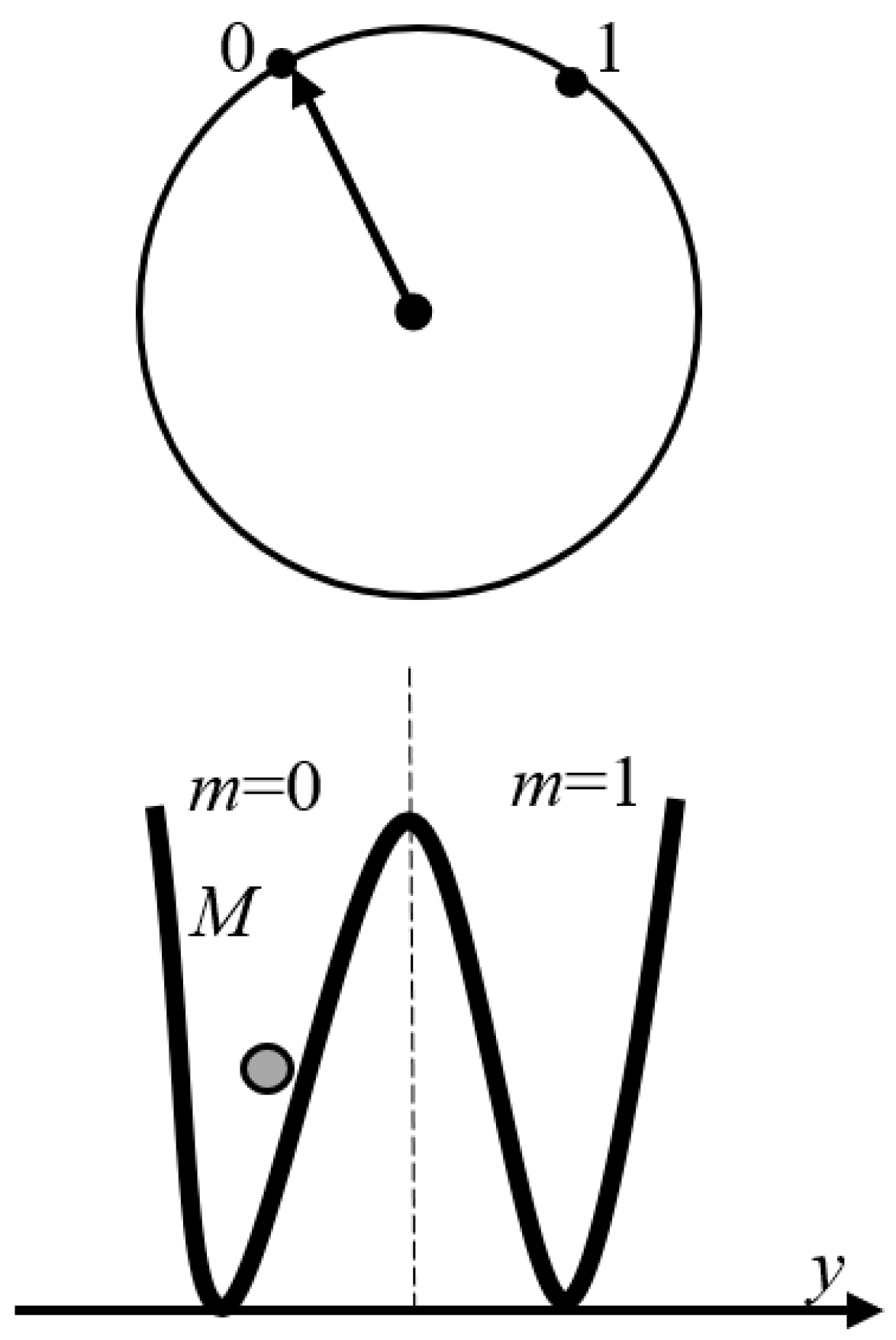
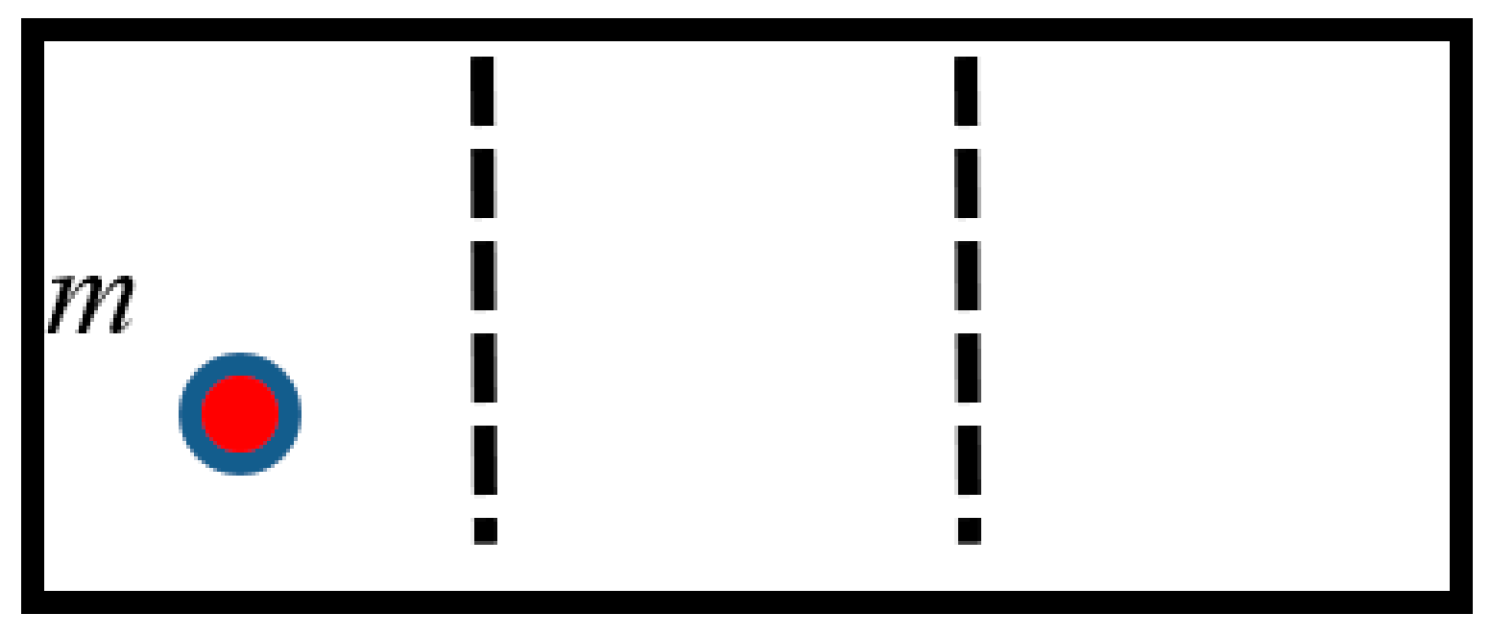
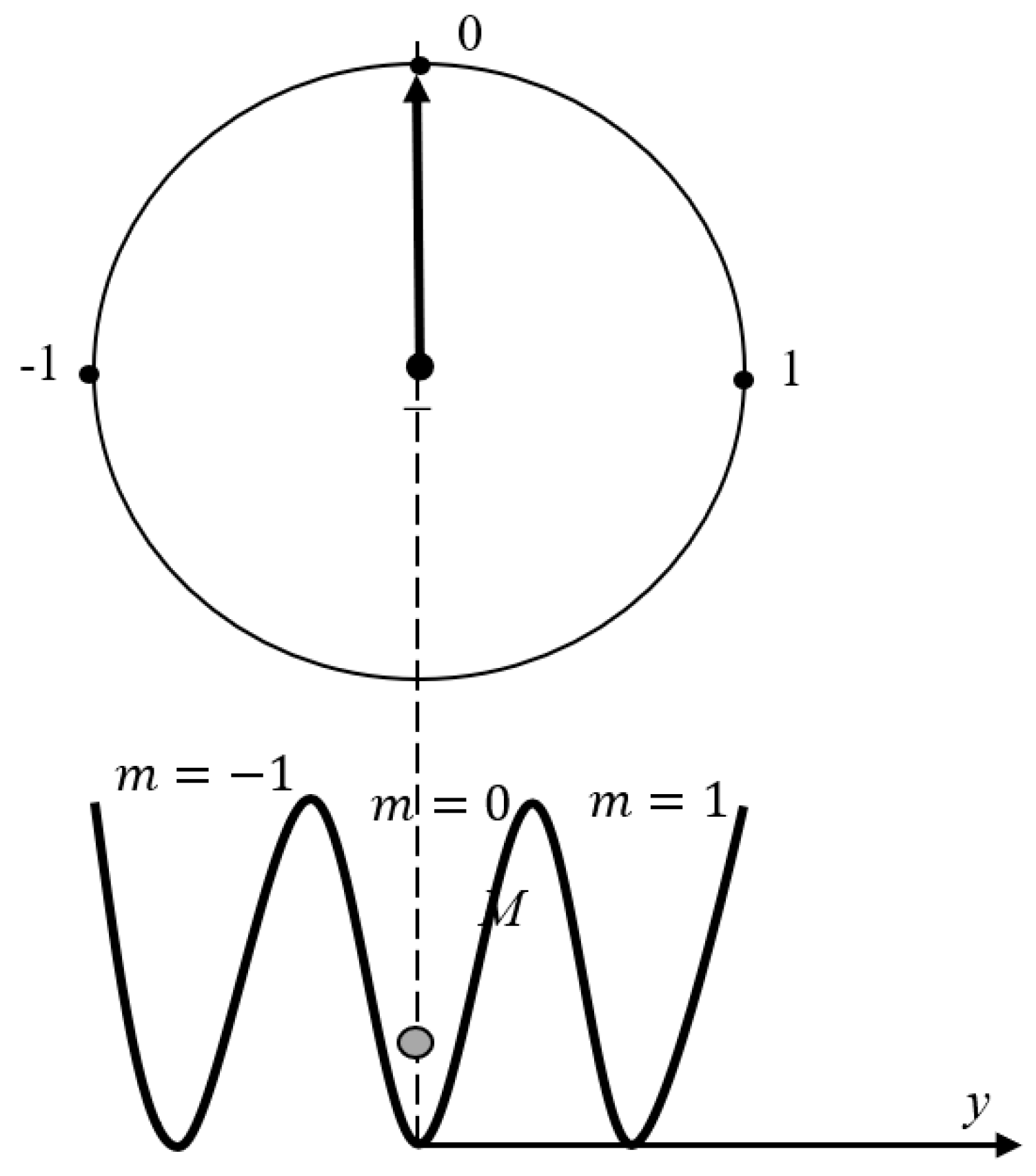
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glusker, M.; Hogan, D.M.; Vass, P. The ternary calculating machine of Thomas Fowler. IEEE Ann. Hist. Comput. 2005, 27, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousentsov, N.P. An experience of the ternary computer development. Bull. Mosc. Univ. Math. Mech. 1965, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Stakhov, A. Brousentsov’s ternary principle, Bergman’s number system and ternary mirror-symmetrical arithmetic. Comput. J. 2005, 45, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, Z. A Treatise on Many-Valued Logics (Studies in Logic and Computation); Kings College London: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C. Algebraic analysis of many valued logics. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1958, 88, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, G.; Fong, A.; Chao, C.Y. A Balanced Ternary Computer. In Proceedings of the 1973 International Symposium on Multiple-valued Logic, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–25 May 1973; pp. 68–88. [Google Scholar]
- Landauer, R. Dissipation and heat generation in the computing process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1961, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Information is physical. Phys. Today 1991, 44, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Minimal energy requirements in communication. Science 1996, 272, 1914–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, J.M.R.; Horowitz, J.M.; Sagawa, T. Thermodynamics of information. Nature Phys. 2015, 11, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeb, D.; Wolf, M.N. An improved Landauer principle with finite-size corrections. New J. Phys. 2004, 16, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Van den Broeck, C. Second law and Landauer principle far from equilibrium. EPL 2011, 95, 40004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goold, J.; Paternostro, M.; Modi, K. Nonequilibrium quantum Landauer Principle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 060602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, S.; Shabbir, S.; Anders, J.; Lutz, E. Landauer’s principle in the quantum regime. Phys. Rev. E. 2011, 83, 030102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, L. The Gibbs Paradox, the Landauer Principle and the irreversibility associated with tilted observers. Entropy 2017, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L. The mass of a bit of information and the Brillouin’s Principle. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2014, 13, 14500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffertshofer, A.; Plastino, A.R. Forgetting and gravitation: From Landauer’s principle to Tolman’s temperature. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 362, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. The mass-energy-information equivalence principle. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 095206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilard, L. Über die Entropieverminderung in einem thermodynamischen System bei Eingriffen intelligenter Wesen. Z. Phys. 1929, 53, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, E.; Ciliberto, S. Information: From Maxwell’s demon to Landauer’s eraser. Phys. Today 2015, 68, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Shkorbatov, A.; Gendeman, O. The Carnot engine based on the small thermodynamic system: Its efficiency and the ergodic hypothesis. Am. J. Phys. 2007, 75, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bub, J. Maxwell’s Demon and the thermodynamics of computation. Maxwell’s Demon and the thermodynamics of computation. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. B 2000, 32, 569–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bérut, A.; Arakelyan, A.; Petrosyan, A.; Ciliberto, S.; Dillenschneider, R.; Lutz, E. Experimental verification of Landauer’s principle linking information and thermodynamics. Nature 2012, 483, 7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.; Gavrilov, M.; Bechhoefer, J. High-Precision test of Landauer’s Principle in a feedback trap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 190601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudenzi, R.; Burzuri, E.; Maegawa, S.; van der Zant, H.; Luis, F. Quantum Landauer erasure with a molecular nanomagnet. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.L.; Xiong, T.P.; Rehan, K.; Zhou, F.; Liang, D.F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yang, W.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Feng, M. Single-atom demonstration of the quantum Landauer principle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 210601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Suarez, M.; Neri, I.; Gammaitoni, L. Sub-kBT micro-electromechanical irreversible logic gate. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, L.B. Comments on “Sub-kBT micro-electromechanical irreversible logic gate”. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2016, 15, 1620001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, D.E. The Art of Computer Programming: Seminumerical Algorithms, 3rd ed.; Addison Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, J.D. Eaters of the lotus: Landauer’s principle and the return of Maxwell’s demon. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. B 2005, 36, 375–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.D. Waiting for Landauer. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. B 2011, 42, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H. Notes on Landauer’s principle, reversible computation, and Maxwell’s Demon. Stud. Hist. Philos. Mod. Phys. 2003, 34, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Breki, A.D. Ternary logic of motion to resolve kinematic frictional paradoxes. Entropy 2019, 21, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bormashenko, E. Generalization of the Landauer Principle for Computing Devices Based on Many-Valued Logic. Entropy 2019, 21, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121150
Bormashenko E. Generalization of the Landauer Principle for Computing Devices Based on Many-Valued Logic. Entropy. 2019; 21(12):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121150
Chicago/Turabian StyleBormashenko, Edward. 2019. "Generalization of the Landauer Principle for Computing Devices Based on Many-Valued Logic" Entropy 21, no. 12: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121150
APA StyleBormashenko, E. (2019). Generalization of the Landauer Principle for Computing Devices Based on Many-Valued Logic. Entropy, 21(12), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21121150




