Communication Enhancement through Quantum Coherent Control of N Channels in an Indefinite Causal-Order Scenario
Abstract
1. Introduction
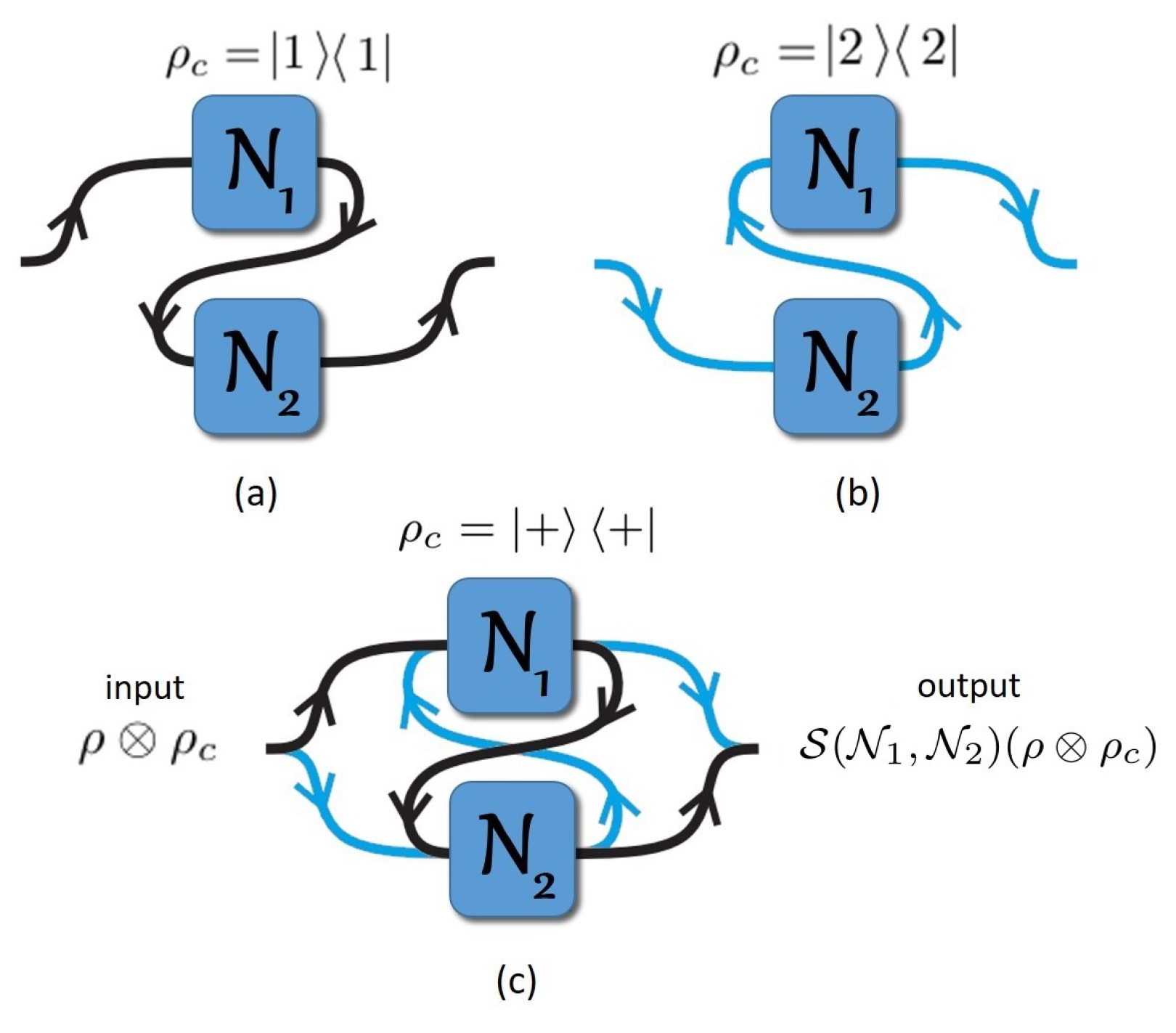
2. Transmission over Multiple Channels in Quantum Superposition of Causal Order
The Formalism for a Quantum N-Switch Channel
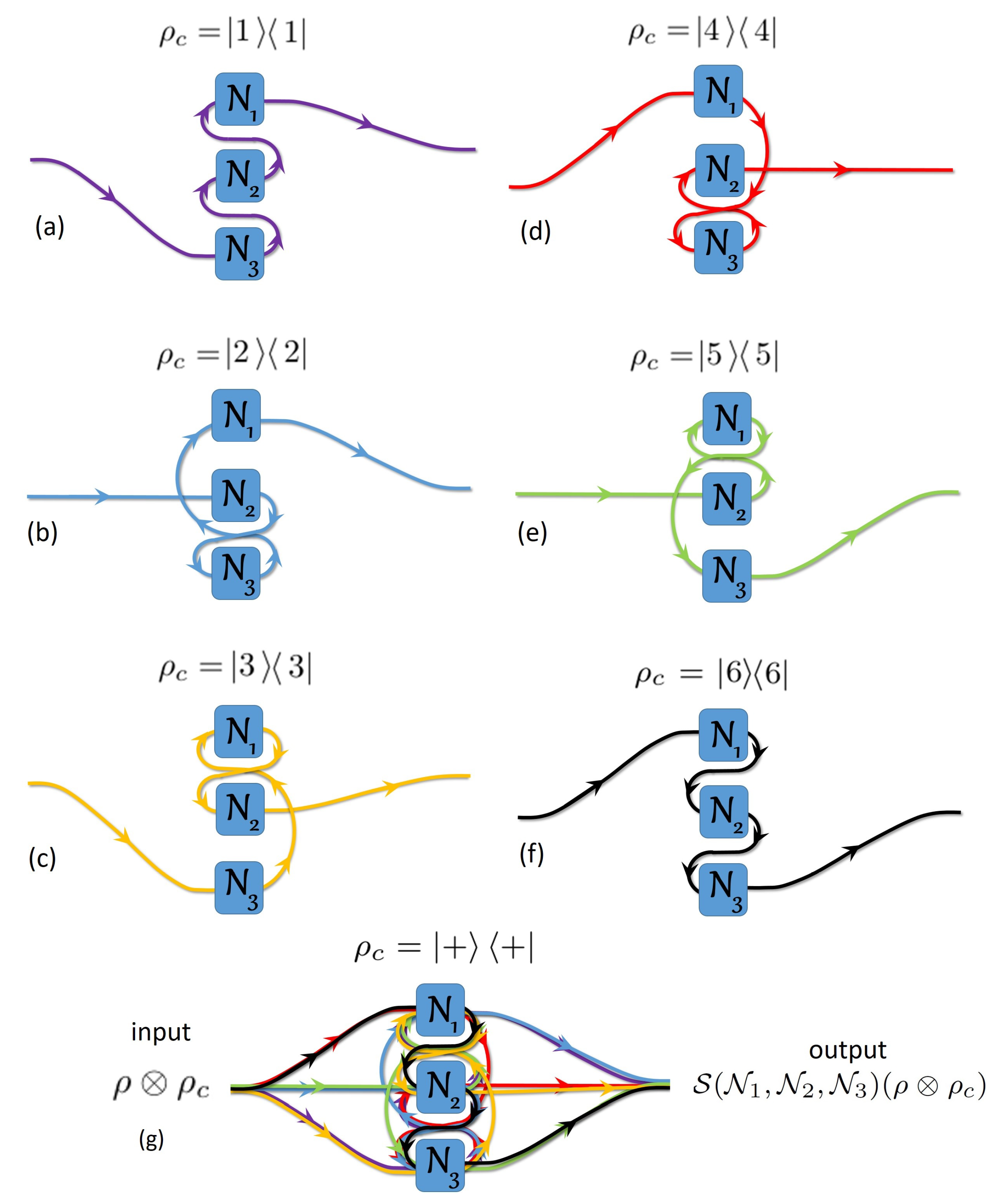
3. The Quantum Switch Matrices for and
3.1. Evaluation of for
3.2. Evaluation of for
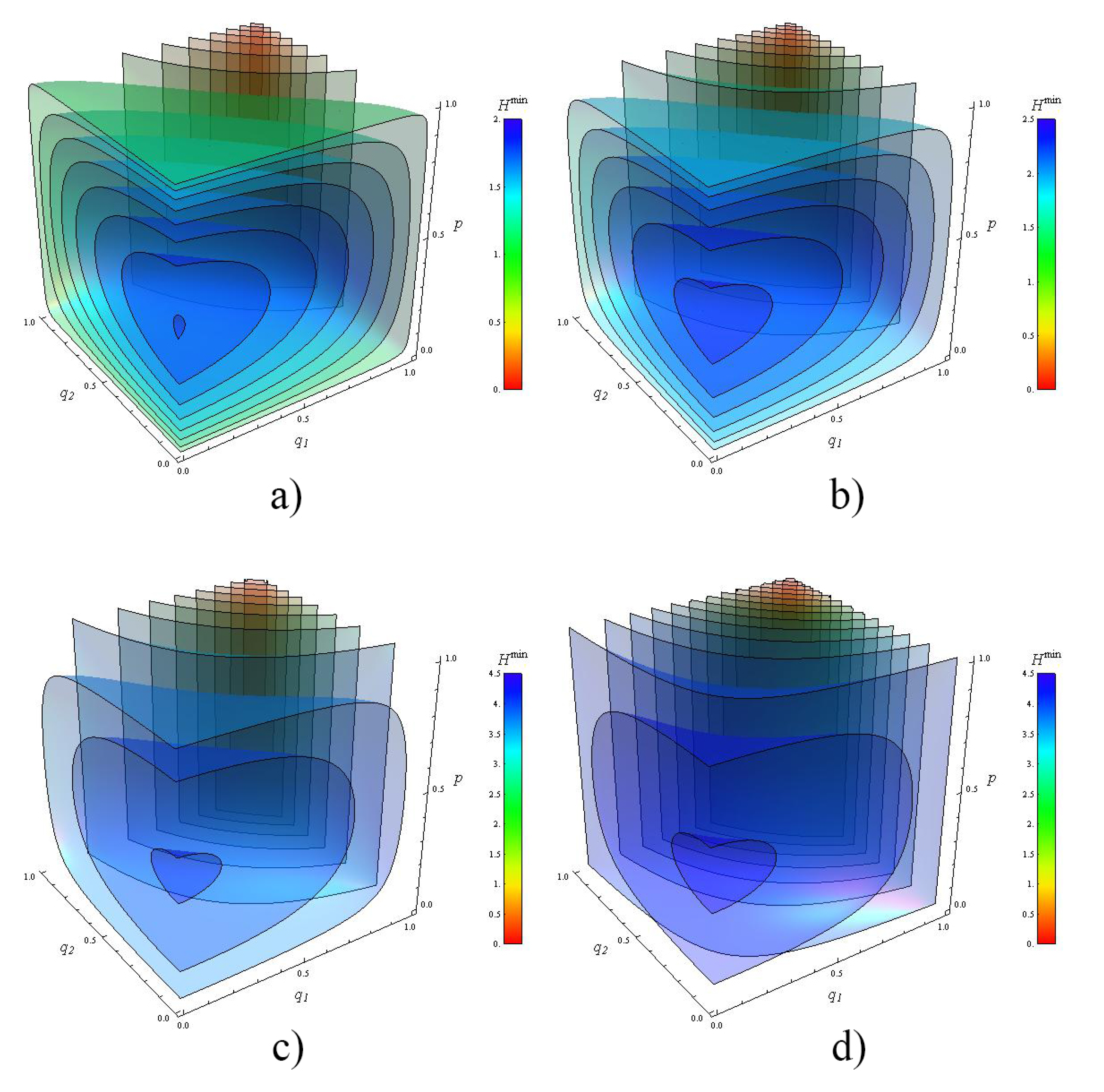
4. Holevo Information Limit for Two and Three Channels
- The diagonalization and minimization of is performed on all possible states given by . It is done analytically for channels and arbitrary . For channels, we compute the eigenvalues of the full quantum 3-switch matrix numerically.
- was analytically calculated following [9].
- We deduce from the analytical expressions of .
4.1. Holevo Information Limit for Channels
4.1.1. Calculation of
4.1.2. Derivation of
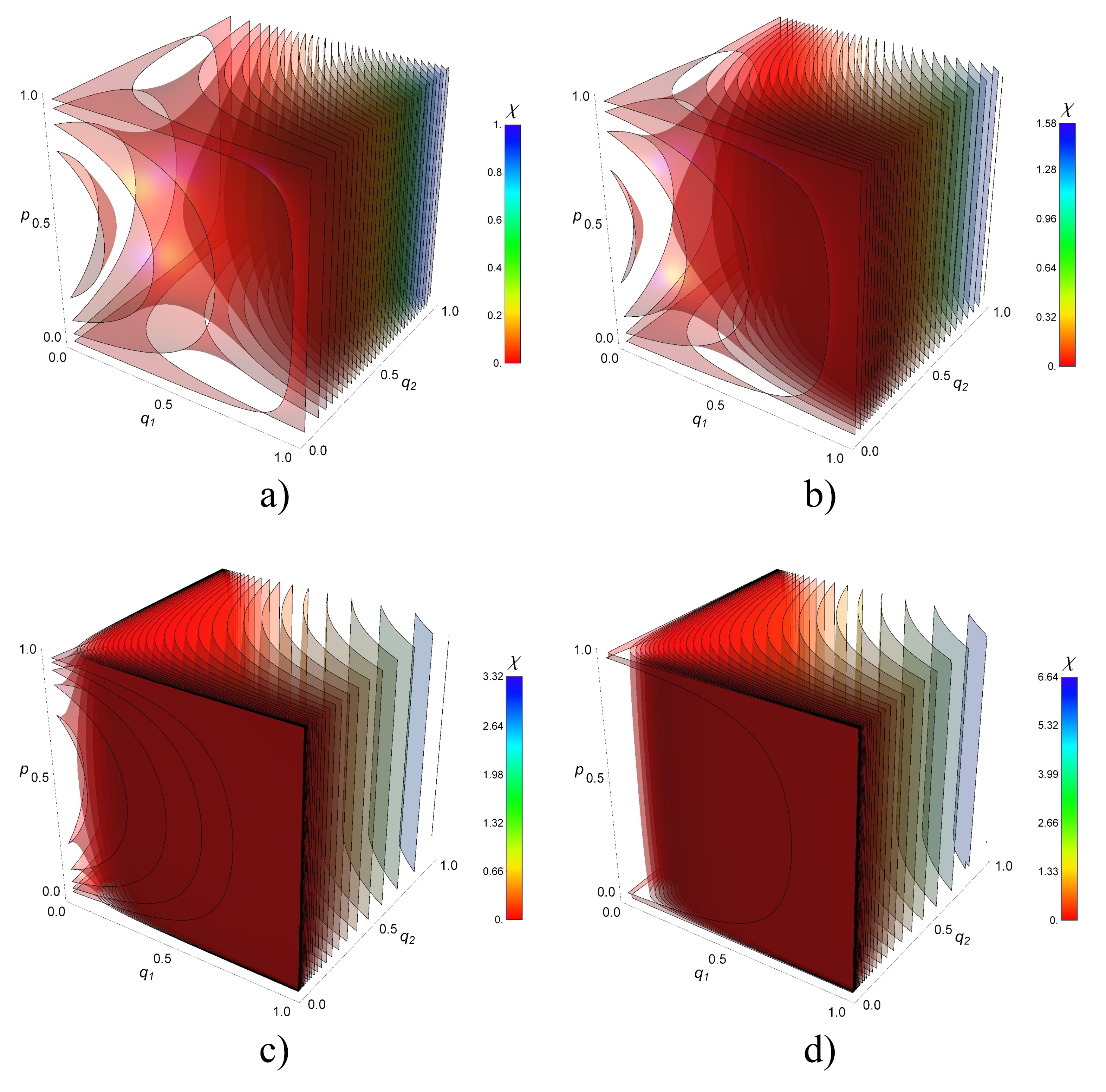
4.2. Holevo Information for Channels
- For a fixed dimension d, the Holevo information for indefinite causal order is always higher than the one obtained using one of the definite causal order shown in Figure 2. This is especially the case for totally depolarized channels i.e., . For completely clean channels (), the Holevo information for indefinite and definite causal order converges to the same value depending on d (not shown).
- Two regions can be distinguished. In the strongly depolarized region (roughly for and for ), the increase of the dimension d of the target system is detrimental to the Holevo information transmitted by the quantum switch. In contrast, in the moderately depolarized region ( for and for ), the Holevo information increases both with q and d, a maximum (not shown) as expected for completely clean channels.
- In the strongly depolarized region, increasing the number of channels to is definitively advantageous for information extraction. For instance, in the case of totally depolarized channels (), the Holevo information is approximately doubled with with respect to for all values of the dimension d calculated up to
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Completeness Property for Wi
Appendix B. Relations to Evaluate Coefficients
Appendix C. Matrices for the Quantum 3-Switch
References
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Labs. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Holevo, A.S. The capacity of the quantum channel with general signal states. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1998, 44, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, B. Quantum coding. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 51, 2738. [Google Scholar]
- Chiribella, G.; D’Ariano, G.M.; Perinotti, P.; Valiron, B. Quantum computations without definite causal structure. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 022318. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.A.; Wechs, J.; Horsman, D.; Mhalla, M.; Branciard, C. Communication through coherent control of quantum channels. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.09826. [Google Scholar]
- Chiribella, G.; Banik, M.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Guha, T.; Alimuddin, M.; Roy, A.; Saha, S.; Agrawal, S.; Kar, G. Indefinite causal order enables perfect quantum communication with zero capacity channel. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.10457. [Google Scholar]
- Ebler, D.; Salek, S.; Chiribella, G. Enhanced communication with the assistance of indefinite causal order. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 120502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, K.; Cao, Y.; Paz-Silva, G.A.; Romero, J.; White, A. Communicating via ignorance. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.07383v3. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Hou, Z.-B.; Cao, H.; Cui, J.-M.; Liu, B.-H.; Huang, Y.-F.; Li, C.-F.; Guo, G.-C. Experimental investigating communication in a superposition of causal orders. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07526. [Google Scholar]
- Chiribella, G. Perfect discrimination of no-signalling channels via quantum superposition of causal structures. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 040301. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, M.; Costa, F.; Brukner, Č. Computational advantage from quantum-controlled ordering of gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 250402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salek, S.; Ebler, D.; Chiribella, G. Quantum communication in a superposition of causal orders. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.06655. [Google Scholar]
- Guérin, P.A.; Feix, A.; Araújo, M.; Brukner, Č. Exponential communication complexity advantage from quantum superposition of the direction of communication. Phys. Rev. Lett 2016, 117, 100502. [Google Scholar]
- Procopio, L.M.; Moqanaki, A.; Araújo, M.; Costa, F.; Calafell, I.A.; Dowd, E.G.; Hamel, D.R.; Rozema, L.A.; Brukner, Č.; Walther, P. Experimental superposition of orders of quantum gates. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7913. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, K.; Giarmatzi, C.; Kewming, M.; Costa, F.; Branciard, C.; Romero, J.; White, A.G. Indefinite causal order in a quantum switch. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 090503. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Tischler, N.; Zhao, S.-R.; Li, Y.-H.; Arrazola, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; You, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. Experimental quantum switching for exponentially superior quantum communication complexity. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.10238. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, G.; Rozema, L.A.; Feix, A.; Araújo, M.; Zeuner, J.M.; Procopio, L.M.; Brukner, Č.; Walther, P. Experimental verification of an indefinite causal order. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602589. [Google Scholar]
- Wechs, J.; Abbott, A.A.; Branciard, C. On the definition and characterisation of multipartite causal (non) separability. New J. Phys. 2018, 21, 013027. [Google Scholar]
- Oreshkov, O.; Giarmatzi, C. Causal and causally separable processes. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 093020. [Google Scholar]
- Chiribella, G.; Kristjánsson, H. A second-quantised shannon theory. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.05292. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, R.A.; Johnson, C.R. Matrix Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, B.; Westmoreland, M.D. Sending classical information via noisy quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 1997, 56, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Wilde, M.M. Quantum Information Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, R. Positive Definite Matrices; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]

| d | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.0487 | 0.0980 | 2.0123 |
| 3 | 0.0183 | 0.0339 | 1.8524 |
| 4 | 0.0085 | 0.0159 | 1.8705 |
| 5 | 0.0046 | 0.0087 | 1.8913 |
| 6 | 0.0027 | 0.0053 | 1.9629 |
| 7 | 0.0018 | 0.0034 | 1.8888 |
| 8 | 0.0012 | 0.0023 | 1.9166 |
| 9 | 0.0008 | 0.0016 | 2 |
| 10 | 0.0006 | 0.0012 | 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Procopio, L.M.; Delgado, F.; Enríquez, M.; Belabas, N.; Levenson, J.A. Communication Enhancement through Quantum Coherent Control of N Channels in an Indefinite Causal-Order Scenario. Entropy 2019, 21, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21101012
Procopio LM, Delgado F, Enríquez M, Belabas N, Levenson JA. Communication Enhancement through Quantum Coherent Control of N Channels in an Indefinite Causal-Order Scenario. Entropy. 2019; 21(10):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21101012
Chicago/Turabian StyleProcopio, Lorenzo M., Francisco Delgado, Marco Enríquez, Nadia Belabas, and Juan Ariel Levenson. 2019. "Communication Enhancement through Quantum Coherent Control of N Channels in an Indefinite Causal-Order Scenario" Entropy 21, no. 10: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21101012
APA StyleProcopio, L. M., Delgado, F., Enríquez, M., Belabas, N., & Levenson, J. A. (2019). Communication Enhancement through Quantum Coherent Control of N Channels in an Indefinite Causal-Order Scenario. Entropy, 21(10), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21101012






