Dissolution or Growth of a Liquid Drop via Phase-Field Ternary Mixture Model Based on the Non-Random, Two-Liquid Equation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description
3. Numerical Methods
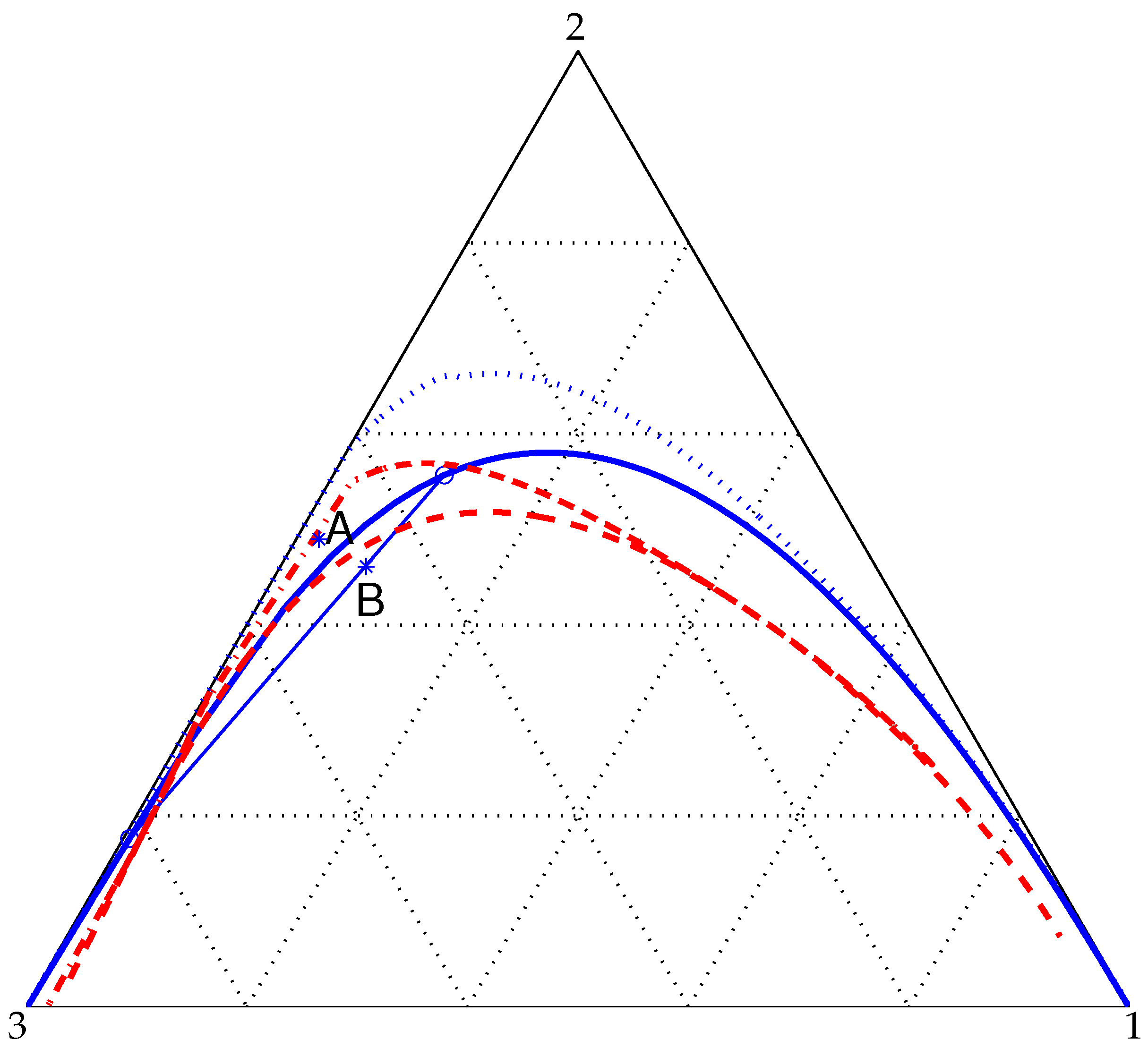
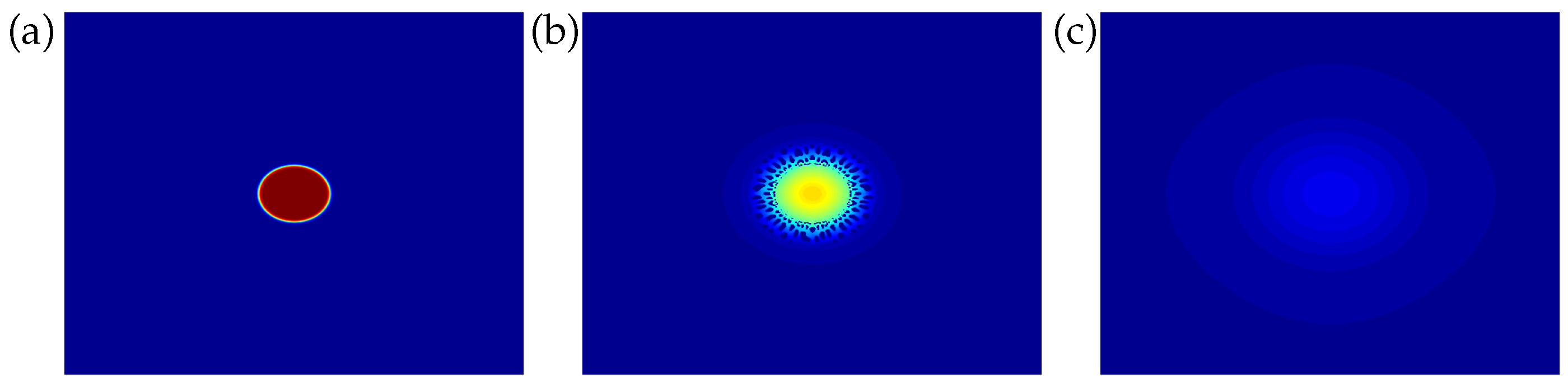
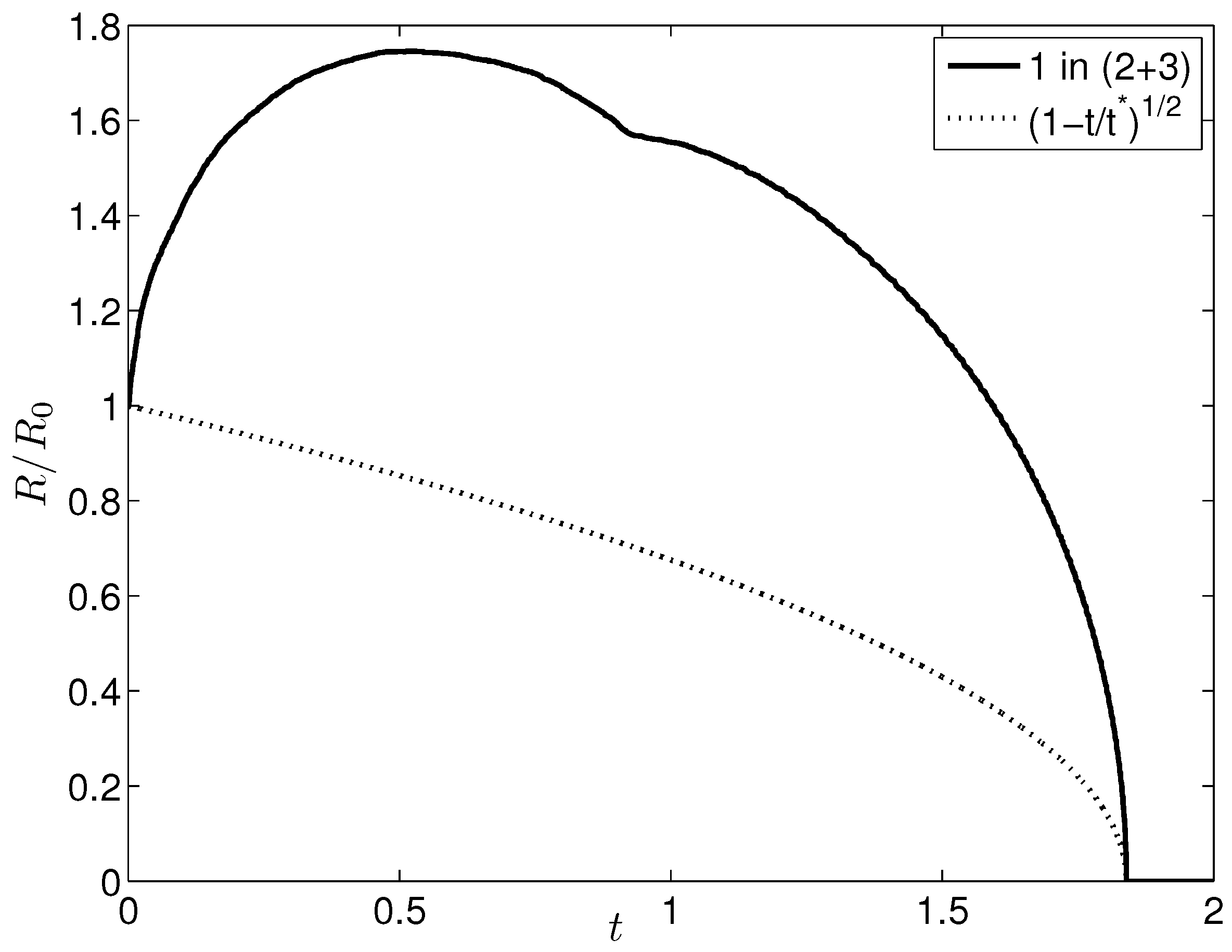
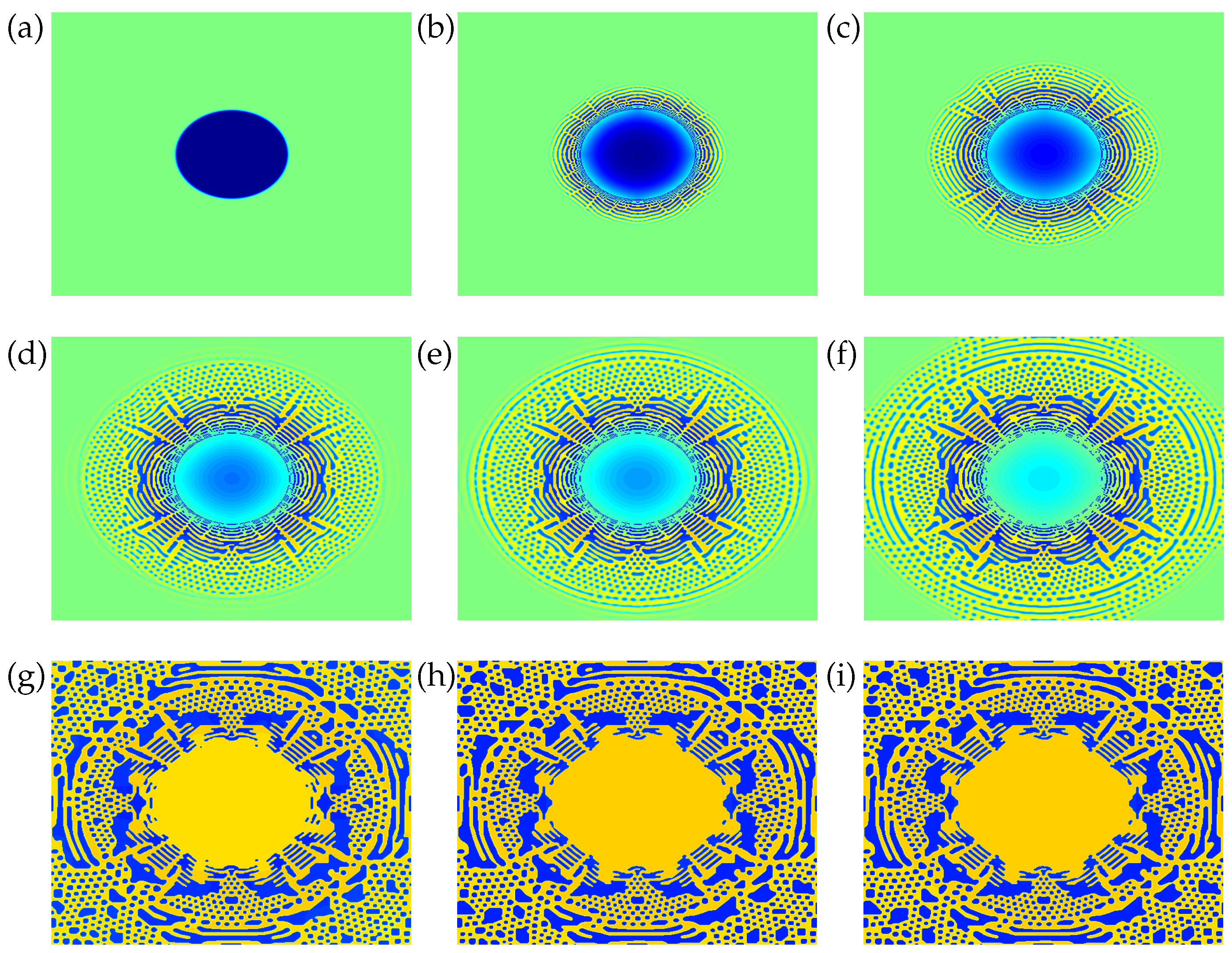
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UNIQUAC | UNIversal Quasi-Chemical |
| NRTL | Non-Random, Two-Liquid |
Appendix A. Hessian Determinant Based on the NRTL Equation
References
- Epstein, P.S.; Plesset, M.S. On the stability of liquid bubbles in liquid-gas solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1950, 18, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.B.; Needham, D. Microdroplet dissolution into a second-phase solvent using a micropipet technique: Test of the Epstein-Plesset model for an aniline-water system. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.T.; Needham, D. Mass transfer in the dissolution of a multicomponent liquid droplet in an immiscible liquid environment. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.; Prosperetti, A. Dissolution and growth of a multicomponent drop in an immiscible liquid. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 798, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Diffusion-driven dissolution or growth of a liquid drop embedded in a continuous phase of another liquid via phase-field ternary mixture model. Langmuir 2017, 33, 13125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, J.P.; Haile, J.M. Thermodynamics: Fundamentals for Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Renon, H.; Prausnitz, J.M. Local compositions in thermodynamics excess functions for liquid mixtures. AIChE J. 1968, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.M. Vapor-liquid equilibrium. XI. A new expression for the excess free energy of mixing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, J.M.; Lichtenthaler, R.N.; Gomes de Azevedo, E. Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Phase-field modeling of interfacial dynamics in emulsion flows: Nonequilibrium surface tension. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2016, 85, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R.; Sagis, L.M.C. Modeling soft interface dominated systems: A comparison of phase field and Gibbs dividing surface models. Phys. Rep. 2017, 675, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Mauri, R.; Anderson, P.D. Phase separation of viscous ternary liquid mixtures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.R.; Mazur, P. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mauri, R. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics in Multiphase Flows; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, S.I. Chemical, Biochemical, and Engineering Thermodynamics, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vladimirova, N.; Malagoli, A.; Mauri, R. Two-dimensional model of phase segregation in liquid binary mixtures. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 60, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimirova, N.; Malagoli, A.; Mauri, R. Two-dimensional model of phase segregation in liquid binary mixtures with an initial concentration gradient. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Phase separation of liquid mixtures. Nonlinear Dynamics and Control in Process Engineering; Continillo, G., Crescitelli, S., Giona, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Nucleation and spinodal decomposition of liquid mixtures. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 034107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Diffuse-interface modeling of phase segregation in liquid mixtures. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2008, 34, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Liquid mixture convection during phase separation in a temperature gradient. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 034102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Molin, D.; Mauri, R. Phase-field approach to multiphase flow modeling. Milan J. Math. 2011, 79, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Spinodal decomposition of chemically reactive binary mixtures. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 022605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cash, J.R.; Karp, A.H. A variable order Runge-Kutta method for initial value problems with rapidly varying right-hand sides. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1990, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Phase-field modeling of mixing/demixing of regular binary mixtures with a composition-dependent viscosity. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 134302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner, J.H. Explicit Runge-Kutta methods with estimates of the local truncation error. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1978, 15, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Grossmann, I.E. Computation of phase and chemical equilibria. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1981, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Mauri, R.; Shinnar, R. Liquid-liquid extraction using the composition-induced phase separation process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachford, H.H., Jr.; Rice, J.D. Procedure for use of electronic digital computers in calculating flash vaporization hydrocarbon equilibrium. J. Pet. Technol. 1952, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, R.; Califano, F.; Calvi, E.; Gupta, R.; Shinnar, R. Convection-driven phase segregation of deeply quenched liquid mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonicola, G.; Mauri, R.; Shinnar, R. Phase separation of initially inhomogeneous liquid mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califano, F.; Mauri, R. Drop size evolution during the phase separation of liquid mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califano, F.; Mauri, R.; Shinnar, R. Large-scale, unidirectional convection during phase separation of a density-matched liquid mixture. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 094109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Binary Parameter | 300 K | 333 K |
|---|---|---|
| 693.61 | 998.2 | |
| 92.47 | 65.74 | |
| 3892.44 | 3883.2 | |
| 3952.2 | 3849.57 | |
| 415.38 | 363.57 | |
| 1016.28 | 1262.4 | |
| 0.67094 | 0.88577 | |
| 0.23906 | 0.24698 | |
| 0.20202 | 0.3565 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamorgese, A.; Mauri, R. Dissolution or Growth of a Liquid Drop via Phase-Field Ternary Mixture Model Based on the Non-Random, Two-Liquid Equation. Entropy 2018, 20, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020125
Lamorgese A, Mauri R. Dissolution or Growth of a Liquid Drop via Phase-Field Ternary Mixture Model Based on the Non-Random, Two-Liquid Equation. Entropy. 2018; 20(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamorgese, Andrea, and Roberto Mauri. 2018. "Dissolution or Growth of a Liquid Drop via Phase-Field Ternary Mixture Model Based on the Non-Random, Two-Liquid Equation" Entropy 20, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020125
APA StyleLamorgese, A., & Mauri, R. (2018). Dissolution or Growth of a Liquid Drop via Phase-Field Ternary Mixture Model Based on the Non-Random, Two-Liquid Equation. Entropy, 20(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020125






