Making the Coupled Gaussian Process Dynamical Model Modular and Scalable with Variational Approximations †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
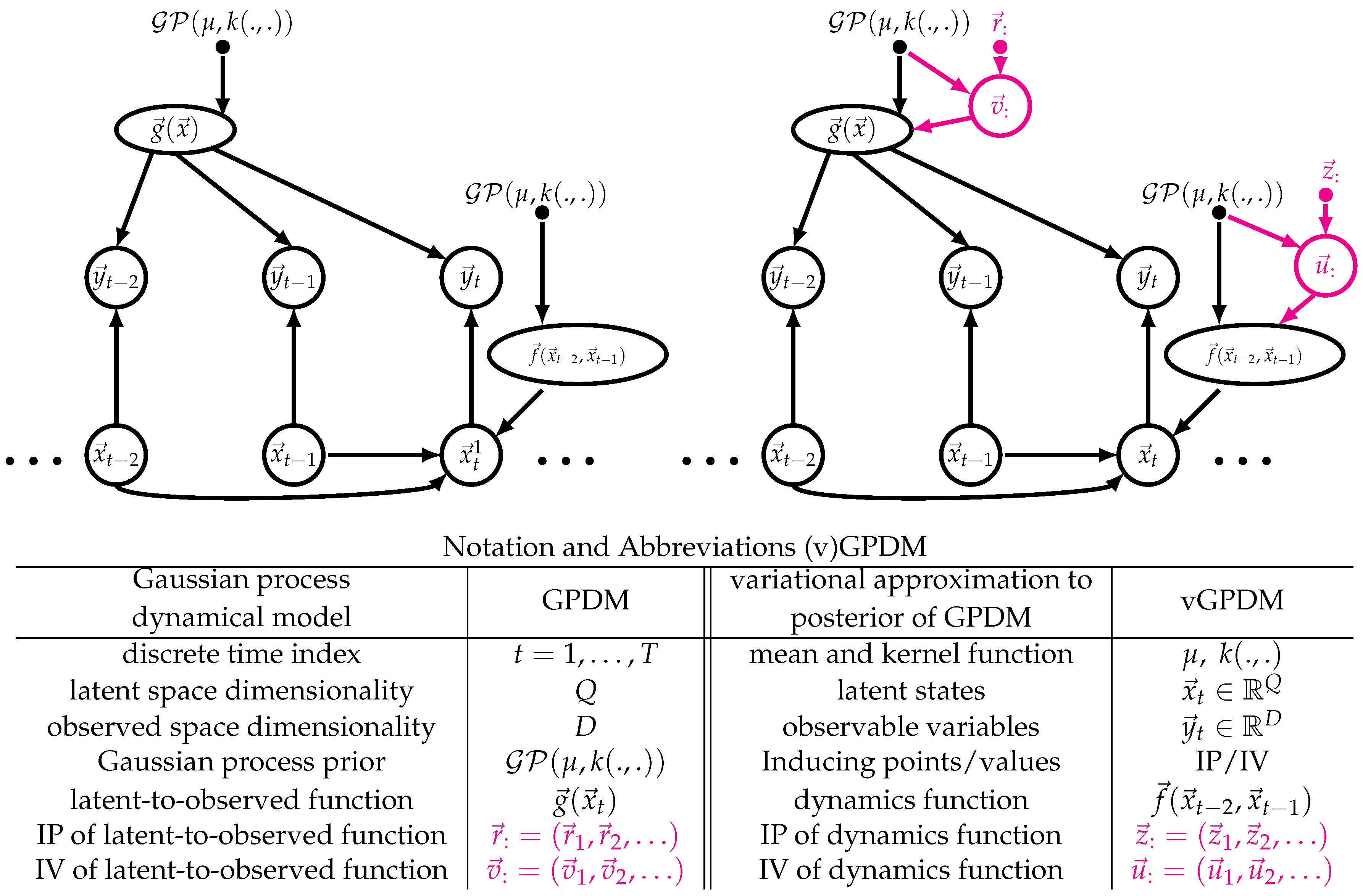
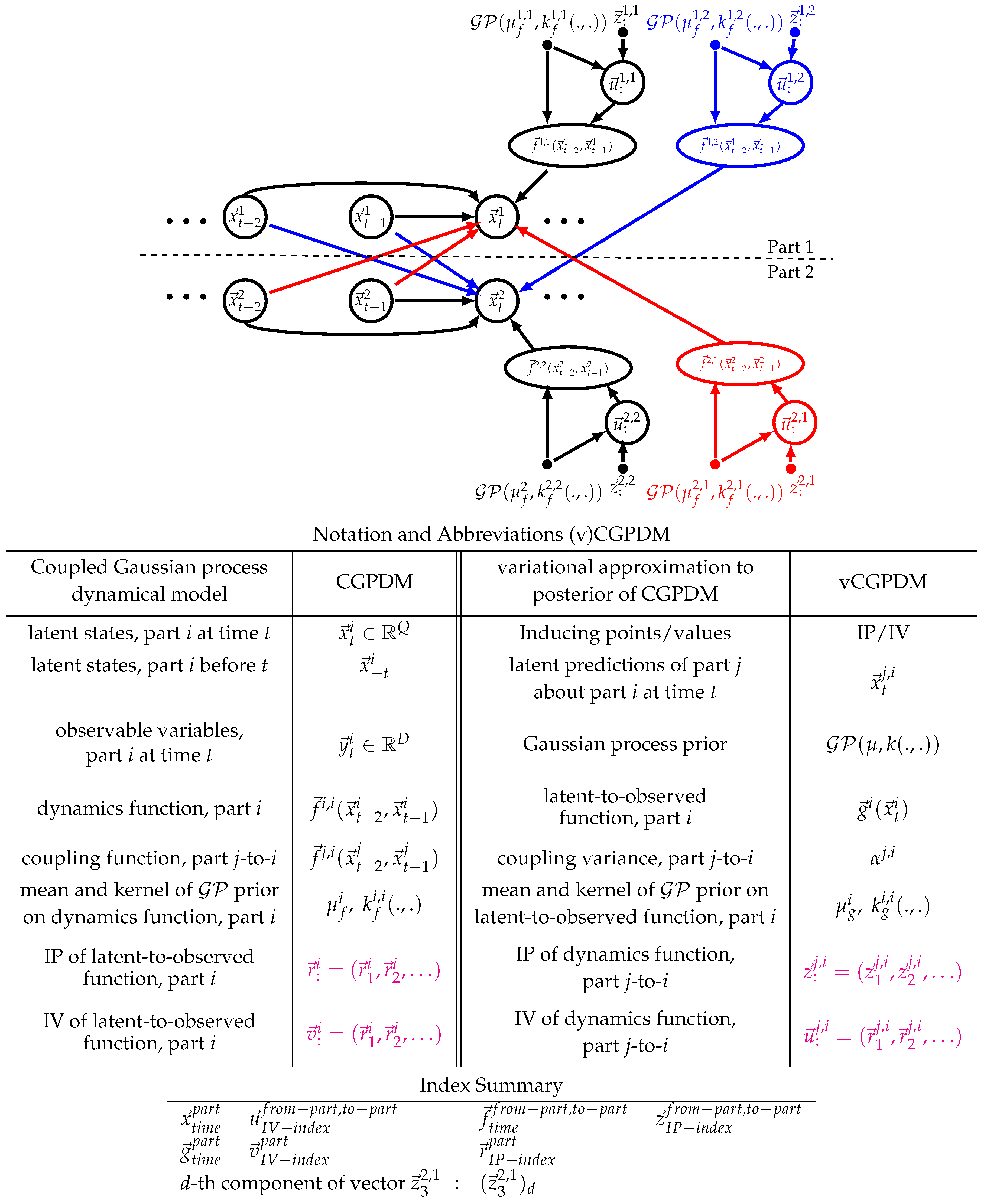
3. The Model
4. Computing an Evidence Lower Bound for the vCGPDM: An Overview
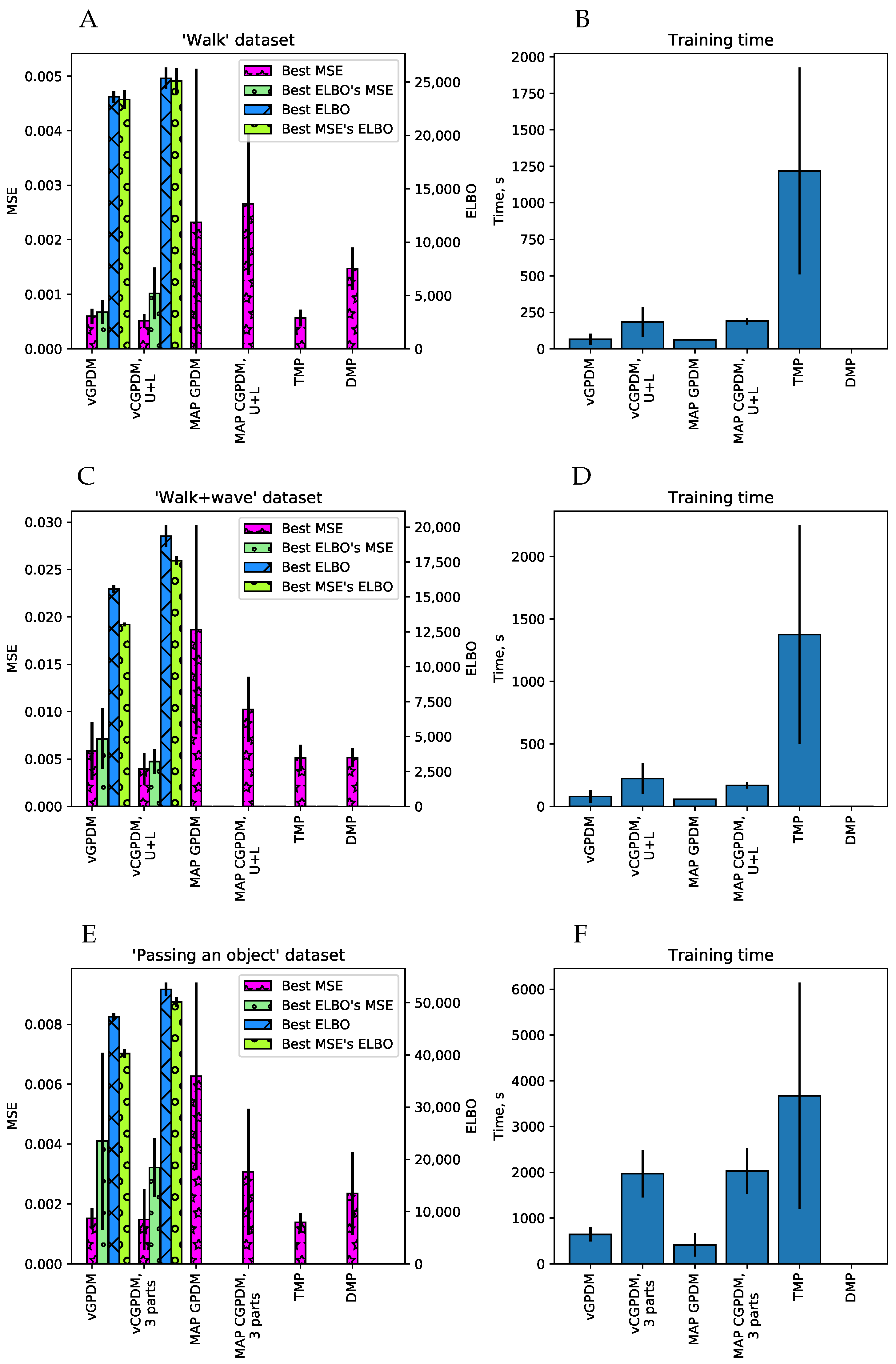
5. Results
5.1. Synthetic Data
5.2. Human Movement Data
5.3. Variational Approximations are Better than MAP
- a fully marginalized two-part (upper/lower body) CGPDM with MAP estimation of the latent variables [14], called MAP CGPDM U+L;
- a three-part CGPDM model (left hand, right hand, and body) for the non-periodic “passing a bottle” dataset;
- their variational counterparts, vCGPDM 3-part, vCGPDM U+L and vGPDM;
- temporal MPs (TMP, instantaneous linear mixtures of functions of time) [9]; and
- DMPs [12].
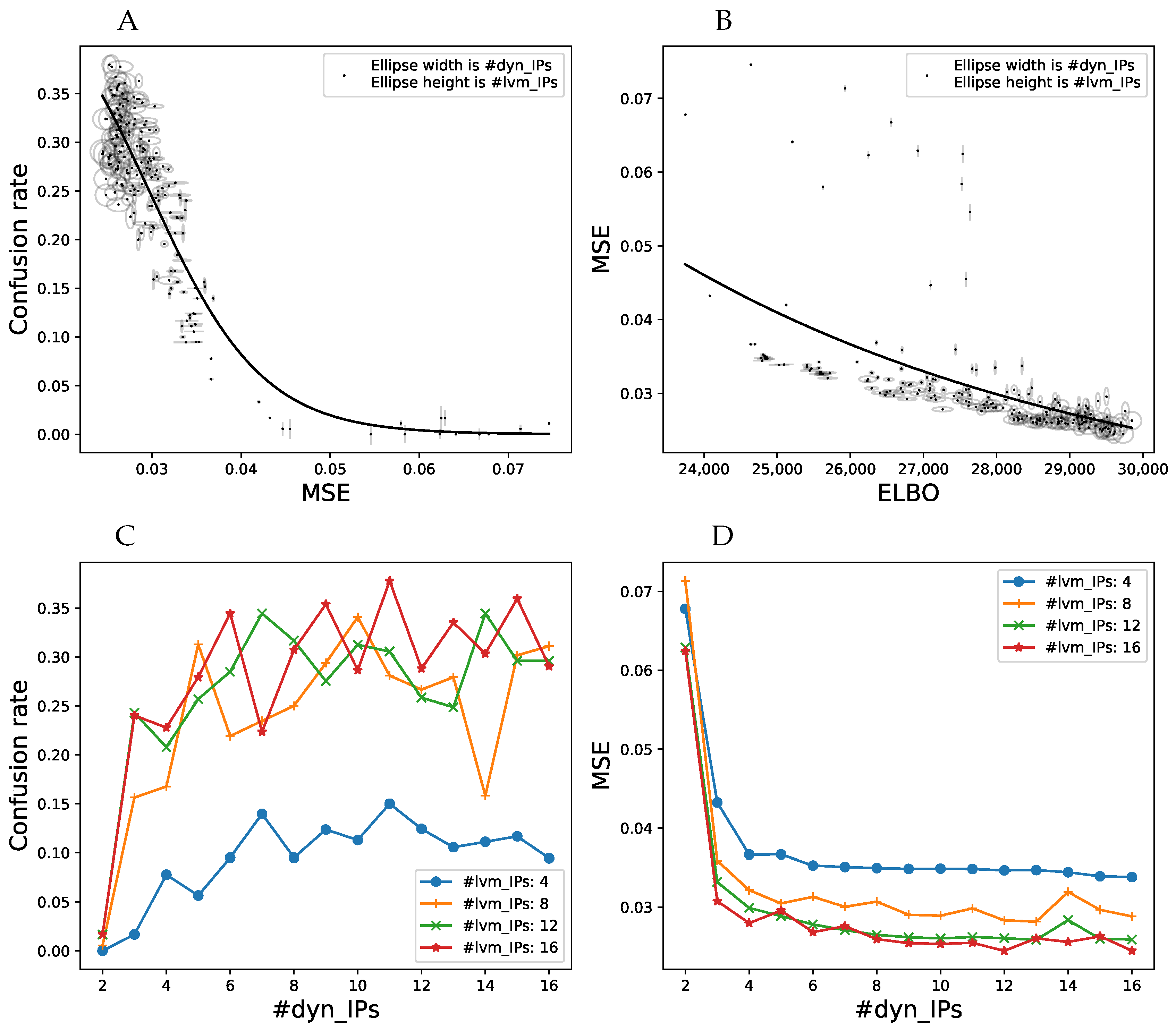
5.4. A Small Number of IPs Yields Perceptually Convincing Movements
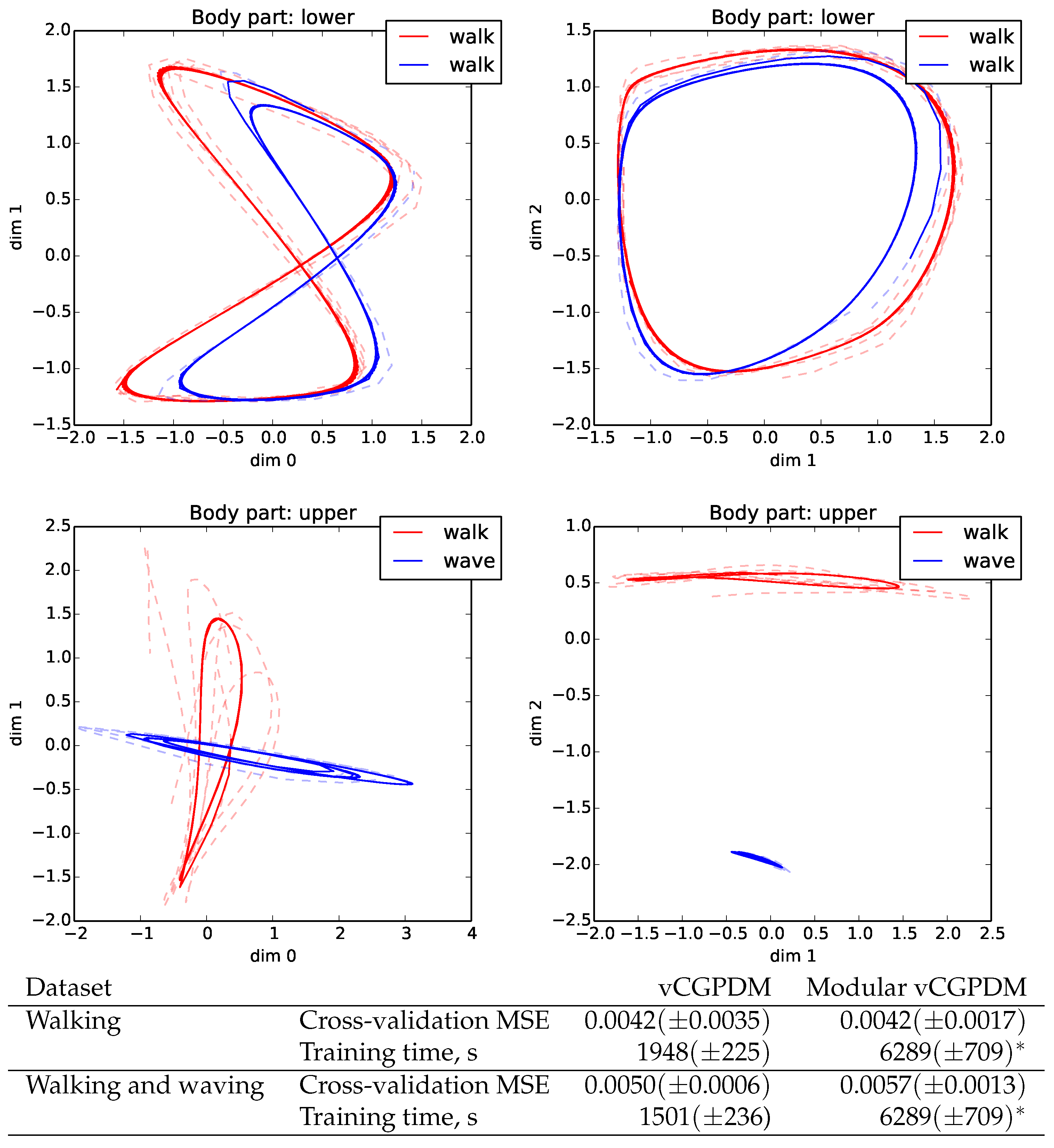
5.5. Modularity Test
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MP | movement primitive |
| DMP | dynamical movement primitive |
| Gaussian process | |
| GPDM | Gaussian process dynamical model |
| CGPDM | coupled Gaussian process dynamical model |
| vCGPDM | variational coupled Gaussian process dynamical model |
| IP | inducing point |
| IV | inducing value |
| MSE | mean squared error |
Appendix A. Exact Variational Optimization of Parts of the ELBO
Appendix B. ARD RBF Kernel Ψ Statistics. Full Covariance Variational Parameters Case.
Appendix C. vCGPDM Dynamics ELBO Derivation
References
- Bizzi, E.; Cheung, V.; d’Avella, A.; Saltiel, P.; Tresch, M. Combining modules for movement. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 57, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endres, D.; Chiovetto, E.; Giese, M. Model selection for the extraction of movement primitives. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaal, S. Dynamic Movement Primitives -A Framework for Motor Control in Humans and Humanoid Robotics. In Adaptive Motion of Animals and Machines; Kimura, H., Tsuchiya, K., Ishiguro, A., Witte, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Giese, M.A.; Mukovskiy, A.; Park, A.N.; Omlor, L.; Slotine, J.J.E. Real-Time Synthesis of Body Movements Based on Learned Primitives. In Statistical and Geometrical Approaches to Visual Motion Analysis; Cremers, D., Rosenhahn, B., Yuille, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5604, pp. 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, K.H.; Clever, D.; Mombaur, K.; Endres, D.M. Learning Movement Primitives from Optimal and Dynamically Feasible Trajectories for Humanoid Walking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids 2015), Seoul, Korea, 3–5 November 2015; pp. 866–873. [Google Scholar]
- Chiovetto, E.; Berret, B.; Pozzo, T. Tri-dimensional and triphasic muscle organization of whole-body pointing movements. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omlor, L.; Giese, M.A. Anechoic Blind Source Separation using Wigner Marginals. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 1111–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Chiovetto, E.; Giese, M.A. Kinematics of the coordination of pointing during locomotion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clever, D.; Harant, M.; Koch, K.H.; Mombaur, K.; Endres, D.M. A novel approach for the generation of complex humanoid walking sequences based on a combination of optimal control and learning of movement primitives. Robot. Autom. Syst. 2016, 83, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa-Ivaldi, F.A.; Solla, S.A. Neural Primitives for Motion Control. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.B.; Giszter, S. Distinguishing Synchronous and Time Varying Synergies using Point Process Interval Statistics: Motor Primitives in Frog and Rat. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijspeert, A.J.; Nakanishi, J.; Hoffmann, H.; Pastor, P.; Schaal, S. Dynamical Movement Primitives: Learning Attractor Models for Motor Behaviors. Neural Comput. 2013, 25, 328–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rückert, E.; d’Avella, A. Learned Parameterized Dynamic Movement Primitives with Shared Synergies for Controlling Robotic and Musculoskeletal Systems. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velychko, D.; Endres, D.; Taubert, N.; Giese, M.A. Coupling Gaussian Process Dynamical Models with Product-of-Experts Kernels. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning (Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning); The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Titsias, M.K.; Lawrence, N.D. Bayesian Gaussian Process Latent Variable Model. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 844–851. [Google Scholar]
- Bizzi, E.; Cheung, V.C. The Neural Origin of Muscle Synergies. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Földiák, P.; Endres, D. Sparse coding. Scholarpedia 2008, 3, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velychko, D.; Knopp, B.; Endres, D. The variational coupled Gaussian Process Dynamical Model. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, J.Q.; Rasmussen, C.E. A Unifying View of Sparse Approximate Gaussian Process Regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 1939–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Snelson, E.; Ghahramani, Z. Sparse Gaussian processes using pseudo-inputs. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 1257–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, N.D. Learning for Larger Datasets with the Gaussian Process Latent Variable Model. Artif. Intell. Stat. 2007, 2, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Titsias, M.K. Variational Learning of Inducing Variables in Sparse Gaussian Processes. Artif. Intell. Stat. 2009, 5, 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Damianou, A.C.; Titsias, M.; Lawrence, N.D. Variational Gaussian Process Dynamical Systems. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 24; Shawe-Taylor, J., Zemel, R., Bartlett, P., Pereira, F., Weinberger, K., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 2510–2518. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.M.; Fleet, D.J.; Hertzmann, A. Gaussian Process Dynamical Models for Human Motion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urtasun, R.; Fleet, D.J.; Lawrence, N.D. Modeling Human Locomotion with Topologically Constrained Latent Variable Models. In Human Motion–Understanding, Modeling, Capture and Animation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4814, pp. 104–118. [Google Scholar]
- Taubert, N.; Endres, D.; Christensen, A.; Giese, M.A. Shaking Hands in Latent Space. In Annual Conference on Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 7006, pp. 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S.; Wang, J.M.; Haraux, A.; Popović, Z.; Koltun, V. Continuous Character Control with Low-Dimensional Embeddings. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kim, M.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Q. Switching Gaussian Process Dynamic Models for simultaneous composite motion tracking and recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2009 (CVPR 2009), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, C.L.C.; Dai, Z.; Damianou, A.; Forth, J.; Barreto, G.A.; Lawrence, N.D. Recurrent Gaussian Processes. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1511.06644. [Google Scholar]
- Frigola, R.; Lindsten, F.; Schön, T.B.; Rasmussen, C. Bayesian Inference and Learning in Gaussian Process State-Space Models with Particle MCMC. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26; Burges, C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Frigola, R.; Chen, Y.; Rasmussen, C. Variational Gaussian Process State-Space Models. In Advances in NIPS 27; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Weinberger, K., Eds.; NIPS Foundation: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014; pp. 3680–3688. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M.; van der Wilk, M.; Rasmussen, C. Understanding Probabilistic Sparse Gaussian Process Approximations. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.04820. [Google Scholar]
- Taubert, N.; Christensen, A.; Endres, D.; Giese, M. Online simulation of emotional interactive behaviors with hierarchical Gaussian process dynamical models. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Perception (SAP ’12), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 3–4 August 2012; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E. Products of Experts. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN’99), Edinburgh, UK, 7–10 September 1999; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (Information Science and Statistics); Springer: Secaucus, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bastien, F.; Lamblin, P.; Pascanu, R.; Bergstra, J.; Goodfellow, I.J.; Bergeron, A.; Bouchard, N.; Bengio, Y. Theano: New features and speed improvements. arXiv, 2012; arXiv:1211.5590. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python. Available online: https://www.scipy.org/ (accessed on 9 October 2015).
- Sakoe, H.; Chiba, S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1978, 26, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubert, N.; Löffler, M.; Ludolph, N.; Christensen, A.; Endres, D.; Giese, M. A virtual reality setup for controllable, stylized real-time interactions between humans and avatars with sparse Gaussian process dynamical models. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Perception (SAP ’13), Dublin, Ireland, 22–23 August 2013; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschos, A.; Daniel, C.; Peters, J.; Neumann, G. Probabilistic Movement Primitives. In Advances in NIPS 26; Burges, C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K., Eds.; NIPS Foundation: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2013; pp. 2616–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, P.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Righetti, L.; Schaal, S. Towards Associative Skill Memories. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Osaka, Japan, 29 November–1 December 2012; pp. 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Land, W.M.; Rosenbaum, D.A.; Seegelke, C.; Schack, T. Whole-body posture planning in anticipation of a manual prehension task: Prospective and retrospective effects. Acta Psychol. 2013, 144, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deisenroth, M.; Fox, D.; Rasmussen, C. Gaussian Processes for Data-Efficient Learning in Robotics and Control. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. IEEE Trans. 2015, 37, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.B.; Pedersen, M.S. The Matrix Cookbook; Version 20121115; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]


| Modular | Scalable | Compact | Canonical Dynamics | Learned Dynamics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vCGPDM | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| CGPDM | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| vGPDM | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| GPDM | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| TMP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| DMP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velychko, D.; Knopp, B.; Endres, D. Making the Coupled Gaussian Process Dynamical Model Modular and Scalable with Variational Approximations. Entropy 2018, 20, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100724
Velychko D, Knopp B, Endres D. Making the Coupled Gaussian Process Dynamical Model Modular and Scalable with Variational Approximations. Entropy. 2018; 20(10):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100724
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelychko, Dmytro, Benjamin Knopp, and Dominik Endres. 2018. "Making the Coupled Gaussian Process Dynamical Model Modular and Scalable with Variational Approximations" Entropy 20, no. 10: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100724
APA StyleVelychko, D., Knopp, B., & Endres, D. (2018). Making the Coupled Gaussian Process Dynamical Model Modular and Scalable with Variational Approximations. Entropy, 20(10), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100724






