Entropy Characterization of Random Network Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Probability Models for Network Generation: Random Network Models
2.1. Sample Space
2.2. Set of Events
2.3. Probability Measure
2.3.1. Erdös–Renyi (ER) Model [14]
2.3.2. Gilbert Model [15]
2.3.3. Random Networks with Hidden Variables
2.3.4. Kronecker Graphs [20]
2.3.5. Exponential Random Graphs Models (ERGMs) [21]
2.4. Inference of Random Network Models
Inference of Markov Graphs
3. Network Properties and Derived Random Variables: Complexity of Successive Approximation Models
3.1. Network Properties and Derived Random Variables
3.1.1. Degree Distribution Associated with an RNM
3.1.2. Degree Distribution of a Sample Network
3.2. Successive Approximation Models
4. Entropy of RNMs
Entropy Reduction via Restrictions in the RNM
5. Entropies Associated with Derived Variables and Degree Distributions
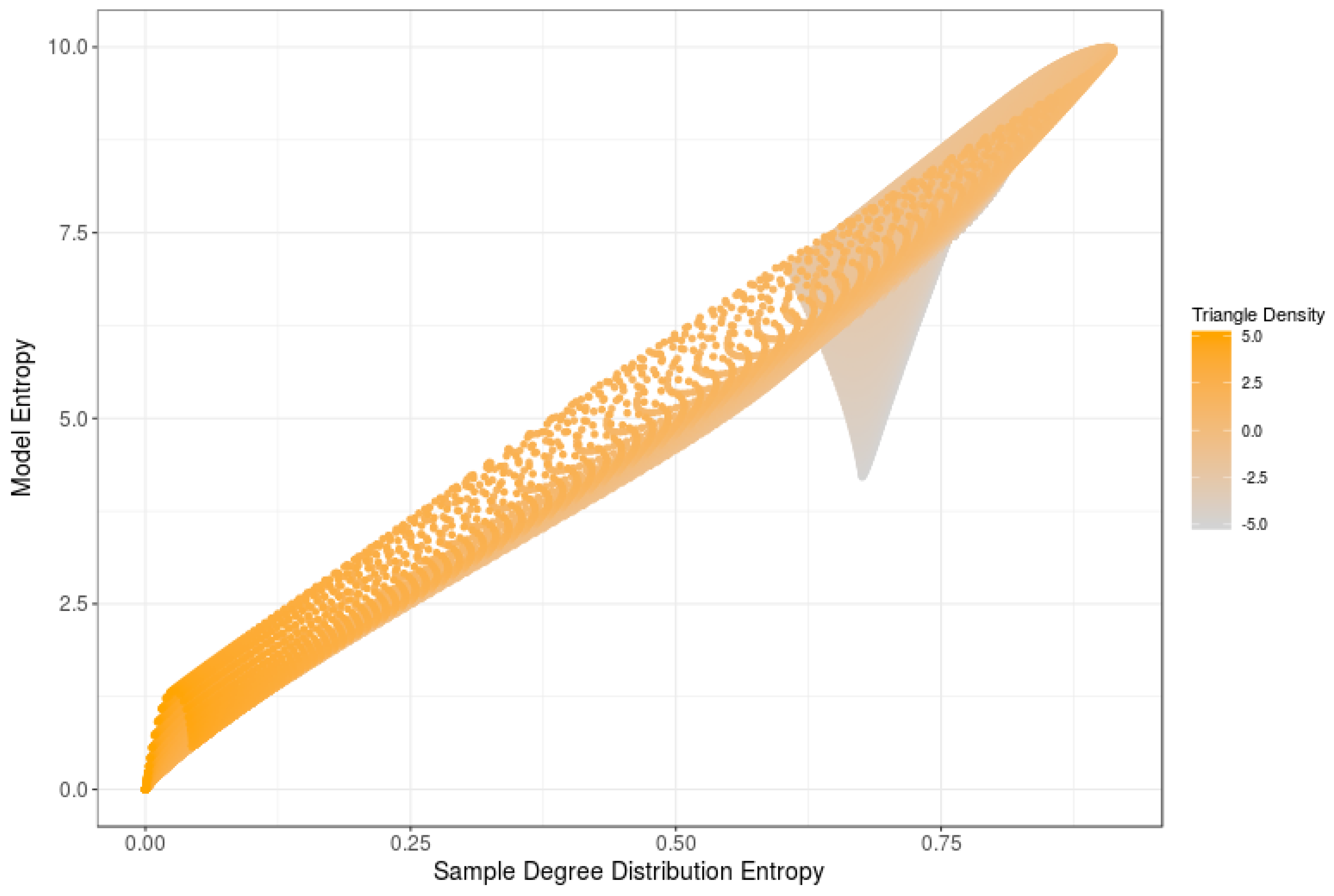
5.1. Entropies of Degree Distributions
5.2. Other Measures of Sample Entropies
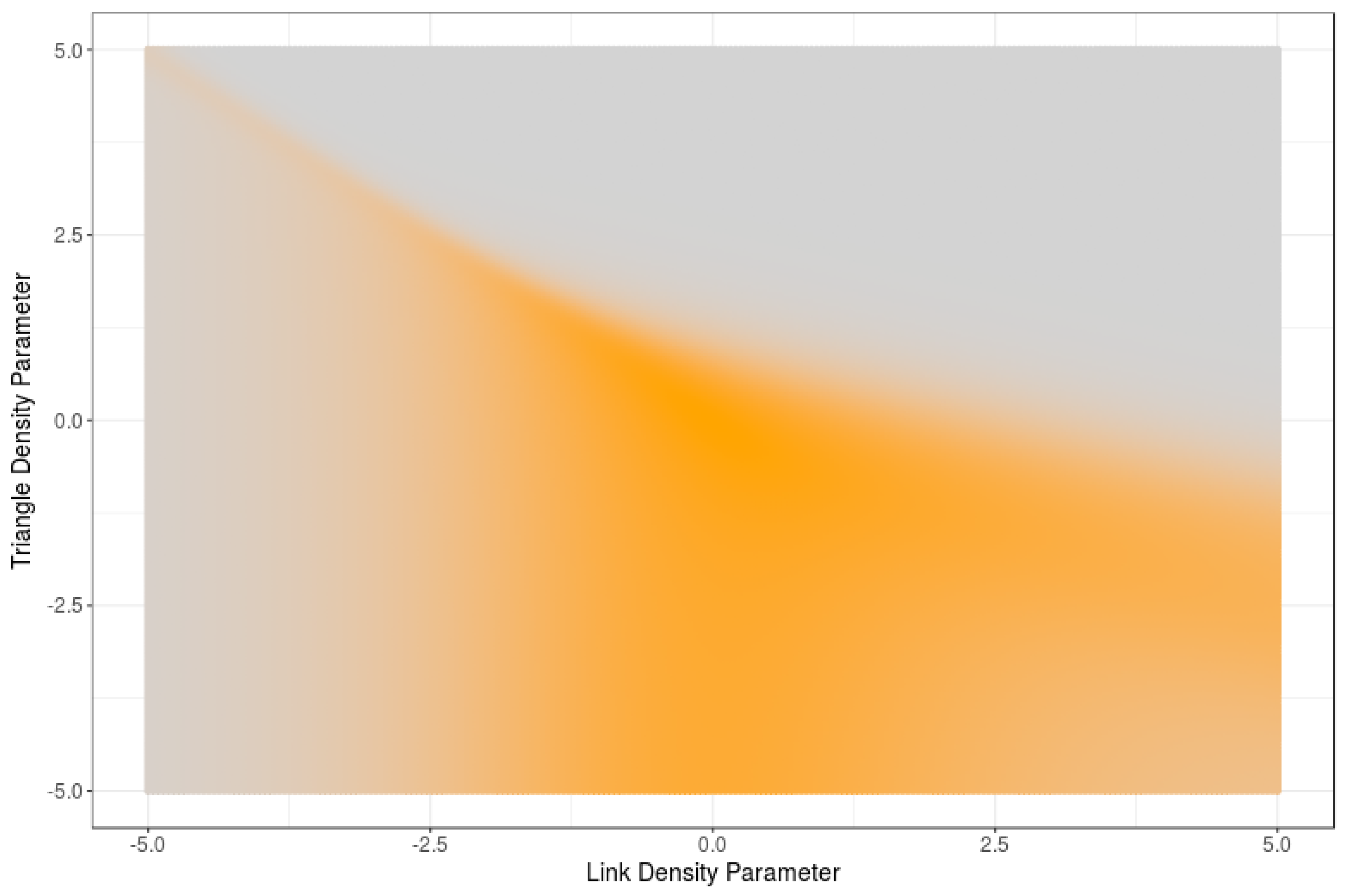
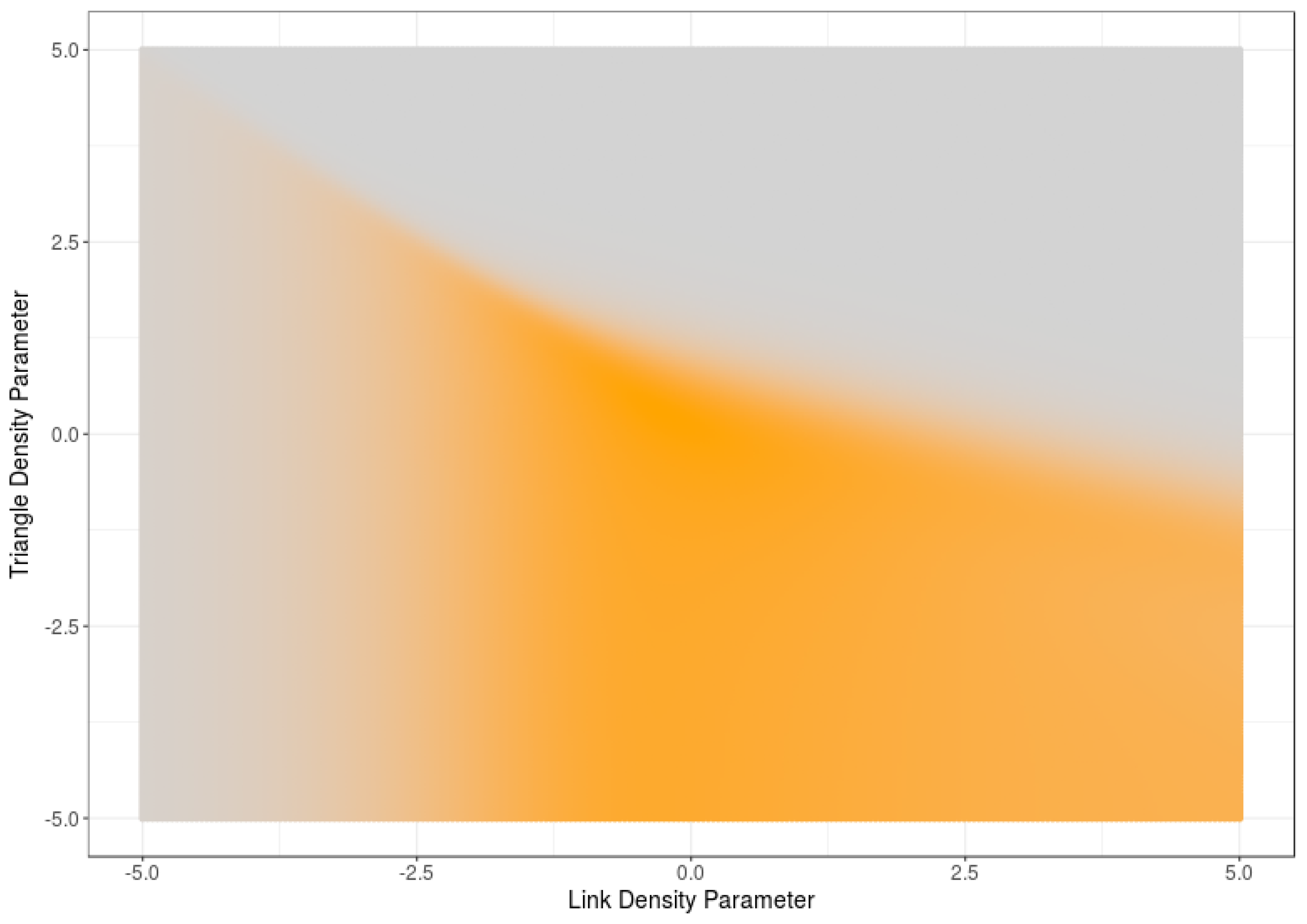
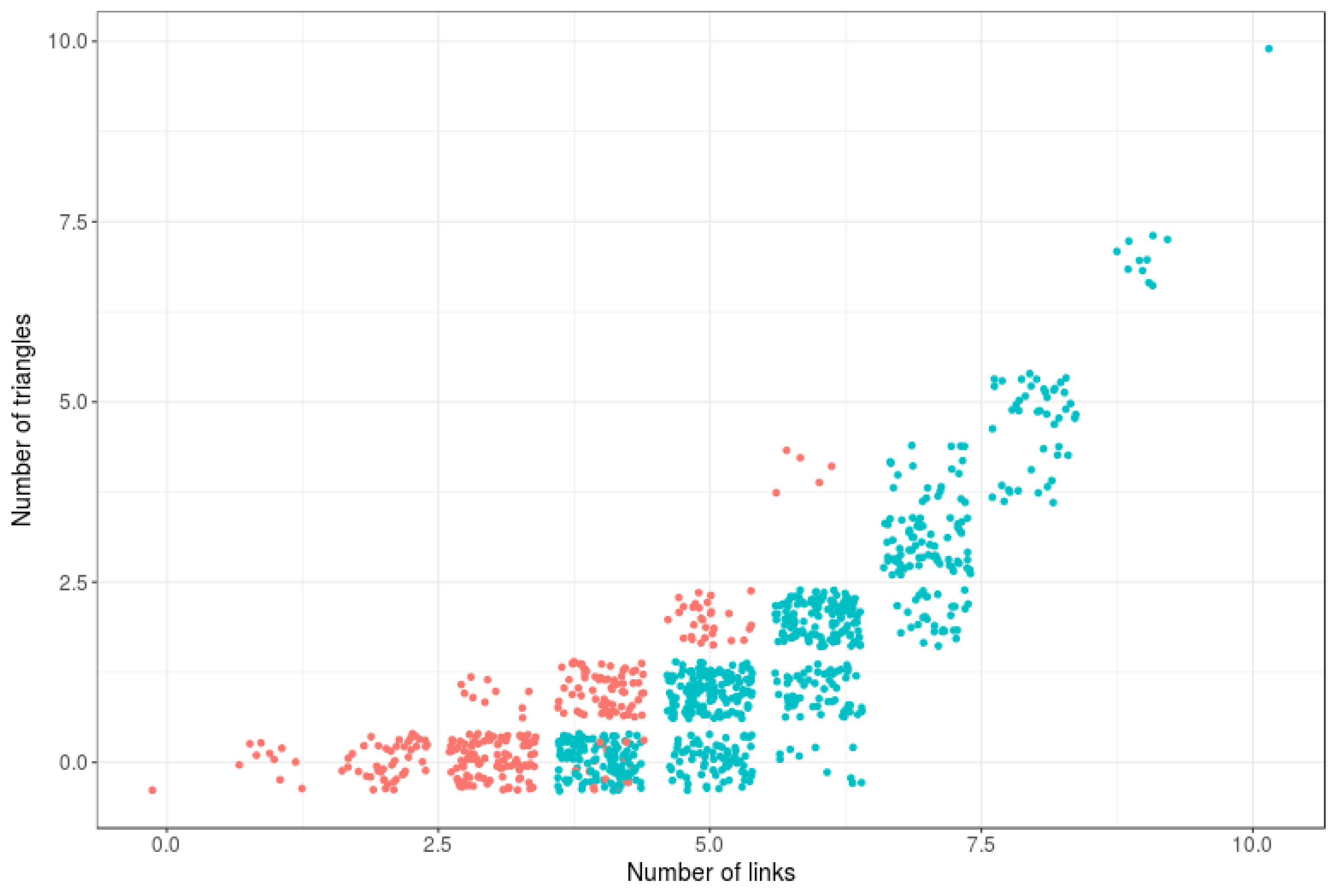
6. Computational Estimations
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barabási, A.L.; Frangos, J. Linked: The New Science of Networks Science of Networks; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.E. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorogovtsev, S.N.; Mendes, J.F. Evolution of Networks: From Biological Nets to the Internet and WWW; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Onnela, J.P.; Saramäki, J.; Hyvönen, J.; Szabó, G.; Lazer, D.; Kaski, K.; Kertész, J.; Barabási, A.L. Structure and tie strengths in mobile communication networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7332–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Tombor, B.; Albert, R.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabási, A.L. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 2000, 407, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faloutsos, M.; Faloutsos, P.; Faloutsos, C. On Power-Law Relationships of the Internet Topology; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Chang, H.; Govindan, R.; Jamin, S. The origin of power laws in Internet topologies revisited. In Proceedings of the INFOCOM 2002. Twenty-First Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, New York, NY, USA, 23–27 June 2002; Volume 2, pp. 608–617. [Google Scholar]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Redner, S. How popular is your paper? An empirical study of the citation distribution. Eur. Phys. J. B Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 1998, 4, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdos, P.; Rényi, A. On the evolution of random graphs. Bull. Inst. Int. Stat. 1961, 38, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.O.; Rogers, B.W. Meeting strangers and friends of friends: How random are social networks? Am. Econ. Rev. 2007, 93, 890–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.; Zufiria, P.J. Generating scale-free networks with adjustable clustering coefficient via random walks. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Workshop Network Science, West Point, NY, USA, 22–24 June 2011; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Erdos, P.; Rényi, A. On random graphs. Publ. Math. Debr. 1959, 6, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.N. Random plane networks. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1961, 9, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarelli, G.; Capocci, A.; De Los Rios, P.; Muñoz, M.A. Scale-free networks from varying vertex intrinsic fitness. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 258702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boguñá, M.; Pastor-Satorras, R. Class of correlated random networks with hidden variables. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 036112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grindrod, P. Range-dependent random graphs and their application to modeling large small-world proteome datasets. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 066702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boguñá, M.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Díaz-Guilera, A.; Arenas, A. Models of social networks based on social distance attachment. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 056122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskovec, J.; Chakrabarti, D.; Kleinberg, J.; Faloutsos, C.; Ghahramani, Z. Kronecker graphs: An approach to modeling networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 985–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Bhamidi, S.; Bresler, G.; Sly, A. Mixing time of exponential random graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE 49th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS’08), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25–28 October 2008; pp. 803–812. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, O.; Strauss, D. Markov graphs. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Diaconis, P. Estimating and understanding exponential random graph models. Ann. Stat. 2013, 41, 2428–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, D.; Koskinen, J.; Robins, G. Exponential Random Graph Models for Social Networks: Theory, Methods, and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Geman, S.; Geman, D. Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1984, 6, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besag, J. Spatial interaction and the statistical analysis of lattice systems. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1974, 36, 192–236. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, T.A. Markov chain Monte Carlo estimation of exponential random graph models. J. Soc. Struct. 2002, 3, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bianconi, G. The entropy of randomized network ensembles. Europhys. Lett. 2007, 81, 28005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, G. Entropy of network ensembles. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 036114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsini, C.; Dankulov, M.M.; Jamakovic, A.; Mahadevan, P.; Colomer-de, S.P.; Vahdat, A.; Bassler, K.E.; Toroczkai, Z.; Boguñá, M.; Caldarelli, G.; et al. Quantifying randomness in real network. Nat. Commun. 2015, 8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2001, 5, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Bing, H.W.; Wen, X.W.; Tao, Z. Network entropy based on topology configuration and its computation to random networks. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E. Assortative mixing in networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 208701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, R.; Valverde, S. Information Theory of Complex Networks: On Evolution and Architectural Constraints; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, K.; Safar, M.; Sorkhoh, I. Entropy of robust social networks. In Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference E-Society, Algarve, Portugal, 9–12 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zufiria, P.J.; Barriales-Valbuena, I. Entropy Characterization of Random Network Models. Entropy 2017, 19, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19070321
Zufiria PJ, Barriales-Valbuena I. Entropy Characterization of Random Network Models. Entropy. 2017; 19(7):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19070321
Chicago/Turabian StyleZufiria, Pedro J., and Iker Barriales-Valbuena. 2017. "Entropy Characterization of Random Network Models" Entropy 19, no. 7: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19070321
APA StyleZufiria, P. J., & Barriales-Valbuena, I. (2017). Entropy Characterization of Random Network Models. Entropy, 19(7), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19070321




