An Enhanced Set-Membership PNLMS Algorithm with a Correntropy Induced Metric Constraint for Acoustic Channel Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Related Algorithms
2.1. The Review of the SM Filtering Theory
2.2. The Review of the SM-PNLMS Algorithm
3. The Proposed CIMSM-PNLMS Algorithm
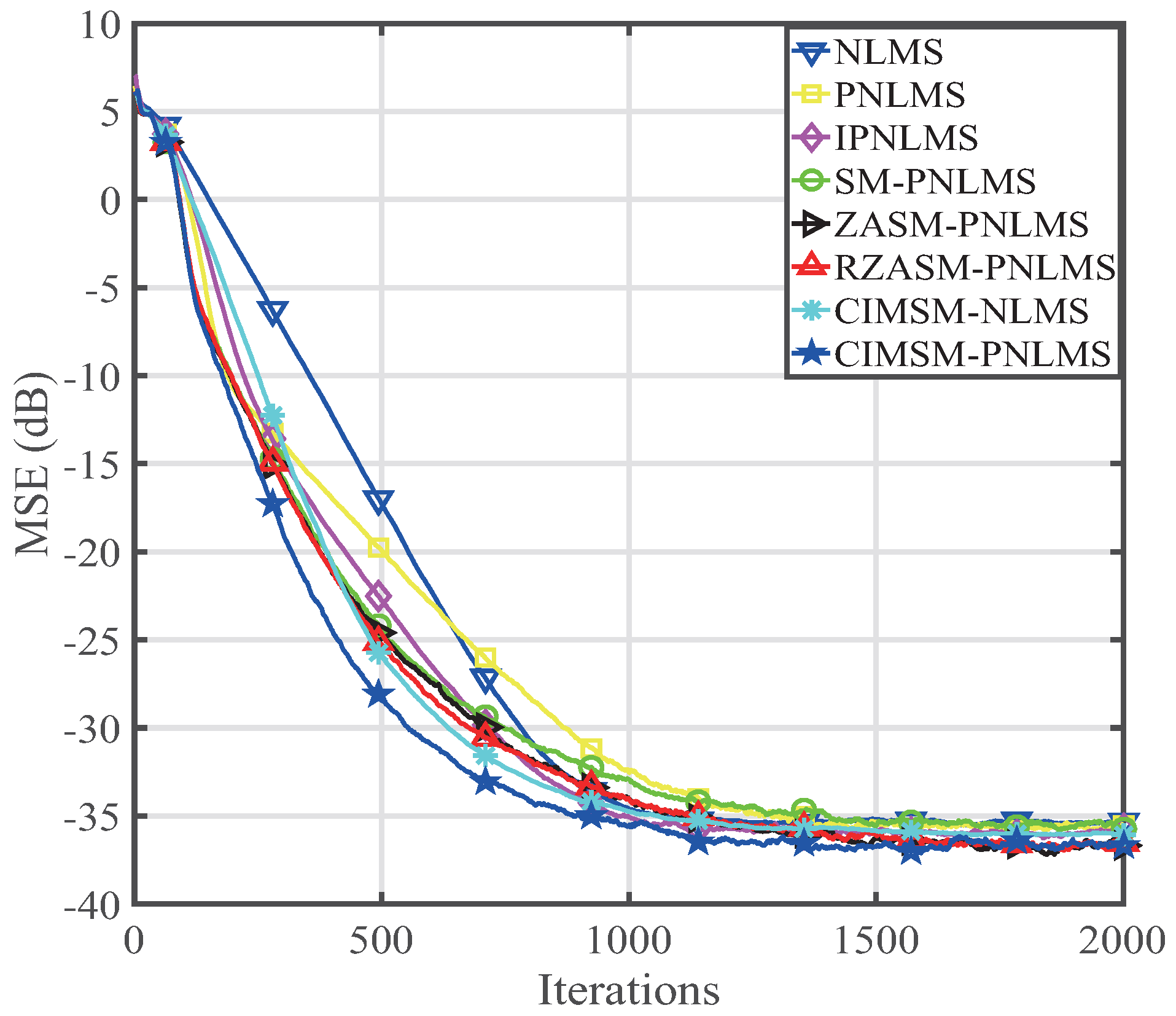
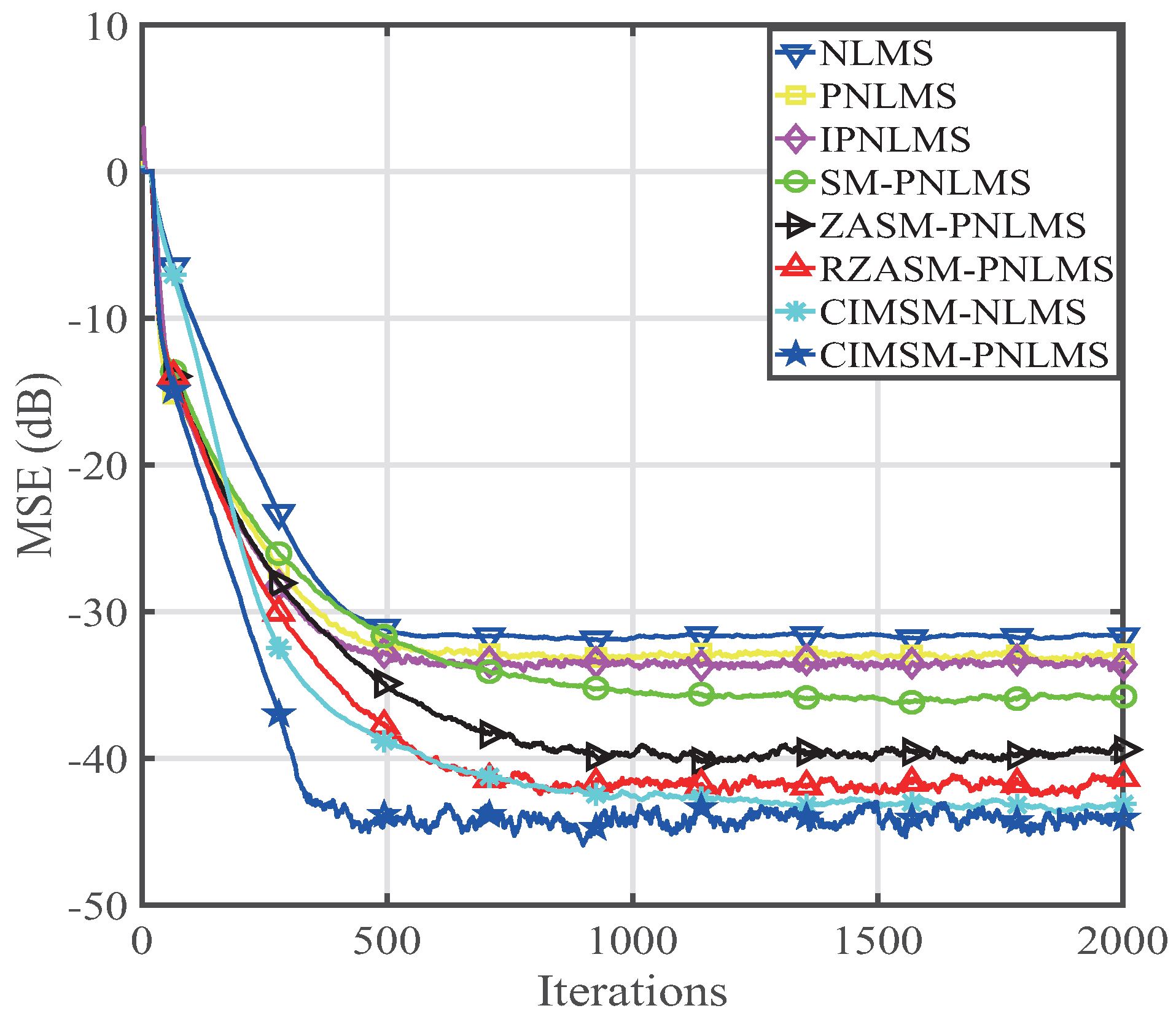
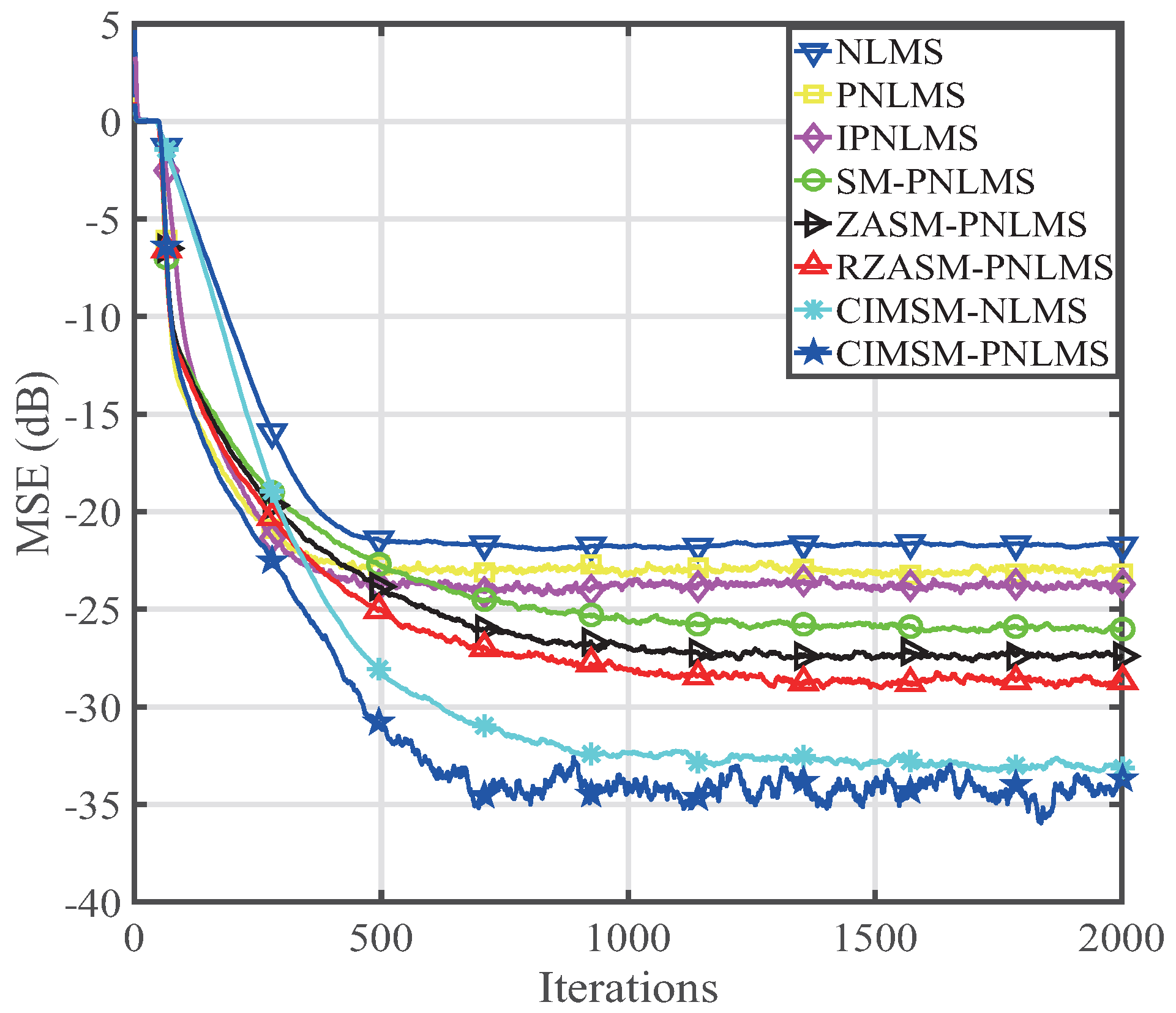
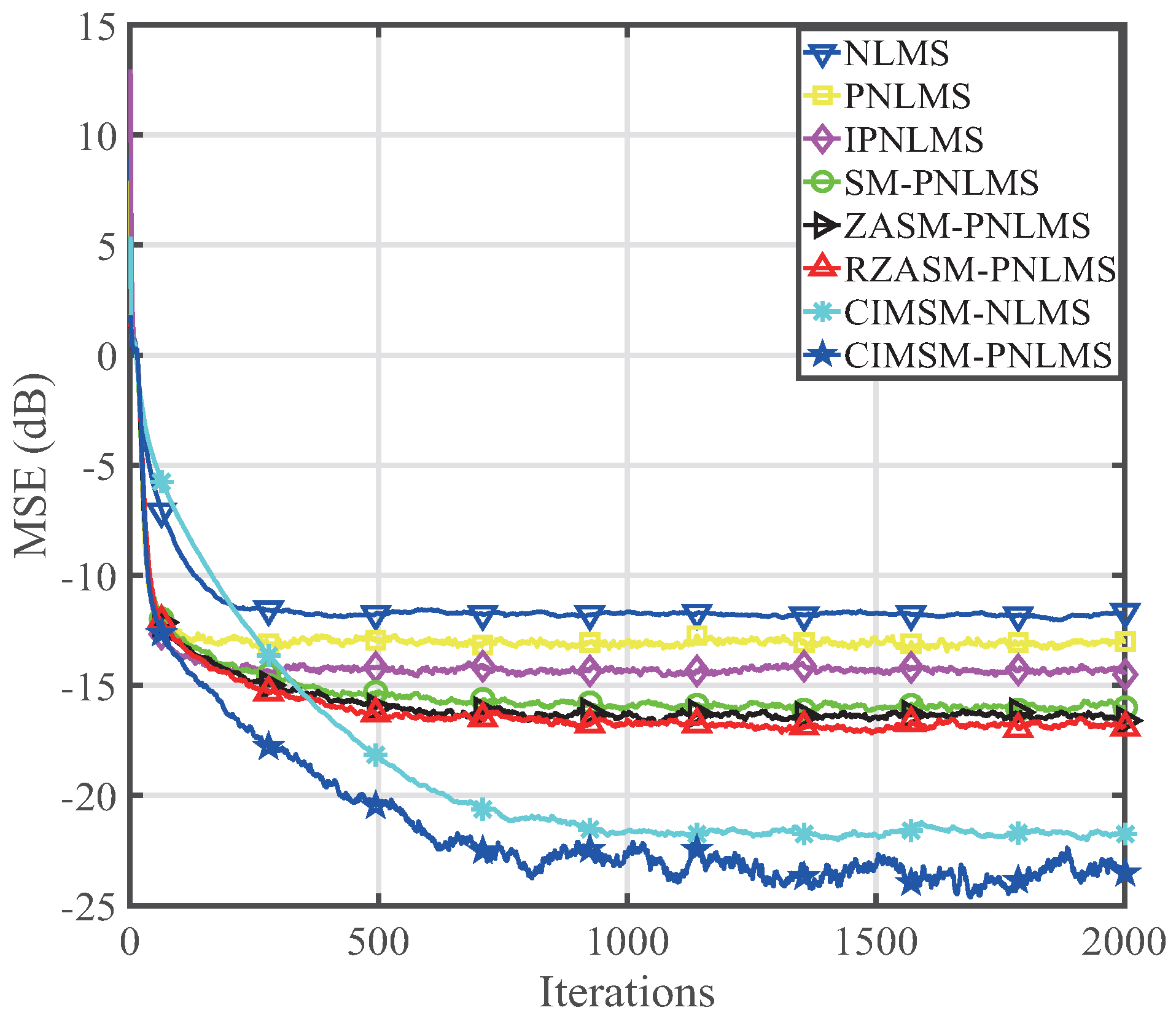
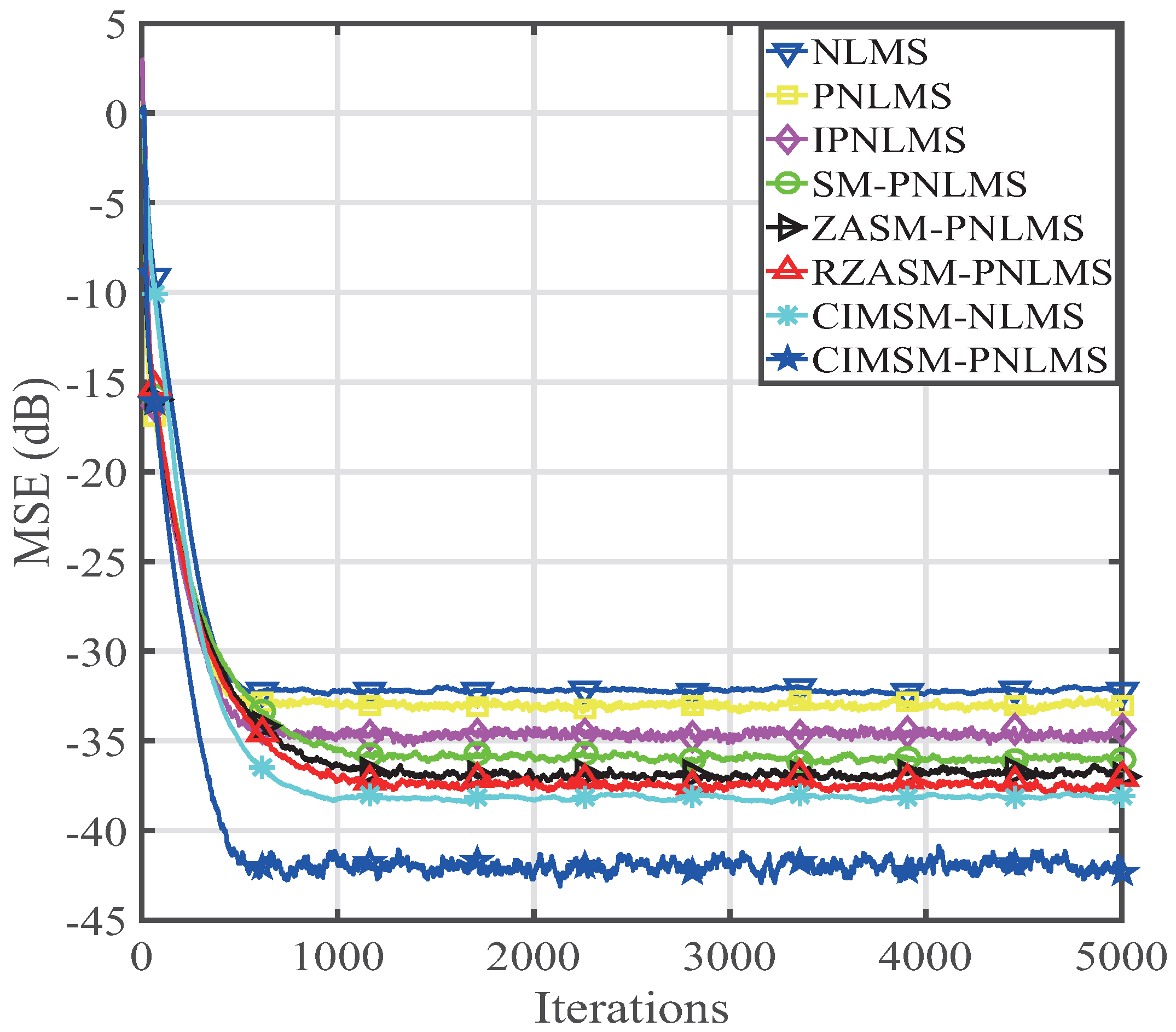
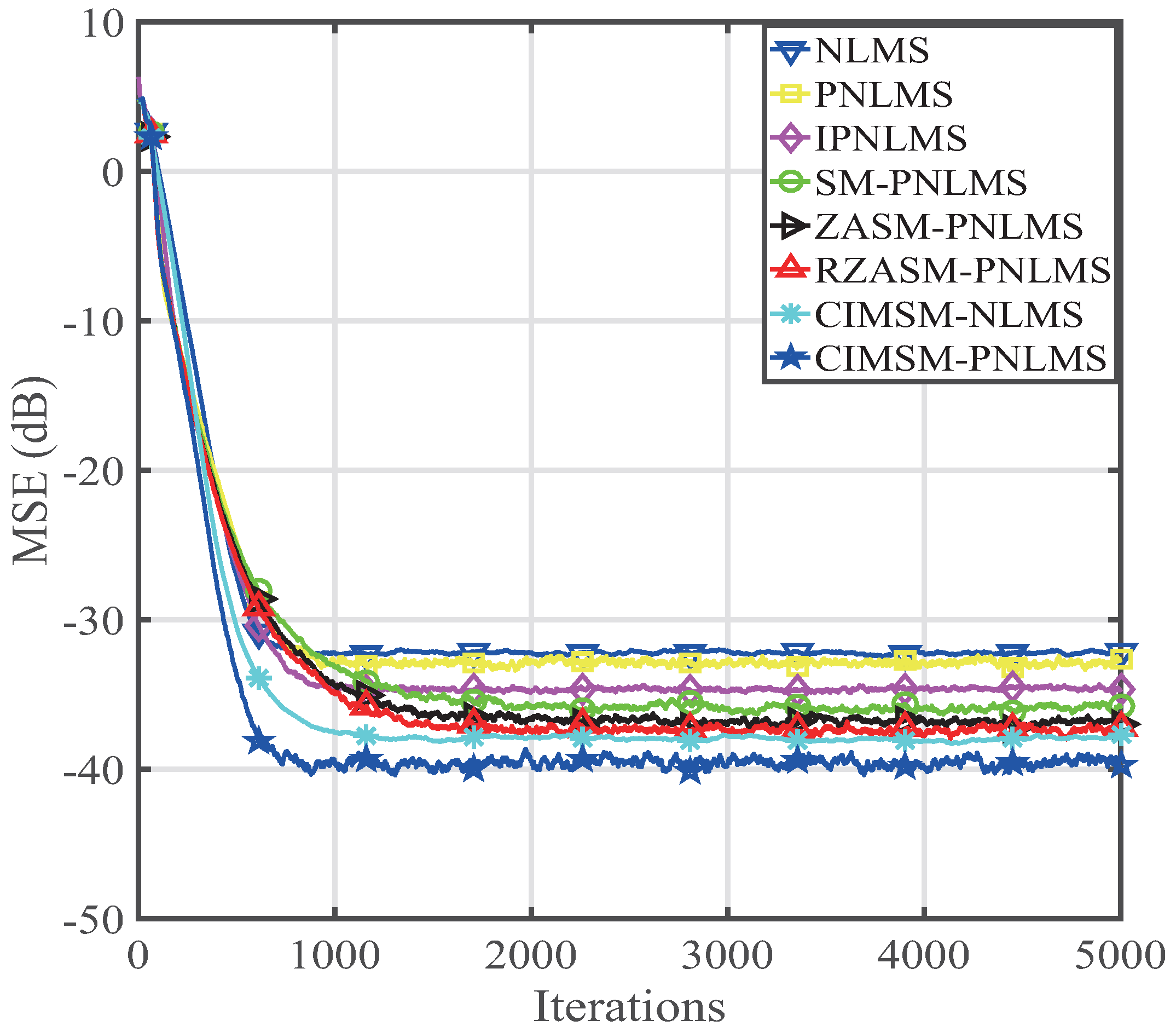
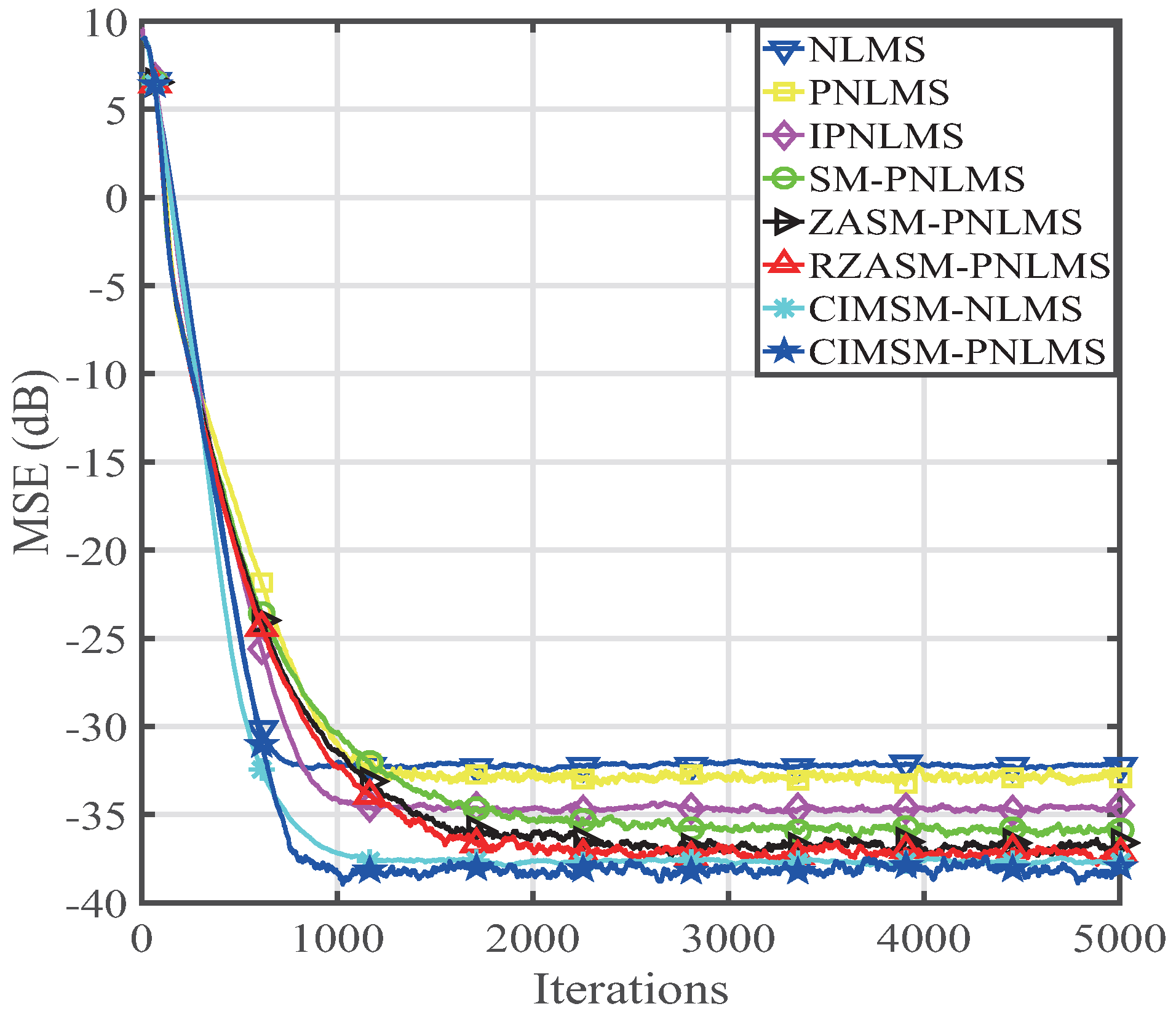
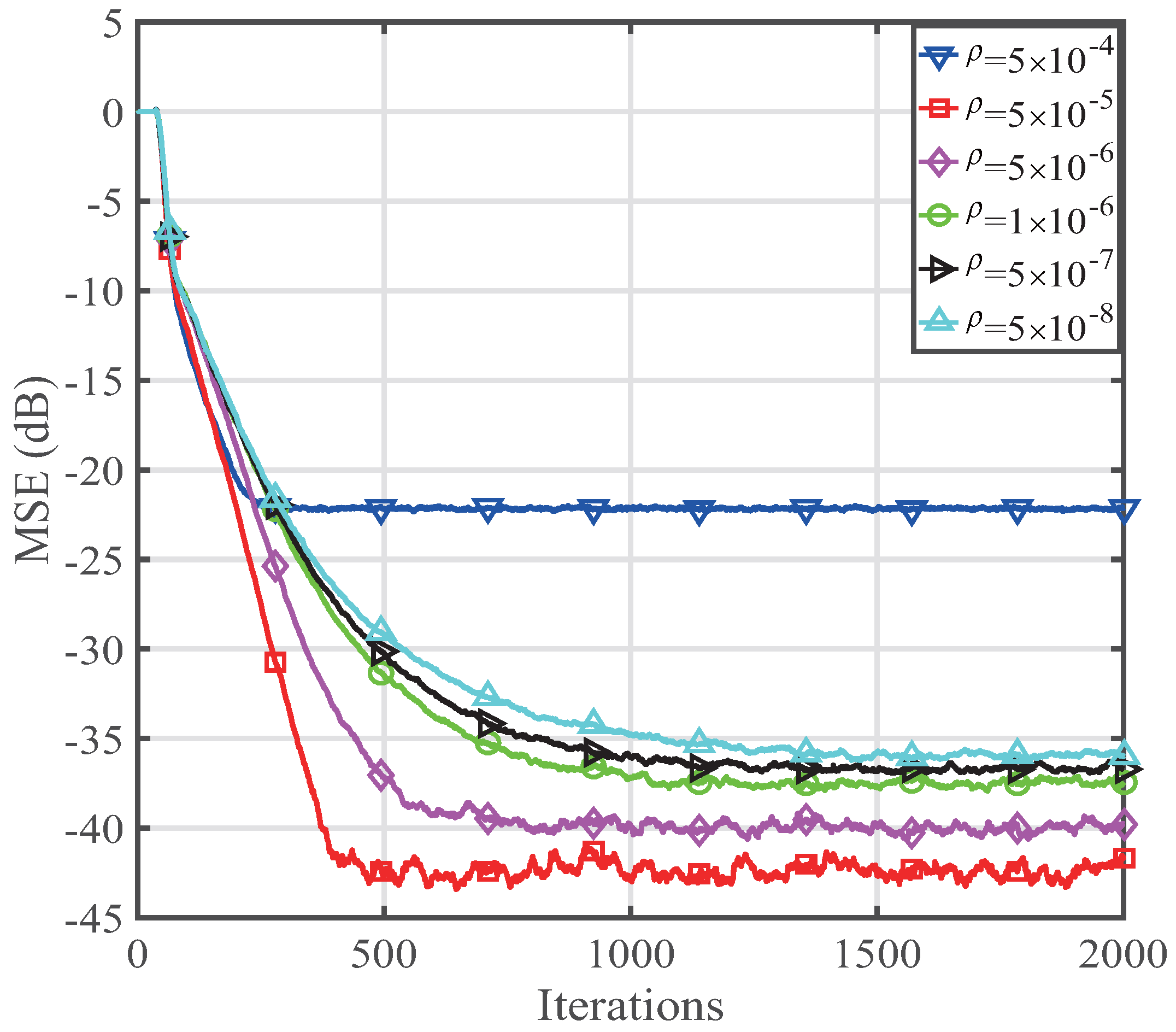
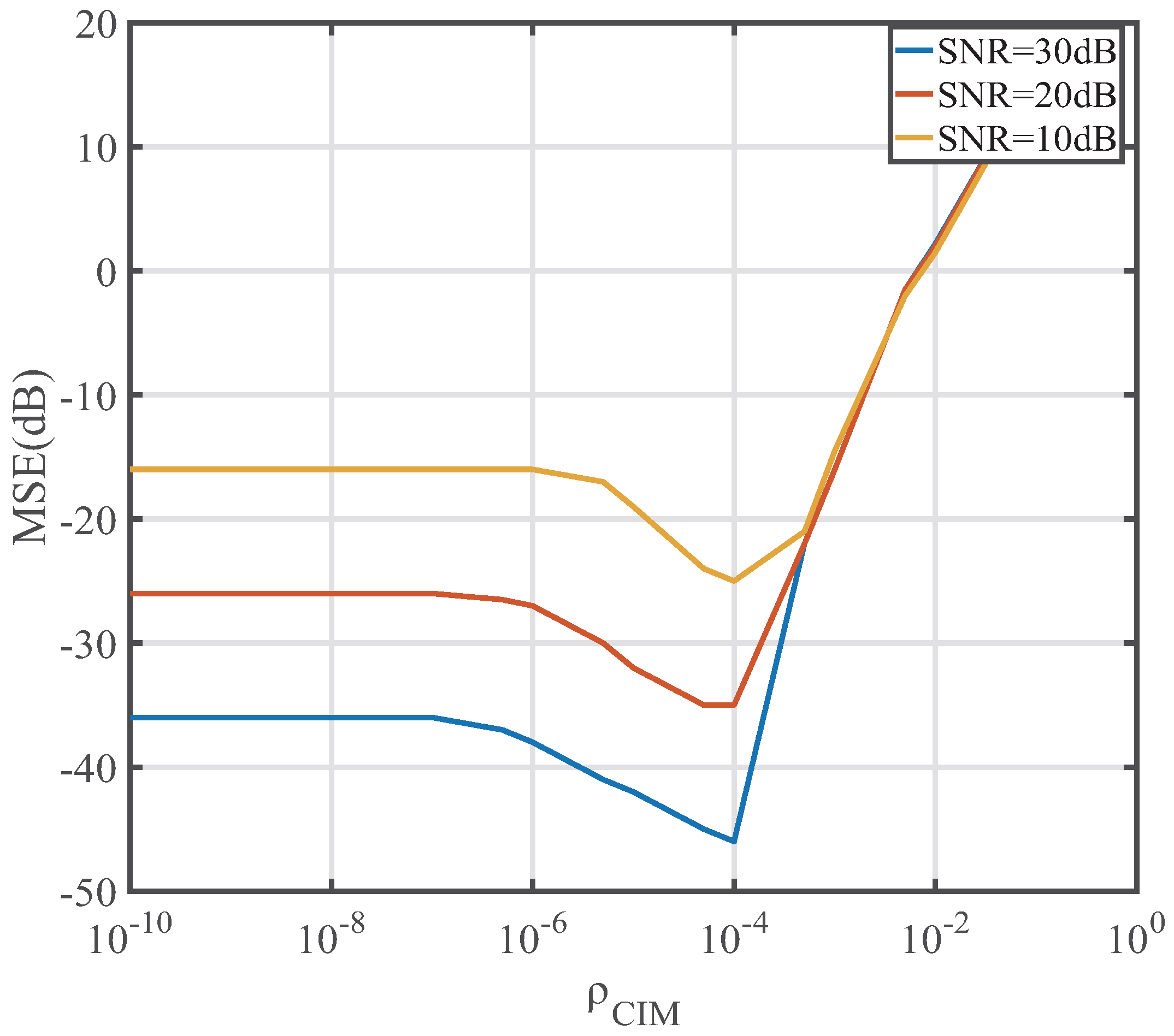
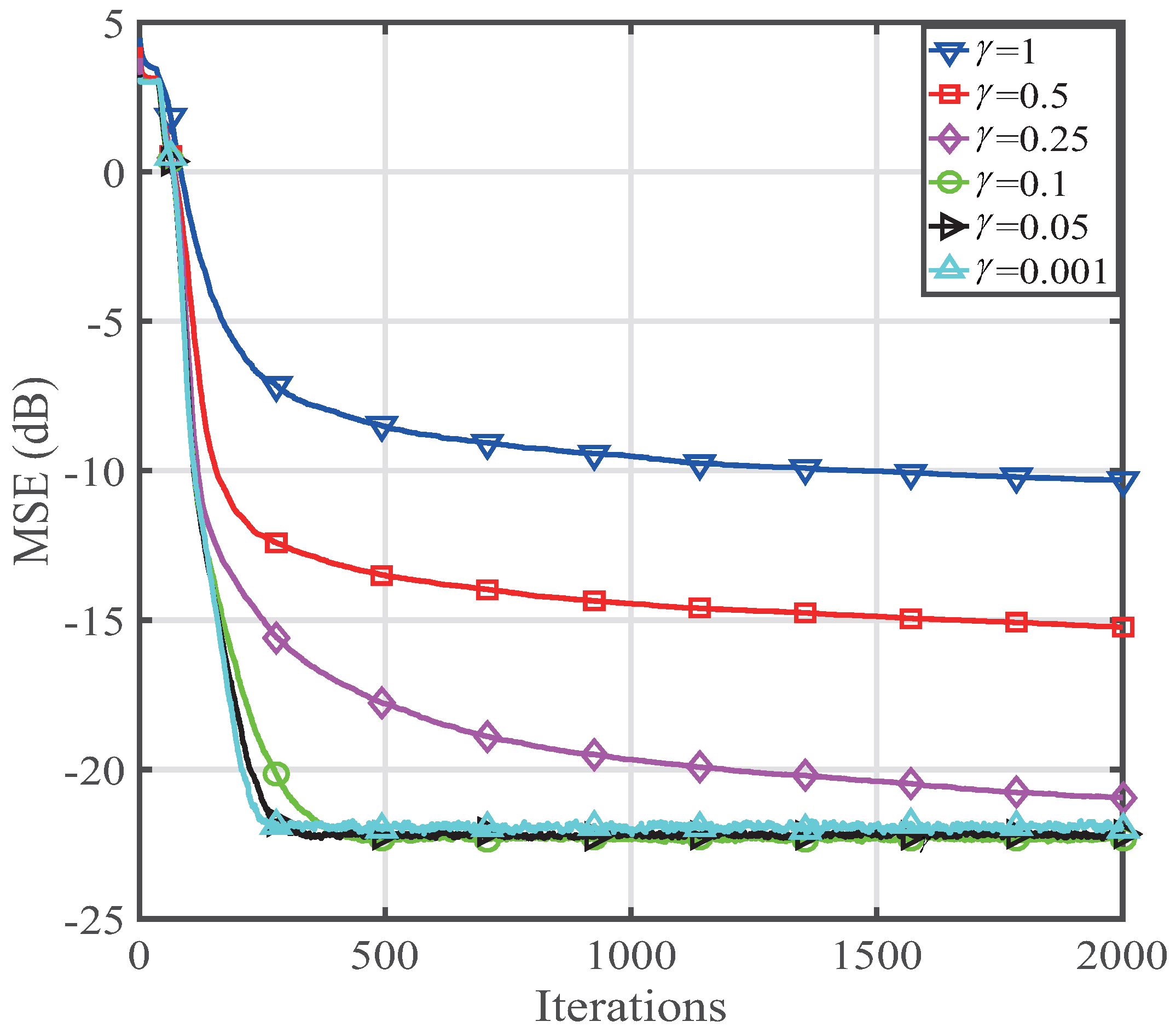
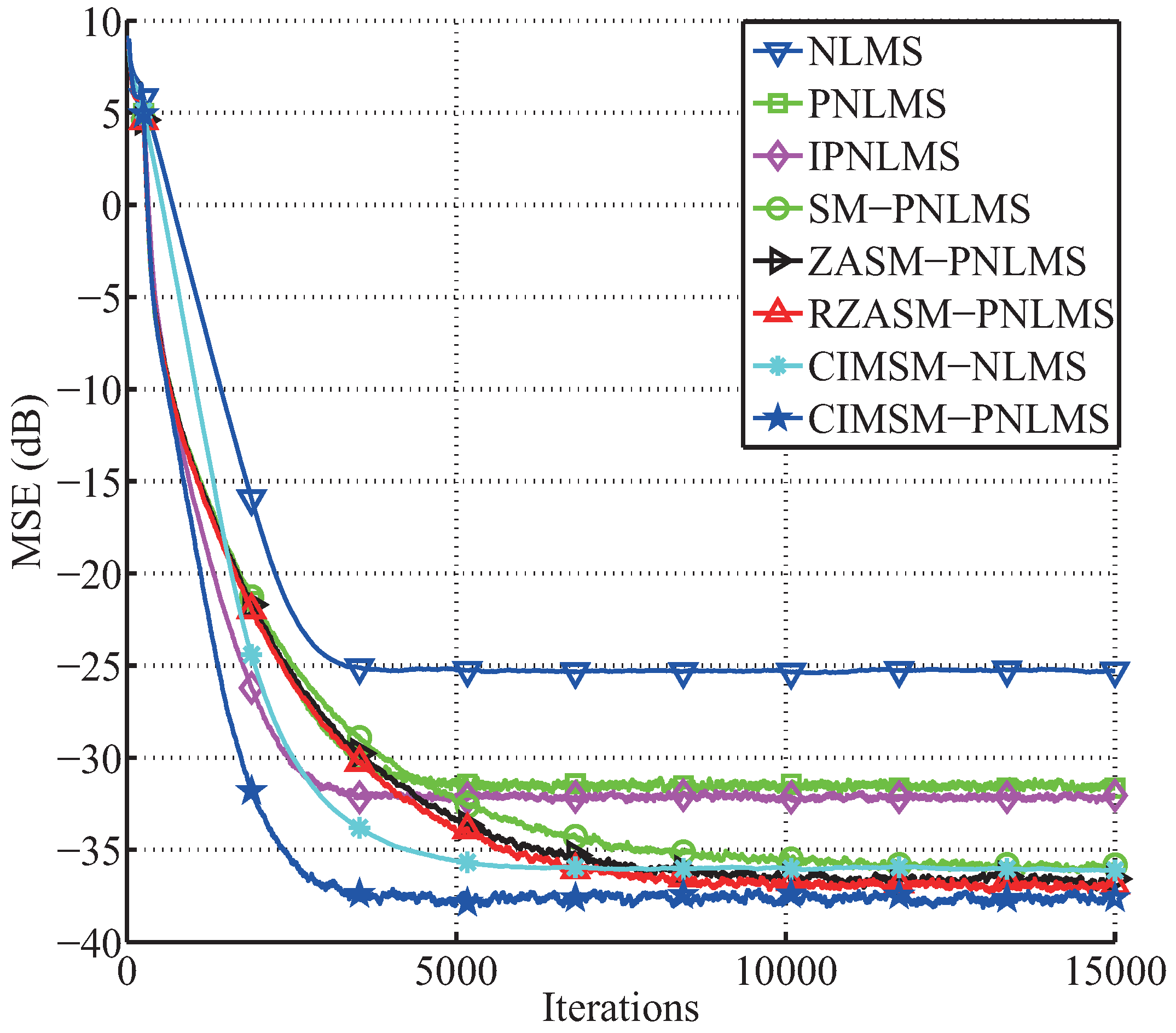
4. Performance of the Proposed CIMSM-PNLMS Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haykin, S. Adaptive Filter Theory, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, P.S.R. Adaptive Filtering: Algorithms and Practical Implementaion, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, A.H. Fundamentals of Adaptive filtering; Wiley-IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Combettes, P.L. The foundations of set theoretic estimation. Proc. IEEE 1993, 81, 182–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, S.; Gollamudi, S.; Kapoor, S.; Huang, Y. An adaptive set-membership filtering technique with sparse updates. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1999, 47, 2928–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Diniz, P.S.R. Set-membership affine projection algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2001, 8, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollamudi, S.; Nagaraj, S.; Huang, Y.F. Blind equalization with a deterministic constant modulus cost-a set-membership filtering approach. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Istanbul, Turkey, 5–9 June 2000; pp. 2765–2768. [Google Scholar]
- Gollamudi, S.; Nagaraj, S.; Huang, Y.F. Set-membership filtering and a set-membership normalized LMS algorithm with an adaptive step size. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1998, 5, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, P.S.R. Adaptive Filtering:Algorithms and Practical Implementations, 2nd ed.; Kluwer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 234–237. [Google Scholar]
- De Lamare, R.C.; Diniz, P.S.R. Set-membership adaptive algorithms based on time-vary error bounds for CDMA interference suppression. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhotto, M.Z.A.; Antoniou, A. Robust set-membership affine projection adaptive-filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.M.; Nayeri, M.; Deller, J.R., Jr. Consistently convergent OBE algorithm with automatic selection of error bounds. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 1998, 12, 302–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lamare, R.C.; Sampaio-Neto, R. Adaptive reduced-rank MMSE filtering with interpolated FIR filters and adaptive interpolators. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2005, 12, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.; Lamare, R.C.D. Low-complexity reduced-rank linear interference suppression based on set-membership joint iterative optimization for DS-CDMA systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 4324–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lamare, R.C.D. Set-membership adaptive constant modulus beamforming based on generalized sidelobe cancellation with dynamic bounds. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems, Ilmenau, German, 27–30 August 2013; pp. 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Jin, J.; Mei, S. l0 norm constraint LMS algorithms for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 16, 774–777. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, O.; Vorobyov, S.A. Sparse channel estimation with lp-norm and reweighted l1-norm penalized least mean squares. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 2864–2867. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Sparse channel estimation based on a p-norm-like constrained least mean fourth algorithm. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Sinal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, G.; Adachi, F. Improved least mean square algorithm with application to adaptive sparse channel estimation. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2013, 2013, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Low complexity non-uniform penalized affine projection algorithm for sparse system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, W.; Wan, J.; Li, Z. Sparse adaptive channel estimation based on lp-norm penalized affine projection algorithm. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 434659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttweiler, D.L. Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptition in echo cancelers. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2000, 8, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Doroslova, M. Improved convergence of the PNLMS algorithm for sparse impluse response identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2005, 12, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hamamura, M. An improved proportionate normalized least-mean-square algorithm for broadband multipath channel estimation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hamamura, M. Zero-attracting variable-step-size least mean square algorithms for adaptive sparse channel estimation. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2015, 29, 1189–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.; Peng, W.; Adachi, F. Sparse least mean fourth algorithm for adaptive channel estimation in low signal-to-noise ratio region. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2014, 27, 3147–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.; Xu, L.; Matsushita, S. Improved adaptive sparse channel estimation using mixed square/fourth error criterion. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 4579–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.; Mehbodniya, A.; Adachi, F. Least mean square/fourth algorithm for adaptive sparse channel estimation. In Proceedings of the 24th IEEE International Symposium on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013; pp. 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Norm-adaption penalized least mean square/fourth algorithm for sparse channel estimation. Signal Process. 2016, 128, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Gay, S.L. An improved PNLMS algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Sparse-aware Set-membership NLMS algorithms and their application for sparse channel estimation and echo cancellation. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Hero, A.O. Sparse LMS for system identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hamamura, M. Smooth approximation l0-norm constrained affine projection algorithm and its applications in sparse channel estimation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 937252. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, R.; de Lamare, R.C.; Nascimento, V.H. Sparsity-aware affine projection adaptive algorithms for system identification. In Proceedings of the Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD), London, UK, 27–29 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M.V.S.; Martins, W.A.; Diniz, P.S.R. Affine projection algorithms for sparse system identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M.V.S.; Ferreira, T.N.; Martins, W.A.; Diniz, P.S.R. Sparsity-Aware Data-Selective Adaptive Filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 4557–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.V.S.; Sobron, I.; Martins, W.A.; Diniz, P.S.R. Stability and MSE analyses of affine projection algorithms for sparse system identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 6399–6403. [Google Scholar]
- Seth, S.; Principe, J.C. Compressed signal reconstruction using the correntropy induced metric. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 3845–3848. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Liang, J.; Zheng, N.; Principe, J.C. Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 880–884. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, N.; Principe, J.C. Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3376–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.L.; Chakraborty, M. Improving the performance of the PNLMS algorithm using l1 norm regularization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Prov. 2016, 24, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, Z. A novel matlab-based underwater acoustic channel simulator. J. Commun. Comput. 2013, 10, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Albu, F.; Yang, R. Sparse Channel Estimation Using Correntropy Induced Metric Criterion Based SM-NLMS Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. An Enhanced Set-Membership PNLMS Algorithm with a Correntropy Induced Metric Constraint for Acoustic Channel Estimation. Entropy 2017, 19, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19060281
Jin Z, Li Y, Wang Y. An Enhanced Set-Membership PNLMS Algorithm with a Correntropy Induced Metric Constraint for Acoustic Channel Estimation. Entropy. 2017; 19(6):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19060281
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Zhan, Yingsong Li, and Yanyan Wang. 2017. "An Enhanced Set-Membership PNLMS Algorithm with a Correntropy Induced Metric Constraint for Acoustic Channel Estimation" Entropy 19, no. 6: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19060281
APA StyleJin, Z., Li, Y., & Wang, Y. (2017). An Enhanced Set-Membership PNLMS Algorithm with a Correntropy Induced Metric Constraint for Acoustic Channel Estimation. Entropy, 19(6), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19060281




