Multicomponent and Longitudinal Imaging Seen as a Communication Channel—An Application to Stroke
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
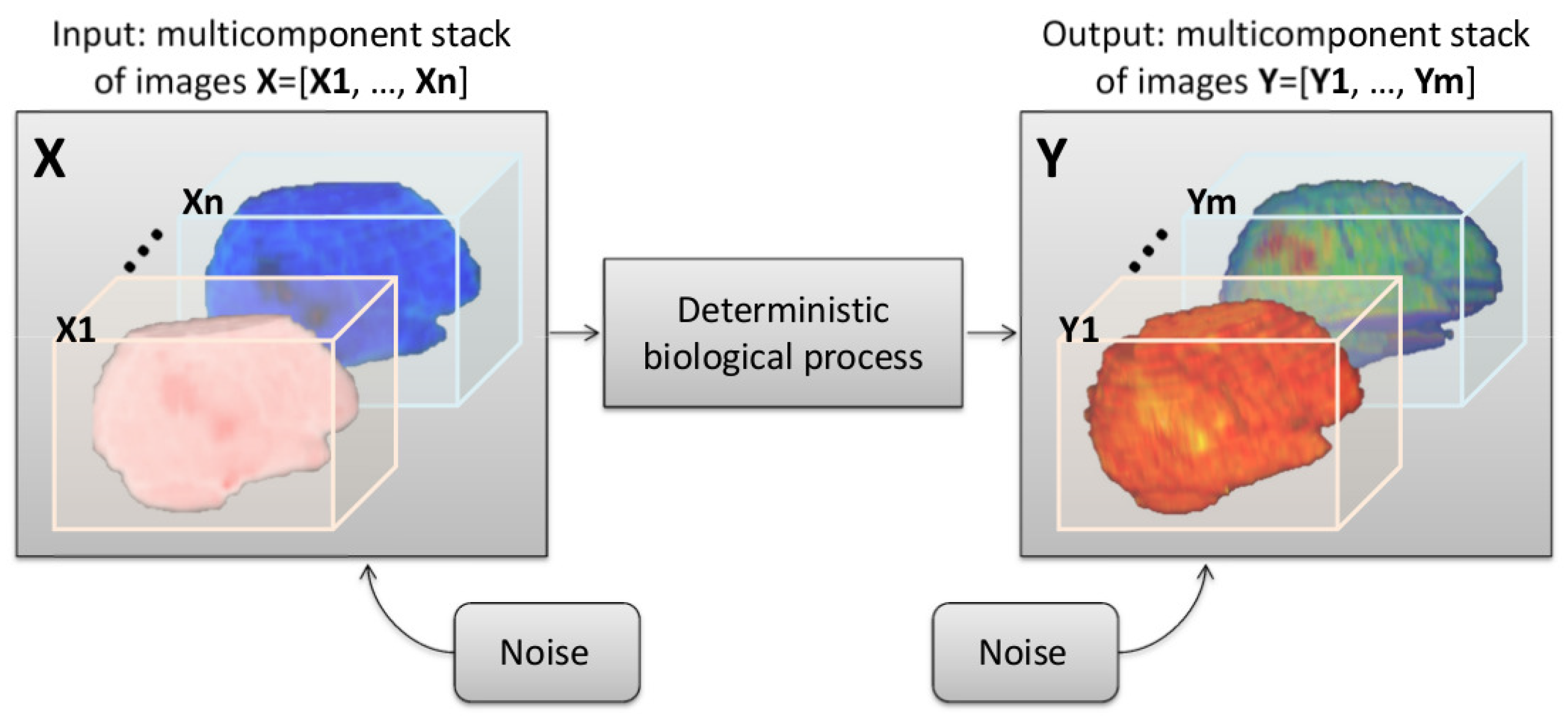
2.1. Modeling a Shannon-Like Communication Channel for Multicomponent and Longitudinal Biomedical Imaging Studies
2.2. Multicomponent and Longitudinal Imaging Studies in Stroke
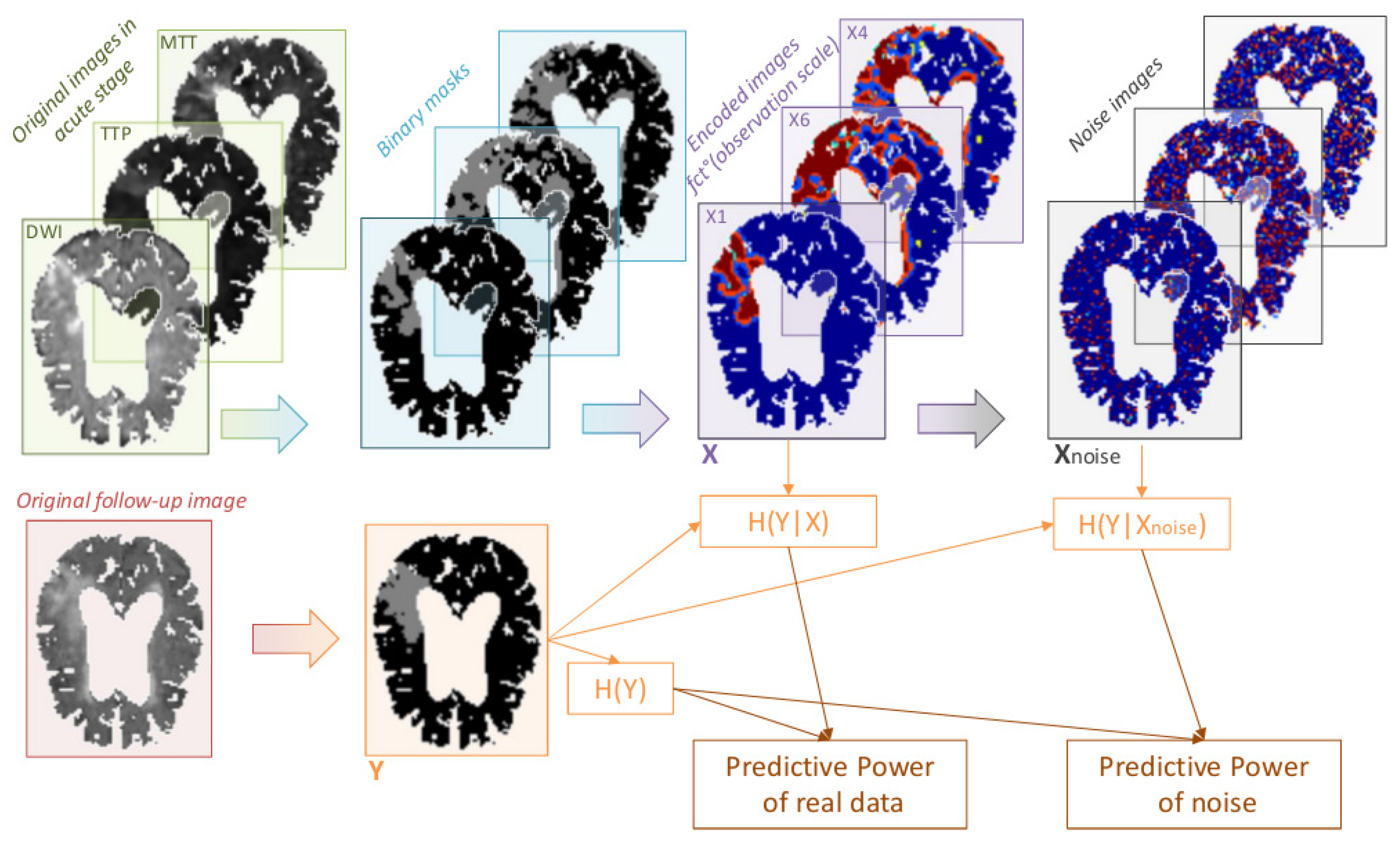
2.2.1. Gain of Predictability with Multicomponent Integration
2.2.2. Optimal Observation Scale for Tissue Fate Prediction
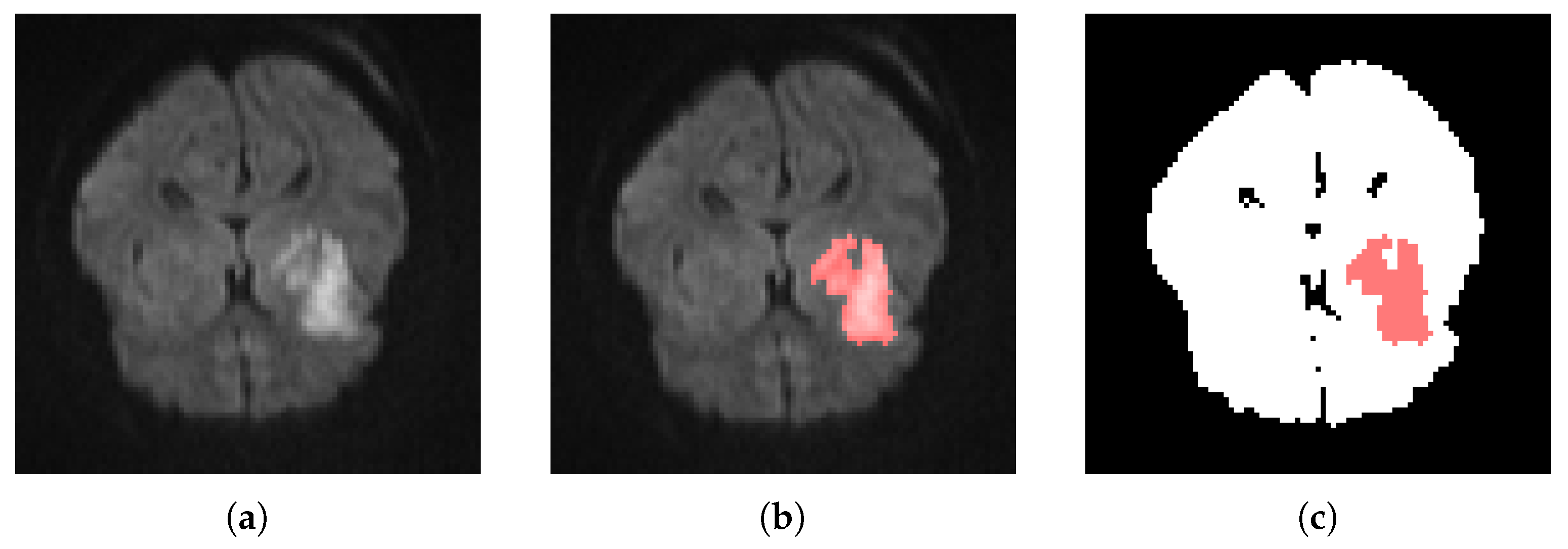
2.2.3. Impact of Noise on Tissue Fate Prediction Accuracy
| Algorithm 1: Pseudo-algorithm for the introduction of noise in a reference mask M. The inside contour is composed of all the voxels which belong to the segmented region and are in contact with its boundary. The outside contour is composed of all the voxels which do not belong to the segmented region but are in contact with its boundary. The optimum values for and , the two parameters of the algorithm, are application-dependent. Here, they were set to and . In any case, we should have and odd . |
 |
3. Material
3.1. Clinical Data for Tissue Fate Prediction
3.2. Impact of Noise on Tissue Fate Prediction Accuracy
4. Results
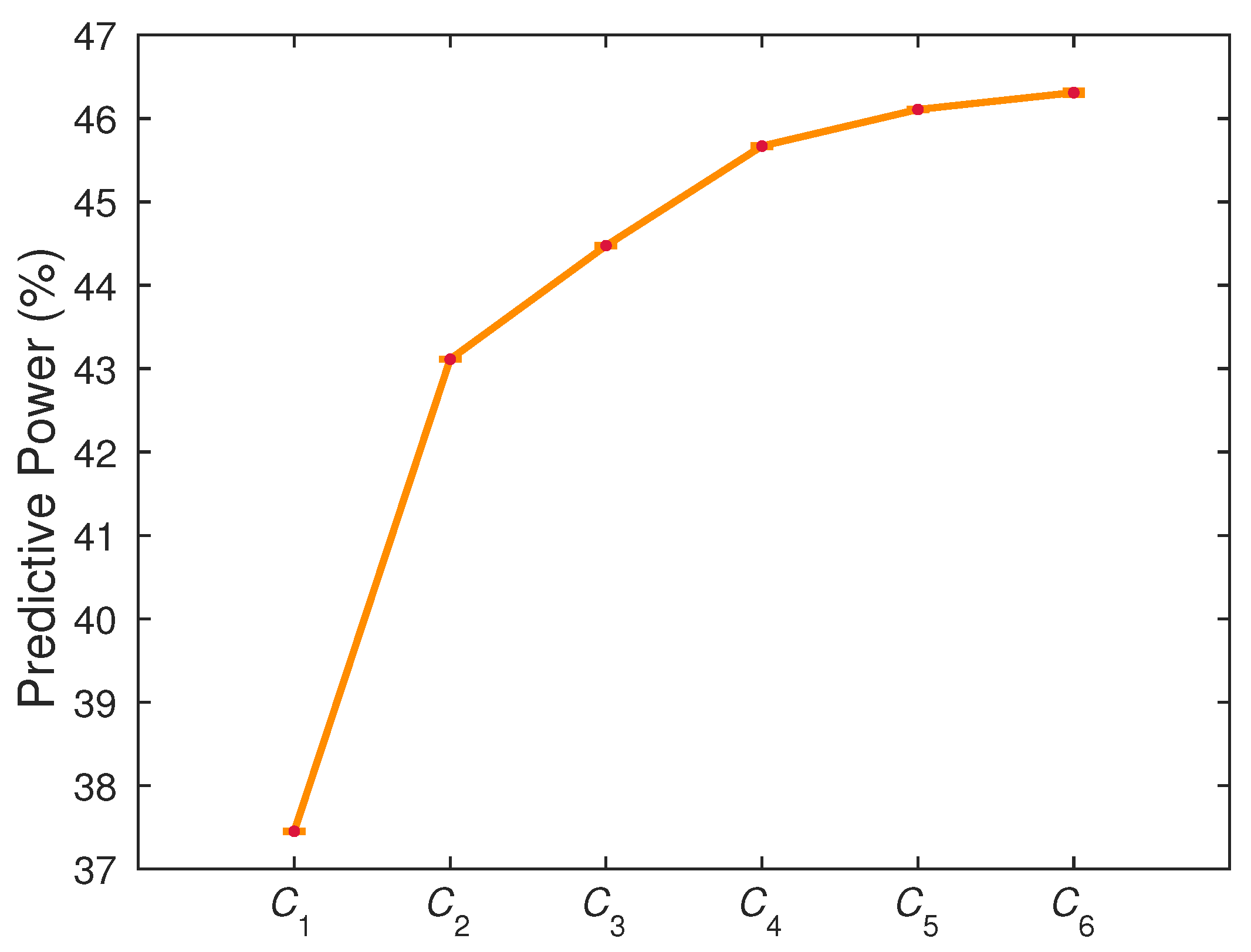
4.1. Gain of Predictability with Multicomponent Integration
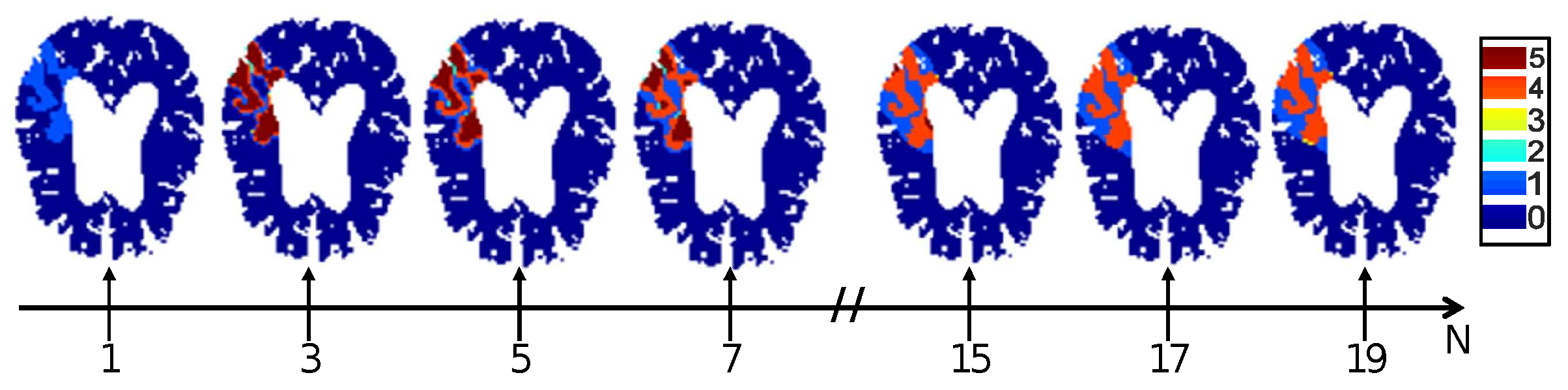
4.2. Optimal Observation Scale for Tissue Fate Prediction
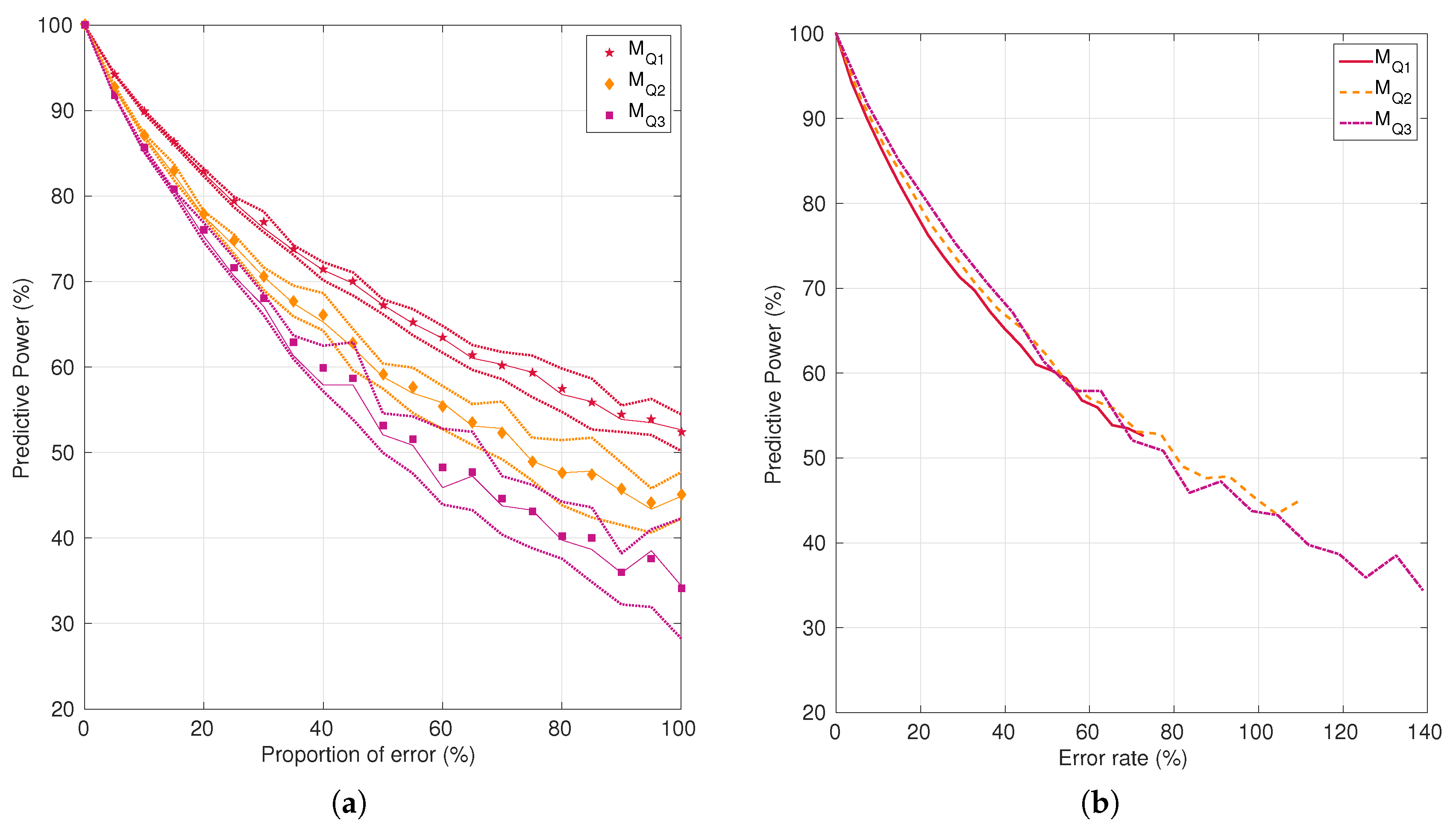
4.3. Impact of Noise on Tissue Fate Prediction Accuracy
5. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, F.E.; Pérez, P.S.; Bonev, B.I. Information Theory in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad-Djafari, A. Entropy, information theory, information geometry and Bayesian inference in data, signal and image processing and inverse problems. Entropy 2015, 17, 3989–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, L.; Belin, É.; Rousseau, D.; Chapeau-Blondeau, F. Information-theoretic modeling of trichromacy coding of light spectrum. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2014, 13, 1450025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, L.; Benoit, R.; Belin, É.; Vadaine, R.; Demilly, D.; Chapeau-Blondeau, F.; Rousseau, D. On the value of the Kullback–Leibler divergence for cost-effective spectral imaging of plants by optimal selection of wavebands. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2016, 27, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaies, A.; Rousseau, D.; Chapeau-Blondeau, F. Joint acquisition-processing approach to optimize observation scales in noisy imaging. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 972–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justesen, J.; Forchhammer, S. Two-Dimensional Information Theory and Coding: With Applications to Graphics Data and High-Density Storage Media; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Feixas, M.; Viola, I.; Bardera, A.; Shen, H.W.; Sbert, M. Information Theory Tools for Visualization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bramon, R.; Boada, I.; Bardera, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Feixas, M.; Puig, J.; Sbert, M. Multimodal data fusion based on mutual information. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2012, 18, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlaily, S.; Amblard, P.O.; Michel, O.; Jutten, C. Impact of noise correlation on multimodality. In Proceedings of the 24th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Budapest, Hungary, 29 August–2 September 2016; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bialek, W.; Nemenman, I.; Tishby, N. Predictability, complexity, and learning. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, 2409–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, F.; Ntranos, V.; Ellison, C.J.; Pollin, S.; Verhelst, M. Understanding interdependency through complex information sharing. Entropy 2016, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T. Measuring information transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amblard, P.O.; Michel, O.J. The relation between Granger causality and directed information theory: A review. Entropy 2012, 15, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, C.S.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Armitage, P.A.; Bastin, M.E.; Hand, P.J.; Dennis, M.S. Acute ischemic stroke lesion measurement on diffusion-weighted imaging–important considerations in designing acute stroke trials with magnetic resonance imaging. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2007, 16, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, A.B.; Jonsdottir, K.Y.; Mouridsen, K.; Hjort, N.; Gyldensted, C.; Bizzi, A.; Fiehler, J.; Gasparotti, R.; Gillard, J.H.; Hermier, M.; et al. Interrater agreement for final infarct MRI lesion delineation. Stroke 2009, 40, 3768–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willats, L.; Calamante, F. The 39 steps: Evading error and deciphering the secrets for accurate dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 913–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, M.; Frindel, C.; Zagala, R.; Cho, T.H.; Berthezène, Y.; Nighoghossian, N.; Rousseau, D. On the Influence of Normalization Strategies for Perfusion MRI in Acute Stroke. In Current Developments in Stroke; Bentham Science: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Scalzo, F.; Hao, Q.; Alger, J.R.; Hu, X.; Liebeskind, D.S. Tissue fate prediction in acute ischemic stroke using cuboid models. In Advances in Visual Computing, ISVC 2010; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6454, pp. 292–301. [Google Scholar]
- Scalzo, F.; Hao, Q.; Alger, J.R.; Hu, X.; Liebeskind, D.S. Regional prediction of tissue fate in acute ischemic stroke. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 2177–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Shen, Q.; Duong, T.Q. Artificial neural network prediction of ischemic tissue fate in acute stroke imaging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Cooperman, G.; Menenzes, N.; Lopez, C.J.; Melinosky, C.; Wu, O.; Ay, H.; Liu, Y.; Nuutinen, J.; Aronen, H.J.; et al. Stroke tissue outcome prediction using a spatially-correlated model. In Proceedings of the 2008 Pan-Pacific Imaging Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 25–27 June 2008; pp. 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Frindel, C.; Rouanet, A.; Giacalone, M.; Cho, T.H.; Østergaard, L.; Fiehler, J.; Pedraza, S.; Baron, J.C.; Wiart, M.; Berthezène, Y.; et al. Validity of shape as a predictive biomarker of final infarct volume in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsdottir, K.Y.; Østergaard, L.; Mouridsen, K. Predicting Tissue Outcome From Acute Stroke Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Stroke 2009, 40, 3006–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, M.; Frindel, C.; Robini, M.; Cervenansky, F.; Grenier, E.; Rousseau, D. Robustness of spatio-temporal regularization in perfusion MRI deconvolution: An application to acute ischemic stroke. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, O.Y.; Goyal, M.; Liebeskind, D.S. Collateral circulation in ischemic stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 3302–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, O.; Menze, B.H.; von der Gablentz, J.; Häni, L.; Heinrich, M.P.; Liebrand, M.; Winzeck, S.; Basit, A.; Bentley, P.; Chen, L.; et al. ISLES 2015-A public evaluation benchmark for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation from multispectral MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikäinen, M.; Harwood, D. A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recogn. 1996, 29, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietikäinen, M.; Zhao, G. Two decades of local binary patterns: A survey. In Advances in Independent Component Analysis and Learning Machines; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 175–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bagher-Ebadian, H.; Jafari-Khouzani, K.; Mitsias, P.D.; Lu, M.; Soltanian-Zadeh, H.; Chopp, M.; Ewing, J.R. Predicting final extent of ischemic infarction using artificial neural network analysis of multi-parametric MRI in patients with stroke. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
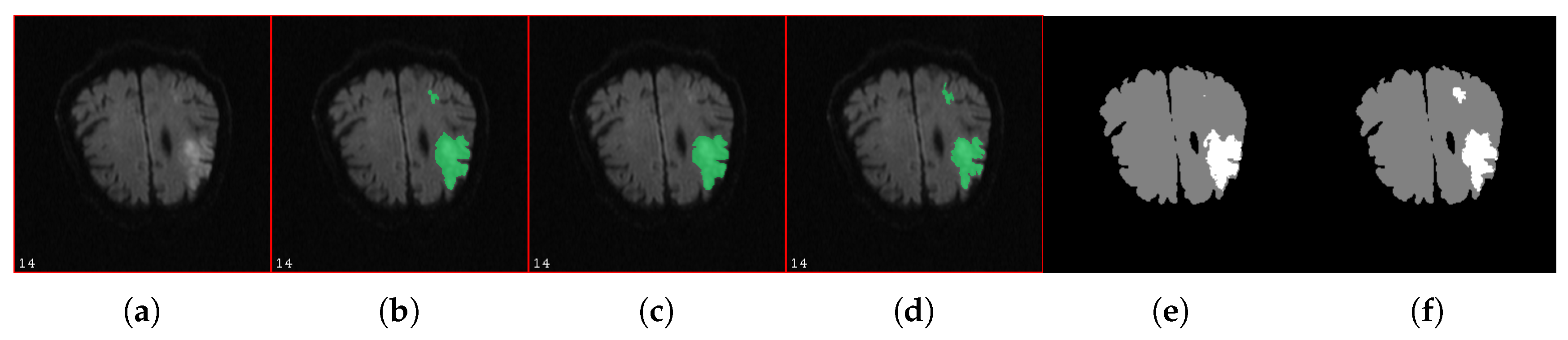

| Label | Voxel in Affected Area | % Of Neighboring Voxels in Affected Area |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | no | |
| 1 | no | |
| 2 | no | |
| 3 | yes | |
| 4 | yes | |
| 5 | yes |
| N | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37.4508 ± 0.0004 | 43.1119 ± 0.0009 | 44.475 ± 0.002 | 45.669 ± 0.005 | 46.108 ± 0.001 | 46.31 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | 42.294 ± 0.002 | 48.46 ± 0.01 | 49.90 ± 0.06 | 51.5 ± 0.2 | 52.7 ± 0.8 | 54 ± 2 |
| 5 | 44.903 ± 0.002 | 51.40 ± 0.01 | 52.93 ± 0.06 | 54.6 ± 0.3 | 56 ± 1 | 58 ± 3 |
| 7 | 46.846 ± 0.002 | 53.48 ± 0.01 | 55.10 ± 0.06 | 56.9 ± 0.3 | 58 ± 1 | 60 ± 3 |
| 9 | 48.206 ± 0.002 | 54.95 ± 0.01 | 56.60 ± 0.07 | 58.5 ± 0.3 | 60 ± 1 | 62 ± 4 |
| 11 | 49.103 ± 0.002 | 55.94 ± 0.01 | 57.59 ± 0.07 | 59.6 ± 0.3 | 61 ± 1 | 63 ± 4 |
| 13 | 49.668 ± 0.002 | 56.57 ± 0.01 | 58.33 ± 0.07 | 60.4 ± 0.3 | 62 ± 1 | 64 ± 4 |
| 15 | 50.101 ± 0.002 | 56.92 ± 0.01 | 58.78 ± 0.07 | 60.9 ± 0.3 | 63 ± 1 | 65 ± 4 |
| 17 | 50.437 ± 0.002 | 57.29 ± 0.01 | 59.23 ± 0.07 | 61.4 ± 0.3 | 63 ± 1 | 65 ± 4 |
| 19 | 50.558 ± 0.002 | 57.55 ± 0.01 | 59.50 ± 0.07 | 61.8 ± 0.3 | 64 ± 1 | 65 ± 4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giacalone, M.; Frindel, C.; Grenier, E.; Rousseau, D. Multicomponent and Longitudinal Imaging Seen as a Communication Channel—An Application to Stroke. Entropy 2017, 19, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19050187
Giacalone M, Frindel C, Grenier E, Rousseau D. Multicomponent and Longitudinal Imaging Seen as a Communication Channel—An Application to Stroke. Entropy. 2017; 19(5):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19050187
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiacalone, Mathilde, Carole Frindel, Emmanuel Grenier, and David Rousseau. 2017. "Multicomponent and Longitudinal Imaging Seen as a Communication Channel—An Application to Stroke" Entropy 19, no. 5: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19050187
APA StyleGiacalone, M., Frindel, C., Grenier, E., & Rousseau, D. (2017). Multicomponent and Longitudinal Imaging Seen as a Communication Channel—An Application to Stroke. Entropy, 19(5), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19050187






