Entropy and Compression Capture Different Complexity Features: The Case of Fetal Heart Rate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Bernardes, J.; Costa-Pereira, A.; Pereira-Leite, L. Inconsistencies in classification by experts of cardiotocograms and subsequent clinical decision. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1999, 106, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, J.; Ayres-de-Campos, D. The persistent challenge of foetal heart rate monitoring. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 22, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, J.; Costa-Pereira, A.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; van Geijn, H.P.; Pereira-Leite, L. Evaluation of interobserver agreement of cardiotocograms. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 1997, 57, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, I.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Figueiredo, C.; Bernardes, J. An overview of central fetal monitoring systems in labour. J. Perinat. Med. 2013, 41, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, H.; Rocha, A.P.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Bernardes, J. Linear and nonlinear fetal heart rate analysis of normal and acidemic fetuses in the minutes preceding delivery. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, M.; Signorini, M.G.; Magenes, G. Complexity analysis of the fetal heart rate variability: Early identification of severe intrauterine growth-restricted fetuses. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2009, 47, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plsek, P.E.; Greenhalgh, T. Complexity science: The challenge of complexity in health care. BMJ 2001, 323, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.; Holt, T.; Greenhalgh, T. Complexity science: Complexity and clinical care. BMJ 2001, 323, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cilibrasi, R.; Vitanyi, P.M.B. Clustering by compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2005, 51, 1523–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilibrasi, R.; Vitányi, P.; Wolf, R.D. Algorithmic clustering of music based on string compression. Comput. Music J. 2004, 28, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, S. Analyzing worms and network traffic using compression. J. Comput. Secur. 2007, 15, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.C.; Bernardes, J.; Vitanyi, P.M.B.; Antunes, L. Clustering fetal heart rate tracings by compression. In Proceedings of the 19th IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 22–23 June 2006; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, T.; Goncalves, H.; Antunes, L.; Matias, M.; Bernardes, J.; Costa-Santos, C. Entropy and compression: Two measures of complexity. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2013, 19, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Spong, C.Y.; Chandraharan, E. Figo consensus guidelines on intrapartum fetal monitoring: Cardiotocography. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2015, 131, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Sousa, P.; Costa, A.; Bernardes, J. Omniview-sisporto® 3.5—A central fetal monitoring station with online alerts based on computerized cardiotocogram+ST event analysis. J. Perinat. Med. 2008, 36, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, H.; Rocha, A.P.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Bernardes, J. Internal versus external intrapartum foetal heart rate monitoring: The effect on linear and nonlinear parameters. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Rei, M.; Nunes, I.; Sousa, P.; Bernardes, J. Sisporto 4.0—Computer analysis following the 2015 figo guidelines for intrapartum fetal monitoring. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, H.; Rocha, A.P.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Bernardes, J. Frequency domain and entropy analysis of fetal heart rate: Appealing tools for fetal surveillance and pharmacodynamic assessment of drugs. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 8, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarelli, M.; Romano, M.; Bifulco, P. Comparison of short term variability indexes in cardiotocographic foetal monitoring. Comput. Biol. Med. 2009, 39, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, M.; Baier, V.; Voss, A.; Brechtel, L.; Haueisen, J. Estimating the complexity of heart rate fluctuations—An approach based on compression entropy. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2005, 5, L557–L563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, A.; Schulz, S.; Schroeder, R.; Baumert, M.; Caminal, P. Methods derived from nonlinear dynamics for analysing heart rate variability. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
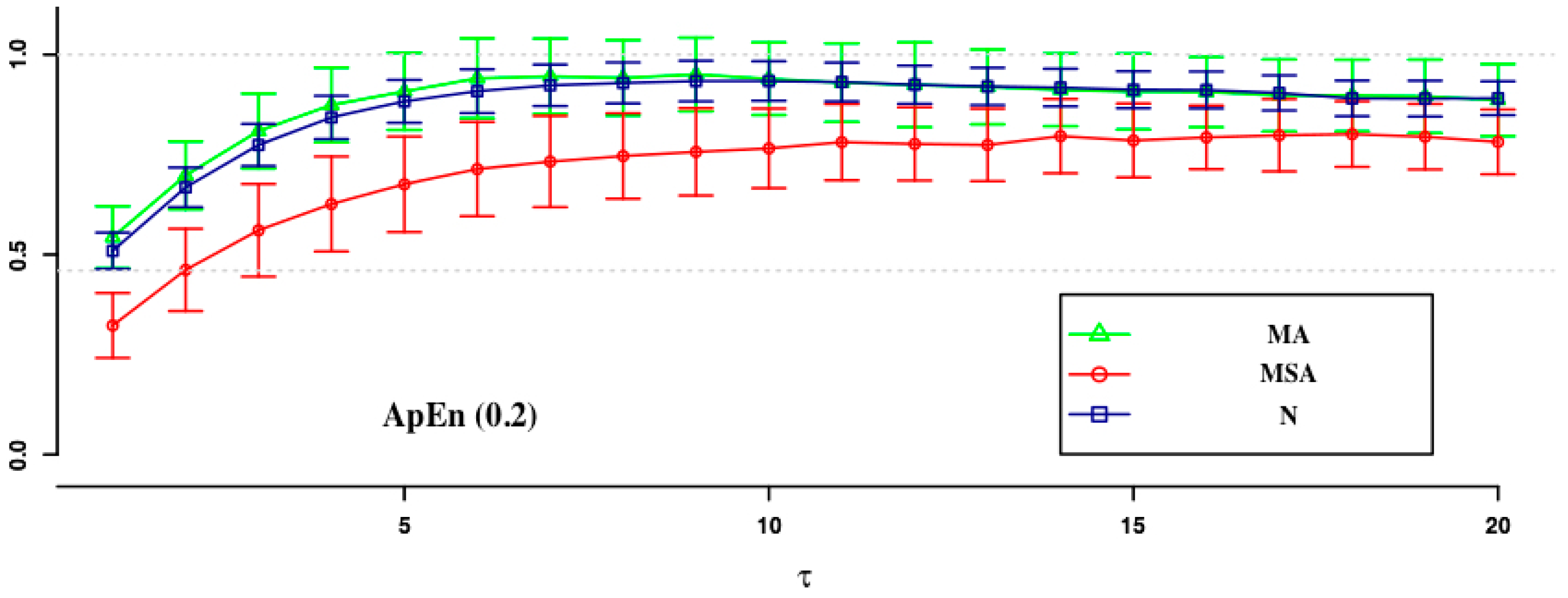
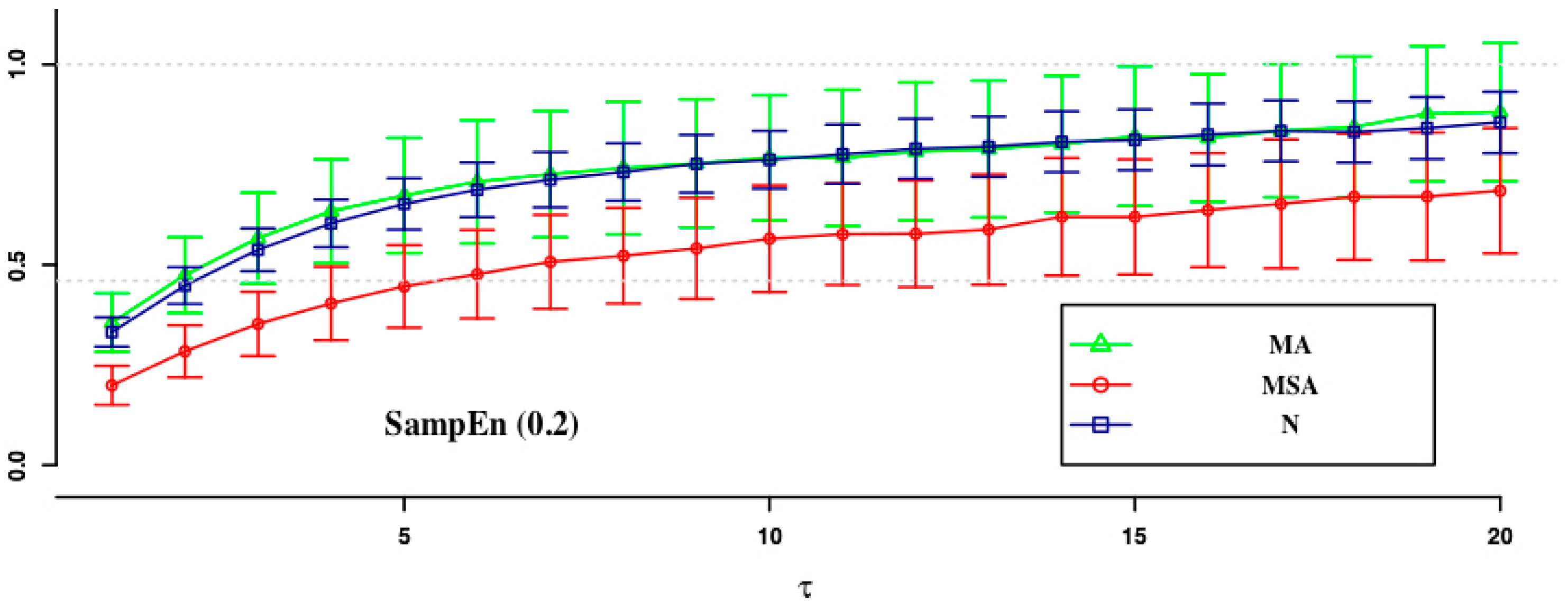


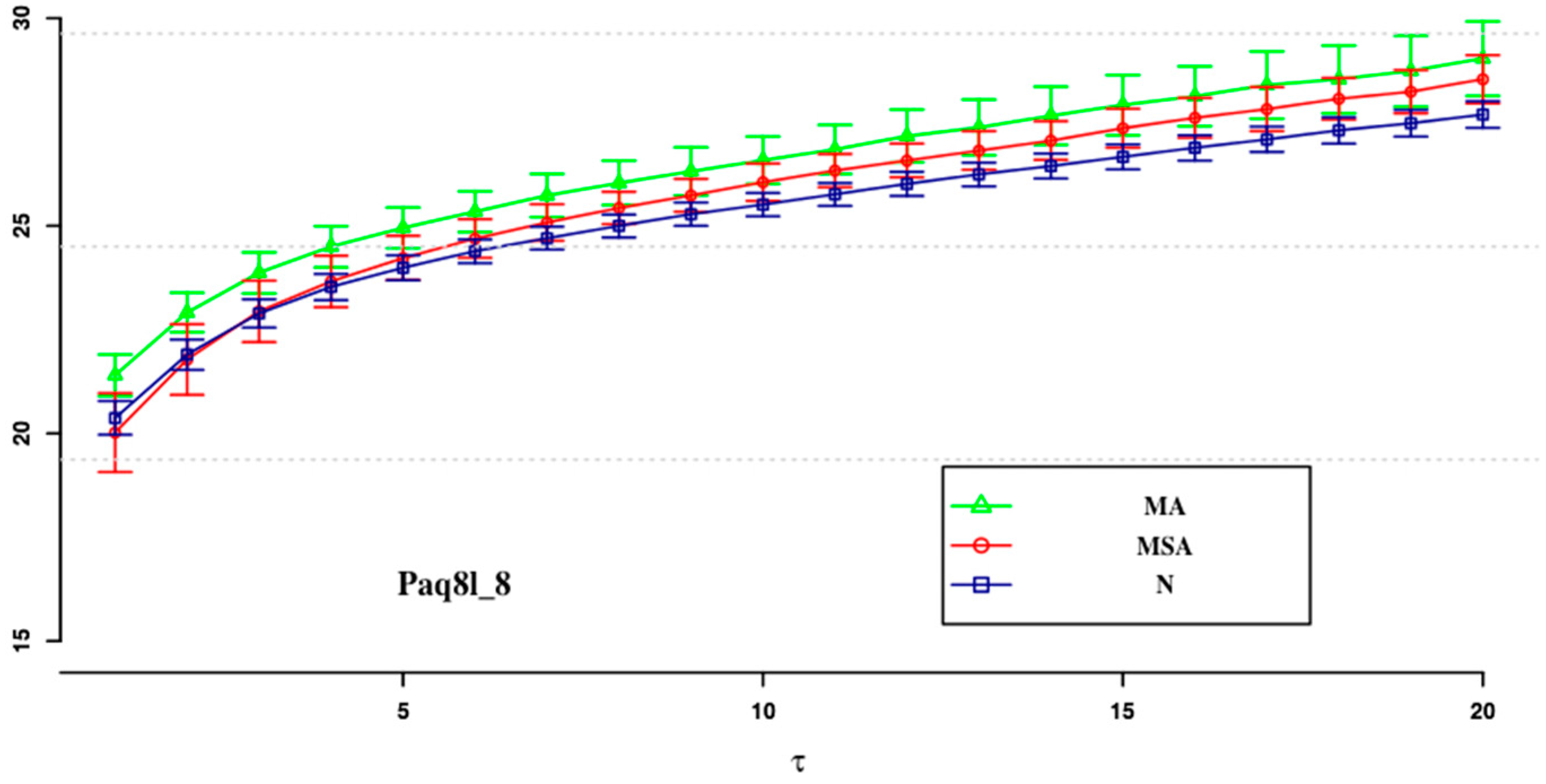
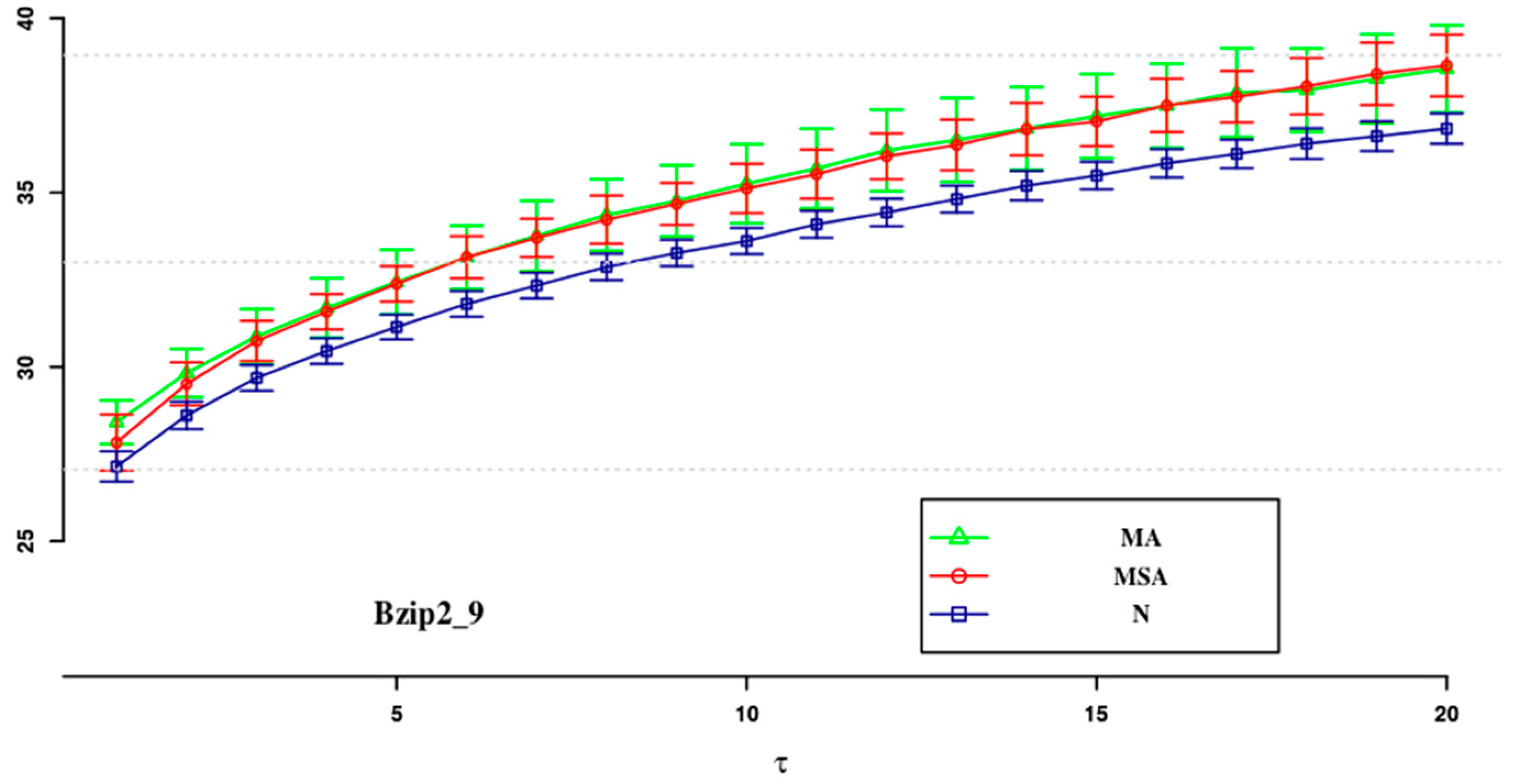
| ApEn (0.1) | ApEn (0.15) | SampEn (0.2) | SampEn (0.1) | SampEn (0.15) | SampEn (0.2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brotli_1 | 0.285 * | 0.267 * | 0.298 * | 0.341 ** | 0.294 * | 0.331 ** |
| Brotli_11 | 0.506 ** | 0.486 ** | 0.508 ** | 0.543 ** | 0.496 ** | 0.531 ** |
| Gzip1 | 0.407 ** | 0.393 ** | 0.424 ** | 0.452 ** | 0.406 ** | 0.448 ** |
| Gzip_9 | 0.242 * | 0.227 | 0.258 * | 0.285 * | 0.24 * | 0.281 * |
| Bzip2_1 | 0.093 | 0.072 | 0.105 | 0.143 | 0.09 | 0.132 |
| Bzip2_9 | 0.093 | 0.072 | 0.105 | 0.143 | 0.09 | 0.132 |
| Ppmd_2 | 0.256 * | 0.247 * | 0.28 * | 0.293 * | 0.247 * | 0.288 * |
| Ppmd_16 | 0.172 | 0.152 | 0.182 | 0.221 | 0.17 | 0.21 |
| Paq8l_1 | 0.531 ** | 0.511 ** | 0.538 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.52 ** | 0.559 ** |
| Paq8l_8 | 0.573 ** | 0.549 ** | 0.573 ** | 0.606 ** | 0.556 ** | 0.592 ** |
| Lzma_6 | 0.355 ** | 0.356 ** | 0.382 ** | 0.366 ** | 0.331 ** | 0.36 ** |
| %abSTV | Mean STV | %abLTV | Baseline | Acc | Dec | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %abSTV | 1 | |||||
| Mean STV | −0.796 ** | 1 | ||||
| %abLTV | 0.706 ** | −0.444 ** | 1 | |||
| baseline | 0.324 ** | −0.201 | 0.27 * | 1 | ||
| Acc | −0.480 ** | 0.357 ** | −0.651 ** | −0.138 | 1 | |
| Dec | −0.375 ** | 0.539 ** | −0.101 | −0.015 | −0.035 | 1 |
| ApEn (0.1) | ApEn (0.15) | ApEn (0.2) | SampEn (0.1) | SampEn (0.15) | SampEn (0.2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %abSTV | −0.557 ** | −0.541 ** | −0.561 ** | −0.617 ** | −0.586 ** | −0.624 ** |
| Mean STV | 0.34 ** | 0.331 ** | 0.353 ** | 0.339 ** | 0.302 * | 0.338 ** |
| %abLTV | −0.319 ** | −0.321 ** | −0.328 * | −0.451 ** | −0.441 ** | −0.459 ** |
| baseline | −0.268 * | −0.29 * | −0.284 * | −0.312 ** | −0.309 * | −0.313 ** |
| Acc | 0.093 | 0.077 | 0.080 | 0.199 | 0.178 | 0.206 |
| Dec | −0.024 | −0.020 | 0.029 | −0.058 | −0.103 | −0.072 |
| Brotli_1 | Brotli_11 | Gzip_1 | Gzip_9 | Bzip2_1 | Bzip2_9 | Ppmd_2 | Ppmd_16 | Paq8l_1 | Paq8l_8 | Lzma_6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %abSTV | −0.886 ** | −0.934 ** | −0.908 ** | −0.851 ** | −0.796 ** | −0.796 ** | −0.838 ** | −0.808 ** | −0.935 ** | −0.931 ** | −0.882 ** |
| Mean STV | 0.783 ** | 0.829 ** | 0.794 ** | 0.774 ** | 0.729 ** | 0.729 ** | 0.774 ** | 0.733 ** | 0.8 ** | 0.783 ** | 0.839 ** |
| %abLTV | −0.622 ** | −0.6 ** | −0.625 ** | −0.575 ** | −0.532 ** | −0.532 ** | −0.591 ** | −0.539 ** | −0.646 | −0.606 | −0.556 ** |
| baseline | −0.236 | −0.295 * | −0.249 * | −0.193 | −0.168 | −0.168 | −0.288 * | −0.175 | −0.3 * | −0.296 * | −0.359 * |
| Acc | 0.564 ** | 0.472 ** | 0.542 ** | 0.562 ** | 0.574 ** | 0.574 ** | 0.548 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.527 ** | 0.485 ** | 0.432 ** |
| Dec | 0.410 ** | 0.387 ** | 0.397 ** | 0.424 ** | 0.441 ** | 0.441 ** | 0.487 ** | 0.423 ** | 0.366 ** | 0.339 ** | 0.544 ** |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monteiro-Santos, J.; Gonçalves, H.; Bernardes, J.; Antunes, L.; Nozari, M.; Costa-Santos, C. Entropy and Compression Capture Different Complexity Features: The Case of Fetal Heart Rate. Entropy 2017, 19, 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19120688
Monteiro-Santos J, Gonçalves H, Bernardes J, Antunes L, Nozari M, Costa-Santos C. Entropy and Compression Capture Different Complexity Features: The Case of Fetal Heart Rate. Entropy. 2017; 19(12):688. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19120688
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonteiro-Santos, João, Hernâni Gonçalves, João Bernardes, Luís Antunes, Mohammad Nozari, and Cristina Costa-Santos. 2017. "Entropy and Compression Capture Different Complexity Features: The Case of Fetal Heart Rate" Entropy 19, no. 12: 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19120688
APA StyleMonteiro-Santos, J., Gonçalves, H., Bernardes, J., Antunes, L., Nozari, M., & Costa-Santos, C. (2017). Entropy and Compression Capture Different Complexity Features: The Case of Fetal Heart Rate. Entropy, 19(12), 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19120688








