Entropy-Complexity Characterization of Brain Development in Chickens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Methods
2.2. Shannon Entropy, Fisher Information Measure and MPR Statistical Complexity
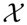 (t) ≡ {xt; t = 1, ···, M}, a set of M measures of the observable
(t) ≡ {xt; t = 1, ···, M}, a set of M measures of the observable
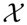 and the associated pdf, given by P ≡{pj ; j = 1, ···, N} with
, and N the number of possible states of the system under study, the Shannon’s logarithmic information measure (Shannon entropy) [26] is defined by:
and the associated pdf, given by P ≡{pj ; j = 1, ···, N} with
, and N the number of possible states of the system under study, the Shannon’s logarithmic information measure (Shannon entropy) [26] is defined by: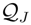 J defined in terms of the Jensen–Shannon divergence. That is,
J defined in terms of the Jensen–Shannon divergence. That is,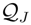 J ≤ 1), are equal to the inverse of the maximum possible value of
J ≤ 1), are equal to the inverse of the maximum possible value of
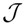 [P, Pe]. This value is obtained when one of the components of the pdf, P, say pm, is equal to one and the remaining pj are equal to zero. The Jensen–Shannon divergence, which quantifies the difference between two (or more) probability distributions, is especially useful to compare the symbolic composition between different sequences [39]. Note that the above introduced statistical complexity depends on two different probability distributions, the one associated with the system under analysis, P, and the uniform distribution, Pe. Furthermore, it was shown that for a given value of HS, the range of possible CJS values varies between a minimum Cmin and a maximum Cmax, restricting the possible values of the statistical complexity in a given entropy-complexity plane [40]. Thus, it is clear that important additional information related to the correlational structure between the components of the physical system is provided by evaluating the statistical complexity measure.
[P, Pe]. This value is obtained when one of the components of the pdf, P, say pm, is equal to one and the remaining pj are equal to zero. The Jensen–Shannon divergence, which quantifies the difference between two (or more) probability distributions, is especially useful to compare the symbolic composition between different sequences [39]. Note that the above introduced statistical complexity depends on two different probability distributions, the one associated with the system under analysis, P, and the uniform distribution, Pe. Furthermore, it was shown that for a given value of HS, the range of possible CJS values varies between a minimum Cmin and a maximum Cmax, restricting the possible values of the statistical complexity in a given entropy-complexity plane [40]. Thus, it is clear that important additional information related to the correlational structure between the components of the physical system is provided by evaluating the statistical complexity measure.2.3. The Bandt–Pompe Approach to the pdf Determination
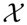 (t) by recourse to information theory tools assume that the underlying pdf is given a priori. In contrast, part of the concomitant analysis involves extracting the pdf from the data, and there is no univocal procedure with which everyone agrees. Almost ten years ago, Bandt and Pompe (BP) introduced a successful methodology for the evaluation of the pdf associated with scalar time series data using a symbolization technique [1]. For a didactic description of the approach, as well as its main biomedical and econophysics applications, see [2].
(t) by recourse to information theory tools assume that the underlying pdf is given a priori. In contrast, part of the concomitant analysis involves extracting the pdf from the data, and there is no univocal procedure with which everyone agrees. Almost ten years ago, Bandt and Pompe (BP) introduced a successful methodology for the evaluation of the pdf associated with scalar time series data using a symbolization technique [1]. For a didactic description of the approach, as well as its main biomedical and econophysics applications, see [2].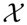 (t) = {xt; t = 1, ···, M} with embedding dimension D > 1 (D ∈ ℕ) and embedding time delay τ (τ ∈ ℕ). We are interested in “ordinal patterns” of order (length) D generated by (s) ↦ (xs− (D−1)τ, xs− (D−2)τ, ···, xs−τ,xs ), which assigns to each time s the D-dimensional vector of values at times s, s − τ, ···, s − (D − 1)τ. Clearly, the greater the D–value, the more information on the past is incorporated into our vectors. By “ordinal pattern” related to the time (s), we mean the permutation π = (r0, r1, ···, rD−1) of [0, 1, ···,D − 1] defined by xs−rD−1τ ≤ xs−rD−2τ ≤ ··· ≤ xs−r1τ ≤ xs−r0τ. In order to get a unique result, we set ri < ri−1 if xs−ri = xs−ri−1. This is justified if the values of xt have a continuous distribution, so that equal values are very unusual. Thus, for all the D! possible permutations π of order D, their associated relative frequencies can be naturally computed by the number of times this particular order sequence is found in the time series divided by the total number of sequences.
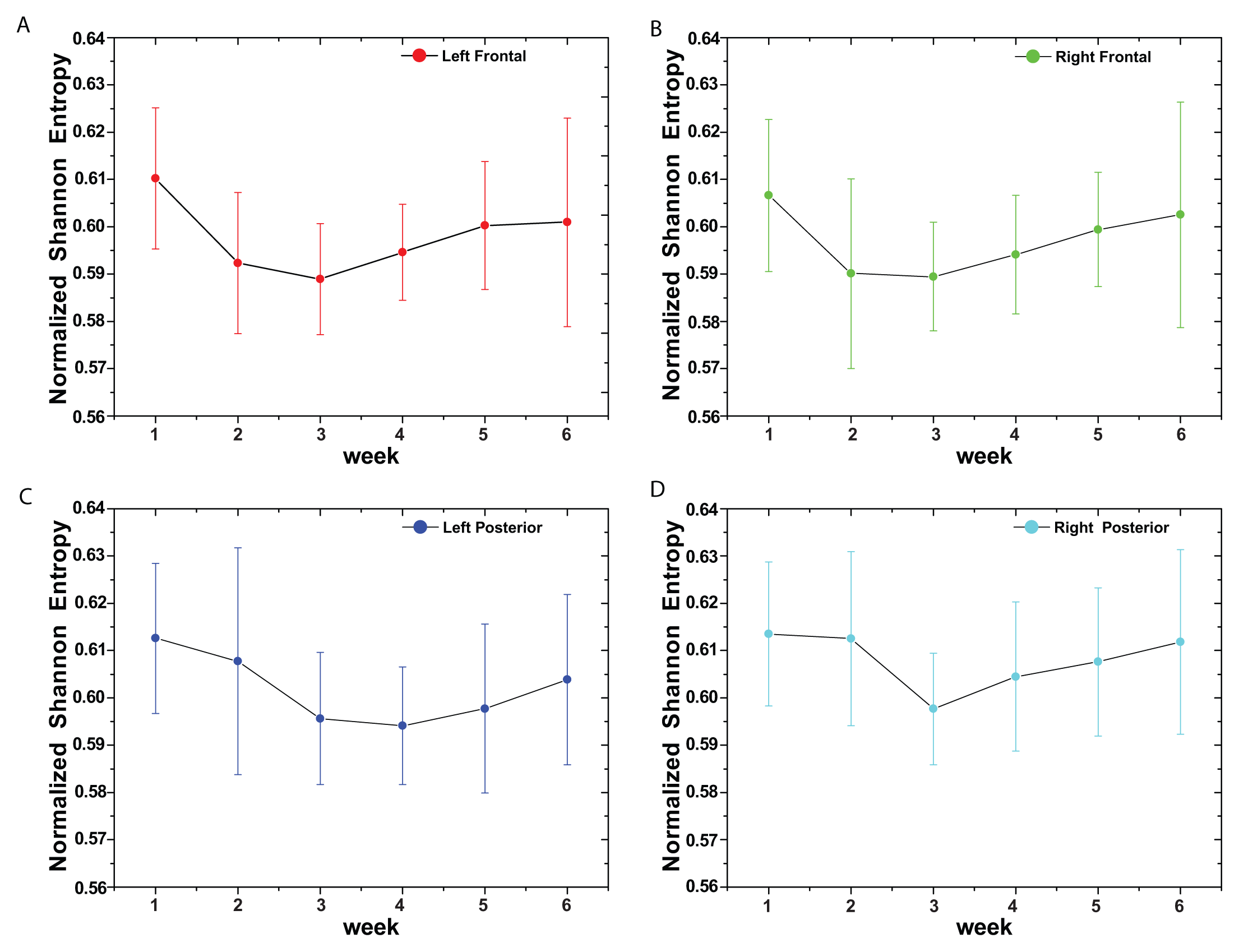
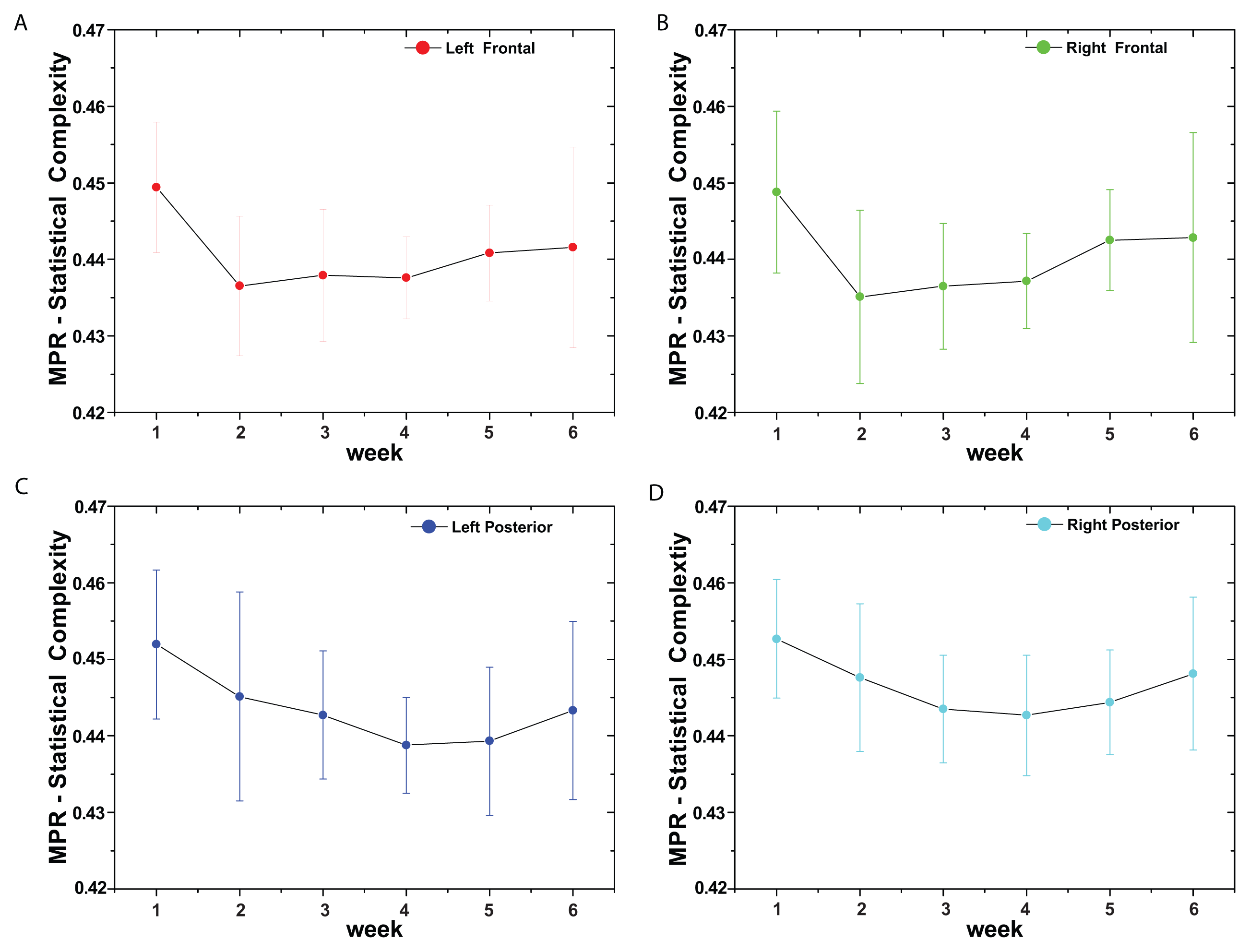
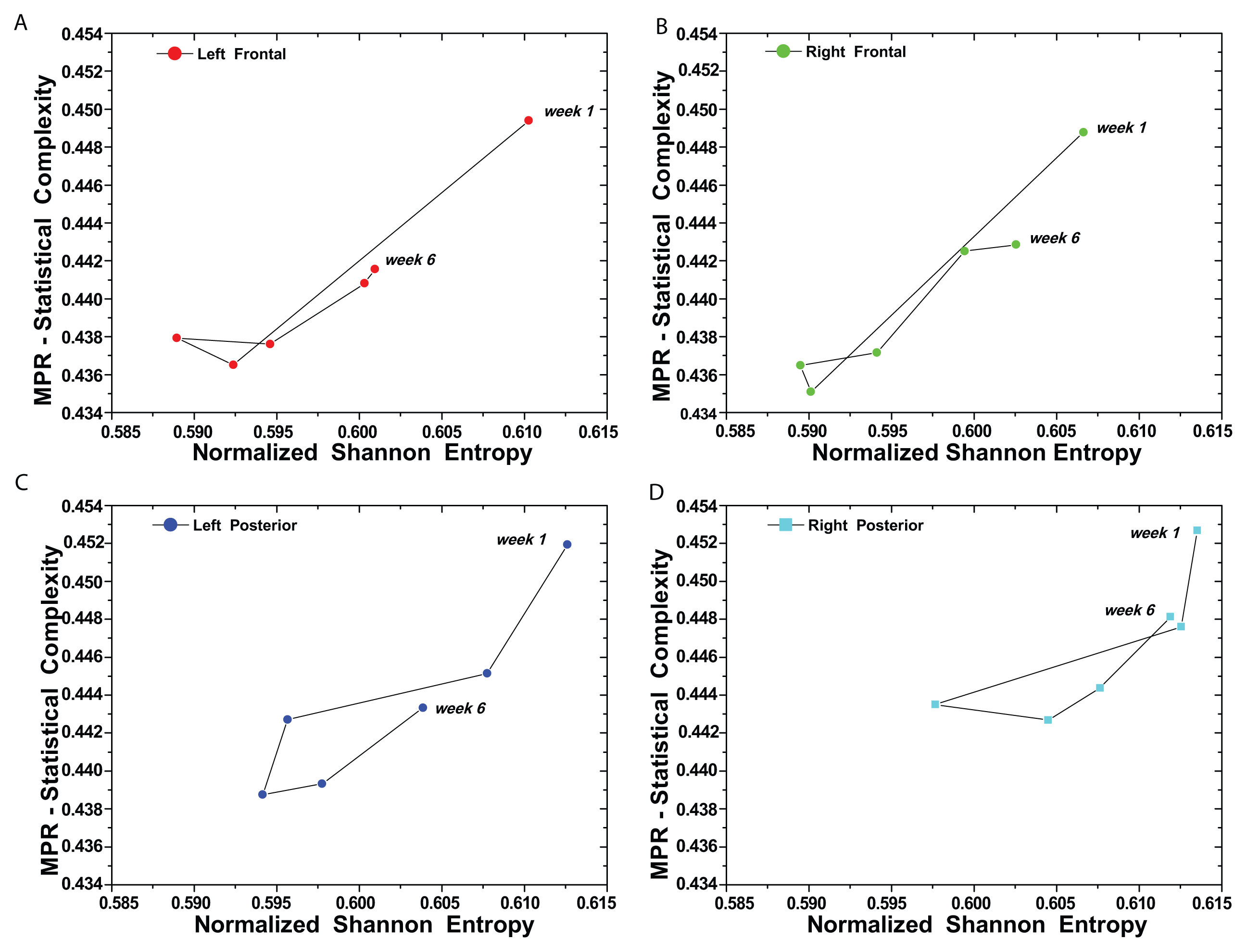
(t) = {xt; t = 1, ···, M} with embedding dimension D > 1 (D ∈ ℕ) and embedding time delay τ (τ ∈ ℕ). We are interested in “ordinal patterns” of order (length) D generated by (s) ↦ (xs− (D−1)τ, xs− (D−2)τ, ···, xs−τ,xs ), which assigns to each time s the D-dimensional vector of values at times s, s − τ, ···, s − (D − 1)τ. Clearly, the greater the D–value, the more information on the past is incorporated into our vectors. By “ordinal pattern” related to the time (s), we mean the permutation π = (r0, r1, ···, rD−1) of [0, 1, ···,D − 1] defined by xs−rD−1τ ≤ xs−rD−2τ ≤ ··· ≤ xs−r1τ ≤ xs−r0τ. In order to get a unique result, we set ri < ri−1 if xs−ri = xs−ri−1. This is justified if the values of xt have a continuous distribution, so that equal values are very unusual. Thus, for all the D! possible permutations π of order D, their associated relative frequencies can be naturally computed by the number of times this particular order sequence is found in the time series divided by the total number of sequences.3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar]
- Zanin, M.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Papo, D. Permutation Entropy and Its Main Biomedical and Econophysics Applications: A Review. Entropy 2012, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, K.; Gast, H.; Stieglitz, L.; Stibal, A.; Hauf, M.; Wiest, R.; Mariani, L.; Rummel, C. Forbidden ordinal patterns of periictal intracranial EEG indicate deterministic dynamics in human epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Veisi, I.; Pariz, N.; Karimpour, A. Fast and Robust Detection of Epilepsy in Noisy EEG Signals Using Permutation Entropy. Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, Boston, MA, USA, 14–17 October 2007; pp. 200–203.
- Cao, Y.; Tung, W.; Gao, J.B.; Protopopescu, V.A.; Hively, L.M. Detecting dynamical changes in time series using the permutation entropy. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 046217. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, G.; Dang, C.; Richards, D.A.; Li, X. Ordinal pattern based similarity analysis for EEG recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol 2010, 121, 694–703. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzo, A.A.; Gesierich, B.; Santi, M.; Tassinari, C.; Birbaumer, N.; Rubboli, G. Permutation entropy to detect vigilance changes and preictal states from scalp EEG in epileptic patients: A preliminary study. Neurol. Sci 2008, 29, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Cui, S.M.E.; Voss, L.J. Using permutation entropy to measure the electroencephalographic effect of sevoflurane. Anesthesiology 2007, 109, 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsen, E.; Sleigh, J.W.; Dahan, V. Permutation entropy of the electroencephalogram: A measure of anaesthetic drug effect. Br. J. Anaesth 2008, 101, 810–821. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, D.; Stockmanns, G.; Kochs, E.F.; Pilge, S.; Schneider, G. Electroencephalographic order pattern analysis for the separation of consciousness and unconsciousness: An analysis of approximate entropy, permutation entropy, recurrence rate, and phase coupling of order recurrence plots. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, N.; Georgiou, J. Detection of epileptic electroencephalogram based on Permutation, Entropy and Support Vector Machines. Expert Syst. Appl 2012, 39, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.E.; Mandell, A.J.; Coppola, R. Spatiotemporal imaging of complexity. Front. Comput. Neurosci 2013, 101, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Schröter, M.S.; Spoormaker, V.I.; Schorer, A.; Wohlschläger, A.; Czisch, M.; Kochs, E.F.; Zimmer, C.; Hemmer, B.; Schneider, G.; Jordan, D.; Ilg, R. Spatiotemporal Reconfiguration of Large-Scale Brain Functional Networks during Propofol-Induced Loss of Consciousness. J. Neurosci 2012, 32, 12832–12840. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, C.; Abela, E.; Hauf, M.; Wiest, R.; Schindler, K. Ordinal patterns in epileptic brains: Analysis of intracranial EEG and simultaneous EEG-fMRI. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top 2013, 222, 569–585. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; Masoller, C. Detecting and quantifying stochastic and coherence resonances via information-theory complexity measurements. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 040106(R). [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; Masoller, C. Detecting and quantifying temporal correlations in stochastic resonance via information theory measures. Eur. Phys. J. B 2009, 69, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; De Micco, K.; Plastino, A.; Larrondo, H. Info-quantifiers’ map-characterization revisited. Physica A 2010, 389, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Olivares, F.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Ambiguities in the Bandt-Pompe’s methodology for local entropic quantifiers. Physica A 2012, 391, 2518–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Olivares, F.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Contrasting chaos with noise via local versus global information quantifiers. Phys. Lett. A 2012, 376, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Changeux, J.P.; Courrege, P.; Danchin, A. A theory of the epigenesis of neuronal networks by selective stabilization of synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 2974–2978. [Google Scholar]
- Rostas, J.A.P.; Kavanagh, J.M.; Dodd, P.R.; Heath, J.W.; Powis, D.A. Mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. Changes in postsynaptic densities and glutamate receptors in chicken forebrain during maturation. Mol. Neurobiol 1991, 5, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Rostas, J.A.P. Molecular mechanisms of neuronal maturation: A model for synaptic plasticity. In Neural and Behavioural Plasticity: The Use of the Domestic Chick as a Model; Andrew, R.J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 177–201. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, M.; Battilana, M.; Bragg, T.; Rostas, J.A.P. EEG as a measure of developmental changes in the chicken brain. Dev. Psychobiol 2000, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Figliola, A.; Rosso, O.A.; Serrano, E. Atenuacion de frecuencias indeseadas usando transformada wavelet. Proceedings of XI Reunión de Trabajo en Procesamiento de la Información y Control; Grupo de Electronica Aplicada: Rio Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina, 2005; pp. 28–32. (In Spanish)[Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, J.G.; Larrondo, H.A.; Figliola, A.; Serrano, E.; Rostas, J.A.P.; Hunter, M.; Rosso, O.A. Brain maturation changes characterized by algorithmic complexity (Lempel and Zip complexity). In AIP Conference Proceedings; Descalzi, O., Larrondo, H.A., Rosso, O.A., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.A. On the mathematical foundations of theoretical statistics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1922, 222, 309–368. [Google Scholar]
- Frieden, B.R. Science from Fisher information: A Unification; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.L.; Pawlowski, C.W.; Cabezas, H. Fisher Information and dinamic regime changes in ecological systems. Ecol. Model 2006, 195, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zografos, K.; Ferentinos, K.; Papaioannou, T. Discrete approximations to the Csiszár, Renyi, and Fisher measures of information. Can. J. Stat 1986, 14, 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, L.; Morales, D.; Ferentinos, K.; Zografos, K. Discretization problems on generalized entropies and R-divergences. Kybernetika 1994, 30, 445–460. [Google Scholar]
- Madiman, M.; Johnson, O.; Kontoyiannis, I. Fisher Information, compound Poisson approximation, and the Poisson channel. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, 2007 (ISIT 2007), Nice, France, 24–29 June 2007; pp. 976–980.
- Sanchez-Moreno, P.; Dehesa, J.S.; Yanez, R.J. Discrete Densities and Fisher Information. In Difference Equations and Applications, Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Difference Equations and Applications; Uğur-Bahçeşehir University Publishing Company: Istanbul, Turkey, 2009; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Pennini, F.; Plastino, A. Reciprocity relations between ordinary temperature and the Frieden-Soffer Fisher temperature. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 047102. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.P.; Crutchfield, J.P. Measures of Statistical Complexity: Why? Phys. Lett. A 1998, 238, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.P.; McTague, C.S.; Crutchfield, J.P. The organization of intrinsic computation: Complexity-entropy diagrams and the diversity of natural information processing. Chaos 2008, 18, 043106. [Google Scholar]
- Lamberti, P.W.; Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Intensive entropic non-triviality measure. Physica A 2004, 334, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- López-Ruiz, R.; Mancini, H.L.; Calbet, X. A statistical measure of complexity. Phys. Lett. A 1995, 209, 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Grosse, I.; Bernaola-Galván, P.; Carpena, P.; Román-Roldán, R.; Oliver, J.; Stanley, H.E. Analysis of symbolic sequences using the Jensen-Shannon divergence. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 041905. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Generalized statistical complexity measures: Geometrical and analytical properties. Physica A 2006, 369, 439–462. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Fuentes, M.A. Distinguishing noise from chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett 2007, 99, 154102. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, O.A.; Olivares, F.; Zunino, L.; De Micco, L.; Aquino, A.L.L.; Plastino, A.; Larrondo, H.A. Characterization of chaotic maps using the permutation Bandt-Pompe probability distribution. Eur. Phys. J. B 2012, 86, 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- Saco, P.M.; Carpi, L.C.; Figliola, A.; Serrano, E.; Rosso, O.A. Entropy analysis of the dynamics of El Niño/Southern Oscillation during the Holocene. Physica A 2010, 389, 5022–5027. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, K.; Sinn, M. Ordinal Analysis of Time Series. Physica A 2005, 356, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zunino, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Fischer, I.; Rosso, O.A.; Mirasso, C.R. Permutation-information -theory approach to unveil delay dynamics from time-series analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 046212. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, M.C.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Fischer, I.; Mirasso, C.R. Time Scales of a Chaotic Semiconductor Laser with Optical Feedback Under the Lens of a Permutation Information Analysis. IEEE J. Quantum Electron 2001, 47, 252–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zunino, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Rosso, O.A. Distinguishing chaotic and stochastic dynamics from time series by using a multiscale symbolic approach. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 046210. [Google Scholar]
- FactoradicPermutation.hh. Available online: http://www.keithschwarz.com/interesting/code/factoradic-permutation/FactoradicPermutation (accessed 21st September 2011).
- Rostas, J.A.P.; Kavanagh, J.M.; Dodd, P.R.; Heath, J.W.; Powis, D.A. Mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. Mol. Neurobiol 1992, 5, 203–216. [Google Scholar]


© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Montani, F.; Rosso, O.A. Entropy-Complexity Characterization of Brain Development in Chickens. Entropy 2014, 16, 4677-4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/e16084677
Montani F, Rosso OA. Entropy-Complexity Characterization of Brain Development in Chickens. Entropy. 2014; 16(8):4677-4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/e16084677
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontani, Fernando, and Osvaldo A Rosso. 2014. "Entropy-Complexity Characterization of Brain Development in Chickens" Entropy 16, no. 8: 4677-4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/e16084677
APA StyleMontani, F., & Rosso, O. A. (2014). Entropy-Complexity Characterization of Brain Development in Chickens. Entropy, 16(8), 4677-4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/e16084677





