Effect of Counterion and Configurational Entropy on the Surface Tension of Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Surfactant and Electrolyte Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Helmholtz free energy
2.2. Configurational entropy
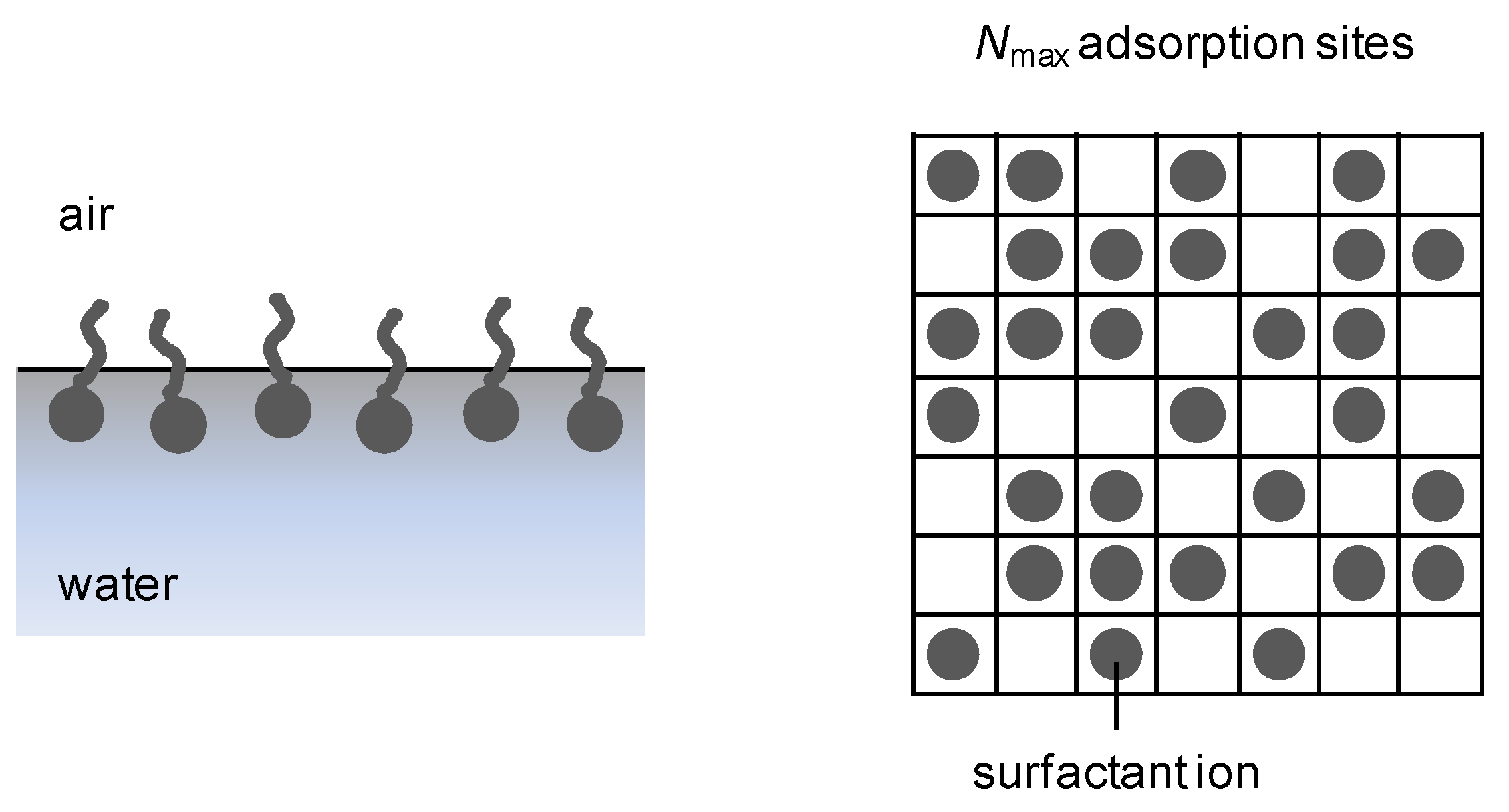
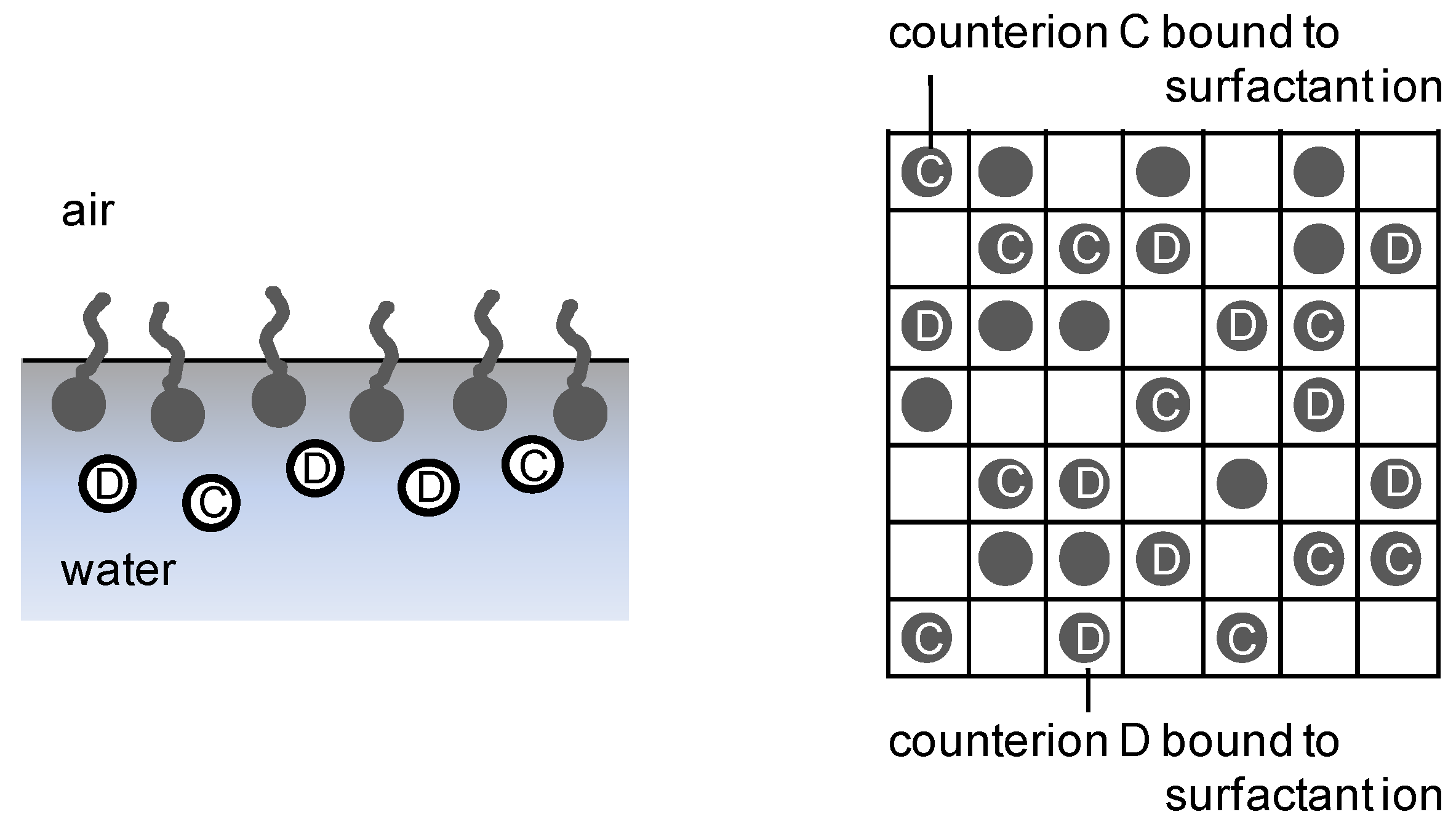
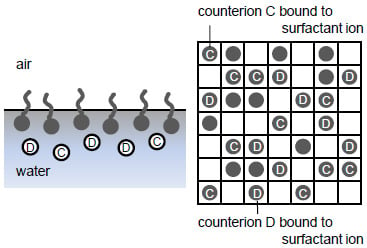
2.3. Surface charge density
2.4. Surface tension
2.5. Surface potential
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials

3.2. Measurements
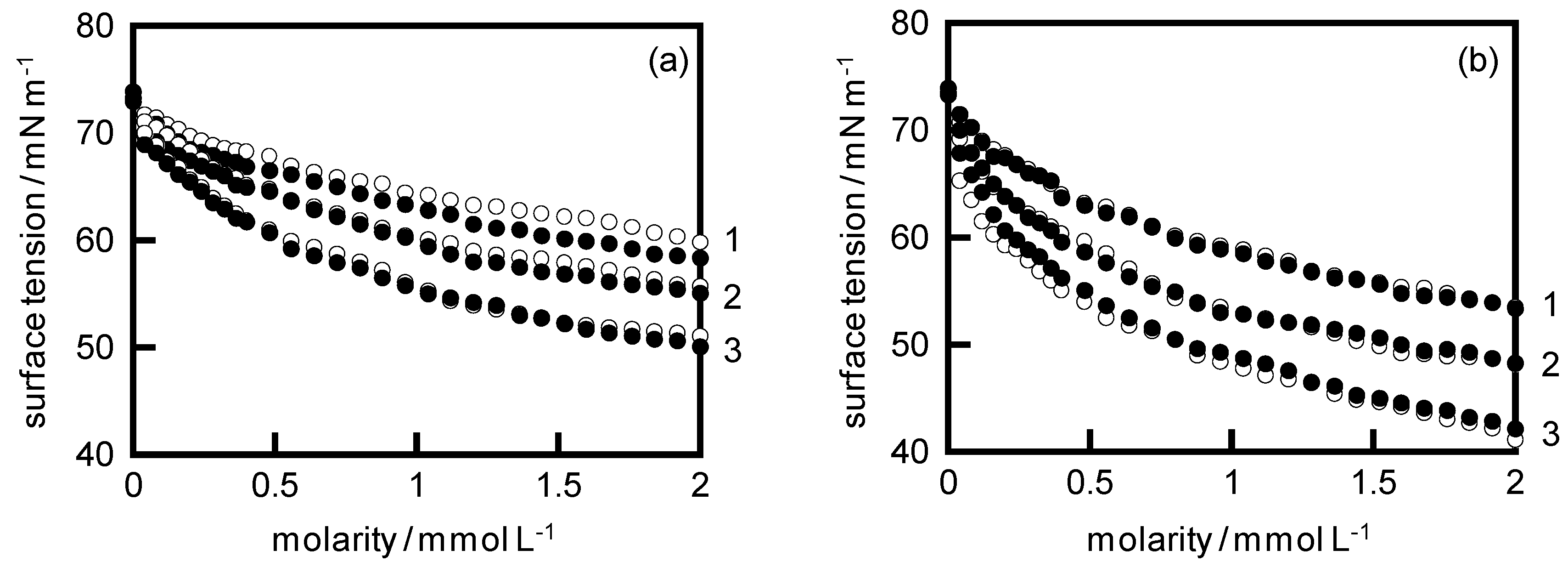
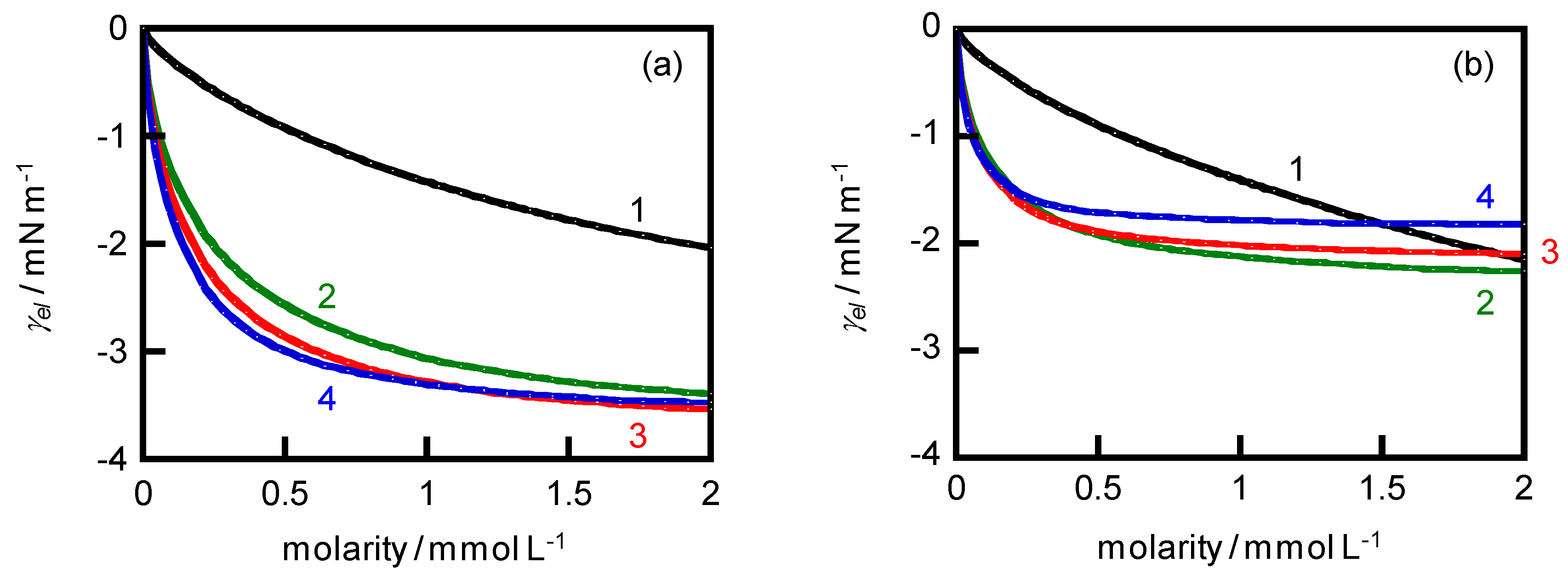
4. Results and Discussion

| System | KA/104 | KC | KD |
|---|---|---|---|
| DTAB-NaCl | 3.7 | 3.1 | 0.7 |
| DTAC-NaBr | 3.7 | 0.7 | 3.1 |

List of Notations
Surface tension of aqueous solution | |
Surface tension of pure water | |
Surface free energy attributable to electrical work | |
Surface free energy attributable to configurational entropy | |
Helmholtz free energy of charged air/water surface | |
Helmholtz free energy of uncharged air/water surface | |
Electrical work required for charging air/water surface | |
Entropic term in Helmholtz free energy | |
Configurational entropy | |
Surface area | |
Absolute temperature | |
Number of ion on air/water surface | |
Number of maximal adsorption sites on air/water surface | |
Number of all possible configurations of components on air/water surface | |
Number of possible configurations of surfactant ion on air/water surface | |
Number of possible configurations of couterions on air/water surface | |
Debye-Hückel parameter | |
Boltzmann constant | |
Relative dielectric constant of aqueous solution | |
Dielectric constant of vacuum | |
Elementary charge | |
Valence of ion | |
Avogadro’s number | |
Molarity of aqueous solution of component | |
Surface charge density | |
| , | Surface potential |
Reduced surface potential | |
Electrochemical potential of ion on air/water surface | |
Constant term in electrochemical potential of ion on air/water surface | |
Chemical potential of ion in bulk phase | |
Standard chemical potential of ion in bulk phase | |
Adsorption constant of surfactant ion | |
| , | Binding constant between adsorbed surfactant ion and counterion |
Maximal adsorption |
References
- Johansson, K.; Eriksson, J.C. and d/dT measurements on aqueous solutions of 1,1-electrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 49, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, L.; Das, K.P.; Chattoraj, D.K. Thermodynamics of adsorption of inorganic electrolytes at air/water and oil/water interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 121, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenborn, P.K.; Pugh, R.J. Surface tension and bubble coalescence phenomena of aqueous solutions of electrolytes. Langmuir 1995, 11, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matubayasi, N.; Matsuo, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Matuzawa, A. Thermodynamic quantities of surface formation of aqueous electrolyte solutions: 1. Aqueous solutions of NaCl, MgCl2, and LaCl3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 209, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Anwar-ul-Haq, S.; Siddiqi, B.S. Concentration and temperature dependence of surface parameters of some aqueous salt solutions. Colloids Surf. A 2006, 272, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, Y.; Flores-Mena, J.E. Surface tension of strong electrolytes. Europhys. Lett. 2001, 56, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H.; Matsubara, H. Surface tension of electrolyte solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 282, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, H.; Ozeki, S.; Ikeda, S. Adsorption of ions on aqueous surfaces of NaBr solutions of dodecyldimethylammonium chloride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 115, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góralczyk, D. Influence of inorganic electrolyte concentration on properties of anionic-cationic adsorption films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 179, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Para, G.; Warszyński, P. Influence of ionic strength on surface tension of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8383–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashimoto, K.; Takata, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Ikeda, N.; Matsubara, H.; Takiue, T.; Aratono, M.; Tanida, H.; Watanabe, I. Study on the surface density of surface-active substances through total-reflection X-ray absorption fine structure measurement. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8403–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralchevsky, P.A.; Danov, K.D.; Broze, G.; Mehreteab, A. Thermodynamics of ionic surfactant adsorption with account for the counterion binding: Effect of salts of various valency. Langmuir 1999, 15, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, V.L.; Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Broze, G.; Mehreteab, A. Comparison of the van der Waals and Frumkin adsorption isotherms for sodium dodecyl sulfate at various salt concentrations. Langmuir 2002, 18, 9106–9109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Para, G.; Jarek, E.; Warszynski, P. The Hofmeister series effect in adsorption of cationic surfactants—theoretical description and experimental results. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 122, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.B.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Lips, A. Adsorption and structure of the adsorbed layer of ionic surfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123–126, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagashira, H.; Takata, Y.; Hyono, A.; Ohshima, H. Adsorption of surfactant ions and binding of their counterions at an air/water interface. J. Oleo Sci. 2009, 58, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, H. Theory of Colloid and Interfacial Electric Phenomena; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Chapter 13. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima, H. Surface charge density/surface potential relationship for a spherical colloidal particle in a solution of general electrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 171, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratono, M.; Uryu, S.; Hayami, Y.; Motomura, K.; Matuura, R. Phase transition in the adsorbed films at water/air interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1984, 98, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, H.; Ikeda, N.; Takiue, T.; Aratono, M.; Bain, C.D. Interfacial films and wetting behavior of hexadecane on aqueous solutions of dodecyltrimethylannmonium bromide. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2249–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Takata, Y.; Tagashira, H.; Hyono, A.; Ohshima, H. Effect of Counterion and Configurational Entropy on the Surface Tension of Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Surfactant and Electrolyte Mixtures. Entropy 2010, 12, 983-995. https://doi.org/10.3390/e12040983
Takata Y, Tagashira H, Hyono A, Ohshima H. Effect of Counterion and Configurational Entropy on the Surface Tension of Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Surfactant and Electrolyte Mixtures. Entropy. 2010; 12(4):983-995. https://doi.org/10.3390/e12040983
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakata, Youichi, Hiroaki Tagashira, Atsushi Hyono, and Hiroyuki Ohshima. 2010. "Effect of Counterion and Configurational Entropy on the Surface Tension of Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Surfactant and Electrolyte Mixtures" Entropy 12, no. 4: 983-995. https://doi.org/10.3390/e12040983
APA StyleTakata, Y., Tagashira, H., Hyono, A., & Ohshima, H. (2010). Effect of Counterion and Configurational Entropy on the Surface Tension of Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Surfactant and Electrolyte Mixtures. Entropy, 12(4), 983-995. https://doi.org/10.3390/e12040983