Eradication of the Invasive Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio from a Large Lake: Lessons and Insights from the Tasmanian Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Common Carp in Tasmania
2.1. The Discovery of Common Carp in Tasmania
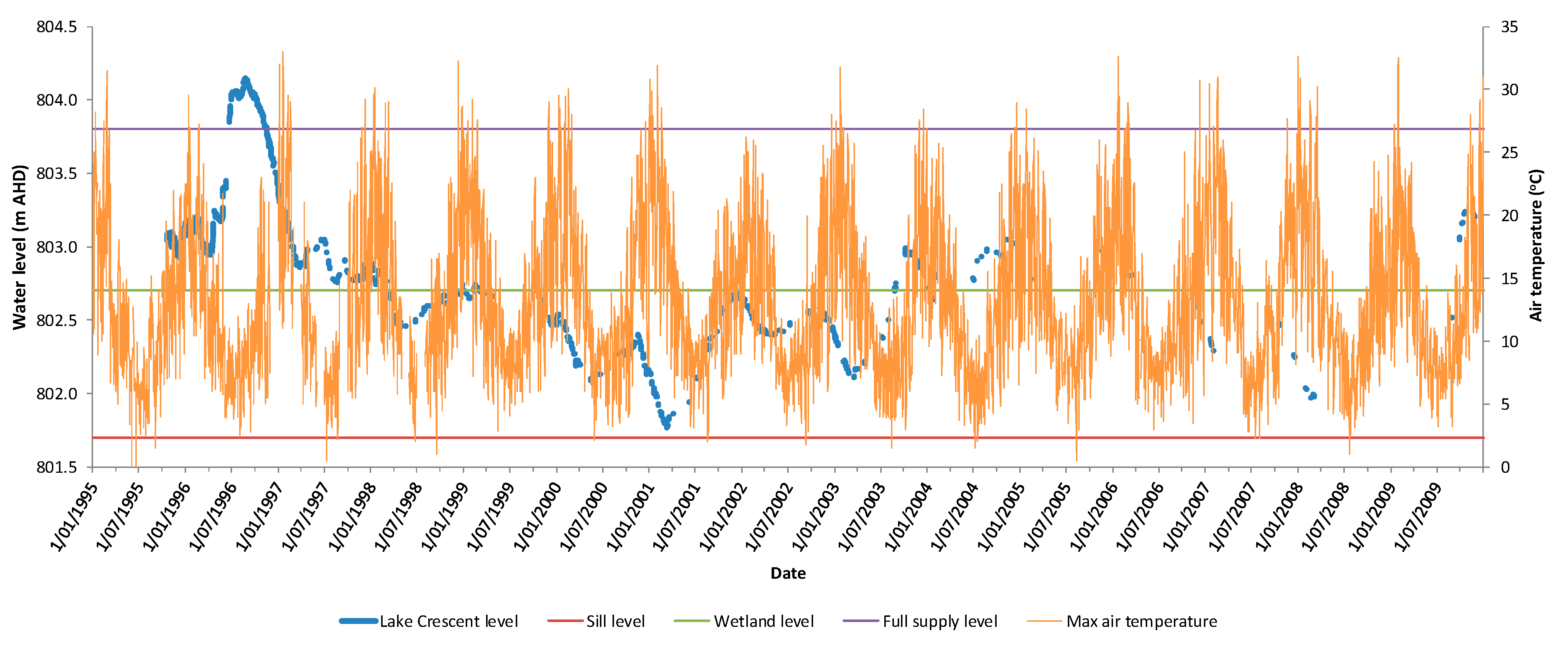
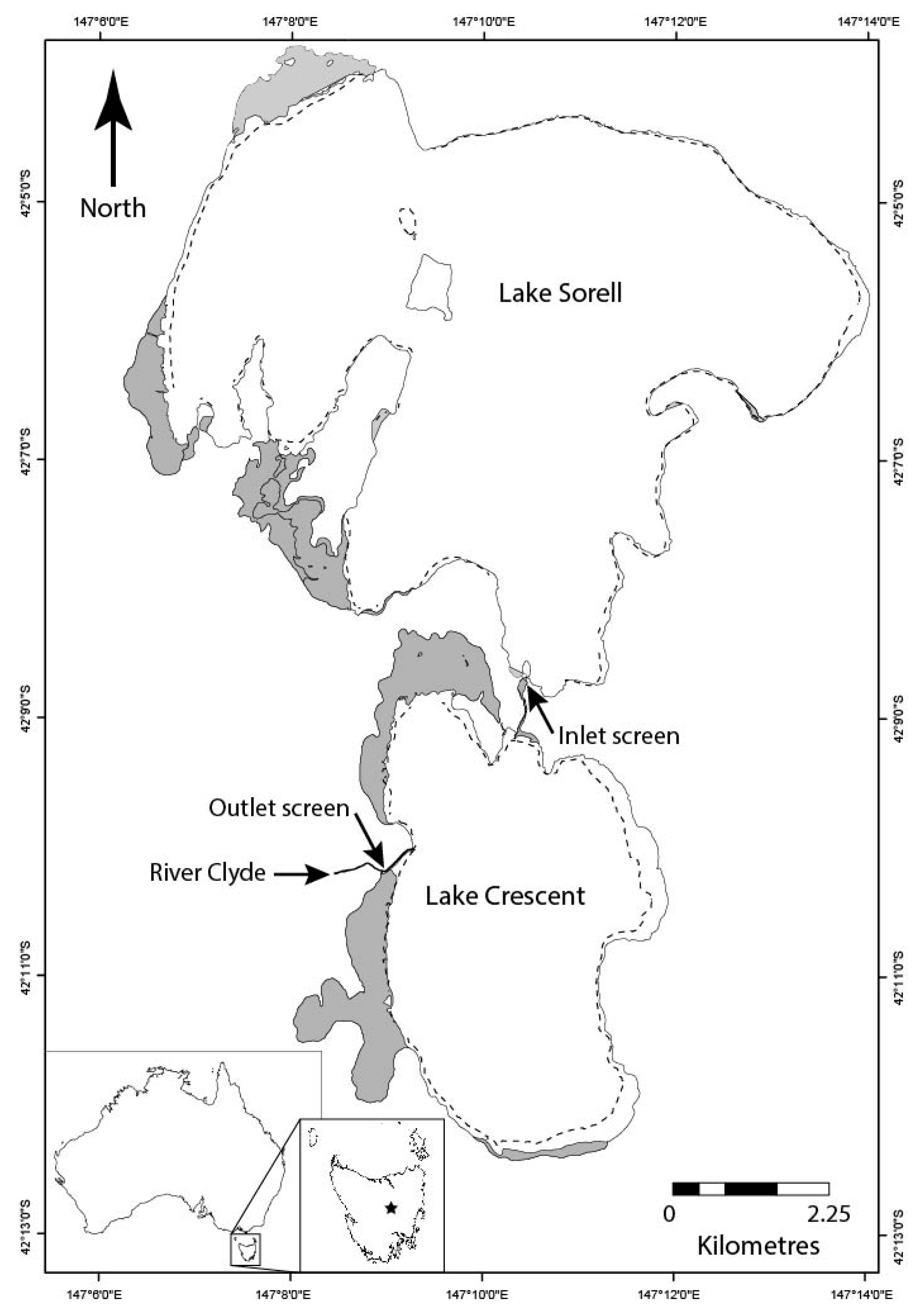
2.2. Lakes Crescent and Sorell
3. Developing a Strategy and Approach to Control Carp in Lakes Sorell and Crescent
3.1. Initial Assessment and Response
3.2. Creation and Implementation of the Adaptive Carp Management Plan
- Contain carp to the lakes Sorell/Crescent catchment;
- Reduce the existing carp population;
- Eradicate carp;
- Develop and implement a water management plan to ensure water supply for reliant townships and irrigators, while facilitating 1–3 above;
- Prevent introduction of carp to new water bodies and it’s reintroduction to cleared waters (from both inter and intrastate sources) and;
- Implement legislative and communication strategies to minimise damage to inland fisheries and tourism, while facilitating the above objectives in a timely fashion.
4. Following the Plan: Reducing Carp Abundance in Lake Crescent
4.1. Step 1: Containment
4.2. Step 2: The Carp Fish-Down and Associated Strategies
Population Estimation
5. Step 3: Preventing and Eliminating Recruitment
5.1. Spawning Prevention by Blocking Adults
5.2. Egg and Fry Removal
5.3. Juvenile Carp Removal
5.4. Recruitment Surveys
6. Step 4: Final Eradication and Monitoring
6.1. Opening the Lake to the Public
6.2. Continued Fish-Down Efforts
6.3. Ongoing Monitoring
7. Summary and Lessons Learned
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; The Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000; Available online: http://www.issg.org/pdf/publications/worst_100/english_100_worst.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Simberloff, D. Impacts of introduced species in the United States. Consequences 1996, 2, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Clavero, M.; García-Berthou, E. Invasive species are a leading cause of animal extinctions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, C.S. The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants, 1st ed.; Methuen & Co. Ltd.: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, B.; Steffen, W. An overview of the implications of global change for natural and managed terrestrial ecosystems. Conserv. Ecol. 1997, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, J.E.; Bruckerhoff, L.A.; Funkhouser, M.A.; Gemberling, A.R. Resistance to desiccation in aquatic invasive snails and implications for their overland dispersal. Hydrobiologia 2014, 741, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, S.J.; Stone, S.F.; Fernandez, L. The economic impacts of aquatic invasive species: A review of the literature. Agric. Resour. Econ. Rev. 2006, 35, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balian, E.V.; Segers, H.; Martens, K.; Lévéque, C. The freshwater animal diversity assessment: An overview of the results. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. Using boat electrofishing to estimate the abundance of invasive common carp in small Midwestern lakes. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2012, 32, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Bajer, P.G. Carp, common. In Encyclopedia of Biological Invasions; Simberloff, D., Rejmanek, M., Eds.; University of California Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, J.D. Carp (Cyprinus carpio) as a powerful invader in Australian waterways. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, J.; Brumley, A.; Gehrke, P. Managing the Impacts of Carp; Bureau of Rural Sciences: Canberra, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Winker, H.; Weyl, O.L.; Booth, A.J.; Ellender, B.R. Life history and population dynamics of invasive common carp, Cyprinus carpio, within a large turbid African impoundment. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.R.; Morison, A.K.; Hume, D.J. Effects of carp, Cyprinus carpio L., on communities of aquatic vegetation and turbidity of waterbodies in the lower Goulburn River basin. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1985, 36, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumley, A.R. Cyprinids of Australasia. In Cyprinid Fishes: Systematics, Biology and Exploitation; Winfield, I.J., Nelson, J.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 264–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. Effects of common carp on phosphorus concentrations, water clarity, and vegetation density: A whole system experiment in a thermally stratified lake. Hydrobiologia 2015, 746, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, S.S.; Usio, N.; Takamura, N.; Washitani, I. Contrasting impacts of invasive engineers on freshwater ecosystems: An experiment and meta-analysis. Oecologia 2009, 158, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Bajer, P.G. Case studies demonstrate that common carp can be sustainably reduced by exploiting source-sink dynamics in Midwestern lakes. Fishes 2020, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, J.W.; Patil, J.G.; Wisniewski, C. A Manual for Carp Control: The Tasmanian Model; Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre: Canberra, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski, C.D.; Diggle, J.D.; Patil, J.G. Managing and Eradicating Carp: A Tasmanian Experience. In New Zealand Invasive Fish Management Handbook; Collier, K.J., Grainger, N., Eds.; LERNZ (The University of Waikato) and Department of Conservation: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2015; pp. 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- IFS. Inland Fisheries Service, Carp Management Program Report Lakes Crescent and Sorell 1995–June 2004; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- DSEWPC. Interlaken Lakeside Reserve Ramsar Site Ecological Character Description; Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities: Canberra, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, S.A. Current Status and Ecology of the Golden Galaxias (Galaxias Auratus); Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Uytendaal, A. Water Clarity in Two Shallow Lake Systems of the Central Plateau, Tasmania, Australia. Honours Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Tyler, P.A. Tasmanian wetlands and their conservation. In The Conservation of Australian Wetlands; McComb, A.J., Lake, P.S., Eds.; Surrey Beatty & Sons Pty: Sydney, Australia, 1988; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, A.H.; Tracey, S.R.; Hartmann, K.; Patil, J.G. Exploiting seasonal habitat use of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio, in a lacustrine system for management and eradication. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Convention on Wetlands of International Importance, Especially as Waterfowl Habitat; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Heffer, D.K. Wetlands of Lakes Sorell and Crescent: Conservation and Management; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.M.H.; Tyler, P.A. Lakes Sorell and Crescent—A Tasmanian paradox. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1973, 58, 307–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, C. Habitat Preferences of the Endemic Hydrobiid Gastropod. “Austropyrgus” sp., and Other Aquatic Gastropods from Lakes Sorell and Crescent, Central Plateau, Tasmania. Honours Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, S.A. Conservation Biology of the Golden Galaxias (Galaxias auratus) (Pisces: Galaxiidae). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diggle, J.; Day, J.R.; Bax, N.J. Eradicating European Carp from Tasmania and Implications for National European Carp Eradication; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Donkers, P.; Patil, J.G.; Wisniewski, C.; Diggle, J.E. Validation of mark-recapture population estimates for invasive common carp, Cyprinus carpio, in Lake Crescent, Tasmania. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomford, M.; O’Brien, P. Eradication or control for vertebrate pests? Wildl. Soc. Bull. 1995, 23, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, R.M.; Donkers, P. An Examination of the Selectivity of Fishing Equipment in Relation to Controlling Carp (Cyprinus carpio) in Lakes Sorell and Crescent, 2nd ed.; Technical Report No. 2; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, A.; Wisniewski, C. The Use of Biotelemetry in Controlling the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) in Lakes Crescent and Sorell, 2nd ed.; Technical Report No. 1; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bajer, P.; Chizinski, C.; Sorensen, P. Using the judas technique to locate and remove wintertime aggregations of invasive common carp. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2011, 18, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamley, J.M. Review of Gillnet Selectivity. J. Fish. Board Can. 1975, 32, 1943–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkers, P.D. An Investigation into the Abundance of European Carp (Cyprinus carpio) in Lakes Sorell and Crescent; Technical Report No. 3; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, C.G.J. The yearly immigration of young plaice in the Limfjord from the German Sea. Rept Dan. Biol Sta 1896, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- McDowall, R.M. New Zealand Freshwater Fishes: A Natural History and Guide; Heinemann Reed MAF Publishing Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Brumley, A.R. Family Cyprinidae—Carps, minnows. In Freshwater Fishes of South-Eastern Australia, 2nd ed.; McDowall, R.M., Ed.; Reed: Chatswood, Australia, 1996; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Penne, C.R.; Pierce, C.L. Seasonal distribution, aggregation, and habitat selection of common carp in Clear Lake, Iowa. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2008, 137, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFS. Inland Fisheries Service, Carp Management Program Annual Report Lakes Crescent and Sorell July 2004–June 2005; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- IFS. Inland Fisheries Service, Carp Management Program Annual Report Lakes Crescent and Sorell July 2005–June 2006; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, J.G.; Wisniewski, W. Hypohysation: A Technique for Deployment of Odour Donor Fish to Control the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio), 2nd ed.; Technical Report No. 5; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Adair, B.J.; Purser, G.J.; Patil, J.G. Peripheral olfactory structures and maturity-related crypt receptor neuron kinetics in the olfactory epithelium of carp Cyprinus carpio (L.): Implications for carnal vulnerability and pest management. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Sorensen, P.W. Common carp implanted with prostaglandin F2α release a sex pheromone complex that attracts conspecific males in both the laboratory and field. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Johnson, N.S. Theory and application of semiochemicals in nuisance fish control. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 698–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IFS. Inland Fisheries Service, Carp Management Program Annual Report 2007–2008; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- IFS. Inland Fisheries Service, Carp Management Program Annual Report 2008–2009; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- IFS. Inland Fisheries Service, Carp Management Program Annual Report 2009–2010; Inland Fisheries Service: Hobart, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]




| Season * | No. of Carp Caught | Primary Technique ** | Secondary Technique *** | Annual Strategy | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
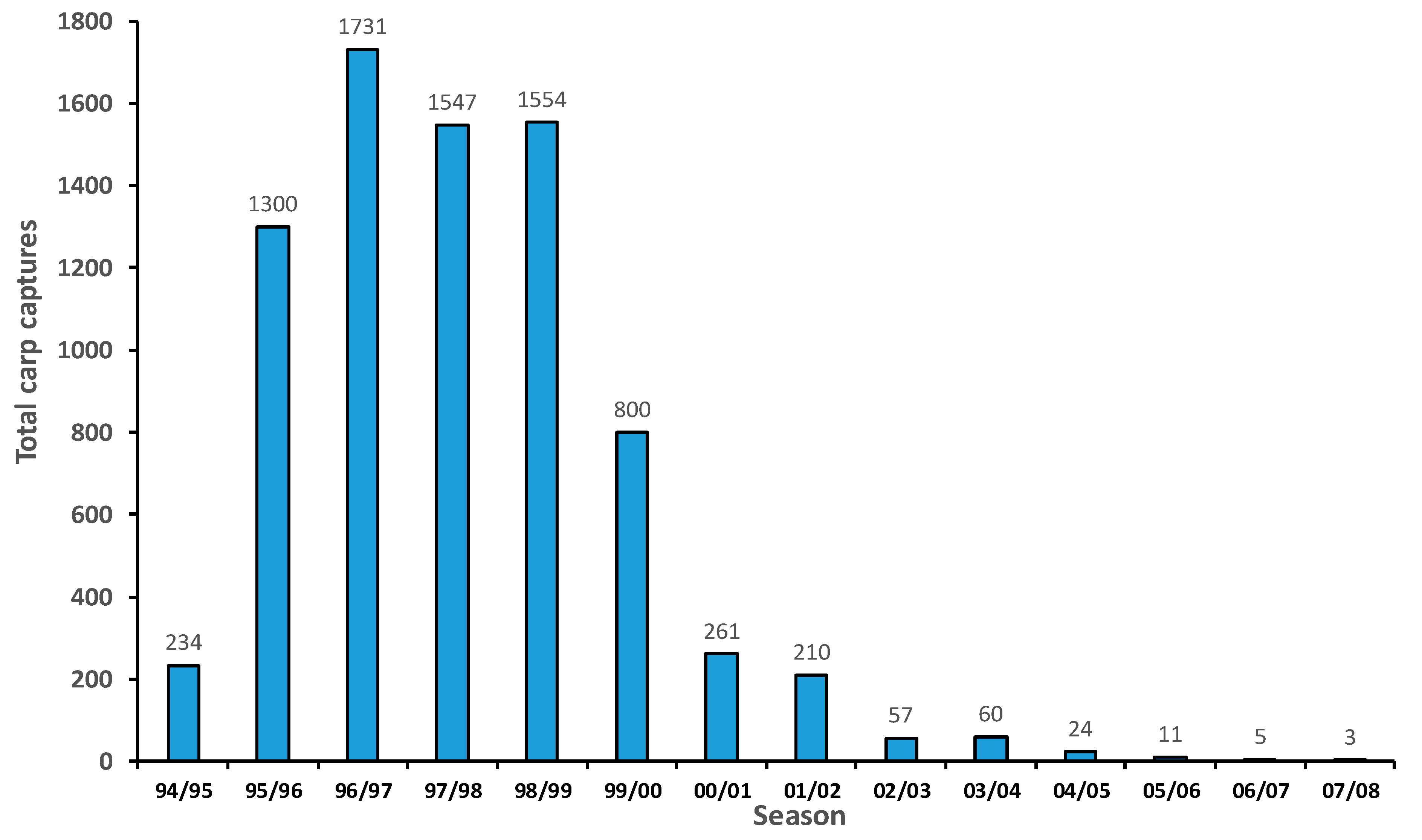
| 94/95 | 234 | SN, E | CT, LC, DS | First carp discovered in Lake Crescent on 1 Feb 1995. Carp contained to lakes Sorell and Crescent via the installation of screens at the Lake Crescent outlet. Populations of carp between the two lakes were isolated via the installation of screen structures at the Lake Sorell outlet. Lake Crescent closed to the public. Carp fish-down commenced, with seine nets and electro-fishing accounting for most carp caught. | |
| 95/96 ϯ | 1300 | SN, E | E, GN | CT, LC, DS | Seine nets and electro-fishing effort accounted for most carp caught. Monofilament gill nets starting to be used. |
| 96/97 ϯ | 1731 | GN+TC+E | FN | CT, LC, DS | Radio transmitter implanted carp deployed for the first time, which were used in conjunction with appropriately sized monofilament gill nets and electro-fishing. This technique accounted for most carp caught this season. |
| 97/98 | 1547 | GN+TC+E | FN | CT, LC, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. |
| 98/99 | 1554 | GN+TC+E | SN, FN, PN | CT, LC, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. Population estimate undertaken. |
| 99/00 | 800 | GN+TC, SN, E | FN | CT, LC, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. |
| 00/01 ϯ | 261 | GN+TC+E | FN | CT, LC, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. |
| 01/02 | 210 | GN+TC+E | SN, FN | CT, LC, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. |
| 02/03 | 57 | GN+TC+E | FN | CT, LC, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. |
| 03/04 | 60 | GN+TC+E | CT, LC, F, DS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. Second population estimate undertaken. Fences with inbuilt traps were installed in front of marshes to prevent access into spawning grounds. | |
| 04/05 | 24 | TP | GN, TC, FN, E | CT, F, DS, RS | Traps built into fences accounted for most carp caught. Lake Crescent re-opened to the public. Annual carp recruitment surveys begin. |
| 05/06 | 11 | GN+TC+E | TP, FN | CT, F, DS, RS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. |
| 06/07 | 5 | GN+TC+E | CT, F, DS, RS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. | |
| 07/08 | 3 | GN+TC+E | CT, F, DS, RS | The combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing accounted for most carp caught. Last carp caught in Lake Crescent in Dec 2007. | |
| 08/09 | 0 | GN+TC+E | CT, F, DS, RS | Combination of monofilament gillnets, transmitter carp and electro-fishing effort applied. | |
| 09/10 | 0 | CT, F, DS, RS | All remaining active transmitter carp removed from the lake. Carp eradication in Lake Crescent declared. | ||
| Total | 7797 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yick, J.L.; Wisniewski, C.; Diggle, J.; Patil, J.G. Eradication of the Invasive Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio from a Large Lake: Lessons and Insights from the Tasmanian Experience. Fishes 2021, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6010006
Yick JL, Wisniewski C, Diggle J, Patil JG. Eradication of the Invasive Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio from a Large Lake: Lessons and Insights from the Tasmanian Experience. Fishes. 2021; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleYick, Jonah L., Chris Wisniewski, John Diggle, and Jawahar G. Patil. 2021. "Eradication of the Invasive Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio from a Large Lake: Lessons and Insights from the Tasmanian Experience" Fishes 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6010006
APA StyleYick, J. L., Wisniewski, C., Diggle, J., & Patil, J. G. (2021). Eradication of the Invasive Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio from a Large Lake: Lessons and Insights from the Tasmanian Experience. Fishes, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6010006






