Internet Usage among Senior Citizens: Self-Efficacy and Social Influence Are More Important than Social Support
Abstract
1. Introduction
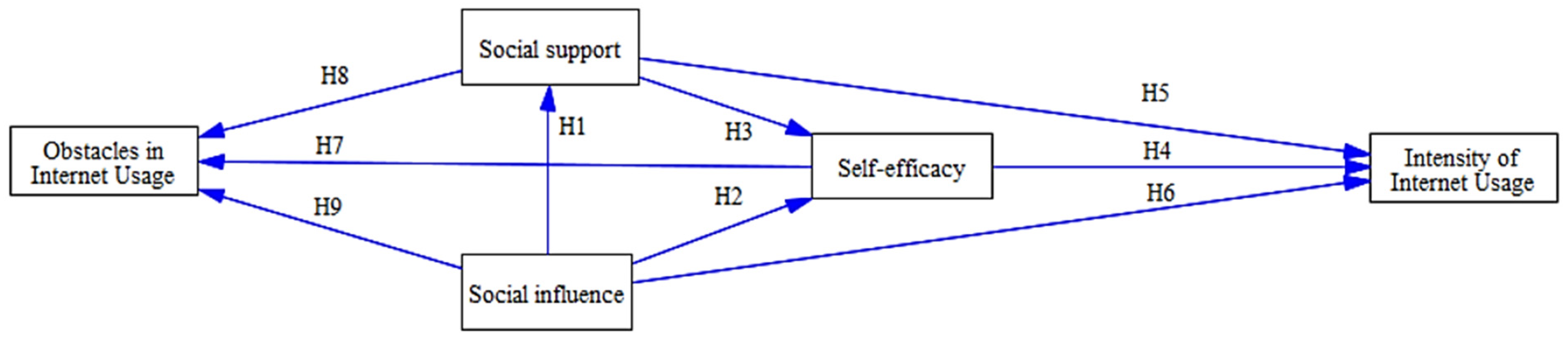
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
3. Methodology
3.1. Data
3.2. Research Instrument
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Sample Characteristics
4.2. Descriptive Statistics
4.3. Exploratory Factor Analysis
4.4. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
4.5. Structural Equation Modelling
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Summary of the Research
6.2. Theoretical Implications
6.3. Practical Implications
6.4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barišić, A.F.; Pejić Bach, M.; Miloloža, I. Human Resources Information Systems: Transactional and Strategic Paradigm. ENTRENOVA—ENTerprise REsearch InNOVAtion 2018, 4, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Barišić, A.F.; Rybacka Barišić, J.; Miloloža, I. Digital Transformation: Challenges for Human Resources Management. ENTRENOVA—ENTerprise REsearch InNOVAtion 2022, 7, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.R.; Feng, Y. Trajectory tracking of changes digital divide prediction factors in the elderly through machine learning. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R. Is There a Barrier between Seniors and Smartphone Use in The Internet Age? A Study of Digital Disconnection among Older Adults. SHS Web Conf. 2023, 155, 03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sum, S.; Mathews, R.M.; Hughes, I.; Campbell, A. Internet use and loneliness in older adults. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Houwelingen, C.T.; Ettema, R.G.; Antonietti, M.G.; Kort, H.S. Understanding older people’s readiness for receiving telehealth: Mixed-method study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2008, 20, e8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B. Older Chinese the Internet and well-being. Care Manag. J. 2007, 8, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaß, W. The elderly and the Internet: How senior citizens deal with online privacy. In Privacy Online: Perspectives on Privacy and Self-Disclosure in the Social Web; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Croatian Bureau of Statistics. Population Estimate of Republic of Croatia. 2022. Available online: https://podaci.dzs.hr/en/statistics/population/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Drobne, S.; Bogataj, M. Migration flows through the lens of human resource ageing. Bus. Syst. Res. Int. J. Soc. Adv. Innov. Res. Econ. 2022, 13, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejašmić, I.; Toskić, A. Starenje stanovništva u Hrvatskoj–sadašnje stanje i perspektive. Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. 2013, 75, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbin Praničević, D.; Peterlin, J.; Bućan, M.J. Do older people benefit from digital services? DIEM Dubrov. Int. Econ. Meet. 2017, 3, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bosilj Vukšić, V.; Milanović Glavan, L.; Ivančić, L. Digital Technology in the Health Care and Social Care of Older Adults. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on the Economics of Decoupling (ICED), Zagreb, Croatia, 30 November–1 December 2022; pp. 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Rashotte, L. Social Influence. In The Blackwell Encyclopedia of Sociology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Friedkin, N.E.; Johnsen, E.C. Social influence and opinions. J. Math. Sociol. 1990, 15, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vries, H.D.; Backbier, E.; Kok, G.; Dijkstra, M. The Impact of Social Influences in the Context of Attitude Self-Efficacy Intention and Previous Behavior as Predictors of Smoking Onset 1. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1995, 25, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of Thought and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Maddux, J.E.; Gosselin, J.T. Self-efficacy. In Handbook of Self and Identity; Leary, M.R., Tangney, J.P., Eds.; The Guilford Press: Ney Work City, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 198–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, A.; Wessels, S. Self-Efficacy; W.H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Davison, R.M. Social support, source credibility, social influence, and impulsive purchase behavior in social commerce. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2019, 23, 297–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.E. Social support: A review. In The Oxford Handbook of Health Psychology; Friedman, H.S., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 189–214. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Wei, J.; Chan, C.M.; Chia, A.B. Senior citizens’ self-efficacy for ICT use: The influence of gender, social influence and social support. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Business (ICEB), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- de Veer, A.J.; Peeters, J.M.; Brabers, A.E.; Schellevis, F.G.; Rademakers, J.J.; Francke, A.L. Determinants of the intention to use e-Health by community dwelling older people. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2015, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.J.P.-A.; Rai, A.; Keil, M. Addressing digital inequality for the socioeconomically disadvantaged through government initiatives: Forms of capital that affect ICT utilisation. Inf. Syst. Res. 2011, 22, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastin, M.S.; LaRose, R. Internet self-efficacy and the psychology of the digital divide. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 2000, 6, JCMC611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrari, H.; Ulrich, F.; Andersen, H.B. Concerns and trade-offs in information technology acceptance: The balance between the requirement for privacy and the desire for safety. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2020, 47, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamari, J.; Koivisto, J. Working out for likes: An empirical study on social influence in exercise gamification. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 50, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Chun, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J. Internet use and well-being in older adults. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Rudkin, L. Social contact socio-economic status and the health status of older Malaysians. Gerontologist 2000, 40, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.S.; Shillair, R.; Cotten, S.R. Social support and “playing around”: An examination of how older adults acquire digital literacy with tablet computers. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2017, 36, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, Y.; Bradley, M.D.; Hodgson, F.; Lloyd, A.D. Learning to use new technologies by older adults: Perceived difficulties, experimentation behaviour and usability. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy mechanisms in human agency. Am. Psychol. 1982, 37, 122–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, H.S. Privacy concern and online transactions: The impact of internet self-efficacy and internet involvement. J. Consum. Mark. 2014, 31, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Minami, C.; Matsuyama, T. Social influence on innovation resistance in internet banking services. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 45, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Pecino, R.; Matos, A.D.; Silva, P. Portuguese older people and the Internet: Interaction, uses, motivations, and obstacles. Communications 2013, 38, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, A.; Nazarian, Z.; Gharibshaeyan, R. An explanation for internet use obstacles concerning e-learning in Iran. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2013, 14, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biljon, J.; Renaud, K. A qualitative study of the applicability of technology acceptance models to senior mobile phone users. In ER Workshops 2008 LNCS 5232; Song, I.-Y., Piattini, M., Phoebe Chen, Y.-P., Hartman, S., Grandi, F., Trujillo, J., Opdahl, A.L., Ferri, F., Grifoni, P., Caschera, M.C., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, J.; Kadylak, T.; Makki, T.W.; Rikard, R.V.; Cotton, S.R. Catalyst to connection: When technical difficulties lead to social support for older adults. Am. Behav. Sci. 2018, 62, 1167–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Mermelstein, R.; Kamarck, T.; Hoberman, H.M. Measuring the functional components of social support. In Social Support: Theory, Research and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Szkody, E.; Stearns, M.; Stanhope, L.; McKinney, C. Stress-buffering role of social support during COVID-19. Fam. Process 2021, 60, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Data. Available online: https://data.oecd.org/pop/elderly-population.htm (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division World Population Ageing 2015 (ST/ESA/SER.A/390). 2015. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/ageing/WPA2015_Report.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Taylor, S.; Todd, P.A. Understanding Information Technology Usage: A Test of Competing Models. Inf. Syst. Res. 1995, 6, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Babin, B.J.; Krey, N. Covariance-Based Structural Equation Modeling in the Journal of Advertising: Review and Recommendations. J. Advert. 2017, 46, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejić Bach, M.; Starešinić, B.; Omazić, M.A.; Aleksić, A.; Seljan, S. M-Banking quality and bank reputation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, J. The Integration of EFA and CFA: One Method of Evaluating the Construct Validity. Glob. J. Hum. Soc. Sci. 2015, 15, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.L.; Gillaspy, J.A.; Purc-Stephenson, R. Reporting practices in confirmatory factor analysis: An overview and some recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2009, 14, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoe, S.L. Issues and procedures in adopting structural equation modelling technique. J. Quant. Methods 2008, 3, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, A.B.; Osborne, J.W. Best practices in exploratory factor analysis: Four recommendations for getting the most from your analysis. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2005, 10, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Amblee, N.; Bui, T.H. The influence of social proof in online shopping: The effect of electronic word of mouth on sales of digital microproducts. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2011, 16, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobas, J.E.; Clyde, L.A. Adults learning to use the Internet: A longitudinal study of attitudes and other factors associated with intended Internet use. Libr. Inf. Sci. Res. 2000, 22, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, W.O.; Netemeyer, R.G.; Teel, J.E. Measurement of consumer susceptibility to interpersonal influence. J. Consum. Res. 1989, 15, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, P.J.-H. Top persuader prediction for social networks. MIS Q. 2018, 42, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.C.-Y.; Lee, M.K.O. Digital inclusiveness—Longitudinal study of Internet adoption by older adults. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2006, 22, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokisch, M.R.; Schmidt, L.I.; Doh, M.; Marquard, M.; Wahl, H.W. The role of internet self-efficacy, innovativeness and technology avoidance in breadth of internet use: Comparing older technology experts and non-experts. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 111, 106408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.T. Obstacles to social networking website use among older adults. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamin, S.T.; Beyer, A.; Lang, F.R. Social support is associated with technology use in old age. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2020, 18, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, J.P.; Boerner, K.; Horowitz, A. Good to have but not to use. Differential impact of perceived and received support on well-being. J. Soc. Pers. Relat. 2006, 23, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, M.; Lakey, B. Where is the support in perceived support? The role of generic relationship satisfaction and enacted support in perceived support’s relation to low distress. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 2003, 22, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, T.; Alexander, S.; Firestone, I.J.; Baltes, B.B. Self-efficacy and independence from social influence: Discovery of an efficacy–difficulty effect. Soc. Influ. 2006, 1, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Taieh, E.M.; AlHadid, I.; Masa’deh, R.E.; Alkhawaldeh, R.S.; Khwaldeh, S.; Alrowwad, A.A. Factors Affecting the Use of Social Networks and Its Effect on Anxiety and Depression among Parents and Their Children: Predictors Using ML, SEM and Extended TAM. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunady, J.; Pisár, P.; Vugec, D.S.; Pejić Bach, M. Digital Transformation in European Union: North is leading, and South is lagging behind. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Proj. Manag. 2022, 10, 58–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Construct | Code | Research Item | Item Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-efficacy of Internet Usage (Guan et al., 2017 [22]; Taylor and Todd, 1995 [44]; Hsieh, Rai and Keil, 2011 [24]) | C11_1 | You feel comfortable using the Internet on your own. | Likert scale (1—do not agree, 7—fully agree) |
| C11_2 | You can easily operate the Internet on your own. | ||
| C11_3 | You feel comfortable using the Internet even if no one is around you to tell you how to use it. | ||
| Social Influence on Internet Usage (Guan et al., 2017 [22]; Taylor and Todd, 1995 [44]; Hsieh, Rai and Keil, 2011 [24]) | C11_4 | Your family thinks that you should use the Internet. | Likert scale (1—do not agree, 7—fully agree) |
| C11_5 | Your relatives think that you should use the Internet. | ||
| C11_6 | Your friends think that you should use the Internet. | ||
| Social Support for Internet Usage (Guan et al., 2017 [22]; Wu and Rudkin, 2000 [30]; Hsieh, Rai and Keil, 2011 [24]) | C11_7 | You have someone to help solve Internet-related problems. | Likert scale (1—do not agree, 7—fully agree) |
| C11_8 | You have friends or family to provide the necessary help to use the Internet. | ||
| C11_9 | You have friends and family to help with solving Internet-related problems. | ||
| C11_10 | You are supported by those around you when you have difficulty using the Internet. | ||
| Obstacles to Internet Usage | C1_sum | The number of obstacles in Internet Usage that the respondent faced in the last 3 months such as: Lack of knowledge about using the device; Not having anyone to help to install and use the device; The appearance of the applications is complicated for the respondent and is not suitable for a user of the third age; Respondent does not understand certain functions because they are in a foreign language; Too much distracting content (advertisements, etc.); Poorly adapted for the vision, hearing and motor skills of older people | 0—no obstacles 1—one obstacle 2—two obstacles 3—three and more obstacles |
| Intensity of Internet Usage | C7_sum | The number of purposes that the Internet was used for by the respondent in the last 3 months such as: Communication with family and friends via video calls (ZOOM, Skype, Teams); Communication with family and friends via e-mail and messaging applications (Viber, WhatsApp, Messenger, etc.); Social networks (Facebook, etc.); News about everyday events (portals, magazines, etc.); For paying bills and other financial transactions; Ordering medical examinations in health institutions; For ordering medicines and referrals, exchanging information with the family doctor; Internet shopping; To perform work (paid or volunteering); For writing and other forms of creative expression; For editing files (video, audio, photo); For watching and listening to movies, music and photos; For learning (independent or e-learning); Using the eCitizen platform service; Using the service of the health care platform | 0—no form of use 1—one form of use 2—two forms of use 3—three and more forms of use |
| Characteristics | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender * | ||
| Male | 273 | 38.9 |
| Female | 428 | 61.1 |
| Age (years) * | ||
| 65–69 | 248 | 35.4 |
| 70–74 | 197 | 28.1 |
| 75–79 | 142 | 20.3 |
| 80–84 | 85 | 12.1 |
| ≥85 | 29 | 4.1 |
| Size of the settlement * | ||
| Urban settlement | 399 | 56.9 |
| Suburban settlement | 113 | 16.1 |
| Rural settlement | 182 | 26.0 |
| A house outside the settlement | 7 | 1.0 |
| Education * | ||
| No education or less than eight grades of primary school | 47 | 6.7 |
| Elementary school (eight-year) | 81 | 11.6 |
| High school (three-year or four-year) | 349 | 49.8 |
| Higher education | 224 | 32.0 |
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Dev. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-efficacy of Internet Usage | |||||
| C11_1 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 4.11 | 2.355 |
| C11_2 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 4.03 | 2.359 |
| C11_3 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 3.98 | 2.348 |
| Social Influence on Internet Usage | |||||
| C11_4 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 4.12 | 2.186 |
| C11_5 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 3.93 | 2.174 |
| C11_6 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 3.77 | 2.134 |
| Social Support for Internet Usage | |||||
| C11_7 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 4.60 | 2.284 |
| C11_8 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 4.62 | 2.315 |
| C11_9 | 701 | 1 | 7 | 4.58 | 2.335 |
| Internet Usage Obstacles | Internet Usage Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of Obstacles | N | % | # of Usages | N | % |
| 0—no obstacles | 258 | 36.8% | 0—no usage | 295 | 42.1% |
| 1—one obstacle | 279 | 39.8% | 1—one form of use | 42 | 6.0% |
| 2—two obstacles | 81 | 11.6% | 2—two forms of use | 55 | 7.8% |
| 3—three and more | 83 | 11.8% | 3—three and more | 309 | 44.1% |
| Total | 701 | 100% | Total | 701 | 100% |
| Variable | C11_1 | C11_2 | C11_3 | C11_4 | C11_5 | C11_6 | C11_7 | C11_8 | C11_9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11_1 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| C11_2 | 0.877 * | 1.000 | |||||||
| C11_3 | 0.875 * | 0.874 * | 1.000 | ||||||
| C11_4 | 0.545 * | 0.549 * | 0.548 * | 1.000 | |||||
| C11_5 | 0.519 * | 0.514 * | 0.517 * | 0.771 * | 1.000 | ||||
| C11_6 | 0.568 * | 0.560 * | 0.579 * | 0.720 * | 0.739 * | 1.000 | |||
| C11_7 | 0.524 * | 0.521 * | 0.509 * | 0.581 * | 0.512 * | 0.507 * | 1.000 | ||
| C11_8 | 0.500 * | 0.507 * | 0.489 * | 0.563 * | 0.525 * | 0.484 * | 0.832 * | 1.000 | |
| C11_9 | 0.521 * | 0.524 * | 0.500 * | 0.570 * | 0.526 * | 0.504 * | 0.826 * | 0.830 * | 1.000 |
| Item | Item Loadings | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| C11_1 | 0.881 | ||
| C11_2 | 0.878 | ||
| C11_3 | 0.880 | ||
| C11_4 | 0.795 | ||
| C11_5 | 0.846 | ||
| C11_6 | 0.794 | ||
| C11_7 | 0.854 | ||
| C11_8 | 0.868 | ||
| C11_9 | 0.856 | ||
| C11_10 | 0.593 | 0.509 | |
| ML Estimate | Acceptable Value | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chi-square (χ2) | 701 | - | - |
| Degrees of freedom (df) | 43.438 | - | - |
| p-value | 24 | - | - |
| Chi-square (χ2) | 0.009 | - | - |
| CFI | 0.997 | >0.94 | [46] |
| TLI | 0.995 | >0.95 | [45] |
| GFI | 0.987 | >0.95 | [45] |
| RMSEA | 0.034 | <0.08 | [45] |
| SRMR | 0.017 | <0.05 | [45] |
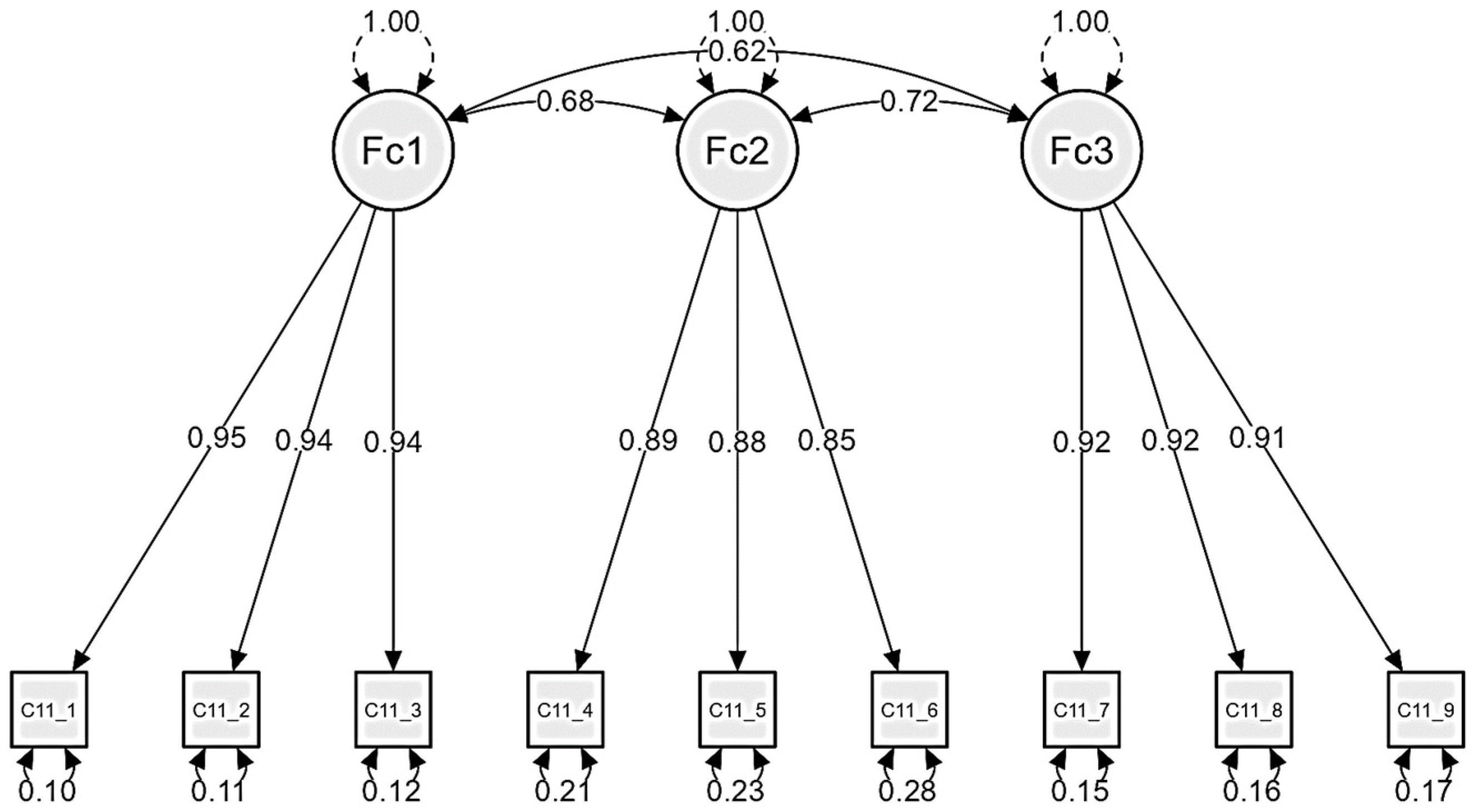
| Factor | Indicator | Symbol | Est. | Std. Est. | Std. Error | z-Value | R-Squared | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-efficacy | C11_1 | λ11 | 2.233 | 0.949 | 0.066 | 33.600 * | 0.900 | 0.891 | 0.976 |
| C11_2 | λ12 | 2.226 | 0.944 | 0.067 | 33.315 * | 0.892 | |||
| C11_3 | λ13 | 2.201 | 0.938 | 0.067 | 32.920 * | 0.880 | |||
| Social influence | C11_4 | λ21 | 1.942 | 0.889 | 0.066 | 29.305 * | 0.790 | 0.760 | 0.972 |
| C11_5 | λ22 | 1.913 | 0.880 | 0.066 | 28.847 * | 0.775 | |||
| C11_6 | λ23 | 1.803 | 0.846 | 0.067 | 27.091 * | 0.715 | |||
| Social support | C11_7 | λ31 | 2.103 | 0.921 | 0.066 | 31.626 * | 0.849 | 0.841 | 0.974 |
| C11_8 | λ32 | 2.121 | 0.917 | 0.068 | 31.363 * | 0.840 | |||
| C11_9 | λ33 | 2.131 | 0.913 | 0.068 | 31.162 * | 0.834 |
| Self-Efficacy | Social Influence | Social Support | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-efficacy | 0.891 | ||
| Social influence | 0.465 | 0.760 | |
| Social support | 0.380 | 0.520 | 0.841 |
| Indicator | Estimated Value | Recommended Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 701 | - | - |
| Chi-square (χ2) | 58.820 | - | - |
| Degrees of freedom (df) | 36 | - | - |
| p-value | 0.010 | - | - |
| Chi-square statistic ratio (χ2/df) | 1.634 | <2 | [45] |
| CFI | 0.997 | >0.94 | [46] |
| TLI | 0.995 | >0.95 | [45] |
| NNFI | 0.995 | >0.9 | [50] |
| NFI | 0.992 | >0.9 | [50] |
| RMSEA | 0.030 | <0.07 | [45] |
| SRMR | 0.014 | <0.08 | [45] |
| Predictor | Outcome | Estimate (Std. Error) | z-Value | p | R-Squared | Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social influence | Self-efficacy | 0.522 (0.051) | 10.230 | <0.001 *** | 0.500 | H1 |
| Social support | Self-efficacy | 0.277 (0.047) | 5.823 | <0.001 *** | H2 | |
| Social support | Social influence | 0.694 (0.033) | 20.830 | <0.001 *** | 0.517 | H3 |
| Self-efficacy | Intensity of Internet usage | 0.912 (0.035) | 26.046 | <0.001 *** | 0.720 | H4 |
| Social influence | Intensity of Internet usage | −0.052 (0.043) | −1.209 | 0.227 | H5 | |
| Social support | Intensity of Internet usage | 0.025 (0.037) | 0.656 | 0.512 | H6 | |
| Self-efficacy | Obstacles to Internet usage | −0.279 (0.059) | −4.723 | <0.001 *** | 0.039 | H7 |
| Social influence | Obstacles to Internet usage | 0.177 (0.077) | 2.312 | 0.021 ** | H8 | |
| Social support | Obstacles to Internet usage | −0.008 (0.066) | −0.120 | 0.905 | H9 |
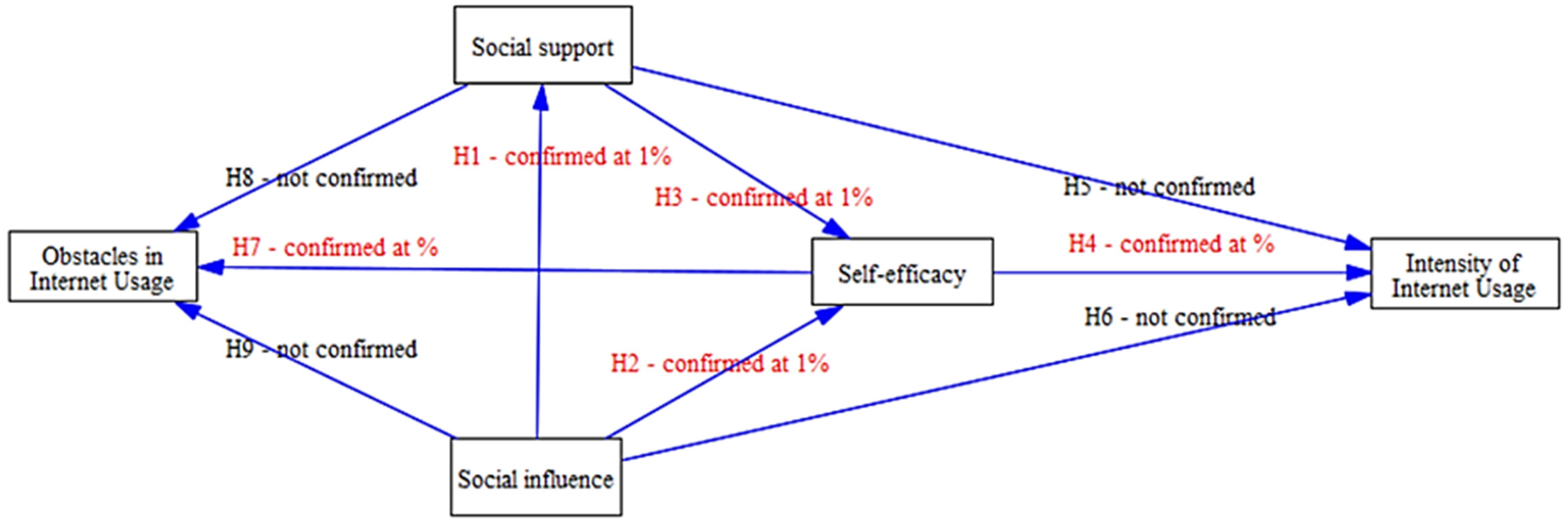
| Hypothesis | Predictor | Outcome | Relationship | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Social influence | Self-efficacy | Positive at 1% | H1—Confirmed |
| H2 | Social support | Self-efficacy | Positive at 1% | H2—Confirmed |
| H3 | Social influence | Social support | Positive at 1% | H3—Confirmed |
| H4 | Self-efficacy | Intensity of Internet usage | Positive at 1% | H4—Confirmed |
| H5 | Social influence | Intensity of Internet usage | Not significant | H5—Not confirmed |
| H6 | Social support | Intensity of Internet usage | Not significant | H6—Not confirmed |
| H7 | Self-efficacy | Obstacles to Internet usage | Negative at 1% | H7—Confirmed |
| H8 | Social influence | Obstacles to Internet usage | Positive at 5% | H8—Not confirmed |
| H9 | Social support | Obstacles to Internet usage | Not significant | H9—Not confirmed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pejić Bach, M.; Ivančić, L.; Bosilj Vukšić, V.; Stjepić, A.-M.; Milanović Glavan, L. Internet Usage among Senior Citizens: Self-Efficacy and Social Influence Are More Important than Social Support. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2023, 18, 1463-1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer18030074
Pejić Bach M, Ivančić L, Bosilj Vukšić V, Stjepić A-M, Milanović Glavan L. Internet Usage among Senior Citizens: Self-Efficacy and Social Influence Are More Important than Social Support. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research. 2023; 18(3):1463-1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer18030074
Chicago/Turabian StylePejić Bach, Mirjana, Lucija Ivančić, Vesna Bosilj Vukšić, Ana-Marija Stjepić, and Ljubica Milanović Glavan. 2023. "Internet Usage among Senior Citizens: Self-Efficacy and Social Influence Are More Important than Social Support" Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 18, no. 3: 1463-1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer18030074
APA StylePejić Bach, M., Ivančić, L., Bosilj Vukšić, V., Stjepić, A.-M., & Milanović Glavan, L. (2023). Internet Usage among Senior Citizens: Self-Efficacy and Social Influence Are More Important than Social Support. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 18(3), 1463-1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer18030074







