Systemic Arterial Hypertension and Factors Associated with Blood Pressure Dysregulation in Companion Animals
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Blood Pressure
3. Systemic Blood Pressure Regulation Systems
3.1. Sympathetic Nervous System
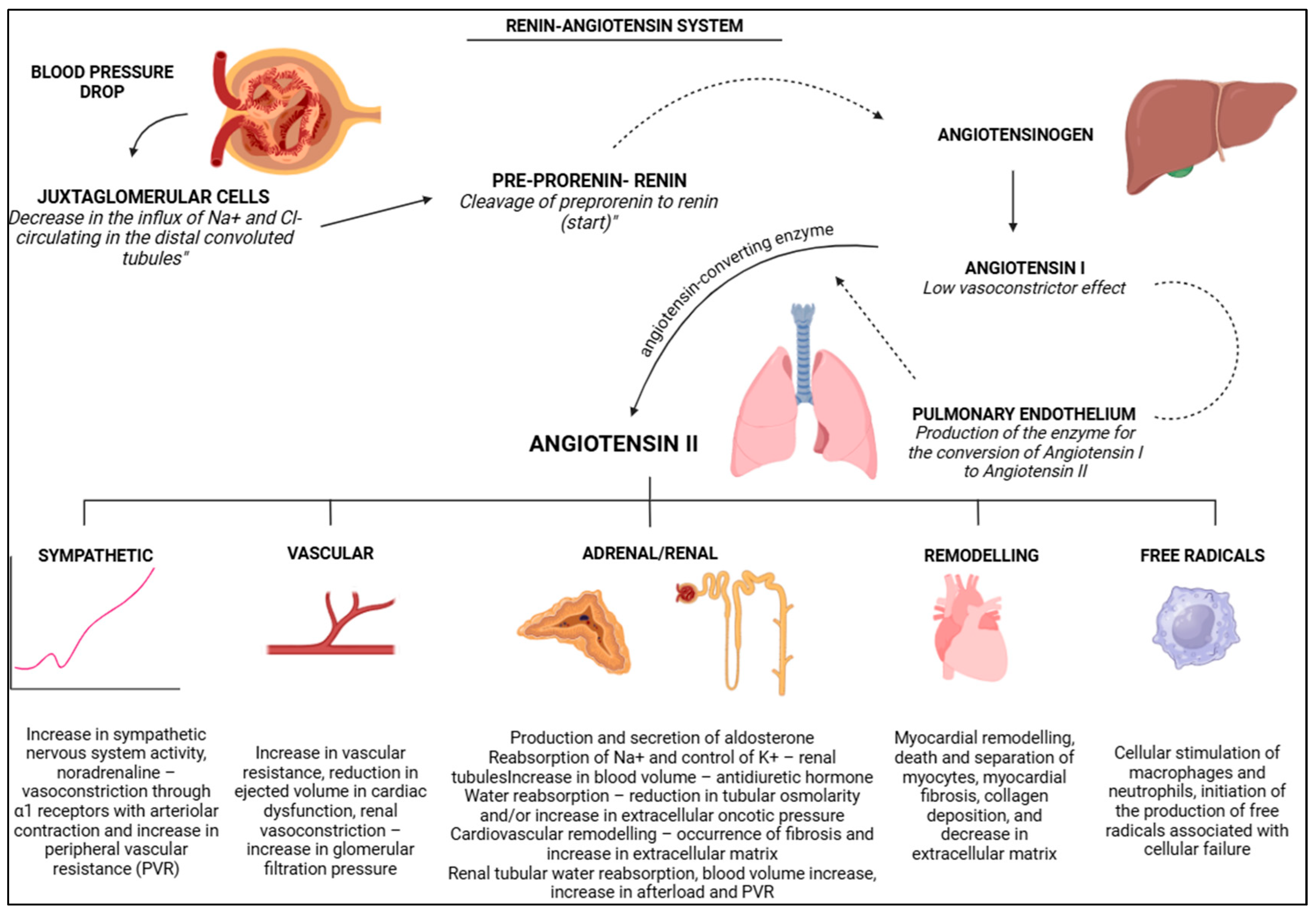
3.2. Renin Angiotensin System
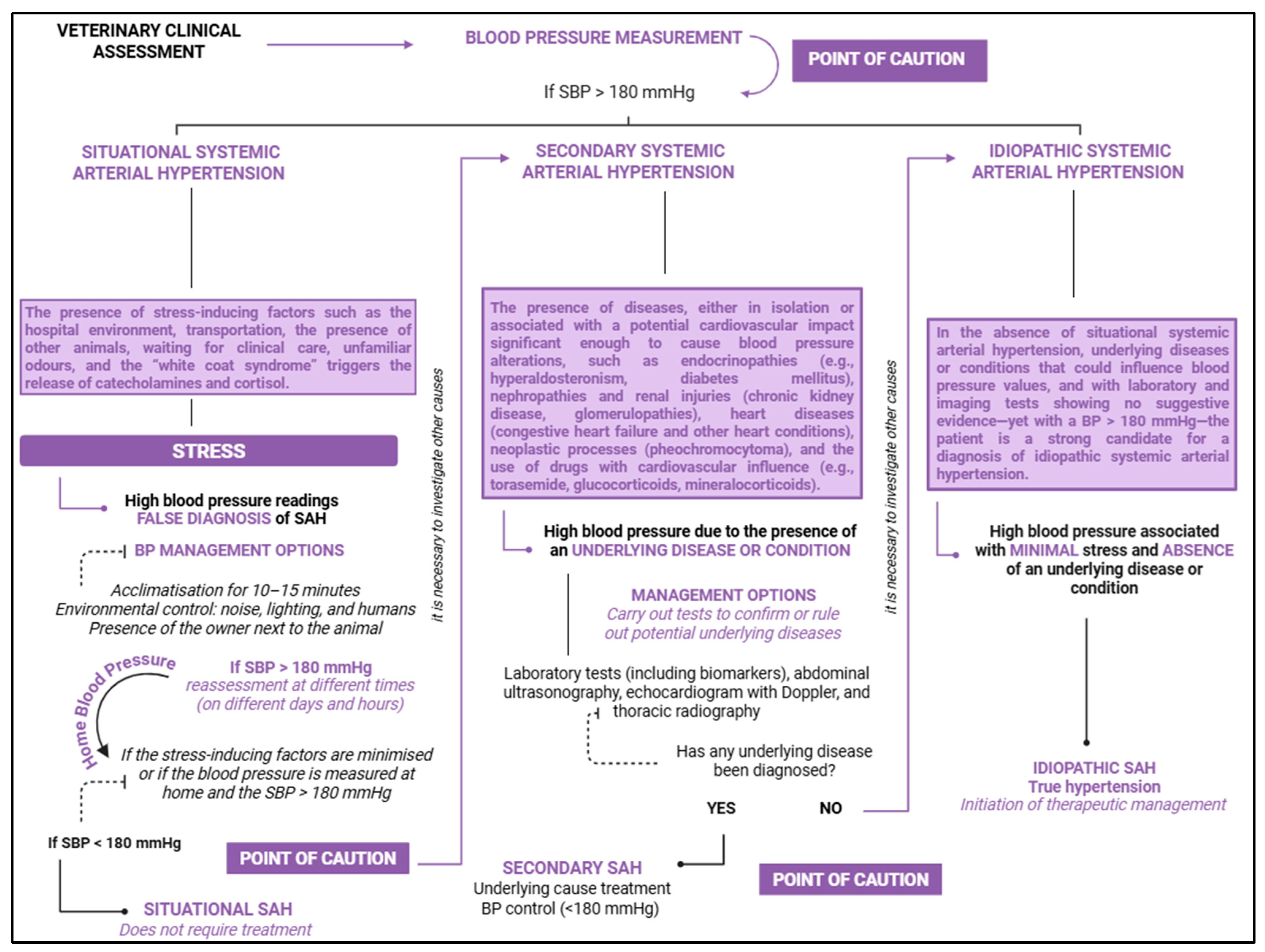
4. Systemic Arterial Hypertension
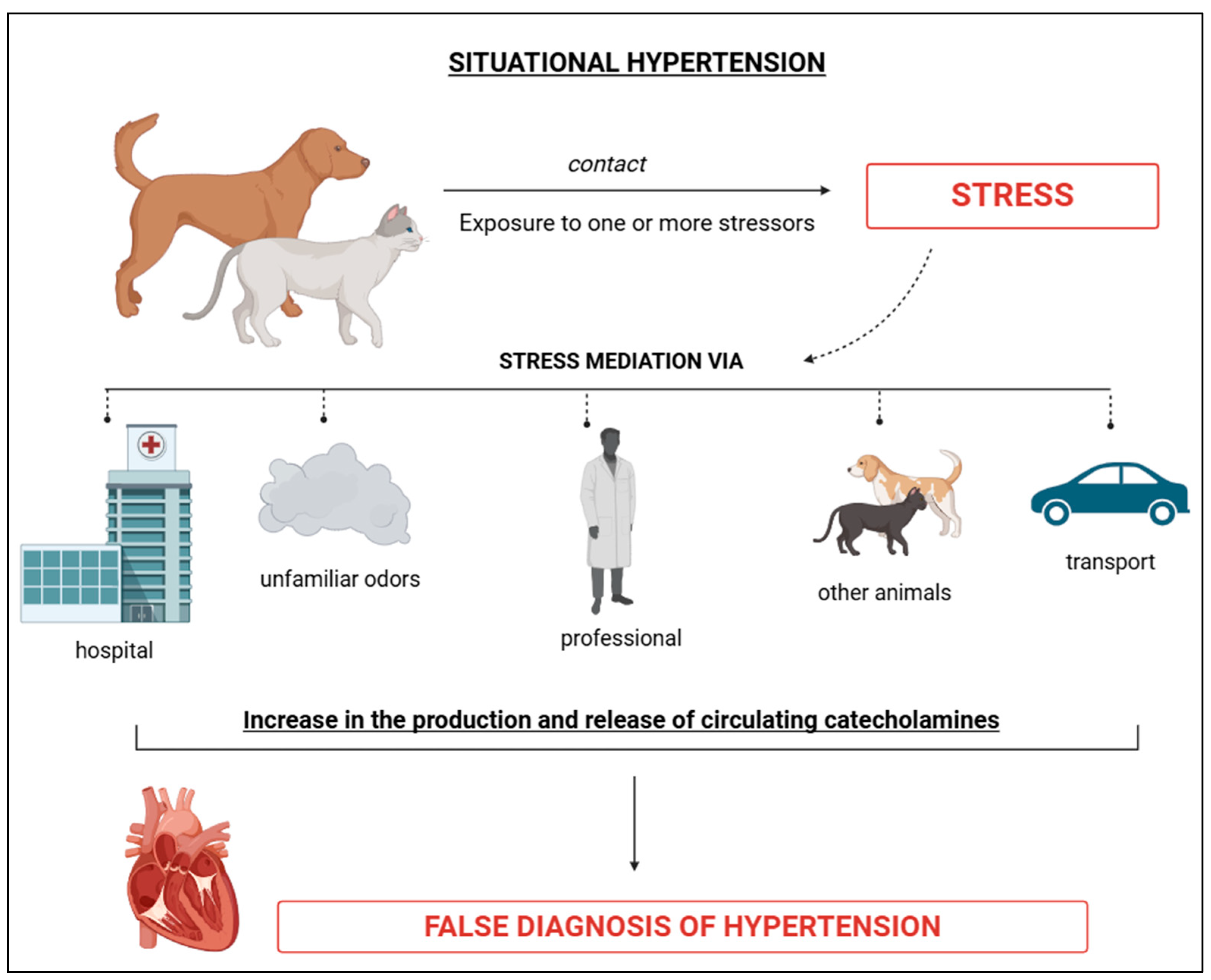
4.1. Situational Arterial Hypertension
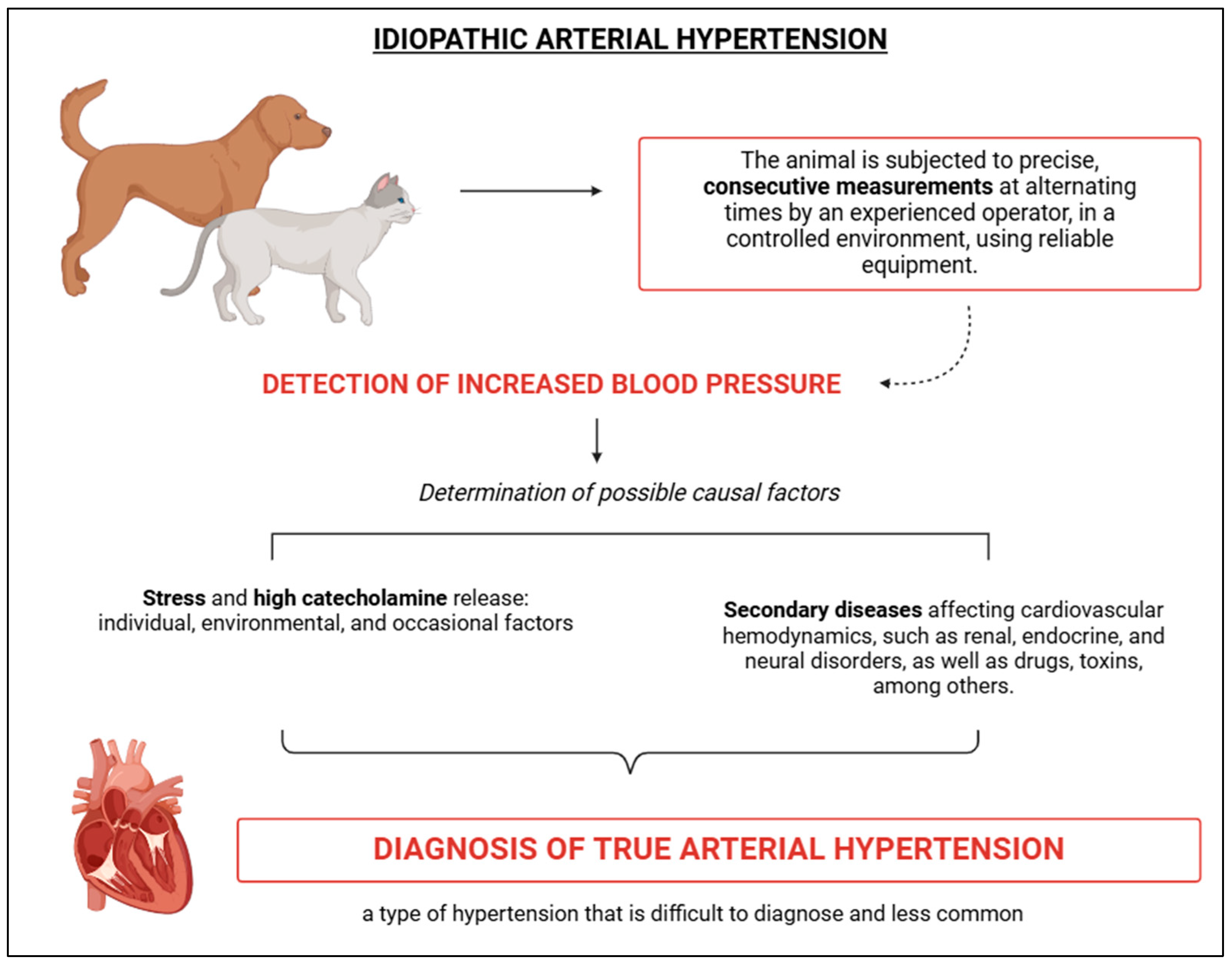
4.2. Idiopathic Arterial Hypertension
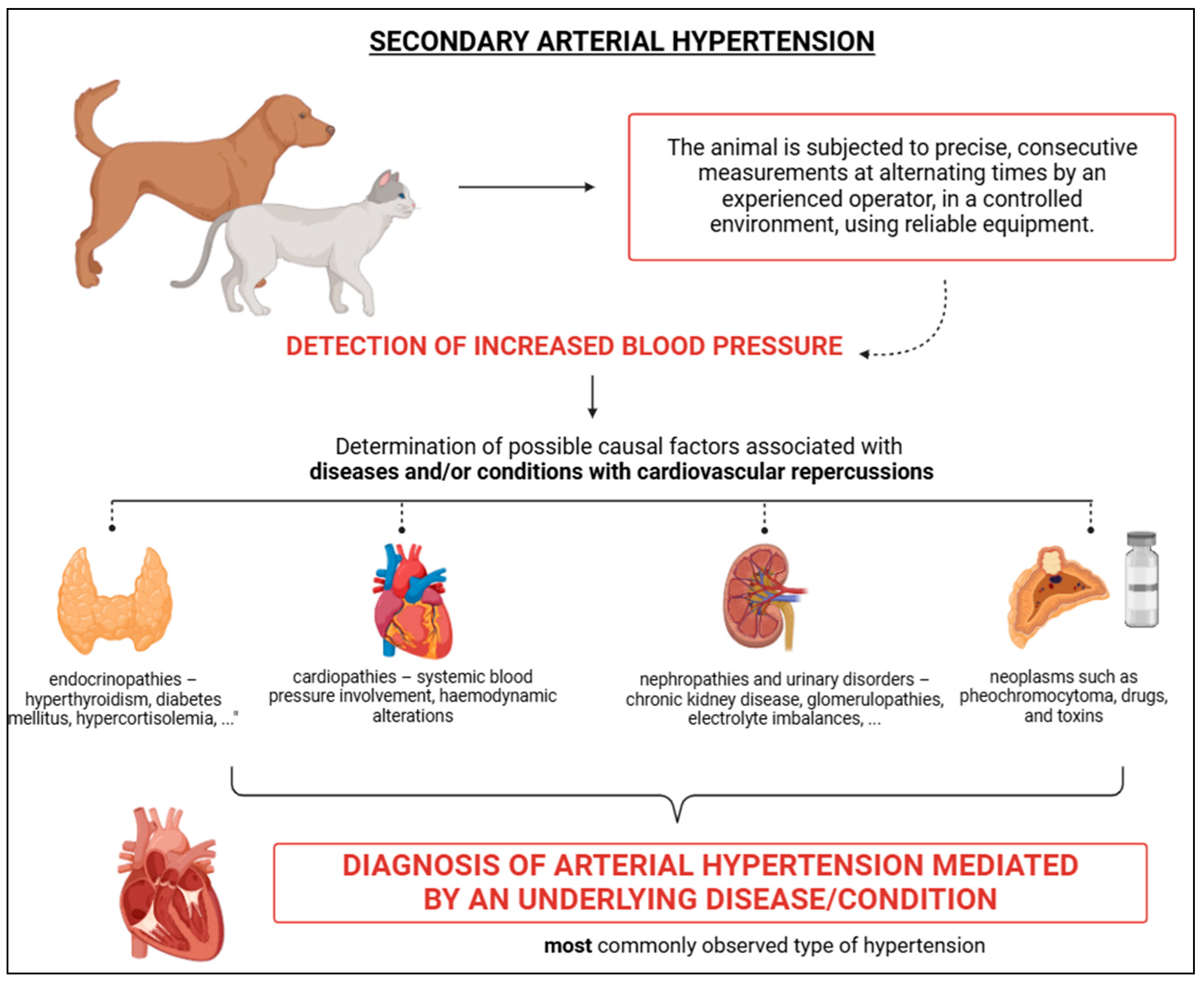
4.3. Secondary Arterial Hypertension
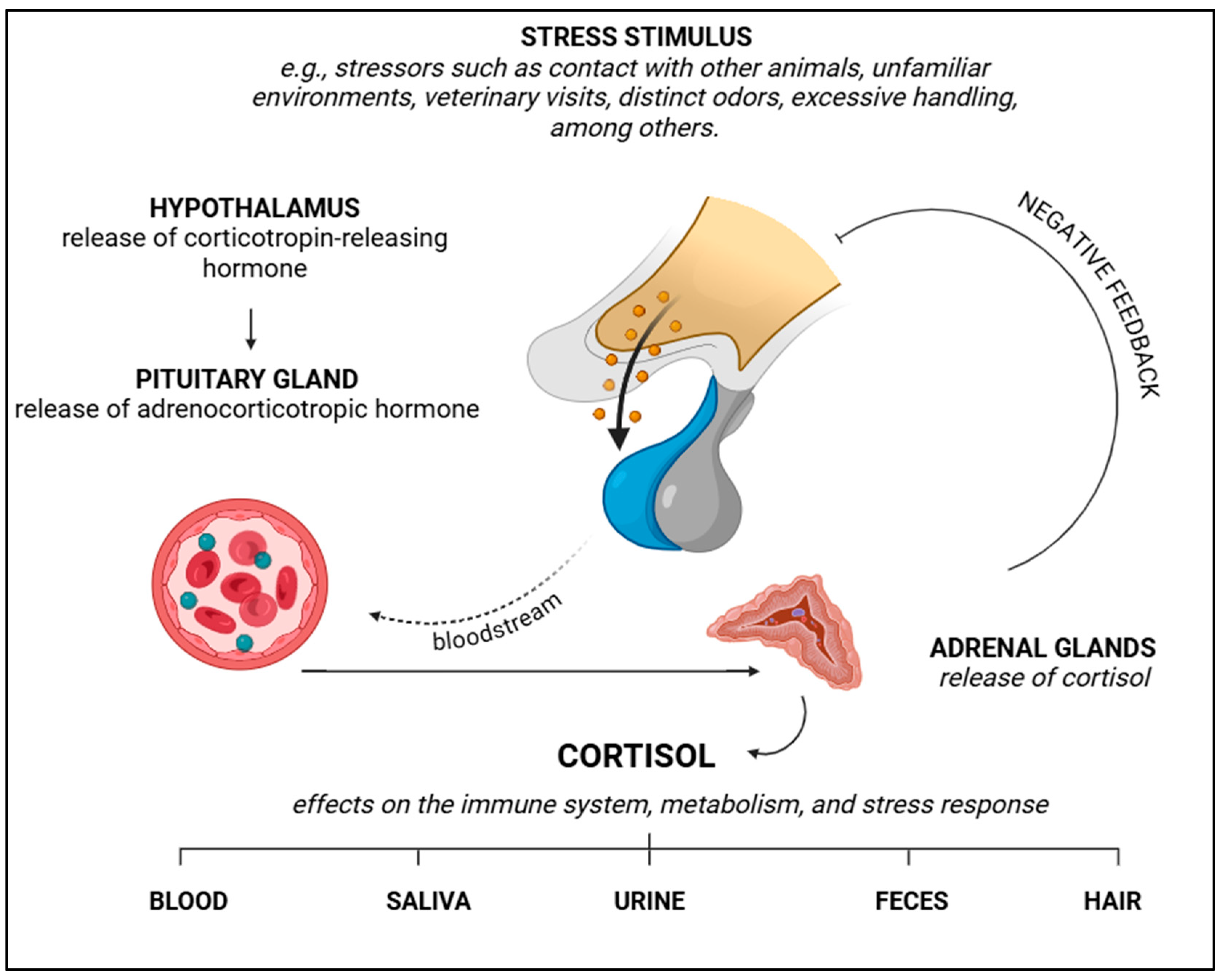
5. Stress and Catecholamine Release
6. Laboratory Biomarkers of Stress
6.1. Cortisol
6.2. Glucose
6.3. Stress Leukogram
7. Diseases Associated with SAH
7.1. Chronic Kidney Disease and Urinary Disorders
7.2. Endocrine Disorders
7.3. Neoplastic Causes, Drugs and Toxins
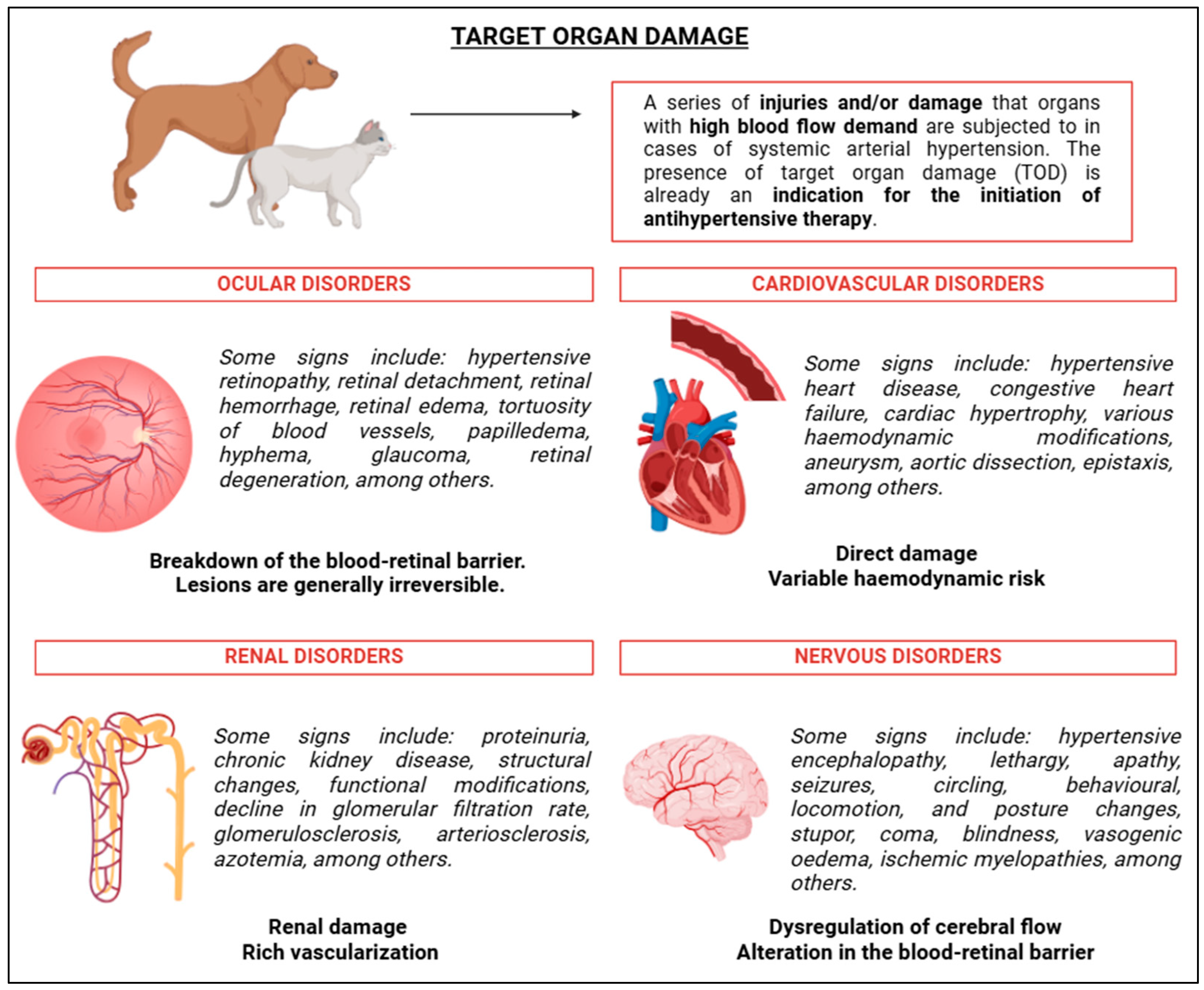
8. Target Organ Damage
9. Diagnosis and Devices of Measurement
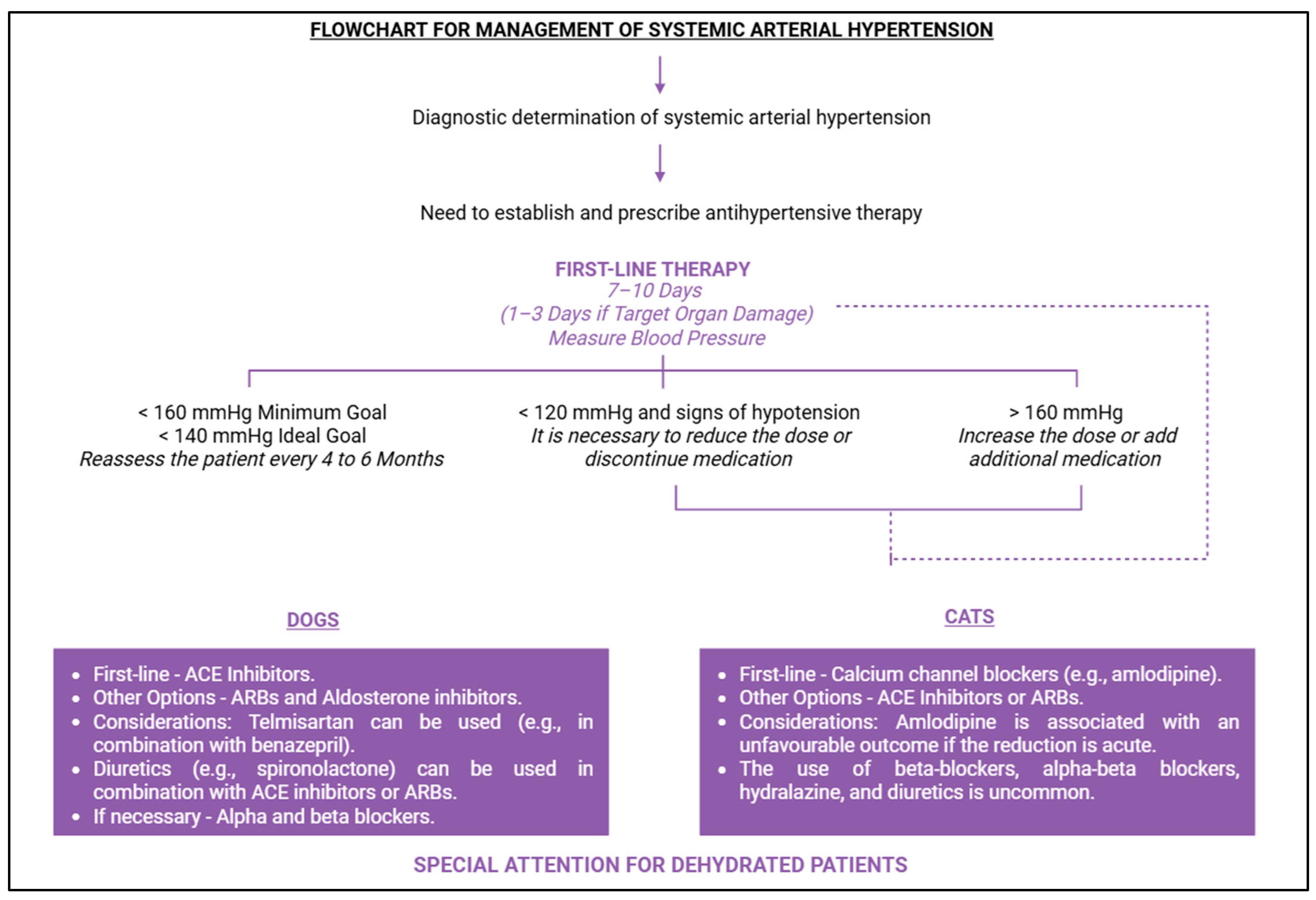
10. Therapeutic Management
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ACVIM | American College Veterinary Internal Medicine |
| ARBs | Angiotensin II receptor blockers |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CO | Cardiac output |
| IRIS | International Renal Interest Society |
| mmHg | millimetres of mercury |
| PNS | Parasympathetic nervous system |
| PVR | Peripheric vascular resistance |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| RAS | Renin–angiotensin system |
| SAH | Systemic arterial hypertension |
| SNS | Sympathetic nervous system |
| TOD | Target organ damage |
| VR | Venous return |
References
- Sousa, F.G.; Oliveira, B.C.G.; Ferreira, N.S.; Baldi, M.L.C.; Queiroz, F.S.F.; Beier, S.L. Hipertensão arterial sistêmica e as diretrizes para identificação, avaliação, controle e manejo hipertensivo em cães e gatos. Vet. Zootec. 2023, 30, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acierno, M.J.; Brown, S.; Coleman, A.E.; Jepson, R.E.; Papich, M.; Stepie, R.L.; Syme, H.M. ACVIM consensus statement: Guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1803–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Pruessner, J.; Sousa, N.; Almeida, O.F.X.; Van Dam, A.M.; Rajkowska, G.; Swaab, D.F.; Czéh, B. Neuropathology of stress. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodeo, C.E.; Lima, N.; da Costa e Nobre, F. História da monitorização ambulatorial da pressão arterial. Rev. Bras. Hipertens. 1998, 5, 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, O. Histórico do tratamento da hipertensão arterial. Rev. Bras. Hipertens. 1998, 5, 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Estañol, B.; Delgado, G.; Borgstein, J. Korotkoff sounds—The improbable also occurs. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2013, 101, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusch, C.E.; Schellenberg, S.; Wenger, M. Endocrine Hypertension in Small Animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.; Hall, J.E. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 205–258. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, M.L.; Ribeiro, V.R.F.R. Fisiologia do Sistema Cardiovascular. In Tratado de Cardiologia Veterinária; Larsson, M.H.M.A., Ed.; Interbook: São Paulo, Brazil, 2020; pp. 7–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, F.G. Avaliação de Efeitos Cardiovasculares da Angiotensina (1–7) Após Administração do Peptídeo em Formulação Oral em Felinos. Master’s Thesis, Escola de Veterinária, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg, M.; Ljungvall, I.; Häggström, J.; Wilson, H.; Palmer, L. Impact of equipment and handling on systolic blood pressure measurements in conscious dogs in an animal hospital environment. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar, M. Ageing and its effects on the cardiovascular system. Drugs 1990, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodey, A.R.; Michell, A.R. Epidemiological study of blood pressure in domestic dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1996, 37, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodey, A.R.; Sansom, J. Epidemiological study of blood pressure in domestic cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 39, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, J.M.; Dentino, M. Indirect arterial blood pressure measurement in nonsedated Irish wolfhounds: Reference values for the breed. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2002, 38, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.R.; Brodbelt, D.C.; Luis Fuentes, V. Blood Pressure Measurements in 780 Apparently Healthy Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijsmans, E.S.; Jepson, R.E.; Chang, Y.M.; Syme, H.M.; Elliott, J. Changes in systolic blood pressure over time in healthy cats and cats with chronic kidney disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surman, S.; Couto, C.G.; Dibartola, S.P.; Chew, D.J. Arterial blood pressure, proteinuria, and renal histopathology in clinically healthy retired racing greyhounds. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, A.P.; Del-Angel-Caraza, J.; Quijano-Hernández, I.A.; Barbosa-Mireles, M.A. Obesity-hypertension and its relation to other diseases in dogs. Vet. Res. Commun. 2015, 39, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishina, M.; Watanabe, T.; Fujii, K.; Maeda, H.; Wakao, Y.; Takahashi, M. Non-invasive blood pressure measurements in cats: Clinical significance of hypertension associated with chronic renal failure. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 60, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodey, A.R.; Rampling, M.W. Comparison of haemorrheological parameters and blood pressure in various breeds of dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1999, 40, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattez, E.P.; Reynolds, B.S.; Concordet, D.; Laysol-Lamour, C.J.; Segalen, M.M.; Chetboul, V.; Lefebvre, H.P. Within-day and between-day variability of blood pressure measurement in healthy conscious beagle dogs using a new oscillometric device. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2010, 12, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.; Brown, C.A.; Hendi, R. Does systemic hypertension damage the canine kidney? J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2000, 14, 805–808. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, J.A.; Morris, P.J.; Bautista, I.; Juste, M.C.; Suarez, L.; Peña, C.; Hackett, R.M.; Rawlings, J. Hypertension: A risk factor associated with weight status in dogs. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2011S–2013S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.C.R.; Sousa, F.G.; Oliveira, B.C.S.; Miranda, G.C.; Kwong, M.A.C. Fatores de risco associados à obesidade e sobrepeso em cães. Med. Veterinária UFRPE 2023, 17, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Neto, G.B.; Brunetto, M.A.; Champion, T.; Ortiz, E.M.G.; Carciofi, A.C.; Camacho, A.A. Avaliação da pressão arterial sistêmica em cães obesos: Comparação entre os métodos oscilométrico e doppler ultrassônico. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2014, 34, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, D.A.; Mackalonis, M.E.; Hess, R.S. Effect of body position on indirect measurement of systolic arterial blood pressure in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 242, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, A.P.; Mawby, D.I.; Price, J.M.; Whittemore, J.C. Effects of various factors on Doppler flow ultrasonic radial and coccygeal artery systolic blood pressure measurements in privately-owned, conscious dogs. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.G.; Yamato, R.J. Insuficiência cardíaca congestiva. In Tratado de Cardiologia Veterinária; Larsson, M.H.M.A., Ed.; Interbook: São Paulo, Brazil, 2020; pp. 331–358. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, E.R.M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Guatimosim, S. Angiotensin-(1-7)-mediated signaling in cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 493129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.A.; Fattah, C.; Loughrey, C.M.; Milligan, G.; Nicklin, S.A. Angiotensin-(1–7) and angiotensin-(1–9): Function in cardiac and vascular remodeling. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, E.O.; Ye, D.; Wu, C.; Lu, H.S.; Uijl, E.; Colafella, K.M.M.; Danser, A.H.J. Angiotensinogen suppression: A new tool to treat cardiovascular and renal disease. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, S.; Mohagaonkar, S.; Nikola, E.V. Regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system by cyclic nucleotides and phosphodiesterases. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1239492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, J.; Kaur, J.; Lappin, S.L. Physiology, Renin Angiotensin System. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470410/ (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- Kanagula, A.K.; Kaur, J.; Batra, J.; Ankireddypalli, A.R.; Velagapudi, R. Renin-Angiotensin System: Updated Understanding and Role in Physiological and Pathophysiological States. Cureus 2023, 15, e40725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, M.A.; Crowley, S.D.; Gurley, S.B.; Mirotsou, M.; Coffman, T.M. Classical Renin-Angiotensin system in kidney physiology. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavishi, C.; Bangalore, S.; Messerli, F.H. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Hypertension: Is There Evidence for Benefit Independent of Blood Pressure Reduction? Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 59, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Kooi, C.W.V.; Daugherty, A. Structure and functions of angiotensinogen. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Thomas, C.M.; Yong, Q.C.; Chen, W.; Baker, K.M. The Intracrine Renin-Angiotensin System. Clin. Sci. 2012, 123, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varagic, J.; Ahmad, S.; Nagata, S.; Ferrario, C.M. ACE2: Angiotensin II/angiotensin-(1-7) balance in cardiac and renal injury. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, R.A.V.; Millána, J.M.V.; Bonilla, E.F. Renin-angiotensin system: Basic and clinical aspects—A general perspective. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. Engl. Ed. 2022, 69, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Bhat, S.A.; Shibata, T.; Giani, J.F.; Rader, F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z. Diverse biological functions of the renin-angiotensin system. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 44, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, A.; Khajehpour, S.; Aghazadeh-Habashi, A. Update on Angiotensin II Subtype 2 Receptor: Focus on Peptide and Nonpeptide Agonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreanez, A.; Mosquera, J.; Munoz, N.; Robalino, J.; Tene, D. Diabetes, heart damage, and angiotensin II. What is the relationship link between them? A minireview. Endocr. Regul. 2022, 56, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Kwon, Y.M.; Omidi, Y.; Speth, R.C. Nanoparticle approaches for the renin-angiotensin system. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, N.M.; Nakagawa, P.; Grobe, J.L.; Sigmund, C.D. Insights Into the Role of Angiotensin-II AT1 Receptor-Dependent β-Arrestin Signaling in Cardiovascular Disease. Hypertension 2024, 81, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knies, M.; Kooistra, H.S.; Teske, E. Prevalence of persistent hypertension and situational hypertension in a population of elderly cats in The Netherlands. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X231172629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, F.; Defrancesco, T.C.; Atkins, C.E.; Sakai, M.; Kallfelz, F.A. Ocular lesions associated with systemic hypertension in cats: 69 cases (1985-1998). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.; Barber, P.J.; Syme, H.M.; Rawlings, J.M.; Markwell, P.J. Feline hypertension: Clinical findings and response to antihypertensive treatment in 30 cases. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2001, 42, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, R.E.; Elliott, J.; Brodbelt, D.; Syme, H.M. Effect of control of systolic blood pressure on survival in cats with systemic hypertension. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goy-Thollot, I.; Péchereau, D.; Kéroack, S.; Dezempte, J.C.; Bonnet, J.M. Investigation of the role of aldosterone in hypertension associated with spontaneous pituitary dependent hyperadrenocorticism in dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 43, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syme, H.M.; Elliott, J. The prevalence of hypertension in hyperthyroid cats at diagnosis and following treatment. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 754. [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes, A.; Garelli-Paar, C.; Blondel, T.; Guillot, E. ‘The Mercury Challenge’: Feline systolic blood pressure in primary care practice—A European survey. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2002, 24, e310–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M. Psychological Indicators of Stress and Welfare. In Ethics, Welfare, Law and Market Forces: The Veterinary Interface; Michell, A.R., Ewbank, R., Eds.; Universities Federation for Animal Welfare: Wheathampstead, UK, 1998; pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mârza, S.M.; Munteanu, C.; Papuc, I.; Radu, L.; Diana, P.; Purdoiu, R.C. Behavioral, Physiological, and Pathological Approaches of Cortisol in Dogs. Animals 2024, 14, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-H.; Jo, W.; Kang, T.-K.; Oh, T.; Kim, K. Assessment of Stress Caused by Environmental Changes for Improving the Welfare of Laboratory Beagle Dogs. Animals 2023, 13, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, I.C.; Michell, A.R. Relationship between blood pressure and stress-prone temperament in dogs. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 60, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Fagard, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Redon, J.; Zanchetta, D.; Böhm, M.; Christiaansen, E.; Cübbel, M.; De Backer, G.; Ducimetière, P.; et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1281–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.S.; O’brien, E.; Staessen, J.A. Masked hypertension: Understanding its complexity. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 38, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, F.A.C.; Neuwald, E.B.; Mombach, V.S.; D’Avila, A.E.R.; Conrado, F.O.; González, F.H.D. Systolic blood pressure of dogs at hospital and domestic environment. Cienc. Rur. 2012, 42, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, F.S.F.; Rosa, D.B.S.K.; Ferreira, R.H.; Masieiro, J.S.; Silva, N.C.P.; Canta, G.N.; Veado, J.C.C. Estudo comparativo da aferição de pressão arterial sistólica em cães nos ambientes ambulatorial e domiciliar. In Proceedings of the Simpósio CBNUV 2021-Polêmicas da Nefrologia, Plataforma Online, São Paulo, Brazil, 20 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, S.T.; Carr, A.P. Comparison of home blood pressure and office blood pressure measurement in dogs and cats. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 86, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kartashova, I.A.; Ganina, K.K.; Karelina, E.A.; Tarasov, S.A. How to evaluate and manage stress in dogs: A guide for veterinary specialists. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 243, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente-Moreno, E.; Paredes-Ramos, P.; Carrasco-García, A.; Hernandez-Cruz, B.; Alvarado, M.; Edwards, C. Salivary cortisol in guide dogs. Animals 2023, 13, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.A.; Stromin, J.I.; Steenkamp, N.; Combrinck, M.I. Understanding the Relationships between Physiological and Psychoso cial Stress, Cortisol and Cognition. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1085950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. In The ECPH Encyclopedia of Psychology; Springer: Singapore, 2024; Available online: https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-981-99-6000-2_586-1 (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Petersson, M.; Uvnäs-Moberg, K.; Nilsson, A.; Gustafson, L.-L.; Hydbring-Sandberg, E.; Handlin, L. Oxytocin and Cortisol Levels in Dog Owners and Their Dogs Are Associated with Behavioral Patterns: An Exploratory Study. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, B.; García-Belenguer, S.; León, M.; Chacón, G.; Villegas, A.; Palacio, J. Blood concentrations of serotonin, cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone in aggressive dogs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2010, 123, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, E.J.; Forsburg, Z.R.; Davis, D.R.; Gabor, C.R. Non-Invasive Methods for Measuring and Monitoring Stress Physiology in Imperiled Amphibians. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelíková, E.; Bolechová, P.; Chaloupková, H.; Svobodová, I.; Jovičić, M.; Sedmíková, M. Salivary cortisol as a marker of acute stress in dogs: A review. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2020, 72, 106428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, S.Y.; Isparta, S.; Saral, B.; Keskin Yilmaz, N.; Adiay, D.; Matsui, H.; Töre-Yargin, G.; Musa, S.A.; Atilgan, D.; Öztürk, H.; et al. Acute and chronic stress alter behavioral laterality in dogs. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähler, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Zablotski, Y.; Schroers, M. Salivary cortisol measurements in brachycephalic dog breeds as part of a standardized stress test. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 13, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilez, E.; Burchell, R.K.; Thorstensen, E.B.; Weidgraaf, K.; Parbhu, S.E.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Gal, A. Cortisol urinary metabolites in dogs with hypercortisolism, congestive heart failure, and healthy dogs: Pilot investigation. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, M.; Tomori, S.; Mogi, K.; Kikusui, T. Attachment-like behavioral expressions to humans in puppies are related to oxytocin and cortisol: A comparative study of Akitas and Labrador Retrievers. Peptides 2024, 177, 171224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botschek, T.; Hußlein, V.; Peters, E.M.J.; Brosig, B. Hair Cortisol as Outcome Parameter for Psychological and Neuropsychiatric Interventions—A Literature Review. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1227153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagley, S.P.; Hopper, K.; Epstein, S.E.; Hagley, S.P.; Hopper, K.; Epstein, S.E. Etiology and prognosis for dogs with abnormal blood glucose concentrations evaluated in an emergency room. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2020, 30, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magomedova, L.; Cummins, C.L. Glucocorticoids and Metabolic Control. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2016, 233, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Yue, T.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Hypothalamus-sympathetic-liver axis mediates the early phase of stress-induced hyperglycemia in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, J.S.; Kinnaird, E.; Baglioni, A.; Blackshaw, J.; Priest, J. Acute stress hyperglycemia in cats is associated with struggling and increased concentrations of lactate and norepinephrine. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2002, 16, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, K.R.; Rand, J.S. Changes in blood glucose concentration are associated with relatively rapid changes in circulating fructosamine concentrations in cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.W. Avaliação Laboratorial do Pâncreas e Metabolismo da Glicose. In Hematologia e Bioquímica Clínica Veterinária, 2nd ed.; Thrall, M.A., Weiser, G., Allison, R., Campbell, T.W., Eds.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015; pp. 904–937. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, O.M.; Olaifa, F.H.; Adah, A.S.; Basiru, A.; Akorede, G.J.; Ambali, H.M.; Suleiman, K.Y.; Sanusi, F.; Bolaji, M. Effect of heat stress on vital and hematobiochemical parameters of healthy dogs. Vet. World 2022, 15, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, G. Introdução aos leucócitos e ao leucograma. In Hematologia e Bioquímica Clínica Veterinária, 2nd ed.; Thrall, M.A., Weiser, G., Allison, R., Campbell, T.W., Eds.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015; pp. 257–267. [Google Scholar]
- Nibblett, B.M.; Ketzis, J.K.; Grigg, E.K. Comparison of stress exhibited by cats examined in clinic versus a home setting. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2015, 173, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Nelson, L.; Baumwart, R.; Haines, J. Adverse effects of trazodone in dogs on primary hemostasis and electrocardiogram: A single-blinded placebo-controlled crossover study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 37, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, S.; Palma, D. Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations of Systemic Hypertension. In Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine: Diseases of the Dog and the Cat, 8th ed.; Ettinger, S.J., Feldman, E.C., Côté, E., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017; pp. 1712–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, J.S.; Jepson, R.E. The intermingled relationship between chronic kidney disease and hypertension. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 23, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Renal Interest Society. Iris Guidelines. Available online: https://www.iris-kidney.com/iris-guidelines-1/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Quimby, J.M. Update on Medical Management of Clinical Manifestations of Chronic Kidney Disease. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 46, 1163–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, M.K.; Atkins, C.E.; Pitt, B. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its suppression. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.W.; Maggiore, A.-M. Endocrine Disorders. In Small Animal Veterinary Medicine, 6th ed.; Nelson, R.W., Couto, C.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 740–857. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, I.; Ojamaa, K. Thyroid hormone and the cardiovascular system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamato, R.J. Hipertensão Arterial Sistêmica. In Tratado de Cardiologia Veterinária; Larsson, M.H.M.A., Ed.; Interbook: São Paulo, Brazil, 2020; pp. 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.L.; Elliott, J.; Syme, H.M. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity in hyperthyroid cats with and without concurrent hypertension. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammeleer, L.; Xifra, P.; Serrano, S.I.; Rishniw, M.; Daminet, S.; Peterson, M.E. Blood pressure in hyperthyroid cats before and after radioiodine treatment. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Magbool, F.; Khan, F.; Hassan, F.I.; Momtaz, S.; Abdollahi, M. Comparative occurrence of diabetes in canine, feline, and few wild animals and their association with pancreatic diseases and ketoacidosis with therapeutic approach. Vet. World 2018, 11, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöppl, A.G.; Hummel, J.; Vicente, G. Obesidade e Alterações Endócrinas. In Tratado de Fisioterapia e Fisiatria de Pequenos Animais; Paya: São Paulo, Brazil, 2018; pp. 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, F.S.M.; Carvalho, G.L.C.; Jesus, L.; Pöpp, A.L.; González, F.H.D. Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory aspects in a case series of canine hyperadrenocorticism: 115 cases (2010–2014). Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2019, 39, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, R.E. Hypertension and Adrenal Gland Disease. In Hypertension in the Dog and Cat, 1st ed.; Elliott, J., Syme, H.M., Jepson, R.E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 101–130. [Google Scholar]
- San José, P.G.; Bermejo, C.A.; Moral, I.C.; Alvaro, P.C.; Alenza, M.D.P. Prevalence and risk factors associated with systemic hypertension in dogs with spontaneous hyperadrenocorticism. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smets, P.M.; Lefebvre, H.P.; Meij, B.P.; Croubels, S.; Meyer, E.; Van De Maele, I.; Daminet, S. Long-term follow-up of renal function in dogs after treatment for ACTH-dependent hyperadrenocorticism. J. Vet. Intern Med. 2012, 26, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Lien, Y.H.; Huang, H.P. Association of renal resistive index, renal pulsatility index, systemic hypertension, and albuminuria with survival in dogs with pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism. Int. J. Endrocrinol. 2016, 2016, 3814034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedrano, C.; Chetboul, V.; Gouni, V.; Levy, J.K.; Falcão, M.; Tissier, R.; Bonnet, M.; Deshayes, A.; Serra, P. Systolic and diastolic myocardial dysfunction in cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or systemic hypertension. J. Vet. Intern Med. 2006, 20, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misbach, C.; Gouni, V.; Tissier, R.; Trehiou-Sechi, E.; Petit, A.M.P.; Sampedrano, C.C.; Pouchelon, J.-L.; Chetboul, V. Echocardiographic and tissue Doppler imaging alterations associated with spontaneous canine systemic hypertension. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.; Hudson, J.; Hofmeister, E. An observational thoracic radiographic study of aortic remodeling in dogs with confirmed systemic hypertension. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2022, 63, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansom, J.; Bodey, A. Ocular signs in four dogs with hypertension. Vet. Rec. 1997, 140, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, N.L.; Stepien, R.L.; Bentley, E. Ocular lesions associated with systemic hypertension in dogs: 65 cases (2005–2007). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 238, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.M.; Irving, A.C.; Bridges, J.P.; Jones, B.R. The prevalence of ocular lesions associated with hypertension in a population of geriatric cats in Auckland, New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2014, 62, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violette, N.P.; Ledbetter, E.C. Punctate retinal hemorrhage and its relation to ocular and systemic disease in dogs: 83 cases. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2018, 21, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, R.F. Hypertension: Why Is It Critical? Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.P.; Jepson, R.; Dawson, C.; Humm, K. Hypertension, retinopathy, and acute kidney injury in dogs: A prospective study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1940–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, E. Hypertension and the Eye. In Hypertension in the Dog and Cat, 1st ed.; Elliott, J., Syme, H.M., Jepson, R.E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Syme, H.M.; Elliott, J. Clinicopathological variables predicting progression of azotemia in cats with chronic kidney disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littman, M.P. Spontaneous systemic hypertension in 24 cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1994, 8, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Syme, H.; Brown, C.A.; Elliot, J.; Moore, P.A.; Newell, M.A.; Munday, J.S.; Cartier, L.M.; Sheldon, S.E.; Brown, S.A. Effects of the calcium channel antagonist amlodipine in cats with surgically induced hypertensive renal insufficiency. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolio, T.A.; Olson, J.; Longstreth, W.T. Hypertension and cognitive function: Pathophysiologic effects of hypertension on the brain. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2003, 5, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrie, M.; De Risio, L.; Dennis, R.; Murray, J.; Smith, P.; Hussain, S. Concurrent medical conditions and long-term outcome in dogs with nontraumatic intracranial hemorrhage. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2012, 53, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, J.; Kent, M.; Glass, E.N.; Platt, S.R. Clinicopathologic and MRI characteristics of presumptive hypertensive encephalopathy in two cats and two dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2013, 49, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höglund, K.; Hanås, S.; Carnabuci, C.; Ljungvall, I.; Tidholm, A.; Häggström, J. Blood pressure, heart rate, and urinary catecholamines in healthy dogs subjected to different clinical settings. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, I.; Summers, S.; Rishniw, M.; Quimby, J. Cross-sectional survey of non-invasive indirect blood pressure measurement practices in cats by veterinarians. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouni, V.; Tissier, R.; Misbach, C.; Chezel, J.; Gouni, S.; Del Grosso, A.; Leray, V.; Laurent, R.; Coulomb, A.; Lecomte, P.; et al. Influence of the observer’s level of experience on systolic and diastolic arterial blood pressure measurements using Doppler ultrasonography in healthy conscious cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015, 17, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prost, K. Under pressure: A survey of Canadian veterinarians in the diagnosis and treatment of feline hypertension. Can. Vet. J. 2023, 64, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.S.; Sparkes, A.H.; Briscoe, K.; Carter, J.; Sala, S.C.; Jepson, R.E.; Scansen, B.A. ISFM Consensus Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension in Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VACHON, C.; BELANGER, M.C.; BURNS, P.M. Evaluation of oscillometric and Doppler ultrasonic devices for blood pressure measurements in anesthetized and conscious dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, I.R.; Price, J.M.; Whittemore, J.C. Indirect Doppler flow systolic blood pressure measurements taken with and without headphones in privately-owned, conscious dogs. Peer J. 2019, 7, e744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, S.; Summers, S.; Keys, D.; Quimby, J. Effect of audible static on blood pressure measurement by Doppler ultrasonic sphygmomanometry in cats. J. Feline. Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, E.; Egner, B.; Brown, S.A.; King, J.N.; Laveissiere, A.; Champeroux, P.; Richard, S. Comparison of high-definition oscillometry—A non-invasive technology for arterial blood pressure measurement—With a direct invasive method using radio-telemetry in awake healthy cats. J. Feline. Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjos, T.M.; Veado, J.C.C.; Araújo, R.B.; Leme, F.O.P.; Diniz, S.A.; Castro, M.C.N.; Costa, F.V.A.; Tavares, C.A.P.; David, L.M.; Quites, K.X.; et al. Avaliação e comparação entre métodos de mensuração de pressão arterial sistólica em gatos hígidos conscientes. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2016, 68, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, M.M.; Costa, A.C.A.; de Lima, M.T.; dos Santos, L.F.N.; Silva, K.F.; Martins, A.R.C.; Navarro, A.W.M.; Akabane, R.S.; Fantoni, D.T. Agreement and diagnostic accuracy of new linear deflection oscillometry and Doppler devices for hypotension detection compared to invasive blood pressure in anesthetized dogs. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.N.; Font, A.; Rousselot, J.F.; Ash, R.A.; Bonfanti, U.; Brovida, C.; Crowe, I.D.; Lanore, D.; Pechereau, D.; Seewald, W.; et al. Effects of Benazepril on Survival of Dogs with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Multicenter, Randomized, Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Vet. Intern Med. 2017, 31, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishina, M.; Watanabe, T. Development of hypertension and effects of benazepril hydrochloride in a canine remnant kidney model of chronic renal failure. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2008, 70, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, M.K.; Atkins, C.E.; Lee, S.; Lantis, A.C.; Zumbrunnen, J.R. Effects of high doses of enalapril and benazepril on the pharmacologically activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in clinically normal dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 76, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, B.L.; Stefanovski, D.; Hess, R.S.; Mcgonigle, K. Effect of telmisartan, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition, or both, on proteinuria and blood pressure in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecavalier, J.; Fifle, L.; Javard, R. Treatment of proteinuria in dogs with telmisartan: A retrospective study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Matsumoto, I.; Horii, A.; Ohmori, T.; Hirao, D.; Hasegawa, H.; Yoshimura, A.; Baba, T.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Use of amlodipine in the treatment of cats with systemic hypertension in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 86, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtinen, M.; Derré, G.; Renoldi, H.J.; Rinkinen, M.; Adler, K.; Aspegrén, J.; Zemirline, C.; Elliott, J. Randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of a chewable formulation of amlodipine for the treatment of hypertension in client-owned cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sent, U.; Gössl, R.; Elliott, J.; Syme, H.M.; Zimmering, T. Comparison of efficacy of long-term oral treatment with telmisartan and benazepril in cats with chronic kidney disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Systolic Blood Pressure | Classification | Risk for TOD |
|---|---|---|
| <140 mmHg | normotensive | minimal |
| 140–159 mmHg | prehypertensive | low |
| 160–179 mmHg | hypertensive | moderate |
| ≥180 mmHg | severely hypertensive | high |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Sousa, F.G.; Queiroz, F.S.F.; Muzzi, R.A.L.; Veado, J.C.C.; Beier, S.L. Systemic Arterial Hypertension and Factors Associated with Blood Pressure Dysregulation in Companion Animals. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050453
de Sousa FG, Queiroz FSF, Muzzi RAL, Veado JCC, Beier SL. Systemic Arterial Hypertension and Factors Associated with Blood Pressure Dysregulation in Companion Animals. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050453
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Sousa, Felipe Gaia, Fabiana Silva Fádel Queiroz, Ruthnéa Aparecida Lázaro Muzzi, Júlio César Cambraia Veado, and Suzane Lilian Beier. 2025. "Systemic Arterial Hypertension and Factors Associated with Blood Pressure Dysregulation in Companion Animals" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050453
APA Stylede Sousa, F. G., Queiroz, F. S. F., Muzzi, R. A. L., Veado, J. C. C., & Beier, S. L. (2025). Systemic Arterial Hypertension and Factors Associated with Blood Pressure Dysregulation in Companion Animals. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050453









