Spatiotemporal Diffusion, Colonization, and Antibody Responses in Susceptible C57BL/6J Mice Orally Infected with Toxoplasma gondii Cysts
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasite Strains, Cell Culture Conditions, and Purification
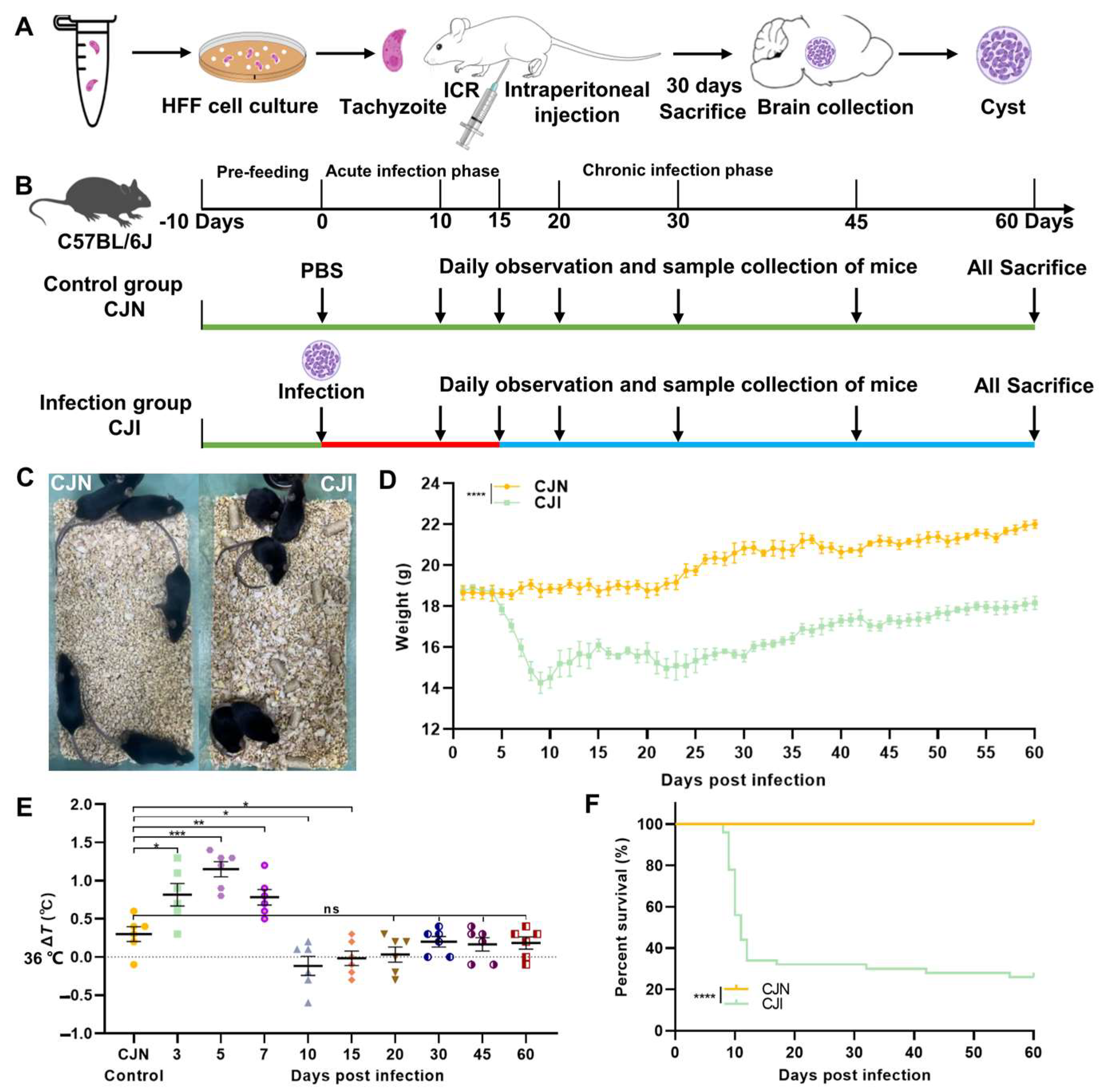
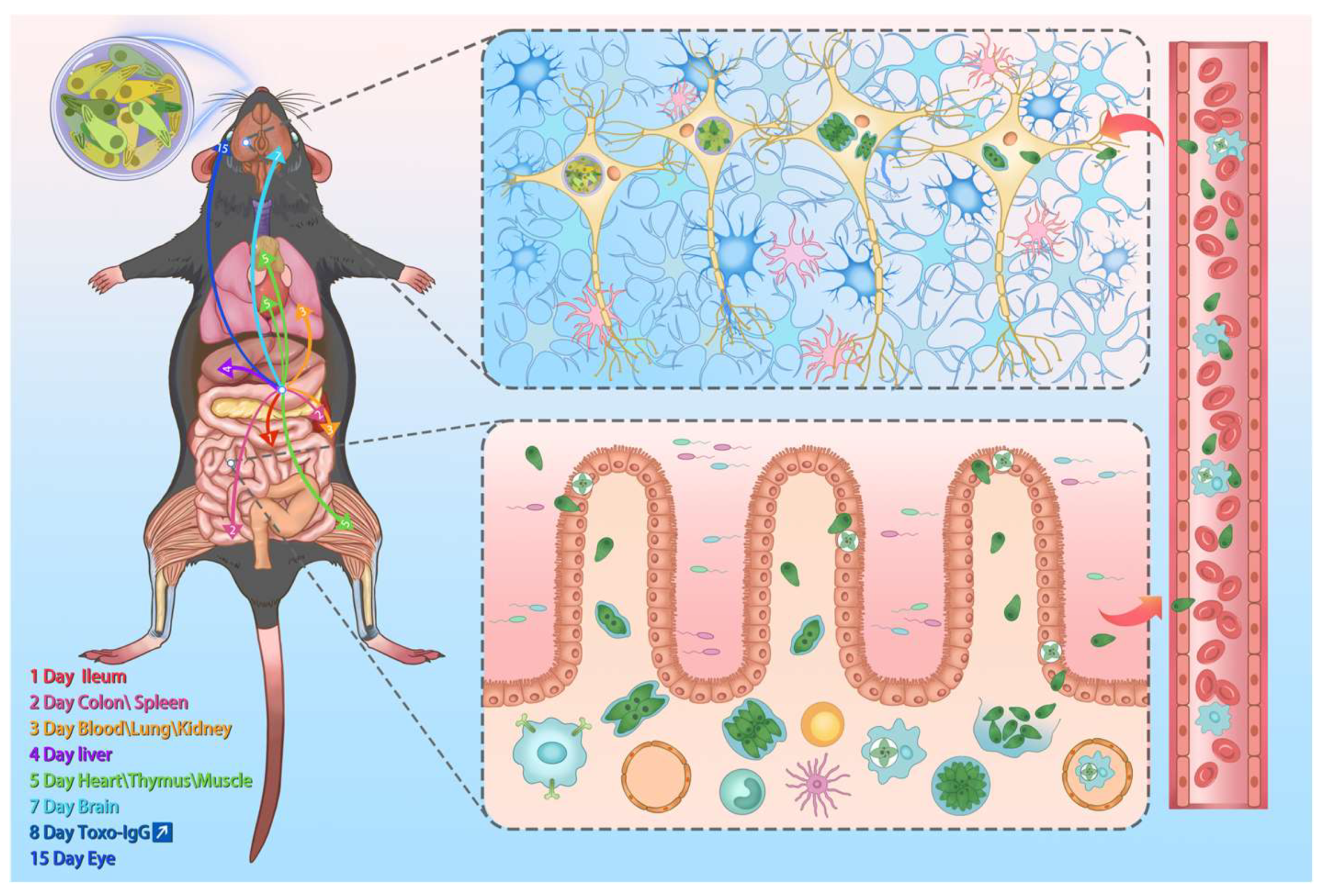
2.2. Mice and T. gondii Infection
2.3. Clinical Observation and Sample Collection of Mice
2.4. Detection of T. gondii with Real-Time q-PCR
2.5. Serum T. gondii-Specific Antibodies
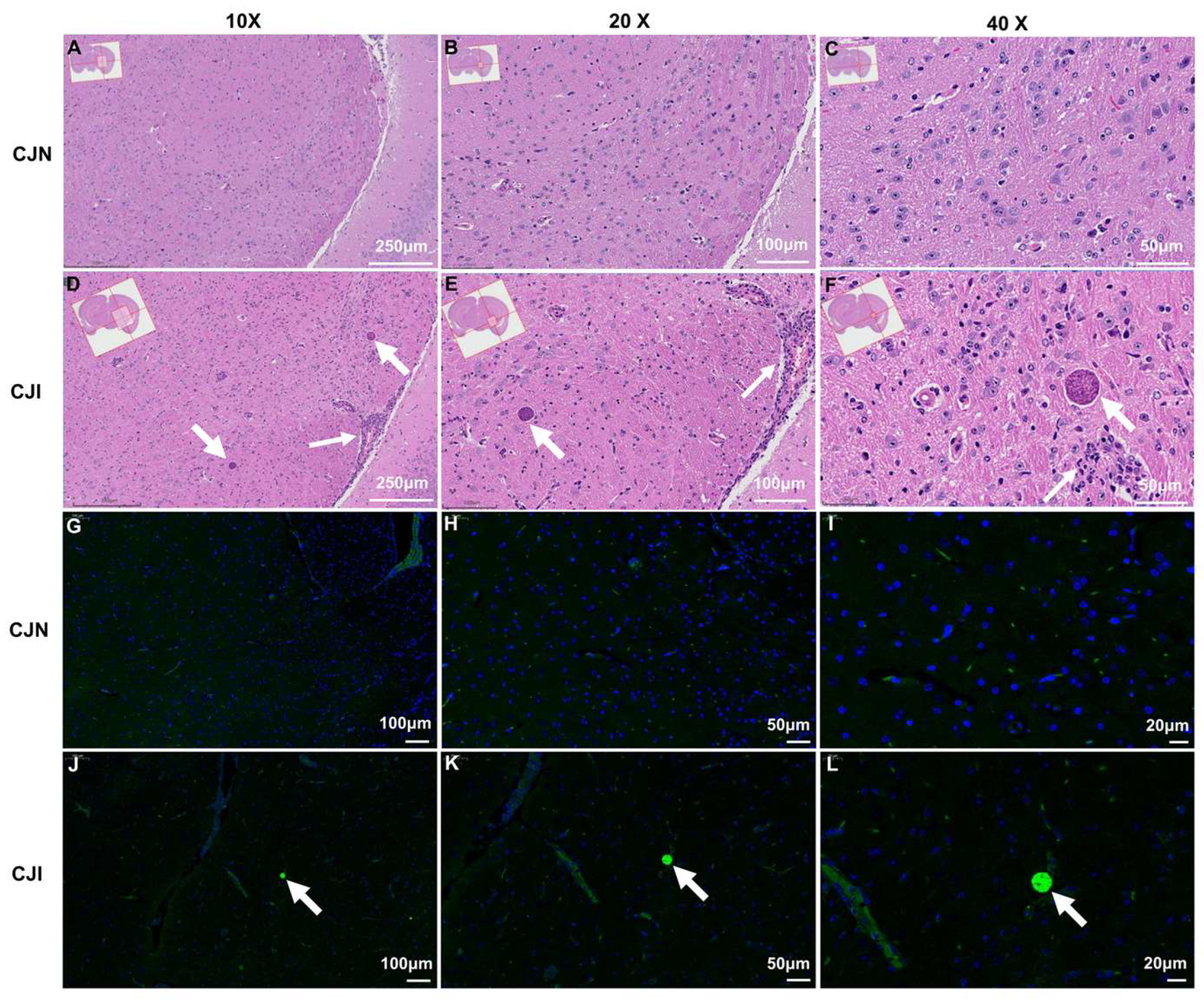
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. T. gondii-Infected Mouse Model and Analysis of Clinical Status
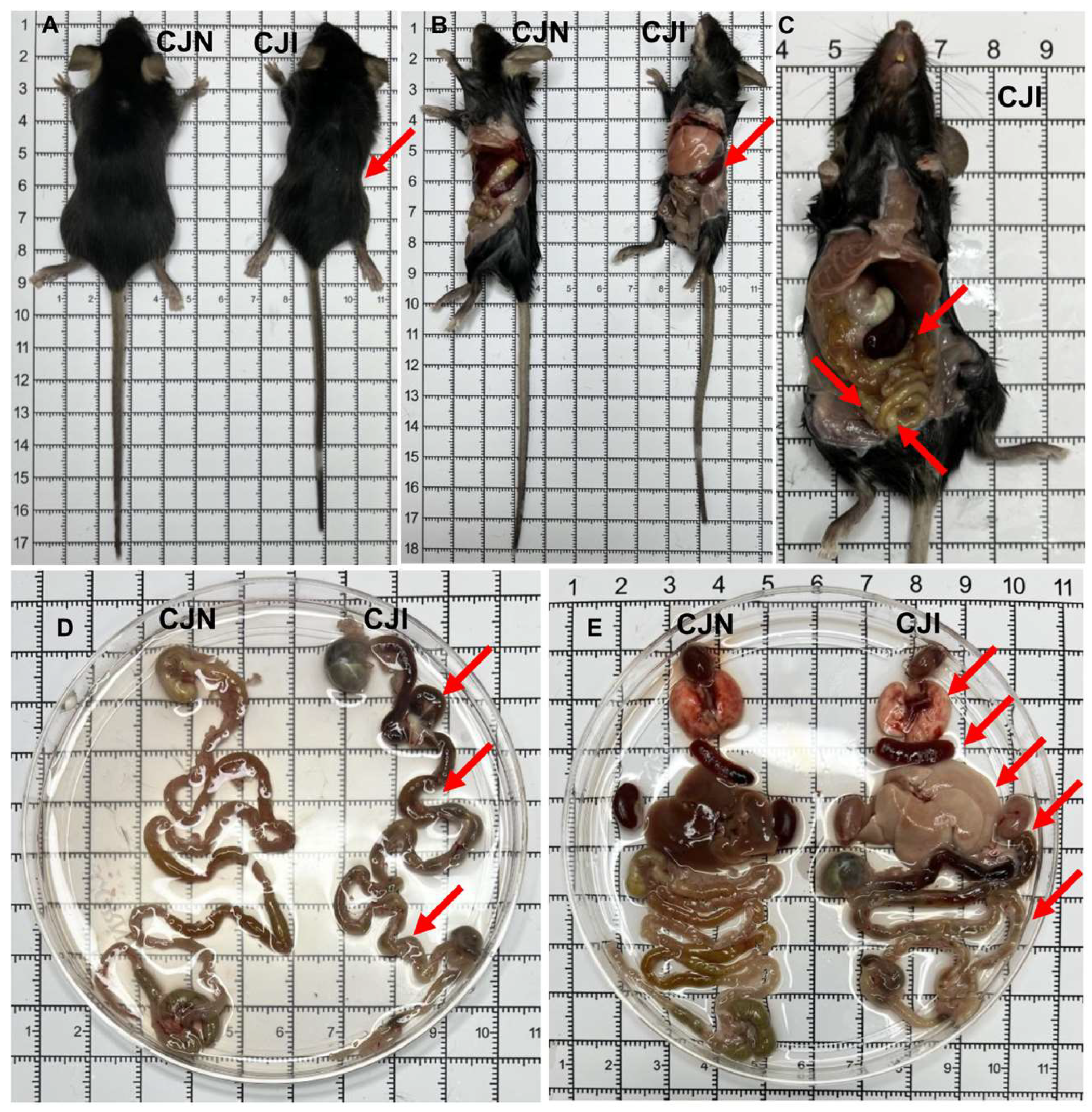
3.2. Oral Infection of Mice with T. gondii Cysts Induces Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Multi-Organ System Damage
3.3. T. gondii Loads Vary Across Multiple Time Points and Various Organs
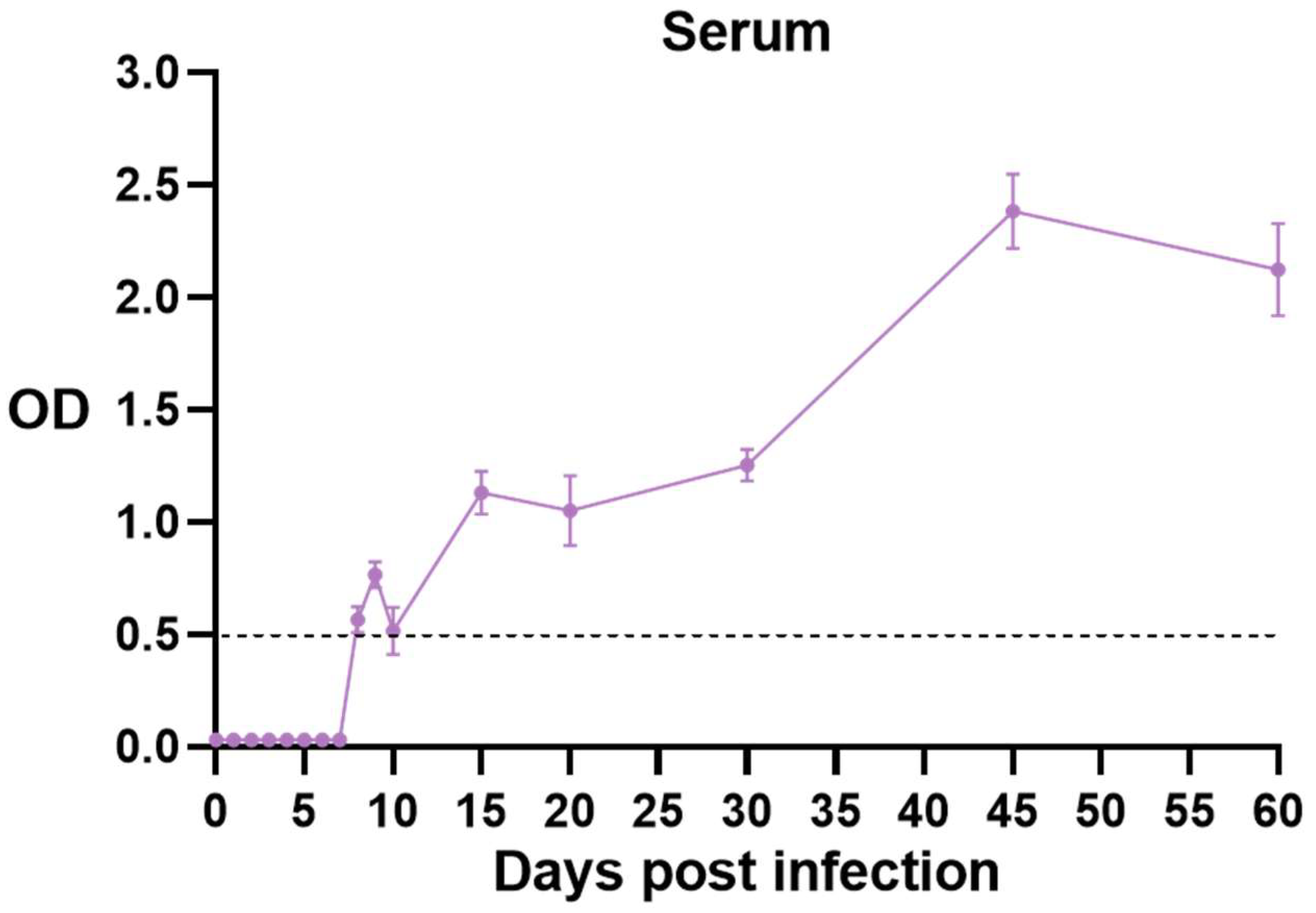
3.4. Changes in Toxoplasma-Specific Antibodies in Mouse Serum
3.5. Histological and Immunofluorescence Analysis of Mouse Brain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 22–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Sun, C.Y.; Yang, R.D.; Xu, C.J.; Chen, M.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cong, W.; Zhu, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zou, F.C. A large-scale serological survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection among persons participated in health screening in Yunnan province, Southwestern China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Miller, N.L. Toxoplasma gondii in cats: Fecal stages identified as coccidian oocysts. Science 1970, 167, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrey, E.F.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma oocysts as a public health problem. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of cerebral toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, N.; Zhang, R.L.; Lin, R.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Food-borne parasitic zoonoses in China: Perspective for control. Trends Parasitol. 2008, 24, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.C.; Goulart, C.; Hayward, J.A.; Kupz, A.; Miller, C.M.; van Dooren, G.G. Control of human toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Roussos, N.; Falagas, M.E. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: Global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Gamble, H.R.; Fakhri, Y.; Nourollahpour Shiadeh, M.; Danesh, M.; Behniafar, H.; Paktinat, S.; Foroutan, M.; Mokdad, A.H.; et al. Global prevalence of latent toxoplasmosis in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Hung, J.H.; Hsu, S.M. Ocular toxoplasmosis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, S.K.; Rinkenberger, N.; Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii infection and its implications within the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Li, D.; Qin, L.; Yu, X. The complete telomere-to-telomere sequence of a mouse genome. Science 2024, 386, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacesa, M.; Pelea, O.; Jinek, M. Past, present, and future of CRISPR genome editing technologies. Cell 2024, 187, 1076–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.R.; Didion, J.P.; Buus, R.J.; Bell, T.A.; Welsh, C.E.; Bonhomme, F.; Yu, A.H.; Nachman, M.W.; Pialek, J.; et al. Subspecific origin and haplotype diversity in the laboratory mouse. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Grigg, M.E. Toxoplasma gondii: Laboratory maintenance and growth. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2017, 44, 20C–21C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilue, J.; Doran, A.G.; Fiddes, I.T.; Abrudan, M.; Armstrong, J.; Bennett, R.; Chow, W.; Collins, J.; Collins, S.; Czechanski, A.; et al. Sixteen diverse laboratory mouse reference genomes define strain-specific haplotypes and novel functional loci. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sibley, L.D. Assays for monitoring Toxoplasma gondii infectivity in the laboratory mouse. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2071, 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Ferreira, L.R.; Martins, J.; McLeod, R. Oral oocyst-induced mouse model of toxoplasmosis: Effect of infection with Toxoplasma gondii strains of different genotypes, dose, and mouse strains (transgenic, out-bred, in-bred) on pathogenesis and mortality. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesenfeld, O. Oral infection of C57BL/6 mice with Toxoplasma gondii: A new model of inflammatory bowel disease? J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, S96–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, C.E.; Cohen, S.B.; Denkers, E.Y. Insights into inflammatory bowel disease using Toxoplasma gondii as an infectious trigger. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, L.B.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Araujo, E.C.B.; Franca, F.B.F.; Almeida, M.P.O.; Cariaco, Y.; Czarnewski, P.; Silva, N.M. Both C57BL/KsJ (h2(d) haplotype) and CB10-h2 (h2(b) haplotype) mice are highly susceptible to congenital toxoplasmosis. Acta Trop. 2023, 248, 107022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, E.C.; Barbosa, B.F.; Coutinho, L.B.; Barenco, P.V.; Sousa, L.A.; Milanezi, C.M.; Bonfá, G.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Silva, J.S.; Ferro, E.A.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 activity is involved in the control of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the lung of BALB/c and C57BL/6 and in the small intestine of C57BL/6 mice. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Medeiros Brito, R.M.; Meurer, Y.D.S.R.; Batista, J.A.L.; de Sá, A.L.; de Medeiros Souza, C.R.; de Souto, J.T.; de Andrade-Neto, V.F. Chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection contributes to perineuronal nets impairment in the primary somatosensory cortex. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, N.Z.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.X.; Zhang, Z.W.; Fu, B.Q.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. The transcription factor AP2XI-2 is a key negative regulator of Toxoplasma gondii merogony. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.H.; Chen, T.C.; Kuo, T.T.; Tseng, C.C.; Tseng, C.P. Real-time PCR for quantitative detection of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4121–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Su, R.; Li, T.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Isolation, genotyping and pathogenicity of a Toxoplasma gondii strain isolated from a serval (Leptailurus serval) in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Mao, J.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, K.M.; Eom, G.D.; Chu, K.B.; Moon, E.K.; Quan, F.S. The detection of Toxoplasma gondii ME49 infections in BALB/c mice using various techniques. Parasites Hosts Dis. 2023, 61, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Léon, M.; Bastidas-Quintero, A.M.; Steinfeldt, T. Decoding Toxoplasma gondii virulence: The mechanisms of IRG protein inactivation. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, L.L.; Sibley, L.D. The hitchhiker’s guide to parasite dissemination. Cell Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, B.S.; Schwarz, D.; Wadsworth, M.H.; Saeij, J.P.; Shalek, A.K.; Lourido, S. Identification of a master regulator of differentiation in Toxoplasma. Cell 2020, 180, 359–372.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liang, Q.L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Sibley, L.D.; Zhu, X.Q. The protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme is a key regulator of starch metabolism and bradyzoite differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluco, S.; Simonato, G.; Mancin, M.; Pietrobelli, M.; Ricci, A. Toxoplasma gondii infection and food consumption: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case-controlled studies. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, M.; Fakhri, Y.; Riahi, S.M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Namroodi, S.; Taghipour, A.; Spotin, A.; Gamble, H.R.; Rostami, A. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 269, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, M.; Liesenfeld, O. Small intestinal inflammation following oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii does not occur exclusively in C57BL/6 mice: Review of 70 reports from the literature. Mem. Inst. Oswal Cruz. 2009, 104, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; El-Fahmawi, A.; Christian, D.A.; Fang, Q.; Radaelli, E.; Chen, L.; Sullivan, M.C.; Misic, A.M.; Ellringer, J.A.; Zhu, X.Q.; et al. Infection-induced intestinal dysbiosis is mediated by macrophage activation and nitrate production. mBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraav, I.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Olias, P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Mack, M.; Baldridge, M.T.; Stappenbeck, T.; et al. Chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection enhances susceptibility to colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106730118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.X.; Jiang, P.C.; Han, B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Guan, J.Y.; Liu, Z.R.; He, S.Y.; Zhou, C.X. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii effect of tylosin in vitro and in vivo. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.; Safronova, A.; Burger, E.; López-Yglesias, A.; Giri, S.; Camanzo, E.T.; Martin, A.T.; Grivennikov, S.; Yarovinsky, F. IFN-γ mediates Paneth cell death via suppression of mTOR. eLife 2021, 10, e60478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sher, A.; Yap, G.; Park, D.; Neyer, L.E.; Liesenfeld, O.; Fort, M.; Kang, H.; Gufwoli, E. IL-10 is required for prevention of necrosis in the small intestine and mortality in both genetically resistant BALB/c and susceptible C57BL/6 mice following peroral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5375–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, M.J.; Grainger, J.R.; Bouladoux, N.; Hand, T.W.; Koo, L.Y.; Naik, S.; Quinones, M.; Dzutsev, A.K.; Gao, J.; Trinchieri, G.; et al. Intraluminal containment of commensal outgrowth in the gut during infection-induced dysbiosis. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Fuchs, D.; Struck, D.; Niebergall, J.; Jahn, H.; Dunay, I.R.; Moter, A.; Gescher, D.M.; et al. Gram-negative bacteria aggravate murine small intestinal Th1-type immunopathology following oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8785–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Jiang, K. Gut microbiota-related metabolite alpha-linolenic acid mitigates intestinal inflammation induced by oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiome 2023, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Rahman, S.U.; Gong, H.Y.; Mi, R.S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, J.L.; Yin, C.C.; Qian, M.; Chen, Z.G. Transcriptome analysis of a newly established mouse model of Toxoplasma gondii pneumonia. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Liu, G.H.; Meng, Q.F.; Dong, W.; Qin, S.Y.; Zhang, F.K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Qian, A.D.; Zhu, X.Q. Toxoplasma gondii infection in cancer patients: Prevalence, risk factors, genotypes and association with clinical diagnosis. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradt, C.; Ueno, N.; Christian, D.A.; Delong, J.H.; Pritchard, G.H.; Herz, J.; Bzik, D.J.; Koshy, A.A.; McGavern, D.B.; Lodoen, M.B.; et al. Endothelial cells are a replicative niche for entry of Toxoplasma gondii to the central nervous system. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Figueroa Velez, D.X.; Azevedo, R.; Hoover, E.M.; Tran, C.J.; Lo, C.; Vadpey, O.; Gandhi, S.P.; Lodoen, M.B. Imaging the dynamic recruitment of monocytes to the blood–brain barrier and specific brain regions during Toxoplasma gondii infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24796–24807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.C.; Olivera, G.C.; Barragan, A. Early passage of Toxoplasma gondii across the blood–brain barrier. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.S.; Lodoen, M.B. Mechanisms of human innate immune evasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, S.; Jeong, H.E.; Han, S.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.; Yang, J.; Oh, H.J.; Chung, S.; Lee, S. Microfluidic model for in vitro acute Toxoplasma gondii infection and transendothelial migration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Toxoplasma gondii: An underestimated threat? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, D.; Barragan, A. Advances and challenges in understanding cerebral toxoplasmosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y. The immune system utilizes two distinct effector mechanisms of t cells depending on two different life cycle stages of a single pathogen, Toxoplasma gondii, to control its cerebral infection. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 76, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skariah, S.; McIntyre, M.K.; Mordue, D.G. Toxoplasma gondii: Determinants of tachyzoite to bradyzoite conversion. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, L.; Wek, R.C.; Sullivan, W.J. Host sensing and signal transduction during Toxoplasma stage conversion. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Guerrero, G.; Gonzalez-Reyes, R.E.; De-la-Torre, A.; Medina-Rincón, G.; Nava-Mesa, M.O. Pathophysiological mechanisms of cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration by Toxoplasma gondii infection. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, E.; Faizi, F.; Heidarimoghadam, R.; Davoodi, L.; Mohammadi, Y. Association of T. gondii infection with suicide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Prandovszky, E.; Kannan, G.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Dickerson, F.; Severance, E.G.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma gondii: Biological parameters of the connection to schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yang, X.; Tan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; He, C.; Yin, K.; et al. Gut microbiota mediates anxiety-like behaviors induced by chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2391535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchanian, S.B.; Lodoen, M.B. Monocytes as primary defenders against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degrandi, D.; Kravets, E.; Konermann, C.; Beuter-Gunia, C.; Klümpers, V.; Lahme, S.; Rasch, E.; Mausberg, A.K.; Beer-Hammer, S.; Pfeffer, K. Murine guanylate binding protein 2 (mGBP2) controls Toxoplasma gondii replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Lempke, S.L.; Urbán Arroyo, J.C.; Brown, I.G.; Yin, B.; Magaj, M.M.; Holness, N.K.; Smiley, J.; Redemann, S.; Ewald, S.E. iNOS is necessary for GBP-mediated T. gondii clearance in murine macrophages via vacuole nitration and intravacuolar network collapse. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Duval, I.; Cardozo, M.E.; Souza, J.L.N.; de Medeiros Brito, R.M.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Bueno, L.L.; Magalhães, L.M.D. Parasite infections: How inflammation alters brain function. Trends Parasitol. 2025, 41, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, E.M.; Wilson, C.B.; Thompson, G.R.; Koshy, A.A.; Hunter, C.A. Infection with Toxoplasma gondii triggers coagulation at the blood-brain barrier and a reduction in cerebral blood flow. J. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, R.; Belloy, M.; Audibert, A.; Bassot, E.; Aïda, A.; Alis, M.; Miranda-Capet, R.; Jourdes, A.; van Gisbergen, K.P.J.M.; Masson, F.; et al. Protective function and differentiation cues of brain-resident CD8+ T cells during surveillance of latent Toxoplasma gondii infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2403054121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracha, S.; Johnson, H.J.; Pranckevicius, N.A.; Catto, F.; Economides, A.E.; Litvinov, S.; Hassi, K.; Rigoli, M.T.; Cheroni, C.; Bonfanti, M.; et al. Engineering Toxoplasma gondii secretion systems for intracellular delivery of multiple large therapeutic proteins to neurons. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 2051–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
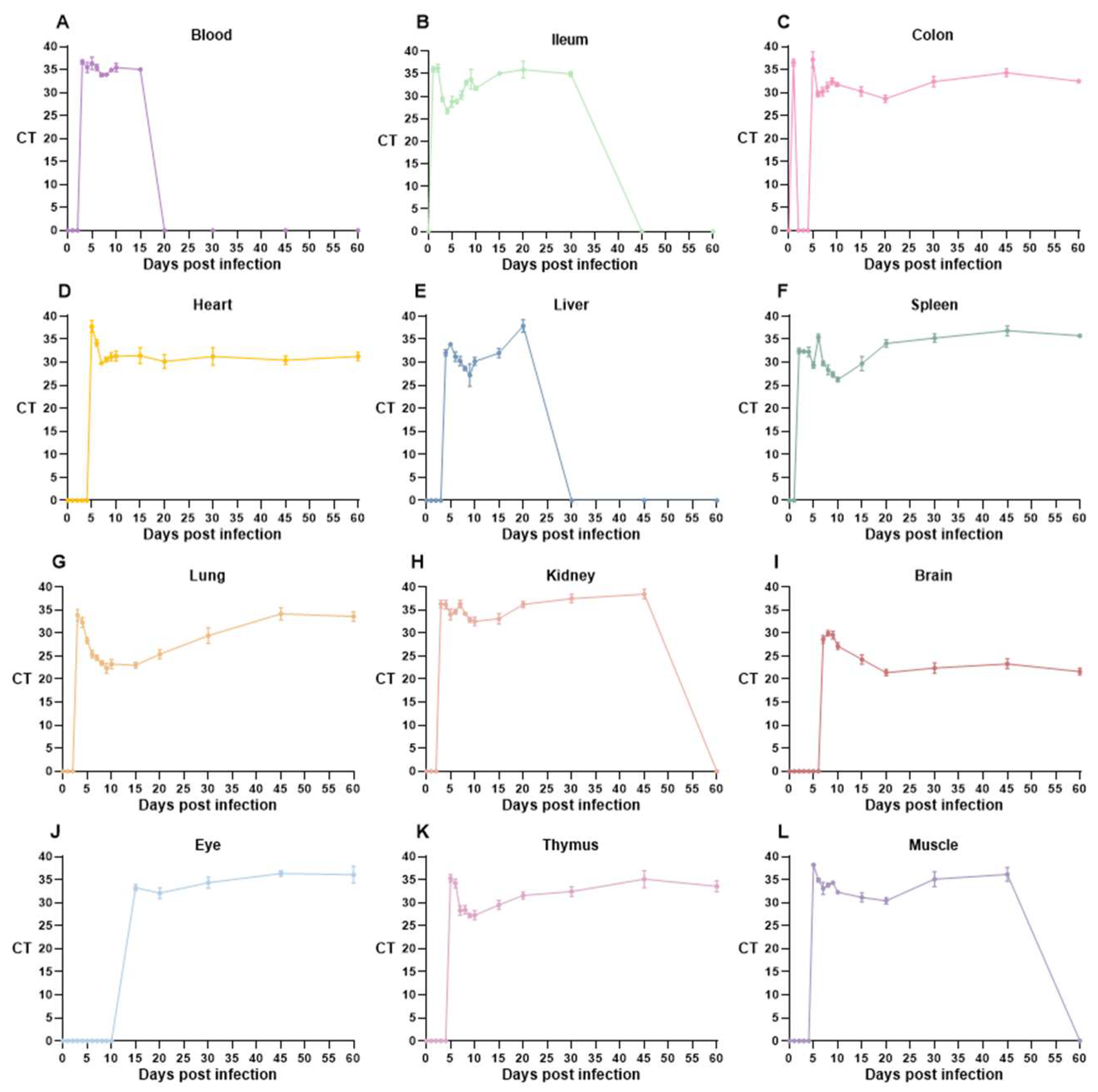
| Sample | CT Value Classification with Days Post Infection | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 60 | |
| Blood | − | − | ± | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| Ileum | + | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | − | − |
| Colon | − | + | − | − | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| Heart | − | − | − | − | + | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Liver | − | − | − | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | − | − | − |
| Spleen | − | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | + | + |
| Lung | − | − | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Kidney | − | − | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ± | − |
| Brain | − | − | − | − | − | − | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | +++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++++ |
| Eye | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | ++ | ++ | + | + | + |
| Thymus | − | − | − | − | + | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| Muscle | − | − | − | − | ± | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Liu, Q.-S.; Hu, J.-J.; Deng, C.-Q.; Li, T.; Zheng, W.-B.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Zou, F.-C. Spatiotemporal Diffusion, Colonization, and Antibody Responses in Susceptible C57BL/6J Mice Orally Infected with Toxoplasma gondii Cysts. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030212
Li Z, Liu Q-S, Hu J-J, Deng C-Q, Li T, Zheng W-B, Zhu X-Q, Zou F-C. Spatiotemporal Diffusion, Colonization, and Antibody Responses in Susceptible C57BL/6J Mice Orally Infected with Toxoplasma gondii Cysts. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhao, Qi-Shuai Liu, Jun-Jie Hu, Cai-Qin Deng, Tao Li, Wen-Bin Zheng, Xing-Quan Zhu, and Feng-Cai Zou. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Diffusion, Colonization, and Antibody Responses in Susceptible C57BL/6J Mice Orally Infected with Toxoplasma gondii Cysts" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030212
APA StyleLi, Z., Liu, Q.-S., Hu, J.-J., Deng, C.-Q., Li, T., Zheng, W.-B., Zhu, X.-Q., & Zou, F.-C. (2025). Spatiotemporal Diffusion, Colonization, and Antibody Responses in Susceptible C57BL/6J Mice Orally Infected with Toxoplasma gondii Cysts. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030212






