Multi-Component Protein Vaccine Induces a Strong and Long-Term Immune Response Against Monkeypox Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
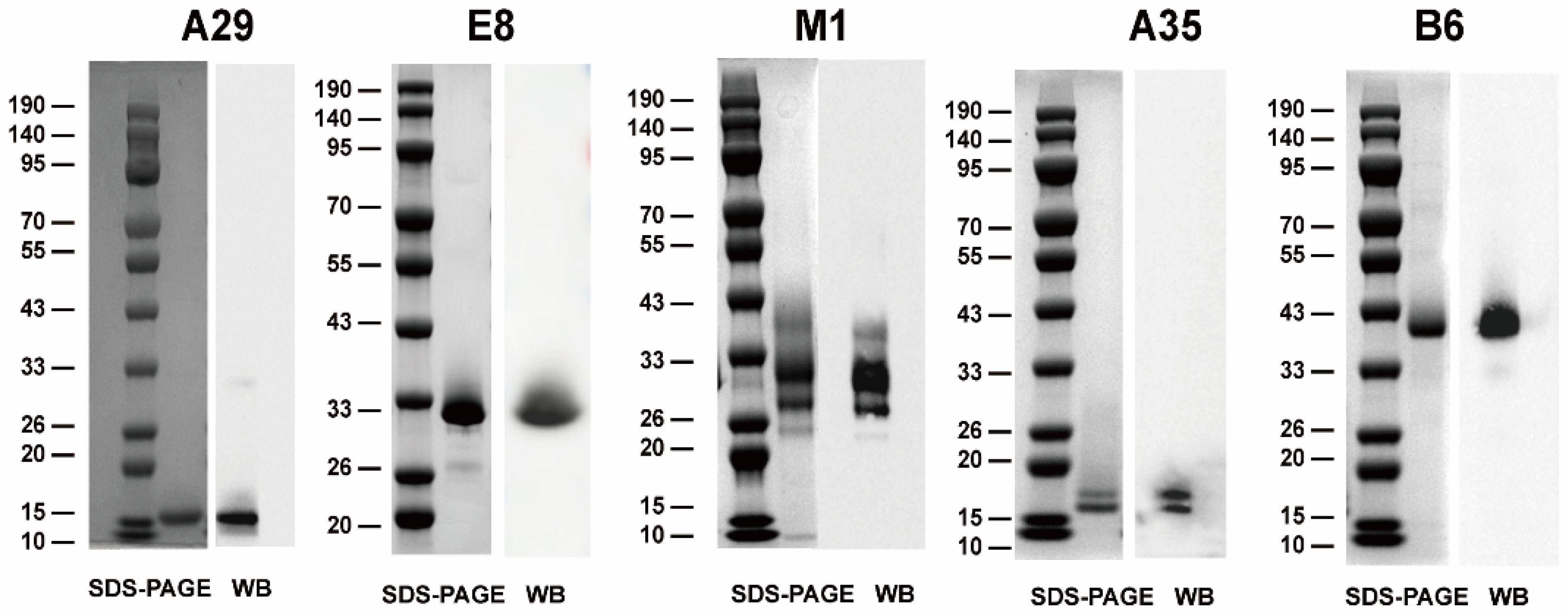
2.2. Protein Expression, Purification, and Identification
2.3. Mouse Immunization and Challenge Protocol
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test
2.6. IFN-γ ELISpot Assay
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR and Measurement of Infectious Virus Particles
3. Results
3.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant MPXV Proteins
3.2. Multiple Multi-Component Protein Vaccines Elicited Robust Antibody Responses at High Titers
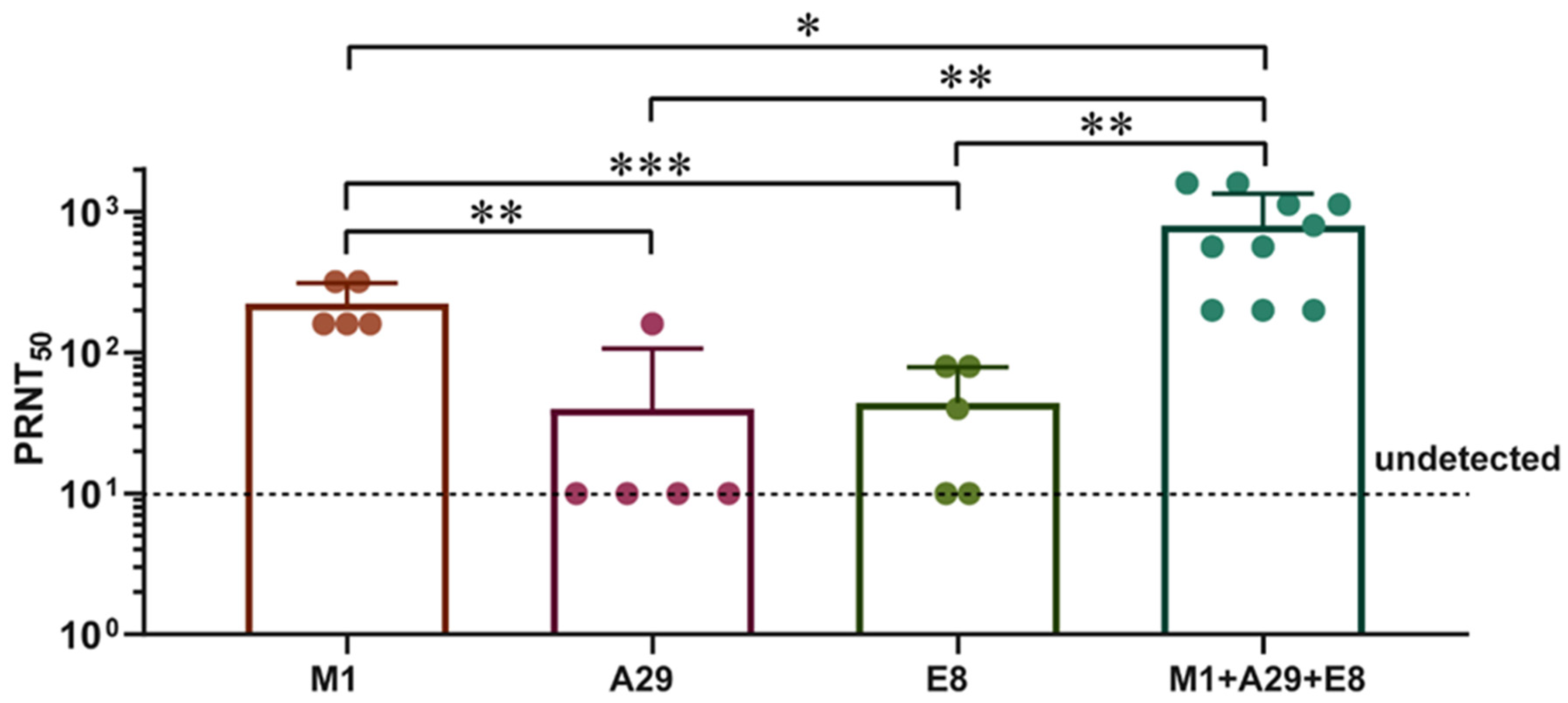
3.3. M1 Elicited Greater Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies in Contrast to the A29 and E8
3.4. Multiple Multi-Component Protein Vaccines Induced Cellular Immunity in Mice
3.5. Multiple Multi-Component Protein Vaccines Inhibited VACV Proliferation
3.6. Multiple Multi-Component Vaccines Induce a Long-Term Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karagoz, A.; Tombuloglu, H.; Alsaeed, M.; Tombuloglu, G.; AlRubaish, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.; Smajlović, S.; Ćordić, S.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alsuhaimi, E. Monkeypox (mpox) virus: Classification, origin, transmission, genome organization, antiviral drugs, and molecular diagnosis. J. Infect Public Health. 2023, 16, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Orgnization. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Extraordinary Meeting of the Standing Committee on Health Emergency Prevention, Preparedness and Response—15 August 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-extraordinary-meeting-of-the-standing-committee-on-health-emergency-prevention--preparedness-and-response---15-august-2024 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Cunha, B.E. Monkeypox in the United States: An occupational health look at the first cases. AAOHN J. 2004, 52, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.T.; Wenner, H.A. Monkeypox virus. Bacteriol. Rev. 1973, 37, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, F.M.; Torres-Ruesta, A.; Tay, M.Z.; Lin, R.T.; Lye, D.C.; Rénia, L.; Ng, L.F. Monkeypox: Disease epidemiology, host immunity and clinical interventions. Nature reviews. Immunology 2022, 22, 597–613. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, M.G.; Damon, I.K. Outbreaks of human monkeypox after cessation of smallpox vaccination. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmiche, M.C.; Goenaga, J.; Wittek, R.; Rindisbacher, L. Neutralizing and protective antibodies directed against vaccinia virus envelope antigens. Virology 1999, 254, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, L.A.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Prigge, J.T.; Yang, M.; Satishchandran, A.; Wu, L.; Hammarlund, E.; Khan, A.S.; Babas, T.; Rhodes, L.; et al. Multivalent smallpox DNA vaccine delivered by intradermal electroporation drives protective immunity in nonhuman primates against lethal monkeypox challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Sigal, L.J. Antibodies and CD8+ T cells are complementary and essential for natural resistance to a highly lethal cytopathic virus. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 6829–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarín-Vicente, E.J.; Alemany, A.; Agud-Dios, M.; Ubals, M.; Suñer, C.; Antón, A.; Arando, M.; Arroyo-Andrés, J.; Calderón-Lozano, L.; Casañ, C.; et al. Clinical presentation and virological assessment of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in Spain: A prospective observational cohort study. Lancet 2022, 400, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivancos, R.; Anderson, C.; Blomquist, P.; Balasegaram, S.; Bell, A.; Bishop, L.; Brown, C.S.; Chow, Y.; Edeghere, O.; Florence, I.; et al. Community transmission of monkeypox in the United Kingdom, April to May 2022. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Les Mal. Transm. = Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2022, 27, 2200422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Lu, H.; Yu, C.; Sun, H.; Long, J.; Cao, Y.; Mai, J.; Miao, Y.; et al. Monkeypox virus quadrivalent mRNA vaccine induces immune response and protects against vaccinia virus. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiani, A.; Dulberger, C.L.; De Silva, N.S.; Marquette, M.; Lu, Y.J.; Palowitch, G.M.; Dokic, A.; Sanchez-Velazquez, R.; Schlatterer, K.; Sarkar, S.; et al. A multivalent mRNA monkeypox virus vaccine (BNT166) protects mice and macaques from orthopoxvirus disease. Cell 2024, 187, 1363–1373.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, S.; Hickman, R.L.; Wooding, W.L., Jr.; Huxsoll, D.L. Monkeypox: Experimental infection in chimpanzee (Pan satyrus) and immunization with vaccinia virus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1968, 29, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.K.; Petersen, B.W.; Whitehill, F.; Razeq, J.H.; Isaacs, S.N.; Merchlinsky, M.J.; Campos-Outcalt, D.; Morgan, R.L.; Damon, I.; Sánchez, P.J.; et al. Use of JYNNEOS (Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine, Live, Nonreplicating) for Preexposure Vaccination of Persons at Risk for Occupational Exposure to Orthopoxviruses: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, B.W.; Harms, T.J.; Reynolds, M.G.; Harrison, L.H. Use of Vaccinia Virus Smallpox Vaccine in Laboratory and Health Care Personnel at Risk for Occupational Exposure to Orthopoxviruses—Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalca, A.; Zumbrun, E.E. ACAM2000: The new smallpox vaccine for United States Strategic National Stockpile. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2010, 4, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeck, L.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Verstrepen, B.E.; Bestebroer, T.M.; van Royen, M.E.; Götz, H.; Shamier, M.C.; van Leeuwen, L.P.M.; Schmitz, K.S.; Alblas, K.; et al. Low levels of monkeypox virus-neutralizing antibodies after MVA-BN vaccination in healthy individuals. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Bruel, T.; Porrot, F.; Planas, D.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Wiedemann, A.; Burrel, S.; Marot, S.; Palich, R.; et al. Complement-dependent mpox-virus-neutralizing antibodies in infected and vaccinated individuals. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 937–948.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulter, E.A.; Appleyard, G. Differences between extracellular and intracellular forms of poxvirus and their implications. Prog. Med. Virol. 1973, 16, 86–108. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D.H.; McCausland, M.M.; Valdez, C.; Huynh, D.; Hernandez, J.E.; Mu, Y.; Hirst, S.; Villarreal, L.; Felgner, P.L.; Crotty, S. Vaccinia virus H3L envelope protein is a major target of neutralizing antibodies in humans and elicits protection against lethal challenge in mice. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11724–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Cheng, H.; Dai, Z.; Bu, Z.; Sigal, L.J. Immunization with a single extracellular enveloped virus protein produced in bacteria provides partial protection from a lethal orthopoxvirus infection in a natural host. Virology 2006, 345, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.W.; Custer, D.M.; Thompson, E. Four-gene-combination DNA vaccine protects mice against a lethal vaccinia virus challenge and elicits appropriate antibody responses in nonhuman primates. Virology 2003, 306, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.W.; Golden, J.W.; Ferro, A.M.; King, A.D. Smallpox DNA vaccine delivered by novel skin electroporation device protects mice against intranasal poxvirus challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucker, E.M.; Golden, J.W.; Hammerbeck, C.D.; Kishimori, J.M.; Royals, M.; Joselyn, M.D.; Ballantyne, J.; Nalca, A.; Hooper, J.W. A Nucleic Acid-Based Orthopoxvirus Vaccine Targeting the Vaccinia Virus L1, A27, B5, and A33 Proteins Protects Rabbits against Lethal Rabbitpox Virus Aerosol Challenge. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0150421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhu, Y.L.; Tang, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wu, M.; Ming, T.; Deng, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.; et al. Rational development of multicomponent mRNA vaccine candidates against mpox. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2192815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Du, S.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Rcheulishvili, N.; Wang, P.G.; Lin, J. A Subunit Vaccine Candidate Composed of Mpox Virus A29L, M1R, A35, and B6R Elicits Robust Immune Response in Mice. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Fan, H.; Xu, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Dan, D.; Du, H.; et al. Recombinant proteins A29L, M1R, A35R, and B6R vaccination protects mice from mpox virus challenge. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1203410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Zhao, J.; Gu, G.; Fang, M.; et al. Mpox multi-antigen mRNA vaccine candidates by a simplified manufacturing strategy afford efficient protection against lethal orthopoxvirus challenge. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2204151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.W.; Thompson, E.; Wilhelmsen, C.; Zimmerman, M.; Ichou, M.A.; Steffen, S.E.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Jahrling, P.B. Smallpox DNA vaccine protects nonhuman primates against lethal monkeypox. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4433–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchuk, I.; Gilchuk, P.; Sapparapu, G.; Lampley, R.; Singh, V.; Kose, N.; Blum, D.L.; Hughes, L.J.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Townsend, M.B.; et al. Cross-Neutralizing and Protective Human Antibody Specificities to Poxvirus Infections. Cell 2016, 167, 684–694.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Y.; Xing, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; et al. Enhanced Influenza VLP vaccines comprising matrix-2 ectodomain and nucleoprotein epitopes protects mice from lethal challenge. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; Ning, N.; Zhang, L.; Gu, H.; Li, D.; Yu, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. The immunodominance of RBD antigen of delta variant as vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Luo, D.; Ning, N.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Yu, W.; Wei, W.; et al. An omicron-based vaccine booster elicits potent neutralizing antibodies against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants in adults. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2207670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Pan, H.; He, P.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Ning, N.; Fang, X.; Yu, W.; Wei, M.; Gao, H.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 and phase 2 clinical trial to evaluate efficacy and safety of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine SCoK in adults. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Ning, N.; Jin, S.; Shi, Z.; Gu, H.; Li, D.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H. An updated RBD-Fc fusion vaccine booster increases neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yin, P.; Zheng, T.; Qin, L.; Li, S.; Han, P.; Qu, X.; Wen, J.; Ding, H.; Wu, J.; et al. Rational design of a ‘two-in-one’ immunogen DAM drives potent immune response against mpox virus. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Gu, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Wang, H. Multi-Component Protein Vaccine Induces a Strong and Long-Term Immune Response Against Monkeypox Virus. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121410
Yang X, Sun Y, Gu H, Li D, Zhang L, Li T, Wang H. Multi-Component Protein Vaccine Induces a Strong and Long-Term Immune Response Against Monkeypox Virus. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121410
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaolan, Yakun Sun, Hongjing Gu, Deyu Li, Liangyan Zhang, Tao Li, and Hui Wang. 2024. "Multi-Component Protein Vaccine Induces a Strong and Long-Term Immune Response Against Monkeypox Virus" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121410
APA StyleYang, X., Sun, Y., Gu, H., Li, D., Zhang, L., Li, T., & Wang, H. (2024). Multi-Component Protein Vaccine Induces a Strong and Long-Term Immune Response Against Monkeypox Virus. Vaccines, 12(12), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121410




