Summary of the Current Status of DNA Vaccination for Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
Vaccines and Neurological Diseases
2. Alzheimer Disease
Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease
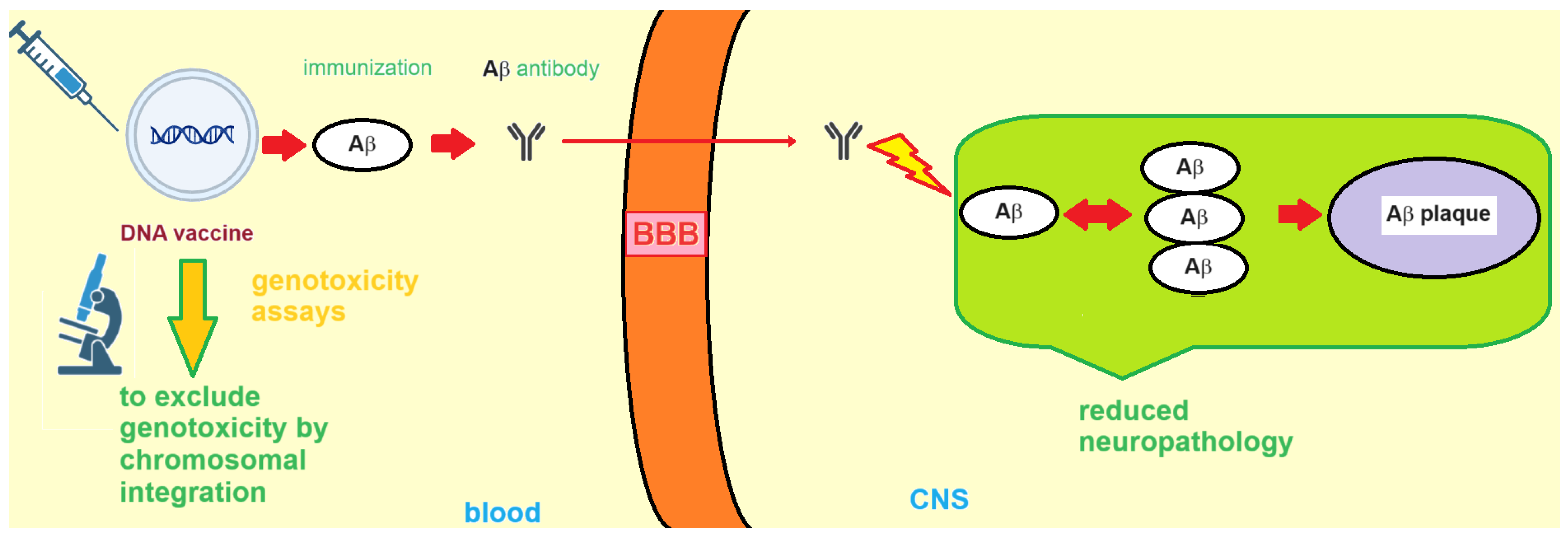
3. DNA Vaccines against AD
3.1. Formulation and Delivery of DNA-Based AD Vaccines
3.2. RNA Vaccines for Treatment of Alzheimer Disease
3.3. Nucleic Acid-Based AD Vaccines: Side Effects and Genosafety Profile
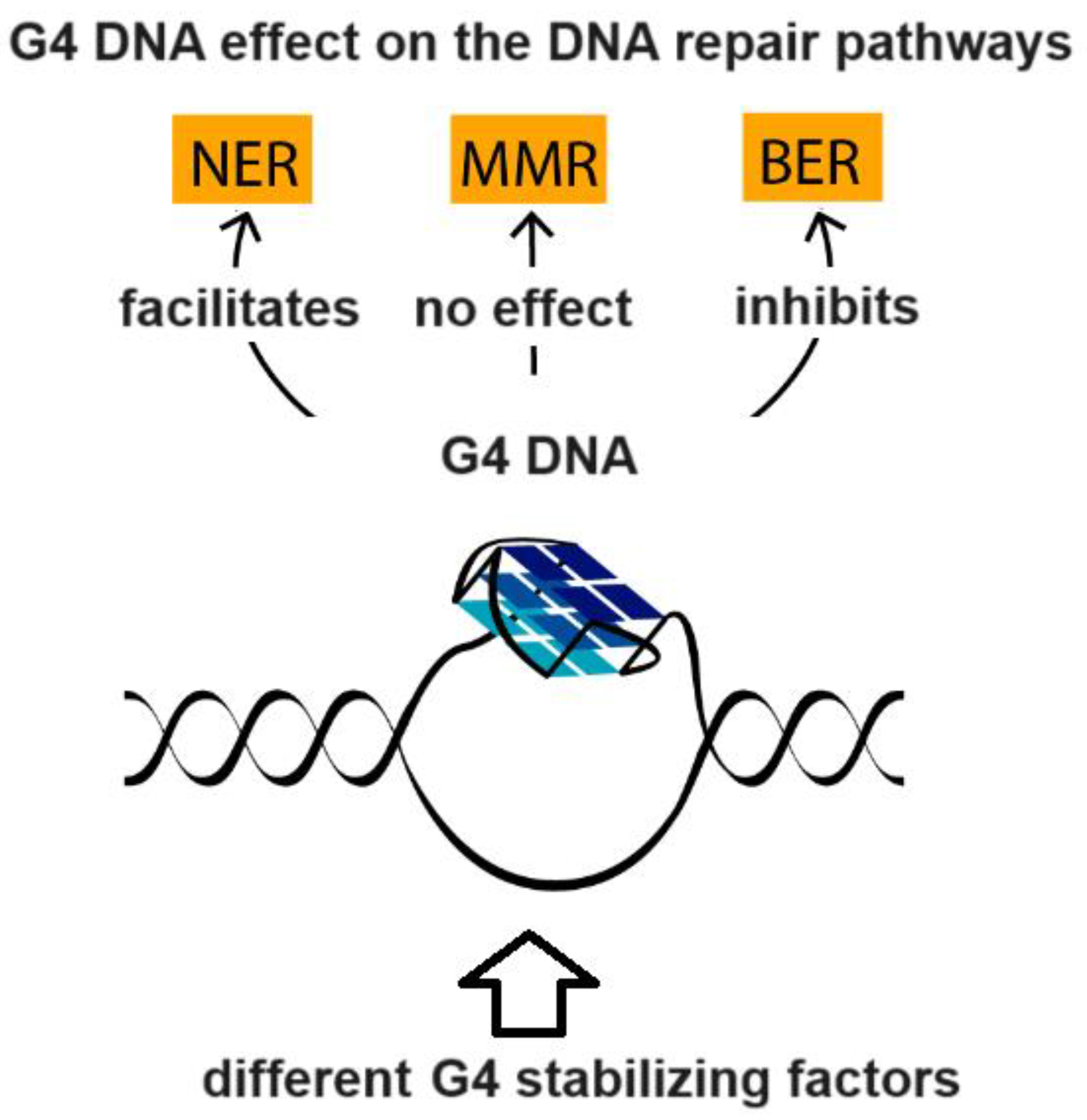
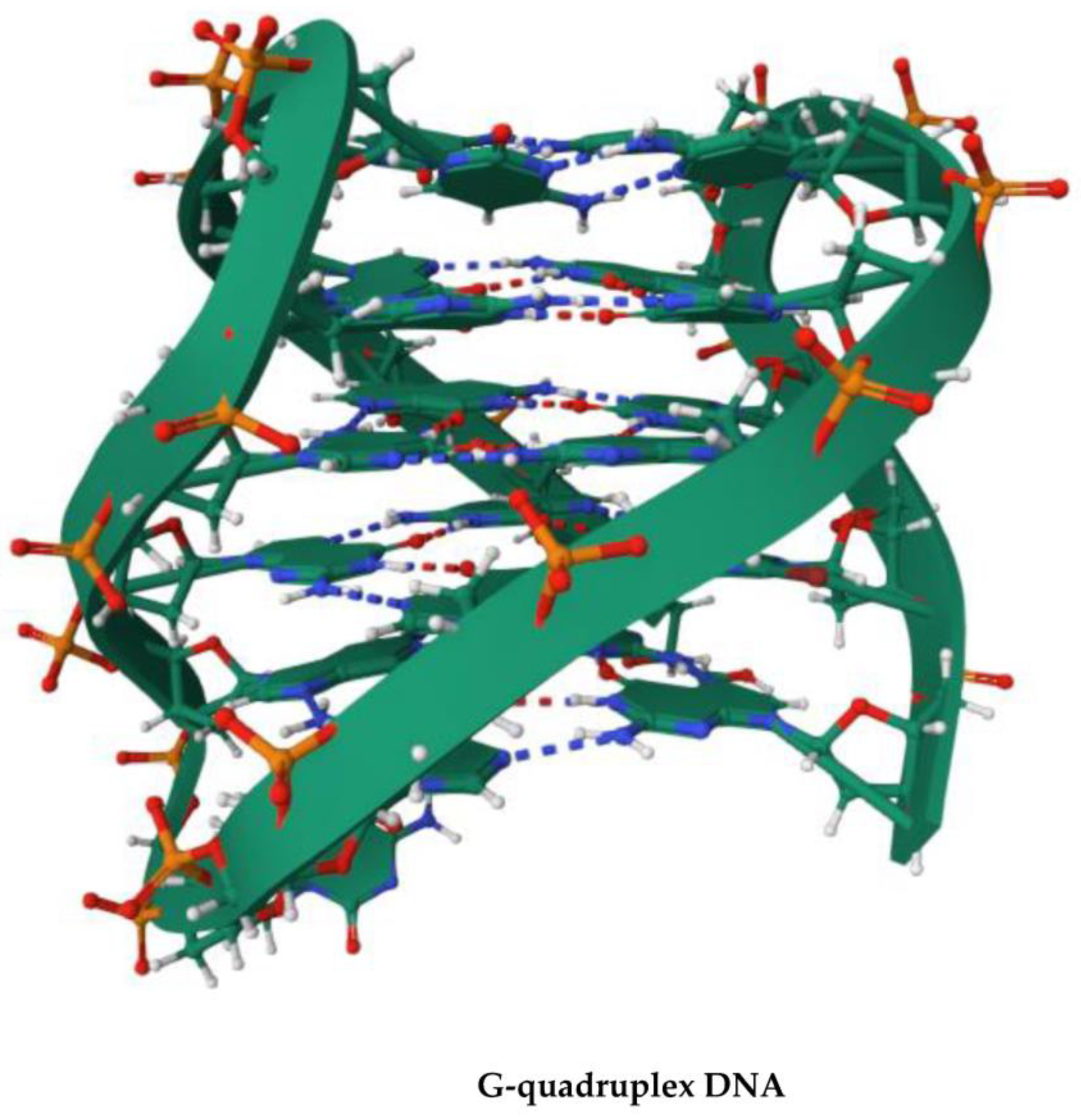
4. G-Quadruplex DNA and Alzheimer Disease: G4 Implication in AD and G4-Forming Sites in DNA Vaccines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wouk, J.; Rechenchoski, D.Z.; Rodrigues, B.C.D.; Ribelato, E.V.; Faccin-Galhardi, L.C. Viral infections and their relationship to neurological disorders. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J. The relationship between amyloid and tau. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2003, 20, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari-Souza, J.P.; Lussier, F.Z.; Leffa, D.T.; Therriault, J.; Tissot, C.; Bellaver, B.; Ferreira, P.C.; Malpetti, M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Povala, G. APOE ε4 associates with microglial activation independently of Aβ plaques and tau tangles. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang-Nunes, S.X.; Maat-Schieman, M.L.; van Duinen, S.G.; Roos, R.A.; Frosch, M.P.; Greenberg, S.M. The cerebral β-amyloid angiopathies: Hereditary and sporadic. Brain Pathol. 2006, 16, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorszewska, J.; Prendecki, M.; Oczkowska, A.; Dezor, M.; Kozubski, W. Molecular basis of familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, D.S.; Younger, A.P.J.; Guttmacher, S. Childhood Vaccination. Neurol. Clin. 2016, 34, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A. Vaccines: The Fourth Century. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.M.C.; Pinto, M.V.; Sadarangani, M.; Plotkin, S.A. Whither vaccines? J. Infect. 2017, 74, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, W.; Verlinde, C. Non-communicable diseases. Insulin 2006, 106, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, M.; van der Burg, S.H.; Melief, C.J.; Bhardwaj, N. Therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Seyedpour, S.; Khodaei, B.; Loghman, A.-H.; Seyedpour, N.; Yazdi, M.-H.; Rezaei, N. Cancer vaccines for triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review. Vaccines 2023, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, D.; Li, J.; Huang, M.; Cui, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, K. Dendritic cell vaccines in breast cancer: Immune modulation and immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.; De Giglio, M.A.; Roviello, G.N. Anti-coronavirus vaccines: Past investigations on SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV, the approved vaccines from BioNTech/Pfizer, Moderna, Oxford/AstraZeneca and others under Development Against SARSCoV-2 Infection. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borbone, N.; Piccialli, I.; Falanga, A.P.; Piccialli, V.; Roviello, G.N.; Oliviero, G. Nucleic Acids as Biotools at the Interface between Chemistry and Nanomedicine in the COVID-19 Era. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, V.; Roviello, G.N. The Potential Role of Vaccines in Preventing Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): An Update and Future Perspectives. Vaccines 2023, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, Y.; Matsumoto, Y. Recent advance in immunotherapies for Alzheimer disease, with special reference to DNA vaccination. Hum. Vaccines 2014, 5, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Imbimbo, B.P. Toxicity of β-amyloid vaccination in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. Off. J. Am. Neurol. Assoc. Child Neurol. Soc. 2002, 51, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, J.; Budson, A. Current understanding of Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and treatment. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, R.J.; Rolston, R.K.; Smith, M.A. Alzheimer disease. Dis. A-Mon. 2010, 56, 484–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippius, H.; Müller, N. The work of Emil Kraepelin and his research group in München. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 258, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.A. Neuropathology of dementia disorders. CONTINUUM Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2022, 28, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, S. Non-Alzheimer’s disease—Related memory impairment and dementia. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodintsev, A.N.; Izmozherova, N.V.; Popov, A.A.; Volkova, L.I.; Antropova, I.P.; Ryabinina, A.V. Biochemical Platelet Markers of Cognitive Impairments in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. J. 2023, 17, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.K.; Padmanabhan, P.; Yang, C.-T.; Ng, D.C.E.; Palanivel, M.; Mishra, S.; Halldin, C.; Gulyás, B. Positron emission tomographic imaging in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Nho, K.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Wang, X.; Risacher, S.L.; Fan, K.-H.; Snitz, B.E.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Mathis, C.A.; Lopez, O.L. Genome-wide association study of brain amyloid deposition as measured by Pittsburgh Compound-B (PiB)-PET imaging. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Sehar, U.; Bisht, J.; Selman, A.; Culberson, J.; Reddy, P.H. Phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, S.; Biernat, J.; Mandelkow, E. A current view on Tau protein phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2021, 69, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Klug, A.; Crowther, R.A. Tau protein, the paired helical filament and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2006, 9, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzioras, M.; McGeachan, R.I.; Durrant, C.S.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Clinical trials of amyloid-based immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: End of beginning or beginning of end? Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, K.A.; Brown, M.E.; McLaurin, J. Reduced oligomeric and vascular amyloid-β following immunization of TgCRND8 mice with an Alzheimer’s DNA vaccine. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okura, Y.; Miyakoshi, A.; Kohyama, K.; Park, I.-K.; Staufenbiel, M.; Matsumoto, Y. Nonviral Aβ DNA vaccine therapy against Alzheimer’s disease: Long-term effects and safety. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9619–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okura, Y.; Matsumoto, Y. DNA Vaccine Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Present Status and Future Direction. Rejuvenation Res. 2008, 11, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambracht-Washington, D.; Qu, B.-x.; Fu, M.; Anderson, L.D.; Eagar, T.N.; Stüve, O.; Rosenberg, R.N. A peptide prime-DNA boost immunization protocol provides significant benefits as a new generation Aβ42 DNA vaccine for Alzheimer disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 254, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Niimi, N.; Kohyama, K. Development of a New DNA Vaccine for Alzheimer disease Targeting a Wide Range of Aβ Species and Amyloidogenic Peptides. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75203. [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs, D.H. Abeta DNA Vaccination for Alzheimers Disease: Focus on Disease Prevention. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Harahap-Carrillo, I.S.; Davtyan, H.; Antonyan, T.; Chailyan, G.; Kazarian, K.; Antonenko, M.; Jullienne, A.; Hamer, M.M.; et al. Characterization and preclinical evaluation of the cGMP grade DNA based vaccine, AV-1959D to enter the first-in-human clinical trials. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiukas, Z.; Ephraim, R.; Tangalakis, K.; Davidson, M.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Feehan, J. Immunotherapies for Alzheimer’s Disease—A Review. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Sha, S.; Xing, X.-N.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.-W.; Shen, X.-L.; Cao, Y.-P. DNA vaccines targeting amyloid-β oligomer ameliorate cognitive deficits of aged APP/PS1/tau triple-transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.F.; Davtyan, H.; Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Davtyan, A.; Hannaman, D.; Cribbs, D.H.; Agadjanyan, M.G.; Ghochikyan, A. Epitope-based DNA vaccine for Alzheimer’s disease: Translational study in macaques. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 10, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambracht-Washington, D.; Fu, M.; Wight-Carter, M.; Riegel, M.; Hynan, L.S.; Rosenberg, R.N. DNA Aβ42 immunization via needle-less Jet injection in mice and rabbits as potential immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 446, 120564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kumar, S.A.; Jhan, Y.Y.; Bishop, C.J. Engineering DNA vaccines against infectious diseases. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davtyan, H.; Bacon, A.; Petrushina, I.; Zagorski, K.; Cribbs, D.H.; Ghochikyan, A.; Agadjanyan, M.G. Immunogenicity of DNA-and recombinant protein-based Alzheimer disease epitope vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Takeshita, F.; Xin, K.-Q.; Ishii, N.; Okuda, K. Adjuvant formulations and delivery systems for DNA vaccines. Methods 2003, 31, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, J.B.; Mason, P.W.; Geall, A.; Mandl, C.W. RNA-based vaccines. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4414–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessel, J. A vaccine to prevent initial loss of cognition and eventual Alzheimer’s disease in elderly persons. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2021, 7, e12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Logroscino, G. Anti-tau vaccine in Alzheimer’s disease: A tentative step. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davtyan, H.; Chen, W.W.; Zagorski, K.; Davis, J.; Petrushina, I.; Kazarian, K.; Cribbs, D.H.; Agadjanyan, M.G.; Blurton-Jones, M.; Ghochikyan, A. MultiTEP platform-based DNA epitope vaccine targeting N-terminus of tau induces strong immune responses and reduces tau pathology in THY-Tau22 mice. Vaccine 2017, 35, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardomi, A.; Mousavi, T.; Farnood, F.; Khosroshahi, H.T. Genotoxicity: A neglected but potentially critical aspect of adenoviral COVID-19 vaccines. Future Med. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimolai, N. Do RNA vaccines obviate the need for genotoxicity studies? Mutagenesis 2020, 35, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falanga, A.P.; Terracciano, M.; Oliviero, G.; Roviello, G.N.; Borbone, N. Exploring the Relationship between G-Quadruplex Nucleic Acids and Plants: From Plant G-Quadruplex Function to Phytochemical G4 Ligands with Pharmaceutic Potential. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipps, H.J.; Rhodes, D. G-quadruplex structures: In vivo evidence and function. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.; Zhang, R.; Cucchiarini, A.; Mehawej, C.; Mergny, J.-L.; Mroueh, M.; Faour, W.H. G-quadruplex forming sequences in the genes coding for cytochrome P450 enzymes and their potential roles in drug metabolism. Biochimie 2023, 214, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.-D.; Zhong, M.-Q.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Jia, M.-H.; Hu, X.-H.; Xu, Y.; Shen, X.-C. A Unique G-Quadruplex Aptamer: A Novel Approach for Cancer Cell Recognition, Cell Membrane Visualization, and RSV Infection Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: A novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, A.V.; Kubareva, E.A.; Monakhova, M.V.; Zvereva, M.I.; Dolinnaya, N.G. Impact of G-quadruplexes on the regulation of genome integrity, DNA damage and repair. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay Kumar, M.J.; Morales, R.; Tsvetkov, A.S. G-quadruplexes and associated proteins in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging 2023, 4, 1164057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brčić, J.; Plavec, J. NMR structure of a G-quadruplex formed by four d(G4C2) repeats: Insights into structural polymorphism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 11605–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, F.; Spanevello, A.; Reboldi, G.; Visca, D.; Verdecchia, P. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: Lights and shadows. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 88, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartas, M.; Volná, A.; Brázda, V.; Pecinka, P. G-quadruplex forming sites in DNA/RNA vaccines. In Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting on Quadruplex Nucleic Acids, Marienbad, Czech Republic, 28 June 2022; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361813967_G-quadruplex_forming_sites_in_DNARNA_vaccines (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Brazda, V.; Kolomaznik, J.; Mergny, J.-L.; Stastny, J. G4Killer web application: A tool to design G-quadruplex mutations. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3246–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, A.; Roviello, G.N. Exploring the Protective Effect of Food Drugs against Viral Diseases: Interaction of Functional Food Ingredients and SARS-CoV-2, Influenza Virus, and HSV. Life 2023, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | Animal Model | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ-Fc | APP23 mice | reduced Aβ burden no excessive neuroinflammation/T cell responses | no major weaknesses noted |
| YM3711 | B6C3-Tg 85Dbo/J mice; New Zealand white rabbits; cynomolgus monkeys | significant reduction in Aβ and other amyloidogenic peptides in the brain | no major weaknesses noted |
| AV-1955 | rhesus macaques | generates long-term and potent anti-Aβ antibodies | repeated (up to five times) immunization steps needed to achieve acceptable anti-Aβ antibody levels |
| AV-1959D | Tg2576 and Tg-SwDI mice | induces strong and therapeutically potent anti-Aβ antibodies with a favorable safety profile | low-grade reactions at the injection site |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicidomini, C.; Borbone, N.; Roviello, V.; Roviello, G.N.; Oliviero, G. Summary of the Current Status of DNA Vaccination for Alzheimer Disease. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111706
Vicidomini C, Borbone N, Roviello V, Roviello GN, Oliviero G. Summary of the Current Status of DNA Vaccination for Alzheimer Disease. Vaccines. 2023; 11(11):1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111706
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicidomini, Caterina, Nicola Borbone, Valentina Roviello, Giovanni N. Roviello, and Giorgia Oliviero. 2023. "Summary of the Current Status of DNA Vaccination for Alzheimer Disease" Vaccines 11, no. 11: 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111706
APA StyleVicidomini, C., Borbone, N., Roviello, V., Roviello, G. N., & Oliviero, G. (2023). Summary of the Current Status of DNA Vaccination for Alzheimer Disease. Vaccines, 11(11), 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111706










