Subchronic and Chronic Toxicity Assessment of Sublancin in Sprague–Dawley Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Treatments
2.3. Experiment 1: Observation and Measurement of Indicators of the Subchronic Toxicity Test for 90 Days
2.3.1. General Observations
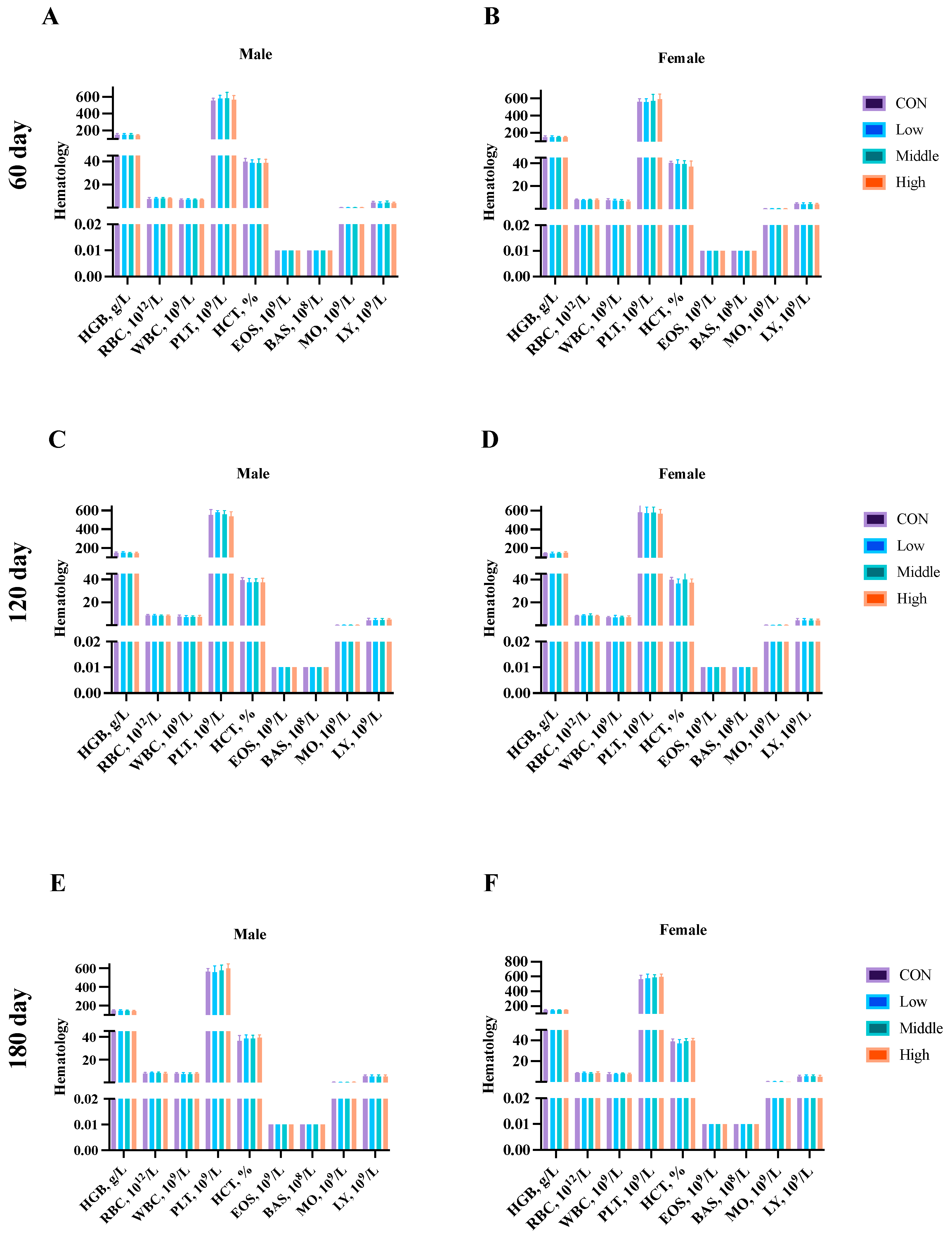
2.3.2. Hematology
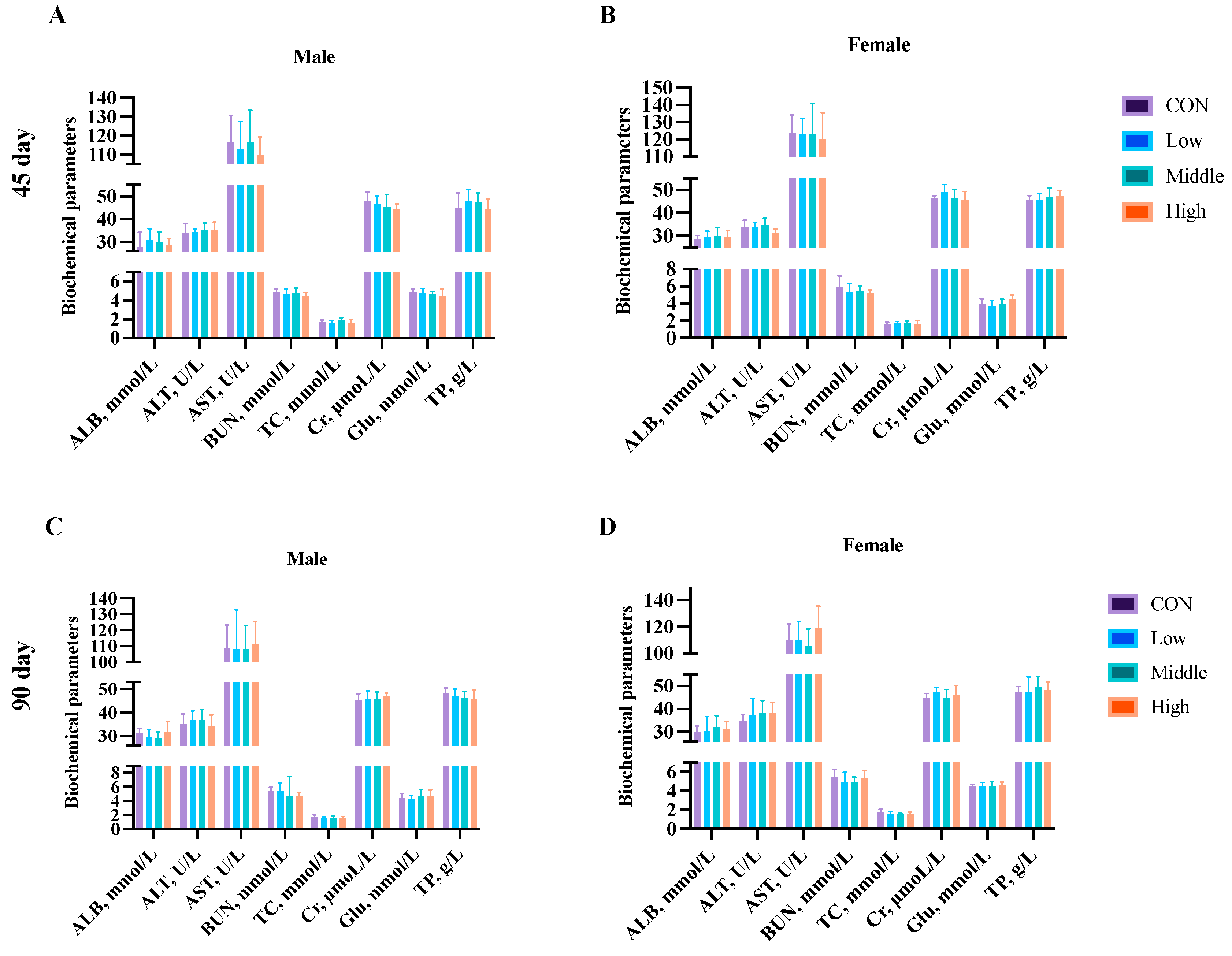
2.3.3. Serum Biochemical Parameters
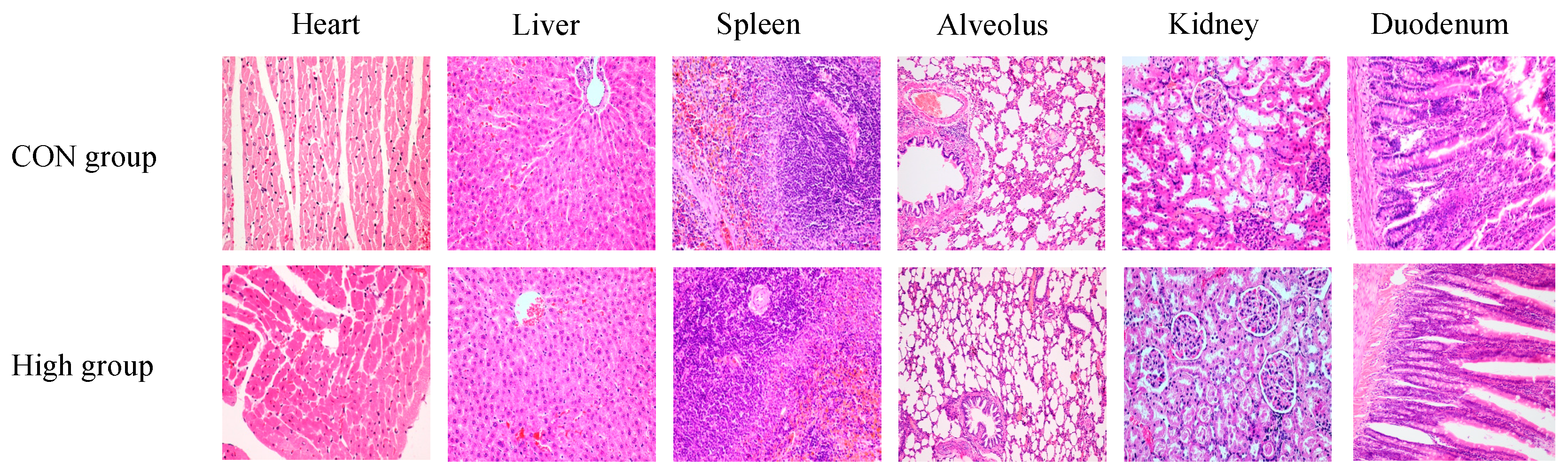
2.3.4. Pathological Examination
2.4. Experiment 2: Observation and Measurement of Indicators of the Chronic Toxicity Test for 180 Days
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Symptoms
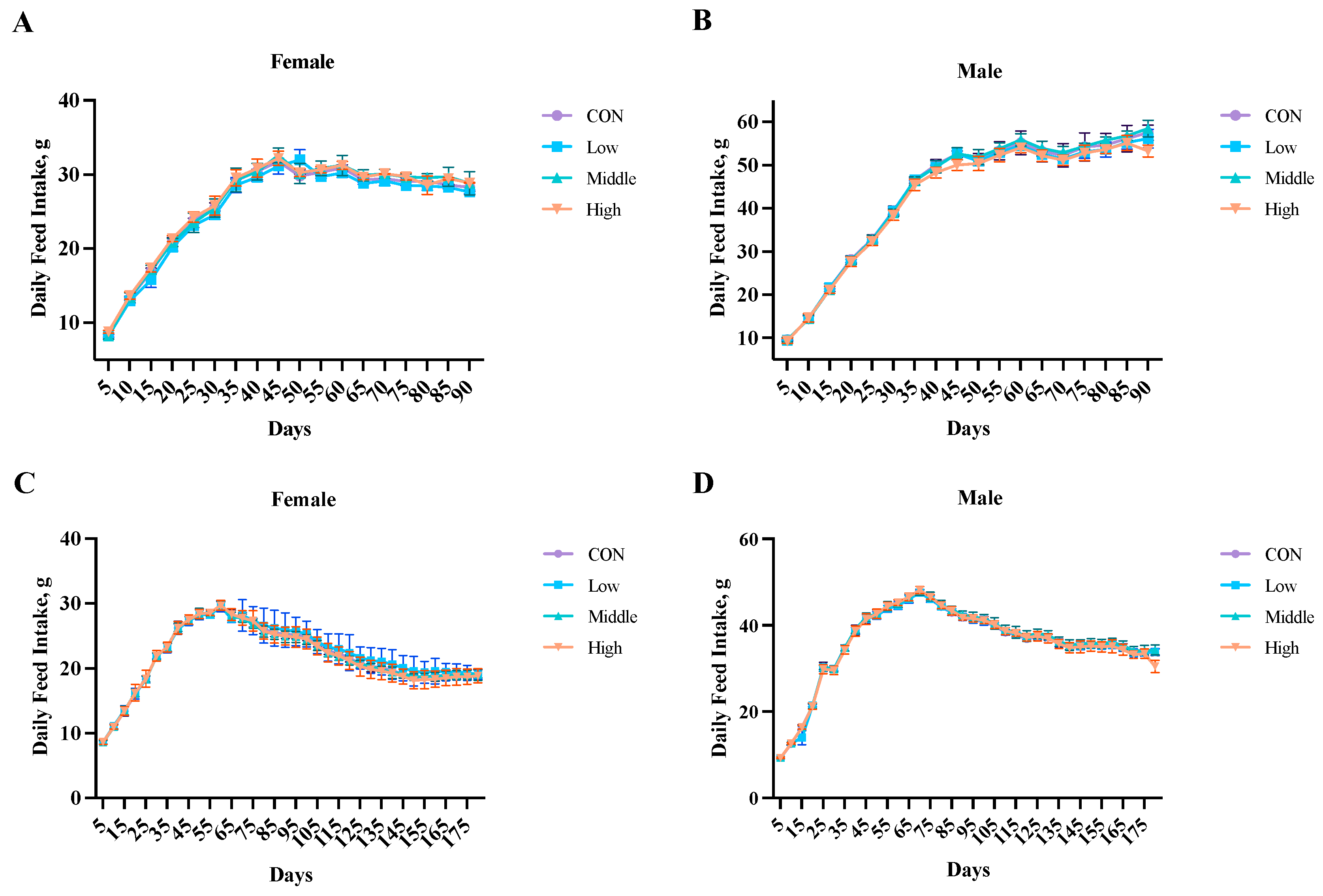
3.2. Food Intake
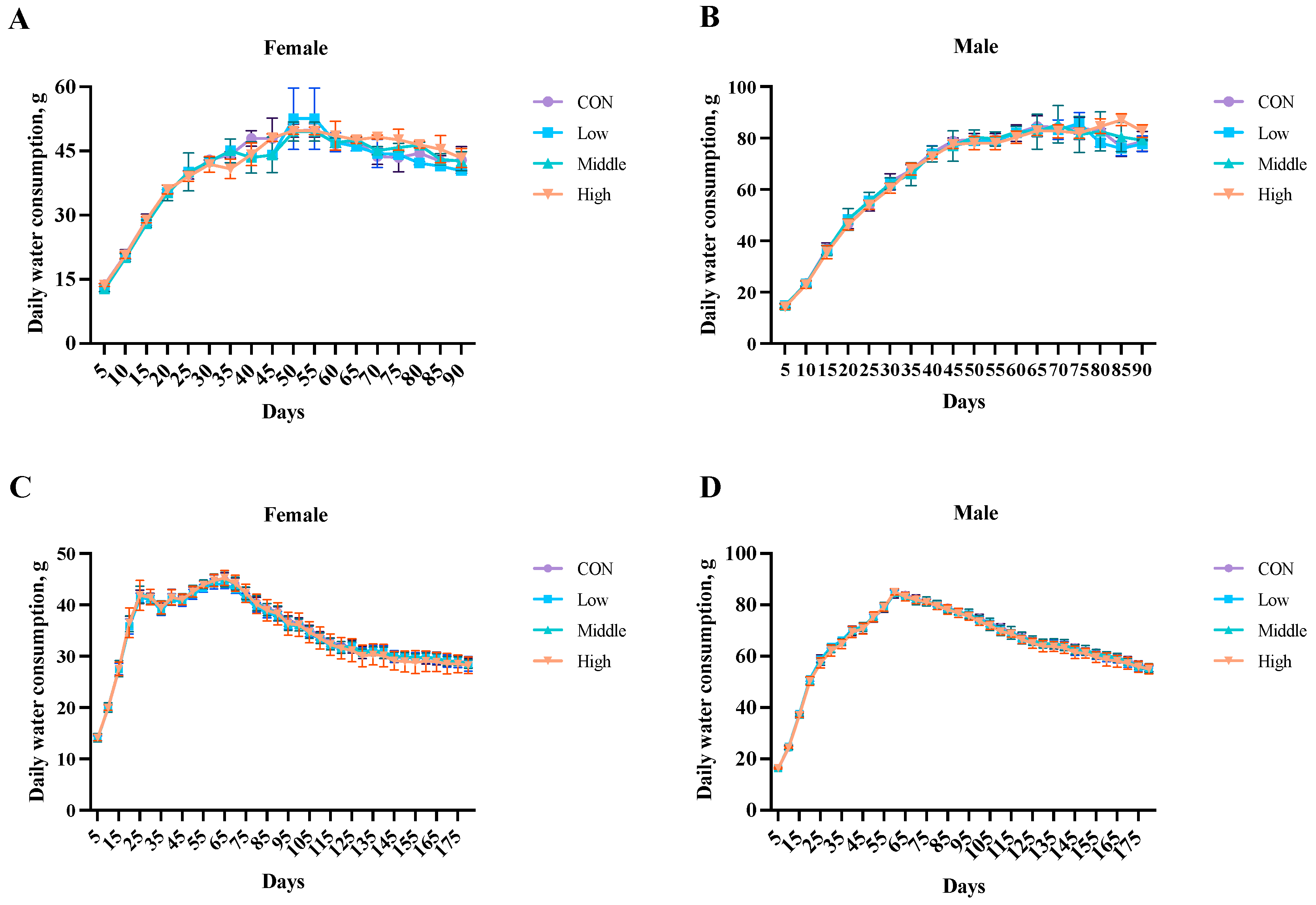
3.3. Water Intake
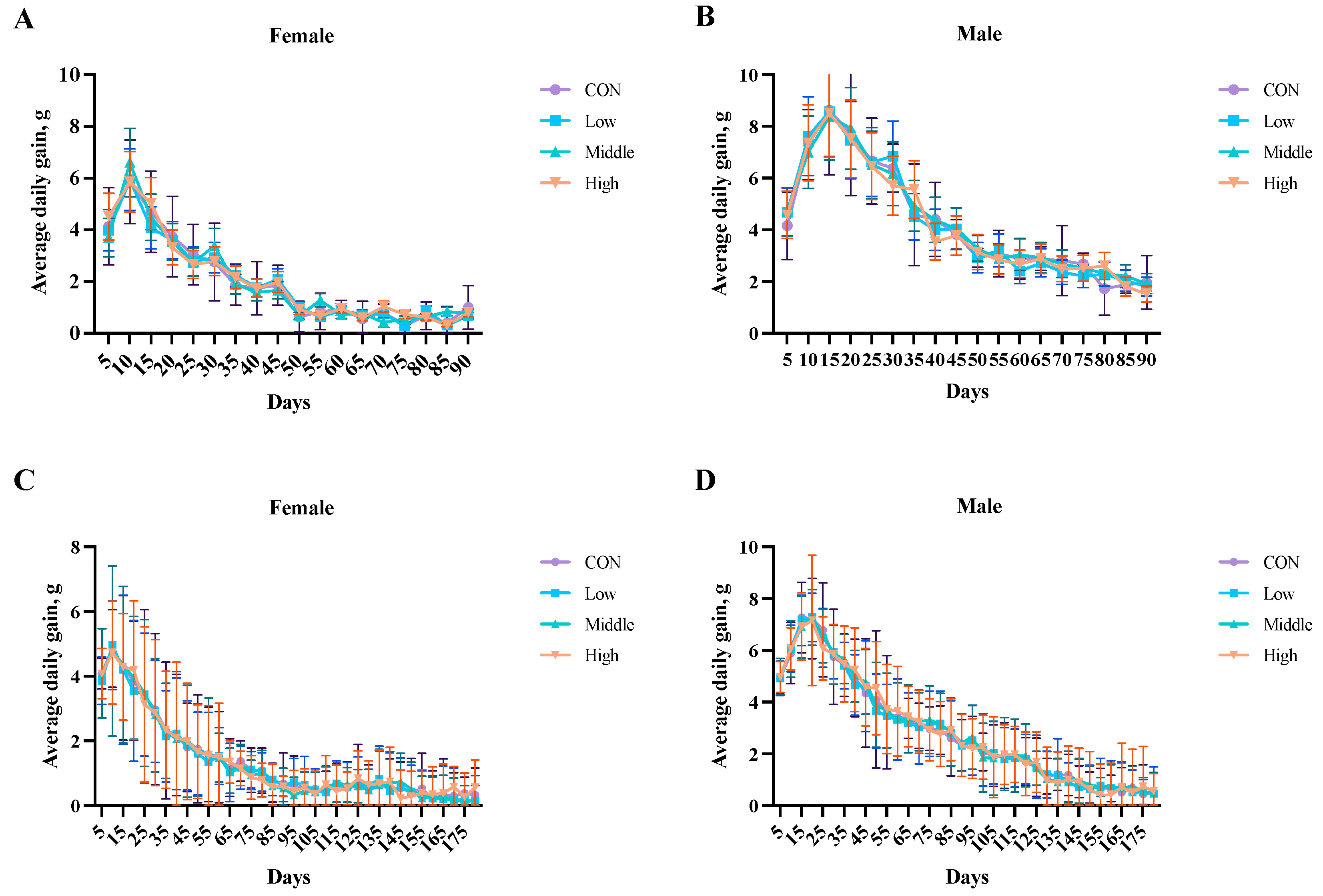
3.4. Average Daily Weight Gain
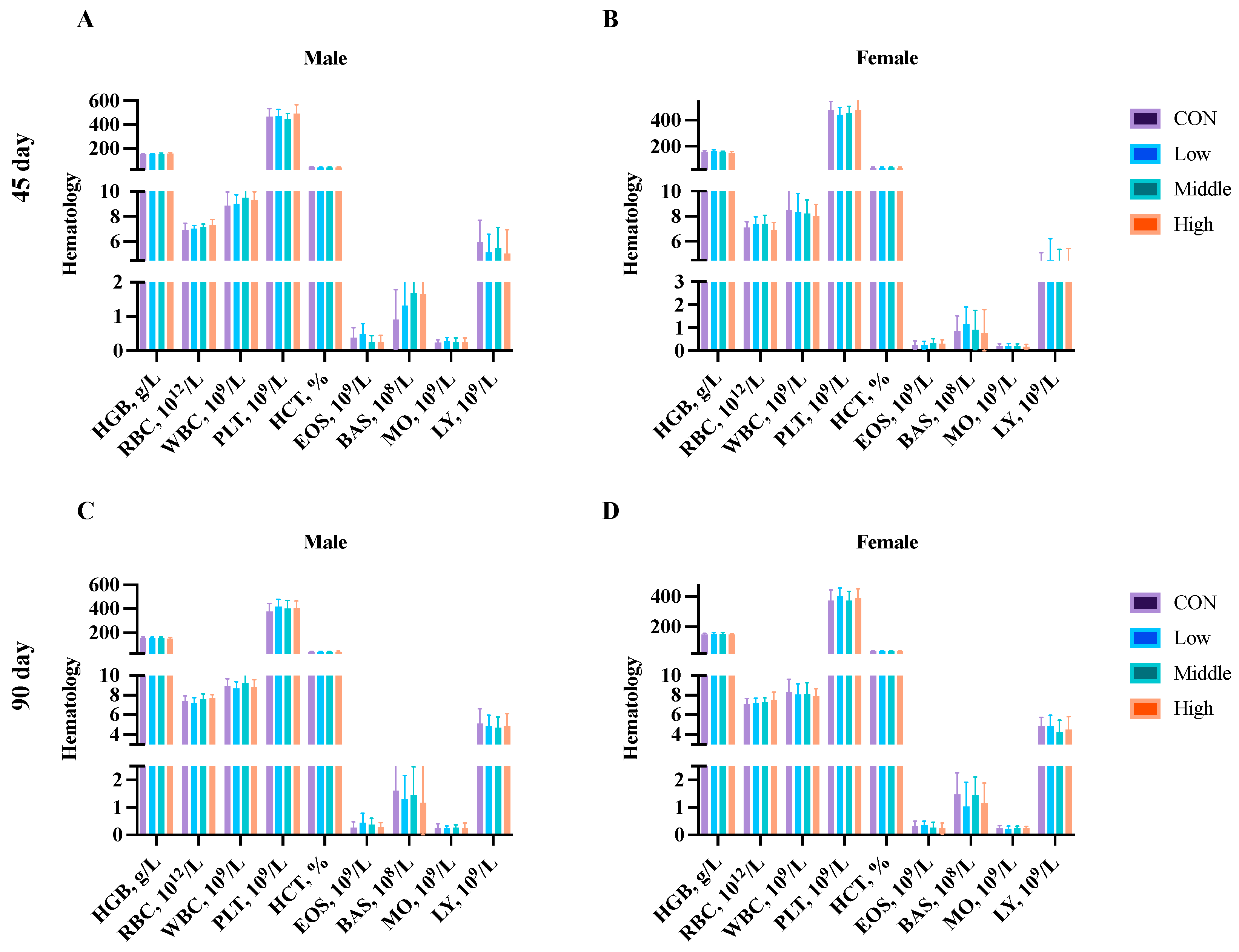
3.5. Hematological Parameters
3.6. Clinical Biochemistry
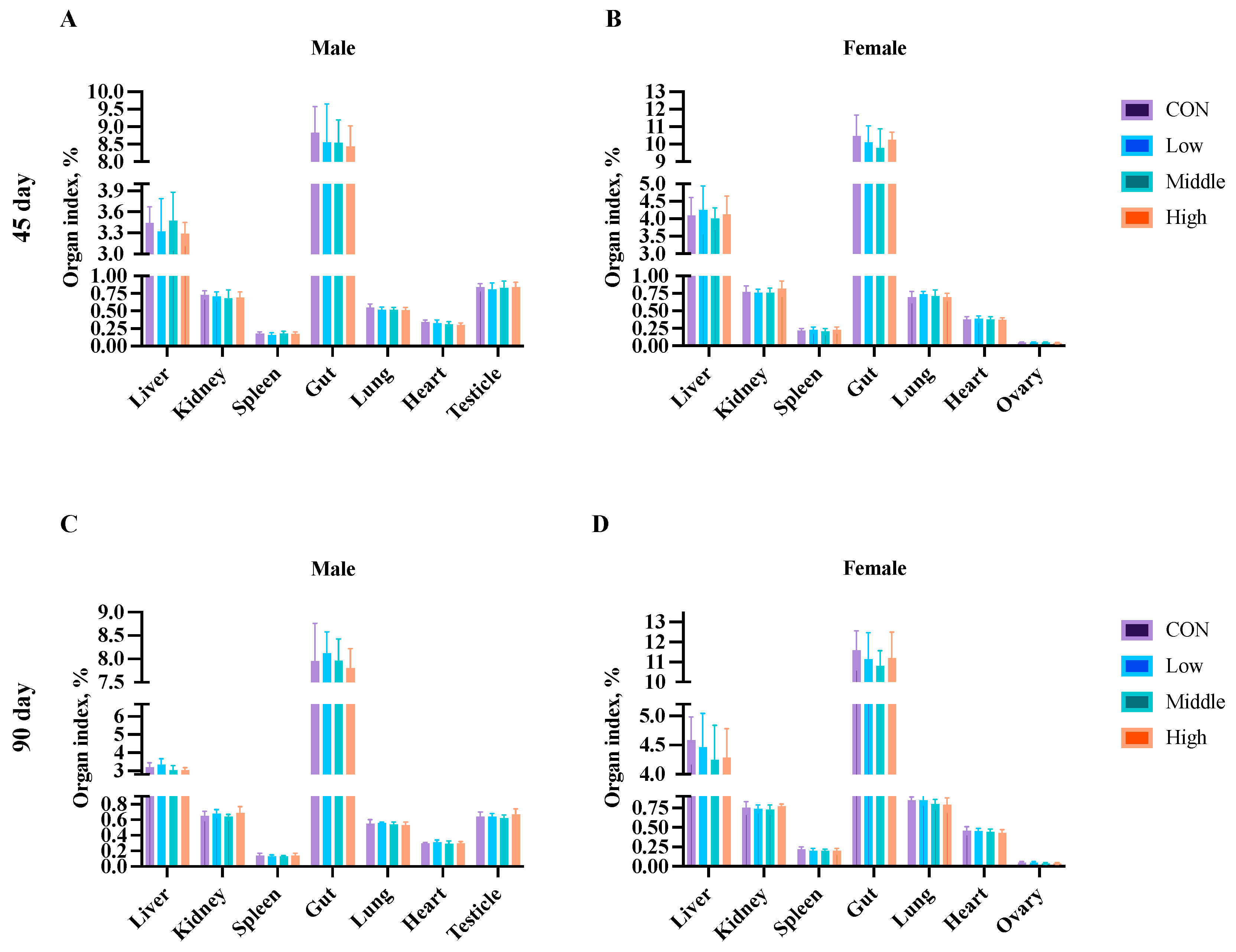
3.7. Organ Index
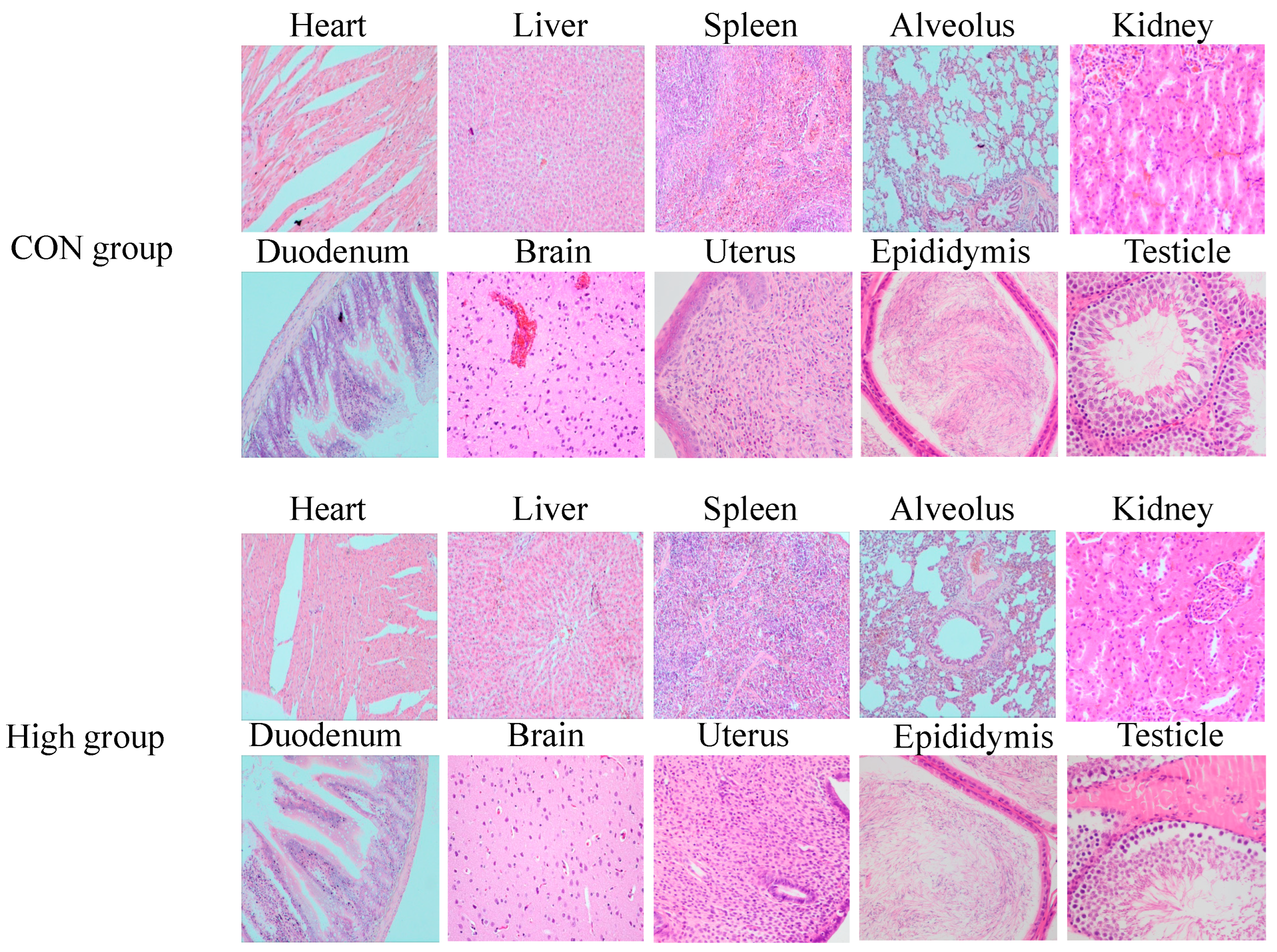
3.8. Histopathology Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SD | Sprague–Dawley |
| NOEL | No-observed-effect level |
| NOAEL | No-observed-adverse-effect level |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
| E | Glutamic acid |
| S | Serine |
| K | Lysine |
| I | Isoleucine |
| C | Cysteine |
| T | Threonine |
| W | Tryptophan |
| L | Leucine |
| G | Glycine |
| T | Threonine |
| Q | Glutamine |
| N | Asparagine |
| Y | Tyrosine |
| R | Arginine |
| N | Asparagine |
| HGB | Hemoglobin |
| RBC | Red blood cell count |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
| PLT | Platelet count |
| HCT | Hematocrit |
| EOS | Eosinophils |
| BAS | Basophils |
| MO | Monocytes |
| LY | Lymphocytes |
| TP | Total protein |
| ALB | Albumin |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| Cr | Creatinine |
| Glu | Glucose |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| AMPs | Antimicrobial peptides |
References
- Yang, L.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Advances in research on solid-state fermented feed and its utilization: The pioneer of private customization for intestinal microorganisms. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.H.; Chakicherla, A.; Hansen, J.N. Identification and Characterization of the Structural and Transporter Genes for, and the Chemical and Biological Properties of, Sublancin 168, a Novel Lantibiotic Produced by Bacillus subtilis 168. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 23134–23142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Garcia De Gonzalo, C.V.; Repka, L.M.; van der Donk, W.A. Structure-Activity Relationships of the S-Linked Glycocin Sublancin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2965–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Ye, Q.; Huang, S.; Yu, H.; Yang, T.; Qiao, S. Use of the Antimicrobial Peptide Sublancin with Combined Antibacterial and Immunomodulatory Activities To Protect against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8595–8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Wang, S.; Hou, C.; Yang, F.; Ma, X.; Thacker, P.; Qiao, S. The bacteriocin sublancin attenuates intestinal injury in young mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus. Anat. Rec. 2014, 297, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ye, Q.; Wang, K.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Yu, H.; Ge, Q.; Qi, D.; Qiao, S. Enhancement of Macrophage Function by the Antimicrobial Peptide Sublancin Protects Mice from Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 3979352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, X.F.; Wang, Q.W.; Zhu, J.L.; Peng, Q.; Hou, C.L.; Thacker, P.; Qiao, S.Y. The antimicrobial peptide sublancin ameliorates necrotic enteritis induced by Clostridium perfringens in broilers. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 4750–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, G.; Tao, L. Sublancin protects against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection by the combined modulation of innate immune response and microbiota. Peptides 2021, 141, 170533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; He, T.; Zhou, R. A Novel Adjuvant “Sublancin” Enhances Immune Response in Specific Pathogen-Free Broiler Chickens Inoculated with Newcastle Disease Vaccine. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1016567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Meirinhos, C.; Cunha, E.; Gomes, D.; Pereira, M.; Dias, R.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. Nisin Mutant Prevention Concentration and the Role of Subinhibitory Concentrations on Resistance Development by Diabetic Foot Staphylococci. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia De Gonzalo, C.V.; Zhu, L.; Oman, T.J.; van der Donk, W.A. NMR structure of the S-linked glycopeptide sublancin 168. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, S.; Ye, Q.; Zeng, X.; Yu, H.; Qi, D.; Qiao, S. Prevention of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression in Mice with the Antimicrobial Peptide Sublancin. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 4353580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oman, T.J.; Boettcher, J.M.; Wang, H.; Okalibe, X.N.; van der Donk, W.A. Sublancin is not a lantibiotic but an S-linked glycopeptide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawabjan, S.A.; Singh, K.; Iswarya, G.S.M.; Au-Yeung, R.K.H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; El-Nezami, H.; Chow, B.K.C. Preclinical toxicity evaluation of the novel anti-hypertensive compound KSD179019. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 196, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maache, S.; Tahraoui, A.; Soulo, N.; Benlabchir, A.A.; Nouioura, G.; Bouslamti, M.; Aldisi, D.; Saghrouchni, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Aboul-Soud, M.A.M.; et al. Sub-chronic and acute toxicity of aqueous extracts Salvia blancoana subsp. mesatlantica (Maire) Figuerola to rodents. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, C.; Shi, L.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, T.; Zhuo, Q. Ninety-Day Feeding Test of Stacked DBN9936 × DBN9501 Maize on Sprague Dawley Rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 45, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.C.; Li, C.C.; Liu, C.W.; Chen, J.Y. A Pilot Safety Assessment for Recombinant Epinephelus lanceolatus Piscidin Yeast Powder as a Drug Food Additive after Subacute and Subchronic Administration to SD Rats. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taychaworaditsakul, W.; Saenjum, C.; Lumjuan, N.; Chawansuntati, K.; Sawong, S.; Jaijoy, K.; Na Takuathung, M.; Sireeratawong, S. Safety of Oral Carica papaya L. Leaf 10% Ethanolic Extract for Acute and Chronic Toxicity Tests in Sprague Dawley Rats. Toxics 2024, 12, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, M.; Staveley, J.; Samel, A.; Aufderheide, J.; Blickley, T.M.; Bone, A.; Bruns, E.; Catron, T.; Edwards, D.; Gallagher, S.; et al. Critical review of chronic toxicity testing approaches with the saltwater mysid (Americamysis bahia) used in pesticide registration. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, 44, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas-Herbada, R.; Fernández-Carballido, A.; Aparicio-Blanco, J.; Slowing, K.; Rubio-Retama, J.; López-Cabarcos, E.; Torres-Suárez, A.-I. Controlled Release of Highly Hydrophilic Drugs from Novel Poly(Magnesium Acrylate) Matrix Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátis, G.; Tráj, P.; Hanyecz, V.; Mackei, M.; Márton, R.A.; Vörösházi, J.; Kemény, Á.; Neogrády, Z.; Sebők, C. Immunomodulatory properties of chicken cathelicidin-2 investigated on an ileal explant culture. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayatipour, F.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Zamani, J.; Fotouhi, F.; Aminzadeh, S. In-vitro antimicrobial activity of AF-DP protein and in-silico approach of cell membrane disruption. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Niu, J.; Wang, X.; Niu, M.; Liao, C. The Contribution of Antimicrobial Peptides to Immune Cell Function: A Review of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Luo, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Geng, S.; Wang, Y. BamA-targeted antimicrobial peptide design for enhanced efficacy and reduced toxicity. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbediwi, M.; Rolff, J. Metabolic pathways and antimicrobial peptide resistance in bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 79, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Beltrán, J.M.; Arizcun, M.; Chaves-Pozo, E. Antimicrobial Peptides from Photosynthetic Marine Organisms with Potential Application in Aquaculture. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Ito, T.; Kurashima, M.; Matsunaga, N.; Demizu, Y.; Misawa, T. Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Substitutions of Cationic Amino Acid Residues on Antimicrobial Peptides. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, W.; Baloch, A.R.; Wang, M.; Cao, B. Improved production of sublancin via introduction of three characteristic promoters into operon clusters responsible for this novel distinct glycopeptide biosynthesis. Microb. Cell Factories 2015, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.S.; Wilkinson, B.L.; O’Connell, M.R.; Mackay, J.P.; Matthews, J.M.; Payne, R.J. Synthesis of the bacteriocin glycopeptide sublancin 168 and S-glycosylated variants. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1910–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Biswas, S.; Garcia De Gonzalo, C.V.; van der Donk, W.A. Investigations into the Mechanism of Action of Sublancin. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, G.E.; Patchett, M.L. The glycocins: In a class of their own. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 40, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Mao, J.; Shi, W.; Ren, L.; Li, J.; Geng, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Subchronic toxicity study of ferric oxide nanoparticles through intragastric administration: A 94-d, repeated dose study in Sprague Dawley rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 140, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, R.E.; Azimonti, G.; Bonos, E.; Christensen, H.; Durjava, M.; Dusemund, B.; Gehring, R.; Glandorf, B.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; et al. Safety of a feed additive consisting of Duddingtonia flagransNCIMB 30336 (BioWorma®) for all grazing animals (International Animal Health Products Pty Ltd.). EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, Z.S.; Cao, S.J.; Chang, Y.F.; Cao, Y.-Q.; Li, J.-B.; Yao, Z.-X.; Wen, Y.-P.; Huang, X.-B.; Wu, R.; et al. Acute oral toxicity test and assessment of combined toxicity of cadmium and aflatoxin B1 in kunming mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, S. Toxicity testing in the 21st century: A vision and a strategy. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Shang, L.; Wang, F.; Zeng, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, S. Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide Microcin C7 on Growth Performance, Immune and Intestinal Barrier Functions, and Cecal Microbiota of Broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 813629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, J. Effects of maggot antimicrobial peptides on growth performance, immune function, and cecal flora of yellow-feathered broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1156964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque-Borda, C.A.; Pereira, L.P.; Guastalli, E.A.L.; Soares, N.M.; Mac-Lean, P.A.B.; Salgado, D.D.; Meneguin, A.B.; Chorilli, M.; Vicente, E.F. HPMCP-Coated Microcapsules Containing the Ctx(Ile21)-Ha Antimicrobial Peptide Reduce the Mortality Rate Caused by Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis in Laying Hens. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ma, X.; Jiang, X. Effects of Immobilized Antimicrobial Peptides on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Index, Inflammatory Factors, Intestinal Morphology, and Microbial Community in Weaning Pigs. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 872990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, S.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, C.; Wen, L.; Xu, G.; Zou, J. Effects of mixed antimicrobial peptide on the growth performance, antioxidant and immune responses and disease resistance of Pengze crucian carp (Carassius auratus var. Pengze). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 114, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Chen, F.; Hao, H.; Xiong, M.; Peng, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, K.J. Growth-promoting effect of antimicrobial peptide Scy-hepc on mariculture large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea and the underlying mechanism. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 134, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Lei, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, Q.; et al. Antimicrobial peptides act on the rumen microbiome and metabolome affecting the performance of castrated bulls. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmal, H.; Ahmad, S.; Abbasi, M.H.; Jabeen, F.; Shahzad, K. A study on assessing the toxic effects of ethyl paraben on rohu (Labeo rohita) using different biomarkers; hemato-biochemical assays, histology, oxidant and antioxidant activity and genotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, W.; Song, L.; Su, P.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Comparative study of the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of reduning injection and atomization inhalation. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Kumar, D.; Singh, J.; Jangra, A. Environmental toxicants and nephrotoxicity: Implications on mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Toxicology 2024, 504, 153784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Shang, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Zeng, X.; Ding, X.; Huang, J.; Qiao, S.; Yu, H. Engineering and Purification of Microcin C7 Variants Resistant to Trypsin and Analysis of Their Biological Activity. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balog, S.; Jeong, S.; Asahina, K. Recruitment of large peritoneal macrophages to capsular fibrosis developed on the liver surface. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ning, Z.H.; Tai, H.W.; Long, S.; Qin, W.C.; Su, L.M.; Zhao, Y.H. Relationship between lethal toxicity in oral administration and injection to mice: Effect of exposure routes. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Guo, G.; He, T.; Lai, Y. Subchronic and Chronic Toxicity Assessment of Sublancin in Sprague–Dawley Rats. Toxics 2025, 13, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050413
Guo Y, Li Z, Xu P, Guo G, He T, Lai Y. Subchronic and Chronic Toxicity Assessment of Sublancin in Sprague–Dawley Rats. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050413
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yong, Zhihao Li, Penglong Xu, Gantong Guo, Tao He, and Yujiao Lai. 2025. "Subchronic and Chronic Toxicity Assessment of Sublancin in Sprague–Dawley Rats" Toxics 13, no. 5: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050413
APA StyleGuo, Y., Li, Z., Xu, P., Guo, G., He, T., & Lai, Y. (2025). Subchronic and Chronic Toxicity Assessment of Sublancin in Sprague–Dawley Rats. Toxics, 13(5), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050413







