Analysis of Acute and Short-Term Fluoride Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryo and Sac–Fry Stages Based on Bayesian Model Averaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Selection Rationale of Fluoride Concentrations in the Current Study
2.3. Environmental Conditions for Zebrafish Experiments
2.4. The Environmental Exposure of Embryo and Sac–Fry Stages Zebrafish to Fluoride
2.5. Toxicological Indicators
2.6. LC/EC50 and BMC/BMCL Estimates
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
3. Results
3.1. General Situation and Toxicological Indicators Results
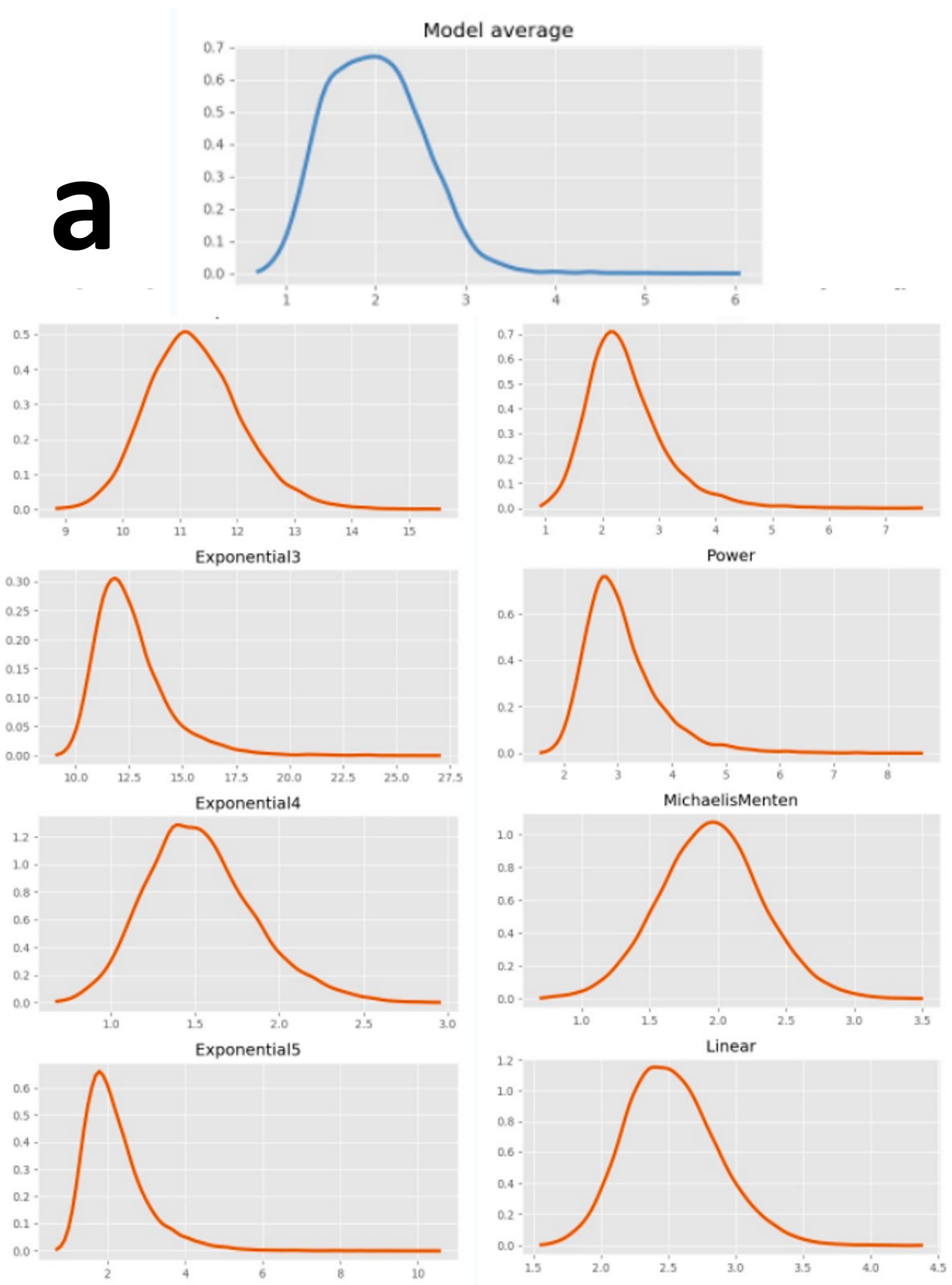
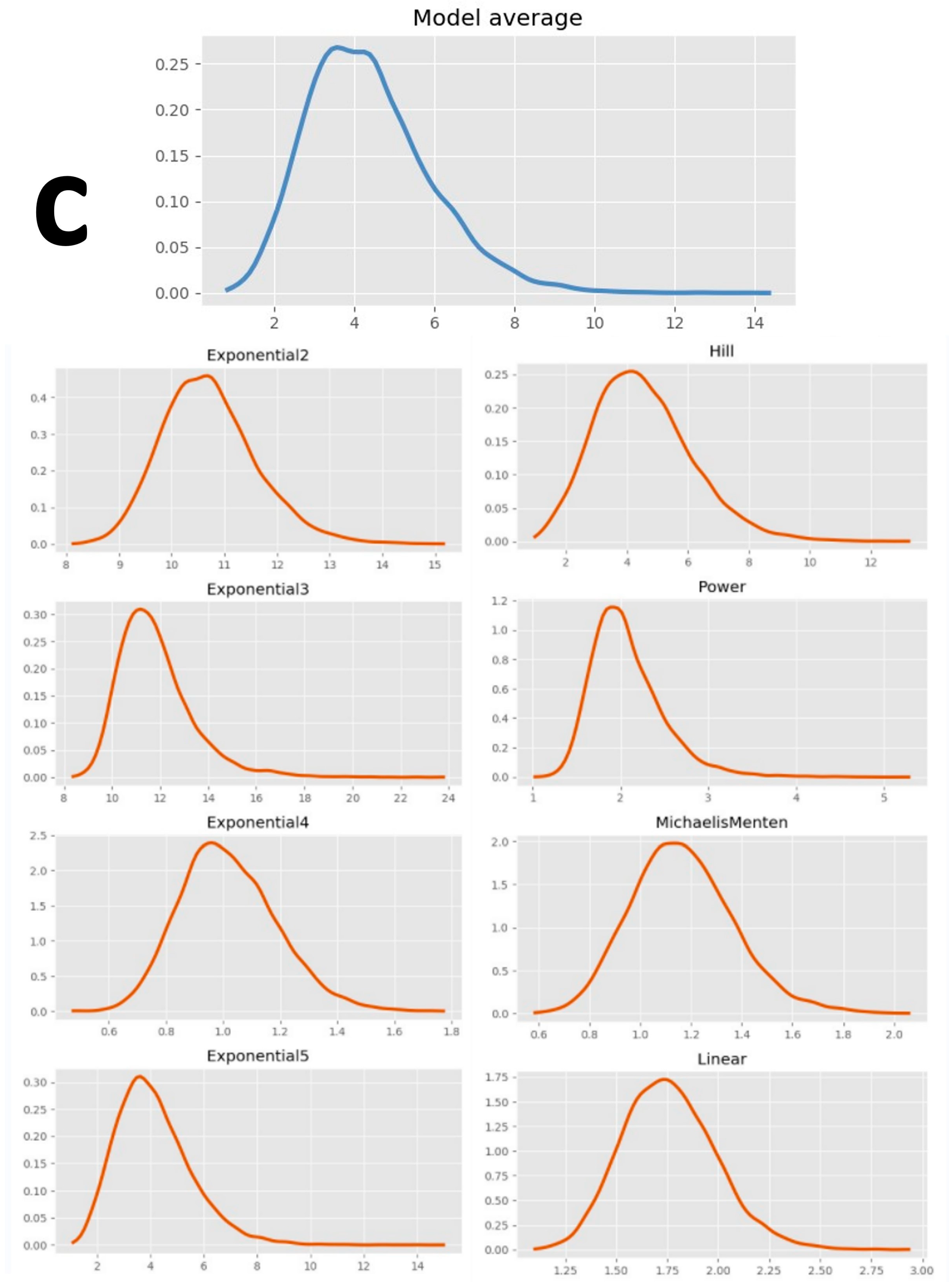
3.2. The LC50/EC50 and BMC/BMCL Estimation Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBMD | Bayesian benchmark dose analysis system. |
| BMA | Bayesian model averaging. |
| BMC | benchmark concentration. |
| BMCL | lower bound of the credible interval of benchmark concentration. |
| BMD | benchmark dose. |
| BMDL | lower bound of the credible interval of benchmark dose. |
| BMR | benchmark response. |
| CM | cumulative mortality. |
| CMA | cumulative malformation rate. |
| dpf | days post-fertilization. |
| EC50 | effect concentration for 50% effect. |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority. |
| EFSA SC | EFSA Scientific Committee. |
| EPA | U.S. environmental protection agency. |
| ESLC | environmental standard limit concentration. |
| hpf | hours post-fertilization. |
| ICs | internal plate controls. |
| LC50 | median lethal dose. |
| LOAEL | lowest observed adverse effect level. |
| LSD | least significant difference. |
| NaF | sodium fluoride. |
| NOAEL | no observed adverse effect level. |
| OECD | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. |
| SD | standard deviation. |
| UFs | uncertainty factors. |
| W-F | water fluoride. |
| WHO | World health organization. |
References
- Botham, P.A. Acute Systemic Toxicity. ILAR J. 2002, 43 (Suppl. S1), S27–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish, Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 212: Fish, Short-term Toxicity Test. on Embryo and Sac-Fry. Stages; OECD: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sobanska, M.; Scholz, S.; Nyman, A.-M.; Cesnaitis, R.; Alonso, S.G.; Klüver, N.; Kühne, R.; Tyle, H.; de Knecht, J.; Dang, Z.; et al. Applicability of the fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test (OECD 236) in the regulatory context of Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Bhattacharya, P. Fluoride in the environment: Sources, distribution and defluoridation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saether, O.M.; Andreassen, B.T.; Semb, A. Amounts and sources of fluoride in precipitation over southern Norway. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Solomon, S.; Turnipseed, A.A.; Warren, R.F. Atmospheric Lifetimes of Long-Lived Halogenated Species. Science 1993, 259, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Legrand, M. Origins and variations of fluoride in Greenland precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsvath, D.L. Fluoride and environmental health: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2009, 8, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kumari, B.; Sinam, G.; Kriti; Kumar, N.; Mallick, S. Fluoride distribution and contamination in the water, soil and plants continuum and its remedial technologies, an Indian perspective–A review. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Sharma, S.; Bansal, M.; Singh, A.; Panday, V.; Maheshwari, R. Effects of fluoride accumulation on growth of vegetables and crops in Dausa District, Rajasthan, India. Adv. Biores. 2012, 3, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; An, Y.-J. Effects of fluorine on crops, soil exoenzyme activities, and earthworms in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Tripathy, S. Fluoride and human health: Systematic appraisal of sources, exposures, metabolism, and toxicity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 1116–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathne, T.; Stockwell, C.E.; Yokelson, R.J.; Nakao, S.; Stone, E.A. Emissions of Fine Particle Fluoride from Biomass Burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12636–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skórka-Majewicz, M.; Goschorska, M.; Żwierełło, W.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Styburski, D.; Kapczuk, P.; Gutowska, I. Effect of fluoride on endocrine tissues and their secretory functions—Review. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Flora, S.J.S. Fluoride in Drinking Water and Skeletal Fluorosis: A Review of the Global Impact. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, A.M.; Quiñonez, C.; Hosein, F.S.; McLaren, L. Fluoride exposure and reported learning disability diagnosis among Canadian children: Implications for community water fluoridation. Can. J. Public. Health 2017, 108, e229–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfiqar, S.; Ajaz, H.; Rehman, S.U.; Elahi, S.; Shakeel, A.; Yasmeen, F.; Altaf, S. Effect of excess Fluoride consumption on Urine-Serum Fluorides, Dental state and Thyroid Hormones among children in “Talab Sarai” Punjab Pakistan. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global analysis and prediction of fluoride in groundwater. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearcy, K.; Elphick, J.; Burnett-Seidel, C. Toxicity of fluoride to aquatic species and evaluation of toxicity modifying factors. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzykwa, J.C.; Saeid, A.; Jeffries, M.K.S. Identifying sublethal endpoints for evaluating neurotoxic compounds utilizing the fish embryo toxicity test. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, C.A.; Lee, D.H.Y.; Chapman, P.M. Development of a fluoride chronic effects benchmark for aquatic life in freshwater. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2621–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, R.; Bulkley, R.V. Influence of water hardness on fluoride toxicity to rainbow trout. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1983, 2, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Saxena, A.; Batra, M. Acute toxicity bioassay in sodium fluoride exposed amur carp (cyprinus carpio haematopterus) fry. J. Exp. Zool. India 2020, 23, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Andreev, P.S.; Sansom, I.J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.-C.; Peng, L.; Jia, L.; Qiao, T.; Zhu, M. Spiny chondrichthyan from the lower Silurian of South China. Nature 2022, 609, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, L. Influence of sublethal doses of acetamiprid and halosulfuron-methyl on metabolites of zebra fish (Brachydanio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 191, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.S.; Salgado, R.; Pereira, V.J.; Carvalho, G.; Oehmen, A.; Reis, M.A.M.; Noronha, J.P. Ecotoxicity of ketoprofen, diclofenac, atenolol and their photolysis byproducts in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-L.; Shih, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Lu, J.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-J. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Zebrafish Embryos in Aquatic Ecosystems. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Bao, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H. Enantioselective developmental toxicity and immunotoxicity of pyraclofos toward zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yichao, J.; Chunqi, L. Conversion Method for Zebrafish Quasi Human Dose for Safety Evaluation. CN113496072A, 2 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Volume 60, p. 1432. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Hosmer, T.; Le Cessie, S.; Lemeshow, S. A comparison of goodness-of-fit tests for the logistic regression model. Stat. Med. 1997, 16, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Sun, X. Comparing lethal dose ratios using probit regression with arbitrary slopes. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.V.; Slaght, K.S.; Boogaard, M.A. An automated approach to Litchfield and Wilcoxon’s evaluation of dose–effect experiments using the R package LW1949. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 3058–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.S.; Stevens, M.W.; Martens, M.A.; Ekuta, J. Comparison of BMD with NOAEL and LOAEL Values Derived from Subchronic Toxicity Studies. In Toxicology in Transition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Slob, W. The difference between NOAEL and BMD approach. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 295, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Risk Assessment in the Federal Government: Managing the Process; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, S. Quantitative Health Risk Assessment. NSW Public Health Bull. 2003, 14, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, K.; Gift, J.S. Model Uncertainty and Bayesian Model Averaged Benchmark Dose Estimation for Continuous Data. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D. On the Quantification of Model Uncertainty: A Bayesian Perspective. Psychometrika 2021, 86, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, D.; Raftery, A.E. Model Selection and Accounting for Model Uncertainty in Graphical Models Using Occam’s Window. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E. Approximate Bayes factors and accounting for model uncertainty in generalised linear models. Biometrika 1996, 83, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, O.; Santos-Fernandez, E.; Wu, P.P.-Y.; Xie, H.-B.; Schwenn, P.E.; Lagopoulos, J.; Mills, L.; Sacks, D.D.; Hermens, D.F.; Mengersen, K. clusterBMA: Bayesian model averaging for clustering. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, E.S.; More, S.J.; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Hernández-Jerez, A.F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lambré, C.; et al. Guidance on the use of the benchmark dose approach in risk assessment. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07584. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Determination of Fluoride-Ion Selective Electrode Method. [GB 7484-87]. 1987. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/198708/t19870801_66705.shtml (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. E3 Medium (for Zebrafish Embryos). Available online: https://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2011/10/pdb.rec66449 (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064 (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- National Disease Control and Prevention Administration. Standards for Drinking Water Quality. [GB 5749-2022]. 2022. Available online: https://www.ndcpa.gov.cn/jbkzzx/c100201/common/content/content_1665979083259711488.html (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for Groundwater Quality. [GB/T14848-2017]. 2017. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=F745E3023BD5B10B9FB5314E0FFB5523 (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. [GB 3838-2002]. 2003. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/200206/t20020601_66497.htm (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality Standard for Fisheries. [GB 11607-89]. 1989. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/199003/t19900301_66502.shtml (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Secondary Drinking Water Standards: Guidance for Nuisance Chemicals. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/secondary-drinking-water-standards-guidance-nuisance-chemicals (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. [GB 8978-1996]. 1996. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/swrwpfbz/199801/t19980101_66568.shtml (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. [GB 5085.3-2007]. 2007. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/gthw/wxfwjbffbz/200705/t20070522_103957.shtml (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. National Recommended Water Quality Criteria—Aquatic Life Criteria Table. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wqc/national-recommended-water-quality-criteria-aquatic-life-criteria-table (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- OECD. Test No. 210: Fish, Early-life Stage Toxicity Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, K.; Andrew, J.S. A Web-Based System for Bayesian Benchmark Dose Estimation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 017002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-c.; Wang, X.-P. Standardization research on Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices in China. Acta Psychol. Sin. 1989, 21, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of Fluorine in Foods. [GB/T 5009.18-2003]. 2003. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=53B882FC979093D5333F58A5AE68172E (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Tahir, M.A.; Rasheed, H. Fluoride in the drinking water of Pakistan and the possible risk of crippling fluorosis. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2013, 6, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaka, L.A.; Wilke, F.D.H.; Olago, D.O.; Odada, E.O.; Mulch, A.; Musolff, A. Groundwater fluoride enrichment in an active rift setting: Central Kenya Rift case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiglieri, G.; Pistis, M.; Abebe, B.; Azagegn, T.; Engidasew, T.A.; Pittalis, D.; Soler, A.; Barbieri, M.; Navarro-Ciurana, D.; Carrey, R.; et al. Three-dimensional hydrostratigraphical modelling supporting the evaluation of fluoride enrichment in groundwater: Lakes basin (Central Ethiopia). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; See, I.; Edwards, J.R. Bayesian model averaging: Improved variable selection for matched case-control studies. Epidemiol. Biostat. Public. Health 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Bakhai, A. Comparison of Bayesian model averaging and stepwise methods for model selection in logistic regression. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 3451–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genell, A.; Nemes, S.; Steineck, G.; Dickman, P.W. Model selection in Medical Research: A simulation study comparing Bayesian Model Averaging and Stepwise Regression. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2010, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennifer, A.H.; David, M.; Adrian, E.R.; Chris, T.V. Bayesian model averaging: A tutorial (with comments by M. Clyde, David Draper and E. I. George, and a rejoinder by the authors). Stat. Sci. 1999, 14, 382–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D.; Yavuz, S. An Approach to Addressing Multiple Imputation Model Uncertainty Using Bayesian Model Averaging. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2020, 55, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Möller, A. Joint probabilistic forecasting of wind speed and temperature using Bayesian model averaging. Environmetrics 2015, 26, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.Y.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayesian model averaging: Development of an improved multi-class, gene selection and classification tool for microarray data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.M.; Nyhan, B. Bayesian Model Averaging: Theoretical Developments and Practical Applications. Political Anal. 2010, 18, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Ley, E.; Steel, M.F.J. Benchmark priors for Bayesian model averaging. J. Econom. 2001, 100, 381–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowles, J.R.; Alexeeff, G.V.; Dodge, D. The Use of Benchmark Dose Methodology with Acute Inhalation Lethality Data. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1999, 29, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, S.; Christopher, J.P.; Krewski, D. A Signal-to-Noise Crossover Dose as the Point of Departure for Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.C.; Kavlock, R.J.; Kimmel, C.A.; Faustman, E.M. Dose-Response Assessment for Developmental Toxicity: II. Comparison of Generic Benchmark Dose Estimates with No Observed Adverse Effect Levels. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1994, 23, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntire, K.M.; Juliano, S.A. How can mortality increase population size? A test of two mechanistic hypotheses. Ecology 2018, 99, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, M.; Nilsson, K.A. Experimental evidence for emergent facilitation: Promoting the existence of an invertebrate predator by killing its prey. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlberger, J.; Langangen, Ø.; Edeline, E.; Claessen, D.; Winfield, I.J.; Stenseth, N.C.; Vøllestad, L.A. Stage-specific biomass overcompensation by juveniles in response to increased adult mortality in a wild fish population. Ecology 2011, 92, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardini, E.A.; Drake, J.M.; Chase, J.M.; Knight, T.M. Complex population dynamics and control of the invasive biennial Alliaria petiolata (garlic mustard). Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipkin, E.F.; Sullivan, P.J.; Cooch, E.G.; Kraft, C.E.; Shuter, B.J.; Weidel, B.C. Overcompensatory response of a smallmouth bass (Micropterus dolomieu) population to harvest: Release from competition? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonzén, N.; Lundberg, P. Temporally structured density-dependence and population management. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1999, 36, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, S.; Loreau, M.; Jiang, L. Consistently positive effect of species diversity on ecosystem, but not population, temporal stability. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, C.J. Developmental genetics. Experientia 1986, 42, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Nawrot, T.S.; Baccarelli, A.A. Hallmarks of environmental insults. Cell 2021, 184, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Long, T.; Chang, C.; Meng, T.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. A Review of the Ethical Use of Animals in Functional Experimental Research in China Based on the “Four R” Principles of Reduction, Replacement, Refinement, and Responsibility. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e938807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embry, M.R.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T.A.; Galay-Burgos, M.; Halder, M.; Hinton, D.E.; Léonard, M.A.; Lillicrap, A.; Norberg-King, T.; Whale, G. The fish embryo toxicity test as an animal alternative method in hazard and risk assessment and scientific research. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Ross, J.A. Catecholamine dysregulation and neurodegenerative disease: From molecular mechanisms to circuit dysfunction. Brain Res. 2019, 1702, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.G.; Bernier, N.J.; Perry, S.F. The adrenergic stress response in fish: Control of catecholamine storage and release. Communicated by Dr P.W. Hochachka, Editor.1. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 120, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nawale, V.P.; Malpe, D.B.; Marghade, D.; Yenkie, R. Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment with source identification of nitrate and fluoride polluted groundwater of Wardha sub-basin, central India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Huang, T.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Yan, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Bo, W.; et al. A Bayesian benchmark concentration analysis for urinary fluoride and intelligence in adults in Guizhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouheif, E.; Favé, M.-J.; Ibarrarán-Viniegra, A.S.; Lesoway, M.P.; Rafiqi, A.M.; Rajakumar, R. Eco-Evo-Devo: The Time Has Come, in Ecological Genomics: Ecology and the Evolution of Genes and Genomes; Landry, C.R., Aubin-Horth, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Skúlason, S.; Parsons, K.J.; Svanbäck, R.; Räsänen, K.; Ferguson, M.M.; Adams, C.E.; Amundsen, P.-A.; Bartels, P.; Bean, C.W.; Boughman, J.W.; et al. A way forward with eco evo devo: An extended theory of resource polymorphism with postglacial fishes as model systems. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1786–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
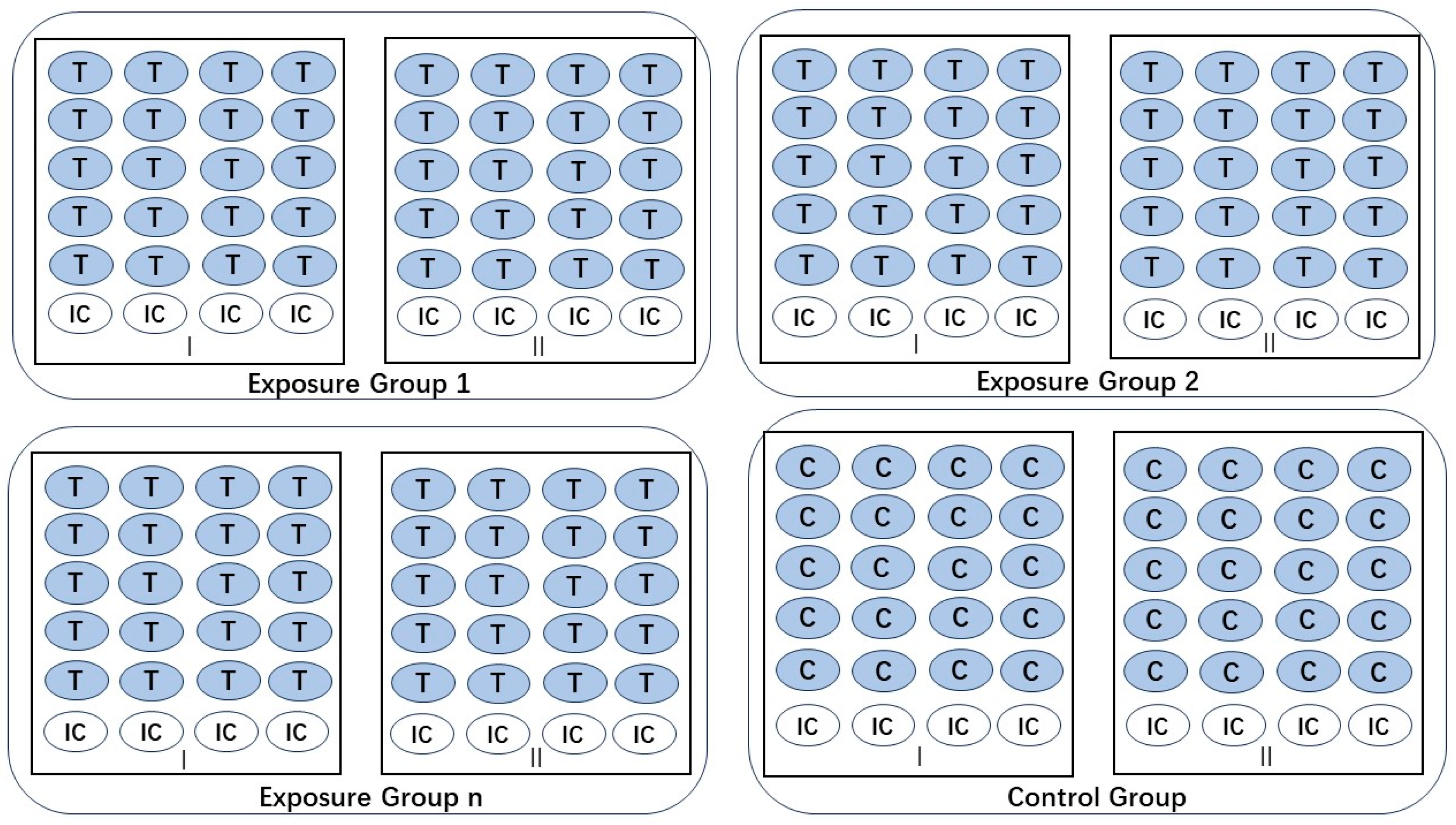
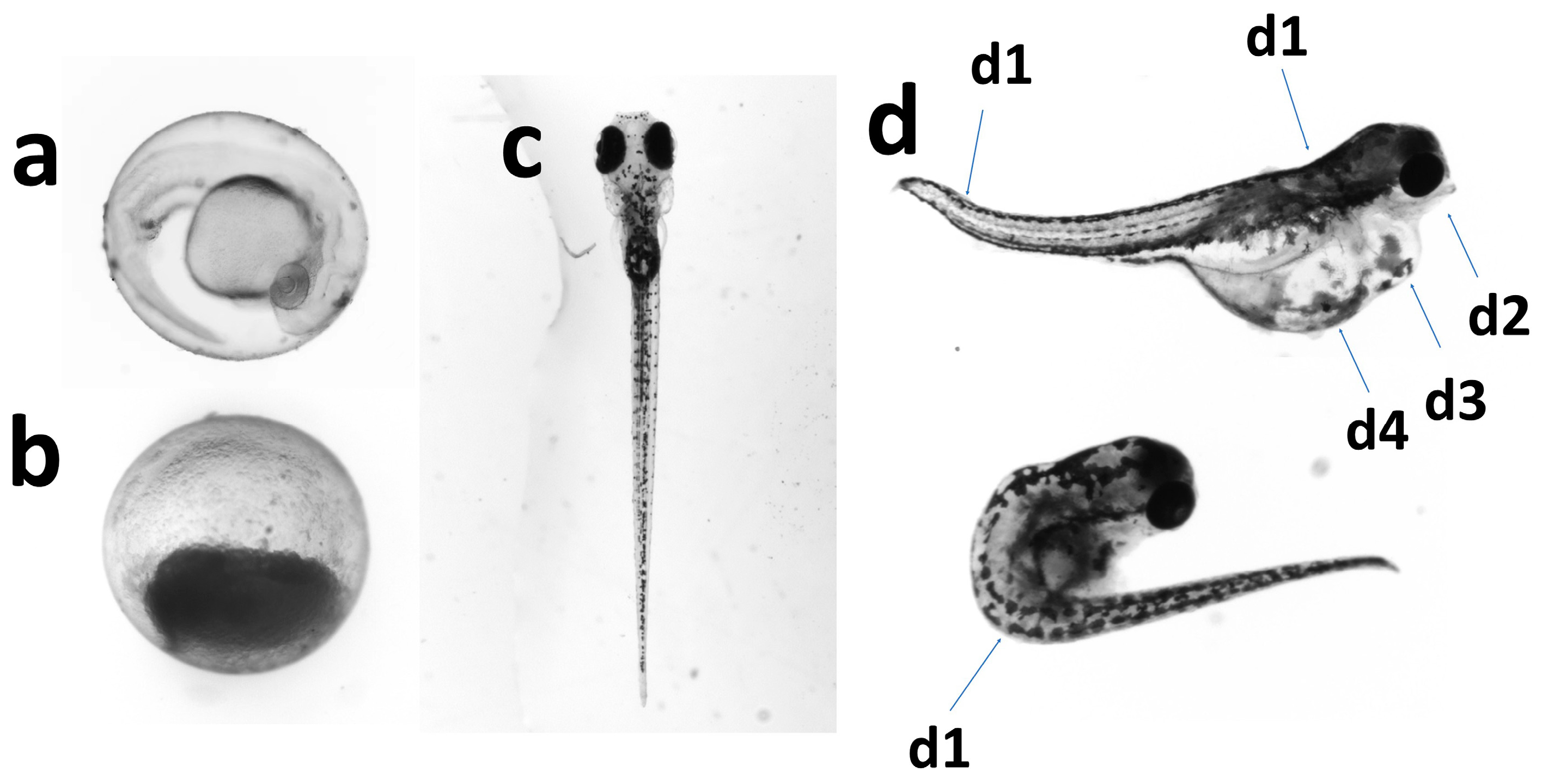



| Toxicity Indicators | Formula |
|---|---|
| CM | N = cumulative dead numbers each day/total |
| CMA at 5 dpf | N = CMA numbers from hatch to 5 dpf/hatched numbers |
| Model | Formula |
|---|---|
| Exponential model 2 | |
| Exponential model 3 | |
| Exponential model 4 | |
| Exponential model 5 | |
| Hill model | |
| Power mode | |
| Michaelis Menten model | |
| Linear model |
| Fluoride Dose (mg/L) | CM at | CMA at 5 dpf | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 dpf | 2 dpf | 3 dpf | 4 dpf | 5 dpf | ||
| 0.0 | 6.11 ± 2.36 | 10.67 ± 3.82 | 10.67 ± 3.82 | 10.67 ± 3.82 | 13.89 ± 3.28 | 9.45 ± 3.10 |
| 0.5 | 8.56 ± 4.45 | 10.89 ± 3.54 | 10.89 ± 3.54 | 10.89 ± 3.54 | 14.78 ± 3.99 | 10.66 ± 5.38 |
| 1.0 | 8.00 ± 4.56 | 9.33 ± 3.50 | 9.33 ± 3.50 | 9.33 ± 3.50 | 14.56 ± 4.39 | 10.56 ± 8.43 |
| 4.0 | 10.00 ± 9.78 | 10.56 ± 9.78 | 10.56 ± 9.78 | 10.56 ± 9.78 | 12.22 ± 10.30 | 8.55 ± 8.49 |
| 10.0 | 13.00 ± 8.99 | 13.17 ± 8.73 | 13.17 ± 8.73 | 14.17 ± 8.33 | 16.83 ± 8.52 | 16.98 ± 4.34 |
| 20.0 | 23.93 ± 6.27 | 24.93 ± 7.74 | 25.43 ± 8.21 | 26.26 ± 7.72 | 27.93 ± 11.10 | 24.86 ± 9.23 |
| 50.0 | 24.44 ± 7.79 | 51.11 ± 24.10 | 51.11 ± 24.10 | 60.56 ± 22.75 | 66.67 ± 16.73 | 27.46 ± 10.06 |
| 80.0 | 35.00 ± 10.90 | 51.11 ± 16.29 | 57.78 ± 22.77 | 78.33 ± 19.41 | 85.56 ± 7.50 | 87.24 ± 12.26 |
| 100.0 | 33.89 ± 7.13 | 61.11 ± 29.34 | 85.00 ± 17.98 | 97.22 ± 3.90 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
| 120.0 | 46.11 ± 2.51 | 76.11 ± 15.41 | 83.89 ± 14.21 | 90.00 ± 10.75 | 100.00 ± 0 | 90.00 ± 10.75 |
| 150.0 | 42.78 ± 9.29 | 76.67 ± 22.11 | 98.33 ± 4.08 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 |
| 200.0 | 54.45 ± 16.82 | 98.33 ± 2.79 | 99.45 ± 1.36 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 |
| 250.0 | 66.67 ± 5.27 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 |
| 300.0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0 |
| Model | 1 dpf CM | 2 dpf CM | 3 dpf CM | 4 dpf CM | 5 dpf CM | 5 dpf CMA | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhat | PPPv | LC50 | Rhat | PPPv | LC50 | Rhat | PPPv | LC50 | Rhat | PPPv | LC50 | Rhat | PPPv | LC50 | Rhat | PPPv | EC50 | |
| Exponential model 2 | 1.0 | 0.259 | 186.00 | 1.0 | 0.263 | 142 | 1.0 | 0.267 | 135 | 1.0 | 0.262 | 135 | 1.0 | 0.260 | 114 | 1.0 | 0.266 | 132 |
| Exponential model 3 | 1.0 | 0.268 | 186.00 | 1.0 | 0.259 | 143 | 1.0 | 0.263 | 134 | 1.0 | 0.261 | 134 | 1.0 | 0.263 | 115 | 1.0 | 0.265 | 134 |
| Exponential model 4 | 1.0 | 0.266 | 147.00 | 1.0 | 0.261 | 75 | 1.0 | 0.261 | 63 | 1.0 | 0.265 | 63 | 1.0 | 0.260 | 45 | 1.0 | 0.260 | 60 |
| Exponential model 5 | 1.0 | 0.269 | 143.00 | 1.0 | 0.259 | 70 | 1.0 | 0.272 | 57 | 1.0 | 0.265 | 57 | 1.0 | 0.259 | 38 | 1.0 | 0.263 | 56 |
| Hill model | 1.0 | 0.254 | 145.00 | 1.0 | 0.260 | 74 | 1.0 | 0.267 | 56 | 1.0 | 0.264 | 56 | 1.0 | 0.264 | 37 | 1.0 | 0.265 | 58 |
| Michaelis Menten model | 1.0 | 0.263 | 150.00 | 1.0 | 0.259 | 93 | 1.0 | 0.266 | 82 | 1.0 | 0.266 | 82 | 1.0 | 0.266 | 69 | 1.0 | 0.258 | 79 |
| Linear model | 1.0 | 0.271 | 148.00 | 1.0 | 0.256 | 81 | 1.0 | 0.269 | 69 | 1.0 | 0.265 | 69 | 1.0 | 0.267 | 50 | 1.0 | 0.258 | 65 |
| Power model | 1.0 | 0.268 | 149.00 | 1.0 | 0.258 | 92 | 1.0 | 0.262 | 81 | 1.0 | 0.264 | 81 | 1.0 | 0.263 | 67 | 1.0 | 0.259 | 77 |
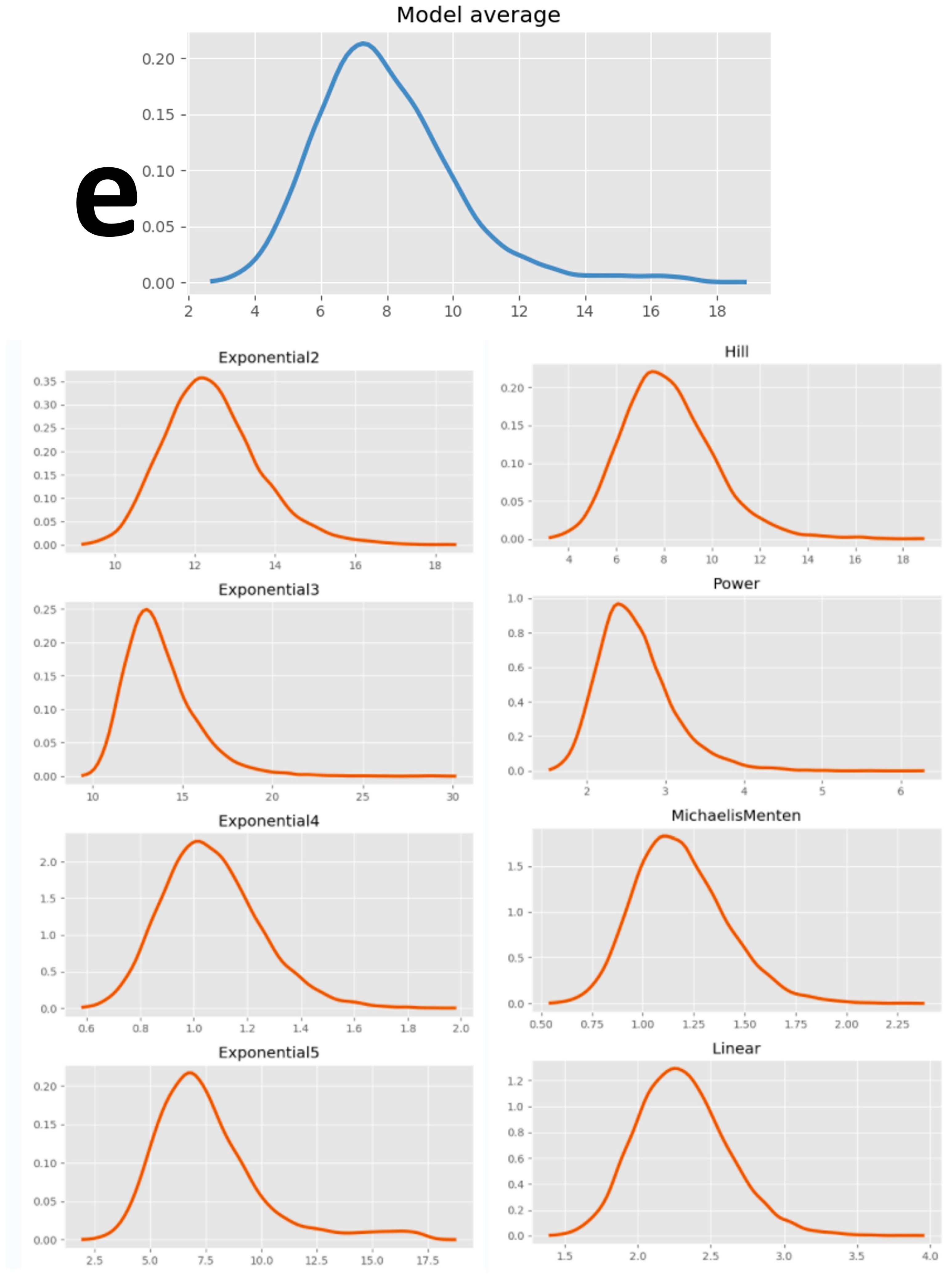
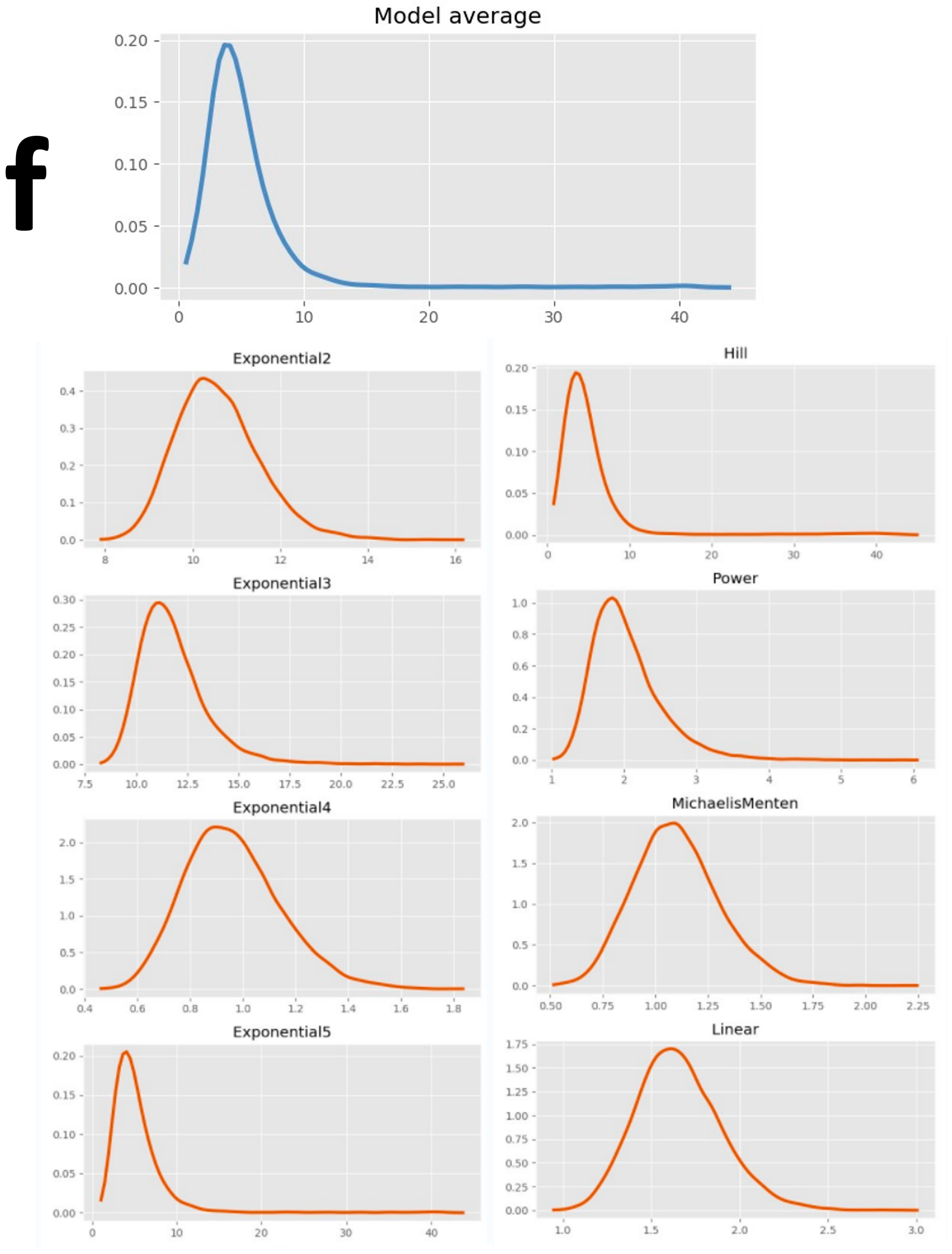
| Average | \ | \ | 147.00 | \ | \ | 80.80 | \ | \ | 61.25 | \ | \ | 56.50 | \ | \ | 37.50 | \ | \ | 59.75 |
| Model | 1 dpf CM | 2 dpf CM | 3 dpf CM | 4 dpf CM | 5 dpf CM | 5 dpf CMA | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | BMC | BMCL | BMCU | Weight (%) | BMC | BMCL | BMCU | Weight (%) | BMC | BMCL | BMCU | Weight (%) | BMC | BMCL | BMCU | Weight (%) | BMC | BMCL | BMCU | Weight (%) | BMC | BMCL | BMCU | |
| Model average | \ | 1.96 | 1.19 | 2.88 | \ | 1.80 | 1.02 | 5.07 | \ | 4.19 | 2.19 | 7.19 | \ | 5.07 | 3.06 | 7.87 | \ | 7.69 | 4.98 | 11.82 | \ | 3.73 | 1.69 | 7.82 |
| Exponential model 2 | 0.00 | 11.20 | 10.03 | 12.69 | 0.00 | 10.85 | 9.66 | 12.41 | 0.00 | 10.64 | 9.36 | 12.33 | 0.00 | 10.82 | 9.40 | 12.72 | 0.00 | 12.32 | 10.67 | 14.59 | 0.00 | 10.31 | 8.96 | 12.13 |
| Exponential model 3 | 0.00 | 12.26 | 10.54 | 15.85 | 0.00 | 11.76 | 10.08 | 14.87 | 0.00 | 11.56 | 9.86 | 14.67 | 0.00 | 11.81 | 9.93 | 15.18 | 0.00 | 13.42 | 11.24 | 17.43 | 0.00 | 11.27 | 9.50 | 14.65 |
| Exponential model 4 | 27.40 | 1.50 | 1.05 | 2.12 | 23.10 | 1.20 | 0.89 | 1.61 | 1.70 | 1.01 | 0.76 | 1.32 | 0.00 | 0.81 | 0.62 | 1.05 | 0.00 | 1.05 | 0.80 | 1.39 | 3.70 | 0.87 | 0.64 | 1.17 |
| Exponential model 5 | 4.60 | 2.04 | 1.27 | 3.80 | 24.60 | 3.01 | 1.59 | 5.60 | 45.60 | 3.95 | 2.18 | 6.74 | 0.40 | 4.54 | 2.75 | 7.26 | 0.41 | 7.12 | 4.56 | 12.67 | 62.20 | 3.88 | 1.98 | 8.04 |
| Hill model | 6.40 | 2.31 | 1.51 | 3.74 | 28.60 | 2.77 | 1.44 | 5.77 | 51.50 | 4.37 | 2.20 | 7.44 | 0.60 | 5.34 | 3.32 | 8.02 | 0.59 | 8.00 | 5.40 | 11.53 | 29.80 | 3.30 | 1.36 | 6.91 |
| Michaelis Menten model | 33.10 | 1.95 | 1.33 | 2.58 | 23.30 | 1.40 | 1.03 | 1.82 | 1.10 | 1.15 | 0.85 | 1.52 | 0.00 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 1.21 | 0.00 | 1.17 | 0.86 | 1.59 | 4.20 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 1.33 |
| Linear model | 24.70 | 2.51 | 2.01 | 3.14 | 0.20 | 2.02 | 1.64 | 2.50 | 0.00 | 1.75 | 1.41 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 1.59 | 1.28 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 2.29 | 1.84 | 2.85 | 0.00 | 1.52 | 1.19 | 1.93 |
| Power model | 3.80 | 2.93 | 2.21 | 4.39 | 0.30 | 2.35 | 1.80 | 3.41 | 0.00 | 2.01 | 1.54 | 2.83 | 0.00 | 1.79 | 1.37 | 2.47 | 0.00 | 2.55 | 1.98 | 3.50 | 0.00 | 1.79 | 1.33 | 2.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, T.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, C.; Yan, R.; Yang, Q.; Huang, H.; An, Y. Analysis of Acute and Short-Term Fluoride Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryo and Sac–Fry Stages Based on Bayesian Model Averaging. Toxics 2024, 12, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120902
Jin T, Yang X, Zhu Y, Yan C, Yan R, Yang Q, Huang H, An Y. Analysis of Acute and Short-Term Fluoride Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryo and Sac–Fry Stages Based on Bayesian Model Averaging. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120902
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Tingxu, Xiumei Yang, Yuanhui Zhu, Cheng Yan, Rui Yan, Qianlei Yang, Hairu Huang, and Yan An. 2024. "Analysis of Acute and Short-Term Fluoride Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryo and Sac–Fry Stages Based on Bayesian Model Averaging" Toxics 12, no. 12: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120902
APA StyleJin, T., Yang, X., Zhu, Y., Yan, C., Yan, R., Yang, Q., Huang, H., & An, Y. (2024). Analysis of Acute and Short-Term Fluoride Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryo and Sac–Fry Stages Based on Bayesian Model Averaging. Toxics, 12(12), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120902









