The Association Between Brominated Flame Retardants Exposure and Liver-Related Biomarkers in US Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
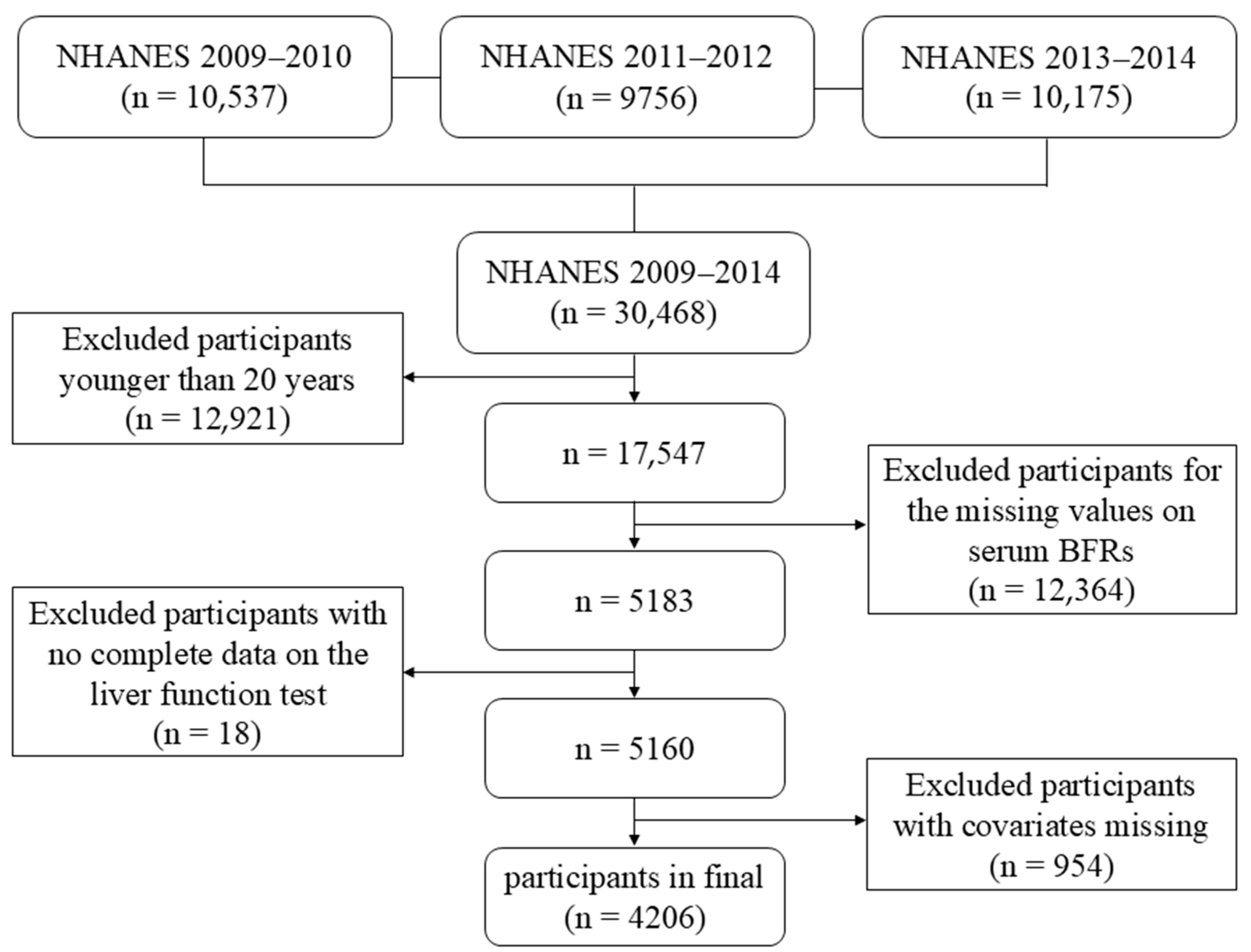
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Exposure Variables
2.3. The Indicators of LFTs
2.4. The Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4)
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Participants
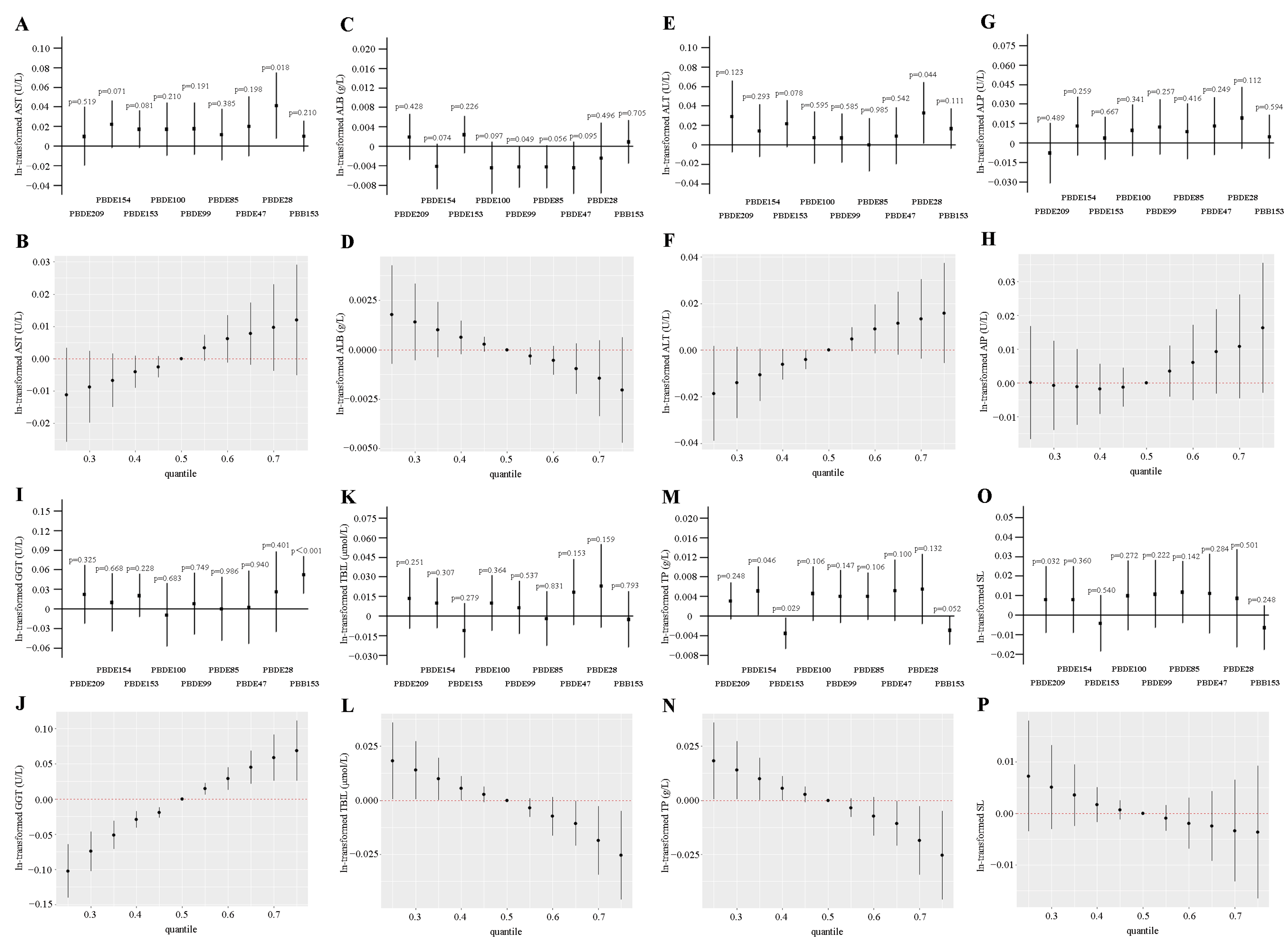
3.2. Association Between Each Kind of Serum BFR with LFTs
3.3. WQS and QGC Models to Assess the Associations Between Co-Exposure of BFRs and LFTs
3.4. BKMR Model to Assess the Associations Between Co-Exposure of BFRs and LFTs
3.5. Association Between Each Kind of Serum BFR with Liver Fibrosis Indicator
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frederiksen, M.; Vorkamp, K.; Thomsen, M.; Knudsen, L.E. Human internal and external exposure to PBDEs—A review of levels and sources. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Lai, C.; Xu, F.; Huang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; et al. A review of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in Chinese aquatic environment: Source, occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Wang, Q. Association between brominated flame retardants exposure and markers of oxidative stress in US adults: An analysis based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2016. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Romanak, K.A.; Capozzi, S.L.; Xia, C.; Lehman, D.C.; Harrad, S.; Cline-Cole, R.; Venier, M. Socio-Economic Factors Impact US Dietary Exposure to Halogenated Flame Retardants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar-Alemany, Ò.; Yang, X.; Alonso, M.B.; Costa, E.S.; Torres, J.P.M.; Malm, O.; Barceló, D.; Eljarrat, E. Preliminary study of long-range transport of halogenated flame retardants using Antarctic marine mammals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, M.; Harrad, S.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Drage, D.S.; Berresheim, H. Phasing-out of legacy brominated flame retardants: The UNEP Stockholm Convention and other legislative action worldwide. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmlein, S.; Herzke, D.; Law, R.J. BFR-governmental testing programme. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Dietrich, K.N.; Braun, J.M.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A. Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and child behavior: Current findings and future directions. Horm. Behav. 2018, 101, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.D.; Yang, L.W.; Deng, D.Y.; Jiang, R.N.; Song, Z.K.; Zhou, L.T. The effects of brominated flame retardants (BFRs) on pro-atherosclerosis mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.L.; Sousa, S.; Pestana, D.; Faria, A.; Teixeira, D.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Domingues, V.F.; Calhau, C. Impact of brominated flame retardants on lipid metabolism: An in vitro approach. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, J.; Namasivayam, V. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in the atmosphere: Their effects on humans and wildlife. Environ. Int. 2015, 76, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Cheng, H.; Gong, Y.; Huang, T. New brominated flame retardant decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) in water sediments: A review of contamination characteristics, exposure pathways, ecotoxicological effects and health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Hua, Y.Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.L. Modulation of SIRT1-mediated signaling cascades in the liver contributes to the amelioration of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in high fat fed middle-aged LDL receptor knockout mice by dihydromyricetin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 175, 113927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Chao, X.; Williams, J.; Fulte, S.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; Ding, W.X. Autophagy in liver diseases: A review. Mol. Asp. Med. 2021, 82, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, D.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Z.; Xing, C.; Sun, W.; Xu, G. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induces liver lipid metabolism disorder via the ROS/AMPK/CD36 signaling pathway. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 191, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Gu, T.; Ling, J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, J.; Hu, B.; Hua, L.; Wan, C.; Jiang, S. PFOS facilitates liver inflammation and steatosis: An involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, I.; Abeysekera, K.W.M.; Harris, R.; Mansour, D.; McPherson, S.; Rowe, I.; Rosenberg, W.; Dillon, J.F.; Yeoman, A. Identification of liver disease: Why and how. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHANES. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- NHANES. About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about_nhanes.htm (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- CDC. Laboratory Procedure Manual. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/labmethods/PCBPOL_H_MET.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Che, Z.; Jia, H.; Chen, R.; Pan, K.; Fan, Z.; Su, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, T. Associations between exposure to brominated flame retardants and metabolic syndrome and its components in U.S. adults. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858 Pt 2, 159935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, N.E.; Vanga, R.R.; Theethira, T.G.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; Murray, J.A.; Villafuerte, J.; Bonder, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Hansen, J.; Dennis, M.; et al. Prevalence of abnormal liver function tests in celiac disease and the effect of a gluten-free diet in the US population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhan, W.; Ren, J.; Gao, X.; Huang, X.; Ma, Y. Associations between organophosphate esters concentrations and markers of liver function in US adolescents aged 12–19 years: A mixture analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Lei, D.; Peng, D.; Zong, K.; Li, K.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z. Associations between Ethylene Oxide Exposure and Liver Function in the US Adult Population. Toxics 2024, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Cramb, R.; Davison, S.M.; Dillon, J.F.; Foulerton, M.; Godfrey, E.M.; Hall, R.; Harrower, U.; Hudson, M.; Langford, A.; et al. Guidelines on the management of abnormal liver blood tests. Gut 2018, 67, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Hong, T.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Qu, Q.; Zheng, C.; He, X. The Prognostic Value of the CA19-9/TBIL Ratio in Patients with Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs): A Retrospective Study. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 5829893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NHANES. Laboratory Procedure Manual. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/labmethods/BIOPRO_H_MET_ASPARTATE_AMINOTRANSFERASE.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Yu, L.; Yang, M.; Cheng, M.; Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Wang, B.; Chen, W. Associations between urinary phthalate metabolite concentrations and markers of liver injury in the US adult population. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Cheng, S.; Peng, Y.; Jin, Q.; Yang, J. DII modulates the relationship between SVD3 and NAFLD prevalence, rather than liver fibrosis severity, in hospitalized T2DM population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, M.; Lindvig, K.P.; Thorhauge, K.H.; Andersen, P.; Hansen, J.K.; Kastrup, N.; Jensen, J.M.; Hansen, C.D.; Johansen, S.; Israelsen, M.; et al. Using the ELF test, FIB-4 and NAFLD fibrosis score to screen the population for liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, G.; He, B.; Cao, Z.; He, J.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q. Effect of brominated flame retardants exposure on liver function and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the US population. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Senthilkumar, K.; Masunaga, S.; Takasuga, T.; Iseki, N.; Morita, M. Brominated organic contaminants in the liver and egg of the common cormorants (Phalacrocorax carbo) from Japan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4071–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, A.R.; Falkowska, L. Flame retardants at the top of a simulated baltic marine food web--a case study concerning African penguins from the Gdansk Zoo. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Xiao, D.; Han, D. In vitro effects of brominated flame retardants, selected metals and their mixtures on ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity in Mossambica tilapia liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, J.C.; Beck, D.J.; Kaminski, D.A.; Li, A.P. Polybrominated biphenyl induction of cytochrome P450 mixed function oxidase activity in primary rat and human hepatocytes. Toxicology 1995, 99, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.L.; Jiang, S.R.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, M.L.; Li, M.Y. 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromophenyl ether (BDE-153) causes abnormal insulin secretion and disorders of glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2023, 86, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Dutta, A.; Chakraborty, S.B.D. Efficacy and safety of saroglitazar in real-world patients of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with or without diabetes including compensated cirrhosis: A tertiary care center experience. JGH Open 2023, 7, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Niu, P.; Shi, Z. Reduced mitochondrial DNA copy number in occupational workers from brominated flame retardants manufacturing plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, G.; Ma, H.; Feng, B. GSDMD induces hepatocyte pyroptosis to trigger alcoholic hepatitis through modulating mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Div. 2024, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, G. The enrichment and purification of hexabromocyclododecanes and its effects on thyroid in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, H.; Anjum, F.; Lebeche, D.; Ali, S. Boron Facilitates Amelioration of Hepatic Injury by the Osmolyte Glycine and Resolves Injury by Improving the Tissue Redox Homeostasis. J. Diet. Suppl. 2024, 21, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Overall |
|---|---|
| No. subjects | 4206 |
| Age (%) a | 49.16 ± 17.73 |
| 20–40 years | 1440 (34.2) |
| 40–60 years | 1378 (32.8) |
| ≥60 years | 1388 (33.0) |
| Sex (%) b | |
| Male | 2071 (49.2) |
| Female | 2135 (50.8) |
| Race/ethnicity (%) b | |
| Mexican American | 575 (13.7) |
| Other Hispanic | 418 (9.9) |
| Non-Hispanic White | 1864 (44.3) |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 877 (20.9) |
| Other Race—including multi-racial | 472 (11.2) |
| Educational level (%) b | |
| Below High School | 971 (23.1) |
| High School | 952 (22.6) |
| Above High school | 2283 (54.3) |
| Marital status (%) b | |
| Married/living with partner | 2486 (59.1) |
| Widowed/divorced/separated/never married | 1720 (40.9) |
| Poverty income ratio (%) b | |
| ≤1.3 | 1388 (33.0) |
| 1.3–3.5 | 1525 (36.3) |
| >3.5 | 1293 (30.7) |
| Body mass index (%) b | |
| <25 kg/m2 | 1223 (29.1) |
| 25–30 kg/m2 | 1398 (33.2) |
| ≥30 kg/m2 | 1585 (37.7) |
| Cotinine level (%) b | |
| Below LLOD | 1194 (28.4) |
| Above LLOD | 3012 (71.6) |
| Alcohol consumption (%) b | 1124 (26.7) |
| Hypertension (%) b | 2673 (63.6) |
| Diabetes (%) b | 542 (12.9) |
| Strenuous/moderate activity in the past seven days (%) b | 3709 (88.2) |
| GM (95% CI) a | Median (IQR) b | |
|---|---|---|
| Serum BFRs (pg/g) | ||
| PBB153 | 14.274 (13.805, 14.761) | 14.980 (6.627, 27.130) |
| PBDE28 | 6.919 (6.807, 7.036) | 6.992 (4.739, 10.010) |
| PBDE47 | 122.688 (120.422, 124.961) | 118.700 (81.780, 183.600) |
| PBDE85 | 2.344 (2.293, 2.394) | 2.210 (1.485, 3.710) |
| PBDE99 | 23.655 (23.150, 24.167) | 22.280 (14.600, 37.300) |
| PBDE100 | 25.004 (24.533, 25.483) | 23.830 (16.067, 37.070) |
| PBDE153 | 54.423 (53.303, 55.590) | 51.030 (33.930, 82.690) |
| PBDE154 | 2.222 (2.177, 2.268) | 2.150 (1.419, 3.414) |
| PBDE209 | 15.881 (15.611, 16.167) | 15.200 (10.900, 20.960) |
| Liver function tests | ||
| AST (U/L) | 24.144 (23.903, 24.410) | 23.000 (20.000, 28.000) |
| ALB (g/L) | 42.403 (42.309, 42.521) | 43.000 (40.000, 45.000) |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.293 (21.977, 22.624) | 21.000 (16.000, 28.000) |
| ALP (U/L) | 64.563 (63.944, 65.170) | 64.000 (53.000, 79.000) |
| GGT (U/L) | 21.458 (21.031, 21.889) | 19.000 (14.000, 30.000) |
| TBIL (μmol/L) | 11.126 (10.990, 11.257) | 11.970 (8.550, 13.680) |
| TP (g/L) | 71.285 (71.165, 71.450) | 71.000 (68.000, 74.000) |
| AST/ALT | 1.083 (1.074, 1.093) | 1.092 (0.903, 1.313) |
| Fibrosis-4 index | 0.364 (0.358, 0.370) | 0.369 (0.248, 0.530) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ruan, J.; Huang, D.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Qu, J.; Wang, X. The Association Between Brominated Flame Retardants Exposure and Liver-Related Biomarkers in US Adults. Toxics 2024, 12, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120852
Chen Y, Cheng Y, Ruan J, Huang D, Xiao J, Zhao X, Li J, Qu J, Wang X. The Association Between Brominated Flame Retardants Exposure and Liver-Related Biomarkers in US Adults. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120852
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuqing, Yulan Cheng, Jialing Ruan, Donglei Huang, Jing Xiao, Xinyuan Zhao, Jinlong Li, Jianhua Qu, and Xiaoke Wang. 2024. "The Association Between Brominated Flame Retardants Exposure and Liver-Related Biomarkers in US Adults" Toxics 12, no. 12: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120852
APA StyleChen, Y., Cheng, Y., Ruan, J., Huang, D., Xiao, J., Zhao, X., Li, J., Qu, J., & Wang, X. (2024). The Association Between Brominated Flame Retardants Exposure and Liver-Related Biomarkers in US Adults. Toxics, 12(12), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120852






