Polystyrene Nanomicroplastics Aggravate Ammonia-Induced Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization of PSNPs Suspension
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Locomotor Behavior Measurement of Zebrafish Larvae
2.6. Ammonia Content in Zebrafish Larvae
2.7. Pathological Observation
2.8. Gene Expression
2.9. Analysis of DA Content and AChE Activity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
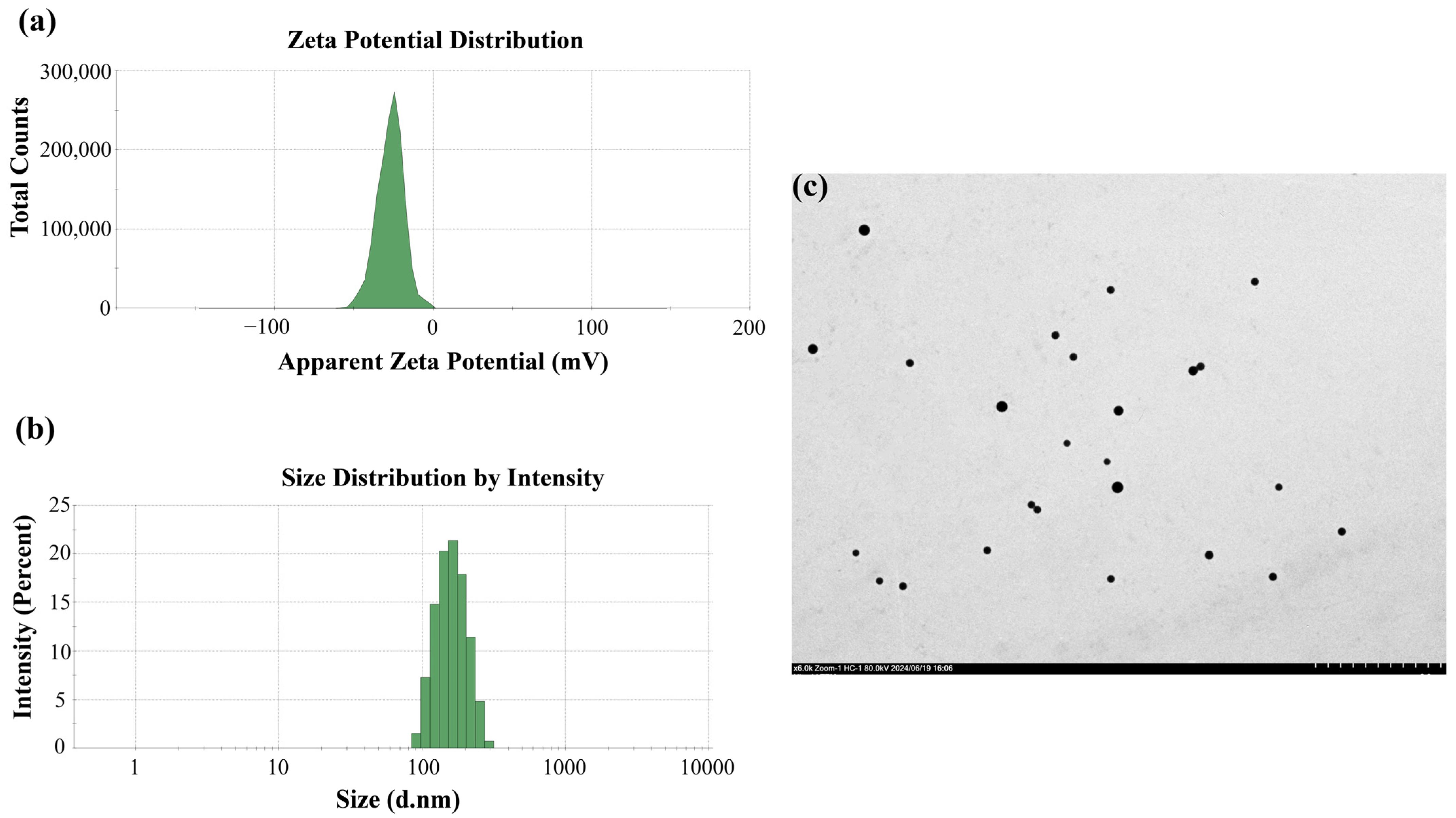
3.1. Characterization of PSNPs
3.2. Adsorption of Ammonia on PSNPs
3.3. Developmental Toxicity of Zebrafish Larvae
3.4. Locomotor Behavior of Larval Zebrafish
3.5. Ammonia Content in Zebrafish Larvae
3.6. Retinal Tissue Pathological Analysis
3.7. DA Content and AChE Activity
3.8. Gene Expression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, N. Removal of Ammonia Nitrogen from Wastewater: A Review. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.; Strader, R.; Davidson, C. Airborne reduced nitrogen: Ammonia emissions from agriculture and other sources. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Ma, H.-L.; Su, Y.-L.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Feng, J.; Xie, J.-W.; Chen, X.-L.; Guo, Z.-X. Ammonia toxicity in the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain): The mechanistic insight from physiology to transcriptome analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 179, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M. The importance of ammonia in mammalian cell culture. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 46, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egnew, N.; Renukdas, N.; Ramena, Y.; Yadav, A.K.; Kelly, A.M.; Lochmann, R.T.; Sinha, A.K. Physiological insights into largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) survival during long-term exposure to high environmental ammonia. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 207, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z. Water quality criteria of total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) and un-ionized ammonia (NH3-N) and their ecological risk in the Liao River, China. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Wu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Lv, J. Gill damage and neurotoxicity of ammonia nitrogen on the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Cheng, C.-A.; Liu, S.-T.; Horng, J.-L. Investigation of ammonia-induced lethal toxicity toward ion regulation in zebrafish embryos. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 276, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, Y. Ammonia production, excretion, toxicity, and defense in fish: A review. Front. Physiol. 2010, 1, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.J.; Tsui, T.K.N. Ammonia toxicity in fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Tse, H.F.; Fok, L. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566-567, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, X.; Ma, J. Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants and metals on micro/nanoplastics in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, L.; Arulmani, S.R.B.; Yan, J.; Wu, L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, T. Adsorption of Different Pollutants by Using Microplastic with Different Influencing Factors and Mechanisms in Wastewater: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yin, D.; Jia, Y.; Schiwy, S.; Legradi, J.; Yang, S.; Hollert, H. Enhanced uptake of BPA in the presence of nanoplastics can lead to neurotoxic effects in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Huo, T.; Du, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shen, J.; Liu, C.; Hung, T.-C.; Yan, W.; Li, G. The joint effect of parental exposure to microcystin-LR and polystyrene nanoplastics on the growth of zebrafish offspring. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Guo, H.; Ouyang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Li, L. Nano-TiO2 aggravates immunotoxic effects of chronic ammonia stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio) intestine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 266, 109548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ruiz, M.; De la Vieja, A.; de Alba Gonzalez, M.; Esteban Lopez, M.; Castaño Calvo, A.; Cañas Portilla, A.I. Toxicity of nanoplastics for zebrafish embryos, what we know and where to go next. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkwitz, S.; Mourrain, P.; Becker, T.S. Zebrafish: An integrative system for neurogenomics and neurosciences. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehlicher, M.; Liedtke, A.; Groh, K.J.; Neuhauss, S.C.F.; Segner, H.; Eggen, R.I.L. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) neuromast: Promising biological endpoint linking developmental and toxicological studies. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 95, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, B.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeong, J. Correction: Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Lin, W.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, F.; Bao, L.-J.; You, J.; Ouyang, G.; Zeng, E.Y. Quantifying nanoplastic-bound chemicals accumulated in Daphnia magna with a passive dosing method. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastic exposure disturbs hepatic glycolipid metabolism at the physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic levels in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Habumugisha, T.; Yan, C.; Shaheen, U.; Zhang, X. Nanoplastic contamination: Impact on zebrafish liver metabolism and implications for aquatic environmental health. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poopal, R.-K.; He, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, B.; Ramesh, M.; Ren, Z. Organophosphorus-based chemical additives induced behavioral changes in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Swimming activity is a sensitive stress indicator. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2021, 83, 106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Bai, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Dong, Q.; Yang, D. BDE-47 disrupts axonal growth and motor behavior in developing zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 120-121, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, X.; Xu, Z.; Gao, P.; Jin, Z.; Hong, H.; Sun, H. Dihalogenated nitrophenols exposure induces developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish embryo. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilton, F.A.; Bammler, T.K.; Gallagher, E.P. Swimming impairment and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in zebrafish exposed to copper or chlorpyrifos separately, or as mixtures. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 153, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.B.M.; Candolin, U. Behavioral responses to changing environments. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 26, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Horng, J.-L.; Cheng, C.-A.; Chang, C.-Y.; Cherng, B.-W.; Liu, S.-T.; Chou, M.-Y. Sublethal ammonia induces alterations of emotions, cognition, and social behaviors in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, X.; Zuo, J.; Pan, M.; Nie, H.; Shen, J.; Yang, Q.; Hung, T.-C.; Li, G. The presence of polystyrene nanoplastics enhances the MCLR uptake in zebrafish leading to the exacerbation of oxidative liver damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: Why it is important to toxicology and toxicologists. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuto, M.; Rampulla, F.; Reali, G.M.; Spanò, S.M.; Trovato Salinaro, A.; Calabrese, V. Hormetic Nutrition and Redox Regulation in Gut–Brain Axis Disorders. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, N.; Lal, G. Cholinergic System and Its Therapeutic Importance in Inflammation and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 660342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Multiple Roles for Cholinergic Signaling from the Perspective of Stem Cell Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, W. Multiple Dopamine Functions at Different Time Courses. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 259–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: How is structure related to function? Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 175, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, H.; Xie, H.Q.; Zhao, B. Acetylcholinesterase Is a Potential Biomarker for a Broad Spectrum of Organic Environmental Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8065–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pino, J.; Zeballos, G.; Anadon, M.J.; Capo, M.A.; Díaz, M.J.; García, J.; Frejo, M.T. Higher sensitivity to cadmium induced cell death of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: A cholinesterase dependent mechanism. Toxicology 2014, 325, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Calisi, A.; Giordano, M.E.; Schettino, T. Acetylcholinesterase as a Biomarker in Environmental and Occupational Medicine: New Insights and Future Perspectives. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 321213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richetti, S.K.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Ventura-Lima, J.; Monserrat, J.M.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Acetylcholinesterase activity and antioxidant capacity of zebrafish brain is altered by heavy metal exposure. NeuroToxicology 2011, 32, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shao, Y.; Duan, X.; Sun, B.; Zhao, X. Nanoplastics aggravated TDCIPP-induced transgenerational developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish depending on the involvement of the dopamine signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 108, 104436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, A.; Gupta, P.; Suman, A.; Ray, S.S.; Malafaia, G.; Singh, R.K. Unraveling the mechanisms of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity and microglial activation in developing zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lam, J.C.-W.; Man, Y.-C.; Lai, N.L.-S.; Kwok, K.Y.; Guo, Y.y.; Lam, P.K.-S.; Zhou, B. Bioconcentration, metabolism and neurotoxicity of the organophorous flame retardant 1,3-dichloro 2-propyl phosphate (TDCPP) to zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 158, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, J.H. The Zebrafish Visual System: From Circuits to Behavior. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2019, 5, 269–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engert, F.; Portugues, R. Adaptive Locomotor Behavior in Larval Zebrafish. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to DE-71 causes alterations in visual behavior in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icha, J.; Kunath, C.; Rocha-Martins, M.; Norden, C. Independent modes of ganglion cell translocation ensure correct lamination of the zebrafish retina. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Trujillo, C.; Zhong, W.; Leung, Y.F. The Expression of irx7 in the Inner Nuclear Layer of Zebrafish Retina Is Essential for a Proper Retinal Development and Lamination. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36145. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Fu, J.; Han, J.; Hu, B.; Zhou, B. Optical toxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 210, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Murakami, S.; Ashikawa, Y.; Sasagawa, S.; Umemoto, N.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, T. Zebrafish as a systems toxicology model for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Congenit. Anom. 2015, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, J.; Qiu, X.; Du, G.; Cristante, L.; Eisenstat, D.D. Dlx1, Dlx2, Pax6, Brn3b, and Chx10 homeobox gene expression defines the retinal ganglion and inner nuclear layers of the developing and adult mouse retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 461, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtoshi, A.; Wang, S.W.; Maeda, H.; Saszik, S.M.; Frishman, L.J.; Klein, W.H.; Behringer, R.R. Regulation of Retinal Cone Bipolar Cell Differentiation and Photopic Vision by the CVC Homeobox Gene Vsx1. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, A.J.; Maksour, S.; St-Clair Glover, M.; Miellet, S.; Dottori, M. Making neurons, made easy: The use of Neurogenin-2 in neuronal differentiation. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Lim, J.-W.; Yellajoshyula, D.; Chang, L.-W.; Kroll, K.L. Neurogenin and NeuroD direct transcriptional targets and their regulatory enhancers. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 5093–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.n.; Lim, D.A.; Dahmane, N.; Sánchez, P.; Brionne, T.C.; Herzberg, C.D.; Gitton, Y.; Carleton, A.; Álvarez-Buylla, A.; Altaba, A.R.i. Sonic hedgehog controls stem cell behavior in the postnatal and adult brain. Development 2005, 132, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, A.; Arranz, L. Nestin-expressing progenitor cells: Function, identity and therapeutic implications. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2177–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Guo, S.; Masai, I.; Nicolson, T.; Wu, C.-F. Zebrafish: From genes and neurons to circuits, behavior and disease. J. Neurogenet. 2017, 31, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.-H.; Gerenza, A.K.; Bingener, G.M.; Bonkowsky, J.L. Hypoplasia of dopaminergic neurons by hypoxia-induced neurotoxicity is associated with disrupted swimming development of larval zebrafish. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 963037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, M.; Messing, A. Regulation of GFAP Expression. ASN Neuro 2021, 13, 1759091420981206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Gene Name | Primer Sequences (from 5′ to 3′) | Gene Bank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| ache | Forward: CCCTCCAGTGGGTACAAGAA | NM_131846 |
| Reverse: GGGCCTCATCAAAGGTAACA | ||
| neurogenin | Forward: CTCCCAGCCCACCAATAAGG | AF024535 |
| Reverse: CATCCGTGTGCGAAAAGCAG | ||
| gfap | Forward: GGATGCAGCCAATCGTAAT | NM_131373 |
| Reverse: TTCCAGGTCACAGGTCAG | ||
| shha | Forward: GCAAGATAACGCGCAATTCGGAGA | DRU30711 |
| Reverse: ATGCTGGAGAAACATGCCATGCAG | ||
| nestin | Forward: ATGCTGGAGAAACATGCCATGCAG | XM_001919887 |
| Reverse: AGGGTGTTTACTTGGGCCTGAAGA | ||
| brn3b | Forward: CATTCCTCGTCCTCCTCCTCTACTC | NC_007112.7 |
| Reverse: CTGATCGTGCTGCTGTGTCTGG | ||
| vsx1 | Forward: GAACTTCAGCCGCACCAGTCAG | NC_007128.7 |
| Reverse: CACAGAAACCCCAAGCCCAAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, D.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, H.; Luan, N.; Liu, X. Polystyrene Nanomicroplastics Aggravate Ammonia-Induced Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics 2024, 12, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120853
Xing D, Zheng W, Zhou H, Li G, Li Y, Jia J, Liu H, Luan N, Liu X. Polystyrene Nanomicroplastics Aggravate Ammonia-Induced Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120853
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Dan, Wenting Zheng, Huiming Zhou, Guangyu Li, Yan Li, Jingwen Jia, Haoling Liu, Ning Luan, and Xiaolin Liu. 2024. "Polystyrene Nanomicroplastics Aggravate Ammonia-Induced Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryos" Toxics 12, no. 12: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120853
APA StyleXing, D., Zheng, W., Zhou, H., Li, G., Li, Y., Jia, J., Liu, H., Luan, N., & Liu, X. (2024). Polystyrene Nanomicroplastics Aggravate Ammonia-Induced Neurotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics, 12(12), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120853





