Real-Time Monitoring of Water Content in Sandy Soil Using Shear Mode Piezoceramic Transducers and Active Sensing—A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Shear Mode Smart Aggregates
3. Principles
3.1. Active Sensing Approach
3.2. Wavelet Packet-Based Energy Approach
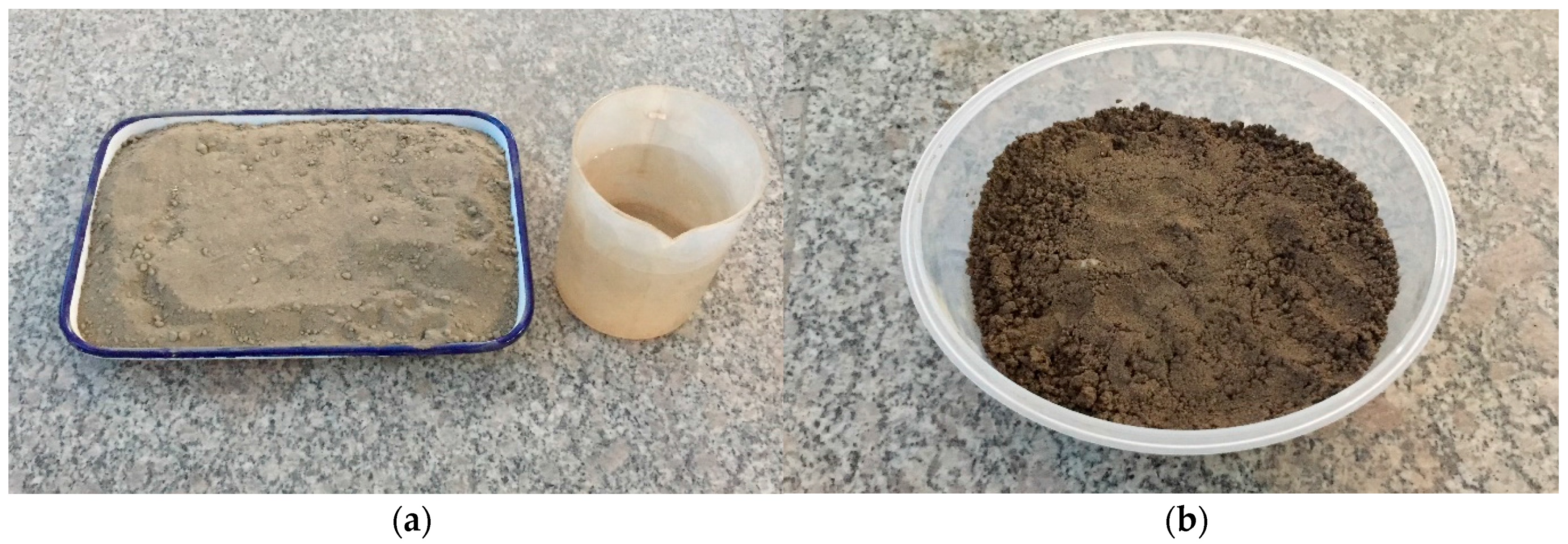
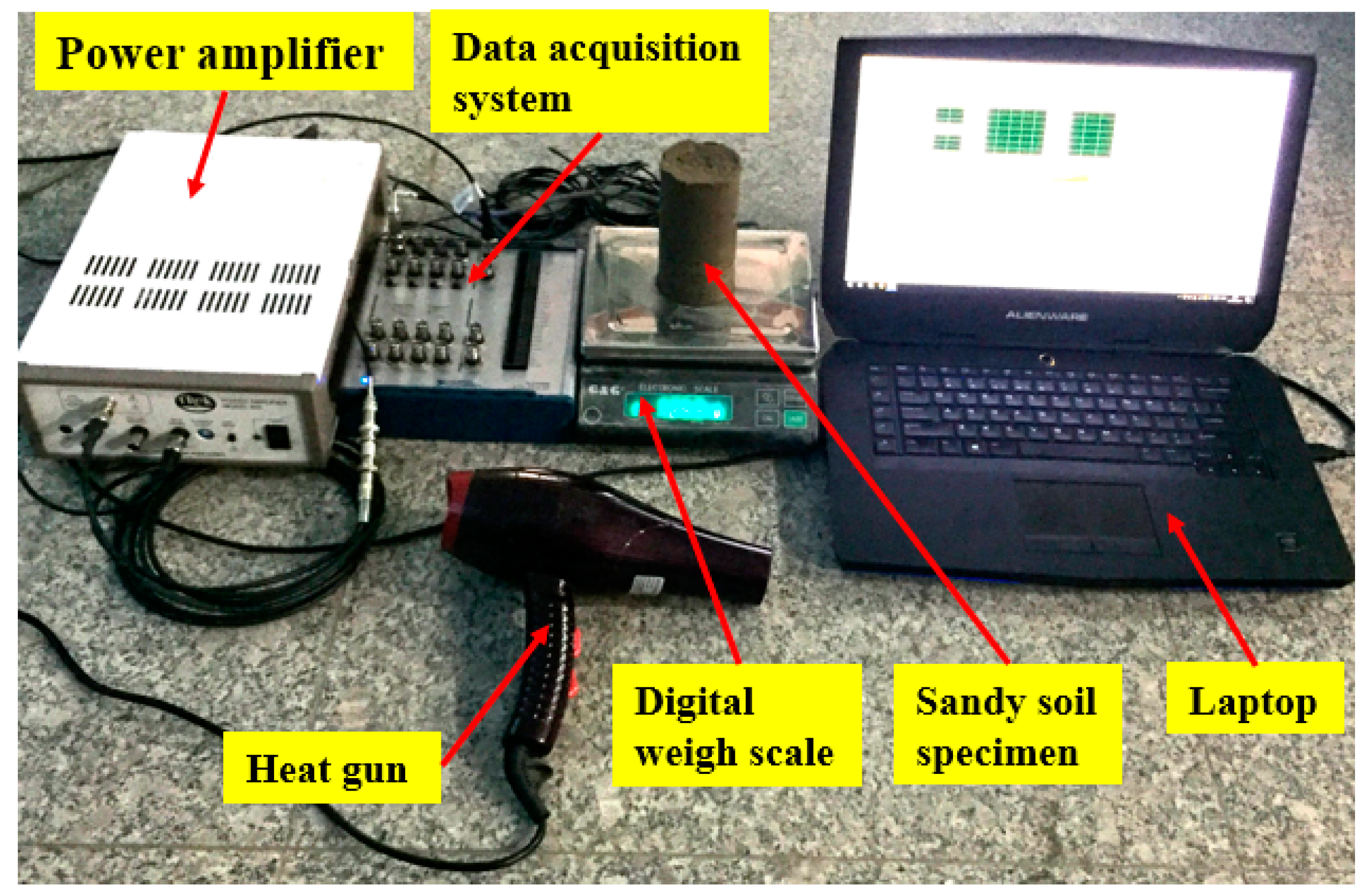
4. Experimental Setup
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Time-Domain Signal Response
5.2. Wavelet Packet-Based Energy Index
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, R.L.; Jacobs, J.M. Relationships among remotely sensed soil moisture, precipitation and landslide events. Nat. Hazards 2007, 43, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saigh, N.H.; Mohammed, Z.S.; Dahham, M.S. Detection of water leakage from dams by self-potential method. Eng. Geol. 1994, 37, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.D.; Malamud, B.D.; Blodgett, T.; Turcotte, D.L. Scale-invariance of soil moisture variability and its implications for the frequency-size distribution of landslides. Eng. Geol. 1997, 48, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthulu, T.V.; Krishnaiah, C.; Shirke, J.M. Detection of seepage paths in earth dams using self-potential and electrical resistivity methods. Eng. Geol. 2001, 59, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, A.; Alva, A.K. Evaluation of capacitance probes for optimal irrigation of citrus through soil moisture monitoring in an entisol profile. Irrig. Sci. 2000, 19, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayde, C.; Gregory, C.; Gil-Rodriguez, M.; Tufillaro, N.; Tyler, S.; van de Giesen, N.; English, M.; Cuenca, R.; Selker, J.S. Feasibility of soil moisture monitoring with heated fiber optics. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, S.G. The gravimetric method of soil moisture determination Part I A study of equipment, and methodological problems. J. Hydrol. 1970, 11, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.H.; Malicki, M.A.; Plagge, R. Empirical evaluation of the relationship between soil dielectric constant and volumetric water content as the basis for calibrating soil moisture measurements by TDR. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1992, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Schmugge, T.J. An empirical model for the complex dielectric permittivity of soils as a function of water content. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1980, GE-18, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wobschall, D. A frequency shift dielectric soil moisture sensor. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 1978, 16, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.J. Remote sensing of soil moisture: Recent advances. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1983, GE-21, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.J.; Jackson, T.J.; McKim, H.L. Survey of methods for soil moisture determination. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, A.E.; Abuarab, M.E. Soil moisture distribution patterns under surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems in sandy soil using neutron scattering technique. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engman, E.T.; Chauhan, N. Status of microwave soil moisture measurements with remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C.; Davidson, A.; Cherneski, P.; L’Heureux, J.; Hadwen, T. Monitoring agricultural risk in Canada using L-band passive microwave soil moisture from SMOS. J. Hydrometeorology 2015, 16, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.J. Satellite remote sensing applications for surface soil moisture monitoring: A review. Front. Earth Sci. China 2009, 3, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Schuckman, B. Experiments and theory of wave-soil interactions. J. Eng. Mech. 1984, 110, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low-frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.C.; Yeh, C.L.; Tsai, C.T. Effect of soil texture on the propagation and attenuation of acoustic wave at unsaturated conditions. J. Hydrol. 2007, 338, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W.; Luthin, J.N. The velocity of sound in soils near the surface as a function of the moisture content. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, F.; Andria, G.; Attivissimo, F.; Giaquinto, N. An acoustic method for soil moisture measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Measur. 2004, 53, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.B.; Hung, H.H.; Chang, D.W. Train-induced wave propagation in layered soils using finite/infinite element simulation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2003, 23, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehler, M.; Pearson, C. Cross-hole seismic surveys: Applications for studying subsurface fracture systems at a hot dry rock geothermal site. Geophysics 1984, 49, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongmans, D.; Demanet, D. The importance of surface waves in vibration study and the use of Rayleigh waves for estimating the dynamic characteristics of soils. Eng. Geol. 1993, 34, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, D.S.; Nash, D.F.; Lings, M.L. Horizontally mounted bender elements for measuring anisotropic shear moduli in triaxial clay specimens. Geotech. Test. J. 2001, 24, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Sawangsuriya, A.; Edil, T.B.; Bosscher, P.J. Modulus-suction-moisture relationship for compacted soils in postcompaction state. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Gu, H.; Mo, Y.L. Smart aggregates: Multi-functional sensors for concrete structures—A tutorial and a review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Feng, Q.; Song, G. Water presence detection in a concrete crack using smart aggregates. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2015, 6, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Du, C.; Li, B. Feasibility of water seepage monitoring in concrete with embedded smart aggregates by P-wave travel time measurement. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 067003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Kong, Q.; Huo, L.; Song, G. Crack detection and leakage monitoring on reinforced concrete pipe. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 115020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhang, H.B.; Ou, J.P. A PZT-based smart aggregate for compressive seismic stress monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tsai, Y.T.; Kee, S.H. Monitoring early age property of cement and concrete using piezoceramic bender elements. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 115014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Song, G. A comparative study of the very early age cement hydration monitoring using compressive and shear mode smart aggregates. IEEE Sensors J. 2017, 17, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Melhem, H. Damage detection of structures by wavelet analysis. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell University. Northeast Region Certified Crop Adviser (NRCCA) Study Resources. Field Capacity. Permanent Wilting Point & Available Water Capacity. Available online: https://nrcca.cals.cornell.edu/soil/CA2/CA0212.1-3.php (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- Ridley, A.M.; Burland, J.B. A new instrument for the measurement of soil moisture suction. Géotechnique 1993, 43, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Q.; Chen, H.; Mo, Y.-l.; Song, G. Real-Time Monitoring of Water Content in Sandy Soil Using Shear Mode Piezoceramic Transducers and Active Sensing—A Feasibility Study. Sensors 2017, 17, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102395
Kong Q, Chen H, Mo Y-l, Song G. Real-Time Monitoring of Water Content in Sandy Soil Using Shear Mode Piezoceramic Transducers and Active Sensing—A Feasibility Study. Sensors. 2017; 17(10):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102395
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Qingzhao, Hongli Chen, Yi-lung Mo, and Gangbing Song. 2017. "Real-Time Monitoring of Water Content in Sandy Soil Using Shear Mode Piezoceramic Transducers and Active Sensing—A Feasibility Study" Sensors 17, no. 10: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102395
APA StyleKong, Q., Chen, H., Mo, Y.-l., & Song, G. (2017). Real-Time Monitoring of Water Content in Sandy Soil Using Shear Mode Piezoceramic Transducers and Active Sensing—A Feasibility Study. Sensors, 17(10), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102395






