Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
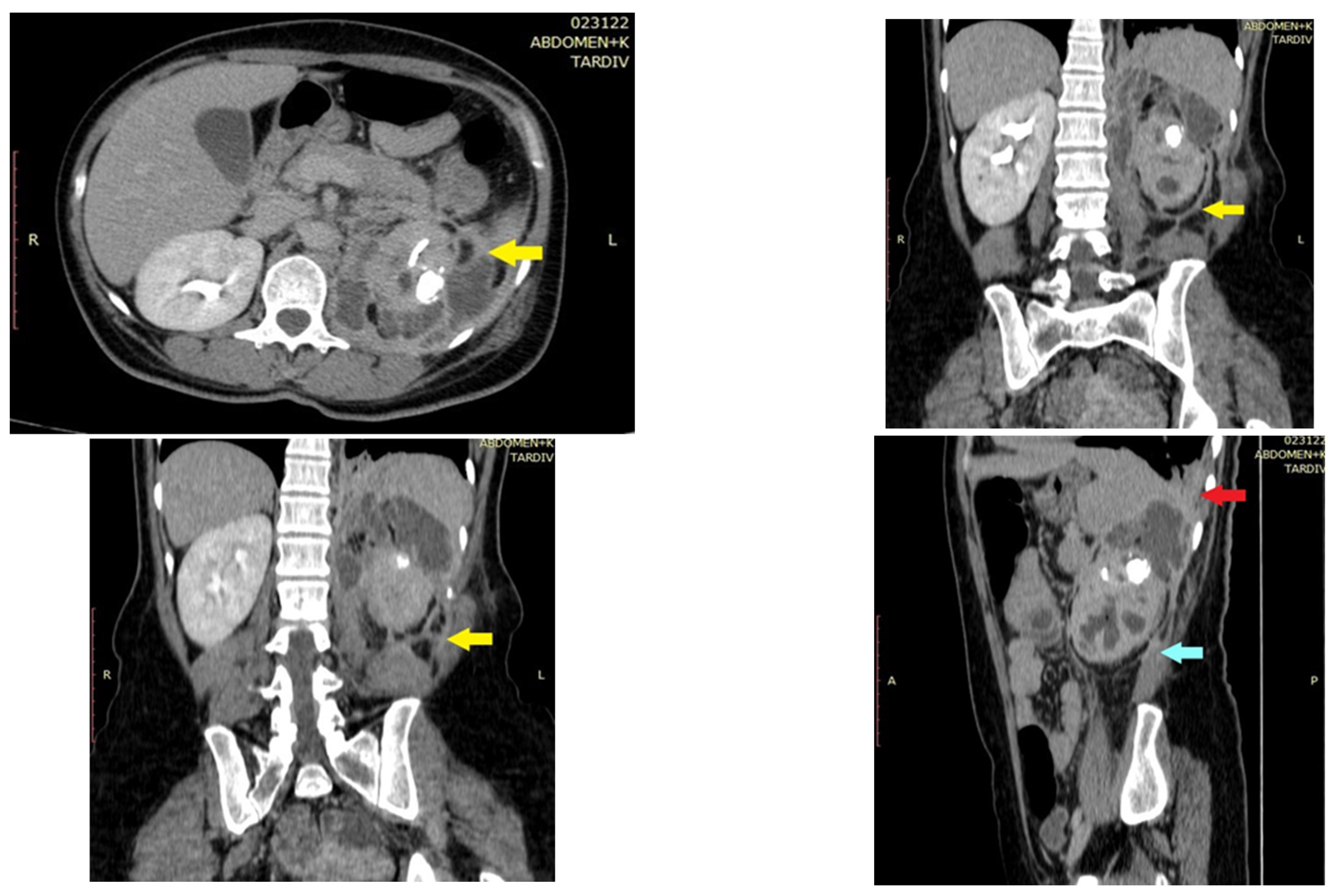
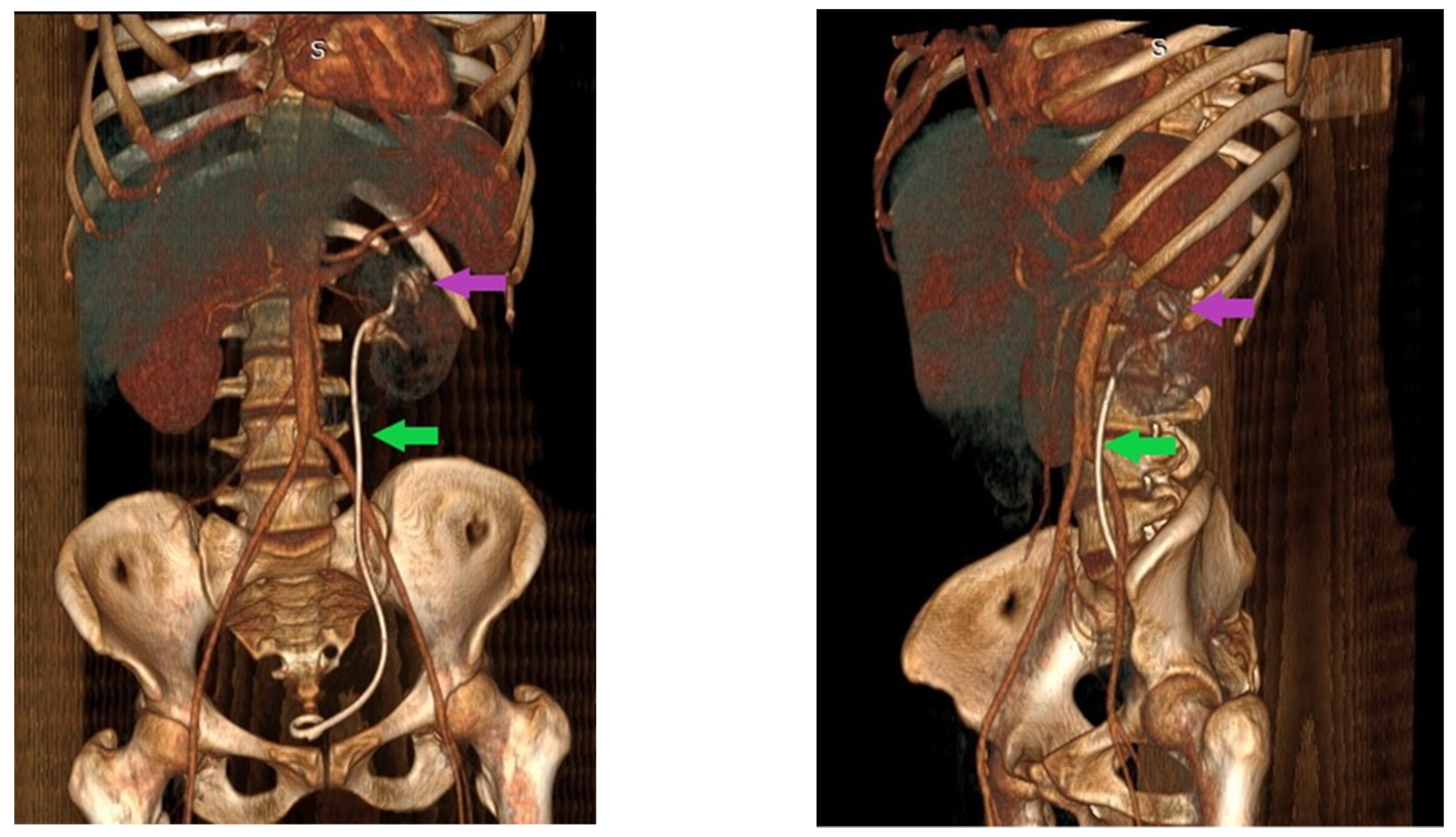
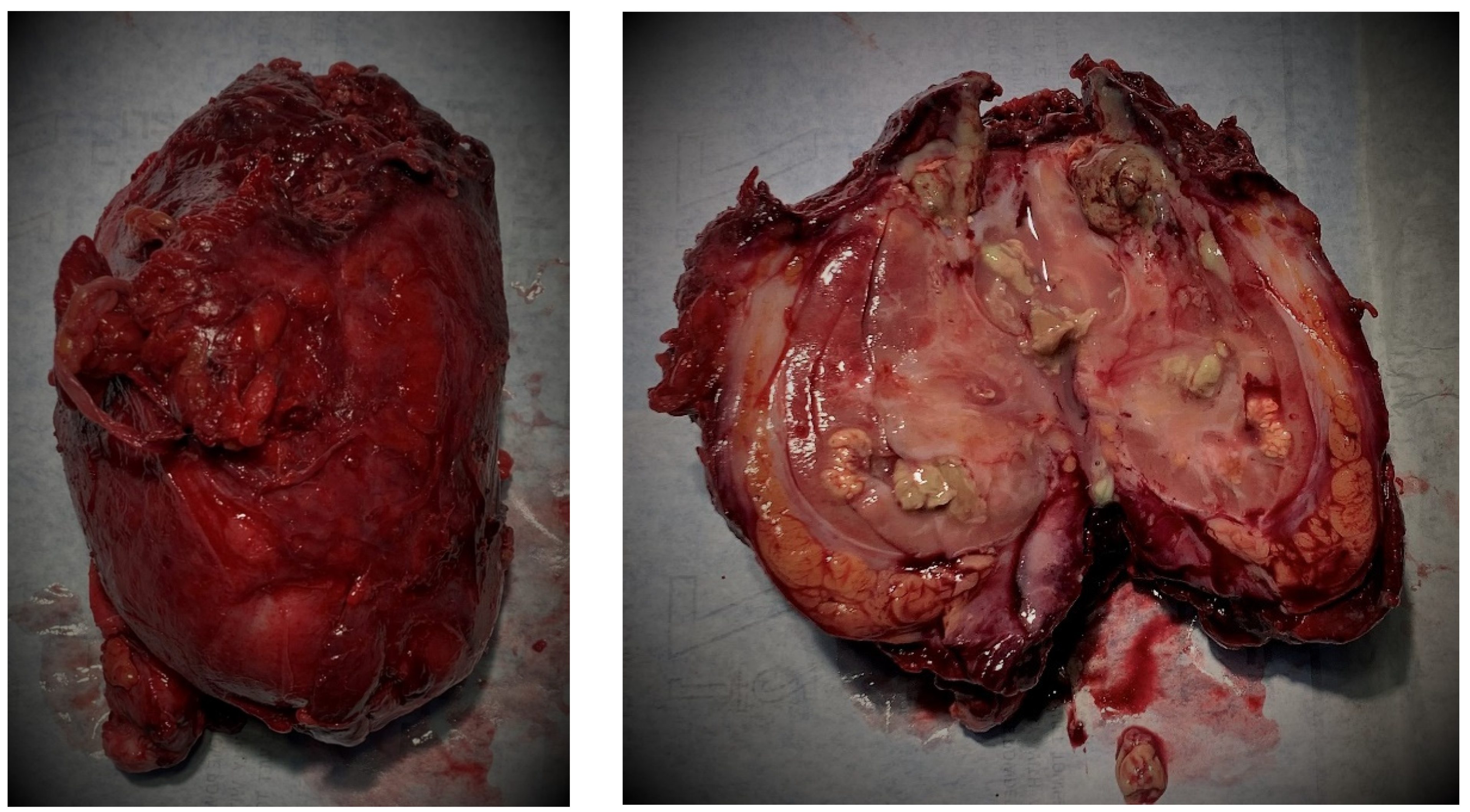
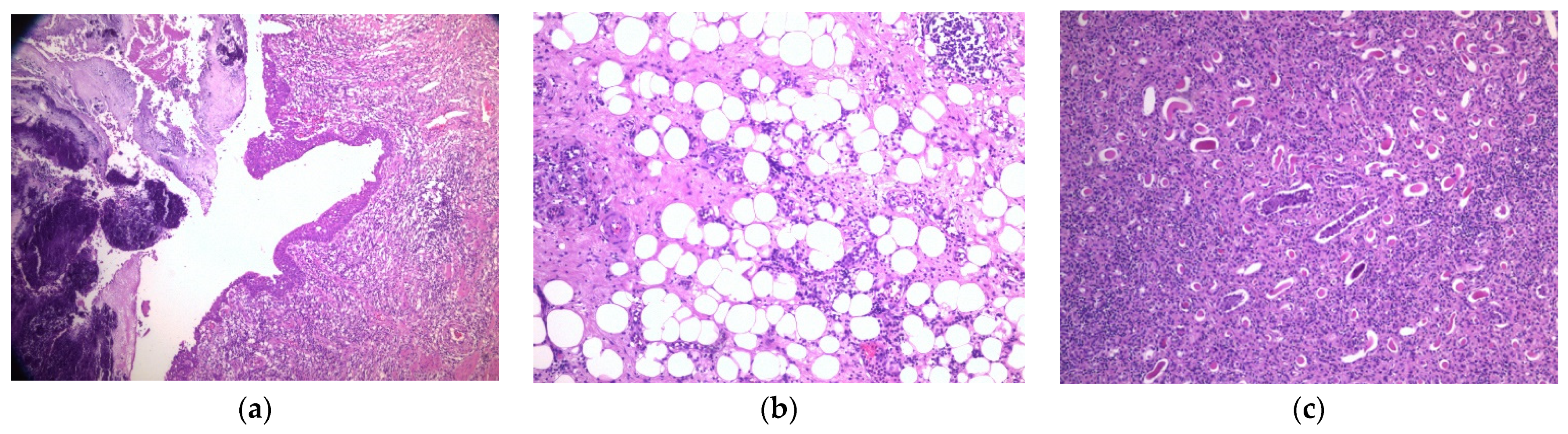
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abadi, A.T.B.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Haertlé, T.; Blatt, N.L. World Health Organization report: Current crisis of antibiotic resistance. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, L.; Manfredi, R.; Chiodo, F. Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia as an emerging opportunistic pathogen in association with HIV infection: A 10-year surveillance study. Infection 2003, 31, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muder, R.R.; Harris, A.P.; Muller, S.; Edmond, M.; Chow, J.W.; Papadakis, K.; Wagener, M.W.; Bodey, G.P.; Steckelberg, J.M. Bacteremia due to Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia: A prospective, multicenter study of 91 episodes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, M.W.; Anderson, D.E.; Campbell, D.M.; Carroll, K.C.; Malone, C.L.; Anderson, J.D.; Hollis, R.J.; Pfaller, M.A. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Emergence of multidrug-resistant strains during therapy and in an in vitro pharmacodynamic chamber model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartivarian, S.; Anaissie, E.; Bodey, G.; Sprigg, H.; Rolston, K. A changing pattern of susceptibility of Xanthomonas maltophilia to antimicrobial agents: Implications for therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looney, W.J.; Narita, M.; Mühlemann, K. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging opportunist human pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, A.A.; Stenström, T.A.; Okoh, A.I. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as an emerging ubiquitous pathogen: Looking beyond contemporary antibiotic therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, C.; Opazo, V.; Bassa, C.; López, L.; Araos, F.; Madrid, P.; Morales, I. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report. Urol. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlagenhauefer, F. Uber eigentumliche staphylmkosen der nieven und der pararenalen bindegewebes. Frankf. Z. Pathol. 1916, 19, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, R.; Baliyan, A.; Dhingra, H.; Bhalla, V.; Punia, R.S. Clinicopathological spectrum of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Indian J. Nephrol. 2019, 29, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çaliskan, S.; Özsoy, E.; Kaba, S.; Koca, O.; Öztürk, M.I. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. Arch. Iran. Med. 2016, 19, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marinacci, L.X.; Rosales, I. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Abad, P.; Rodríguez-Cabello, M.Á.; Vera-Berón, R.; Platas-Sancho, A. Bear Paw Sign: Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkes, F.; Favoretto, R.L.; Bróglio Silva, C.A.; Castro, M.G.; Perez, M.D.C. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Clinical experience with 41 cases. Urology 2008, 71, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, U.S.; Goyal, N.K.; Saxena, V.; Acharya, R.L.; Trivedi, S.; Singh, P.B.; Vyas, N.; Datta, B.; Kumar, A.; Das, S. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Our experience with review of published reports. ANZ J. Surg. 2006, 76, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petca, R.C.; Popescu, R.I.; Mares, C.; Mehedintu, C.; Mastalier, B.; Badiu, D.C.; Maru, N.; Constantin, V.D.; Petca, A. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis: Presentation and management. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2019, 6, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute® (CLSI). M 100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in respiratory tract samples: A 10-year epidemiological snapshot. Health Serv. Res. Manag. Epidemiol. 2019, 6, 2333392819870774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M.; Ábrók, M.; Lázár, A.; Burián, K. Urinary tract infections in elderly patients: A 10-year study on their epidemiology and antibiotic resistance based on the WHO Access, Watch, Reserve (AWaRe) classification. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.H.; Lai, M.Y.; Shen, S.H.; Yang, A.H.; Su, N.W.; Ng, Y.Y. Bilateral xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2008, 71, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siddappa, S.; Ramprasad, K.; Muddegowda, M.K. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A retrospective review of 16 cases. Korean J. Urol. 2011, 52, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, I.; Wirth, B.; Wand, H. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis associated with renal cell carcinoma. Report on two cases and review of the literature. Eur. Urol. 1990, 18, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, B.; Gupta, S.; Edpao, P.; Psutka, S.P.; Limaye, A.P.; Bakthavatsalam, R.; Rakita, R.M. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis with direct extension into the liver. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1054–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, R.S.; Elder, J.S. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A critical analysis of 26 cases and of the literature. J. Urol. 1978, 119, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, A.; Mittal, S.; Patel, K.; Azhar, S.; Prasla, S. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case review of two cases. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 4198–4201. [Google Scholar]
- Hugh, R.; Leifson, E. A description of the type strain of Pseudomonas maltophilia. Int. Bull. Bacteriol. Nomencl. Taxon. 1963, 13, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaleva, J.; Degener, J.E.; van der Mei, H.C. Mimicking disinfection and drying of biofilms in contaminated endoscopes. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 76, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, J.; Yamadori, I.; Xu, G.; Hojo, S.; Negayama, K.; Miyawaki, H.; Yamaji, Y.; Takahara, J. Clinical features of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. Respir. Med. 1996, 90, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, K.; Koksal, I.; Kaygusuz, S.; Kaklikkaya, I.; Caylan, R.; Ozdemir, R. Endocarditis caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 32, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Murder, R.R. Meningitis due to Xanthomonas maltophilia: Case report and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartivarian, S.E.; Papadakis, K.A.; Anaissie, E.J. Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia urinary tract infection. A disease that is usually severe and complicated. Arch. Int. Med. 1996, 156, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Marco, F. Lectura interpretada del antibiograma de bacilos gramnegativos no fermentadores [Interpretive reading of the non-fermenting Gram-negative bacilli antibiogram]. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2010, 28, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Ni, W.; Cai, X.; Zhao, J.; Cui, J. Evaluation of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (SXT), Minocycline, Tigecycline, Moxifloxacin, and Ceftazidime Alone and in Combinations for SXT-Susceptible and SXT-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia by In Vitro Time-Kill Experiments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E. Epidemiological trends and resistance associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia: A 10-year retrospective cohort study in a tertiary-care hospital in hungary. Diseases 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Yu, C.M.; Hsu, S.T.; Wu, R.X. Levofloxacin-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Risk factors and antibiotic susceptibility patterns in hospitalized patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 104, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, E.; Davis, H.; Kim, T.; Duhon, B. Monotherapy with Minocycline or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole for treatment of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemoter. 2016, 71, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, S.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Liao, C.H.; Tsuji, M.; Hsueh, P.R. In vitro activities of cefiderocol, ceftolozane/tazobactam, ceftazidime/avibactam and other comparative drugs against imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, all associated with bloodstream infections in Taiwan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 380–386. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo, T.J.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Pierorazio, P.M.; Varkarakis, J.; Schaeffer, E.M.; Allaf, M.E. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Presentation and management in the era of laparoscopy. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, W.D.; Wagner, B.J.; Travis, M.D. Pyelonephritis: Radiologic-pathologic review. Radiographics 2008, 28, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petca, R.-C.; Dănău, R.-A.; Popescu, R.-I.; Damian, D.; Mareș, C.; Petca, A.; Jinga, V. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081
Petca R-C, Dănău R-A, Popescu R-I, Damian D, Mareș C, Petca A, Jinga V. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review. Pathogens. 2022; 11(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081
Chicago/Turabian StylePetca, Răzvan-Cosmin, Răzvan-Alexandru Dănău, Răzvan-Ionuț Popescu, Daniel Damian, Cristian Mareș, Aida Petca, and Viorel Jinga. 2022. "Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review" Pathogens 11, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081
APA StylePetca, R.-C., Dănău, R.-A., Popescu, R.-I., Damian, D., Mareș, C., Petca, A., & Jinga, V. (2022). Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review. Pathogens, 11(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081







