Molecular Identification of New Cases of Human Dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens) in Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients and Materials
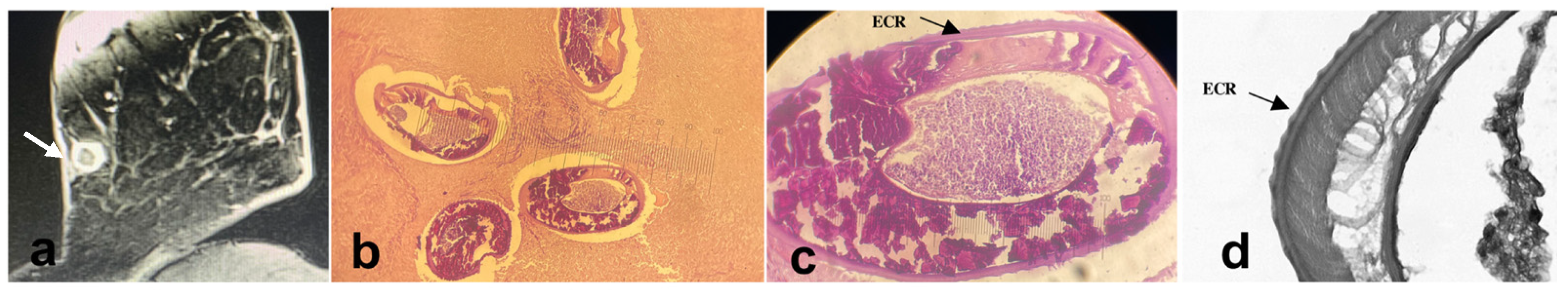
2.2. Clinical Manifestations
2.3. Laboratory Diagnosis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Patients and Materials
5.2. Histological Analysis
5.3. Molecular Analysis
5.4. Serological and Microscopical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pampiglione, S.; Rivasi, F. Human dirofilariasis due to Dirofilaria (Nochtiella) repens: An update of world literature from 1995 to 2000. Parassitologia 2000, 42, 231–254. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. The prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in the Old World. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 280, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellis, F.O.; Kramer, L.H.; Mora, P.; Bartolino, A.; Benedetti, P.; Rivasi, F. A case of human conjunctival dirofilariosis by Dirofilaria immitis in Italy. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foissac, M.; Million, M.; Mary, C.; Dales, J.P.; Souraud, J.B.; Piarroux, R.; Parola, P. Subcutaneous infection with Dirofilaria immitis nematode in human, France. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2013, 19, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Dirofilariosis in the Americas: A more virulent Dirofilaria immitis? Parasit Vectors 2013, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Tsubouchi, H.; Iwasaki, A.; Shiraishi, T.; Nabeshima, K.; Shirakusa, T. Human pulmonary dirofilariasis: A case report and review of the recent Japanese literature. Respirology 2006, 11, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Okata, U.; Matsuzaki, H.; Mori, M.; Chen, K.R.; Iwata, S. Molecular analysis of Dirofilaria repens removed from a subcutaneous nodule in a Japanese woman after a tour to Europe. Parasite 2015, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.K.; Wong, S.S.; Poon, R.W.; Trendell-Smith, N.J.; Ngan, A.H.; Lam, J.W.; Tang, T.H.; Chong, A.K.; Kan, J.C.; Chan, K.H.; et al. A novel Dirofilaria species causing human and canine infections in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3534–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Wongkamchai, S.; Ramünke, S.; Koutsovoulos, G.D.; Blaxter, M.L.; Poppert, S.; Schaper, R.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Krücken, J. High genetic diversity in the Dirofilaria repens species complex revealed by mitochondrial genomes of feline microfilaria samples from Narathiwat, Thailand. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancrini, G.; Scaramozzino, P.; Gabrielli, S.; Di Paolo, M.; Toma, L.; Romi, R. Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens implicated as natural vectors of Dirofilaria repens in Central Italy. J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 1064–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampiglione, S.; Rivasi, F.; Angeli, G.; Boldorini, R.; Incensati, R.M.; Pastormerlo, M.; Pavesi, M.; Ramponi, A. Dirofilariasis due to Dirofilaria repens in Italy, an emergent zoonosis: Report of 60 new cases. Histopathology 2001, 38, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Gabrielli, S.; Pernazza, A.; Pagini, A.; Daralioti, T.; Mantovani, S.; Mattiucci, S.; D’Amati, G.; Mastroianni, C.M. Dirofilaria repens Infection Mimicking Lung Melanoma Metastasis. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019, 6, ofz049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasić, S.; Stoiljković, N.; Miladinović-Tasić, N.; Tasić, A.; Mihailović, D.; Rossi, L.; Gabrielli, S.; Cancrini, G. Subcutaneous dirofilariosis in South-East Serbia—Case report. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrofa, M.S.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Annoscia, G.; Genchi, M.; Traversa, D.; Otranto, D. A duplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of and differentiation between Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in dogs and mosquitoes. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanelli-Sulekova, L.; Gabrielli, S.; De Angelis, M.; Milardi, G.L.; Magnani, C.; Di Marco, B.; Taliani, G.; Cancrini, G. Dirofilaria repens microfilariae from a human node fine-needle aspirate: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bausch, K.; Bosl, M.; Matter, M.; Gabrielli, S.; Neumayr, A. When you hear hoof beats … consider zebras—A diagnostic challenge. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón, F.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Morchón, R.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado, I.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Human and animal dirofilariasis: The emergence of a zoonotic mosaic. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 507–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, G.; Genchi, C.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Brianti, E.; Cardoso, L.; Danesi, P.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Giannelli, A.; Ionică, A.M.; et al. Recent advances on Dirofilaria repens in dogs and humans in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L. Subcutaneous dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens): An infection spreading throughout the old world. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10 (Suppl. 2), 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, A.; Genchi, C.; Cordero, M.; Simón, F. Human dirofilariasis in the European Union. Parasitol. Today 1999, 15, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihel, T.C.; Eberhard, M.L. Zoonotic filariasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasić-Otašević, S.A.; Trenkić Božinović, M.S.; Gabrielli, S.; Genchi, C. Canine and human Dirofilaria infections in the Balkan Peninsula. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 209, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Rivasi, F. Dirofilarial infections in Europe. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, F.; Prieto, G.; Morchón, R.; Bazzocchi, C.; Bandi, C.; Genchi, C. Immunoglobulin G antibodies against the endosymbionts of filarial nematodes (Wolbachia) in patients with pulmonary dirofilariasis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, E.; Barbuto, M.; Bain, O.; Galimberti, A.; Uni, S.; Guerrero, R.; Ferté, H.; Bandi, C.; Martin, C.; Casiraghi, M. Integrated taxonomy: Traditional approach and DNA barcoding for the identification of filarioid worms and related parasites (Nematoda). Front. Zool. 2009, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching-Wai Lau, D.; McLeod, S.; Collaery, S.; Peou, S.; Truc Tran, A.; Liang, M.; Šlapeta, J. Whole-genome reference of Dirofilaria immitis from Australia to determine single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with macrocyclic lactone resistance in the USA. CRPVBD 2021, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Bain, O. Keys to genera of the order Spirurida. Part 3. Diplotriaenoidea, Aproctoidea and Filarioidea. In Commowealth Institute of Helminthology Keys to the Nematodes Parasites of Vertebrates; Anderson, R.C., Chabaud, A.G., Willmott, S., Eds.; CABI Publishing, Nosworthy Way: Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK, 1976; pp. 59–116. [Google Scholar]
- Casiraghi, M.; Anderson, T.J.; Bandi, C.; Bazzocchi, C.; Genchi, C. A phylogenetic analysis of filarial nematodes: Comparison with the phylogeny of Wolbachia endosymbionts. Parasitology 2001, 122, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, M.; Bain, O.; Guerrero, R.; Martin, C.; Pocacqua, V.; Gardner, S.L.; Franceschi, A.; Bandi, C. Mapping the presence of Wolbachia pipientis on the phylogeny of filarial nematodes: Evidence for symbiont loss during evolution. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, J. A method for making microfilarial surveys on day blood. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1939, 33, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Case | Patient Gender | Age (Y) | Province | Site of Infection | Isolate | Species Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 20 | Rome | cheek | live worms | D. repens |
| 2 | F | 56 | Rome | lung | nodule | D. repens |
| 3 | F | 55 | Rome | lung | nodule | D. repens |
| 4 | F | 70 | Rome | calf muscle | live worms | D. repens |
| 5 | F | 46 | Rome | ocular conjunctiva | live worms | D. repens |
| 6 | F | - | Pisa | ocular conjunctiva | live worms | D. repens |
| 7 | F | - | Pescara | coccyx | nodule | D. repens |
| 8 | F | 55 | Latina | breast | nodule | D. repens |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabrielli, S.; Mangano, V.; Furzi, F.; Oliva, A.; Vita, S.; Poscia, R.; Fazii, P.; Di Paolo, J.; Marocco, R.; Mastroianni, C.M.; et al. Molecular Identification of New Cases of Human Dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens) in Italy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020251
Gabrielli S, Mangano V, Furzi F, Oliva A, Vita S, Poscia R, Fazii P, Di Paolo J, Marocco R, Mastroianni CM, et al. Molecular Identification of New Cases of Human Dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens) in Italy. Pathogens. 2021; 10(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020251
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabrielli, Simona, Valentina Mangano, Federica Furzi, Alessandra Oliva, Serena Vita, Roberto Poscia, Paolo Fazii, Josephine Di Paolo, Raffaella Marocco, Claudio Maria Mastroianni, and et al. 2021. "Molecular Identification of New Cases of Human Dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens) in Italy" Pathogens 10, no. 2: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020251
APA StyleGabrielli, S., Mangano, V., Furzi, F., Oliva, A., Vita, S., Poscia, R., Fazii, P., Di Paolo, J., Marocco, R., Mastroianni, C. M., Bruschi, F., & Mattiucci, S. (2021). Molecular Identification of New Cases of Human Dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens) in Italy. Pathogens, 10(2), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020251








