Microstructure, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature and High Temperature of Near-α Titanium Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Relative Density
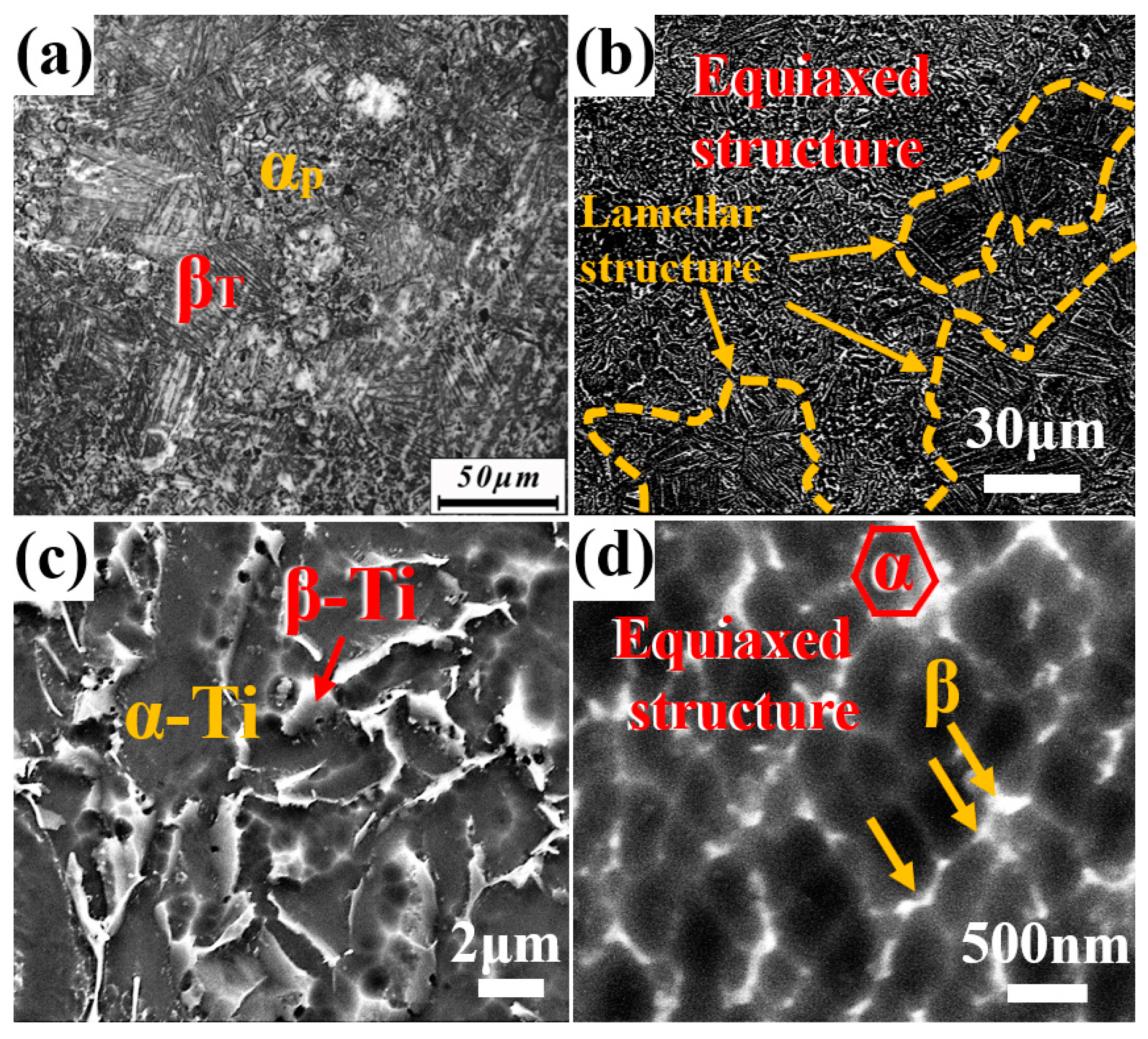
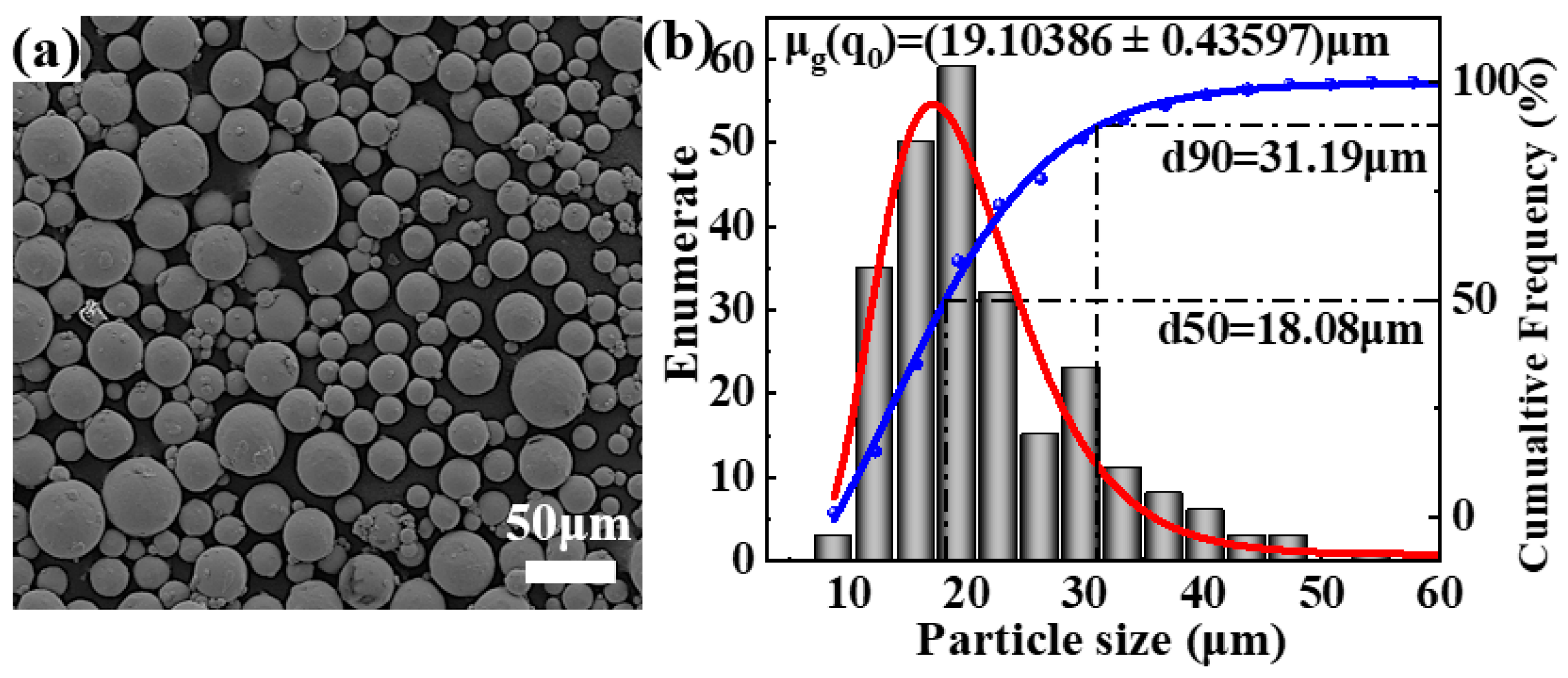
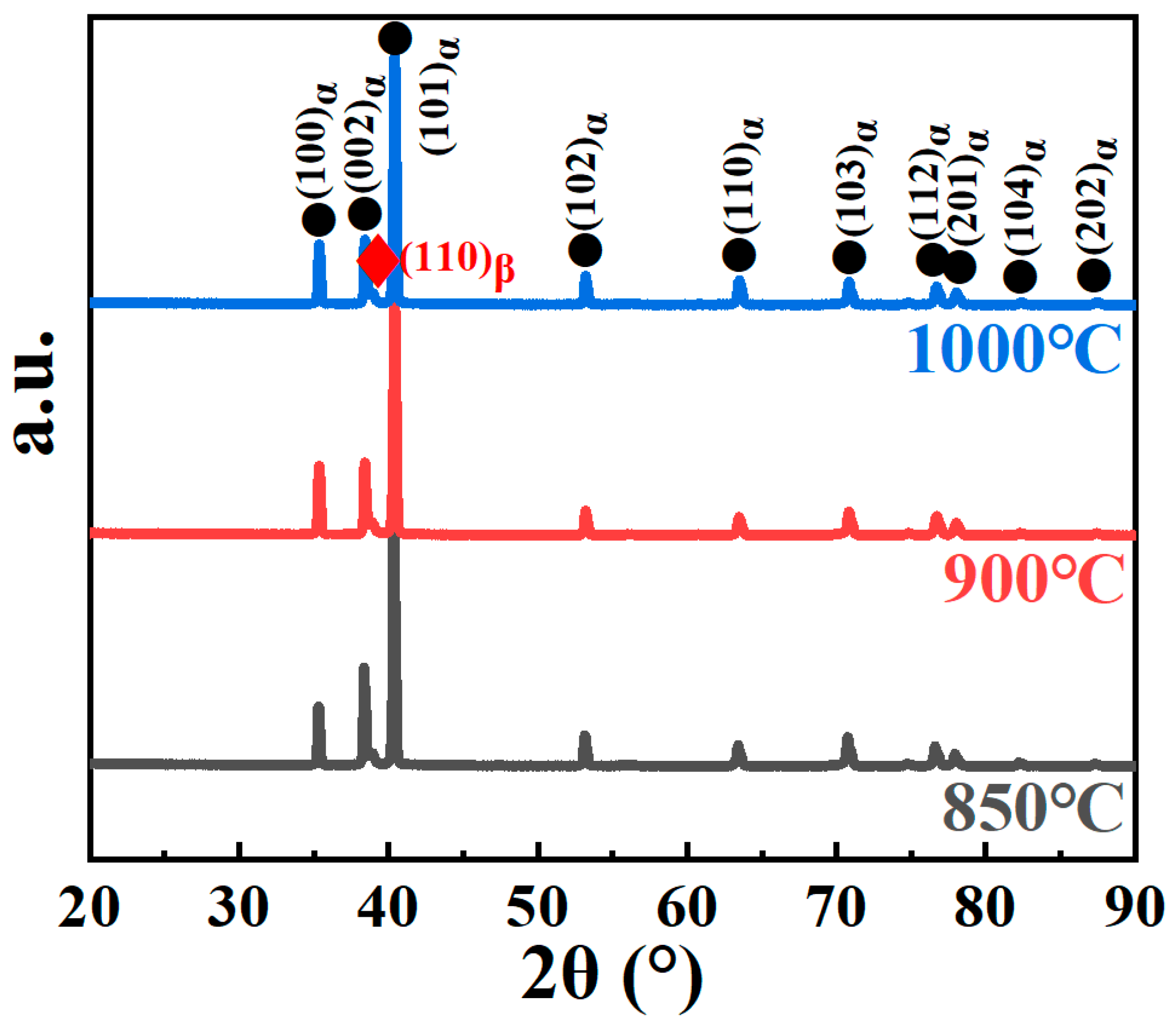
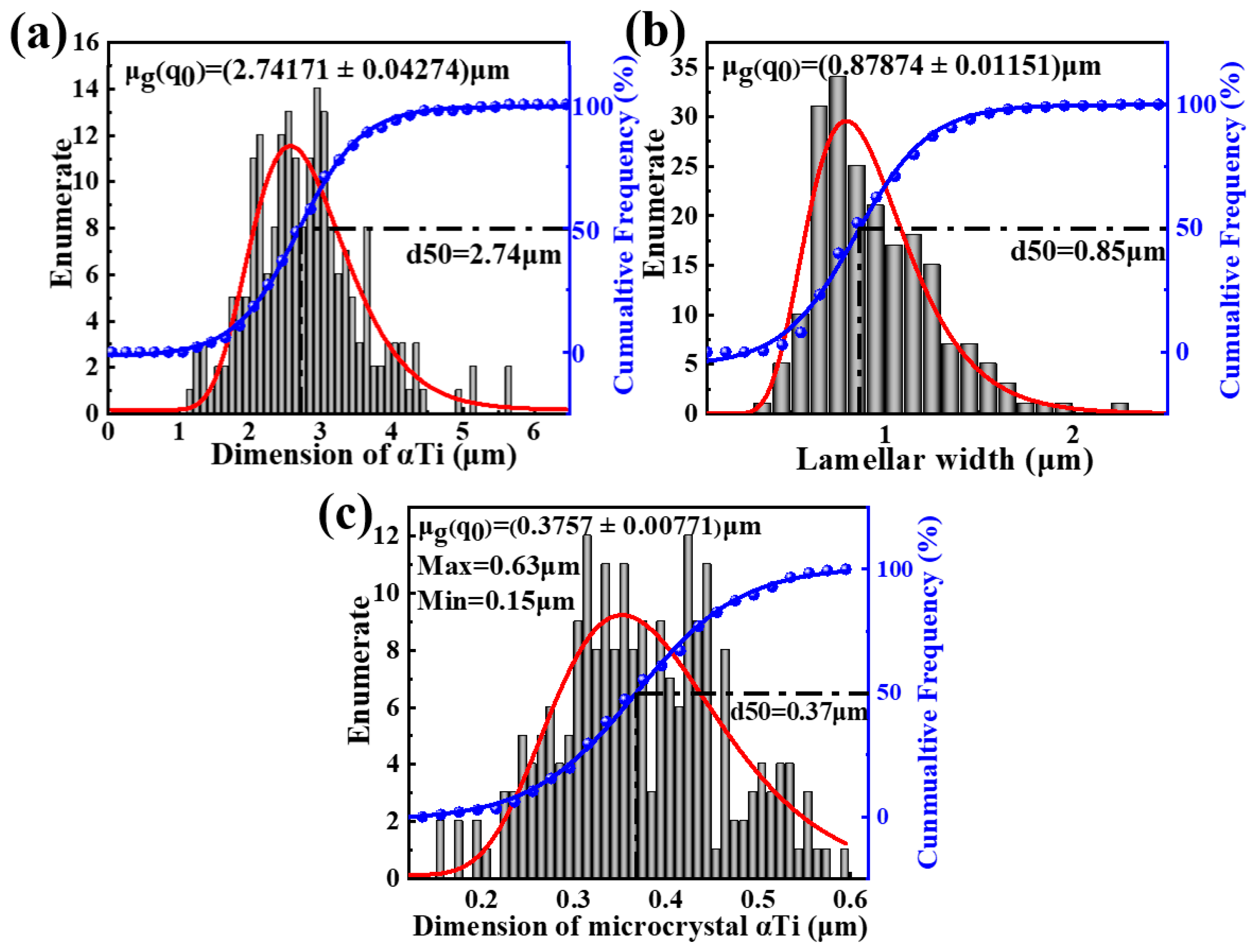
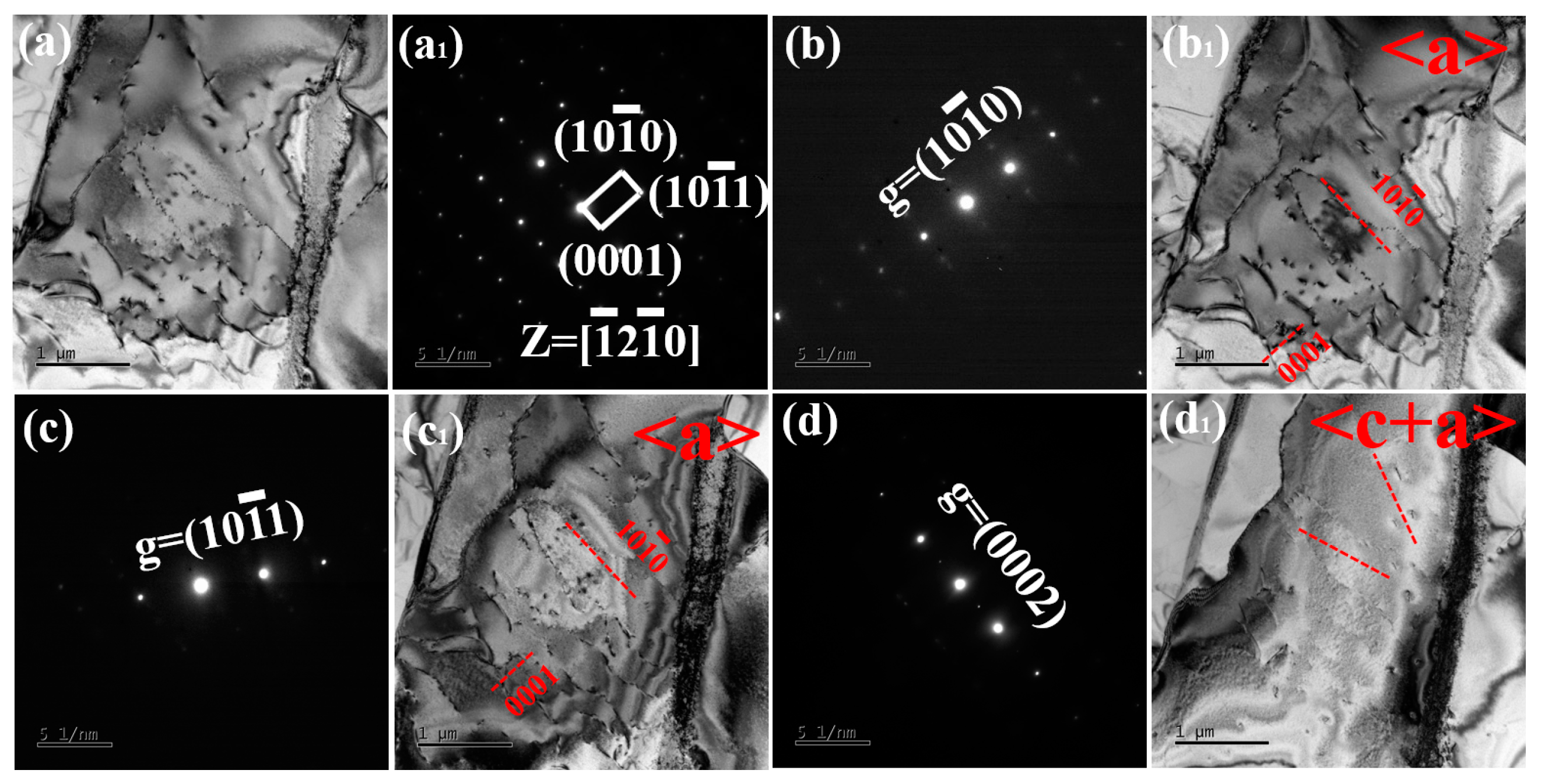
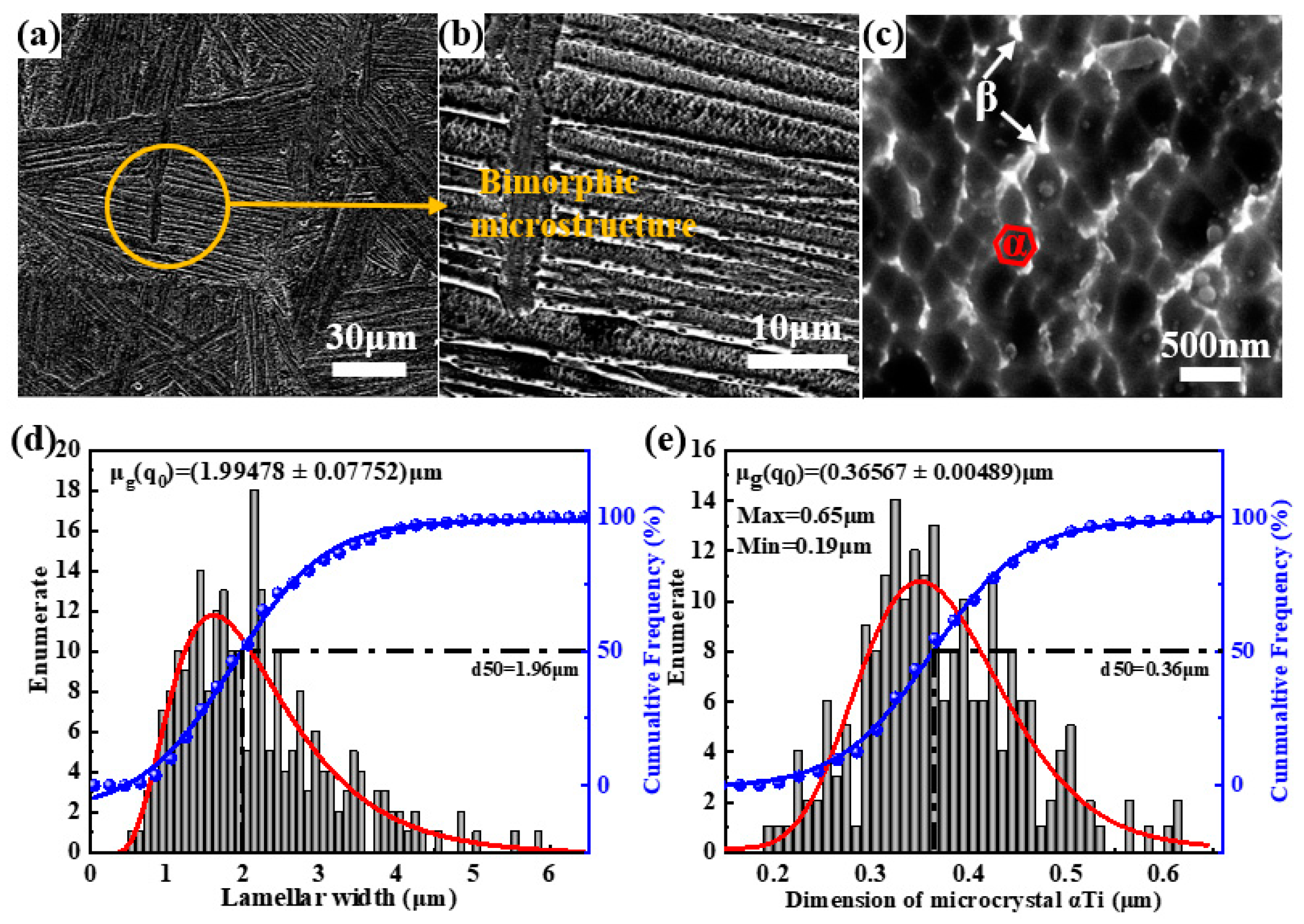
3.2. Microstructures
3.3. Mechanical Properties
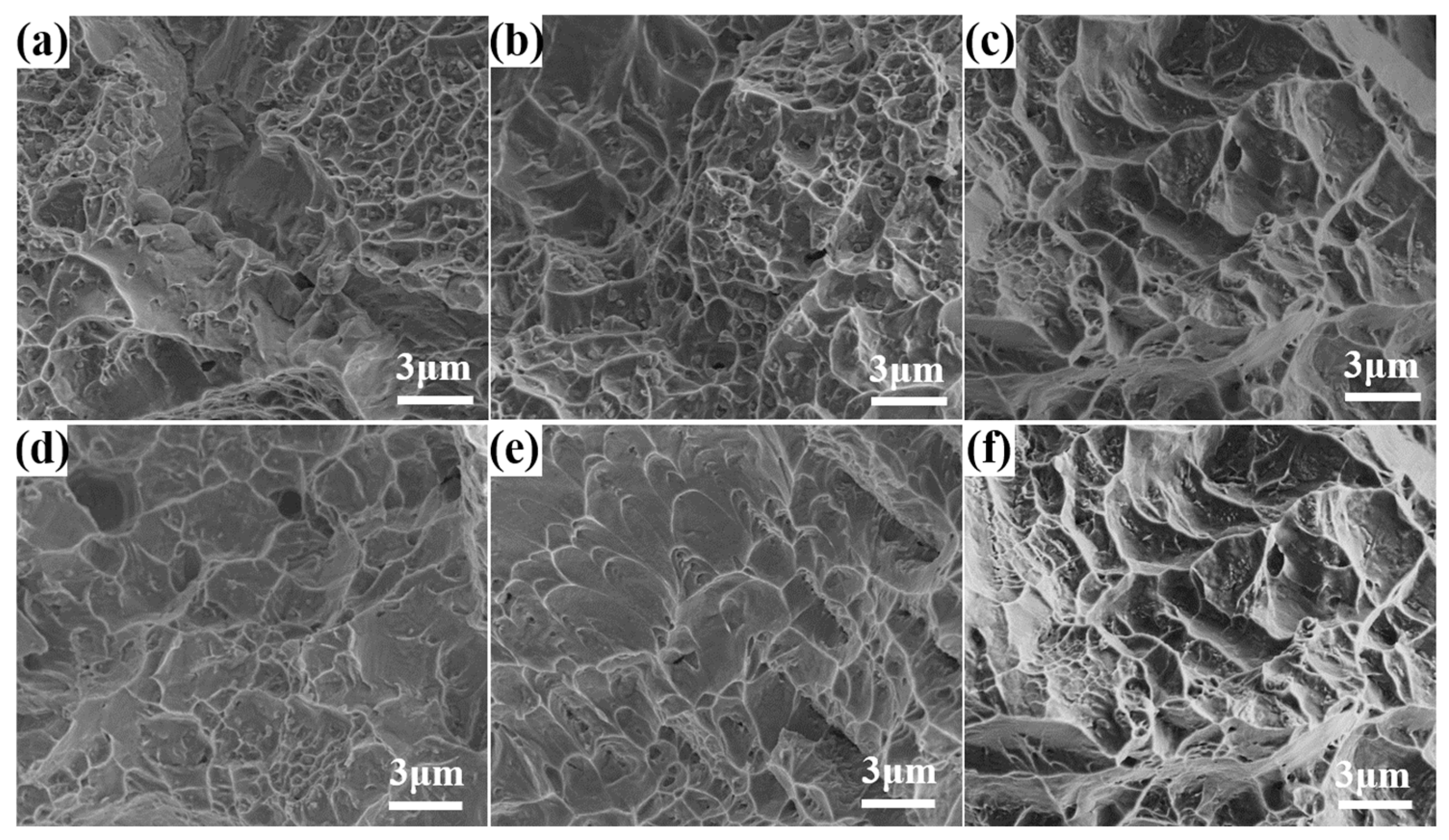
3.4. Fracture
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the increase in sintering temperature, the relative density of Ti60 alloy first increased and then tended to stabilize. After sintering at 850 °C, 900 °C, and 1000 °C, the relative densities of Ti60 alloy were 94.56%, 99.91%, and 99.99%, respectively.
- (2)
- At a sintering temperature of 900 °C, the microstructure of Ti60 alloy exhibits a bimodal characteristic, with approximately 20% equiaxed α phase, having an average size of 2.74 μm. The average width of the lamellar structure is 0.88 μm. Furthermore, within the lamellar structure, ultrafine equiaxed α phase and dispersed nanoscale β phase are observed, with average sizes of 375 nm and 80 nm, respectively.
- (3)
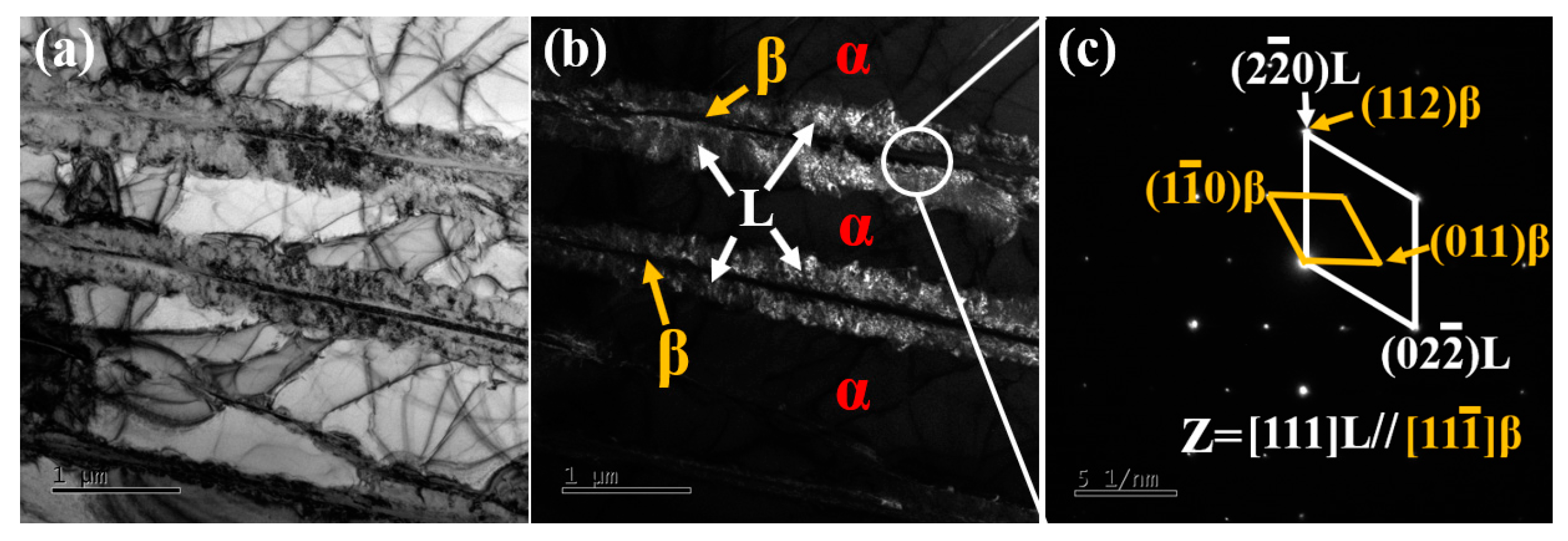
- When the sintering temperature is increased to 1000 °C, the Ti60 alloy exhibits a fully lamellar microstructure, with the lamellar width increasing to approximately 1.99 μm. Additionally, both the 900 °C and 1000 °C sintered Ti60 alloys display a symmetrically distributed L-phase interface layer at the α/β interface, with an orientation relationship described by (112)β//()L and []β//[111]L.
- (4)
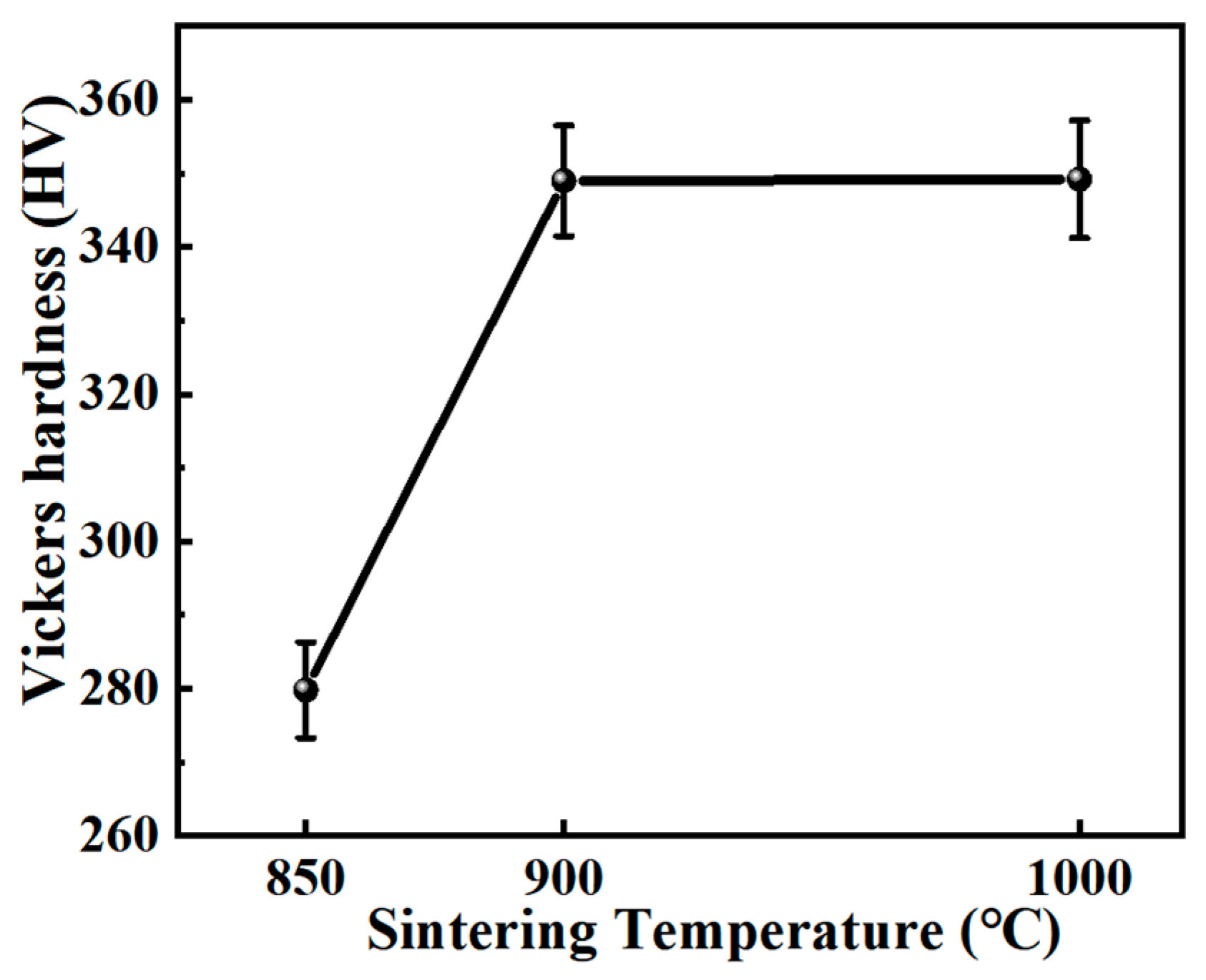
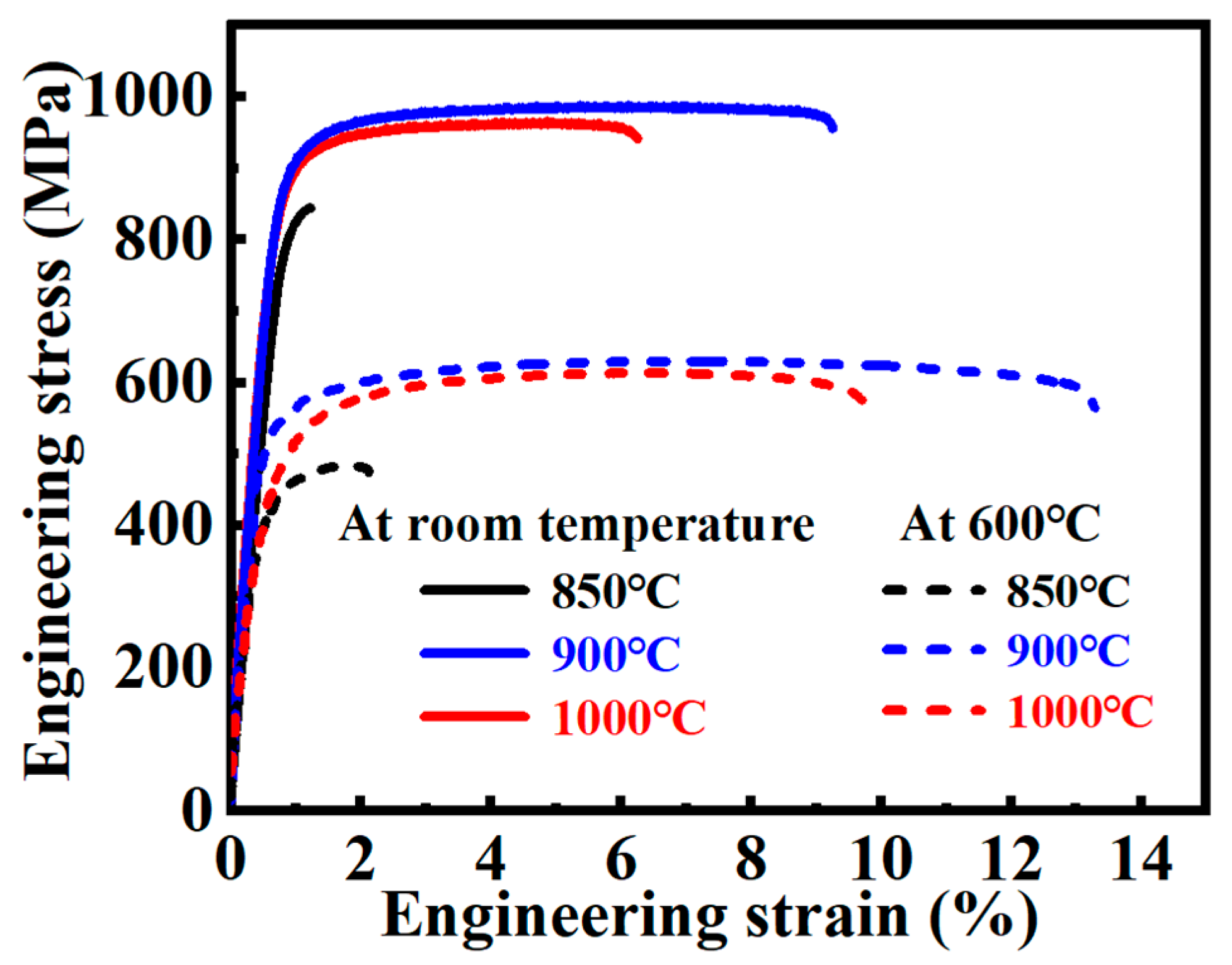
- The Ti60 alloy sintered at 900 °C exhibits the best mechanical properties. Its Vickers hardness is 349 ± 7.5 HV, with a room-temperature yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation of 887 ± 15 MPa, 989 ± 10 MPa, and 9.2 ± 0.5%, respectively. At 600 °C, the yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation are 535 ± 15 MPa, 632 ± 10 MPa, and 13.0 ± 0.5%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. A review of multi-physical fields induced phenomena and effects in spark plasma sintering: Fundamentals and applications. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzker, B.; Sokol, M. Exploring the capabilities of high-pressure spark plasma sintering (HPSPS): A review of materials processing and properties. Mater. Des. 2023, 233, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borse, M.N.; Manokaran, M.; Yebaji, S.G.; Chopra, S.; Sourav, A.; Majumdar, B.; Babu, A.; Thangaraju, S. Development and characterization of a novel Y-Ti-O based aluminum nano-composite processed by high energy ball-milling and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Charact. 2022, 190, 112013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.; Yi, J.; Liu, Y.; Eckert, J.; Zuo, Q. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of functionally graded Fe–8Cr-xNi alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 866, 144648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, H.; Pang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Study of Bulk Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Alloys Fabricated by High-Sphericity Fe84Si7B5C2Cr2 Amorphous Powders at Different Spark-Plasma-Sintering Temperatures. Materials 2022, 15, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Jia, X.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, X. In-situ manipulation of TiB whisker orientation and investigation of its high-temperature mechanical properties in titanium matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 271, 111165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzaska, Z.; Bonnefont, G.; Fantozzi, G.; Monchoux, J. Comparison of densification kinetics of a TiAl powder by spark plasma sintering and hot pressing. Acta Mater. 2017, 135, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Mu, J.; Che, H.; Wang, W. Comparisons of the densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of boron carbide sintered by hot pressing and spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 2615–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Feng, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, F.; Lin, Y. Disruption of oxide films during spark plasma sintering of micrometric-sized Al powders and its effect on microstructure and tensile properties of the consolidated Al. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 712, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, S.G.; Babu, D.A.; Ramakrishna, B.; Singh, S.; Vanitha, C. Influence of sintering process on microstructure and mechanical properties of alumina ceramics: Spark plasma and microwave hybrid sintering. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 11730–11742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.M.; Cai, Y.J.; Luo, X.C.; Li, Z.J.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. Bimorphic microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy manipulated by spark plasma sintering and in-situ press forging. Scr. Mater. 2021, 193, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Suryanarayana, C.; Al-Aqeeli, N. Fabrication of nano-grained Ti–Nb–Zr biomaterials using spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. Phase transition, microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy prepared by plasma activated sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 714, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laptev, A.M.; Bram, M.; Garbiec, D.; Räthel, J.; van der Laan, A.; Beynet, Y.; Huber, J.; Küster, M.; Cologna, M.; Guillon, O. Tooling in Spark Plasma Sintering Technology: Design, Optimization, and Application. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2301391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Ramamurty, U. Boron modified titanium alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 111, 100653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances in silicon containing high temperature titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, P.L.; Kim, S.; Hong, J.; Reddy, N.S.; Yeom, J. Tensile properties of a newly developed high-temperature titanium alloy at room temperature and 650 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 718, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Tang, B.; Kou, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Microstructural evolution and FCC twinning behavior during hot deformation of high temperature titanium alloy Ti65. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 49, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.D.; Singh, H.; He, Z.; Cao, P. Titanium metal matrix composites: An overview. Compos. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; An, Q.; Geng, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, S.; Cui, X.; Zhang, R.; Sun, F.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Multiscale Architecture and Superior High-Temperature Performance of Discontinuously Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2000688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Hao, G.; Fan, H.; Zhai, Y.; Kong, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Study on rolling of a new near-α titanium alloy: Microstructure refinement and dual-scale silicides evolution. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 852, 156867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fox, K.; Rugg, D.; Dunne, F.P.E. Cyclic plasticity and thermomechanical alleviation in titanium alloys. Int. J. Plast. 2020, 134, 102753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Akiyama, H.; Tange, S.; Takebe, H. Age hardening of Si-bearing near-α titanium alloy Ti–6Al–2.75Sn–4Zr–0.4Mo–0.45Si (Ti-1100) with two kinds of initial phases. Mater. Trans. 2023, 64, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Wang, Q.J.; Liu, J.R.; Yang, R. Effect of heat treatment on the crystallographic orientation evolution in a near-α titanium alloy Ti60. Acta. Mater. 2017, 131, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shang, D.; Xiao, N.; Li, X.; Sha, A.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Han, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, D. Fatigue life prediction of Ti60 titanium alloy under very high cycle loading at different temperatures. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 176, 107838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Zeng, W.; He, S.; Gao, X.; Xu, J. The analysis of fracture toughness and fracture mechanism of Ti60 alloy under different temperatures. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 810, 151899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Kok, Y.; Tan, Y.J.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Leong, K.F.; Chua, C.K. Graded microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured Ti–6Al–4V via electron beam melting. Acta. Mater. 2015, 97, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Jing, C.; Shuai, G.; Hua, T.; Xin, L. Influence of α/β interface phase on the tensile properties of laser cladding deposited Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sintering Temperature | Relative Density |
|---|---|
| 850 °C | 94.56% |
| 950 °C | 99.91% |
| 1000 °C | 99.99% |
| Material | Sintering Temperature | Test Temperature | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti60 | 850 °C | 25 °C | 816 ± 15 | 846 ± 20 | 1.2 ± 0.5 |
| 600 °C | 424 ± 10 | 483 ± 15 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | ||
| 900 °C | 25 °C | 887 ± 15 | 989 ± 10 | 9.2 ± 0.5 | |
| 600 °C | 535 ± 15 | 632 ± 10 | 13.0 ± 0.5 | ||
| 1000 °C | 25 °C | 878 ± 10 | 962 ± 10 | 6.1 ± 0.5 | |
| 600 °C | 511 ± 10 | 614 ± 10 | 9.6 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, X.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, X. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature and High Temperature of Near-α Titanium Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040293
Wang Q, Zhang Z, Jia X, He Y, Zhou J, Sun Y, Cheng X. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature and High Temperature of Near-α Titanium Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(4):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040293
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiang, Zhaohui Zhang, Xiaotong Jia, Yangyu He, Jinzhao Zhou, Yuanhao Sun, and Xingwang Cheng. 2025. "Microstructure, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature and High Temperature of Near-α Titanium Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering" Nanomaterials 15, no. 4: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040293
APA StyleWang, Q., Zhang, Z., Jia, X., He, Y., Zhou, J., Sun, Y., & Cheng, X. (2025). Microstructure, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature and High Temperature of Near-α Titanium Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Nanomaterials, 15(4), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15040293






