Exploration of the Reduction Diffusion Temperature for Different Phases of Samarium–Cobalt Magnetic Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
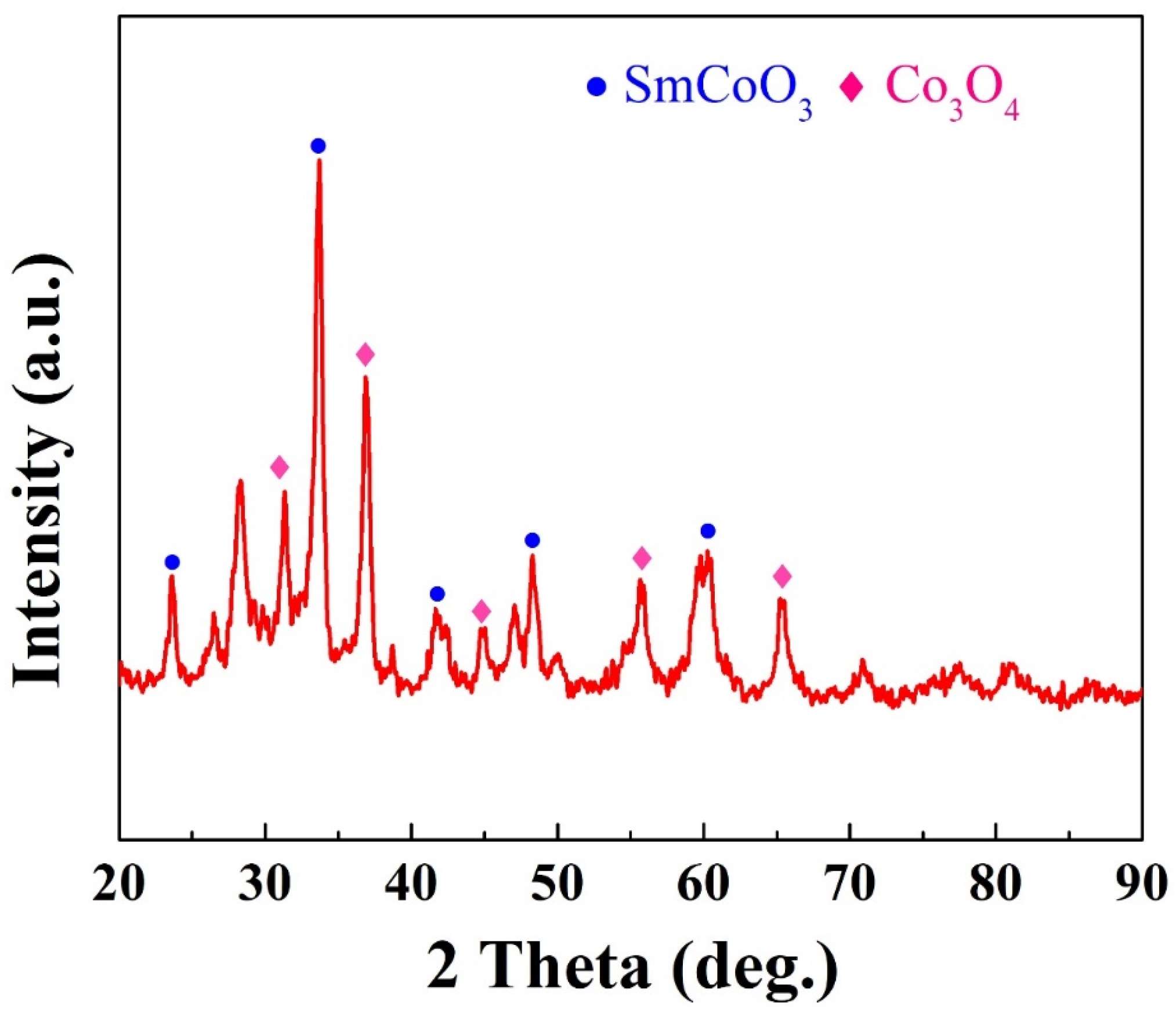
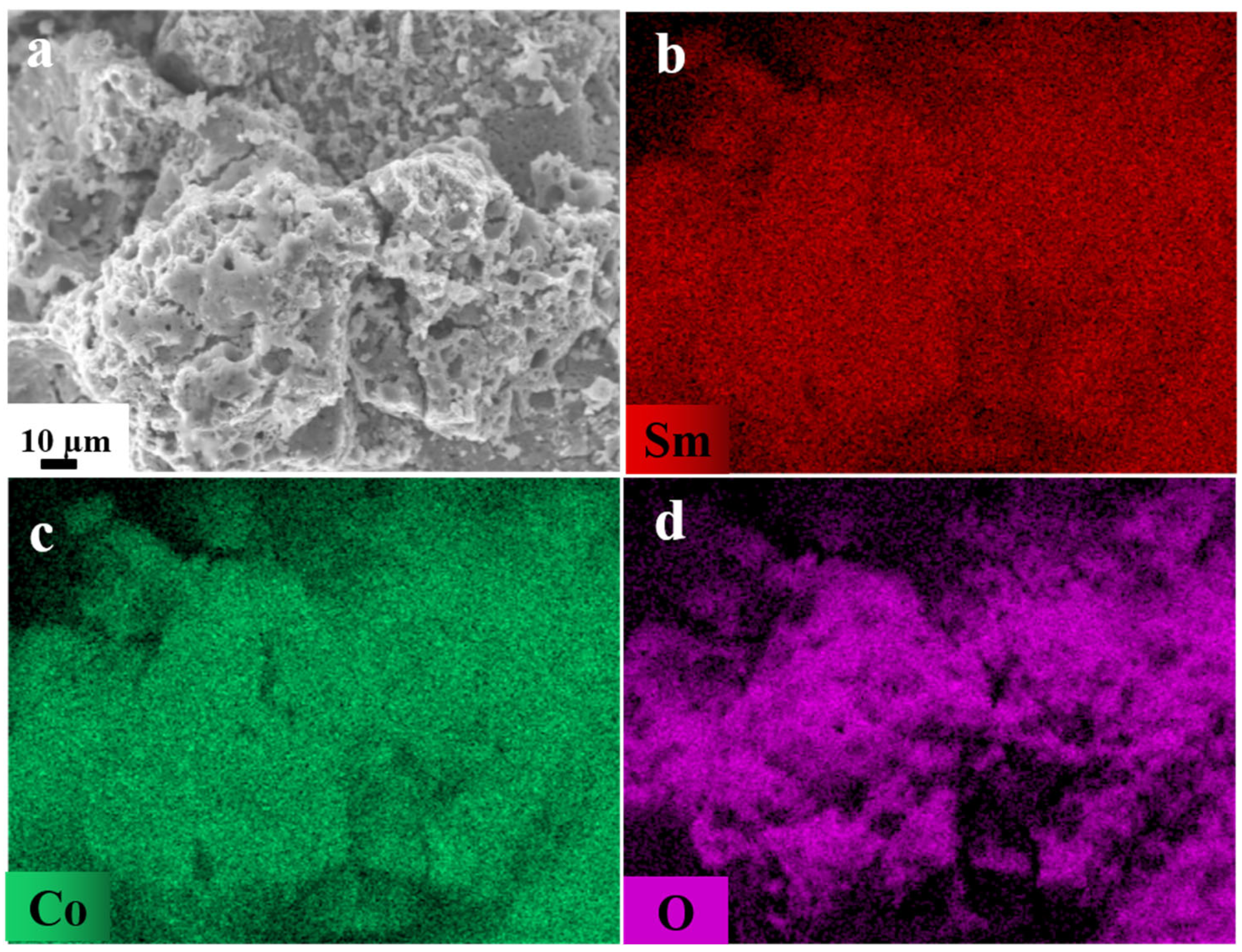
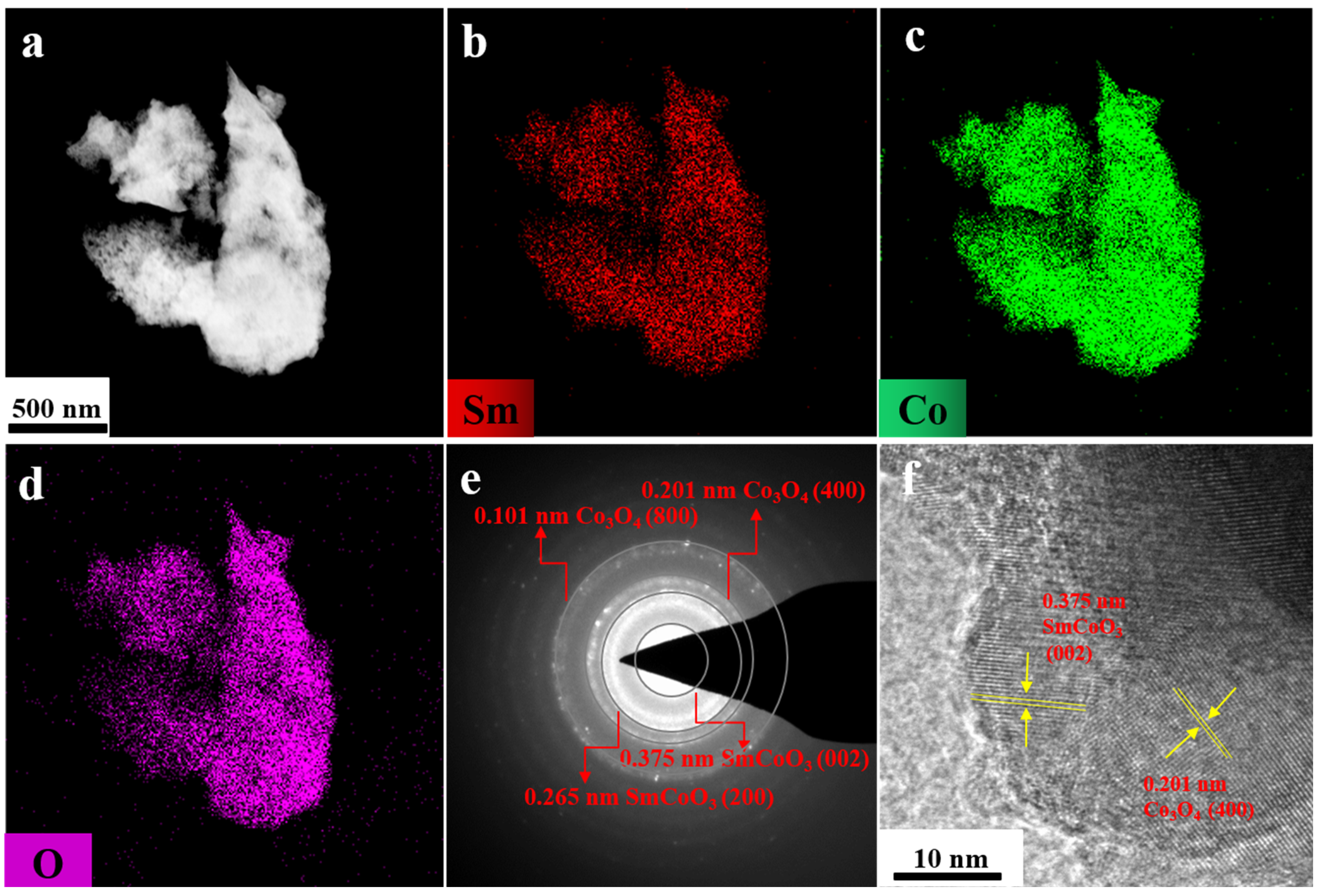
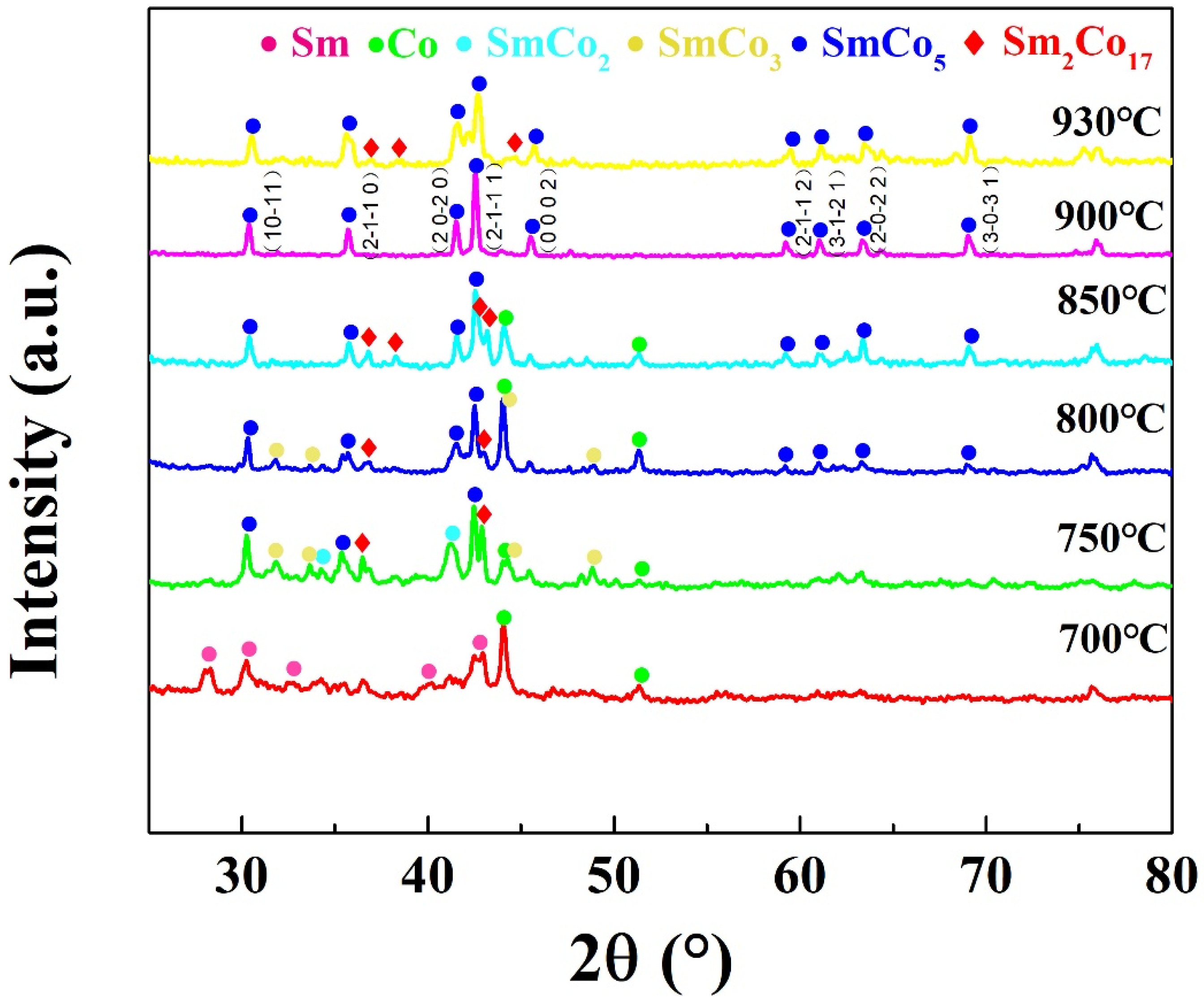
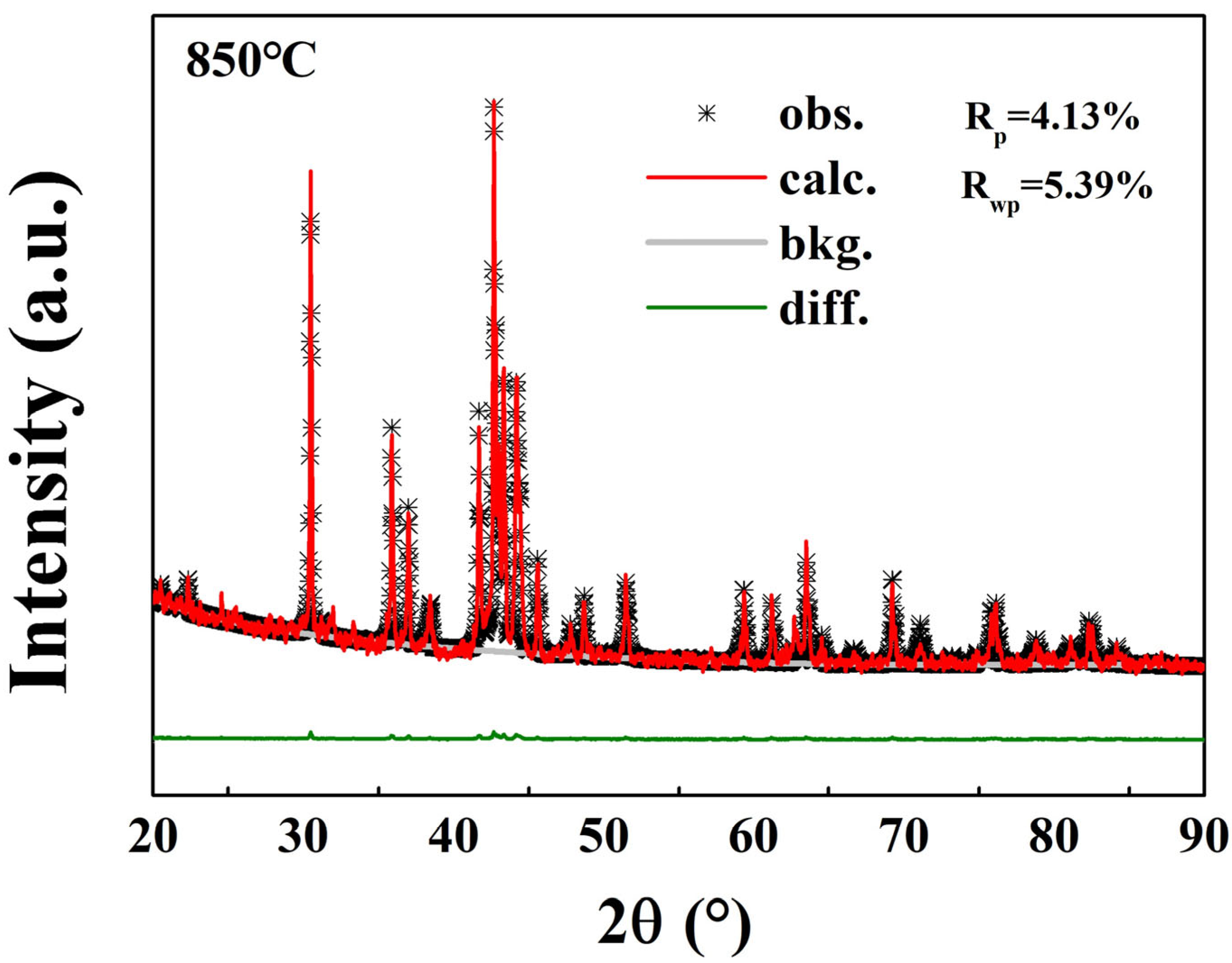
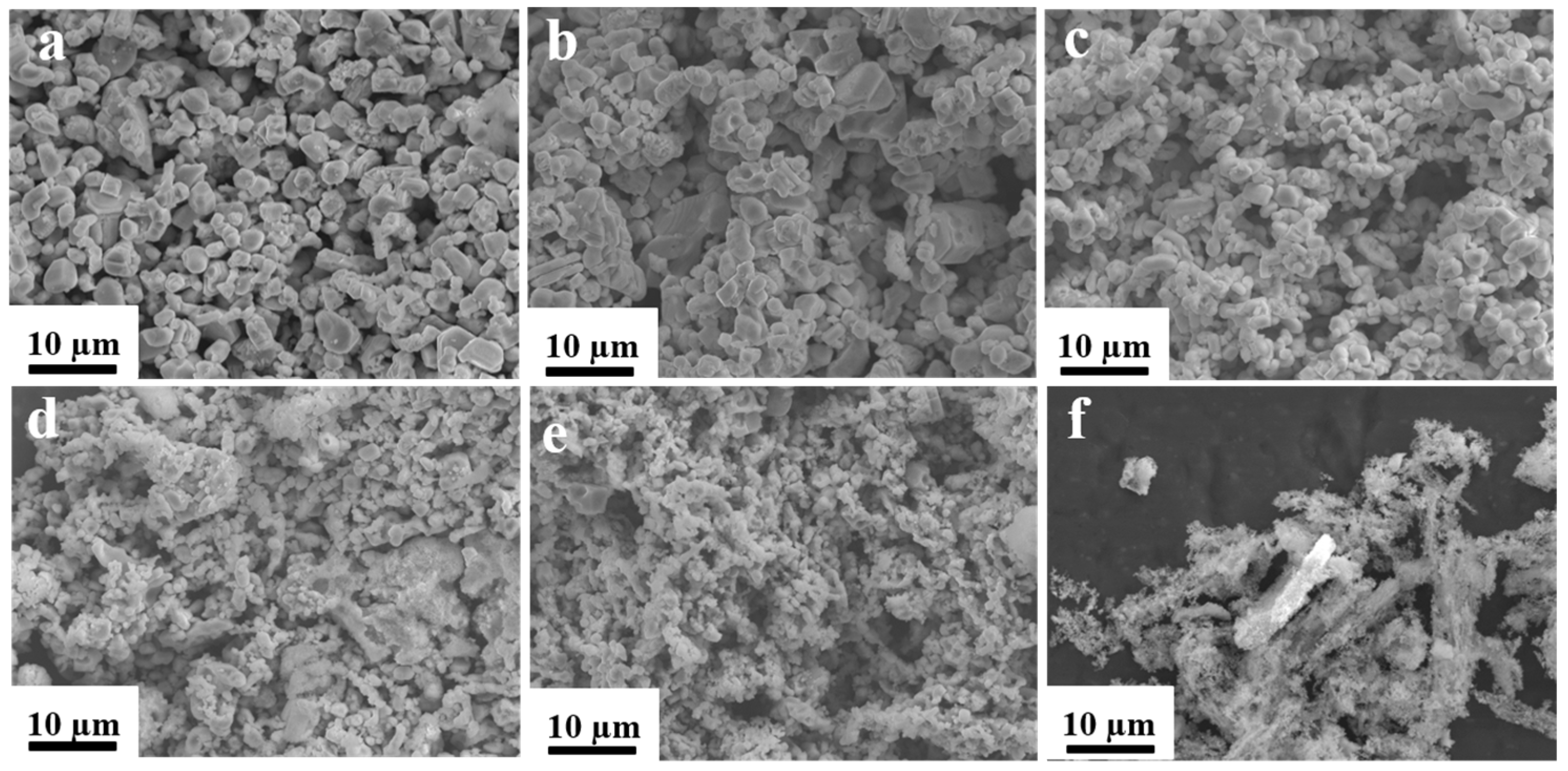
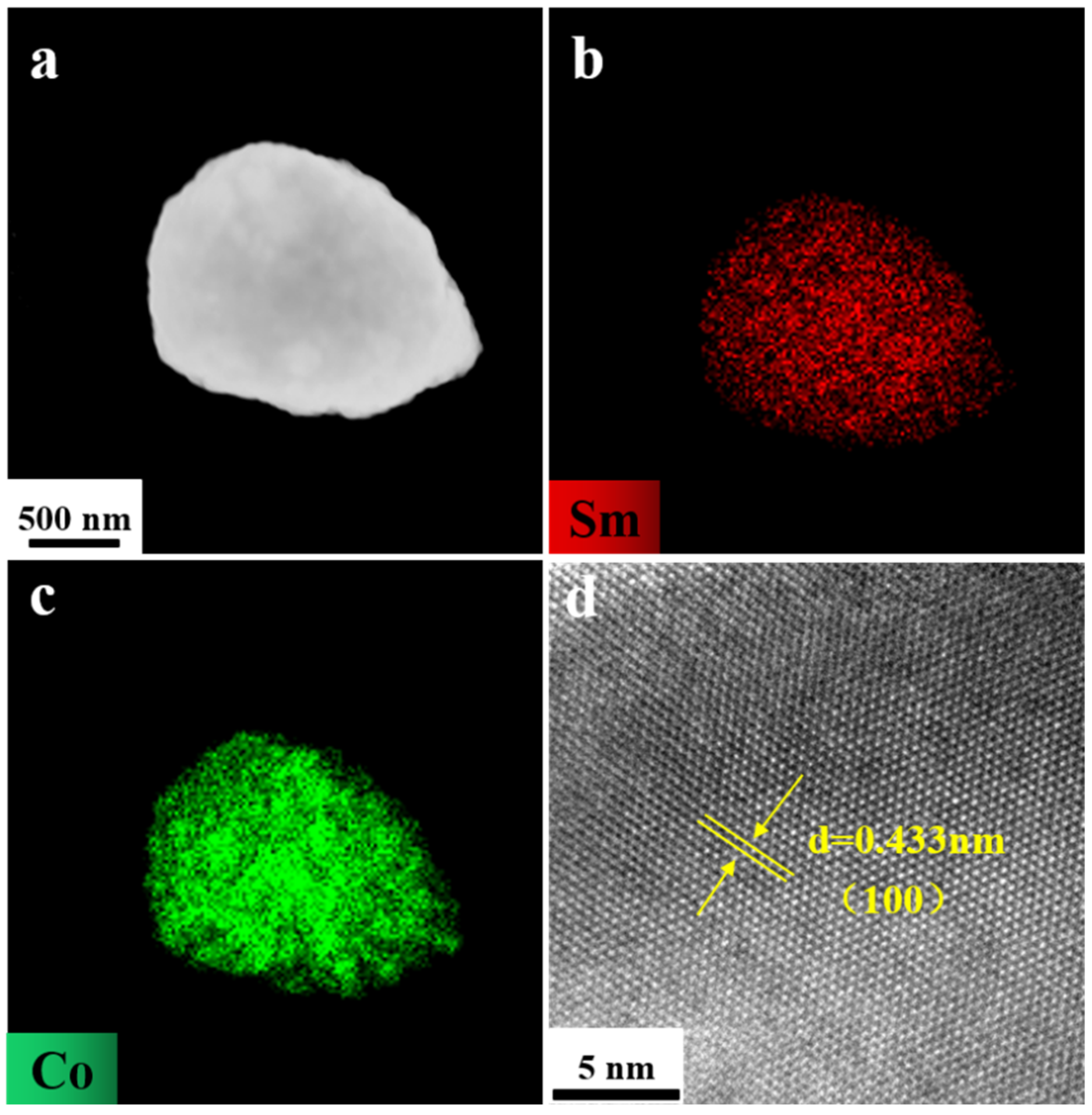
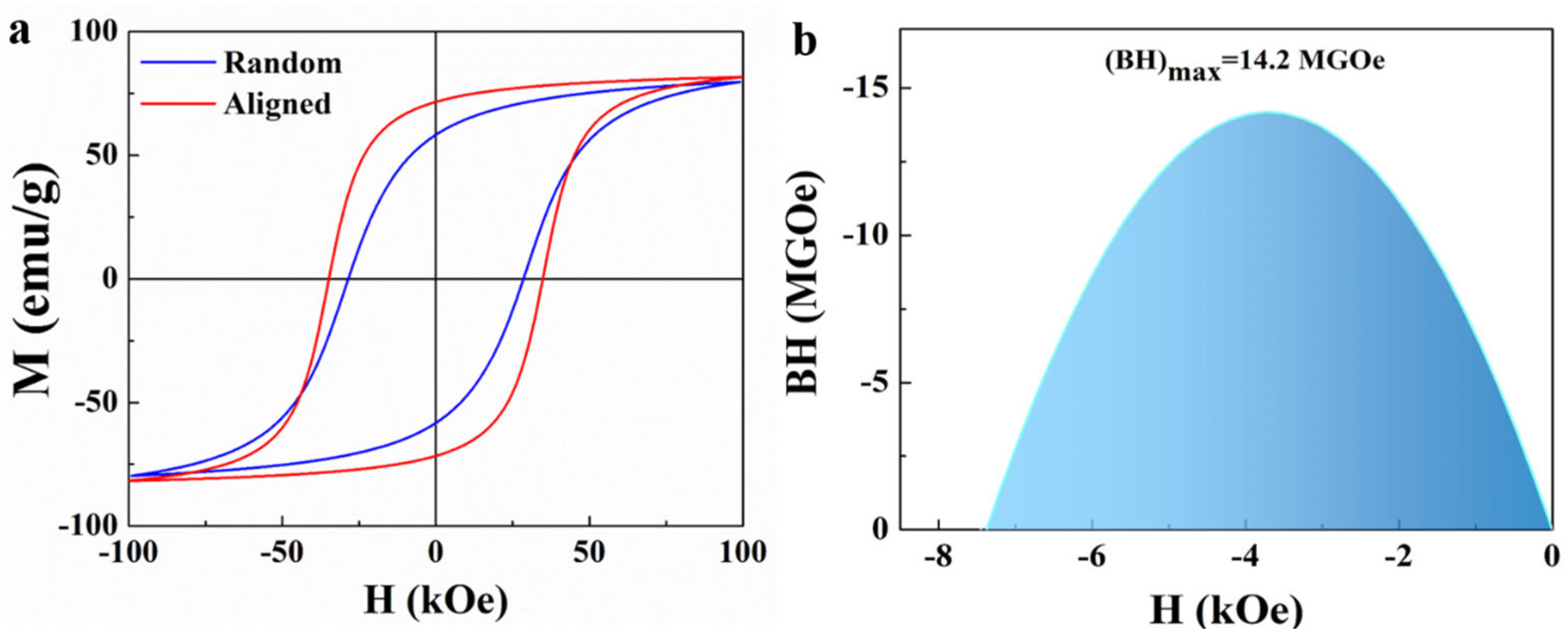
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Experiment
3.1. Synthesis of SmCo-O
3.2. Synthesis of SmCo
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbachev, E.A.; Kozlyakova, E.S.; Trusov, L.A.; Sleptsova, A.E.; Zykin, M.A.; Kazin, P.E. Design of modern magnetic materials with giant coercivity. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021, 90, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfleisch, O.; Willard, M.A.; Brück, E.; Chen, C.H.; Sankar, S.G.; Liu, J.P. Magnetic Materials and Devices for the 21st Century: Stronger, Lighter, and More Energy Efficient. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Sun, S.H. Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles for permanent magnet applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 26, 6757–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, K.; Gao, S.; Hou, Y. Rare earth permanent magnetic nanostructures: Chemical design and microstructure control to optimize magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. FePt/Co core/shell nanoparticle-based anisotropic nanocomposites and their exchange spring behavior. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, W.Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, D.T.; Lu, Q.M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Yue, M. Effects of shape anisotropy on hard-soft exchange-coupled permanent magnets. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, G.; Oh, Y.B.; Hwang, T.Y.; Lim, J.H.; Cho, H.B.; Kim, J.; Choa, Y.H. Exchange-Coupling Interaction in Zero- and One-Dimensional Sm2Co17/FeCo Core-Shell Nanomagnets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26222–26227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Mamakhel, M.A.H.; Christensen, M. Enhancing the coercivity of SmCo5 magnet through particle size control. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.T.; Xu, H.B.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Liu, W.Q.; Yue, M. Strategies for the synthesis of nanostructured SmCo5 magnetic particles for permanent magnetic application. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar]
- Chaubey, G.S.; Poudyal, N.; Liu, Y.Z.; Rong, C.B.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis of Sm-Co and Sm-Co/Fe nanocrystals by reductive annealing of nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 2132–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.B.; Cong, L.Y.; Li, C.L.; Xi, J.H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, W.Q.; Lu, Q.M.; Ming, Y. Microwave-assisted chemical synthesis of SmCo5 magnetic particles with high coercivity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 579, 170855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yu, C.; Su, D.; Yin, Z.Y.; Li, J.R.; Xi, Z.; Sun, S.H. A new strategy to synthesize anisotropic SmCo5 nanomagnets. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8735–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.L.; Xu, Z.C.; Peng, S.; Rong, C.B.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, S.H. A facile synthesis of SmCo5 magnets from core/shell Co/Sm2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Tian, H.; Cong, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Yue, M.; Sun, S.H. A Flame-reaction methodfor the large-scale synthesis of high-performance SmxCoy nanomagnets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 14651–14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Su, X. A pH-responsive ratiometric fluorescence system based on AIZS QDs and azamonardine for urea detection. Spectrochim. Acta A 2022, 279, 121431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Mukasyan, A.S.; Rogachev, A.S.; Manukyan, K.V. Solution combustion synthesis of nanoscale materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14493–14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.P.; Lin, C.H.; Hsu, C.S. Preparation of ultrafine CeO2 powders by microwave-induced combustion and precipitation. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 391, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Zheng, L.Y.; Cui, B.Z.; Gabay, A.M.; Hono, K.; Huang, W.J.; Ni, C.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Effect of ball-milling surfactants on the interface chemistry in hot-compacted SmCo5 magnets. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6685–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Mamakhel, M.A.H.; Dong, M.; Christensen, M. Combustion Assisted Preparation of High Coercivity Sm–Co Hard Magnet with Stable Single-Domain Size. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.B. The synthesis of SmCo5 nanoparticles with small size and high performance by hydrogenation technique. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Yang, S.X.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. The chemical synthesis of SmCo5 single-crystal particles with small size and high performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Peng, S.; Rong, C.B.; Liu, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Kramer, M.J.; Sun, S.H. Chemical synthesis of hard magnetic SmCo nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16873–16876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, Y.L.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, X.C.; Liu, Z.W. Synthesis of hard magnetic NdFeB composite particles by recycling the waste using microwave assisted auto-combustion and reduction method. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J. On the eutectoid decomposition of CaCu5-type rare earth-cobalt phases. J. Less-Common Met. 1974, 37, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Broeder, F.J.A.; Buschow, K.H.J. On the eutectoid decomposition of SmCo5. J. Less-Common Met. 1980, 70, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Liang, J.M.; Ma, W.; Cong, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Yue, M. Chemically synthesized anisotropic SmCo5 nano-magnets with a large energy product. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 12484–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.H.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. A facile synthesis of high performance SmCo5 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Wu, Q.; Ma, Z.H.; Xu, H.H.; Cong, L.Y.; Yue, M. A novel strategy to synthesize anisotropic SmCo5 particles from Co/Sm(OH)3 composites with special morphology. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 8522–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, T.L.; Xia, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Coey, J.M.D.; Jiang, C.B. Dispersible SmCo5 nanoparticles with huge coercivity. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cong, L.Y.; Yue, M.; Li, C.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Ma, X.Y.; Wang, Y.T. A unique synthesis of rare-earth-Co-based single crystal particles by “self-aligned” Co nano-arrays. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13958–13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Yue, M.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.L.; Yu, Y.S. Designing shape anisotropic SmCo5 particles by chemical synthesis to reveal the morphological evolution mechanism. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 10377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, H.; Xiao, T.; Chaudhary, V.; Zhong, Y.; Ramanujan, R.V. High energy product chemically synthesized exchange coupled Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe magnetic powders. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13956–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Yu, C.; Baker, A.A.; McCall, S.K.; Yu, Y.S.; Su, D.; Yin, Z.Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.R.; Sun, S.H. Chemical synthesis of magnetically hard and strong rare earth metal based nanomagnets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.G.; Unruh, K.M. Preparation and magnetic properties of sub-micrometer sized Sm-Co powders prepared from nanostructured precursor oxides. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Starting Raw Materials | Precursors | Coercivity (kOe) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sm(acac)3·xH2O, Co(acac)2, GO, Ca, KCl, oleylamine, oleic acid | Sm2O3-Co@GO | 24.4 | [21] |
| Sm(NO3)3·6H2O, CoCl2·6H2O, NaOH, KCl, Ca | Sm(OH)3, Co(OH)2 | 33.2 | [8] |
| Co(ac)2, Sm(ac)3, n-hexadecyltrimethylammonium hydroxide, 1-octadecene, oleic acid, KCl, Ca | SmCo–O | 7.2 | [22] |
| Sm(NO3)3·6H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, PVP,CoCl2 C2H5OH, CO(NH2)2,NaOH,C11H23COOH,Ca | SmCoO3, Co3O4, Sm2O3, Co | 34.5/47.2 | [9] |
| Sm(NO3)3, Co(NO3)2, citric acid, Ca, CaO | SmCoO3, Co3O4 | 29 | [34] |
| Sm(NO3)3·6H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, CO(NH2)2, Ca(NO3)2, CaH2 | SmCoO3, Co3O4 | 39.2 | [11] |
| Sm(NO3)3·6H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, CO(NH2)2, Ca | SmCoO3, Co3O4 | 35.0 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Ma, X.; Ren, J.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y. Exploration of the Reduction Diffusion Temperature for Different Phases of Samarium–Cobalt Magnetic Particles. Molecules 2025, 30, 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091975
Lu Y, Ma X, Ren J, Kang J, Wang Y. Exploration of the Reduction Diffusion Temperature for Different Phases of Samarium–Cobalt Magnetic Particles. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091975
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yani, Xiangyu Ma, Jinping Ren, Jinke Kang, and Yatao Wang. 2025. "Exploration of the Reduction Diffusion Temperature for Different Phases of Samarium–Cobalt Magnetic Particles" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091975
APA StyleLu, Y., Ma, X., Ren, J., Kang, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). Exploration of the Reduction Diffusion Temperature for Different Phases of Samarium–Cobalt Magnetic Particles. Molecules, 30(9), 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091975





