Genomic and Micro-Evolutionary Features of Mammalian 2 orthobornavirus (Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, VSBV-1)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Characterization and Micro-Evolutionary Dynamics
2.2. Selection Pressure Analyses on the VSBV-1 Genome
2.3. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of VSBV-1
2.4. Co-phylogeny Analysis of Virus-Host Co-evolution or Divergence
3. Results
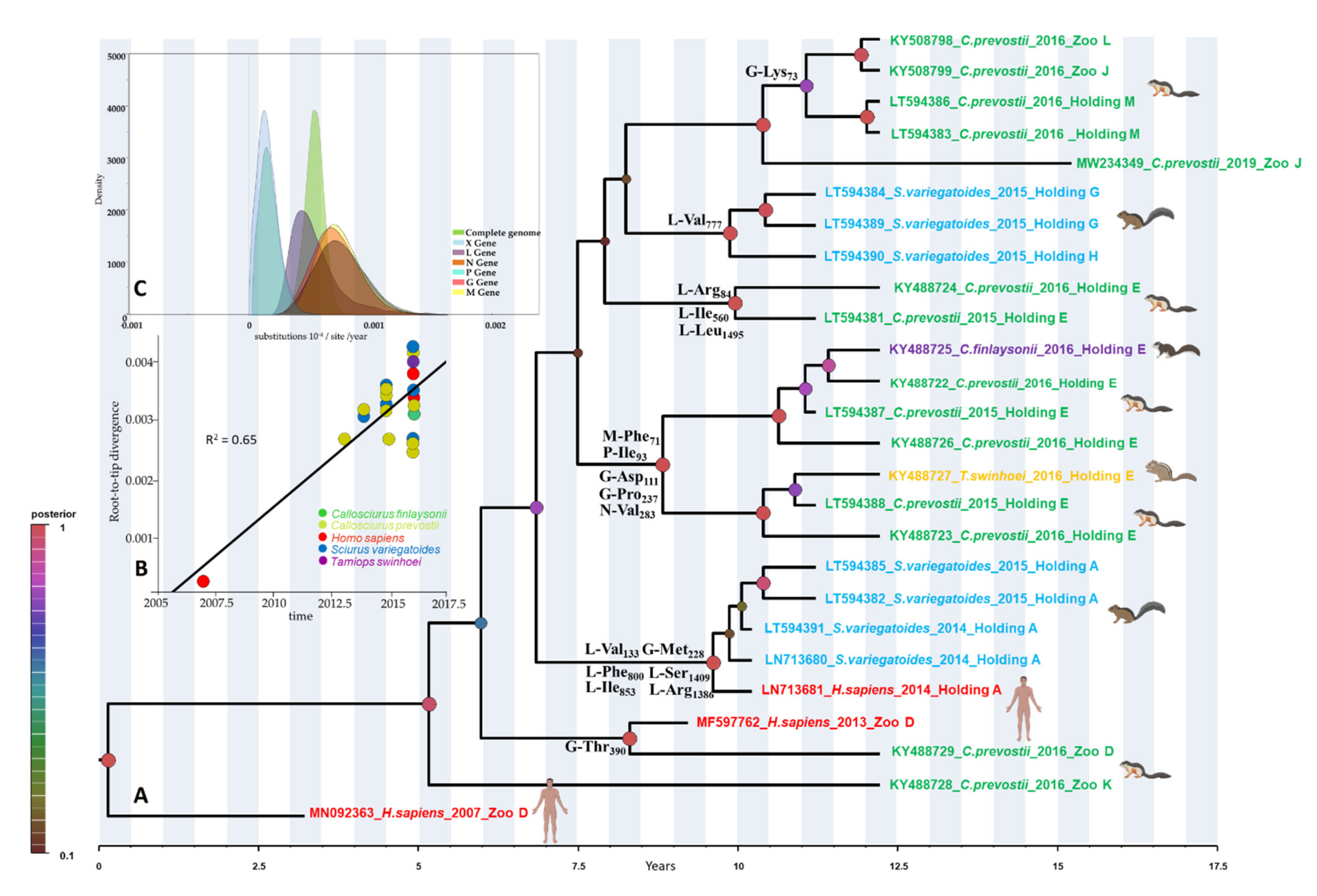
3.1. Genomic Characterization and Molecular Dynamics
3.2. Selection Pressure Analyses on the VSBV-1 Genome
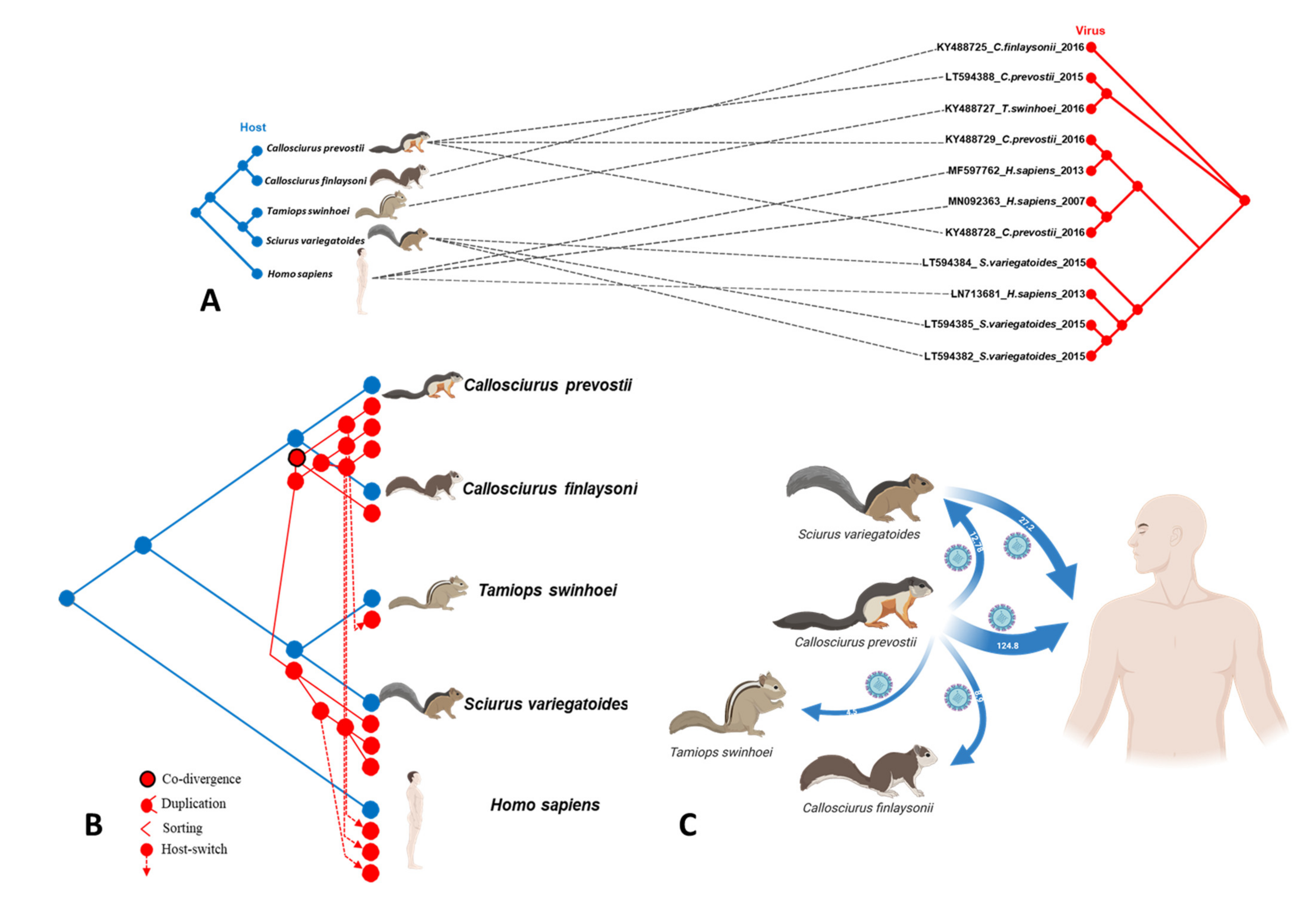
3.3. Analysis of Possible Virus-Host Co-Evolution or Host Switching Events
3.4. Transmission Events of VSBV-1 to Different Hosts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, B.; Tappe, D.; Höper, D.; Herden, C.; Boldt, A.; Mawrin, C.; Niederstraßer, O.; Müller, T.; Jenckel, M.; van der Grinten, E.; et al. A Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus Associated with Fatal Human Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, D.; Schlottau, K.; Cadar, D.; Hoffmann, B.; Balke, L.; Bewig, B.; Hoffmann, D.; Eisermann, P.; Fickenscher, H.; Krumbholz, A.; et al. Occupation-Associated Fatal Limbic Encephalitis Caused by Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, Germany, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisermann, P.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Cadar, D.; Thomé-Bolduan, C.; Eggert, P.; Schlaphof, A.; Leypoldt, F.; Stangel, M.; Fortwängler, T.; Hoffmann, F.; et al. Active case finding of current bornavirus infections in human encephalitis cases of unknown etiology, Germany, 2018–2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlottau, K.; Jenckel, M.; van den Brand, J.; Fast, C.; Herden, C.; Höper, D.; Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Thielebein, J.; Mensing, N.; Diender, B.; et al. Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1 in Squirrels, Germany and the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlottau, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Fast, C.; Ulrich, R.G.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, D. Multiple detection of zoonotic variegated squirrel bornavirus 1 RNA in different squirrel species suggests a possible unknown origin for the virus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, D.; Frank, C.; Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Wilking, H.; Allendorf, V.; Schlottau, K.; Muñoz-Fontela, C.; Rottstegge, M.; Port, J.R.; Rissland, J.; et al. Analysis of exotic squirrel trade and detection of human infections with variegated squirrel bornavirus 1, Germany, 2005 to 2018. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1800483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, D.; Allendorf, V.; Schulze, V.; Ulrich, R.G.; Schlottau, K.; Ebinger, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Hoffmann, D.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Ismer, G.; et al. Introduction and spread of variegated squirrel bornavirus 1 (VSBV-1) between exotic squirrels and spill-over infections to humans in Germany. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, V.; Lurz, P.W.W.; Ferrari, N.; Romeo, C.; Steele, M.A.; Marino, S.; Mazzamuto, M.V.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Schlottau, K.; Beer, M.; et al. Search for polyoma-, herpes-, and bornaviruses in squirrels of the family Sciuridae. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. iModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 9, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.D.; Wertheim, J.O.; Weaver, S.; Murrell, B.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Less Is More: An Adaptive Branch-Site Random Effects Model for Efficient Detection of Episodic Diversifying Selection. In Mol. Biol. Evol.; 2015; Volume 32, pp. 1342–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, J.W.; Byrant, D. Popart: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, D.; Middendorf, M.; Wieseke, N. A parameter-adaptive dynamic programming approach for inferring cophylogenies. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conow, C.; Fielder, D.; Ovadia, Y.; Libeskind-Hadas, R. Jane: A new tool for the cophylogeny reconstruction problem. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuse, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Oshitani, H. Origin of measles virus: Divergence from rinderpest virus between the 11th and 12th centuries. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Ding, N.-Z.; He, C.-Q.; Yan, X.-C.; Teng, C.-B. Dating the divergence of the infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; An, T.Z.; Teng, C.B. Evolution of mammalian and avian bornaviruses. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2014, 79, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, Y.; Kobasa, D.; Rubin, S.A.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Carbone, K.M. Enhanced neurovirulence of borna disease virus variants associated with nucleotide changes in the glycoprotein and L polymerase genes. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8650–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlottau, K.; Nobach, D.; Herden, C.; Finke, S.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, D. First isolation, in-vivo and genomic characterization of zoonotic variegated squirrel Bornavirus 1 (VSBV-1) isolates. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2474–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Murrell, B.; Fourment, M.; Frost, S.D.; Delport, W.; Scheffler, K. A random effects branch-site model for detecting episodic diversifying selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Host | VSBV-1 Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | X | P | M | G | L | |
| Homo sapiens | Leu96Cys, Glu160Asp, Glu275Gly | Gly30Arg | Pro35Ser, Ser51Phe, Val122Ile | Asp43Asn | Asp43Asn, Glu185Ala | Gly54Glu, Arg88His, Gly1084Arg |
| Callosciurus prevostii | Val147Ile, Thr254Ile | Val79Ile | Ser19Leu, Glu61Lys, Ala106Val | Ser19Leu, Glu61Lys, Ala106Val, Val313Ile, Asn188Asp, Gly196Asp | Lys84Arg, Lys141Glu, Val560Ile, Ile1074Val, Lys1191Arg/Leu, Gln1307His, Ser1495Leu | |
| Sciurus variegatoides | Pro21Ser, Thr37Ile | Ser165Gly | Ser165Gly, Thr170Ala, Asn390Ser, Arg244Lys, Asn188Ser | Ala165Thr, Glu164Lys, Cys287Tyr | ||
| Gene | SLAC * | FEL * | MEME * | FUBAR # | Amino Acid Substitution | dN/dS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 0.007 | |||||
| X | 0.019 | |||||
| P | 0.013 | |||||
| G | 238 | 238 | 170, 175, 188, 238, 390 | Thr170Ala, Ser175Asn/Ile, Asn188Asp/Ser, Ser238Leu, Asn390Thr/Ser | 0.031 | |
| M | 0.009 | |||||
| L | 1191 | 1191 | Lys1191Leu/Arg | 0.014 |
| Core-Pa | Reconstruction (qc) | Total Cost | Co-Speciation (Cost) | Duplication (Cost) | Host-Switch (Cost) | Sorting (Cost) | p Value (Tip Mapping) | p Value (Parasite Tree) |
| 1 (0.023) | 23 | 1 (0.106) | 4 (0.169) | 5 (0.552) | 0 | <0.015 | <0.015 | |
| 2 (0.037) | 23 | 2 (0.189) | 2 (0.195) | 3 (0.557) | 1 (0.08) | <0.015 | <0.015 | |
| Jane 4 | Cost Set | Total Cost | Co-Speciation | Duplication | Host-Switch | Losses | Failure to Diverge | p Value |
| 1 | 14 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0.08 | |
| 2 | 14 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cadar, D.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Tappe, D. Genomic and Micro-Evolutionary Features of Mammalian 2 orthobornavirus (Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, VSBV-1). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061141
Cadar D, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Tappe D. Genomic and Micro-Evolutionary Features of Mammalian 2 orthobornavirus (Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, VSBV-1). Microorganisms. 2021; 9(6):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061141
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadar, Dániel, Jonas Schmidt-Chanasit, and Dennis Tappe. 2021. "Genomic and Micro-Evolutionary Features of Mammalian 2 orthobornavirus (Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, VSBV-1)" Microorganisms 9, no. 6: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061141
APA StyleCadar, D., Schmidt-Chanasit, J., & Tappe, D. (2021). Genomic and Micro-Evolutionary Features of Mammalian 2 orthobornavirus (Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, VSBV-1). Microorganisms, 9(6), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061141








