Reduced Presence of SARS-CoV-2 microRNA-like Small RNA in the Serum of Patients with Post-Acute Sequelae SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
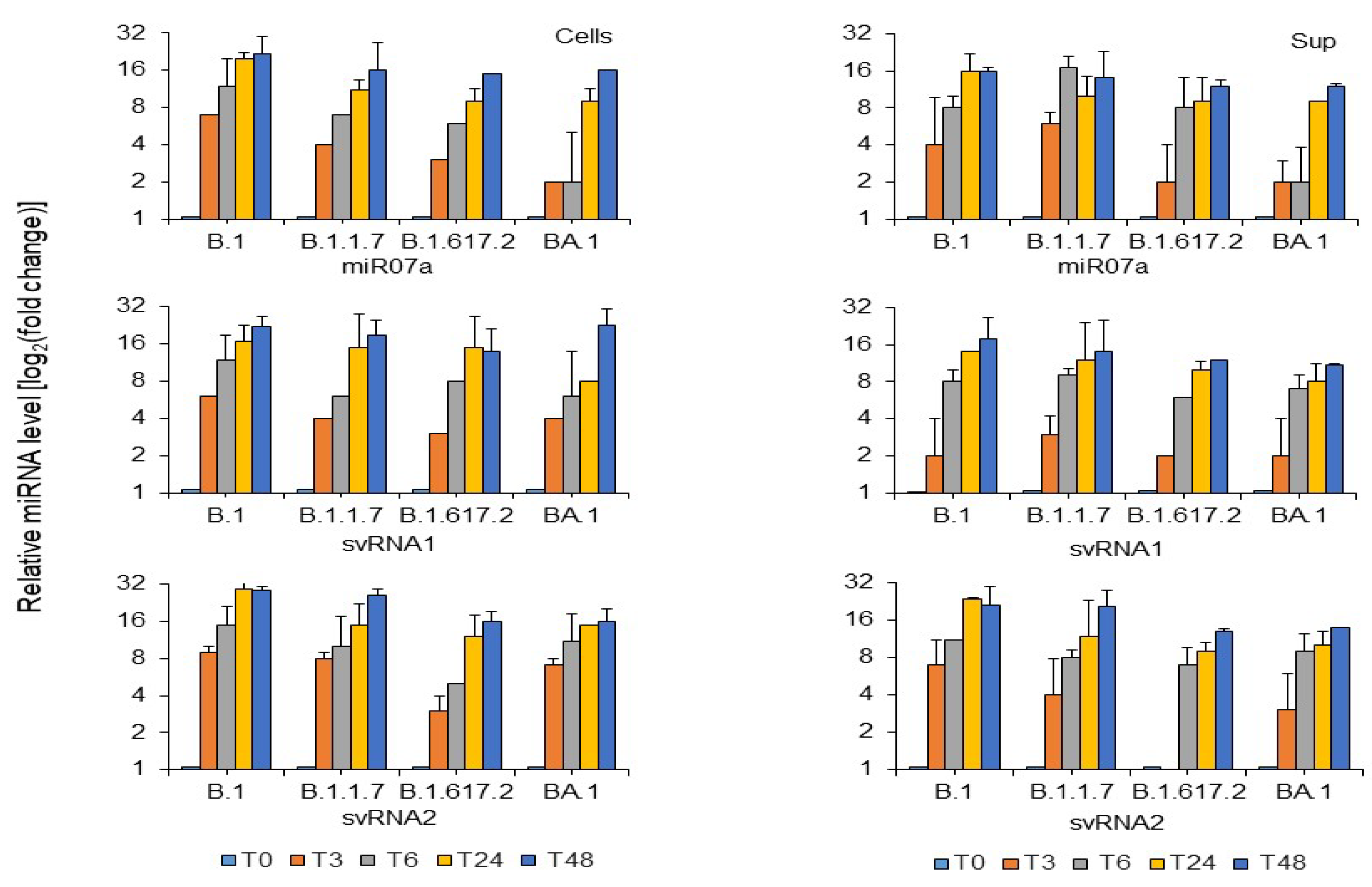
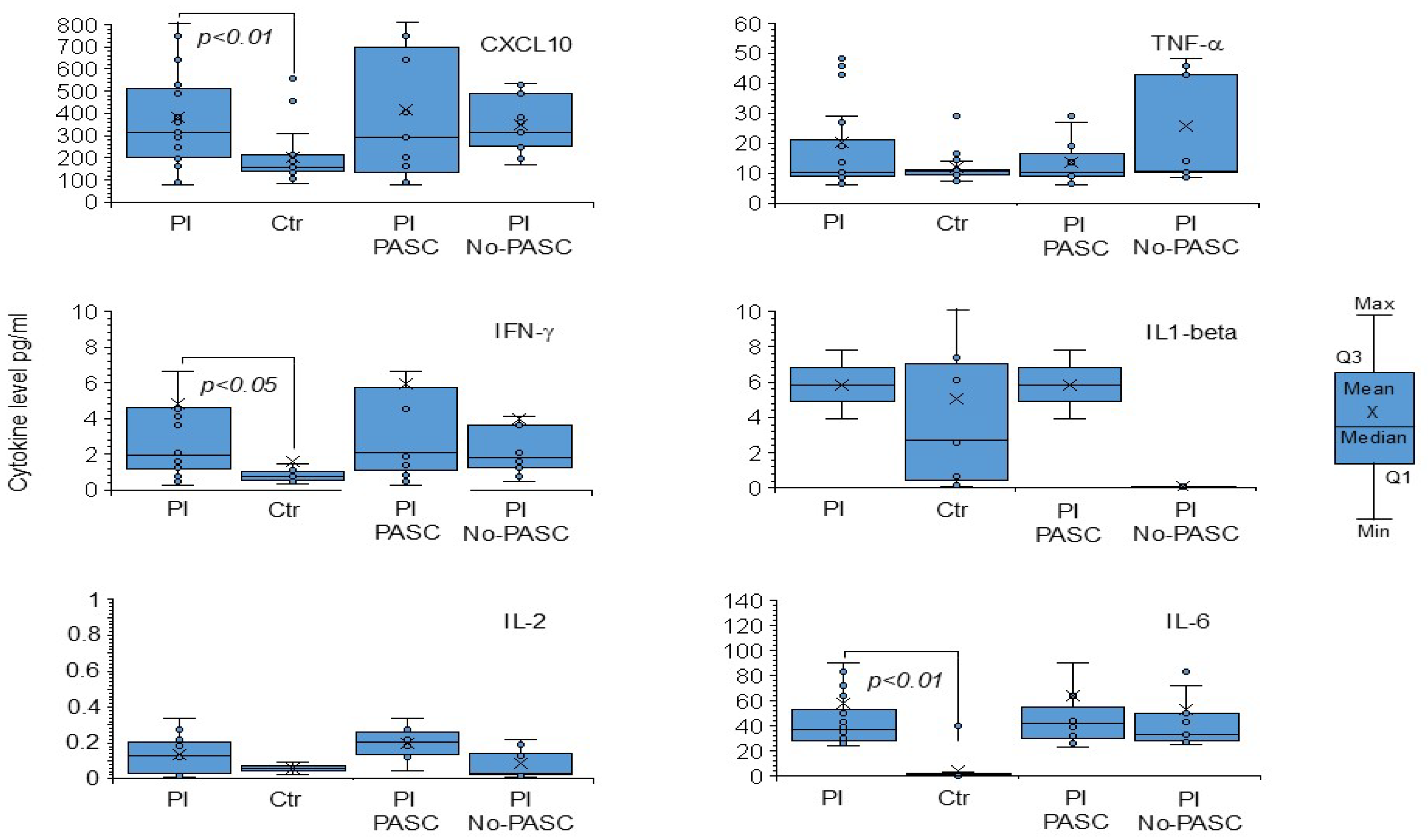
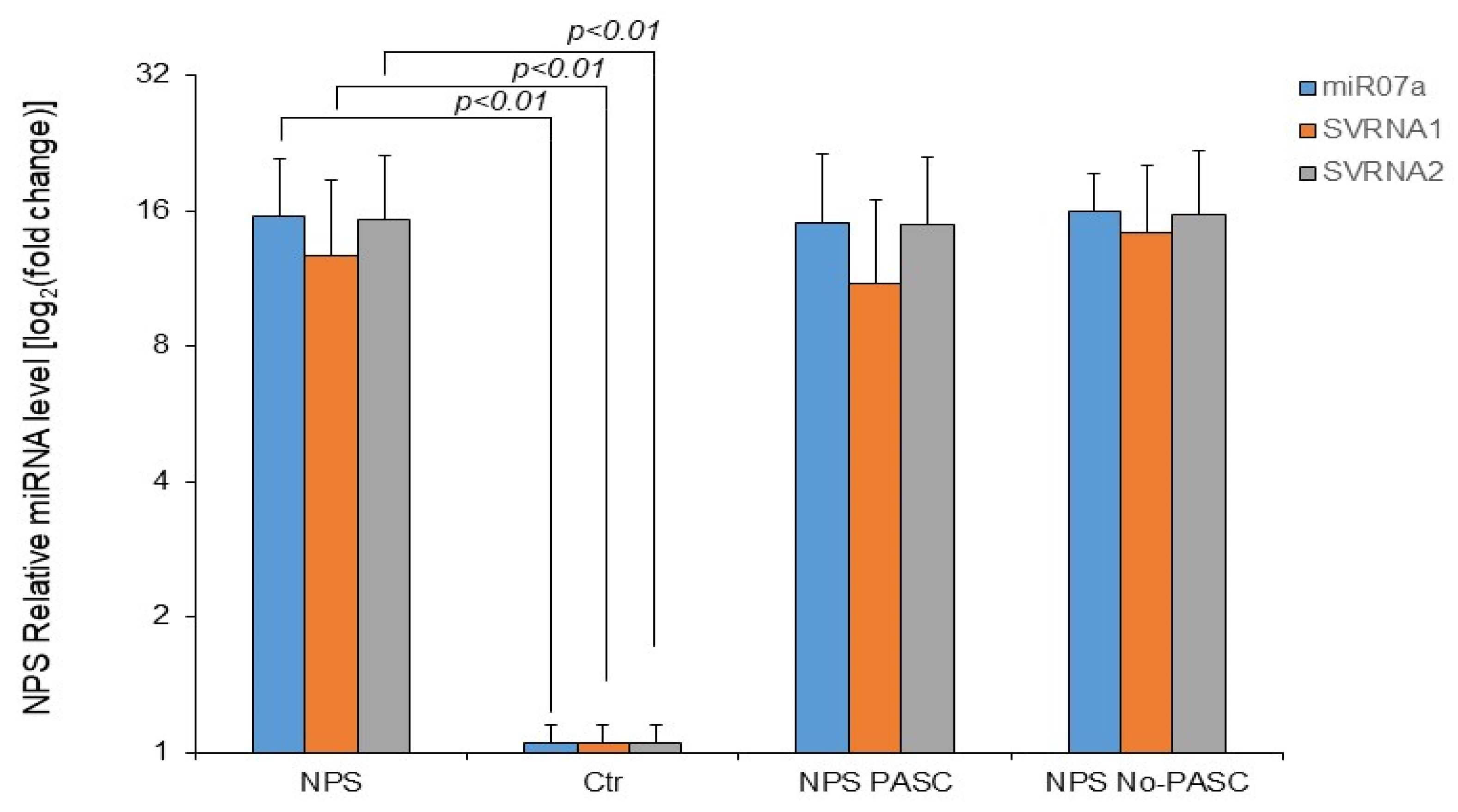
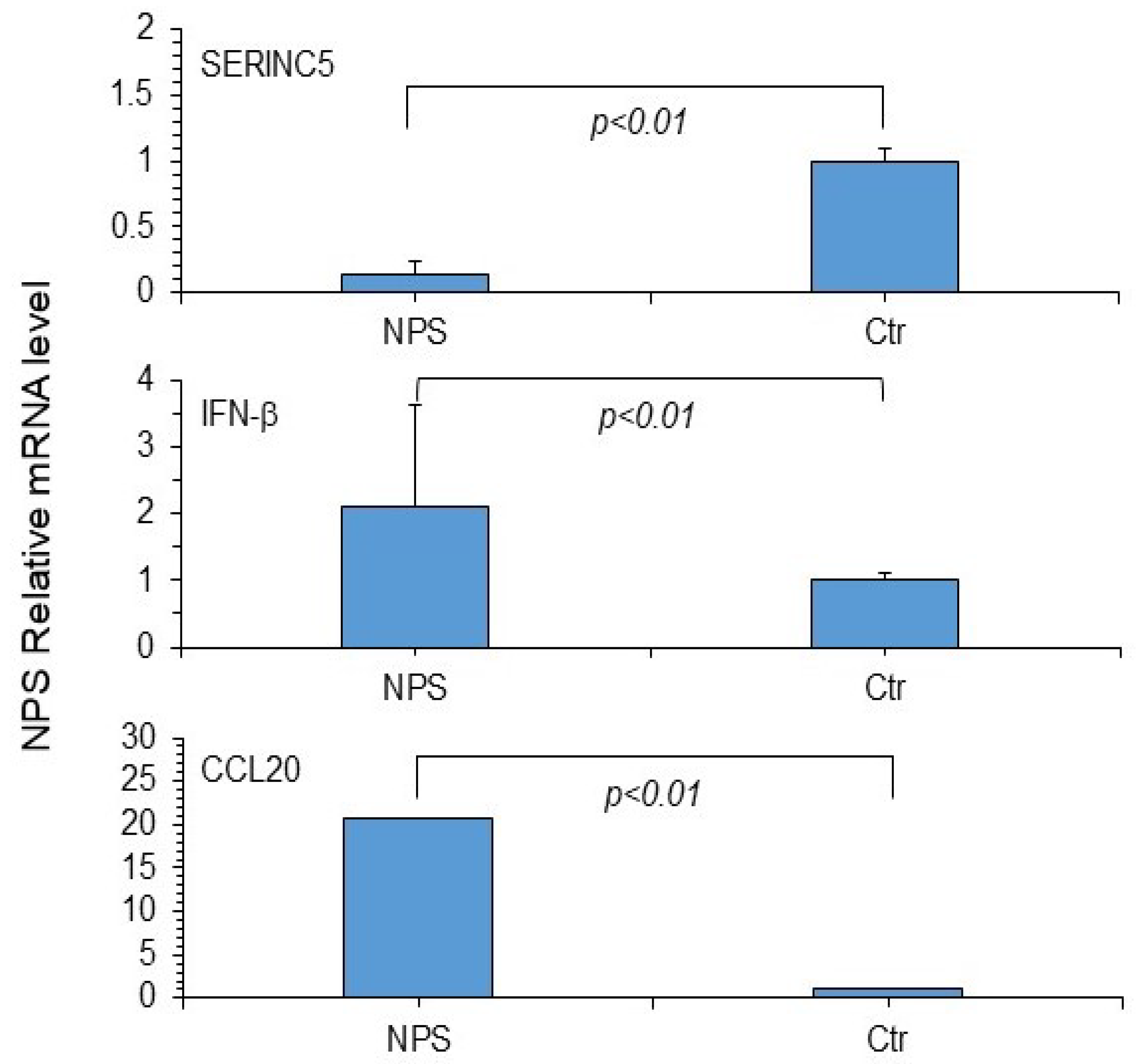
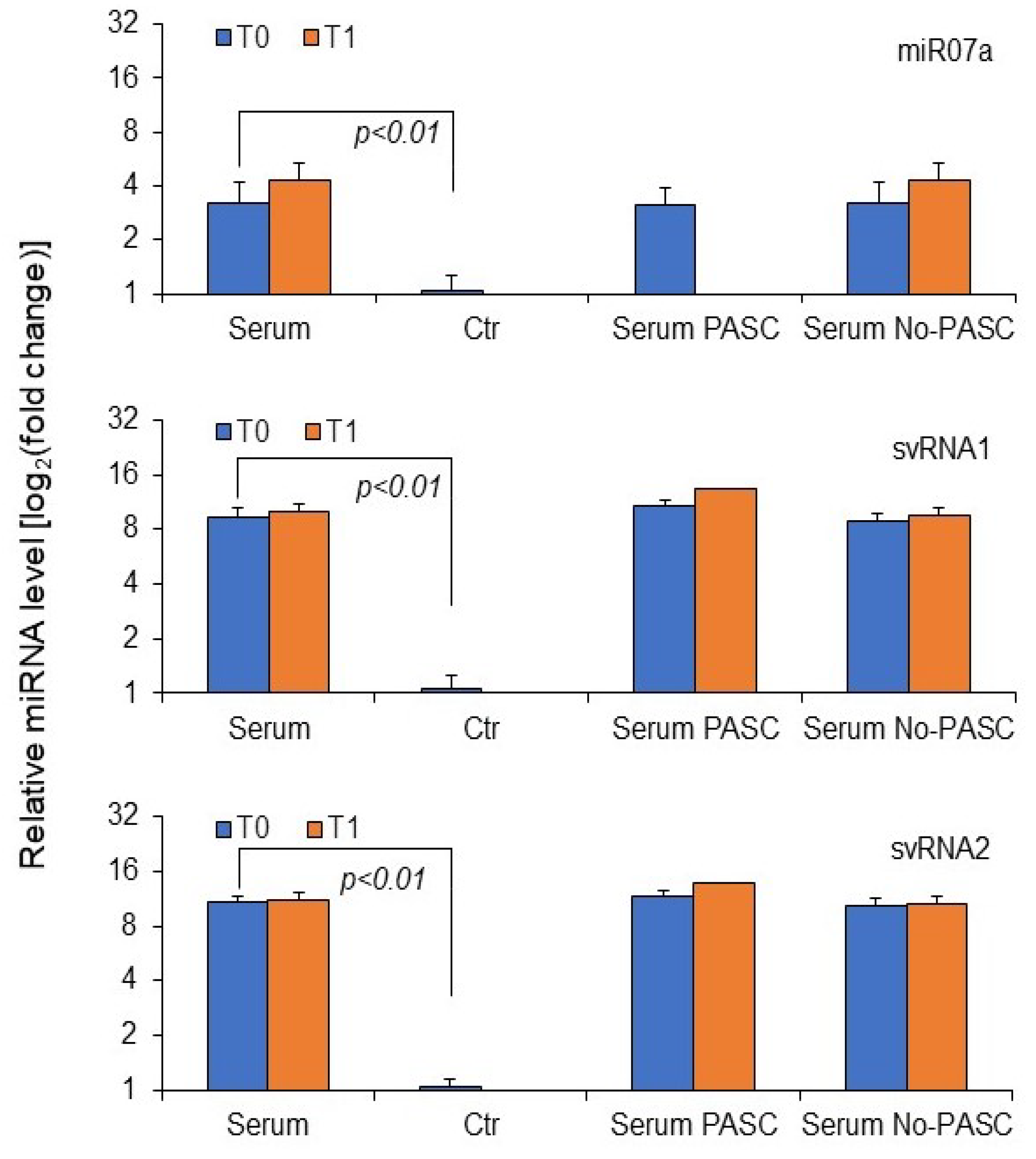
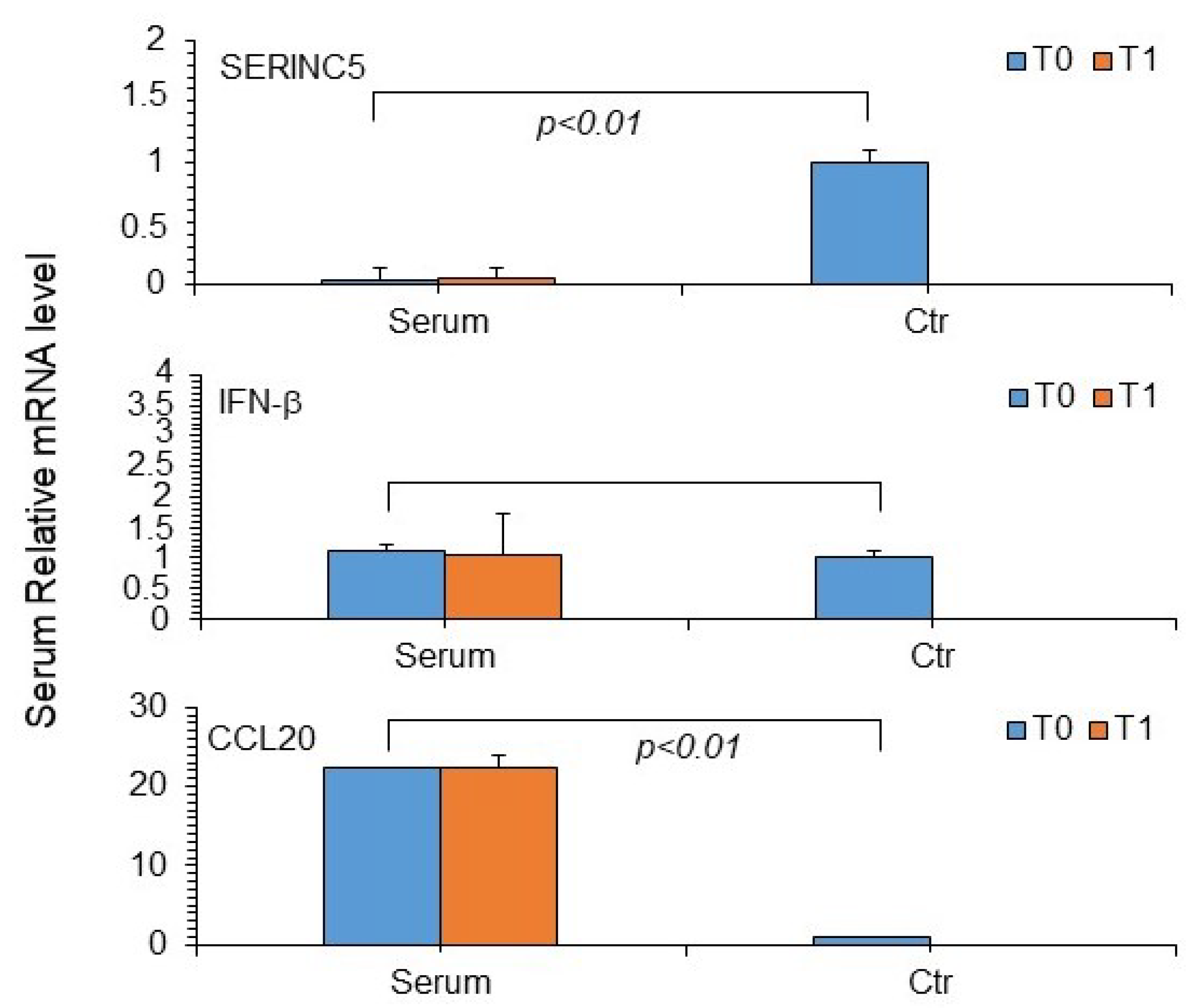
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PASC | post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| MiRNA | microRNA |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 19 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| NPS | nasopharyngeal swabs |
| EV | extracellular vehicles |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| ATTC | American Type Culture Collection |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| MOI | multiplicity of infection |
| SERINC5 | serine incorporator protein 5 |
| IFNβ | interferon beta |
| CCL20 | chemokine ligand 20 |
| CXCL-10/IP-10 | Interferon-gamma Inducible Protein 10 |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL-1 β | Inter-leukin-1β |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| IQR | interquartile ranges |
| SD | standard deviation |
| Ctr | control |
References
- El-Baky, N.A.; Amara, A.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Redwan, E.M. Intrinsic factors behind long COVID: III. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 and its components. J. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 125, e30514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Topol, E. Solving the puzzle of Long COVID. Science 2024, 383, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballering, A.V.; van Zon, S.K.R.; Hartman, T.C.O.; Rosmalen, J.G.M. Persistence of somatic symptoms after COVID-19 in the Netherlands: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2022, 400, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAIR Health. Patients Diagnosed with Post-COVID Conditions: An Analysis of Private Healthcare Claims Using the Official ICD-10 Diagnostic Code; FAIR Health: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Lee, S.S. Regulatory role of miRNAs in the human immune and inflammatory response during the infection of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses: A comprehensive review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2024, 34, e2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Fang, D.; Gao, X.; Deng, X.; Chen, N.; Wu, J.; Zeng, M.; Luo, M. Circulating microRNAs as emerging regulators of COVID-19. Theranostics 2023, 13, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouzouasis, V.; Tastsoglou, S.; Giannakakis, A.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. Virus-derived small RNAs and microRNAs in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2023, 6, 275–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruivinho, C.; Gama-Carvalho, M. Small non-coding RNAs encoded by RNA viruses: Old controversies and new lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1216890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Q.; Xu, L. Identification, characterization and expression analysis of circRNA encoded by SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 2025, bbad537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, A.A.; Al-Chalabi, R.; Shaban, S.A. Integrative role of small non-coding RNAs in viral immune response: A systematic review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grehl, C.; Schultheiß, C.; Hoffmann, K.; Binder, M.; Altmann, T.; Grosse, I.; Kuhlmann, M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 derived small RNAs and changes in circulating small RNAs associated with COVID-19. Viruses 2021, 13, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, G.A.; Raad, J.; Bugnon, L.A.; Yones, C.; Kamenetzky, L.; Claus, J.; Ariel, F.; Milone, D.H.; Stegmayer, G. Novel SARS-CoV-2 encoded small RNAs in the passage to humans. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 5571–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, E.J.; Wong, S.W.; Marri, S.; Ali, S.; Fedele, A.O.; Michael, M.Z.; Rojas-Canales, D.; Li, J.Y.; Lim, C.K.; Gleadle, J.M. SARS-CoV-2 produces a microRNA CoV2-miR-O8 in patients with COVID-19 infection. iScience 2023, 27, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer, S.; Rubio, M.P.; Lainez, B.; Pérez-Benavente, B.; Pérez-Moraga, R.; Romera-Giner, S.; García-García, F.; Martinez-Macias, O.; Cremades, A.; Iborra, F.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-encoded small RNAs are able to repress the host expression of SERINC5 to facilitate viral replication. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1066493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Chazal, M.; Quarato, P.; Bourdon, L.; Malabat, C.; Vallet, T.; Vignuzzi, M.; van der Werf, S.; Behillil, S.; Donati, F.; et al. A virus-derived microRNA targets immune response genes during SARS-CoV-2 infection. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Siu, G.K.; Mok, B.W.; Sun, J.; Fung, K.S.C.; Lam, J.Y.; Wong, N.K.; Gedefaw, L.; Luo, S.; Lee, T.M.H.; et al. Viral MicroRNAs encoded by nucleocapsid gene of SARS-CoV-2 are detected during Infection, and targeting Metabolic Pathways in Host Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, L.; Oliveros, J.C.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; tenOever, B.R.; Enjuanes, L.; Sola, I. SARS-CoV-encoded small RNAs contribute to infection-associated lung pathology. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeb, Z.T.; Ritter, A.J.; Chauhan, L.V.; Katzman, S.; Lipkin, W.I.; Mishra, N.; Sanford, J.R. A potential role for SARS-CoV-2 small viral RNAs in targeting host microRNAs and modulating gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlica, P.; Yario, T.A.; White, S.; Wang, J.; Moss, W.N.; Hui, P.; Vinetz, J.M.; Steitz, J.A. SARS-CoV-2 expresses a microRNA-like small RNA able to selectively repress host genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2116668118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corell-Sierra, J.; Marquez-Molins, J.; Marqués, M.C.; Hernandez-Azurdia, A.G.; Montagud-Martínez, R.; Cebriá-Mendoza, M.; Cuevas, J.M.; Albert, E.; Navarro, D.; Rodrigo, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 remodels the landscape of small non-coding RNAs with infection time and symptom severity. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2024, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcher, H.A.; DeMeis, J.D.; Ghobar, N.; Godang, N.L.; Knight, S.L.; Alqudah, S.Y.; Nguyen, K.N.; Watters, B.C.; Borchert, G.M. SARS-CoV-2 small viral RNA suppresses gene expression via complementary binding to mRNA 3’UTR. MicroPubl. Biol. 2024, 10, 17912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedonks, T.A.P.; Nyberg, L.H.; Conte, A.; Ma, Z.; Pekosz, A.; Duban, E.; Tonevitsky, A.; Sültmann, H.; Turchinovich, A.; Witwer, K.W. Viral and host small RNA transcriptome analysis of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2-infected human cells reveals novel viral short RNAs. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejerina, F.; Catalan, P.; Rodriguez-Grande, C.; Adan, J.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, C.; Muñoz, P.; Aldamiz, T.; Diez, C.; Perez, L.; Fanciulli, C.; et al. Post-COVID-19 syndrome. SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection in plasma, stool, and urine in patients with persistent symptoms after COVID-19. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, B.K.; Francisco, E.B.; Yogendra, R.; Long, E.; Pise, A.; Rodrigues, H.; Hall, E.; Herrera, M.; Parikh, P.; Guevara-Coto, J.; et al. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein in Cd16+ monocytes in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 months post-infection. Front Immunol. 2022, 12, 746021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, V.; Mahajan, A.; Spikes, L.; Krishnamachary, B.; Ram, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Chen, L.; Chalise, P.; Dhillon, N.K. Persistent circulation of soluble and extracellular vesicle-linked spike protein in individuals with Postacute sequelae of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swank, Z.; Senussi, Y.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Yu, X.G.; Li, J.Z.; Alter, G.; Walt, D.R. Persistent circulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike is associated with post-acute coronavirus disease 2019 sequelae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e487–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maradny, Y.A.; Rubio-Casillas, A.; Uversky, V.N.; Redwan, E.M. Intrinsic factors behind long-COVID: I. Prevalence of the extracellular vesicles. J. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 12, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stincarelli, M.A.; Arvia, R.; Giannecchini, S. Extracellular vesicles engagement during respiratory viruses infection. Asp. Mol. Med. 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, M.; Tate, M.; Lloyd, O.; Maraolo, A.E.; Schafers, J.; Ho, A. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e13–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proal, A.D.; VanElzakker, M.B.; Aleman, S.; Bach, K.; Boribong, B.P.; Buggert, M.; Cherry, S.; Chertow, D.S.; Davies, H.E.; Dupont, C.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ng, R.W.Y.; Lui, G.; Ling, L.; Chow, C.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Boon, S.S.; Wang, M.H.; Chan, K.C.C.; Chan, R.W.Y.; et al. Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 subgenomic RNAs in clinical specimens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0018222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, S.; Kratzel, A.; Barut, G.T.; Lang, R.M.; Aguiar Moreira, E.; Thomann, L.; Kelly, J.N.; Thiel, V. SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; He, D.; Liang, C.; Du, S.; Hua, Z.; Nie, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yang, M.; Tan, H.; Xu, J.; et al. The persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in tissues and its association with long COVID symptoms: A cross-sectional cohort study in China. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 22, p845–p855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| All (n = 24) | PASC (n = 11) | No PASC (n = 13) | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age: median (IQR) | 69 (54–73) | 69 (58–72) | 69 (54–76) | 0.7867 |
| Gender: M/F | 10/14 | 4/7 | 6/7 | 0.6968 |
| Treatment n (%): | ||||
| Evusheld | 5 (21) | 2 (18) | 3 (23) | >0.9999 |
| Sotrovimab | 11(46) | 5 (45) | 6 (46) | >0.9999 |
| Paxlovid | 8 (33) | 4 (36) | 4 (31) | >0.9999 |
| SARS-CoV2 RNA in NPS | ||||
| Median Ct values (IQR) | 14.9 (13.1–18.3) | 13.5 (12.8–16.9) | 15.7 (13.4–20.2) | 0.1799 |
| SARS-CoV2-lineage n. (%) | ||||
| BA.2 | 13(54.16) | 3 (27) | 3 (23) | >0.9999 |
| BA.4 | 1(4.16) | 1 (9) | 0 | 0.4583 |
| BA.5 | 7(29.16) | 1 (9) | 6 (46) | 0.0778 |
| BF.5 | 1(4.16) | 0 | 1 (8) | >0.9999 |
| unknown | 2(8.33) | 2 (18) | 0 | 0.1993 |
| T1 median days from diagnosis (IQR) | 151 (92–193) | 181 (107–196) | 111 (92–183) | 0.1543 |
| All (n = 24) | PASC (n = 11) | No PASC (n = 13) | p Value * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPS miR07a at T0 | Negative (%) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.7) | 0.999 |
| Positive (%) | 23 (95.8) | 11 (100) | 12 (92.3) | ||
| NPS svRNA 1 at T0 | Negative (%) | 2 (8.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (15.4) | 0.565 |
| Positive (%) | 22 (91.6) | 11 (100) | 11 (84.6) | ||
| NPS svRNA 2 at T0 | Negative (%) | 2 (8.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (15.4) | 0.565 |
| Positive (%) | 22 (91.6) | 11 (100) | 11 (84.6) | ||
| Total NPS viral small RNA at T0 | |||||
| Negative (%) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.7) | 0.999 | |
| Positive (%) | 23 (95.8) | 11 (100) | 12 (92.3) | ||
| Serum miR07a at T0 | Negative (%) | 22 (91.6) | 10 (90.9) | 12 (92.4) | 0.999 |
| Positive (%) | 2 (8.4) | 1 (9.1) | 1 (7.6) | ||
| Serum svRNA 1 at T0 | Negative (%) | 14 (58.3) | 8 (72.7) | 6 (46.2) | 0.369 |
| Positive (%) | 10 (41.7) | 3 (27.3) | 7 (53.8) | ||
| Serum svRNA 2 at T0 | Negative (%) | 14 (58.3) | 8 (72.7) | 6 (46.2) | 0.369 |
| Positive (%) | 10 (41.7) | 3 (27.3) | 7 (53.8) | ||
| Total serum viral small RNA at T0 | |||||
| Negative (%) | 14 (58.3) | 8 (72.7) | 6 (46.2) | 0.240 | |
| Positive (%) | 10 (41.7) | 3 (27.3) | 7 (53.8) | ||
| Serum miR07a at T1 | Negative (%) | 22 (91.6) | 11 (100) | 11 (84.6) | 0.565 |
| Positive (%) | 2 (8.4) | 0 (0) | 2 (15.4) | ||
| Serum svRNA 1 at T1 | Negative (%) | 18 (75.0) | 10 (90.9) | 8 (61.5) | 0.236 |
| Positive (%) | 6 (25.0) | 1 (9.1) | 5 (38.5) | ||
| Serum svRNA 2 at T1 | Negative (%) | 18 (75.0) | 10 (90.9) | 8 (61.5) | 0.236 |
| Positive (%) | 6 (25.0) | 1 (9.1) | 5 (38.5) | ||
| Total serum viral small RNA at T1 | |||||
| Negative (%) | 16 (66.7) | 10 (90.9) | 6 (46.2) | 0.033 | |
| Positive (%) | 8 (33.3) | 1 (9.1) | 7 (53.8) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stincarelli, M.A.; Abbate, I.; Matusali, G.; Tanturli, M.; Camici, M.; Arvia, R.; Lazzari, E.; Cimini, E.; Vergori, A.; Maggi, F.; et al. Reduced Presence of SARS-CoV-2 microRNA-like Small RNA in the Serum of Patients with Post-Acute Sequelae SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010126
Stincarelli MA, Abbate I, Matusali G, Tanturli M, Camici M, Arvia R, Lazzari E, Cimini E, Vergori A, Maggi F, et al. Reduced Presence of SARS-CoV-2 microRNA-like Small RNA in the Serum of Patients with Post-Acute Sequelae SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleStincarelli, Maria Alfreda, Isabella Abbate, Giulia Matusali, Michele Tanturli, Marta Camici, Rosaria Arvia, Elisabetta Lazzari, Eleonora Cimini, Alessandra Vergori, Fabrizio Maggi, and et al. 2025. "Reduced Presence of SARS-CoV-2 microRNA-like Small RNA in the Serum of Patients with Post-Acute Sequelae SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010126
APA StyleStincarelli, M. A., Abbate, I., Matusali, G., Tanturli, M., Camici, M., Arvia, R., Lazzari, E., Cimini, E., Vergori, A., Maggi, F., & Giannecchini, S. (2025). Reduced Presence of SARS-CoV-2 microRNA-like Small RNA in the Serum of Patients with Post-Acute Sequelae SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms, 13(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010126









