Microbial Community Structure, Diversity, and Succession During Decomposition of Kiwifruit Litters with Different Qualities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Plant Species
2.2. Litter Decomposition Experiment
2.3. Soil Microbial Community Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
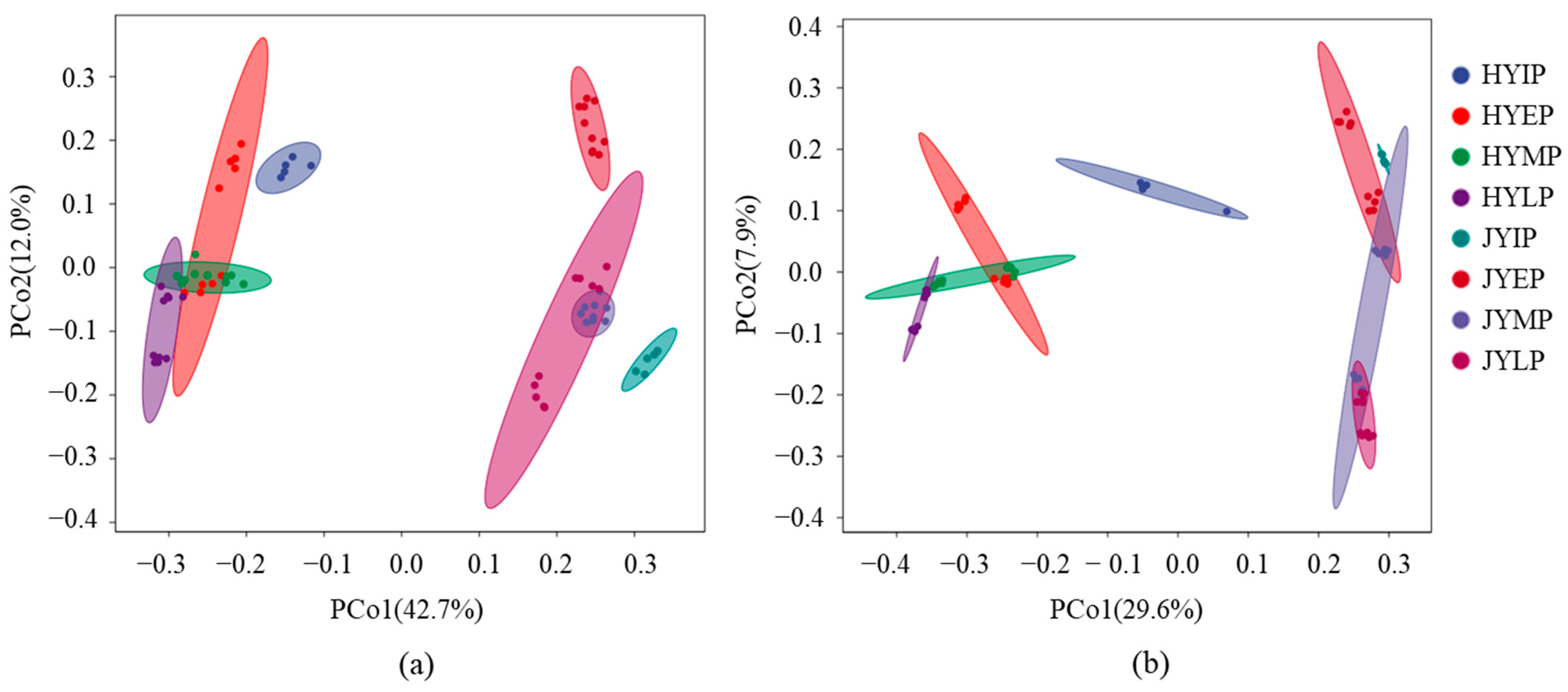
3.1. Microbial Community Structure
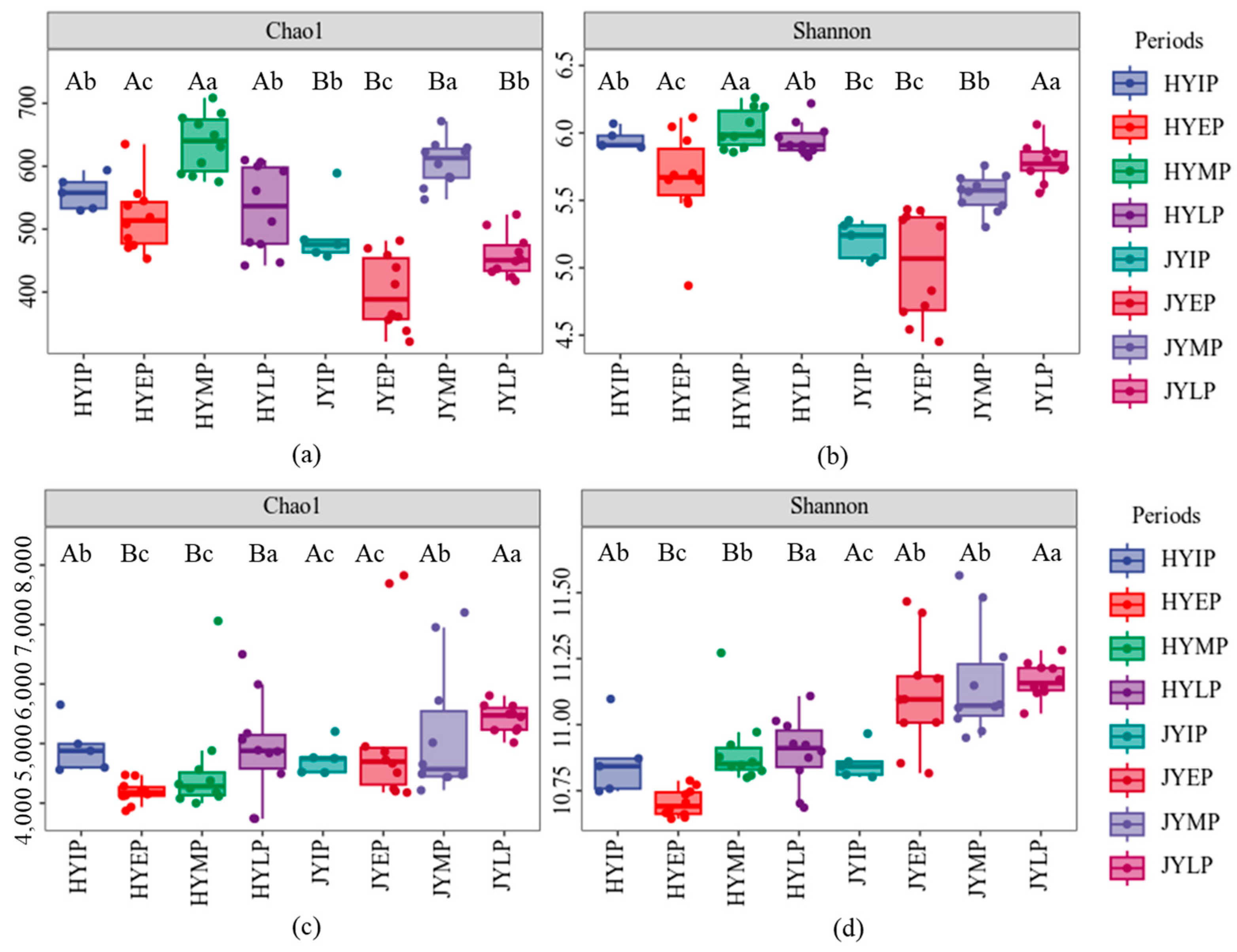
3.2. Microbial Community Diversity
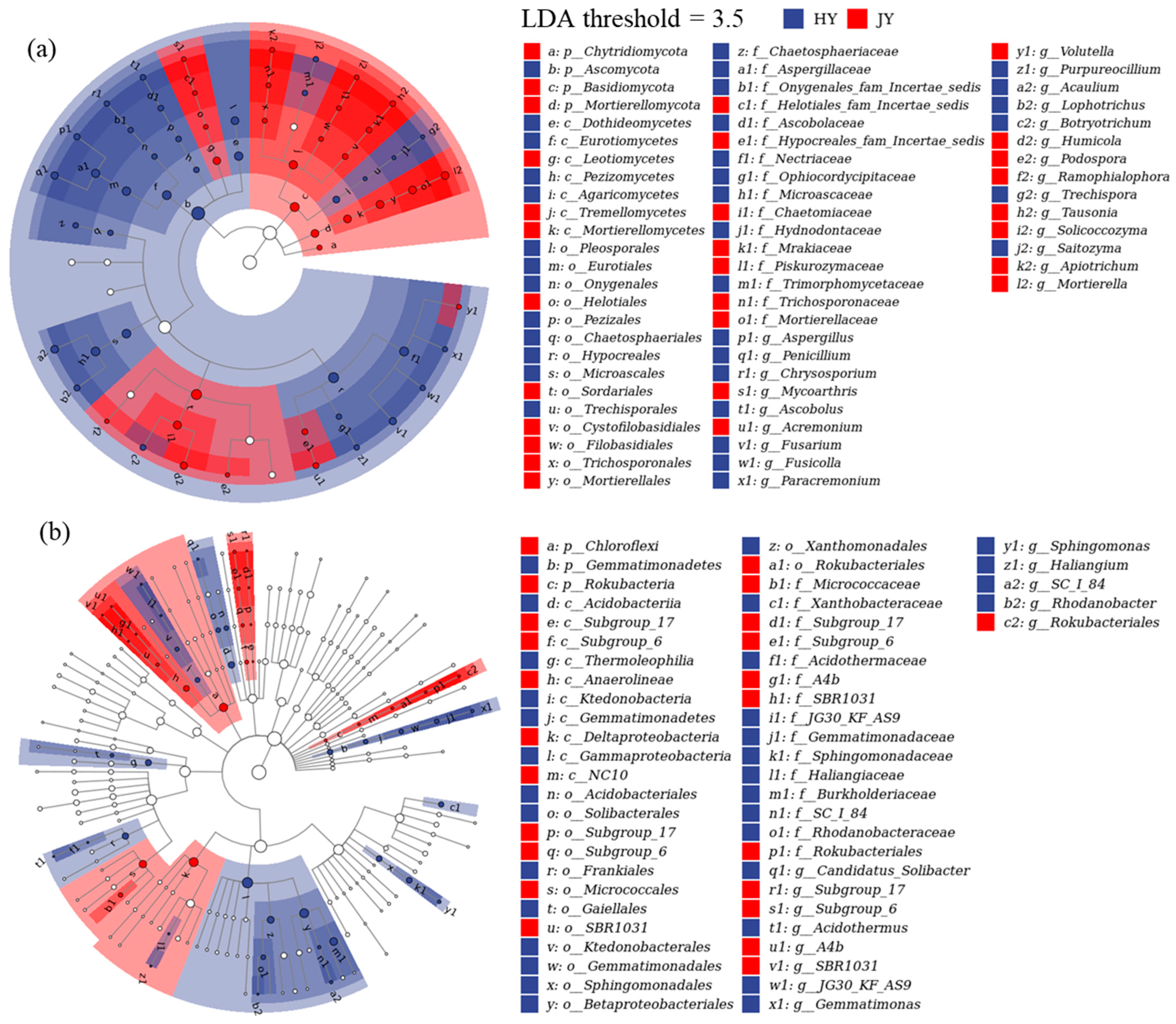
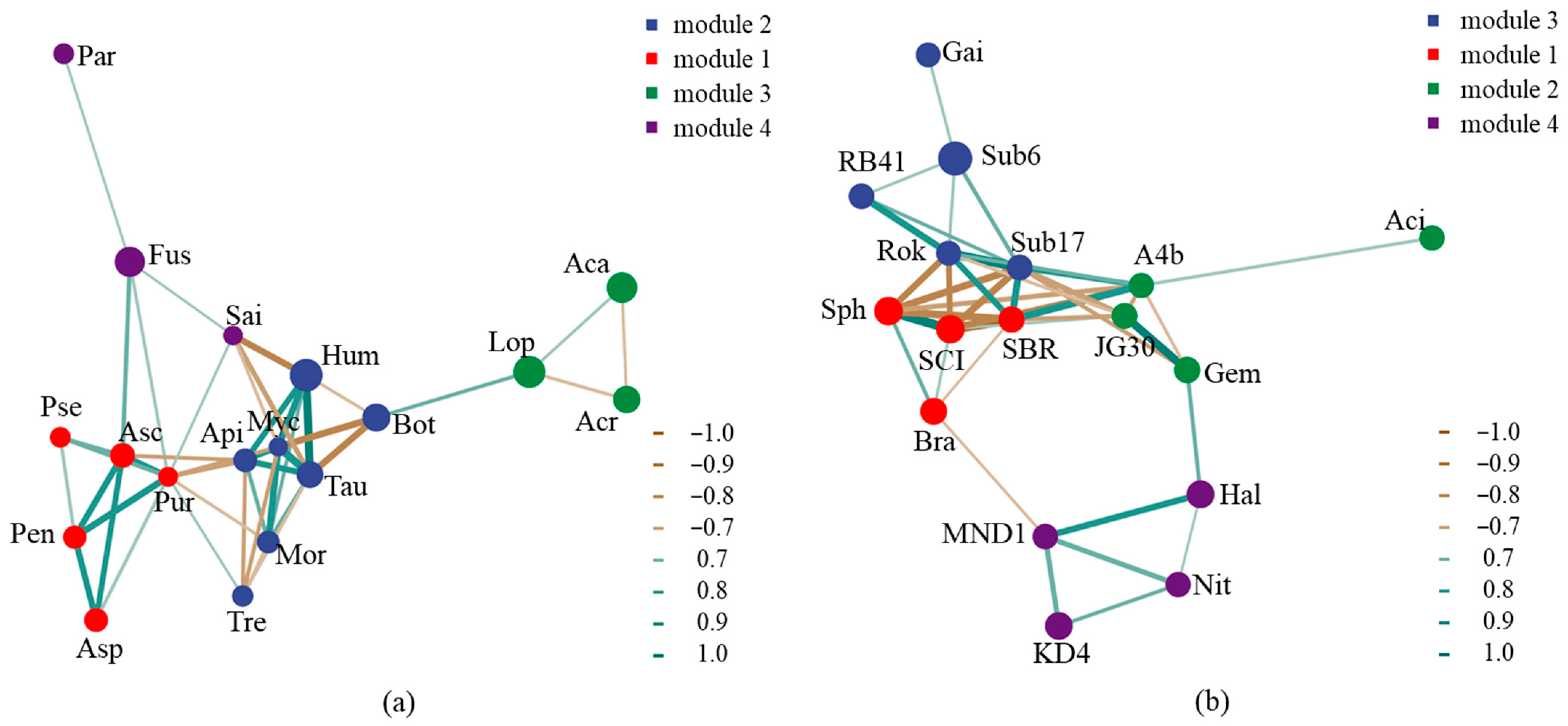
3.3. Microbial Community Succession
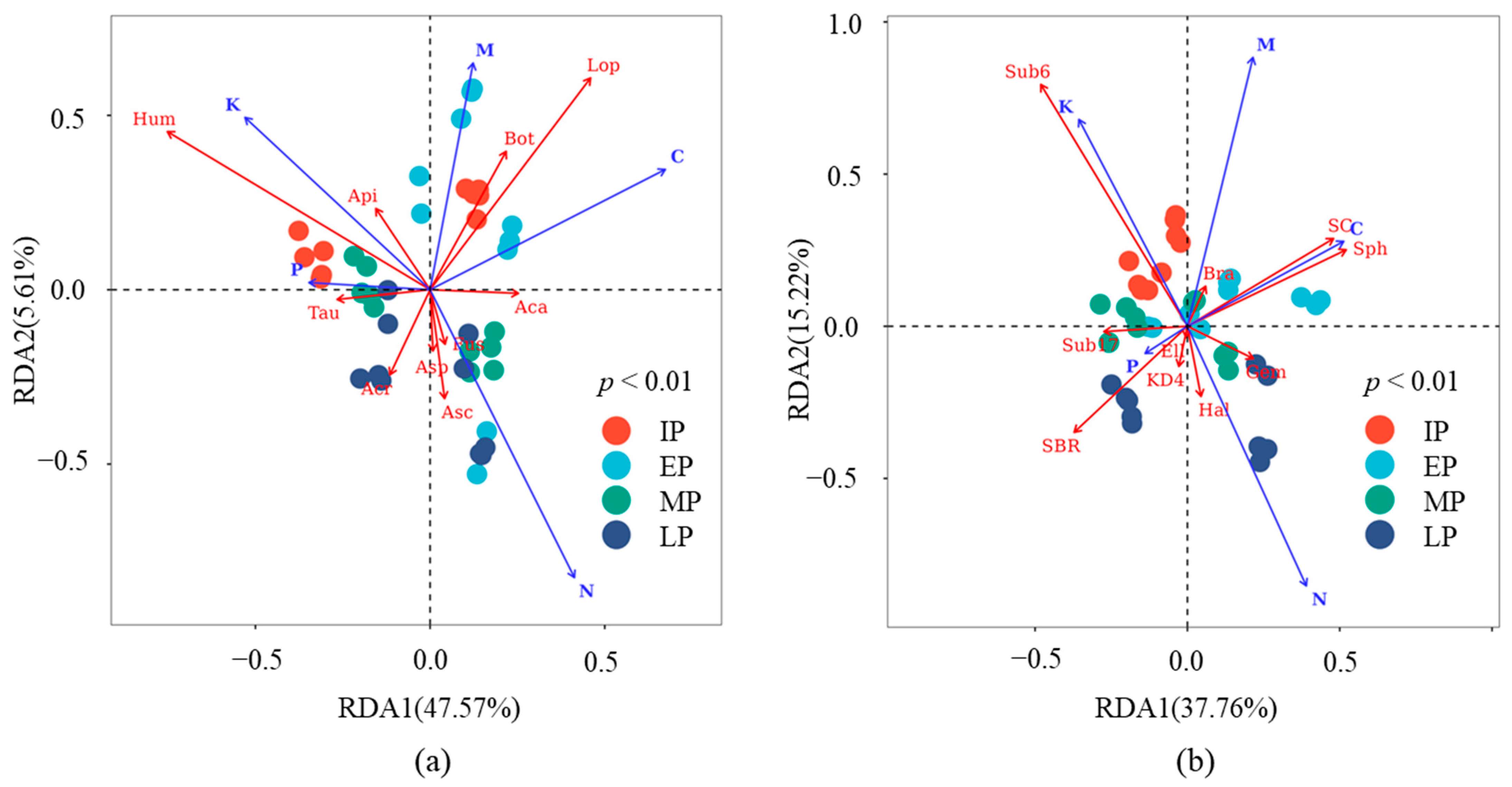
3.4. Effects of Biotic and Abiotic Factors on Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Dominant Microbial Decomposer
4.2. Community Diversity
4.3. Community Succession Along with the Decomposition Period
4.4. Litter Quality and Microbial Community
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishna, M.P.; Mohan, M. Litter decomposition in forest ecosystems: A review. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2017, 2, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giweta, M. Role of litter production and its decomposition, and factors affecting the processes in a tropical forest ecosystem: A review. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołębiewski, M.; Tarasek, A.; Sikora, M.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Tretyn, A.; Niklińska, M. Rapid Microbial Community Changes During Initial Stages of Pine Litter Decomposition. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chai, Q.; Dou, X.; Zhao, C.; Yin, W.; Li, H.; Wei, J. Soil Microorganisms in Agricultural Fields and Agronomic Regulation Pathways. Agronomy 2024, 14, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Qi, X.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhuang, G.; Ma, A. Soil bacterial communities associated with multi-nutrient cycling under long-term warming in the alpine meadow. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1136187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xu, C.; McDowell, N.G.; Johnson, D.J.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z. Linking microbial community composition to C loss rates during wood decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, A.; Pioli, S.; Ventura, M.; Panzacchi, P.; Borruso, L.; Tognetti, R.; Tonon, G.; Brusetti, L. The role of microbial community in the decomposition of leaf litter and deadwood. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, S.R.; Kitajima, K.; Mack, M.C. Temporal dynamics of microbial communities on decomposing leaf litter of 10 plant species in relation to decomposition rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, K.; Lyu, Z.; Zhu, J. Microbial groups and their functions control the decomposition of coniferous litter: A comparison with broadleaved tree litters. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 133, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, S.M.; Beckham, G.T.; Bruce, N.C.; Bugg, T.D.H.; Distel, D.L.; Dupree, P.; Etxabe, A.G.; Goodell, B.S.; Jellison, J.; McGeehan, J.E.; et al. Lignocellulose degradation mechanisms across the Tree of Life. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 29, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janusz, G.; Pawlik, A.; Sulej, J.; Swiderska-Burek, U.; Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A.; Paszczynski, A. Lignin degradation: Microorganisms, enzymes involved, genomes analysis and evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 941–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Yang, T.; Bao, Y.; He, P.; Yang, K.; Mei, X.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Banerjee, S. Network analysis and subsequent culturing reveal keystone taxa involved in microbial litter decomposition dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvadet, M.; Fanin, N.; Chauvat, M.; Bertrand, I. Can the comparison of above- and below-ground litter decomposition improve our understanding of bacterial and fungal successions? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 132, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purahong, W.; Wubet, T.; Lentendu, G.; Schloter, M.; Pecyna, M.J.; Kapturska, D.; Hofrichter, M.; Krüger, D.; Buscot, F. Life in leaf litter: Novel insights into community dynamics of bacteria and fungi during litter decomposition. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4059–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tsang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Fu, X.; Sun, Y. Plant litter composition selects different soil microbial structures and in turn drives different litter decomposition pattern and soil carbon sequestration capability. Geoderma 2018, 319, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, J.M.; Peay, K.G.; Treseder, K.K. Litter chemistry influences decomposition through activity of specific microbial functional guilds. Ecol. Monogr. 2018, 88, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palacios, P.; McKie, B.G.; Handa, I.T.; Frainer, A.; Hättenschwiler, S. The importance of litter traits and decomposers for litter decomposition: A comparison of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems within and across biomes. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murúa, J.M.; Gaxiola, A. Variability in terrestrial litter decomposition can be explained by nutrient allocation strategies among soil decomposer communities. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Čapek, P.; Mooshammer, M.; Lindahl, B.D.; Richter, A.; Šantrůčková, H. Optimal metabolic regulation along resource stoichiometry gradients. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, G.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Nielsen, U.N. Dominant plants affect litter decomposition mainly through modifications of the soil microbial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tian, X.; He, X.; Song, F.; Ren, L.; Jiang, P. Effect of litter quality on its decomposition in broadleaf and coniferous forest. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X. Litter mixing promoted decomposition and altered microbial community in common bean root litter. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.G. Litter decomposition and nutrient release from monospecific and mixed litters: Comparisons of litter quality, fauna and decomposition site effects. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, C.; Carranca, C.; Clemente, J. Senescent leaf decomposition in a Mediterranean pear orchard. Eur. J. Agron. 2009, 30, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jiao, K.; Qin, S.; Lyu, D. The impact of cover crop shoot decomposition on soil microorganisms in an apple orchard in northeast China. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germer, S.; Dongen, R.v.; Kern, J. Decomposition of cherry tree prunings and their short-term impact on soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 117, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Lan, T.; Geng, T.; Ju, Y.; Cheng, G.; Que, Z.; Gao, G.; Fang, Y.; Sun, X. Nutritional properties and biological activities of kiwifruit (Actinidia) and kiwifruit products under simulated gastrointestinal in vitro digestion. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 63, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Mao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Litter Decomposition Characteristics and Variety Differences in a Kiwifruit Orchard in Subtropical Climate Zone of China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytioja, J.; Hildén, K.; Yuzon, J.; Hatakka, A.; de Vries Ronald, P.; Mäkelä Miia, R. Plant-Polysaccharide-Degrading Enzymes from Basidiomycetes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 614–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, L. Responses of microorganisms to different wavelengths of light radiation during green waste composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 171021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhunmwunse, A.S.; Mackowiak, C.L.; Blount, A.R.S.; Dubeux, J.C.B.; Ogram, A.; Liao, H.-L. Short-term perennial peanut integration into bahiagrass system influence on soil microbial-mediated nitrogen cycling activities and microbial co-occurrence networks. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2023, 119, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, G.F.; ten Hooven, F.C.; Weser, C.; Hannula, S.E. Steering the soil microbiome by repeated litter addition. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, G.; Luo, N.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Ngozi, E.A. The priming effect patterns linked to the dominant bacterial keystone taxa during different straw tissues incorporation into Mollisols in Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 197, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Liang, X.; Guo, T.; Wu, T.; Chai, B. Bacterial community succession and influencing factors for Imperata cylindrica litter decomposition in a copper tailings area of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; An, S. Fast bacterial succession associated with the decomposition of Quercus wutaishanica litter on the Loess Plateau. Biogeochemistry 2019, 144, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Ni, R.; Han, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Z. Leaf and Root Litter Species Identity Influences Bacterial Community Composition in Short-Term Litter Decomposition. Forests 2022, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Song, F. Differences in Microbial Community and Metabolites in Litter Layer of Plantation and Original Korean Pine Forests in North Temperate Zone. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, K.; Soromotin, A.V.; et al. Network analysis reveals bacterial and fungal keystone taxa involved in straw and soil organic matter mineralization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 173, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S. Effects of mixed coniferous and broad-leaved litter on bacterial and fungal nitrogen metabolism pathway during litter decomposition. Plant Soil 2020, 451, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.J.; Lazar, C.S.; Teske, A.P.; Dick, G.J. Genomic resolution of linkages in carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycling among widespread estuary sediment bacteria. Microbiome 2015, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Davis, M.; Yang, Y. Litter decomposition, residue chemistry and microbial community structure under two subtropical forest plantations: A reciprocal litter transplant study. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 101, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, M.E.; Rae DeVan, M.; Thompson, J.; Johansen, R.; Gallegos-Graves, L.V.; Lopez, D.; Runde, A.; Yoshida, T.; Munsky, B.; Sevanto, S.; et al. Microbial community composition controls carbon flux across litter types in early phase of litter decomposition. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6676–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Xu, H.; Yan, Z.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Jiang, H.-L. Improved lignin degradation through distinct microbial community in subsurface sediments of one eutrophic lake. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomutovska, N.; Jasser, I.; Isidorov, V.A. Unraveling the Role of Bacteria in Nitrogen Cycling: Insights from Leaf Litter Decomposition in the Knyszyn Forest. Forests 2024, 15, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, F.; Guo, L. Litter quality drives the differentiation of microbial communities in the litter horizon across an alpine treeline ecotone in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Ecological Theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry indicates that litter quality regulates soil microbial nutrient demand in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 123, 103686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Ma, D.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J. Nitrogen input level modulates straw-derived organic carbon physical fractions accumulation by stimulating specific fungal groups during decomposition. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 225, 105560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ren, C.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y. Dynamics of bacterial community in litter and soil along a chronosequence of Robinia pseudoacacia plantations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward An Ecological Classification Of Soil Bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresova, A.; Kopecky, J.; Hrdinkova, V.; Kamenik, Z.; Omelka, M.; Sagova-Mareckova, M. Succession of Microbial Decomposers Is Determined by Litter Type, but Site Conditions Drive Decomposition Rates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01760-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ge, S.; Fan, L.-C.; Guo, S.; Hu, Q.; Ahammed, G.J.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Li, Z.-Z.; Zhang, J.-Y.; et al. Diversity in rhizospheric microbial communities in tea varieties at different locations and tapping potential beneficial microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1027444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tláskal, V.; Voříšková, J.; Baldrian, P. Bacterial succession on decomposing leaf litter exhibits a specific occurrence pattern of cellulolytic taxa and potential decomposers of fungal mycelia. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lu, J. Soil fertility underlies the positive relationship between island area and litter decomposition in a fragmented subtropical forest landscape. Catena 2021, 204, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Cesarano, G.; Gaglione, S.A.; Ippolito, F.; Sarker, T.; Rao, M.A. Soil fertility promotes decomposition rate of nutrient poor, but not nutrient rich litter through nitrogen transfer. Plant Soil 2017, 412, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
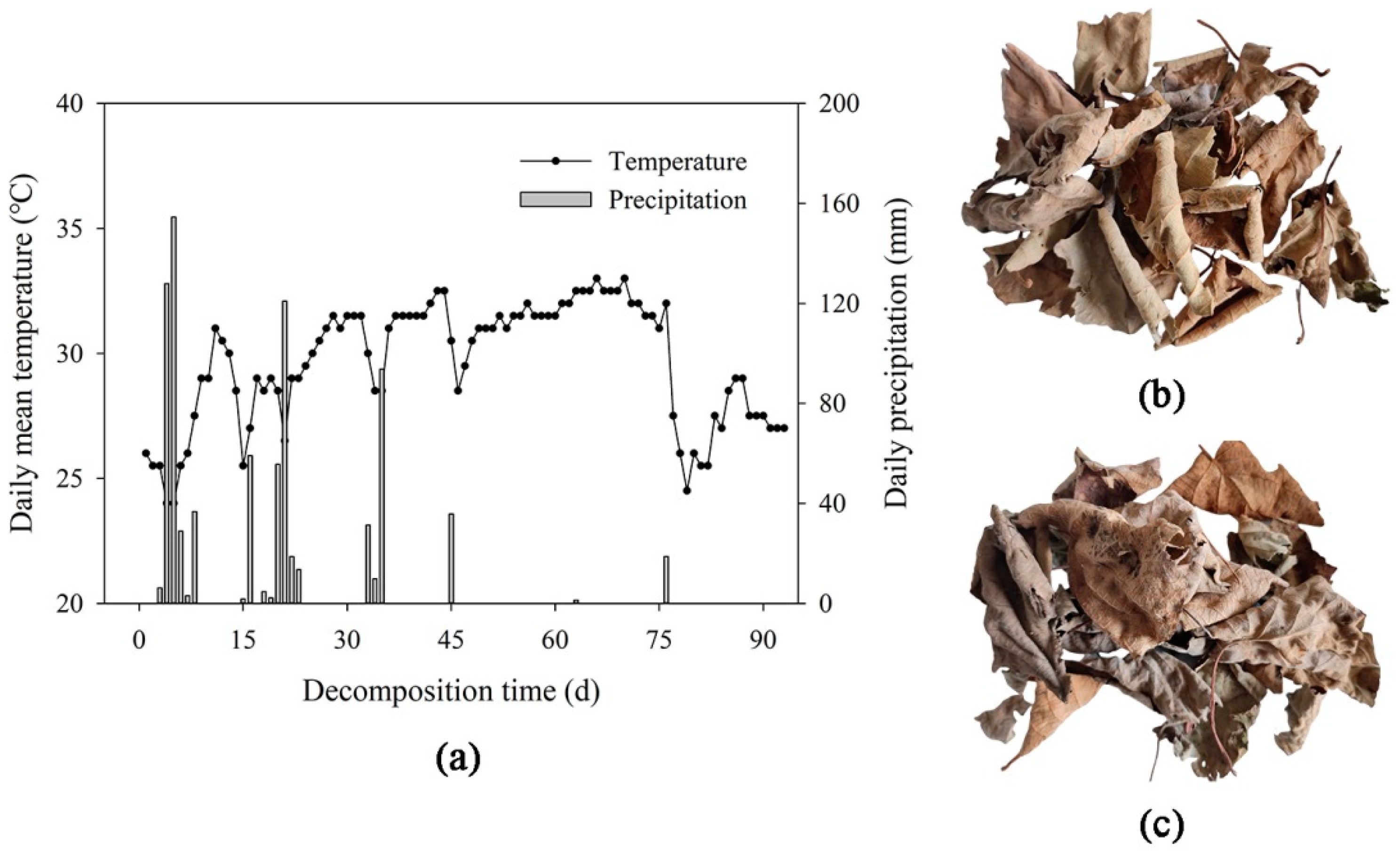
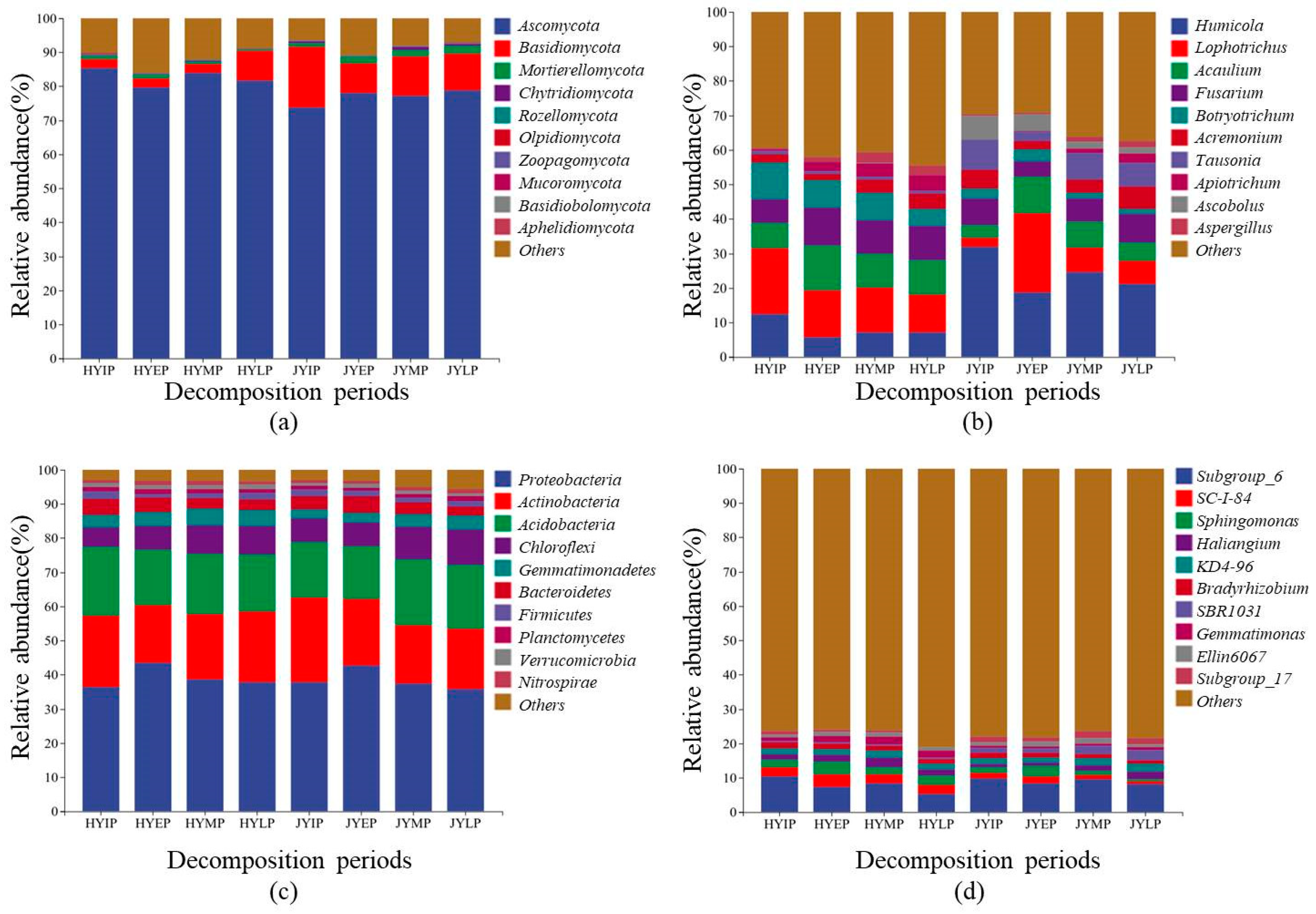


| Nutrient Contents in Litters | HY | JY | Relative Abundance of Fungi in Soil | HY | JY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (mg/g) | 395.4 ± 4.6 * | 334.1 ± 3.1 | Humicola (%) | 12.53 ± 0.91 | 32.02 ± 2.37 ** |
| N (mg/g) | 20.0 ± 1.1 * | 18.7 ± 0.6 | Lophotrichus (%) | 19.05 ± 0.49 ** | 2.63 ± 0.25 |
| P (mg/g) | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 * | Acaulium (%) | 7.29 ± 1.19 | 3.68 ± 0.62 |
| K (mg/g) | 11.1 ± 0.7 | 17.9 ± 0.5 * | Fusarium (%) | 6.82 ± 0.75 | 7.72 ± 0.46 |
| C/N | 19.44 ± 1.16 | 18.11 ± 0.72 | Botryotrichum (%) | 10.70 ± 1.17 * | 2.77 ± 1.44 |
| C/P | 217.50 ± 8.24 ** | 133.75 ± 4.59 | Acremonium (%) | 2.45 ± 0.78 | 5.41 ± 0.80 |
| C/K | 35.56 ± 2.81 ** | 19.08 ± 0.66 | Tausonia (%) | 0.97 ± 0.16 | 8.74 ± 0.64 ** |
| N/P | 11.22 ± 0.81 | 7.39 ± 0.15 | Apiotrichum (%) | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 6.77 ± 0.65 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, D.; Wang, X. Microbial Community Structure, Diversity, and Succession During Decomposition of Kiwifruit Litters with Different Qualities. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122498
Lu Y, Gao Z, Zhu Y, Yao D, Wang X. Microbial Community Structure, Diversity, and Succession During Decomposition of Kiwifruit Litters with Different Qualities. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122498
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yupeng, Zhu Gao, Yulin Zhu, Dongliang Yao, and Xiaoling Wang. 2024. "Microbial Community Structure, Diversity, and Succession During Decomposition of Kiwifruit Litters with Different Qualities" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122498
APA StyleLu, Y., Gao, Z., Zhu, Y., Yao, D., & Wang, X. (2024). Microbial Community Structure, Diversity, and Succession During Decomposition of Kiwifruit Litters with Different Qualities. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122498





